YOLO-Act: Unified Spatiotemporal Detection of Human Actions Across Multi-Frame Sequences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Action Classification
2.2. Action Detection Without Attention Mechanism
2.3. Attention-Based Approaches
2.4. Discussion
| Task | Reference | Input | Model | Dataset | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Action Classification | [12] | Raw frames | 3D CNN | Sports-1M [12] | Hit@1 = 60.9% |
| [36] | Raw Frames Optical Flow | CNN LSTM | Sports-1M [12] UCF-101 [64] | Hit@1 = 73.1% 3-fold Acc = 88.6% | |
| [14] | Single Frame Optical Flow | Two-stream CNN | UCF-101 [64] | Mean Acc = 88.0–59.4% | |
| [25] | Raw frames (low rate and fast rate) | SlowFast | AVA [63] | mAP = 23.8 | |
| [30] | Keyframe | ACAR | AVA [63] | mAP = 33.3 | |
| Action Detection without attention mechanism | [6] | Single frame | Faster R-CNN Binary classifier | Prepared their own DS | Precision = 93.87% |
| [44] | Keyframe | WOO, SlowFast | AVA [63] JHMDB [65] | mAP = 28.3 mAP = 80.5 | |
| [41] | Single frame | CNN | Prepared their own DS | AP50 = 95.20 | |
| [13] | Keyframes | Faster R-CNN AlexNet deep SORT | Prepared their own DS | mAP = 80.6 | |
| [48] | Raw Frames | X3D | AVA [63] | mAP = 27.4 | |
| Attention-Based Approaches | [55] | Keyframes Raw frames | SlowFast Faster R-CNN | ActivityNet [66] THUMOS [67] | AR@AN = 68.99–64.03 |
| [56] | Keyframes Raw frames | 2D CNN 3D CNN | JHMDB [65] UCF101 [64] | mAP = 64.9–79.2 | |
| [54] | Key frames | Object transformer | AVA [63] | mAP = 31.0 | |
| [49] | Raw frame | MViT v1 | AVA [63] | mAP = 28.7 | |
| [50] | Raw frame | MViT v2 | AVA [63] | mAP = 31.6 | |
| [59] | 3D human pose data and tracking information | LART | AVA [63] | mAP = 45.1 | |
| [61] | Raw frames | Hiera | AVA [63] | mAP = 43.3 |
3. The Proposed YOLO-Act Model
3.1. Keyframe Extraction
3.2. Action Detection
3.3. Class Fusion
3.4. Actor Tracking
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset Description
4.2. Experiment Setting and Training
4.3. Testing YOLO-Act
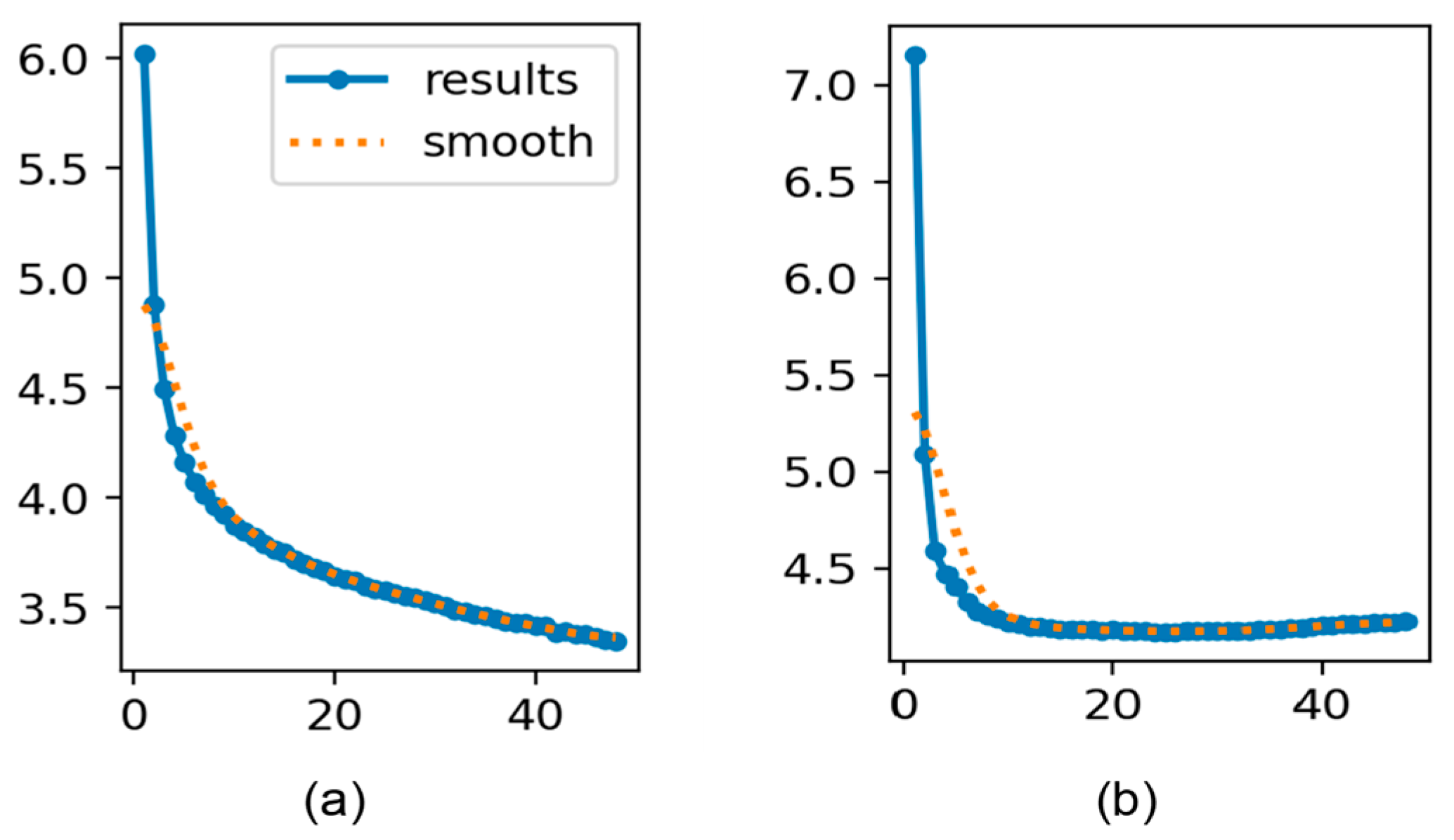
4.4. Experimental Results Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carreira, J.; Zisserman, A. Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4724–4733. [Google Scholar]
- Bah, S.M.; Ming, F. An Improved Face Recognition Algorithm and Its Application in Attendance Management System. Array 2020, 5, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Qin, L.; Chen, Z.; Ji, S.; Zhang, K.; Ma, X. Empirical Study on the Impact of Short Video Content Marketing on Consumer’s Purchasing Intention Based on the Integrated Model of TRA and ELM. In Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Economic Development and Management Innovation (EDMI 2019), Hohhot, China, 28–29 July 2019; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Esteva, A.; Chou, K.; Yeung, S.; Naik, N.; Madani, A.; Mottaghi, A.; Liu, Y.; Topol, E.; Dean, J.; Socher, R. Deep Learning-Enabled Medical Computer Vision. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, G.-C.; Tsai, Y.-P.; Jeng, S.-K. Augmented 3-D Keyframe Extraction for Surveillance Videos. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2010, 20, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hernández, F.; Tabik, S.; Lamas, A.; Olmos, R.; Fujita, H.; Herrera, F. Object Detection Binary Classifiers Methodology Based on Deep Learning to Identify Small Objects Handled Similarly: Application in Video Surveillance. Knowl. Based Syst. 2020, 194, 105590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yao, H.; Zhao, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S. Action Recognition with Multi-Scale Trajectory-Pooled 3D Convolutional Descriptors. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoi, A. Spatio-Temporal Action Recognition: A Survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.09403. [Google Scholar]
- Pareek, P.; Thakkar, A. A Survey on Video-Based Human Action Recognition: Recent Updates, Datasets, Challenges, and Applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 2259–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Zhang, R.; Liu, F.; Yang, S.; Hou, B.; Li, L.; Tang, X. New Generation Deep Learning for Video Object Detection: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 3195–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouyanfar, S.; Sadiq, S.; Yan, Y.; Tian, H.; Tao, Y.; Reyes, M.P.; Shyu, M.L.; Chen, S.C.; Iyengar, S.S. A Survey on Deep Learning: Algorithms, Techniques, and Applications. ACM Comput. Surv. 2018, 51, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathy, A.; Toderici, G.; Shetty, S.; Leung, T.; Sukthankar, R.; Fei-Fei, L. Large-Scale Video Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, A.; Pal, S.K.; Maiti, J.; Mitra, P. Granulated RCNN and Multi-Class Deep SORT for Multi-Object Detection and Tracking. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2021, 6, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-Stream Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition in Videos. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1406.2199. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning Spatiotemporal Features with 3d Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Yu, K. 3D Convolutional Neural Networks for Human Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, C.B.; Hashmi, M.F.; Bokde, N.D.; Geem, Z.W. Investigations of Object Detection in Images/Videos Using Various Deep Learning Techniques and Embedded Platforms-A Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. Switz. 2020, 10, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-Local Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Fan, H.; He, K.; Krähenbühl, P.; Girshick, R. Long-Term Feature Banks for Detailed Video Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dollar, P.; Rabaud, V.; Cottrell, G.; Belongie, S. Behavior Recognition via Sparse Spatio-Temporal Features. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Workshop on Visual Surveillance and Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance, Beijing, China, 15–16 October 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Klaser, A.; Marszałek, M.; Schmid, C. A Spatio-Temporal Descriptor Based on 3D-Gradients. In Proceedings of the BMVC 2008-19th British Machine Vision Conference, Leeds, UK, September 2008; British Machine Vision Association: Glasgow, UK, 2008; pp. 275:1–275:10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Schmid, C. Action Recognition with Improved Trajectories. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 3551–3558. [Google Scholar]
- Sevilla-Lara, L.; Liao, Y.; Güney, F.; Jampani, V.; Geiger, A.; Black, M.J. On the Integration of Optical Flow and Action Recognition; Brox, T., Bruhn, A., Fritz, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Fan, H.; Malik, J.; He, K. SlowFast Networks for Video Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gupta, A. Videos as Space-Time Region Graphs. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 399–417. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Xu, J.; Zou, Y.; Huang, J.-B. DRG: Dual Relation Graph for Human-Object Interaction Detection; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 696–712. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Shrivastava, A.; Vondrick, C.; Sukthankar, R.; Murphy, K.; Schmid, C. Relational Action Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 273–283. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Xia, J.; Mu, X.; Pang, B.; Lu, C. Asynchronous Interaction Aggregation for Action Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.07485. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Chen, S.; Shou, M.Z.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J.; Li, H. Actor-Context-Actor Relation Network for Spatio-Temporal Action Localization. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, M.; Kumar, M. MobileNet for Human Activity Recognition in Smart Surveillance Using Transfer Learning. Neural Comput. Appl. 2025, 37, 3907–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piergiovanni, A.J.; Angelova, A.; Ryoo, M.S. Tiny Video Networks. Appl. AI Lett. 2022, 3, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep Learning Approach to Key Frame Detection in Human Action Videos. IntechOpen. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/71081 (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Arslan, S.; Tanberk, S. Key Frame Extraction with Attention Based Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.13176. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Liu, W. Fairmot: On the Fairness of Detection and Re-Identification in Multiple Object Tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3069–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Ng, H.; Hausknecht, M.; Vijayanarasimhan, S.; Vinyals, O.; Monga, R.; Toderici, G. Beyond Short Snippets: Deep Networks for Video Classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jia, M.; Lin, T.-Y.; Song, Y.; Belongie, S. Class-Balanced Loss Based on Effective Number of Samples. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9268–9277. [Google Scholar]
- Pulakurthi, P.R.; De Melo, C.M.; Rao, R.; Rabbani, M. Enhancing Human Action Recognition with GAN-Based Data Augmentation. In Proceedings of the Synthetic Data for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Tools, Techniques, and Applications II, National Harbor, MD, USA, 7 June 2024; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; Volume 13035, pp. 194–204. [Google Scholar]
- Alshdaifat, N.F.F.; Talib, A.Z.; Osman, M.A. Improved Deep Learning Framework for Fish Segmentation in Underwater Videos. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 59, 101121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, P.; Xie, E.; Ge, C.; Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Shen, J.; Luo, P. Watch Only Once: An End-to-End Video Action Detection Framework. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, P.; Guo, F.; Qin, Y.; Long, S.; Ai, L. Hybrid Learning Architecture for High-Speed Railroad Scene Parsing and Potential Safety Hazard Evaluation of UAV Images. Measurement 2025, 239, 115504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Feng, Z.; Zhu, H. RailFOD23: A Dataset for Foreign Object Detection on Railroad Transmission Lines. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Guan, Q.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D. Radiance Field Learners As UAV First-Person Viewers. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2024; Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15119, pp. 88–107. ISBN 978-3-031-73029-0. [Google Scholar]
- Feichtenhofer, C. X3D: Expanding Architectures for Efficient Video Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Xiong, B.; Mangalam, K.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Malik, J.; Feichtenhofer, C. Multiscale Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 6824–6835. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, C.-Y.; Fan, H.; Mangalam, K.; Xiong, B.; Malik, J.; Feichtenhofer, C. MViTv2: Improved Multiscale Vision Transformers for Classification and Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4804–4814. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders Are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 2022, 35, 10078–10093. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Fan, H.; Xie, S.; Wu, C.-Y.; Yuille, A.; Feichtenhofer, C. Masked Feature Prediction for Self-Supervised Visual Pre-Training. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16000–16009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Krahenbuhl, P. Towards Long-Form Video Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1884–1894. [Google Scholar]
- Vo-Ho, V.-K.; Le, N.; Yamazaki, K.; Sugimoto, A.; Tran, M.-T. Agent-Environment Network for Temporal Action Proposal Generation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021 - 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Köpüklü, O.; Wei, X.; Rigoll, G. You Only Watch Once: A Unified CNN Architecture for Real-Time Spatiotemporal Action Localization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.06644. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, K.; Kataoka, H.; Satoh, Y. Can Spatiotemporal 3D CNNs Retrace the History of 2D CNNs and ImageNet? In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6546–6555. [Google Scholar]
- Rajasegaran, J.; Pavlakos, G.; Kanazawa, A.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Malik, J. On the Benefits of 3D Pose and Tracking for Human Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 640–649. [Google Scholar]
- Rajasegaran, J.; Pavlakos, G.; Kanazawa, A.; Malik, J. Tracking People by Predicting 3D Appearance, Location and Pose. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2740–2749. [Google Scholar]
- Ryali, C.; Hu, Y.-T.; Bolya, D.; Wei, C.; Fan, H.; Huang, P.-Y.; Aggarwal, V.; Chowdhury, A.; Poursaeed, O.; Hoffman, J.; et al. Hiera: A Hierarchical Vision Transformer without the Bells-and-Whistles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; PMLR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 29441–29454. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-Cnn: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 2015, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Sun, C.; Ross, D.A.; Vondrick, C.; Pantofaru, C.; Li, Y.; Vijayanarasimhan, S.; Toderici, G.; Ricco, S.; Sukthankar, R.; et al. AVA: A Video Dataset of Spatio-Temporally Localized Atomic Visual Actions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Soomro, K.; Zamir, A.R.; Shah, M. UCF101: A Dataset of 101 Human Actions Classes from Videos in the Wild. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.0402. [Google Scholar]
- Jhuang, H.; Gall, J.; Zuffi, S.; Schmid, C.; Black, M.J. Towards Understanding Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 3192–3199. [Google Scholar]
- Heilbron, F.C.; Escorcia, V.; Ghanem, B.; Niebles, J.C. Activitynet: A Large-Scale Video Benchmark for Human Activity Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 961–970. [Google Scholar]
- Idrees, H.; Zamir, A.R.; Jiang, Y.-G.; Gorban, A.; Laptev, I.; Sukthankar, R.; Shah, M. The Thumos Challenge on Action Recognition for Videos “in the Wild”. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2017, 155, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. YOLO by Ultralytics (Version 8.0.0). 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Bourdev, L.; Girshick, R.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Dollár, P. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Girdhar, R.; Carreira, J.; Doersch, C.; Zisserman, A. A Better Baseline for AVA. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.10066. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Bing, S.; Xu, M.; Liu, C.; Kundu, K.; Xiong, Y.; Modolo, D.; et al. TubeR: Tubelet Transformer for Video Action Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
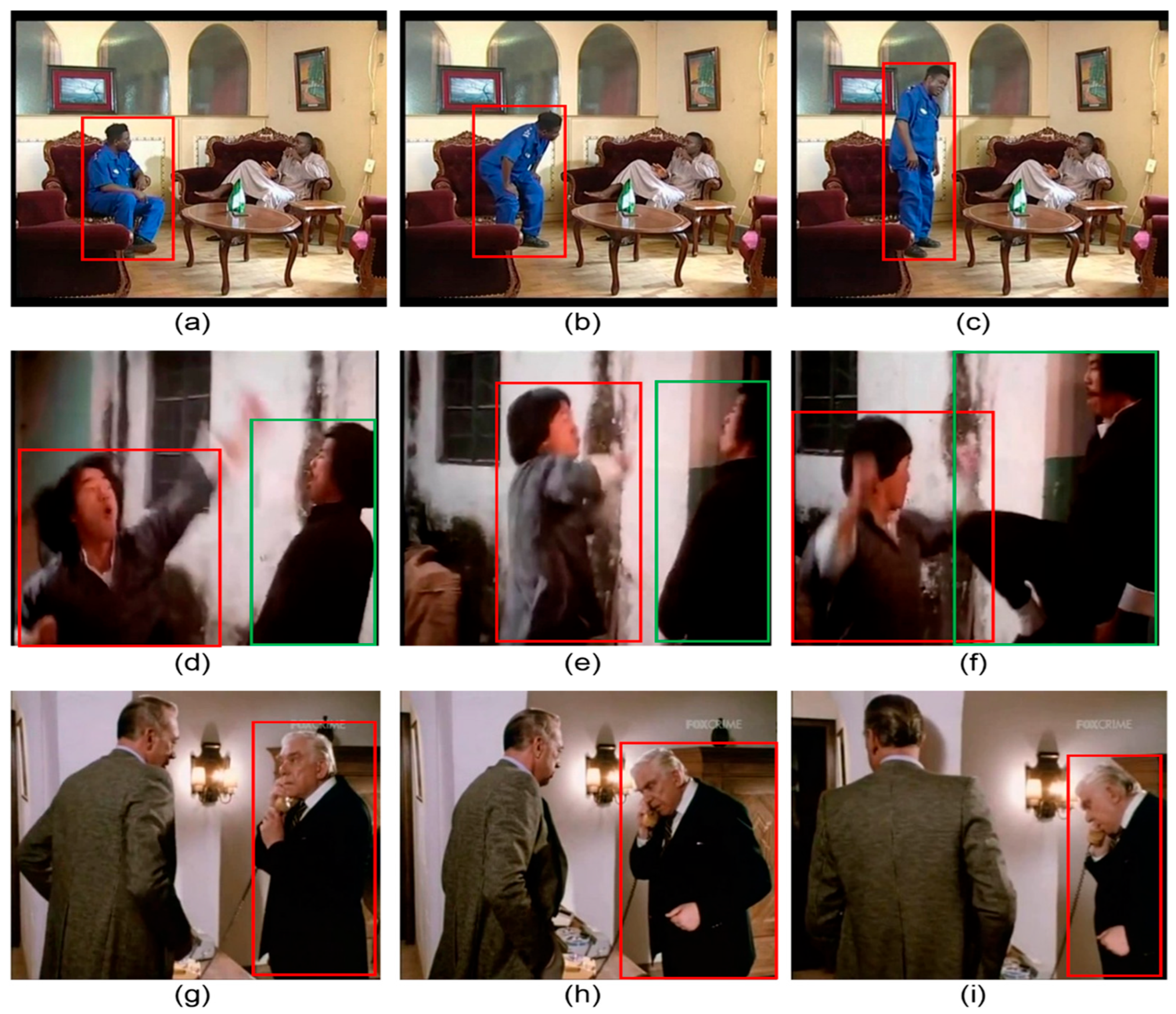

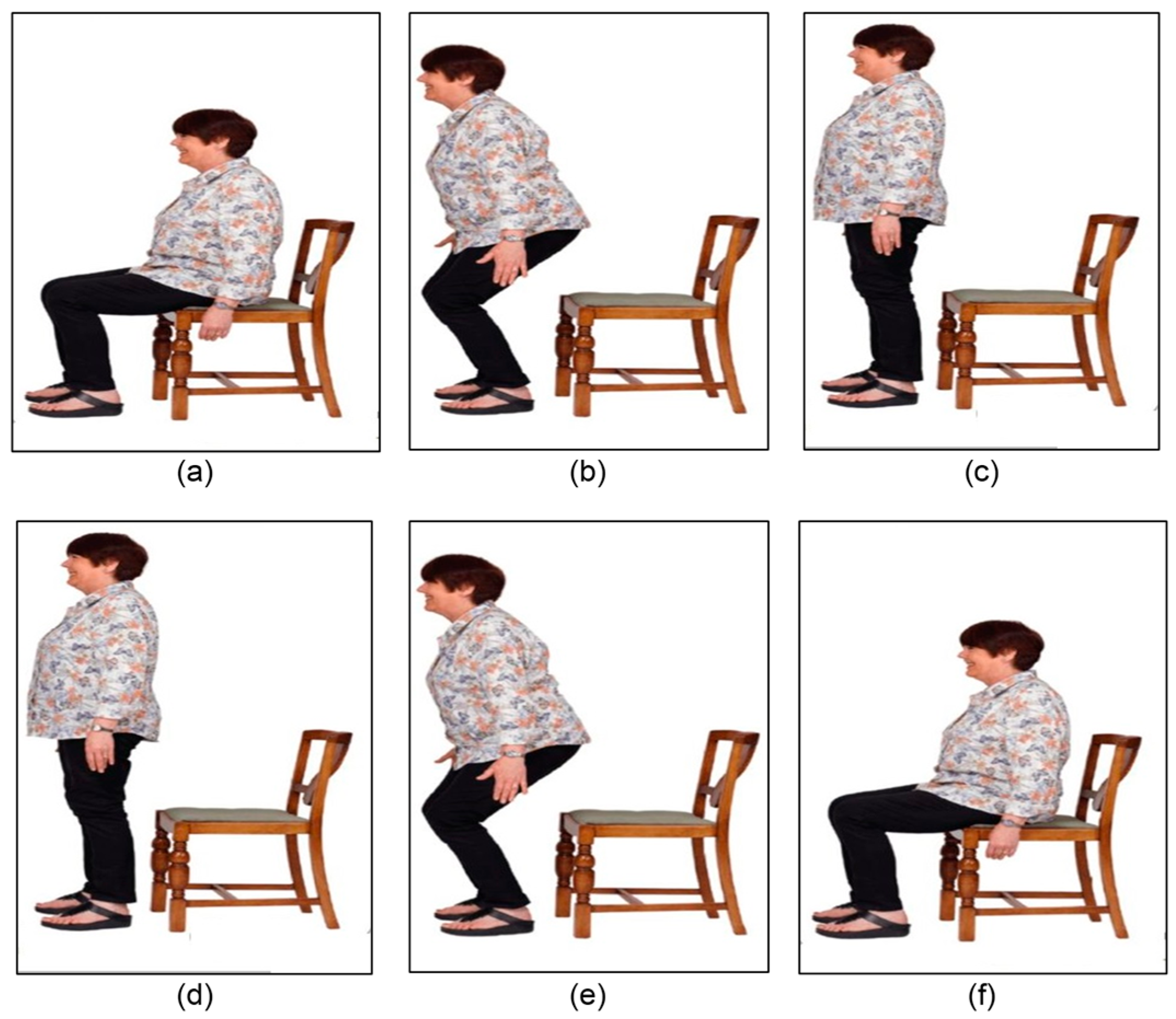






| Feature | Manual Methods | Deep Learning Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Feature Extraction | Hand-crafted, limited flexibility | Automatically learned from data |
| Adaptability | Poor generalization to new actions | High generalization capability |
| Temporal Modeling | Hand-tuned temporal descriptors | End-to-end learned temporal dynamics |
| Robustness | Sensitive to noise and occlusion | More robust through learned representations |
| Scalability | Difficult to extend to new classes | Easily scalable with additional data |
| Mechanism | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attention-less Models | Rely solely on convolutional or temporal pooling operations without selective focus | Simpler, faster inference | May miss subtle or small-scale action cues |
| Attention-based Models | Use spatial, temporal, or spatio-temporal attention to prioritize important regions or frames | Higher accuracy, better interpretability | Increased computational complexity |
| Feature | YOLOv8 | YOLO-Act |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Static object detection | Dynamic action recognition |
| Temporal Modeling | None | Keyframe sequence modeling |
| Tracking | Not integrated | Integrated actor tracking |
| Late Fusion | Not applicable | Enhances multi-frame evidence |
| Application | Object detection tasks | Human action detection |
| Hyperparameters | Value |
|---|---|
| optimizer | AdamW |
| optimizer momentum | 0.937 |
| weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Learning rate schedule | Cosine Decay |
| warm-up epochs | 3.0 |
| drop out | 0.1 |
| learning rate | 0.0001 |
| batch size | 32 |
| epochs | 100 early stopping at epoch 40 |
| Patience/early stopping | 10 |
| Model | mAP | FLOPs |
|---|---|---|
| SlowFast R101, 8×8 [25] | 23.8 | 138 |
| MViTv1-B, 64×3 [49] | 27.3 | 296 |
| SlowFast 16×8 +NL [25] | 27.5 | 296 |
| X3D-XL [48] | 27.4 | 48 |
| WOO [44] | 28.3 | 251.7 |
| MViTv1-B-24, 32×3 [49] | 28.7 | 236 |
| Object Transformer [54] | 31.0 | 244 |
| ACAR R101 [30] | 33.3 | 435 |
| MViT-L1312, 40×3 [50] | 31.6 | 2828 |
| MaskFeat [52] | 39.8 | 2828 |
| Video MAE [51] | 42.6 | 241.61 |
| Hiera [61] | 43.3 | 1158 |
| LART [59] | 45.1 | 1260 |
| YOLO-Act | 73.28 | 114.41 |
| Model | OM | PI | PM | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LART | 37.3 | 45.7 | 63.8 | 45.1 |
| YOLO-Act | 76 | 74.9 | 67.1 | 73.28 |
| Model | Temporal Aggregation | mAP (%) | Performance Drop (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO-Act | ✓ | 73.28 | - |
| Yolov8 | ✗ | 8.40 | 64.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzahrani, N.; Bchir, O.; Ismail, M.M.B. YOLO-Act: Unified Spatiotemporal Detection of Human Actions Across Multi-Frame Sequences. Sensors 2025, 25, 3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103013
Alzahrani N, Bchir O, Ismail MMB. YOLO-Act: Unified Spatiotemporal Detection of Human Actions Across Multi-Frame Sequences. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103013
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzahrani, Nada, Ouiem Bchir, and Mohamed Maher Ben Ismail. 2025. "YOLO-Act: Unified Spatiotemporal Detection of Human Actions Across Multi-Frame Sequences" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103013
APA StyleAlzahrani, N., Bchir, O., & Ismail, M. M. B. (2025). YOLO-Act: Unified Spatiotemporal Detection of Human Actions Across Multi-Frame Sequences. Sensors, 25(10), 3013. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103013






