Real-Time Detection and Localization of Force on a Capacitive Elastomeric Sensor Array Using Image Processing and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Related Work
1.3. Contribution and System Overview
2. Methodology
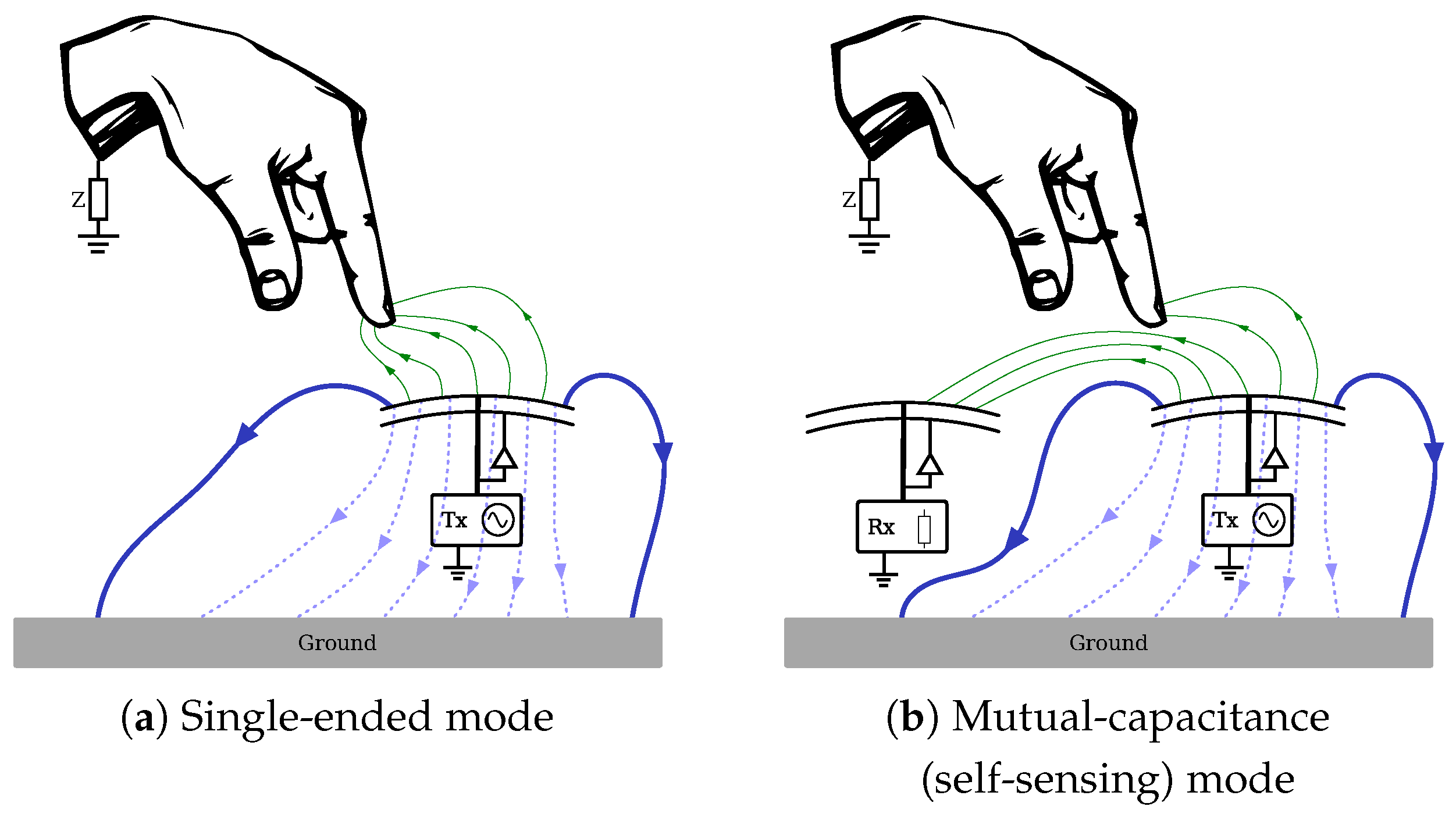
2.1. Capacitive Sensing Principle
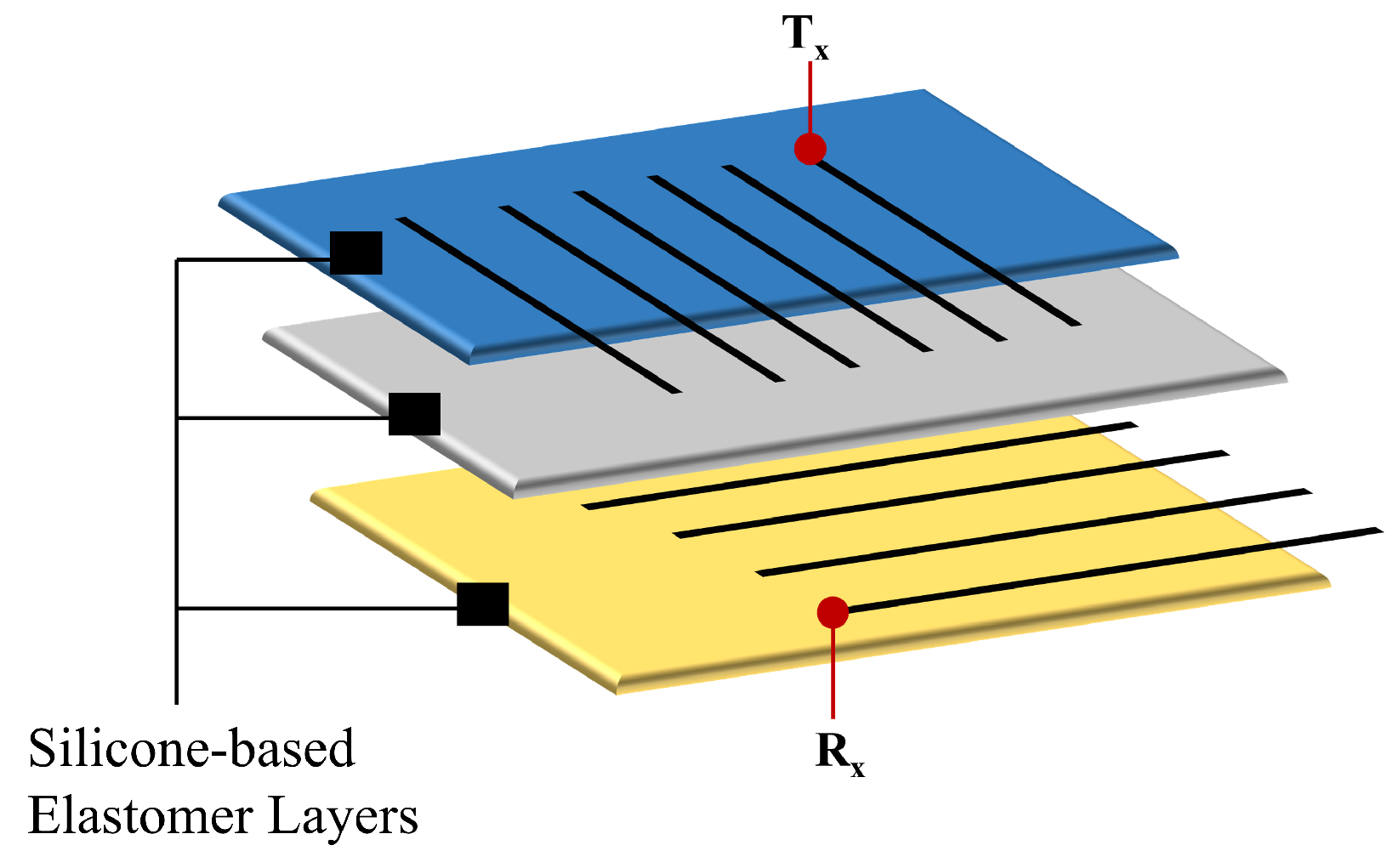
2.2. Elastomeric Sensor Array
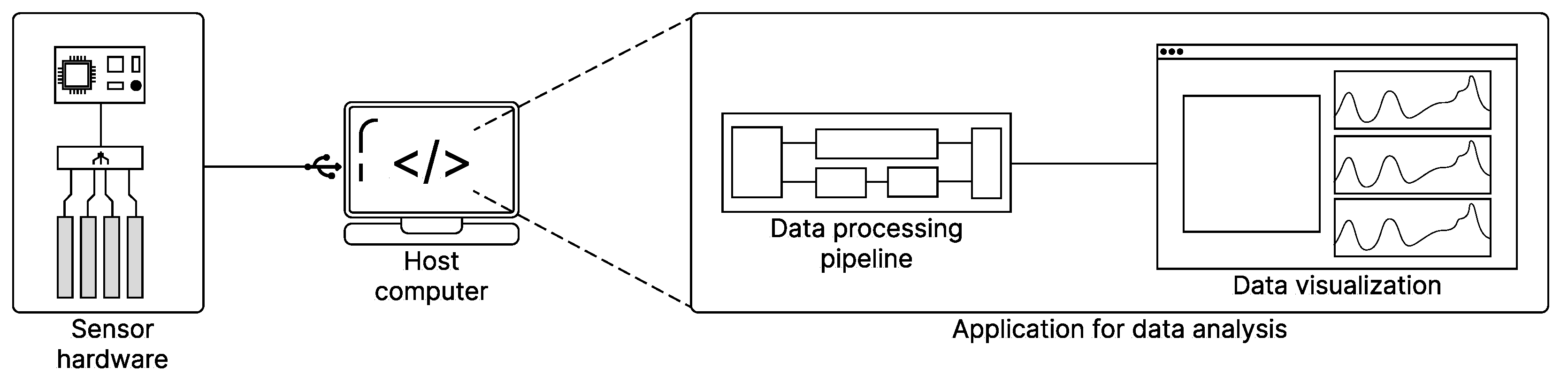
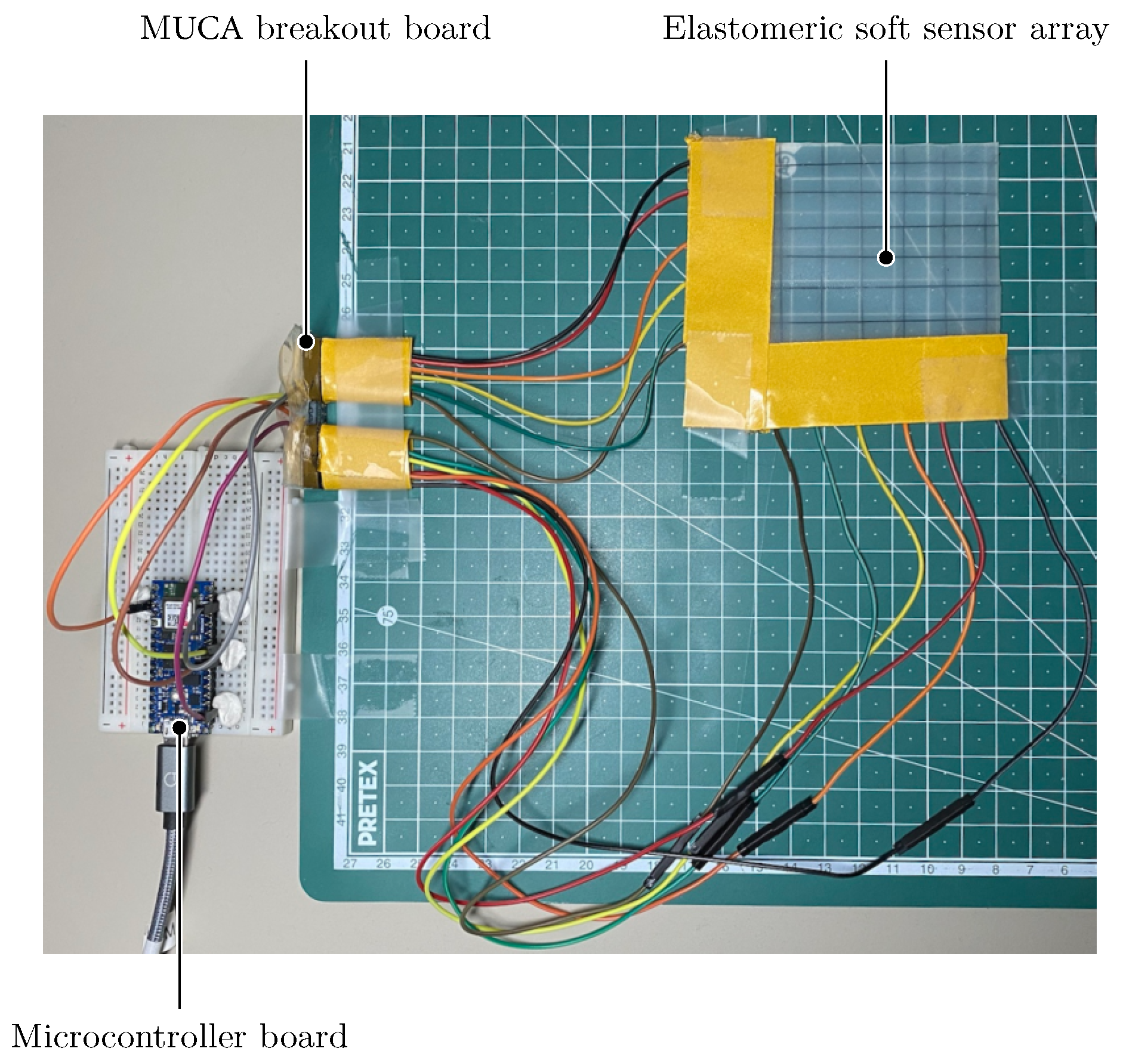
2.3. Data Acquisition and Characterization System
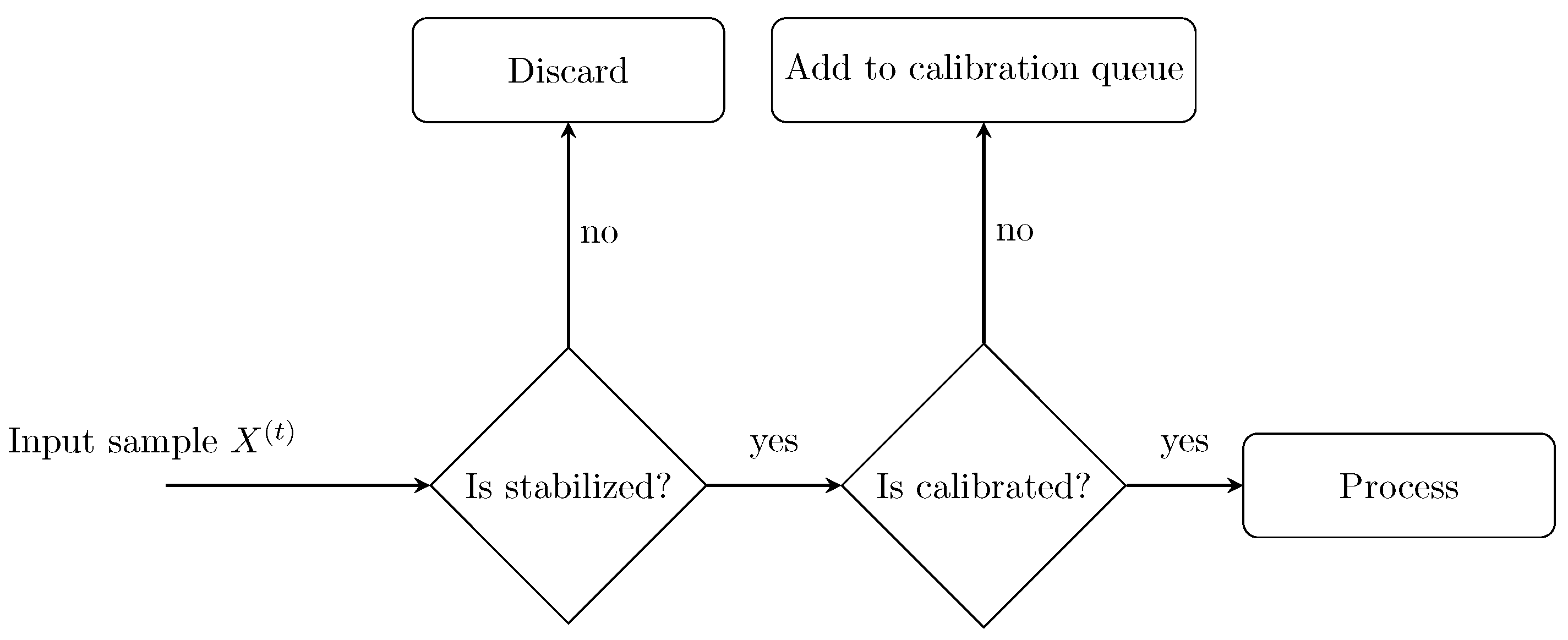
2.4. Signal Preprocessing
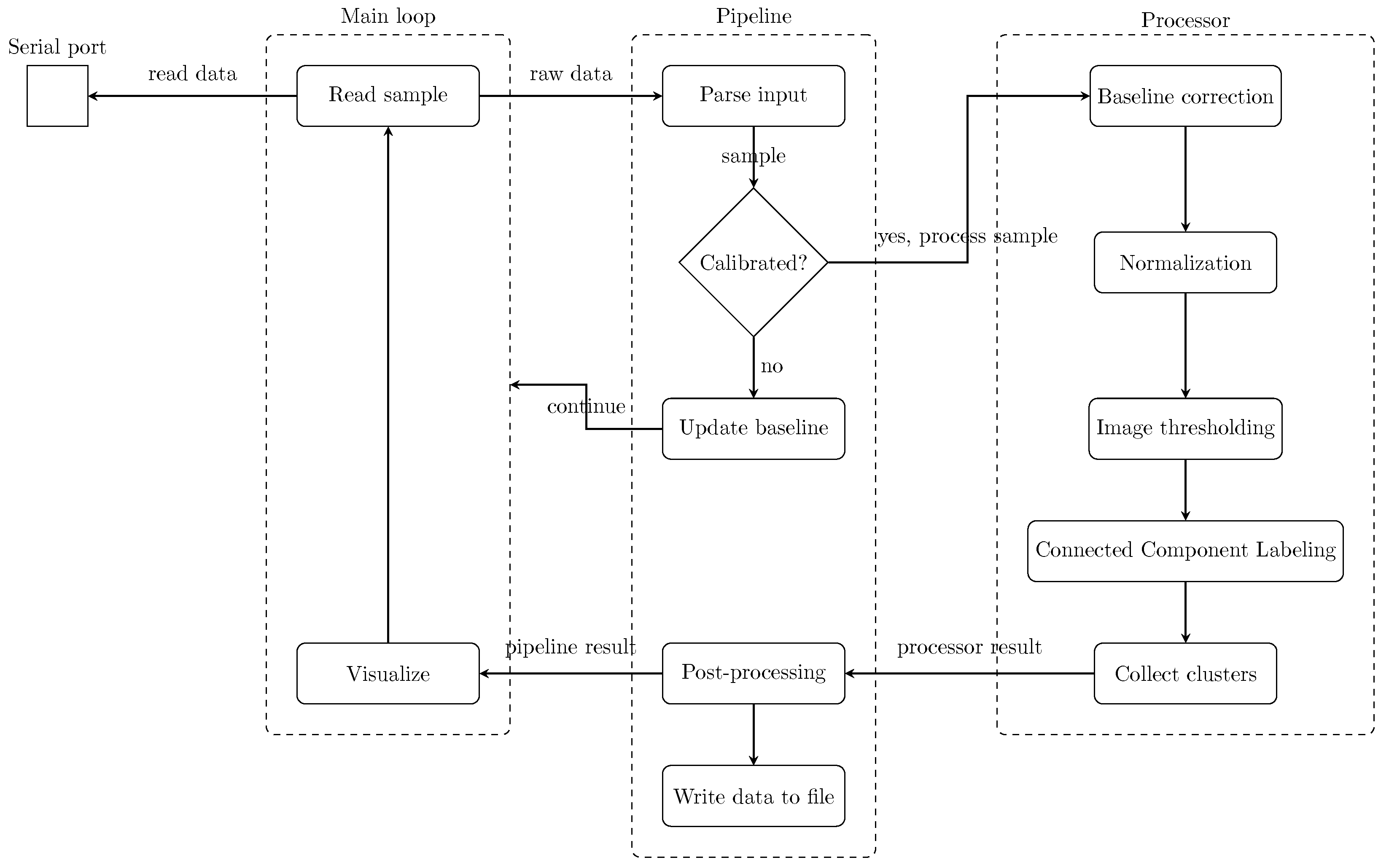
2.4.1. Software Architecture
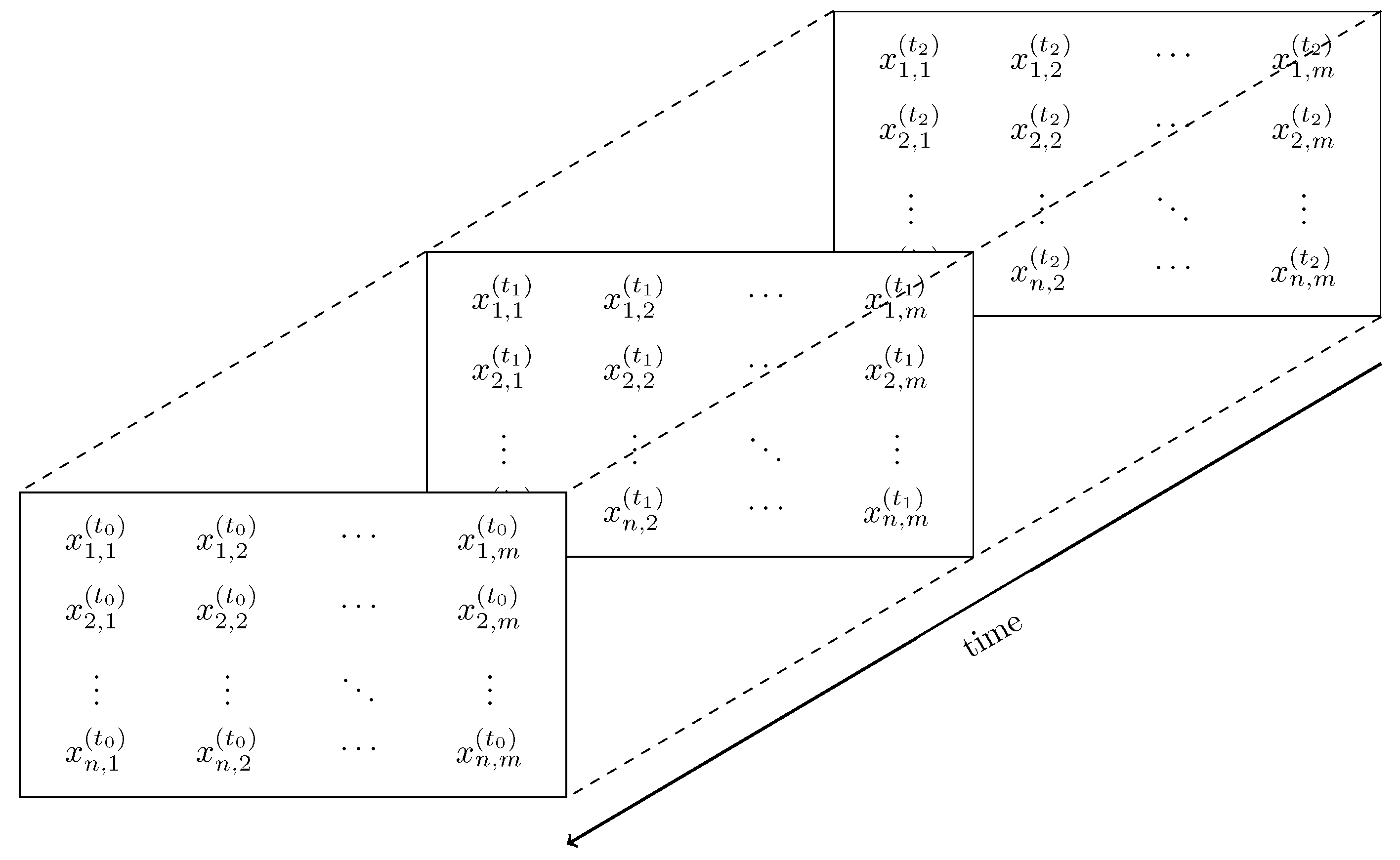
2.4.2. Data Transformation
2.4.3. Signal Filtering
2.5. Force Point Detection and Localization
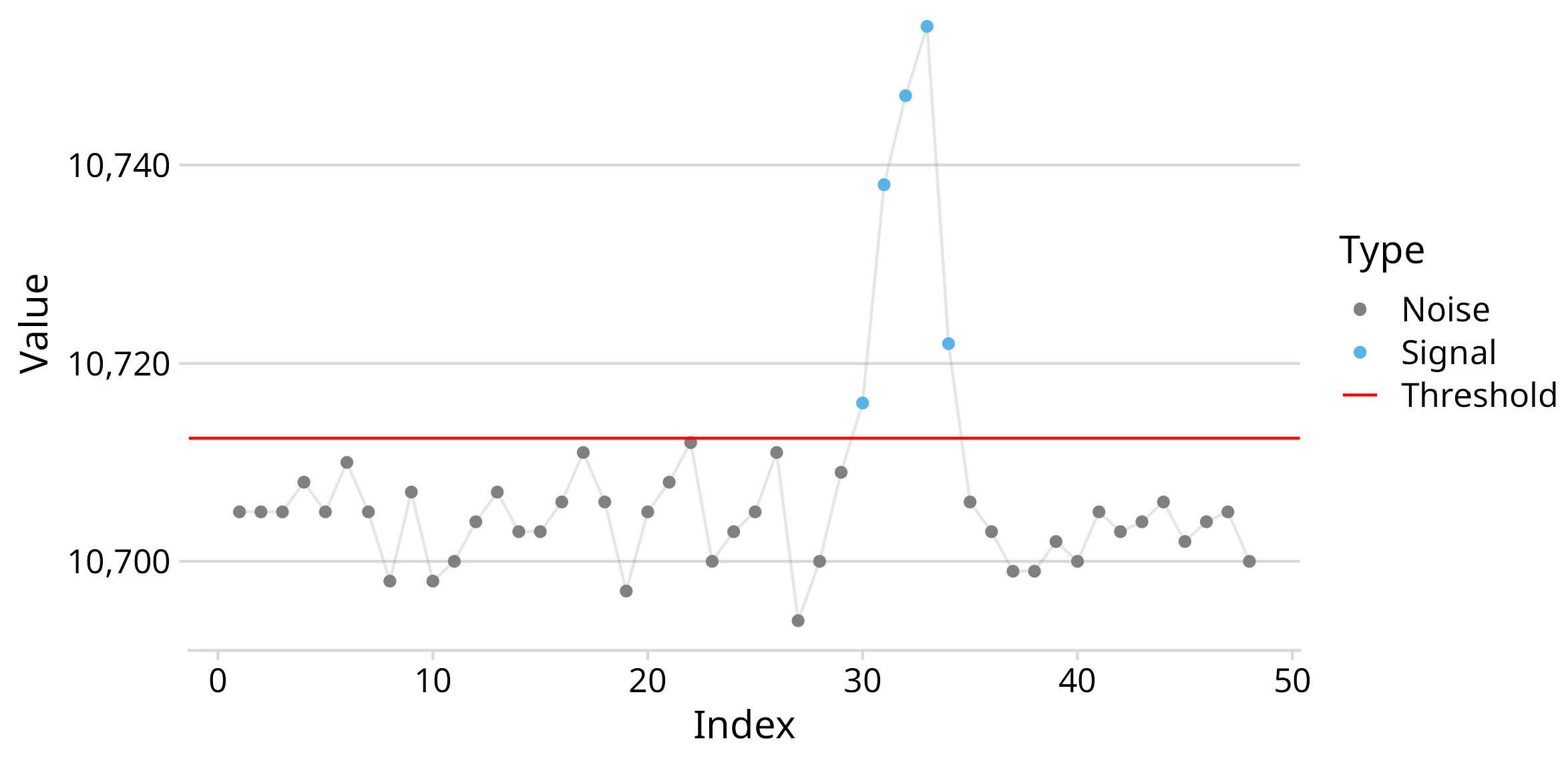
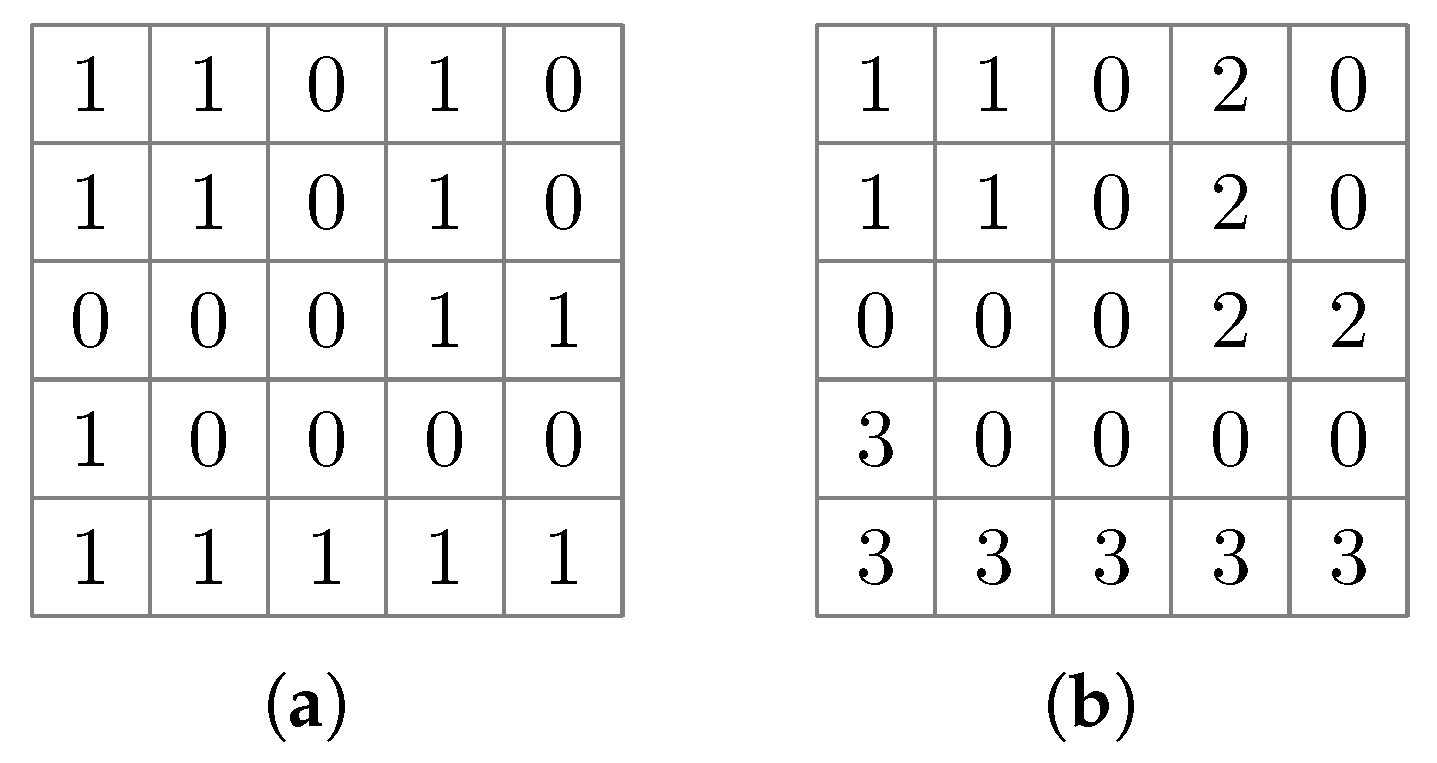
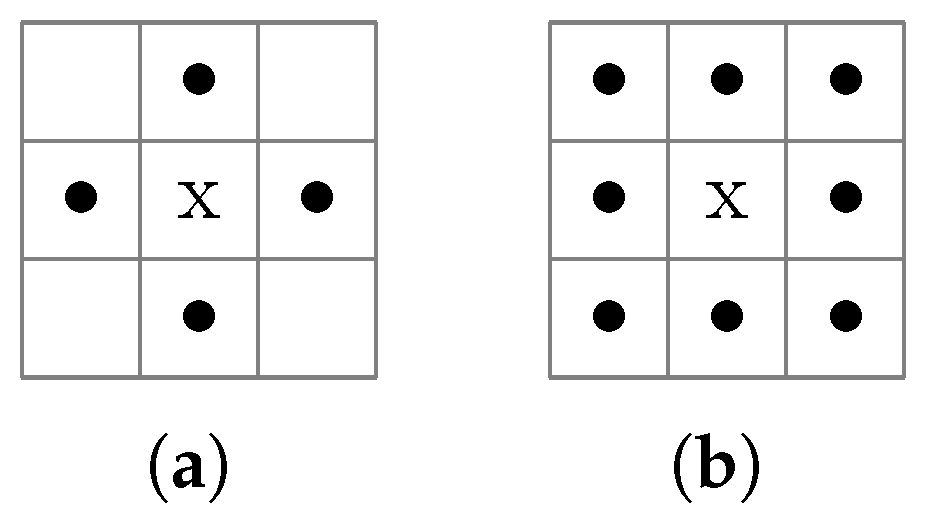
2.5.1. Otsu’s Method and Connected Component Labeling
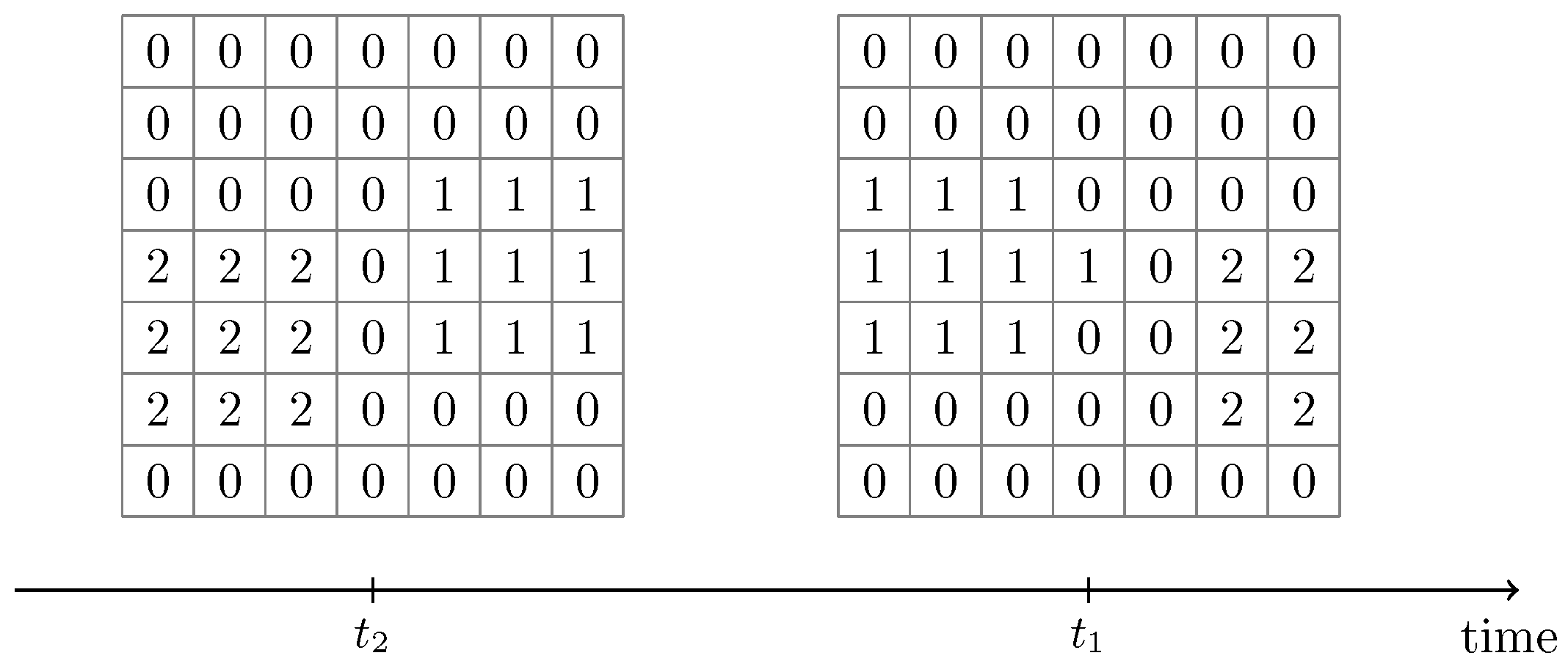
2.5.2. Cluster Tracking
| Algorithm 1: Cluster tracking algorithm |
 |
2.6. Machine Learning Models for Correlation Factor
3. Results
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. Data Visualization
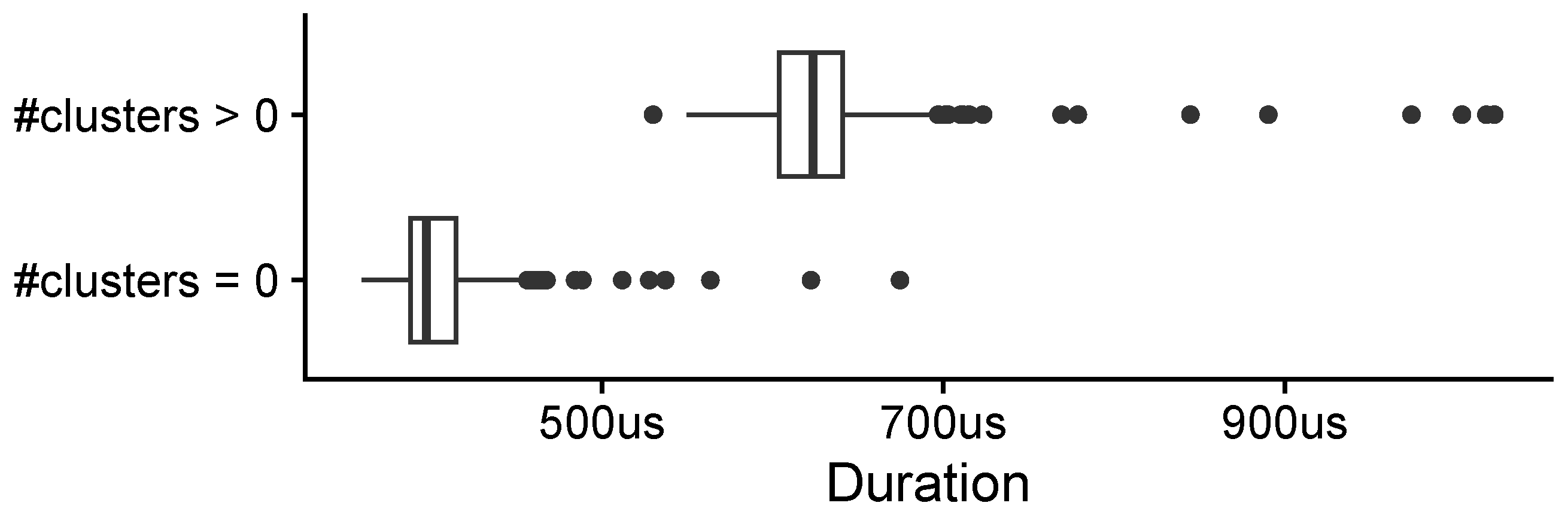
3.3. Algorithm Performance
3.4. Tactile Sensor Performance Evaluation
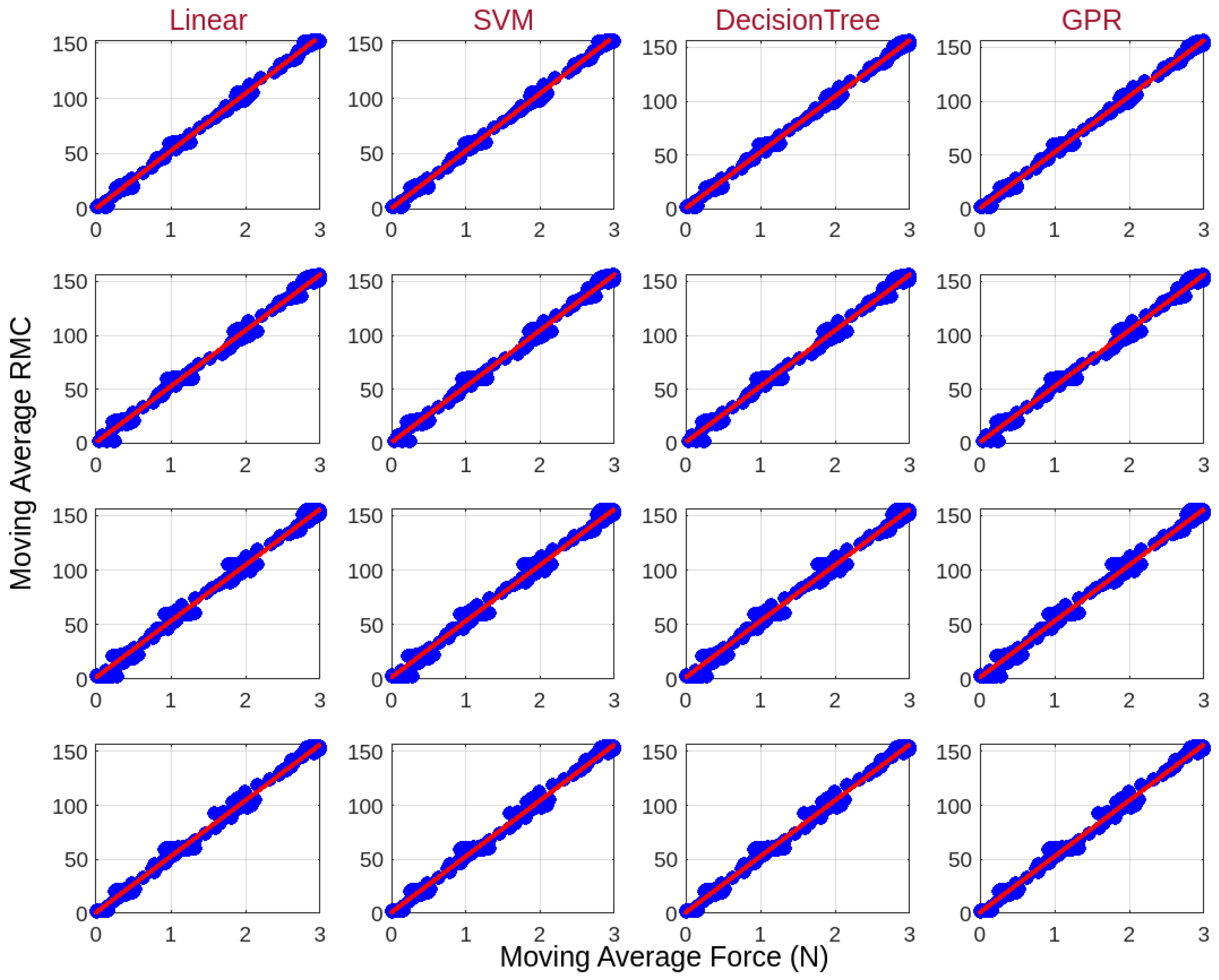
3.5. Force Characterization Using Machine Learning Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCL | Connected Component Labeling |
| DAQ | Data Acquisition System |
| GPR | Gaussian Process Regression |
| I2C | Inter-Integrated Circuit |
| RMC | Ratio of Mutual Capacitance |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
References
- Yuan, B.; Hu, D.; Gu, S.; Xiao, S.; Song, F. The global burden of traumatic amputation in 204 countries and territories. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1258853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF). Diabetes Facts and Figures: Global Prevalence and Future Projections; International Diabetes Federation (IDF): Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Meulenbelt, H.E.; Geertzen, J.H.; Jonkman, M.F.; Dijkstra, P.U. Determinants of Skin Problems of the Stump in Lower-Limb Amputees. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillingham, T.R.; Pezzin, L.E.; MacKenzie, E.J.; Burgess, A.R. Use and Satisfaction with Prosthetic Devices among Persons with Trauma-Related Amputations: A Long-Term Outcome Study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 80, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alluhydan, K.; Siddiqui, M.I.H.; Elkanani, H. Functionality and comfort design of lower-limb prosthetics: A review. J. Disabil. Res. 2023, 2, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddie, M. Redesigning Diabetic Foot Risk Assessment for Amputation Prevention in Low-Resource Settings: Development of a Purely Mechanical Plantar Pressure Evaluation Device; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Paternò, L.; Dhokia, V.; Menciassi, A.; Bilzon, J.; Seminati, E. A personalised prosthetic liner with embedded sensor technology: A case study. BioMed. Eng. Online 2020, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yan, X. Progress in achieving high-performance piezoresistive and capacitive flexible pressure sensors: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Hisano, K.; Zhu, M.; Toyoshi, T.; Pan, M.; Okada, S.; Tsutsumi, O.; Kawamura, S.; Bowen, C. Flexible multifunctional sensors for wearable and robotic applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Loh, K.J.; Pedtke, A. Sensing and actuation technologies for smart socket prostheses. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2020, 10, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyun, K.R.; Kwon, K.; Yoo, M.J.; Kim, K.K.; Gong, D.; Yeo, W.H.; Han, S.; Ko, S.H. Machine-learned wearable sensors for real-time hand-motion recognition: Toward practical applications. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwad298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, D.; Byun, Y.; Kim, I.; Lee, Y. High-Performance and Low-Complexity Multi-Touch Detection for Variable Ground States. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 25, 3138–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zini, M.; Baù, M.; Nastro, A.; Ferrari, M.; Ferrari, V. Flexible passive sensor patch with contactless readout for measurement of human body temperature. Biosensors 2023, 13, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Heever, D.J.; Schreve, K.; Scheffer, C. Tactile sensing using force sensing resistors and a super-resolution algorithm. IEEE Sens. J. 2008, 9, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanelli, D.; Farella, E. Force sensing resistor and evaluation of technology for wearable body pressure sensing. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 9391850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Cui, G.; Li, Z.; Fang, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, A.; Han, M.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Advanced flexible sensing technologies for soft robots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Majidi, C.; Gu, G. Cutaneous ionogel mechanoreceptors for soft machines, physiological sensing, and amputee prostheses. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, S.; Dackermann, U. A systematic review of advanced sensor technologies for non-destructive testing and structural health monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejke, V.; Eng, M.P.; Brinkfeldt, K.; Charnley, J.; Lussey, D.; Lussey, C. Development of prototype low-cost QTSS™ wearable flexible more enviro-friendly pressure, shear, and friction sensors for dynamic prosthetic fit monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Qi, W.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ferrigno, G.; De Momi, E. Deep neural network approach in EMG-based force estimation for human–robot interaction. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Bahreyni, B.; Campi, F. Multi-functional capacitive proximity sensing system for industrial safety applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE SENSORS, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Rotella, N.; Schaal, S.; Righetti, L. Unsupervised contact learning for humanoid estimation and control. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 411–417. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, Y. A comparative analysis of linear regression, neural networks and random forest regression for predicting air ozone employing soft sensor models. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.; Hellebrekers, T.; Majidi, C. Machine learning for soft robotic sensing and control. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1900171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, M.K.; Der, C.S.; Phing, C.C. Enhanced dynamic hand gesture recognition for finger disabilities using deep learning and an optimized Otsu threshold method. Eng. Res. Express 2025, 7, 015228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pan, W.; Zou, T.; Li, C.; Han, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Zou, X. A Review of Perception Technologies for Berry Fruit-Picking Robots: Advantages, Disadvantages, Challenges, and Prospects. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, J.C.; Yuen, M.C.; Jacobs, J.; Kramer-Bottiglio, R. Robotic skins that learn to control passive structures. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gregory, C.; Minor, M.A. Improving mechanical properties of molded silicone rubber for soft robotics through fabric compositing. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 272–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyssier, M.; Parilusyan, B.; Roudaut, A.; Steimle, J. Human-Like Artificial Skin Sensor for Physical Human-Robot Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 3626–3633. [Google Scholar]
- MUCA Breakout · Multi Touch for Arduino. Available online: https://muca.cc/shop/muca-breakout-6 (accessed on 6 June 2024).
- Visual Studio Code. Available online: https://code.visualstudio.com/ (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- PlatformIO. PlatformIO Is a Professional Collaborative Platform for Embedded Development. Available online: https://platformio.org (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Github: MUCA Source Code. Available online: https://github.com/muca-board/Muca (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Poetry. Available online: https://python-poetry.org/ (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Moore, A. Optimal Filtering; Information and System Sciences; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, W. Delay Networks Having Maximally Flat Frequency Characteristics. Proc. IEEE—Part III Radio Commun. Eng. 1949, 96, 487–490. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. Automatica 1975, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L. Connected Component Labeling and Adjacency Graph Construction. In Machine Intelligence and Pattern Recognition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 19, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Otoo, E.; Shoshani, A. Optimizing Connected Component Labeling Algorithms; SPIE: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Walt, S.; Schönberger, J.L.; Nunez-Iglesias, J.; Boulogne, F.; Warner, J.D.; Yager, N.; Gouillart, E.; Yu, T. Scikit-Image: Image Processing in Python. PeerJ 2014, 2, e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. The Distribution of Flora in the Alpine Zone. New Phytol. 1912, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Xu, X. A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. In Proceedings of the KDD’96: 2nd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Macqueen, J. Some Methods for Classification and Analysis of Multivariate Observations. In Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Volume 1: Statistics; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas, G.L.; Khan, S. Improving soft capacitive tactile sensors: Scalable manufacturing, reduced crosstalk design, and machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Tampere, Finland, 30 June 30–3 July 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, S.S.; Ayodele, B.V.; Ali, S.S.; Cheng, C.K.; Mustapa, S.I. Comparative analysis of support vector machine regression and Gaussian process regression in modeling hydrogen production from waste effluent. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, M.E.; Rehan, M.; Saleem, M.M.; Rehman, M.U.; Jabbar, H.; Cheung, R. Development of a Capacitive-Piezoelectric Tactile Force Sensor for Static and Dynamic Forces Measurement and Neural Network-Based Texture Discrimination. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 11944–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, P. Probabilistic uncertainty quantification of microwave circuits using Gaussian processes. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2022, 71, 2360–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, K. Data Visualization: A Practical Introduction; Princeton University Press: Princeton NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Egger, P. Peterpf/Capsense-Monitor. Available online: https://github.com/peterpf/capsensor-monitor (accessed on 20 March 2025).




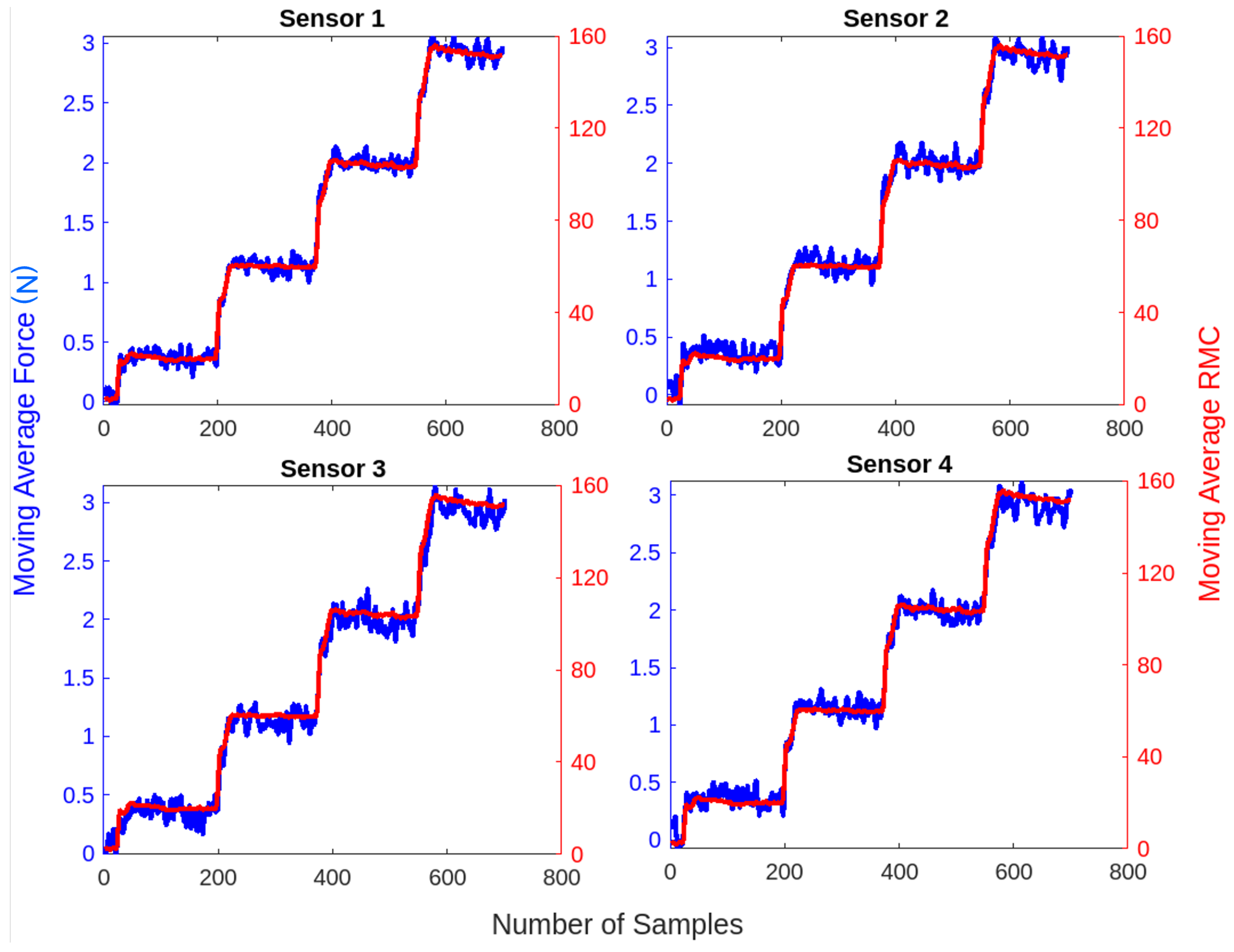
| Connected Component | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sensor | Linear Regression (, RMSE) | SVM (, RMSE) | Decision Tree (, RMSE) | GPR (, RMSE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor 1 | ||||
| Sensor 2 | ||||
| Sensor 3 | ||||
| Sensor 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Egger, P.W.; Srinivas, G.L.; Brandstötter, M. Real-Time Detection and Localization of Force on a Capacitive Elastomeric Sensor Array Using Image Processing and Machine Learning. Sensors 2025, 25, 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103011
Egger PW, Srinivas GL, Brandstötter M. Real-Time Detection and Localization of Force on a Capacitive Elastomeric Sensor Array Using Image Processing and Machine Learning. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103011
Chicago/Turabian StyleEgger, Peter Werner, Gidugu Lakshmi Srinivas, and Mathias Brandstötter. 2025. "Real-Time Detection and Localization of Force on a Capacitive Elastomeric Sensor Array Using Image Processing and Machine Learning" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103011
APA StyleEgger, P. W., Srinivas, G. L., & Brandstötter, M. (2025). Real-Time Detection and Localization of Force on a Capacitive Elastomeric Sensor Array Using Image Processing and Machine Learning. Sensors, 25(10), 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103011







