Emerging Trends in the Integration of Smart Sensor Technologies in Structural Health Monitoring: A Contemporary Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
Objectives of the Review
- Survey the latest developments in innovative sensor technologies and their applications in SHM.
- Discuss the benefits and challenges of integrating smart sensors in SHM systems.
- Identify emerging trends and novel applications in SHM.
- Highlight opportunities for future research and collaboration to address key challenges and advance the state-of-the-art in SHM.
2. Methods
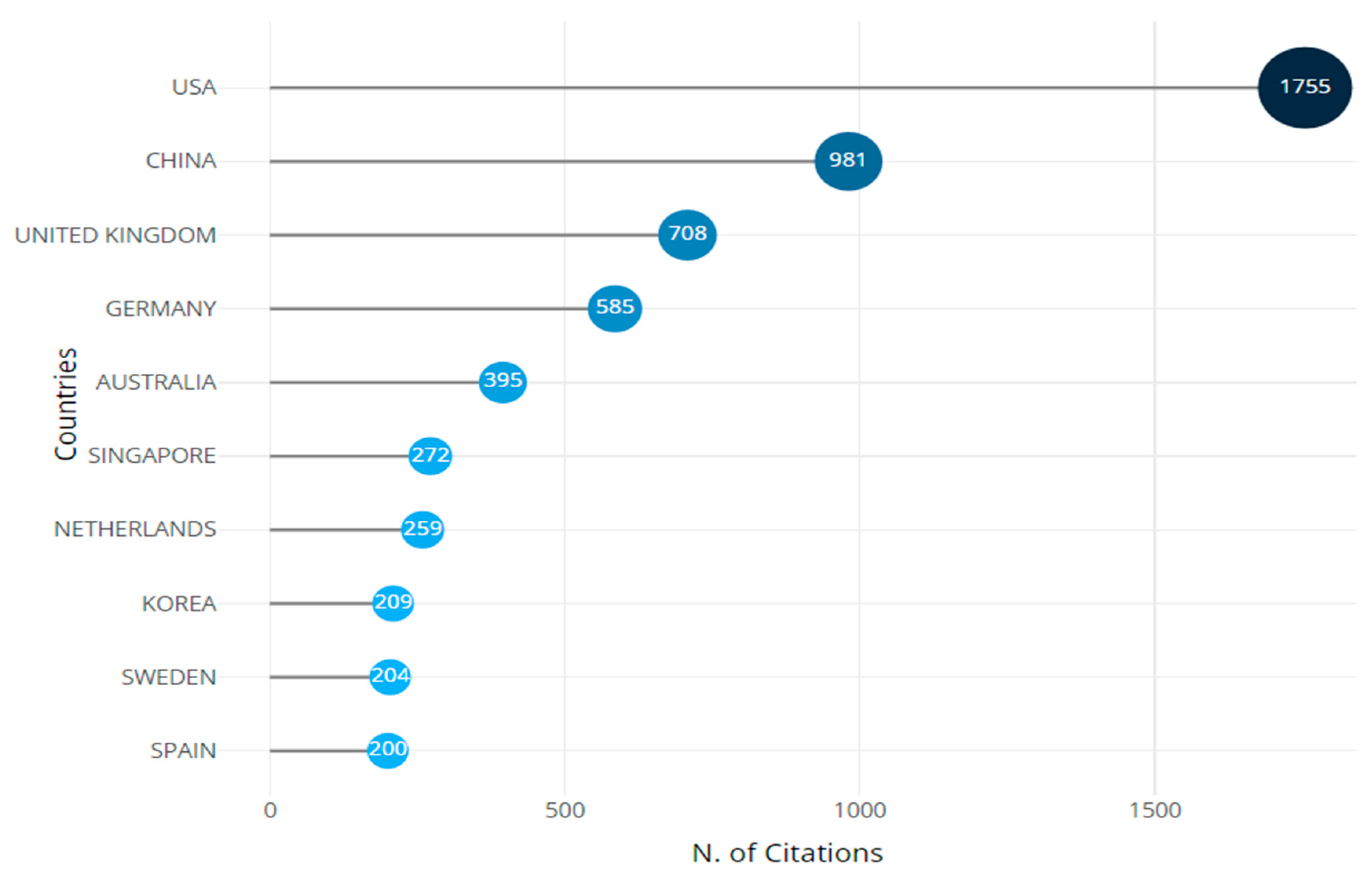
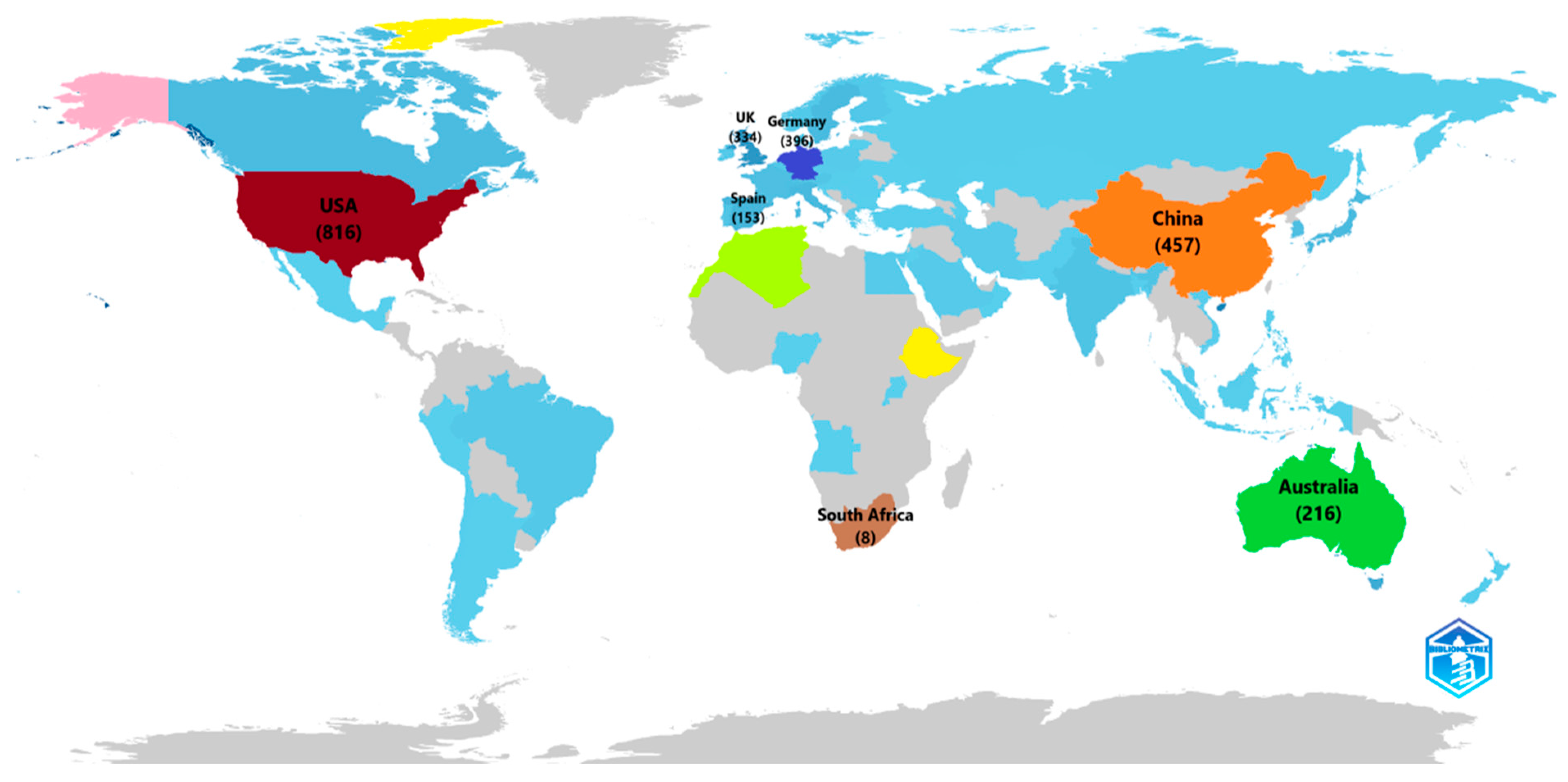
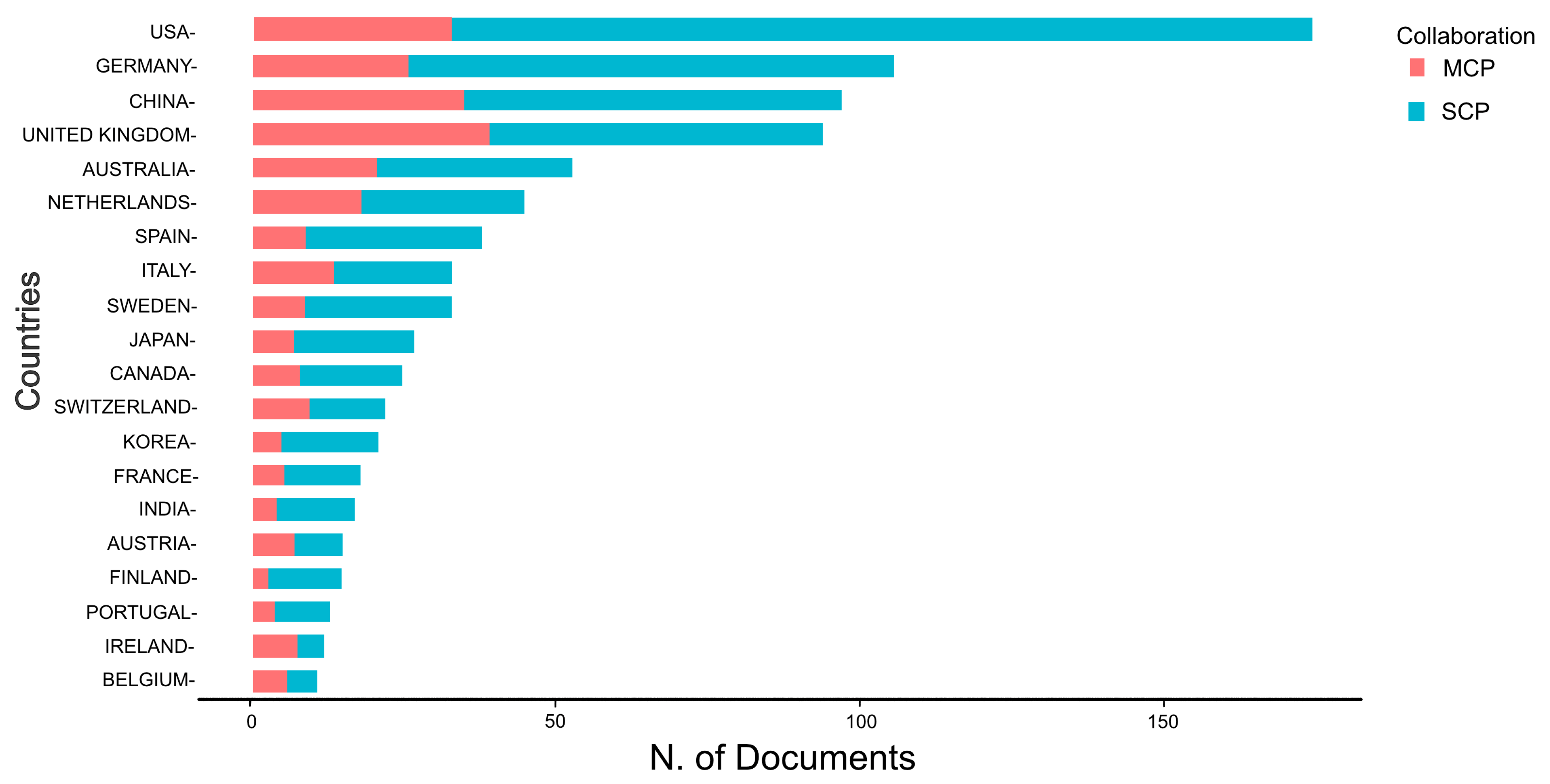
2.1. Countries Production
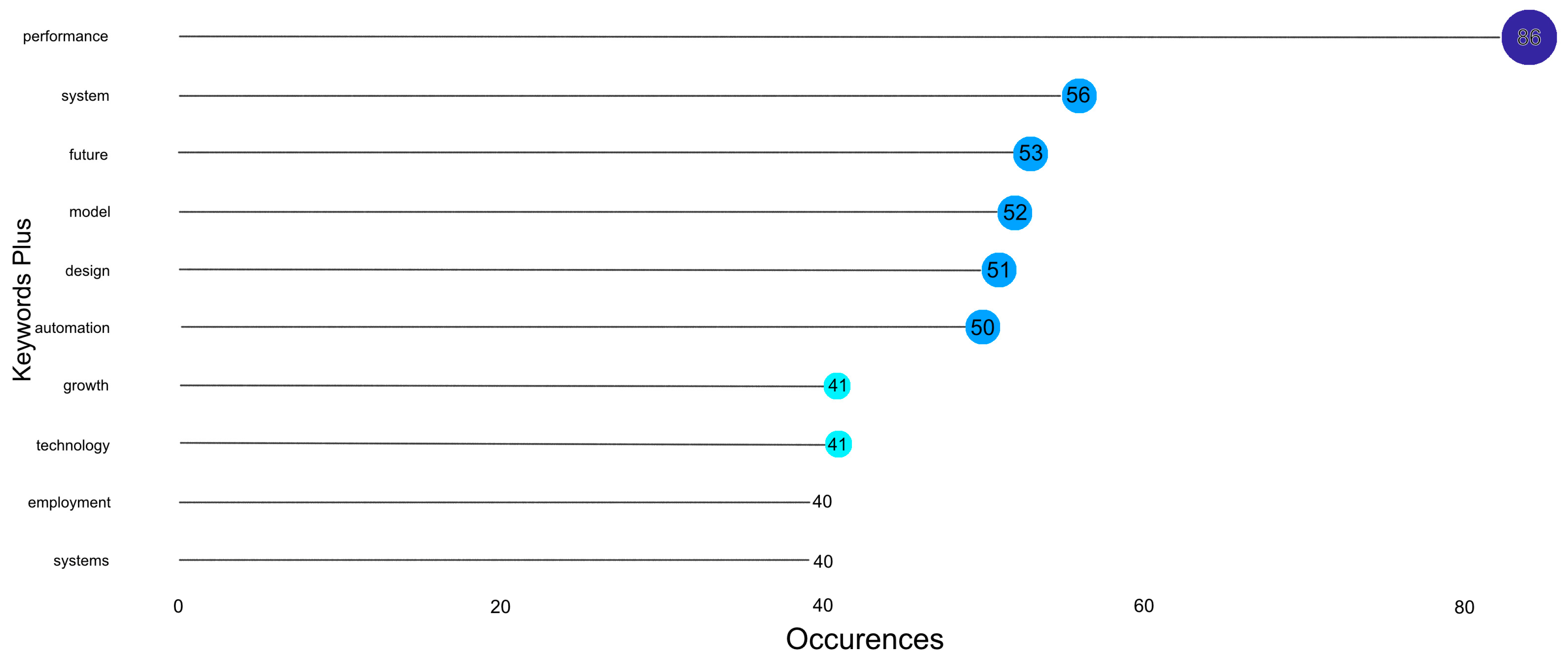
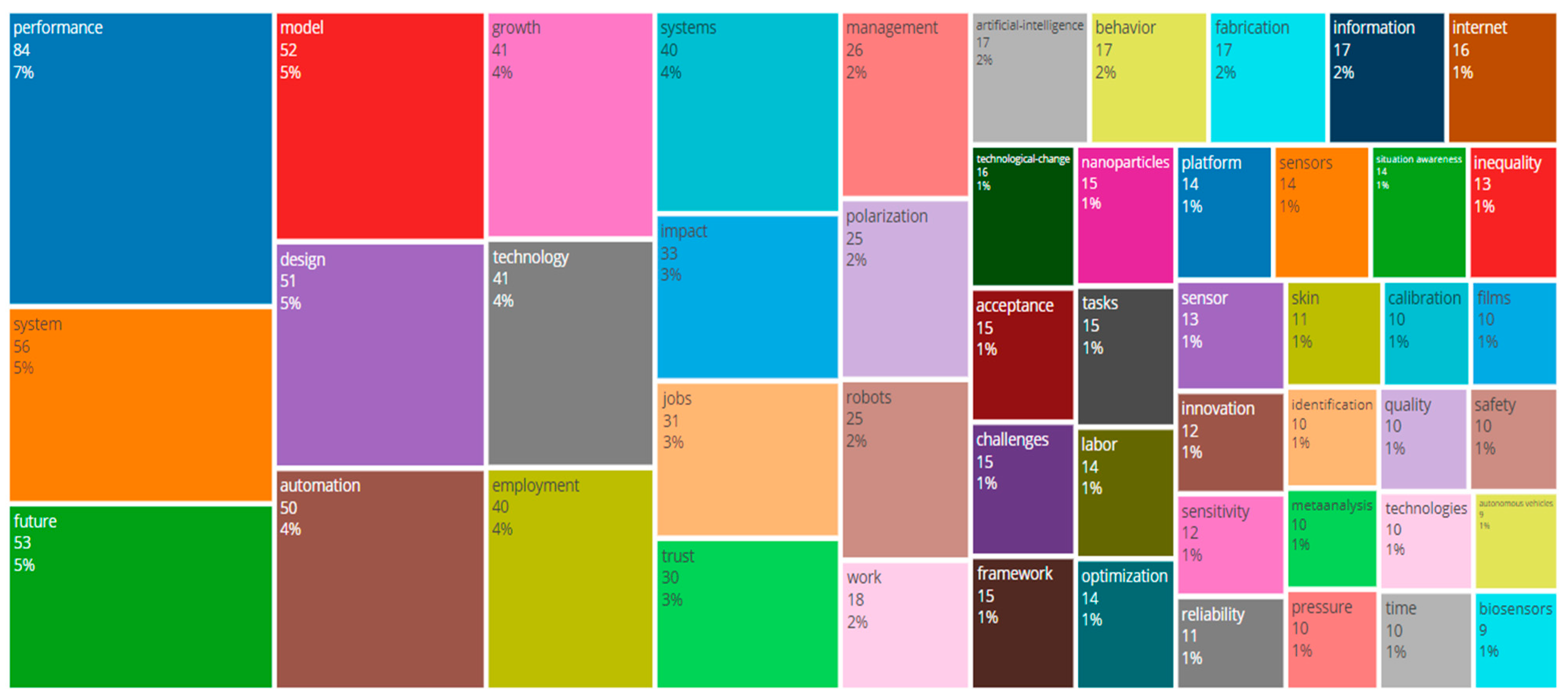
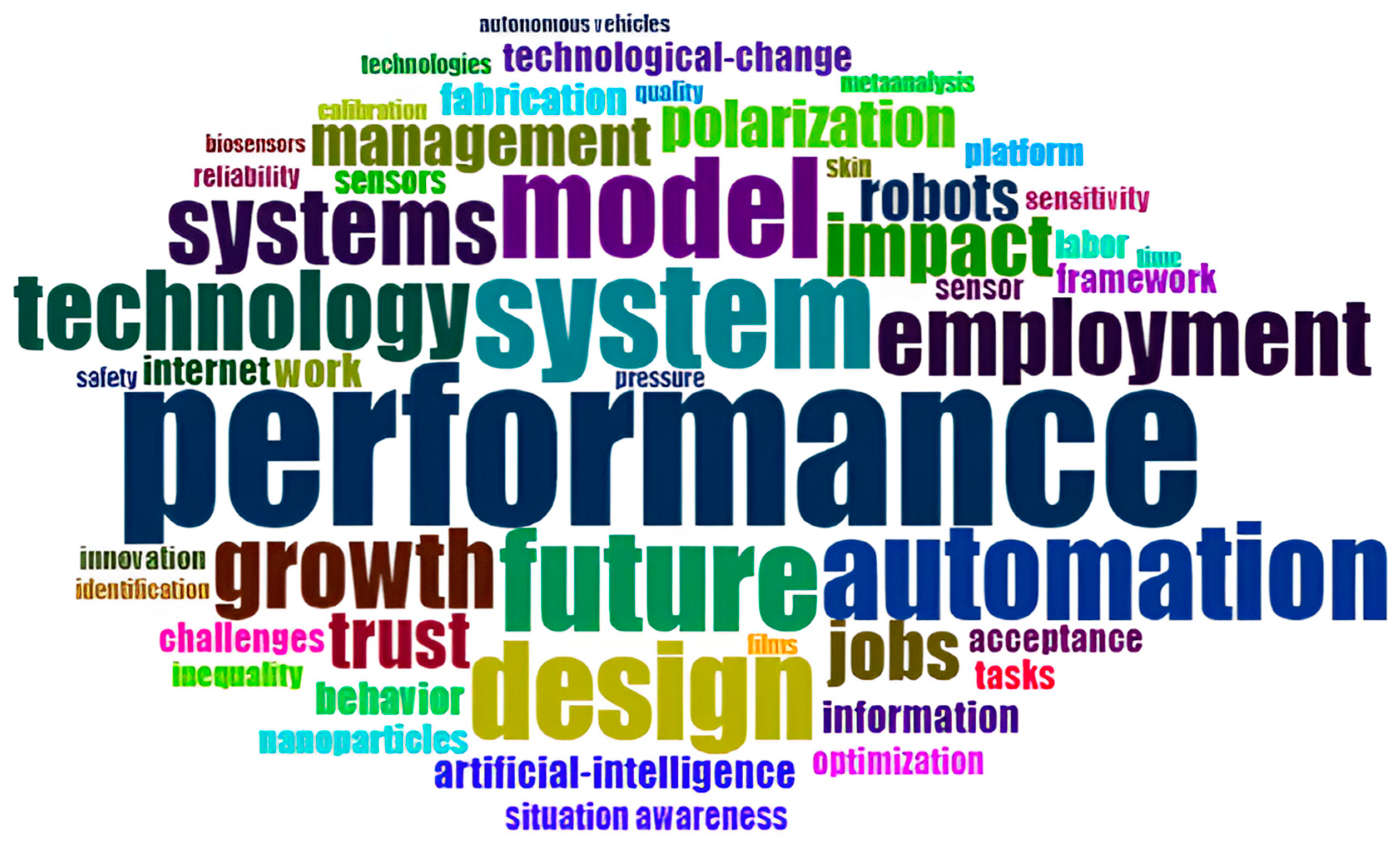
2.2. Most Frequent Words, Tree Maps, and Word Clouds
3. Results
3.1. Significance of SHM
3.2. Need of Sensors in SHM
3.3. Fibre Optic Sensors (FOS)
3.4. Piezoelectric Sensors
3.5. Measuring Acceleration
3.6. Measuring Forces
3.7. Microelectromechanical (MEMS) Devices
3.8. Measuring Displacement
3.9. Global Positioning Satellites (GPS)
3.10. Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)
3.11. Measuring Velocity
3.12. Electromechanical Impedance (EMI) Techniques
3.13. Doppler Effect
3.14. General Operations of Sensors and Data Acquisition in SHM
4. Comparative Analysis and Recommendations
4.1. Comparative Studies and Future Scope of Research Recommendations
- SHM is typically applied in bridges with only a long-term monitoring process; therefore, the sensors and other components of SHM must be insensitive to any environmental change. Since bridge SHM is purely automated, the technician must be conversant with data processing and instrumentation to monitor all telecom activities. It is always cheaper to monitor structures for the long term than for the short term if the sensors and other related settings are appropriately designed and maintained. SHM calls for professional staff and proper installation.
- As opposed to the accelerometer, which is more effective with the least number of sensors, other sensors require a much larger number of sensors for monitoring. Optical fibres can predict frequency levels and accelerometers; other sensors are less accurate. In accelerometers, the level of frequency and deformation may be expected with more accuracy.
- Various sensors can predict dynamic analysis based on vertical deformation and structure conditions [147]. Accelerometers may be applied for model identifications and ambient vibrations for dynamic analysis of all environmental changes.
- Accelerometers are preferable for dynamic analysis because they respond only to static parameters such as temperature, humidity, and elastic deformation. While in static loading conditions, temperature sensors, displacement transducers, and FBG have better results.
- GPS is the most accurate sensor when it comes to predicting the movement of a building. It is sensitive to small movements and is a security camera for real-time structural analysis. The GPS will sound a bell to inform people if the structure moves beyond the permitted limit.
- SHM is forecasted to predict bridges, dams, buildings, and stadiums with a compound annual growth rate of 20%. Most building firms are interested in the SHM method. SHM may be used as a compact testing and continuous monitoring system. The flexible monitoring system can monitor the current state. On the other hand, constant monitoring will acquire real-time data on a structure to identify any damage, improve sensor technologies for identifying structural alterations, and enhance wireless communication technology to enhance the effectiveness of SHM at a cheaper price [148,149].
- In SHM, a multilevel system can integrate global and local diagnostics. Diagnostics will fast condition screening worldwide, and diagnostics will fast location and degree of damage nearby. For an accurate prognosis of the health of any structure, SHM requires a deeper understanding of the equipment, signals, and mathematical techniques. They are designing low-cost dense sensor arrays and techniques for powering the sensing system by utilising energy from the structure’s working environment.
4.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Smart Sensor Technologies in SHM
- Fibre optic sensors (FOS) and piezoelectric sensors allow for the identification of structural changes and their constant monitoring for a long time. However, managing sensor networks over long periods can be expensive and requires professionalism.
- Accelerometers provide dynamic measurements, while displacement measurements are as accurate as GPS sensors. Nevertheless, GPS systems are sensitive to signal interferences, while accelerometers can be less efficient in static observation.
- MEMS and FOS are wireless sensors that allow remote health monitoring, thus enhancing safety and productivity. However, ensuring dependable wireless connections in areas with low or no easy access or where there are physical constraints, such as restricted access to power sources, can be a real problem.
- MEMS and EMI sensors, smart sensors, and analytics for condition-based monitoring help lower repair costs. However, the large volumes of data generated require efficient storage, management and analysis systems.
- MEMS and piezoelectric sensors are small, inexpensive, and ideal for small-scale applications, while integrating large-scale SHM systems involves substantial initial investments in sensors, communication networks, and calibration.
- FOS and piezoelectric sensors, for example, must endure temperature changes, corrosion and mechanical stress. Durability is still essential to sustaining the overall sensor performance and the quality of the data collected.
- The integration of smart sensor technologies in HMS, leveraging IoT-enabled systems enhances energy performance visualisation, building occupancy tracking, and post-occupancy energy analysis. With sensors, the buildings demonstrate how advanced monitoring solutions, combined with BIM, can support sustainable operations and maintenance while achieving significant environmental benefits [151].
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sensor Name | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fibre Optic Sensors | FOS | Measures strain, temperature, vibration, and displacement; highly accurate. |
| Piezoelectric Sensors | PZT | Converts mechanical stress into electrical signals for vibration monitoring. |
| Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems | MEMS | Compact sensors that measure vibrations, accelerations, and strains. |
| Global Positioning System | GPS | Tracks precise displacements and movements in civil structures. |
| Linear Variable Differential Transformer | LVDT | Measures small linear displacements with high resolution and reliability. |
| Electromechanical Impedance Techniques | EMI | Detects structural damage through impedance variations in localised regions. |
| Doppler Effect Sensors | - | Measures velocity by analysing frequency shifts in reflected waves. |
| Accelerometers | - | Monitors dynamic forces, accelerations, and vibrations in civil structures. |
References
- Girotto, C.D.; Piadeh, F.; Bkhtiari, V.; Behzadian, K.; Chen, A.S.; Campos, L.C.; Zolgharni, M. A Critical Review of Digital Technology Innovations for Early Warning of Water-Related Disease Outbreaks Associated with Climatic Hazards. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 100, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broer, A.A.R.; Benedictus, R.; Zarouchas, D. The Need for Multi-Sensor Data Fusion in Structural Health Monitoring of Composite Aircraft Structures. Aerospace 2022, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, M.; Davis, C.; Rosalie, C.; Norman, P.; Rajic, N. Acoustic Emission Detection and Characterisation Using Networked FBG Sensors. Procedia Eng. 2017, 188, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasy Chan, Y.W.; Zhou, Z. Advances of FRP-Based Smart Components and Structures. Pac. Sci. Rev. 2014, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.F.; Ruiz-Sandoval, M.E.; Kurata, N. Smart Sensing Technology: Opportunities and Challenges. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2004, 11, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ručevskis, S.; Rogala, T.; Katunin, A. Optimal Sensor Placement for Modal-Based Health Monitoring of a Composite Structure. Sensors 2022, 22, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennyson, R.C.; Mufti, A.A.; Rizkalla, S.; Tadros, G.; Benmokrane, B. Structural Health Monitoring of Innovative Bridges in Canada with Fiber Optic Sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2001, 10, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Park, J.; Jung, H.J.; Yun, C.B.; Jang, S.; Jo, H.; Spencer, B.F.; Nagayama, T.; Seo, J.W. Structural Health Monitoring of a Cable-Stayed Bridge Using Acceleration Data via Wireless Smart Sensor Network. In Bridge Maintenance, Safety, Management and Life-Cycle Optimization, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Bridge Maintenance, Safety and Management, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 11–15 July 2010; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; Volume 6, pp. 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Liu, G.; Fu, S.; Xing, F. Recent Progress of Fiber-Optic Sensors for the Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure. Sensors 2020, 20, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bado, M.F.; Casas, J.R. A Review of Recent Distributed Optical Fiber Sensors Applications for Civil Engineering Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ou, J. Structural Health Monitoring: From Sensing Technology Stepping to Health Diagnosis. Procedia Eng. 2011, 14, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.F.; Lu, P.; Devkota, J.; Lu, F.; Ziomek-Moroz, M.; Ohodnicki, P.R. Corrosion Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring of Oil and Natural Gas Infrastructure: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, Y.; Tian, S.; Liu, G.; Wu, F.; Wang, P.; Gao, M. Wireless Sensing in High-Speed Railway Turnouts with Battery-Free Materials and Devices. iScience 2024, 27, 108663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonbul, O.S.; Rashid, M. Towards the Structural Health Monitoring of Bridges Using Wireless Sensor Networks: A Systematic Study. Sensors 2023, 23, 8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, P.M.; Machado, M.A.; Carvalho, M.S.; Vidal, C. Embedded Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring: Methodologies and Applications Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, A.R.; Beheiry, S.; Alnabulsi, A.; Obaid, S.; Mansoor, N.; Odeh, N.; Mostafa, A. An IoT-Based Road Bridge Health Monitoring and Warning System. Sensors 2024, 24, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaharuddin, S.; Abdul Maulud, K.N.; Syed Abdul Rahman, S.A.F.; Che Ani, A.I.; Pradhan, B. The Role of IoT Sensor in Smart Building Context for Indoor Fire Hazard Scenario: A Systematic Review of Interdisciplinary Articles. Internet Things 2023, 22, 100803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Ma, H.; Li, P.; Song, G.; Wu, J. Development and Application of a Structural Health Monitoring System Based on Wireless Smart Aggregates. Sensors 2017, 17, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, L. Rapid Structural Condition Assessment Using Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Based Wireless Strain Sensor. Autom. Constr. 2015, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuhammadi, K.; Yudhanto, A.; Lubineau, G. Real-Time Electrical Impedance Monitoring of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Laminates Undergoing Quasi-Static Indentation. Compos. Struct. 2019, 207, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, R.; Zorrilla, R. Structural Health Monitoring in Incrementally Launched Steel Bridges: Patch Loading Phenomena Modeling. Autom. Constr. 2015, 58, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Mou, Y.; Kashiwa, T.; Escalera, S.; Nagai, K.; Nakayama, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Prendinger, H. Vision Based Pixel-Level Bridge Structural Damage Detection Using a Link ASPP Network. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 102973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Huang, Y.; Lehane, B.; Ma, G. XGBoost Algorithm-Based Prediction of Concrete Electrical Resistivity for Structural Health Monitoring. Autom. Constr. 2020, 114, 103155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Scherer, R.J. Concrete Bridge Damage Detection Using Parallel Simulation. Autom. Constr. 2020, 119, 103283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Thostenson, E.T.; Schumacher, T.; Doshi, S.M.; McConnell, J.R. Integration of Carbon Nanotube Sensing Skins and Carbon Fiber Composites for Monitoring and Structural Repair of Fatigue Cracked Metal Structures. Compos. Struct. 2018, 203, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Qing, X. Modified Electromechanical Impedance-Based Disbond Monitoring for Honeycomb Sandwich Composite Structure. Compos. Struct. 2019, 217, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, I.; Jones, R.; Marshall, I.H.; Galea, S. Optical Fibre Sensors for Health Monitoring of Bonded Repair Systems. Compos. Struct. 2000, 50, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wan, B.; Han, B.; Cai, G.; Li, Z. Properties and Mechanisms of Self-Sensing Carbon Nanofibers/Epoxy Composites for Structural Health Monitoring. Compos. Struct. 2018, 200, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanukuttan, S.; Yang, K.; Basheer, P.A.M. Non-Destructive Testing and Structural Health Monitoring. In ICE Handbook of Concrete Durability: A Practical Guide to the Design of Resilient Concrete Structures; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2023; pp. 449–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethichandra, D.M.G.; Suntharavadivel, T.G.; Kalutara, P.; Piyathilaka, L.; Izhar, U. Influence of Smart Sensors on Structural Health Monitoring Systems and Future Asset Management Practices. Sensors 2023, 23, 8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pregnolato, M.; Gunner, S.; Voyagaki, E.; De Risi, R.; Carhart, N.; Gavriel, G.; Tully, P.; Tryfonas, T.; Macdonald, J.; Taylor, C. Towards Civil Engineering 4.0: Concept, Workflow and Application of Digital Twins for Existing Infrastructure. Autom. Constr. 2022, 141, 104421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, P.T. Smart Structures and Materials Systems. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1992, 25, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Adams, B.; Adewale, I.D.; Agunbiade, F.O.; Akinyemi, M.I.; Archer, E.; Badru, F.A.; Barnett, J.; Bishop, I.J.; Di Lorenzo, M.; et al. Wastewater-Based Epidemiology in Hazard Forecasting and Early-Warning Systems for Global Health Risks. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, S.; Dackermann, U. A Systematic Review of Optimization Algorithms for Structural Health Monitoring and Optimal Sensor Placement. Sensors 2023, 23, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.F.; Park, J.W.; Mechitov, K.A.; Jo, H.; Agha, G. Next Generation Wireless Smart Sensors Toward Sustainable Civil Infrastructure. Procedia Eng. 2017, 171, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Graziano, A.; Marchetta, V.; Cafiso, S. Structural Health Monitoring of Asphalt Pavements Using Smart Sensor Networks: A Comprehensive Review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 7, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyeye, K. The Householder Is King: Engendering Householder Participation in Bridging the Performance Gap in Homes. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2023, 103, 103199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Paik, J.H.; Yun, J.; Yun, J.S. Poling Effects on the Performance of a Lead-Free Piezoelectric Nanofiber in a Structural Health Monitoring Sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 263, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Huang, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Deng, Z.; Luo, J. Damage identification of steel bridge based on data augmentation and adaptive optimization neural network. Struct. Health Monit. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Castro, B.; Haro-Baez, A.G.; Arcos-Aviles, D.; Barreno-Riera, M.; Landázuri-Avilés, B. A Systematic Review of Structural Health Monitoring Systems to Strengthen Post-Earthquake Assessment Procedures. Sensors 2022, 22, 9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapha, S.; Lu, Y.; Ng, C.T.; Malinowski, P. Sensor Networks for Structures Health Monitoring: Placement, Implementations, and Challenges—A Review. Vibration 2021, 4, 551–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Li, Y. Deep Learning for Structural Health Monitoring: Data, Algorithms, Applications, Challenges, and Trends. Sensors 2023, 23, 8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Q.A.; Jiao, G.; Dang, P.; Nie, G.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J. Review of Wireless RFID Strain Sensing Technology in Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.C.; Flatau, A.; Liu, S.C. Review Paper: Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructure. Struct. Health Monit. 2003, 2, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbarufatti, C.; Manes, A.; Giglio, M. Application of Sensor Technologies for Local and Distributed Structural Health Monitoring. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2014, 21, 1057–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, W.Y.; Yang, X.P.; Jiang, W.D.; Liu, X.H.; Zhang, W. A Facile and Sensitive Ratiometric Fluorescence Sensor for Rapid Visual Monitoring of Trace Resorcinol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 330, 129390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedűs, G.; Czigány, T. Analysis of the Applicability of Optical Fibers as Sensors for the Structural Health Monitoring of Polymer Composites: The Relationship between Attenuation and the Deformation of the Fiber. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 272, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Oyadiji, S.O. Development of Two-Layer Multiple Transmitter Fibre Optic Bundle Displacement Sensor and Application in Structural Health Monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 244, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, L.; Perry, M.; McAlorum, J.; Vlachakis, C.; Hamilton, A. Geopolymer-Based Moisture Sensors for Reinforced Concrete Health Monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Higuera, J.M.; Cobo, L.R.; Incera, A.Q.; Cobo, A. Fiber Optic Sensors in Structural Health Monitoring. J. Light. Technol. 2011, 29, 587–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, K.; Doherty, G.; O’Callaghan, D. Wireless Sensor Networks. In Understanding the Internet: A Glimpse into the Building Blocks, Applications, Security and Hidden Secrets of the Web; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.W.; Xiao, W.; Deng, Q.X. Review of Fiber Optic Sensors in Geotechnical Health Monitoring. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2020, 54, 102127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Staszewski, W.J.; Swamy, R.N. Smart Sensing Technologies for Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Engineering Structures. Adv. Civil. Eng. 2010, 2010, 724962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianti, M.S.; Prasetyo, E.; Wijaya, A.D.; Berliandika, S.; Marzuki, A. Vibration Measurement of Mathematical Pendulum Based on Macrobending-Fiber Optic Sensor as a Model of Bridge Structural Health Monitoring. Procedia Eng. 2017, 170, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Dutta, S.; Kurup, P.; Yu, T.; Wang, X. A Review of Railway Infrastructure Monitoring Using Fiber Optic Sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 303, 111728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasi, D.; Philip, S.; David, R.; Swathi, J. A Review on Structural Health Monitoring of Railroad Track Structures Using Fiber Optic Sensors. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.S.; Khan, T.; Hussain, T.; Liao, K.; Umer, R. Carbon Coated Piezoresistive Fiber Sensors: From Process Monitoring to Structural Health Monitoring of Composites—A Review. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 141, 106236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Deng, W.; Huang, J.; Ma, H. Fiber Optic Sensors Enabled Monitoring of Thermal Curling of Concrete Pavement Slab: Temperature, Strain and Inclination. Measurement 2020, 165, 108203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, I.; Adam, J.M.; Calderón, P.A.; Sales, S. Fiber Optic Shape Sensors: A Comprehensive Review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 139, 106508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, K.; Wollweber, M.; Weigand, F.; Rahlves, M.; Kuhne, M.; Helbig, R.; Roth, B. Fibre Optic Sensors for the Structural Health Monitoring of Building Structures. Procedia Technol. 2016, 26, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, W.; Chen, G.; Bao, Y. Monitoring Corrosion of Steel Bars in Reinforced Concrete Based on Helix Strains Measured from a Distributed Fiber Optic Sensor. Eng. Struct. 2020, 204, 110039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, T.; Sim, S.H.; Miyamori, Y.; Spencer, B.F. Issues in Structural Health Monitoring Employing Smart Sensors. Smart Struct. Syst. 2007, 3, 299–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navabian, N.; Beskhyroun, S.; Matulich, J. Development of Wireless Smart Sensor Network for Vibration-Based Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Structures. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2022, 18, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.; Torres, L.; Ruiz, A.; Barris, C.; Baena, M. An Emi-Based Clustering for Structural Health Monitoring of NSM FRP Strengthening Systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Adeli, H. Wireless Smart Sensors for Monitoring the Health Condition of Civil Infrastructure. Sci. Iran. 2018, 25, 2913–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, S.; Kaur, N. Prognosis of Low-Strain Fatigue Induced Damage in Reinforced Concrete Structures Using Embedded Piezo-Transducers. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 113, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasni, H.; Alavi, A.H.; Lajnef, N.; Abdelbarr, M.; Masri, S.F.; Chakrabartty, S. Self-Powered Piezo-Floating-Gate Sensors for Health Monitoring of Steel Plates. Eng. Struct. 2017, 148, 584–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharana, S.; Bhalla, S. A Continuum Based Modelling Approach for Adhesively Bonded Piezo-Transducers for EMI Technique. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Bareille, O.; Salvia, M. Cure and Damage Monitoring of Flax Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composite Repairs for Civil Engineering Structures Using Embedded Piezo Micro-Patches. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Bhalla, S.; Naqvi, T. Fatigue Damage and Residual Fatigue Life Assessment in Reinforced Concrete Frames Using PZT-Impedance Transducers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Bhalla, S.; Naqvi, T. Fatigue Damage Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete Frames Using Wavelet Transform Energy of PZT-Based Admittance Signals. Measurement 2020, 164, 108033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.H.; Huang, M.W. Piezoelectric Cement Sensor-Based Electromechanical Impedance Technique for the Strength Monitoring of Cement Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Banerjee, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Cheng, X. Temperature and Loading Effects of Embedded Smart Piezoelectric Sensor for Health Monitoring of Concrete Structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, J.; Feirahi, M.H.; Farahmand-Tabar, S.; Keshvari Fard, A.H. A Novel Approach for Non-Destructive EMI-Based Corrosion Monitoring of Concrete-Embedded Reinforcements Using Multi-Orientation Piezoelectric Sensors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 273, 121689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.F.; Wang, J.; Tong, S.Y.; Ma, S.L.; Tuo, M.B.; Li, W.J. Damage Monitoring of Concrete Laminated Interface Using Piezoelectric-Based Smart Aggregate. Eng. Struct. 2021, 228, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezgy-Nazargah, M.; Saeidi-Aminabadi, S.; Yousefzadeh, M.A. Design and Fabrication of a New Fiber-Cement-Piezoelectric Composite Sensor for Measurement of Inner Stress in Concrete Structures. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2019, 19, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibaduiza Burgos, D.A.; Gomez Vargas, R.C.; Pedraza, C.; Agis, D.; Pozo, F. Damage Identification in Structural Health Monitoring: A Brief Review from Its Implementation to the Use of Data-Driven Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Saha, P. A Review of Some Advanced Sensors Used for Health Diagnosis of Civil Engineering Structures. Measurement 2018, 129, 68–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P. A Summary Review of Wireless Sensors and Sensor Networks for Structural Health Monitoring. Shock Vib. Dig. 2006, 38, 91–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.A.; Mechitov, K.; Sim, S.H.; Nagayama, T.; Jang, S.; Kim, R.; Spencer, B.F.; Agha, G.; Fujino, Y. Flexible Smart Sensor Framework for Autonomous Structural Health Monitoring. Smart Struct. Syst. 2010, 6, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabato, A.; Dabetwar, S.; Kulkarni, N.N.; Fortino, G. Noncontact Sensing Techniques for AI-Aided Structural Health Monitoring: A Systematic Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 4672–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.W.; Jin, T.; Yun, C.B. A Review on Deep Learning-Based Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructures. Smart Struct. Syst. 2019, 24, 567–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagami, A.; Jayakumar, S.; Kandavalli, M.A. Structural Health Monitoring Using Smart Sensors. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamdas, V.G.M.; Bhalla, S.; Soh, C.K. Applications of Structural Health Monitoring Technology in Asia. Struct. Health Monit. 2017, 16, 324–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Mousavi, M.; Gandomi, A.H. Structural Health Monitoring in Composite Structures: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, T.; Sedigh, S.; Bastianini, F. Structural Health Monitoring of Bridges Using Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2010, 13, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreevallabhan, K.; Chand, B.N.; Ramasamy, S. Structural Health Monitoring Using Wireless Sensor Networks. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 263, 1403–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.N.; Ren, L.; Jia, Z.G.; Yi, T.H.; Li, D.S. State-of-the-Art in Structural Health Monitoring of Large and Complex Civil Infrastructures. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2016, 6, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.A.; Mechitov, K.A.; Sim, S.H.; Spencer, B.F.; Agha, G.A. Enabling Framework for Structural Health Monitoring Using Smart Sensors. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2011, 18, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.F.; Jo, H.; Mechitov, K.A.; Li, J.; Sim, S.H.; Kim, R.E.; Cho, S.; Linderman, L.E.; Moinzadeh, P.; Giles, R.K.; et al. Recent Advances in Wireless Smart Sensors for Multi-Scale Monitoring and Control of Civil Infrastructure. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2016, 6, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenath, S.; Malik, H.; Husnu, N.; Kalaichelavan, K. Assessment and Use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle for Civil Structural Health Monitoring. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 170, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, C.L.; Chen, J.H. Optimal Arrangement of Structural Sensors in Soft Rock Tunnels Based Industrial IoT Applications. Comput. Commun. 2020, 156, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Saha, P. Performance of Swarm Intelligence Based Chaotic Meta-Heuristic Algorithms in Civil Structural Health Monitoring. Measurement 2021, 169, 108533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopa, A.K.; Hunashyal, A.M.; Venkaraddiyavar, P.; Ganachari, S.V. Smart Hybrid Nano Composite Concrete Embedded Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 27, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyildiz, C.; Erdem, H.E.; Dirikgil, T.; Dugenci, O.; Kocak, T.; Altun, F.; Gungor, V.C. Structure Health Monitoring Using Wireless Sensor Networks on Structural Elements. Ad Hoc Netw. 2019, 82, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazonov, E.; Janoyan, K.; Jha, R. Wireless Intelligent Sensor Network for Autonomous Structural Health Monitoring. In Smart Structures and Materials 2004: Smart Sensor Technology and Measurement Systems; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5384, p. 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkarem, M.; Samsudin, K.; Rokhani, F.Z.; A Rasid, M.F. Wireless Sensor Network for Structural Health Monitoring: A Contemporary Review of Technologies, Challenges, and Future Direction. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 19, 693–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, A.; Jane Regita, J.; Rane, B.; Lau, H.H. Structural Health Monitoring Using Wireless Smart Sensor Network—An Overview. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2022, 163, 108113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri Aliabadi, M.H.; Khodaei, Z.S. Structural Health Monitoring for Advanced Composite Structures; World Scientific: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthorpe, R.J.; Worden, K. Emerging Trends in Optimal Structural Health Monitoring System Design: From Sensor Placement to System Evaluation. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2020, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zuriqat, T.; Chillón Geck, C.; Dragos, K.; Smarsly, K. Adaptive Fault Diagnosis for Simultaneous Sensor Faults in Structural Health Monitoring Systems. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondolo, F.; Cesetti, A.; Matta, E.; Quattrone, A.; Sabia, D. Smart Reinforcement Steel Bars with Low-Cost MEMS Sensors for the Structural Health Monitoring of RC Structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 173, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidorzi, R.; Diversi, R.; Vincenzi, L.; Mazzotti, C.; Simioli, V. Structural Monitoring of a Tower by Means of MEMS-Based Sensing and Enhanced Autoregressive Models. Eur. J. Control 2014, 20, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.; Kazari, H.; Ozevin, D. Piezoelectric MEMS Acoustic Emission Sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 279, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, G.; Jeon, J. A Study on the Data Compression Technology-Based Intelligent Data Acquisition (IDAQ) System for Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Structures. Sensors 2017, 17, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremer, K.; Weigand, F.; Zheng, Y.; Alwis, L.S.; Helbig, R.; Roth, B. Structural Health Monitoring Using Textile Reinforcement Structures with Integrated Optical Fiber Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarska, K.; Sobotka, P.; Woliński, T.R.; Zakrecka, O.; Pomianek, W.; Nocoń, A.; Lesiak, P. Hybrid Fiber Optic Sensor Systems in Structural Health Monitoring in Aircraft Structures. Materials 2020, 13, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Choi, J.; Chung, J.; Koo, G.; Bae, I.H.; Sohn, H. Structural Displacement Estimation through Multi-Rate Fusion of Accelerometer and RTK-GPS Displacement and Velocity Measurements. Measurement 2018, 130, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez B., G.E.; Gaxiola-Camacho, J.R.; Bennett, R.; Guzman-Acevedo, G.M.; Gaxiola-Camacho, I.E. Structural Evaluation of Dynamic and Semi-Static Displacements of the Juarez Bridge Using GPS Technology. Measurement 2017, 110, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sante, R. Fibre Optic Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring of Aircraft Composite Structures: Recent Advances and Applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 18666–18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Dong, L.; Qian, Y. Deployment of a Smart Structural Health Monitoring System for Long-Span Arch Bridges: A Review and a Case Study. Sensors 2017, 17, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Birgin, H.B.; Cerni, G.; Ubertini, F. Smart Infrastructure Monitoring through Self-Sensing Composite Sensors and Systems: A Study on Smart Concrete Sensors with Varying Carbon-Based Filler. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedon, C.; Bergamo, E.; Izzi, M.; Noè, S. Prototyping and Validation of MEMS Accelerometers for Structural Health Monitoring—The Case Study of the Pietratagliata Cable-Stayed Bridge. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2018, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, A.S.; Kudus, S.A.; Jamadin, A.; Mustaffa, N.K.; Sugiura, K. Recent Vibration-Based Structural Health Monitoring on Steel Bridges: Systematic Literature Review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuc, T.; Nguyen, T.A.; Dao, H.; Catbas, F.N. Swaying Displacement Measurement for Structural Monitoring Using Computer Vision and an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Measurement 2020, 159, 107769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, E.J.; Riggio, M.; Barbosa, A.R. A Methodological Approach for Structural Health Monitoring of Mass-Timber Buildings under Construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havaran, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Markers Tracking and Extracting Structural Vibration Utilizing Randomized Hough Transform. Autom. Constr. 2020, 116, 103235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.K.; Ong, W.H.; Kuen, T.; Courtney, F. Large Structures Monitoring Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Procedia Eng. 2017, 188, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, B.W.; Mohamad, H.; Ahmad, N.R. Rock Stiffness Measurements Fibre Bragg Grating Sensor (FBGs) and the Effect of Cyanoacrylate and Epoxy Resin as Adhesive Materials. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1677–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenthal, G.; Eick, J.F.; Rau, S.; Taraben, J. Wireless Sensor Networks Composed of Standard Microcomputers and Smartphones for Applications in Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.F.; Qiao, Z.H.; Li, N.L.; Luo, J.B.; Shen, S.; Wu, M.H.; Zhang, Y. Structural Health Monitoring System Based on FBG Sensing Technique for Chinese Ancient Timber Buildings. Sensors 2020, 20, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Y.; Safak, E. Real-Time Structural Health Monitoring and Damage Detection. In Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 39, pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, L.; Cheng, H.; Kong, Q.; Chen, X. Bond-Slip Monitoring of Concrete Structures Using Smart Sensors—A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.D.S.; Sobrinho, J.M.B.; Souto, C.R.; Gomes, R.M. Application of Electromechanical Impedance Technique in the Monitoring of Sigma Phase Embrittlement in Duplex Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 788, 139457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, W.; Lan, C.; Wei, P.; Luo, W. Electromechanical Impedance Instrumented Piezoelectric Ring for Pipe Corrosion and Bearing Wear Monitoring: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 315, 112276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ai, D.; Zhu, H.; Luo, H. Integrated Electromechanical Impedance Technique with Convolutional Neural Network for Concrete Structural Damage Quantification under Varied Temperatures. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2021, 152, 107467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ai, D.; Zhu, H.; Luo, H. An Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Based Signal Compression and Reconstruction Approach for Electromechanical Admittance Based Structural Health Monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2019, 133, 106276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwis, L.S.M.; Bremer, K.; Roth, B. Fiber Optic Sensors Embedded in Textile-Reinforced Concrete for Smart Structural Health Monitoring: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, M.A.; Monteiro, A.V.; Filho, J.V. A New Structural Health Monitoring Strategy Based on PZT Sensors and Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soman, R.; Wee, J.; Peters, K. Optical Fiber Sensors for Ultrasonic Structural Health Monitoring: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panah, R.S.; Kioumarsi, M. Application of Building Information Modelling (BIM) in the Health Monitoring and Maintenance Process: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, M.; Eslamlou, A.D.; Pekcan, G. Data-Driven Structural Health Monitoring and Damage Detection through Deep Learning: State-of-the-Art Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.Z.; Ye, X.W.; Jin, T. Identification of Structural Dynamic Characteristics Based on Machine Vision Technology. Measurement 2018, 126, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, S.J.; Allen, M.S.; Castellini, P.; Di Maio, D.; Dirckx, J.J.J.; Ewins, D.J.; Halkon, B.J.; Muyshondt, P.; Paone, N.; Ryan, T.; et al. An International Review of Laser Doppler Vibrometry: Making Light Work of Vibration Measurement. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 99, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linzer, L.; Mhamdi, L.; Schumacher, T. Application of a Moment Tensor Inversion Code Developed for Mining-Induced Seismicity to Fracture Monitoring of Civil Engineering Materials. J. Appl. Geophy 2015, 112, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, D.S.; Rose, A.L.; Arvindan, S.; Revathy, J.; Amuthadevi, C. Automation Systems in Smart Buildings: A Review. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, H.H.; Gindy, M.; Davis, J. Comparison of Laser Doppler Vibrometer with Contact Sensors for Monitoring Bridge Deflection and Vibration. NDT E Int. 2005, 38, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduge, S.K.; Thilakarathna, S.; Perera, J.S.; Arashpour, M.; Sharafi, P.; Teodosio, B.; Shringi, A.; Mendis, P. Artificial Intelligence and Smart Vision for Building and Construction 4.0: Machine and Deep Learning Methods and Applications. Autom. Constr. 2022, 141, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, H.; Beddelee, A.A.A.M.; Ghazali, M.F.; Lee, H.E.; Chaiyasarn, K.; Nasir, M.Y.M. Distributed Fibre Optic Inclinometer with Cloud-Based Monitoring System. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2023, 41, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei, M.; Nakhaei, P.; Gheibi, M.; Chahkandi, B.; Wacławek, S.; Behzadian, K.; Chen, A.S.; Campos, L.C. Enhancing Community Resilience in Arid Regions: A Smart Framework for Flash Flood Risk Assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnanunni, A.V.; Kaur, N.; Bhalla, S.; Singh, N.; Balguvhar, S. Efficacy of Singly Curved Thin Piezo Transducers for Structural Health Monitoring and Energy Harvesting for RC Structures. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 2506–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéguen, P.; Tiganescu, A. Condition-Based Decision Using Traffic-Light Concept Applied to Civil Engineering Buildings. Procedia Eng. 2017, 199, 2096–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, L.; Fayaz, J.; Varga, L. Domain-Informed Variational Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines Based Leakage Detection Framework to Augment Self-Healing in Water Distribution Networks. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiantong, P.; Bongkarn, T.; Rianyoi, R.; Julphunthong, P. Fabrication and Characterisation of 0–3 KNLNTS Piezoelectric Ceramic/Alite Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement Composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 1563–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, H. Development and Experimental Verification of an IoT Sensing System for Drive-by Bridge Health Monitoring. Eng. Struct. 2023, 293, 116705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, C.; Garrido, D.; Llopis, L.; Rubio, B.; Díaz, M. Facilitating the Monitoring and Management of Structural Health in Civil Infrastructures with an Edge/Fog/Cloud Architecture. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2022, 81, 103600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.C.; Luu, T.H.T.; Nguyen, H.P.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ho, D.D.; Huynh, T.C. Piezoelectric Impedance-Based Structural Health Monitoring of Wind Turbine Structures: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Energies 2022, 15, 5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, Y.; Zhang, S.E.; Nwaila, G.T.; Bourdeau, J.E.; Safari, M.; Hadi Hoseinie, S.; Nwaila, P.; Ruuska, J. Dry Laboratories—Mapping the Required Instrumentation and Infrastructure for Online Monitoring, Analysis, and Characterization in the Mineral Industry. Miner. Eng. 2023, 191, 107971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbek, M. Smart Maintenance and Health Monitoring of Buildings and Infrastructure Using High-Resolution Laser Scanners. Buildings 2022, 12, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, D.S.; Sivasuriyan, A.; Devarajan, P.; Krejsa, M.; Chalecki, M.; Żółtowski, M.; Kozarzewska, A.; Koda, E. Development of Intelligent Technologies in SHM on the Innovative Diagnosis in Civil Engineering—A Comprehensive Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurcjusz, M. Technology vs. creativity in architecture: Striving for synergy. In Defining the Architectural Space, Architecture and Technology; Mielnik, A., Ed.; Oficyna Wydawnicza ATUT—Wrocławskie Wydawnictwo Oświatowe: Wroclaw, Poland, 2024; Volume 4, pp. 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
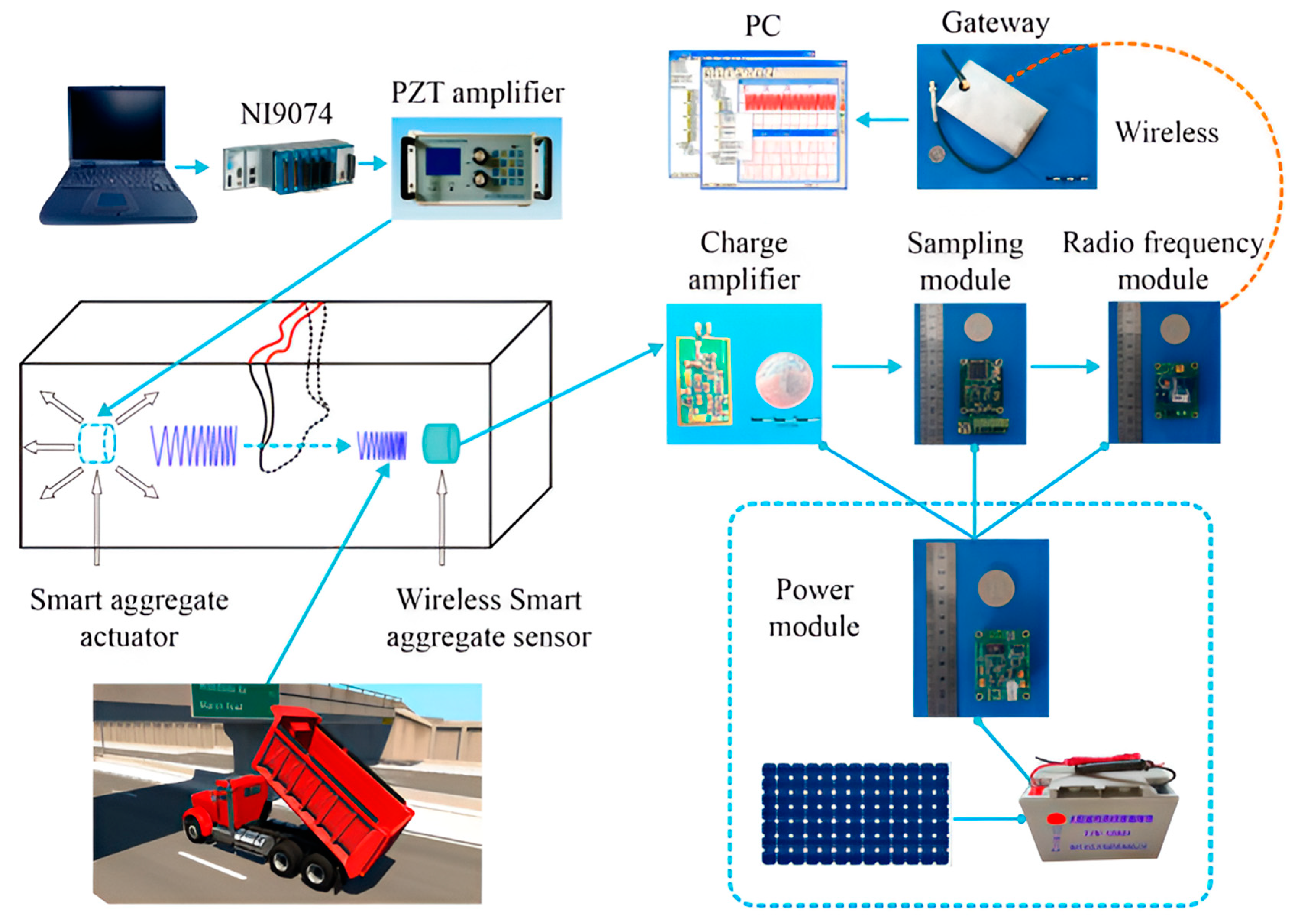
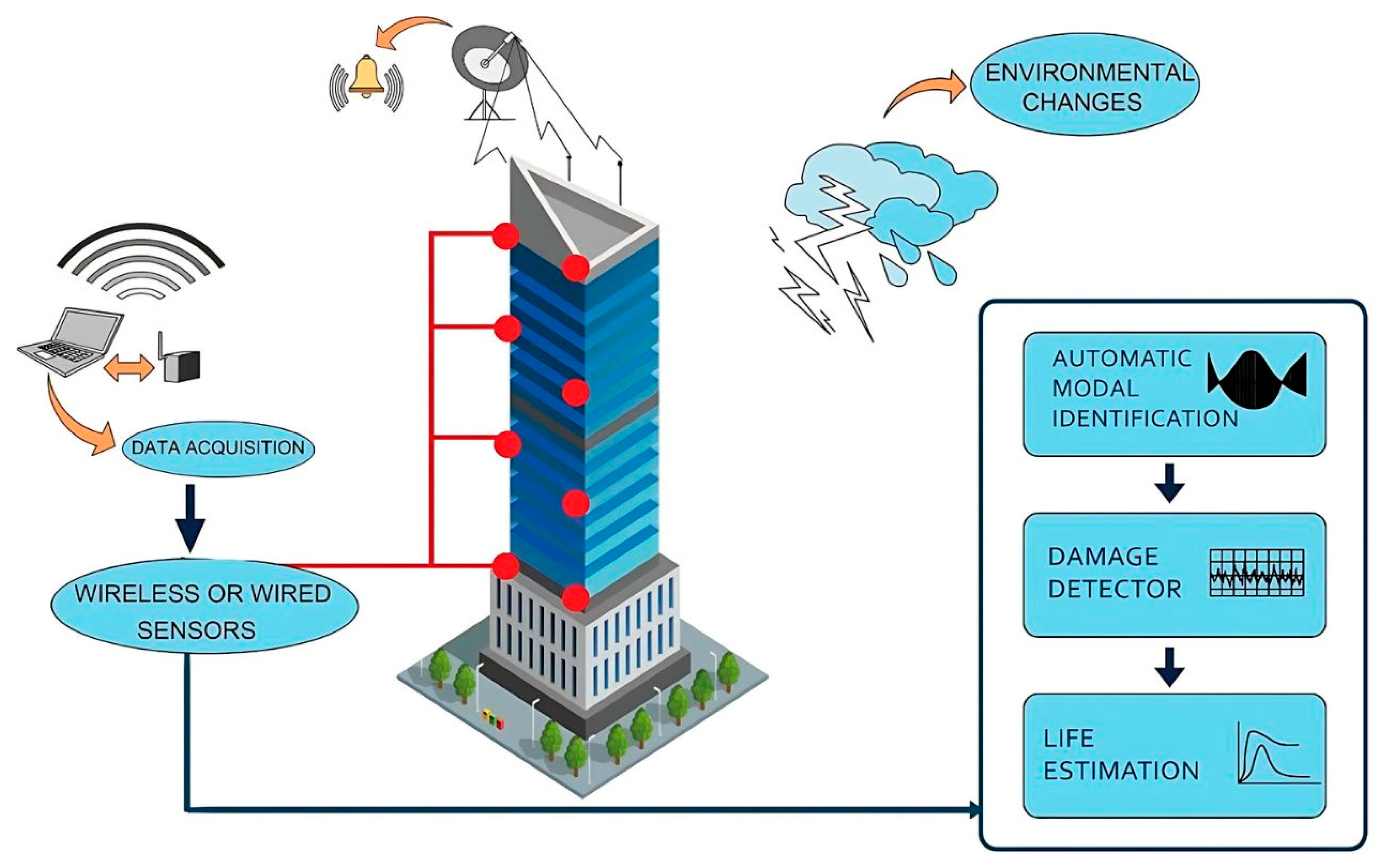


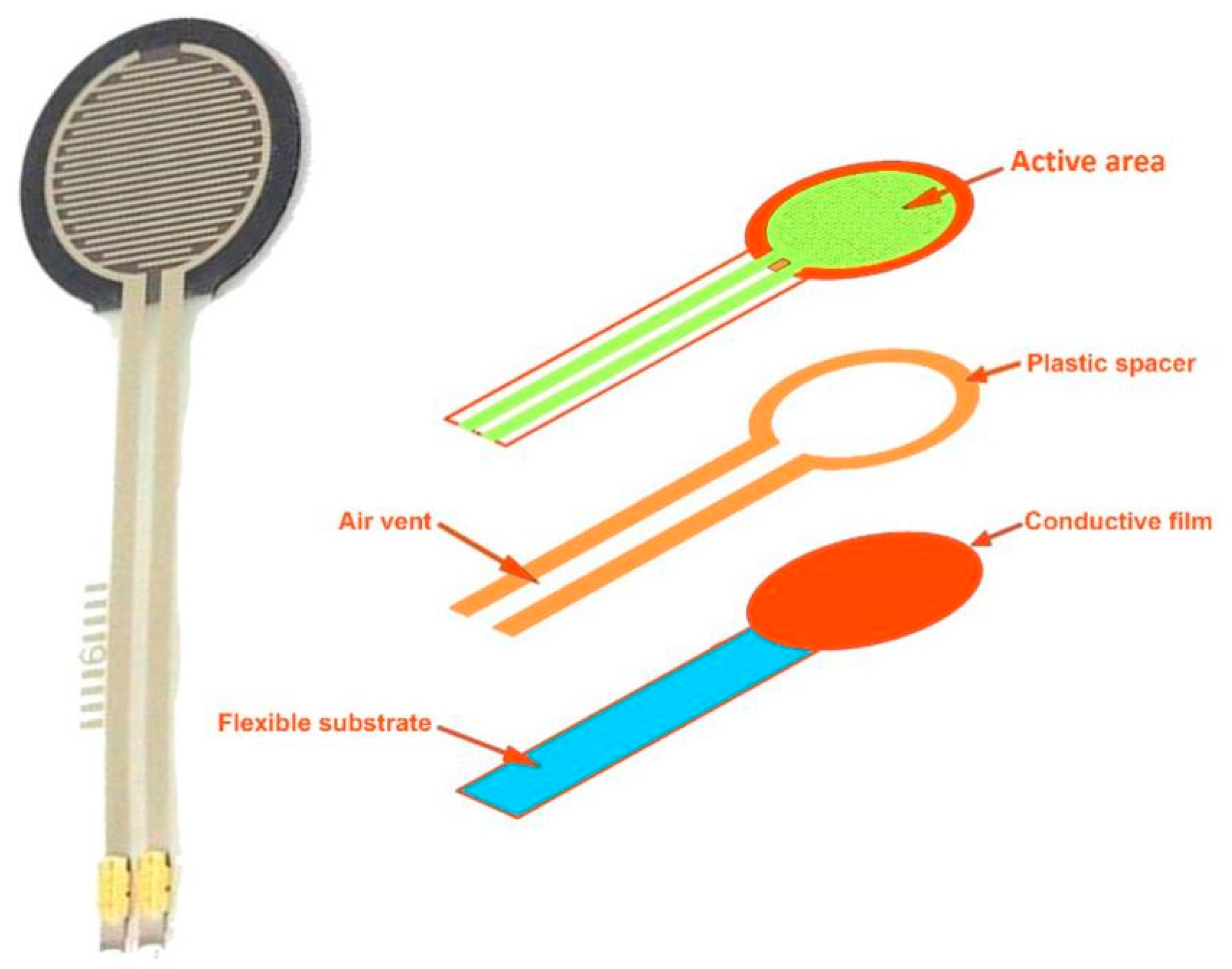
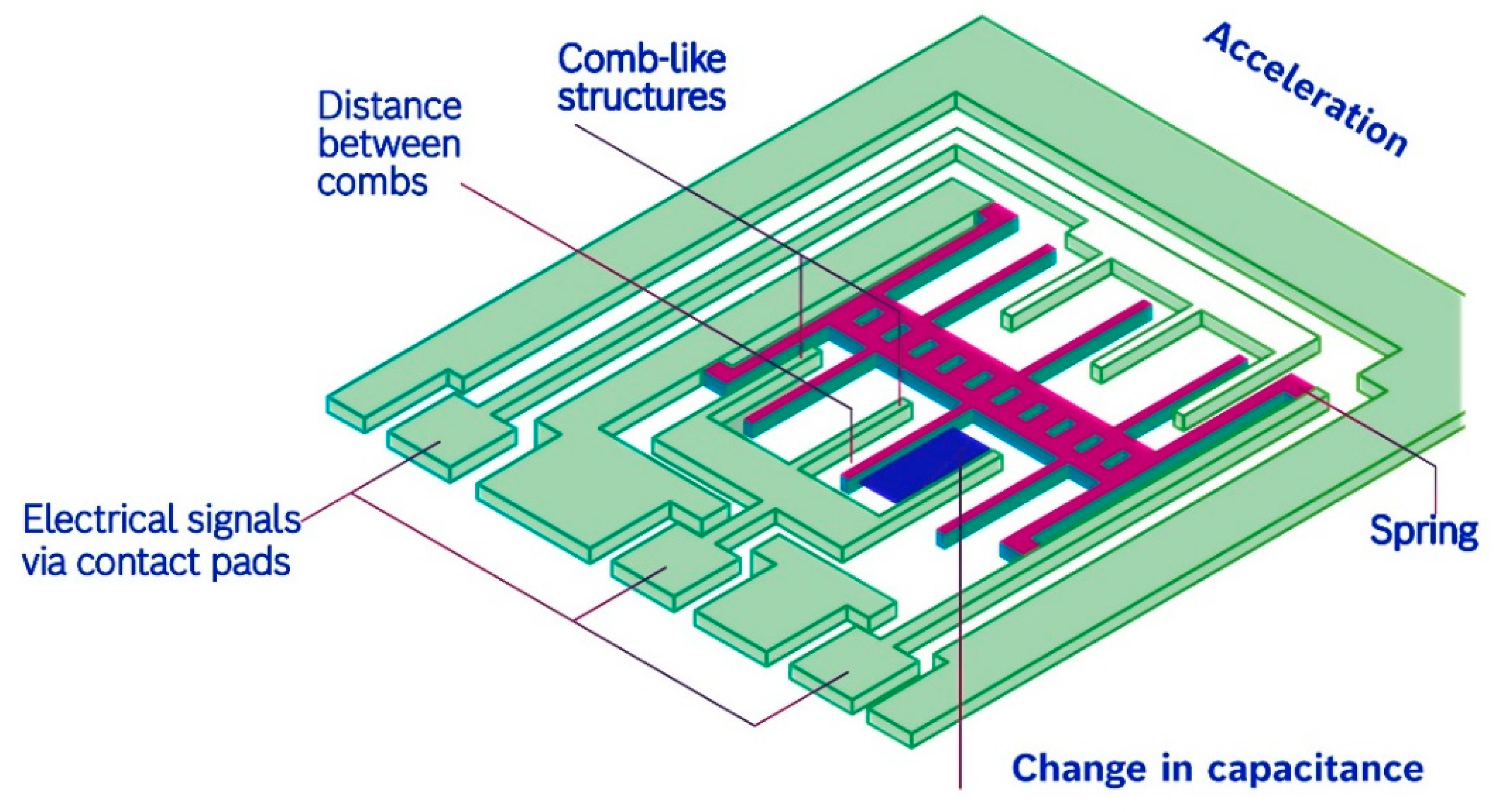



| S. No. | Primary Sensors Used in SHM | Measured Parameters | Types of Structures Adopted These Sensors, Particularly |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fibre optic sensor | Strain Temperature Displacement Pressure | Long pipeline work in the oil and gas sector Bridges |
| 2 | Piezoelectric sensors | Dynamic behaviour Structural stiffness Displacement Strain | Structural elements Spot welded joints Bridges |
| 3 | MEMS accelerometers | Vibration sensing Stress Natural frequency Damping ratios Mode shapes | Heritage buildings Residential buildings Bridges |
| 4 | Global positioning satellites | Acceleration Fluctuation Dynamic displacement | Bridges Dams Tower structures |
| 5 | Linear variable differential transformer | Deflection Crack monitoring Movement in joints Fluctuation | Bridge Dams Buildings |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sivasuriyan, A.; Vijayan, D.S.; Devarajan, P.; Stefańska, A.; Dixit, S.; Podlasek, A.; Sitek, W.; Koda, E. Emerging Trends in the Integration of Smart Sensor Technologies in Structural Health Monitoring: A Contemporary Perspective. Sensors 2024, 24, 8161. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248161
Sivasuriyan A, Vijayan DS, Devarajan P, Stefańska A, Dixit S, Podlasek A, Sitek W, Koda E. Emerging Trends in the Integration of Smart Sensor Technologies in Structural Health Monitoring: A Contemporary Perspective. Sensors. 2024; 24(24):8161. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248161
Chicago/Turabian StyleSivasuriyan, Arvindan, Dhanasingh Sivalinga Vijayan, Parthiban Devarajan, Anna Stefańska, Saurav Dixit, Anna Podlasek, Wiktor Sitek, and Eugeniusz Koda. 2024. "Emerging Trends in the Integration of Smart Sensor Technologies in Structural Health Monitoring: A Contemporary Perspective" Sensors 24, no. 24: 8161. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248161
APA StyleSivasuriyan, A., Vijayan, D. S., Devarajan, P., Stefańska, A., Dixit, S., Podlasek, A., Sitek, W., & Koda, E. (2024). Emerging Trends in the Integration of Smart Sensor Technologies in Structural Health Monitoring: A Contemporary Perspective. Sensors, 24(24), 8161. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248161













