A Second-Order True-VCO ADC Employing a Digital Pseudo-DCO Suitable for Sensor Arrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
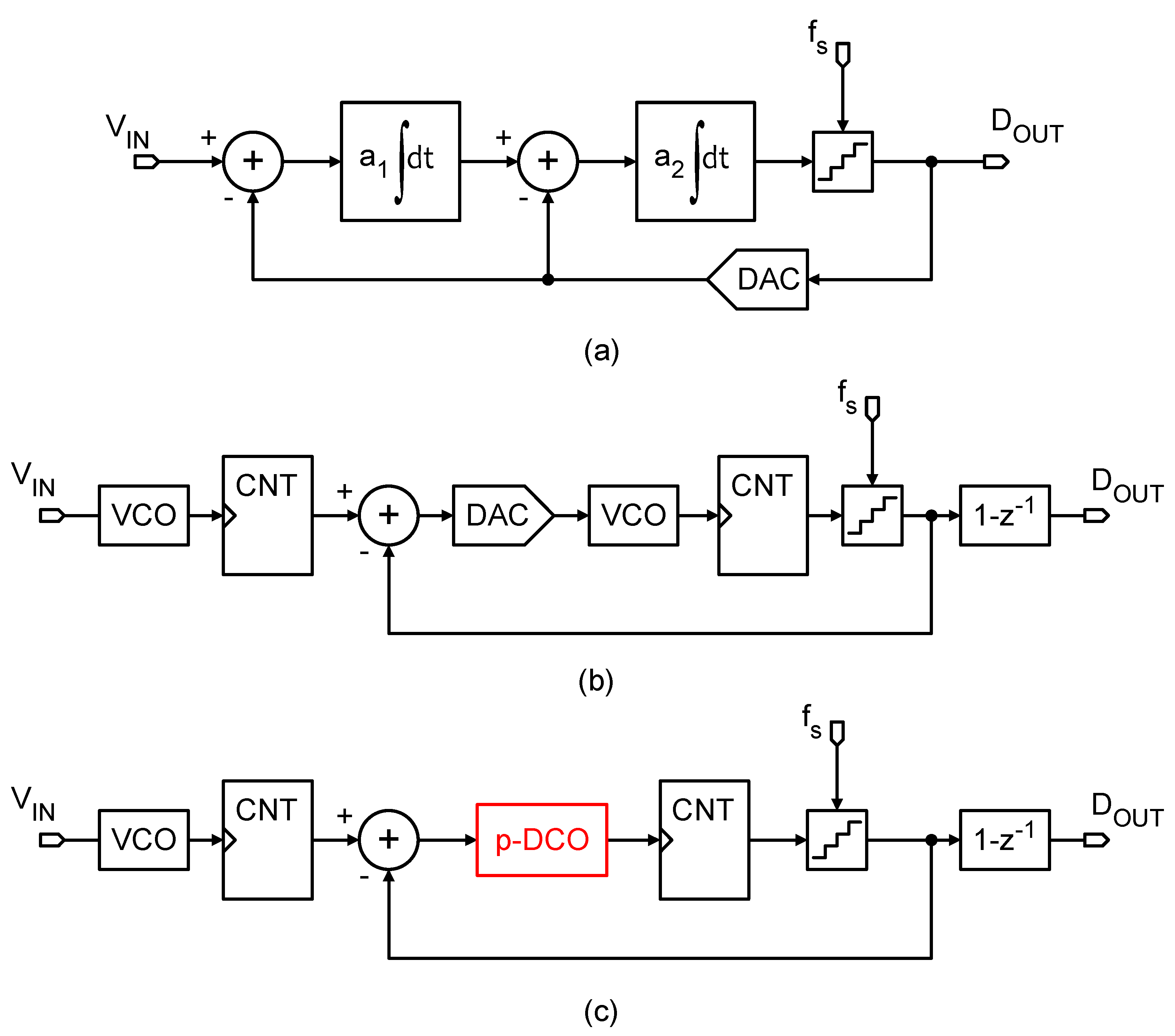
2. System-Level Description of the Proposed Architecture
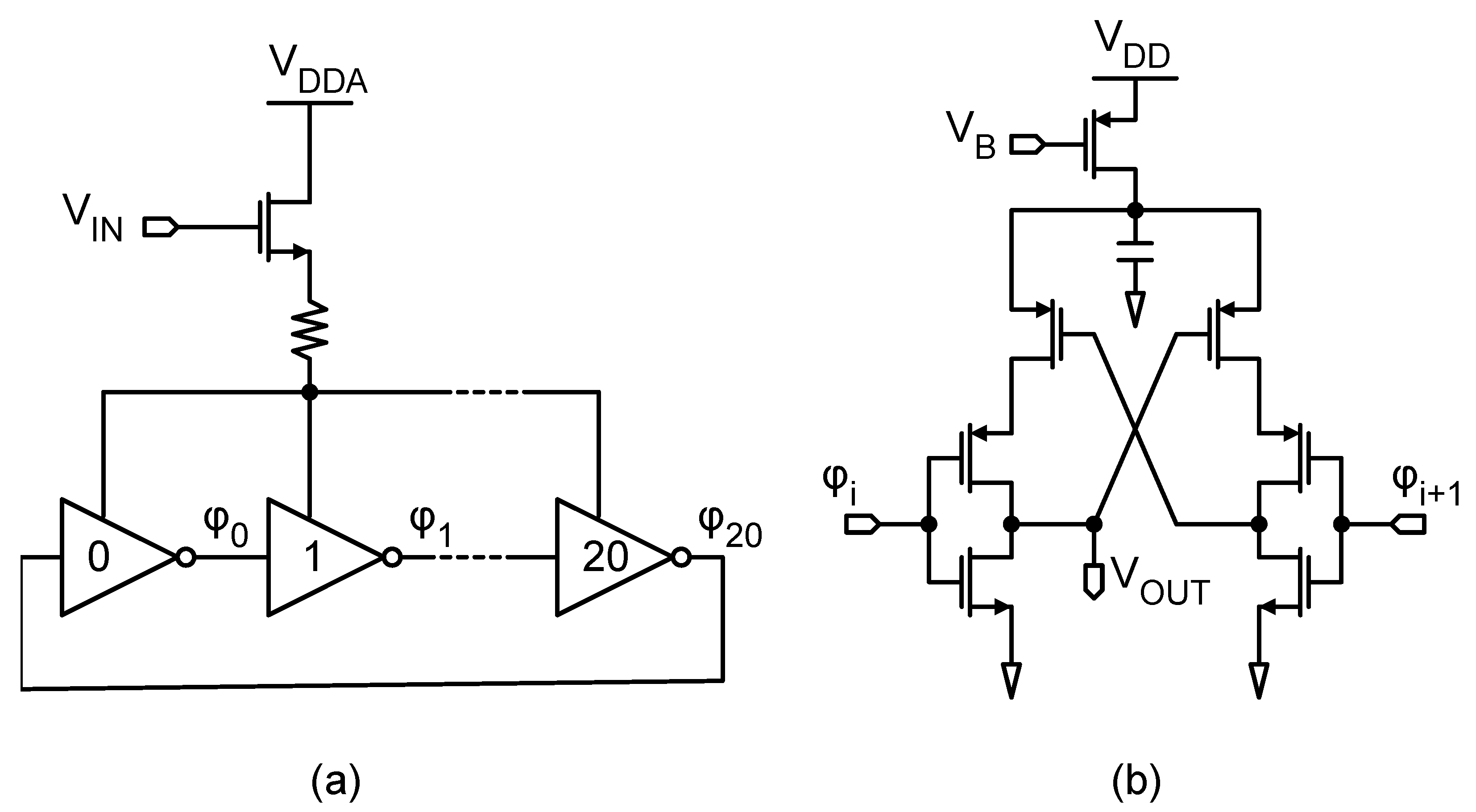
2.1. Pseudo-DCO

2.2. Input VCO and System-Level Simulations
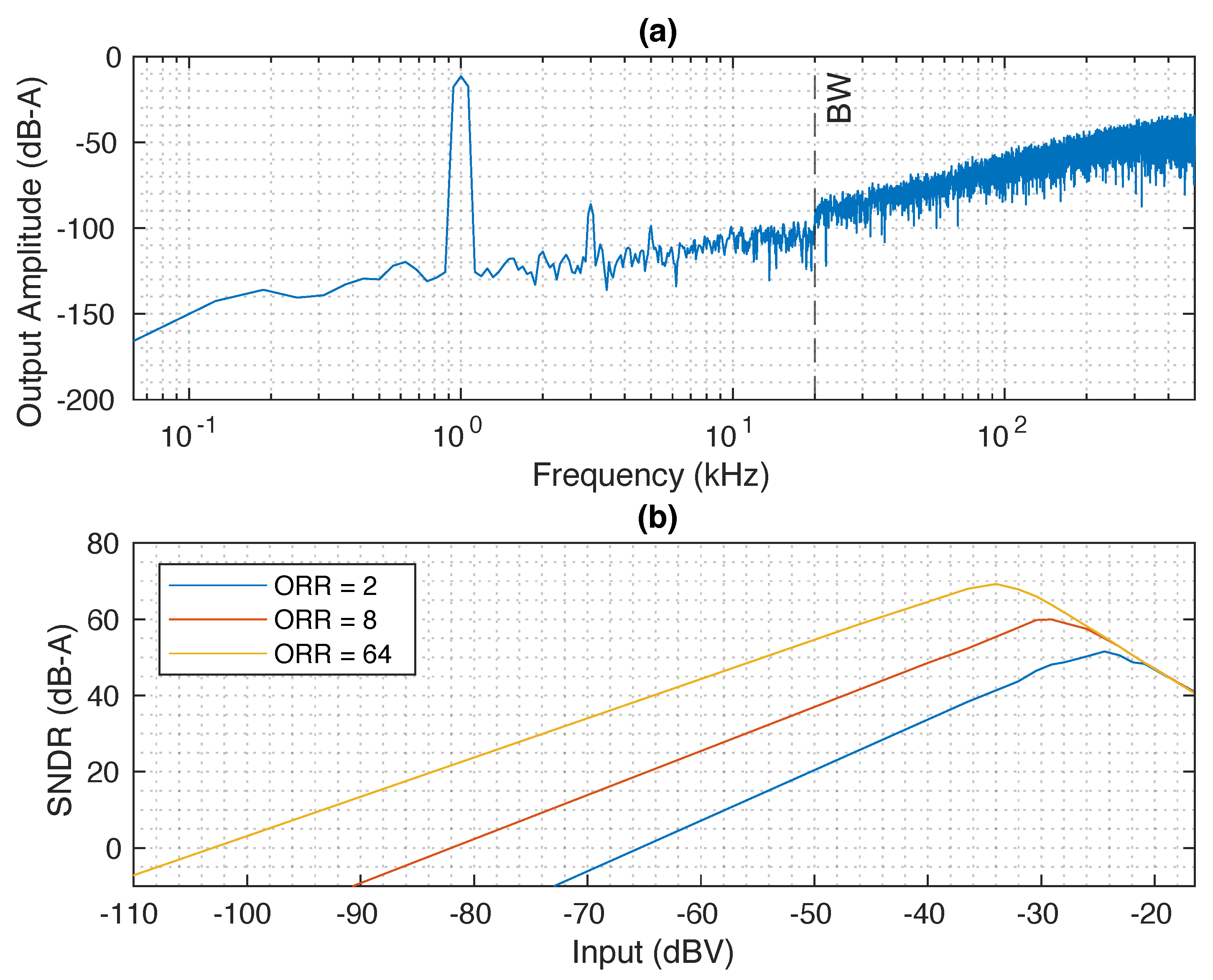
3. Post-Layout Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VCO | Voltage controlled oscillator |
| ADC | Analog-to-digital converter |
| ENOB | Effective number of bits |
| PVT | Process, voltage and temperature |
| CMOS | Complementary metal oxide semiconductor |
| SoC | System on a chip |
| DC | Direct current |
| PFM | Pulse frequency modulation |
| DAC | Digital-to-analog converter |
| DDS | Direct digital synthesis |
| DCO | Digitally controlled oscillator |
| ORR | Overrunning ratio |
| SNDR | Signal-to-noise-and-distortion ratio |
| MEMS | Micro electro-mechanical system |
| FoM | Figure of merit |
References
- Gielen, G.G.; Hernandez, L.; Rombouts, P. Time-Encoding Analog-to-Digital Converters: Bridging the Analog Gap to Advanced Digital CMOS-Part 1: Basic Principles. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2020, 12, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, G.G.; Hernandez, L.; Rombouts, P. Time-Encoding Analog-to-Digital Converters: Bridging the Analog Gap to Advanced Digital CMOS-Part 2: Architectures and Circuits. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2020, 12, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Sun, N. A Survey of Voltage-Controlled-Oscillator-Based ΔΣ ADCs. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, E.; Hernandez, L.; Cardes, F.; Rombouts, P. A Pulse Frequency Modulation Interpretation of VCOs Enabling VCO-ADC Architectures with Extended Noise Shaping. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaie-Fishani, A.; Rombouts, P. True High-Order VCO-based ADC. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaie-Fishani, A.; Rombouts, P. A Mostly Digital VCO-Based CT-SDM with Third-Order Noise Shaping. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 2141–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardes, F.; Gutierrez, E.; Quintero, A.; Buffa, C.; Wiesbauer, A.; Hernandez, L. 0.04-Mm2 103-dB-A Dynamic Range Second-Order VCO-Based Audio ΣΔ-ADC in 0.13-Mm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, V.; Garvi, R.; Granizo, J.; Amaral, P.; Hernandez, L. A Second-Order Audio VCO-ADC with 103-dB-A Dynamic Range and Binary-Weighted Internal Architecture. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.07887. [Google Scholar]
- Loi, D.; Granizo, J.; Hernandez, L. A Scalable and PVT Invariant Spiking Neuron Using Asynchronous CMOS Logic. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Singapore, 19–22 May 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, V.; Rombouts, P.; Hernandez-Corporales, L. A Different View of Sigma-Delta Modulators Under the Lens of Pulse Frequency Modulation [Feature]. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2024, 24, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Garvi, R.; Lopez, G.; Quintero, A.; Leger, F.; Amaral, P.; Wiesbauer, A.; Hernandez, L. A VCO-Based ADC with Direct Connection to a Microphone MEMS, 80-dB Peak SNDR and 438-μW Power Consumption. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 8466–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Spiegel, J.V.D.; Wang, Z. Low Power Circuit Design Using Advanced CMOS Technology, 1st ed.; River Publishers: Aalborg, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Mercier, P.P. A 94.2-dB SNDR 142.6-μW VCO-Based Audio ADC with a Split-ADC Differential Pulse Code Modulation Architecture. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Lett. 2021, 4, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Z. A 0.6-V 94-nW 10-Bit 200-kS/s Single-Ended SAR ADC for Implantable Biosensor Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 17904–17913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference | This Work | [8] | [11] | [12] | [13] | [14] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process | 130 nm | 130 nm | 130 nm | 28 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm |
| Supply (A/D) (V) | 1.2/0.9 | 1.5/0.95 | 1.5/0.95 | 1.1/0.55 | 1/1 | 0.6/0.6 |
| BW (kHz) | 20 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 100 |
| Area (mm2) | 0.034 | 0.095 | 0.14 | 0.095 | 0.11 | 0.022 |
| Power (uW) | 105.6 | 250 | 438.1 | 170.5 | 142.7 | 0.094 |
| Sampling (MHz) | 1 | 3.072 | 3.072 | 2.4 | 2 | 0.2 |
| DR (dB) | 90 | 103 | 108 | 91 | 100.3 | N.A. |
| FOM SNDR (dB) | 153 | 155.5 | 157 | 152.6 | 175.5 | 176.6 |
| FOM DR (dB) | 173 | 182 | 184.6 | 170.4 | 181.8 | N.A. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loi, D.; Medina, V.; Corporales, L.H. A Second-Order True-VCO ADC Employing a Digital Pseudo-DCO Suitable for Sensor Arrays. Sensors 2024, 24, 8029. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248029
Loi D, Medina V, Corporales LH. A Second-Order True-VCO ADC Employing a Digital Pseudo-DCO Suitable for Sensor Arrays. Sensors. 2024; 24(24):8029. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoi, Dante, Victor Medina, and Luis Hernandez Corporales. 2024. "A Second-Order True-VCO ADC Employing a Digital Pseudo-DCO Suitable for Sensor Arrays" Sensors 24, no. 24: 8029. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248029
APA StyleLoi, D., Medina, V., & Corporales, L. H. (2024). A Second-Order True-VCO ADC Employing a Digital Pseudo-DCO Suitable for Sensor Arrays. Sensors, 24(24), 8029. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248029






