Modeling Carbon-Based Nanomaterials (CNMs) and Derived Composites and Devices
Abstract
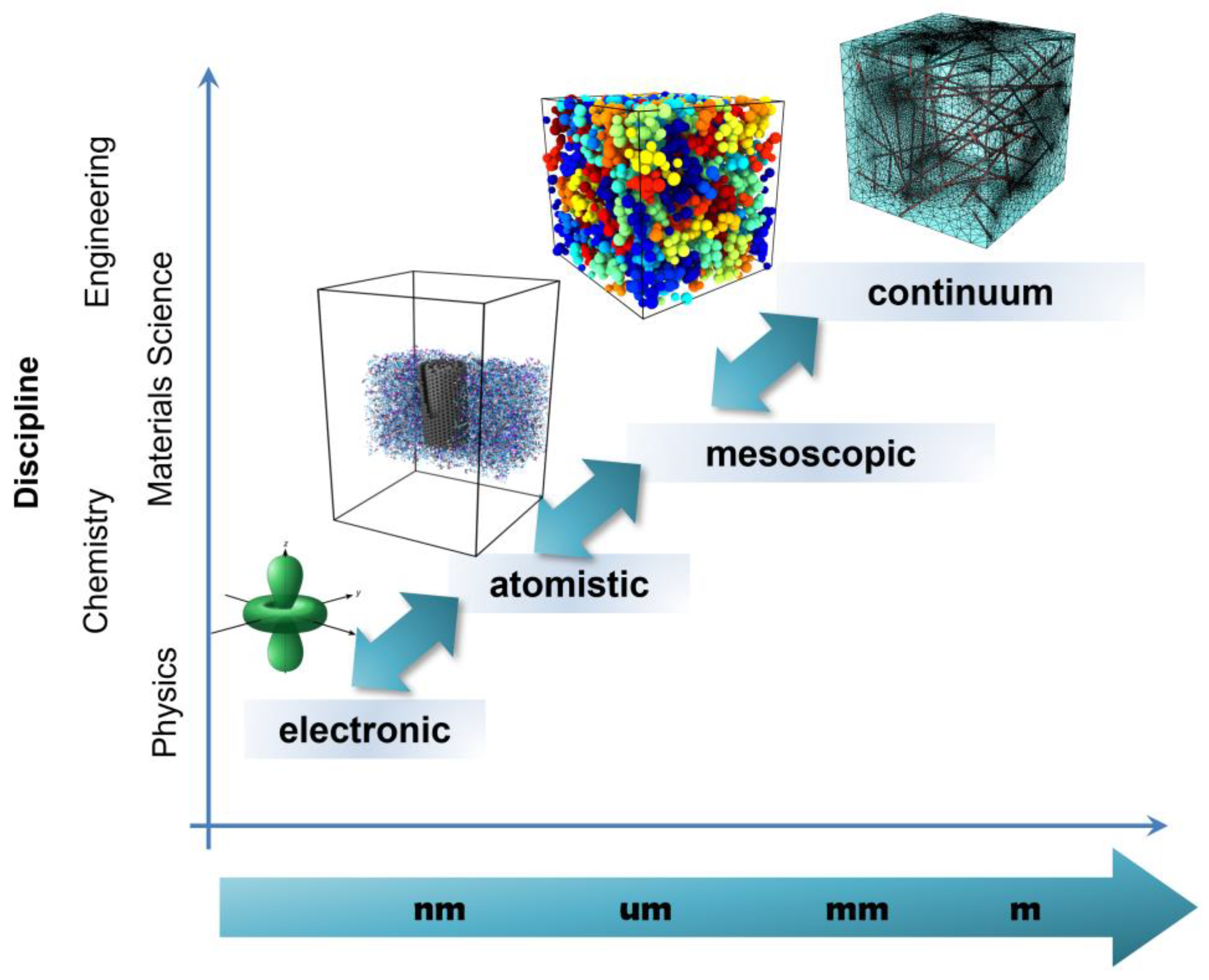
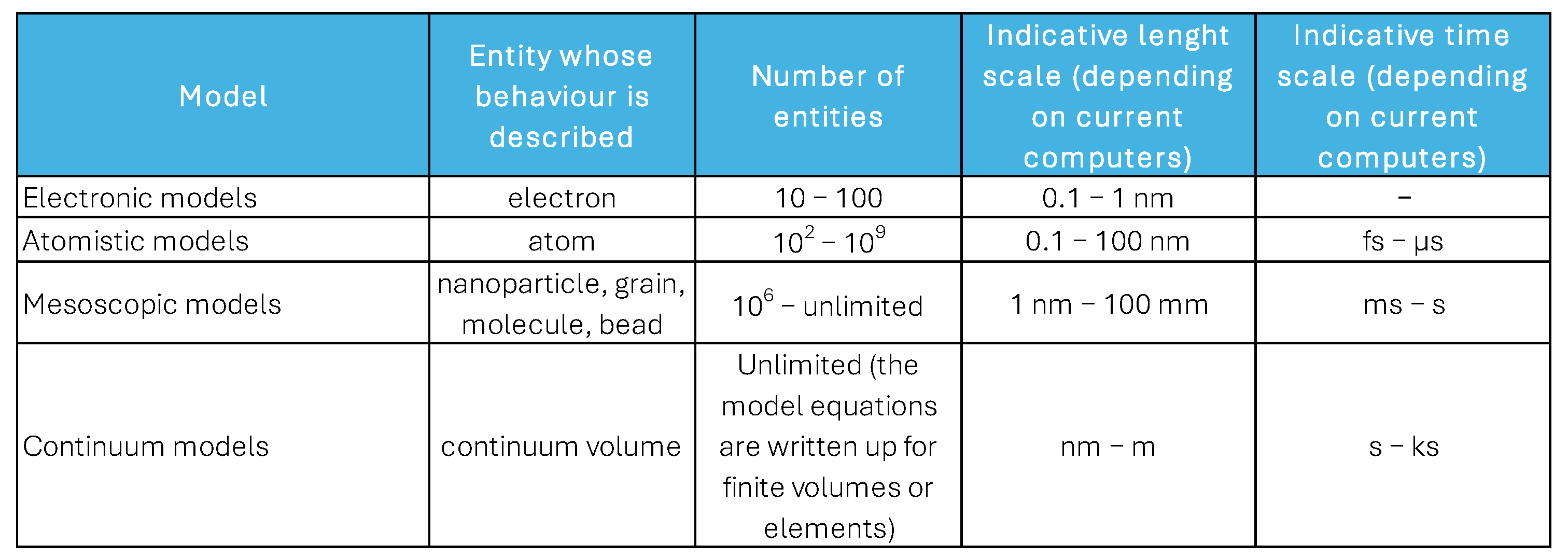
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Modeling of Interactions of Charged Particles with Graphene-Based Nanomaterials and Their Composites
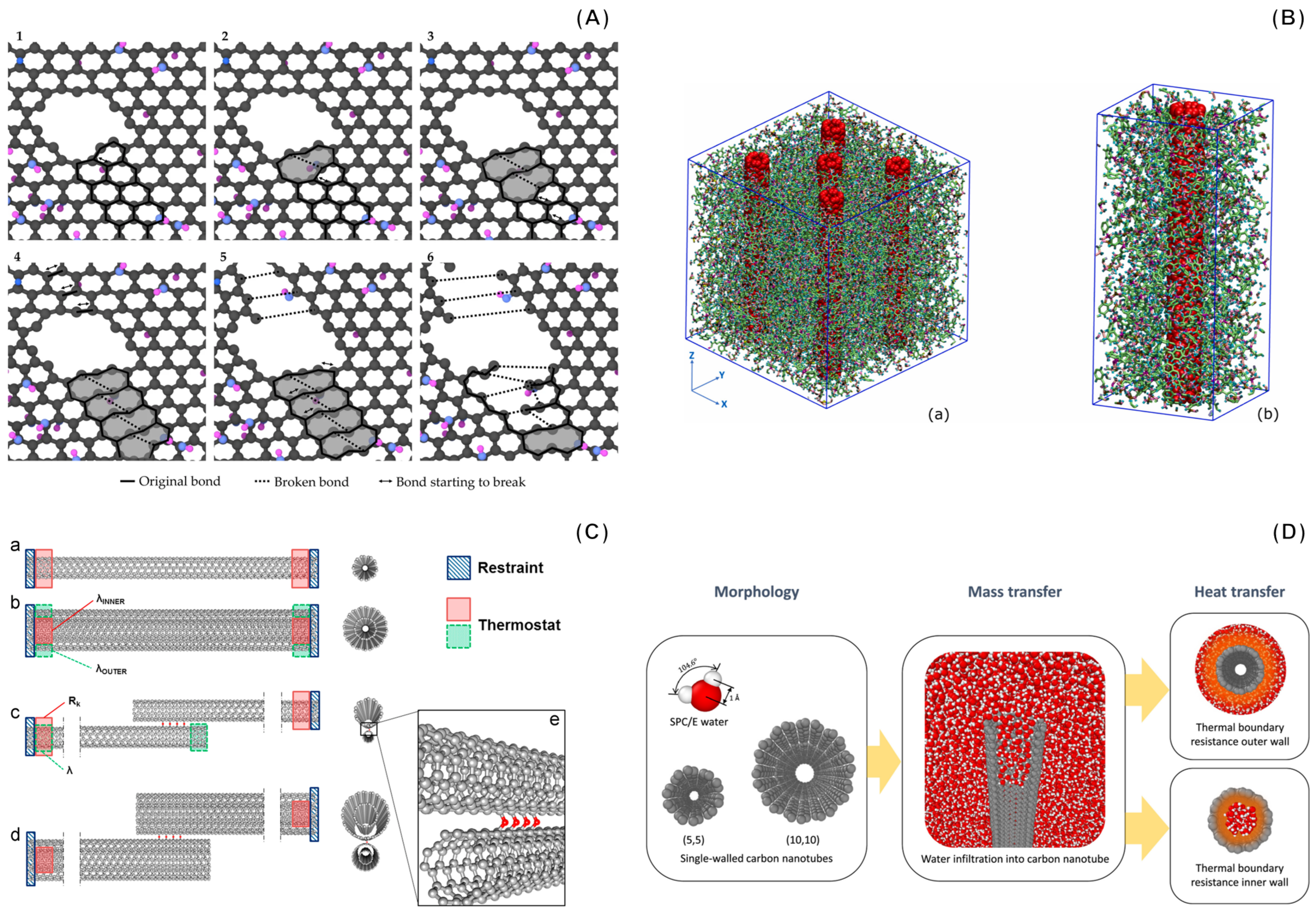
3. Molecular Dynamics Applied to CNM Properties Prediction
- The Adaptive Intermolecular Reactive Bond Order (AIREBO) potential is tailored for carbon systems and describes long-range van der Waals interactions and torsional effects. It is versatile for modeling both sp2- and sp3-hybridized carbon structures [75]. AIREBO might not perform well for systems with significant charge transfer or in the case of interactions with elements outside its parameterization.
- The Tersoff potential considers both the distance between atoms (bond lengths) and their relative orientation (bond angles) to provide a detailed representation of the complex interactions that occur in carbon-based materials [76]. This potential may not be ideal for modeling weak interactions, and it might require recalibration for systems different from its original parameterization.
- ReaxFF is a reactive force field capable of simulating bond formation and breaking during MD simulations. This dynamic nature is achieved by not predefining specific bond types but allowing the system to evolve based on atomic positions and interactions. Due to its reactive nature, ReaxFF can be computationally demanding. It also requires careful system-specific parameterization to ensure reliable results, for example, in the case of condensed carbon phases [77].
- Machine learning (ML) interatomic potentials differ from traditional ones, as they do not depend on fixed mathematical formulas. Instead, they learn representations of the potential energy surface of the system through trainings based on lower-scale simulations. Several implementations for certain carbon forms with near DFT-level accuracy have been reported in the literature, for example, Gaussian Approximation Potential (GAP) [78], hybrid neural network potential [79], GAP-20 potential for various crystalline phases of carbon, and amorphous carbon [80]. Furthermore, MACE—a transferable force field for organic molecules created using ML trained on first-principles reference data—was recently implemented [81]. Despite the good accuracy of current ML-based force fields in predicting the properties of carbon allotropes, various challenges still exist, especially regarding the description of mechanical properties and the curation of reliable training datasets.
4. Continuum Models
- (i)
- Nanocomposites’ stiffness prediction (i.e., response in the elastic range), as the research performed by M.M. Shokrieh for an epoxy resin modified with graphene nanoplatelets [123], the study presented by A. Chiminelli and M. Laspalas for an epoxy resin modified with MWCNTs (see Figure 5A) [124], the study by A. Singh and D. Kumar studying the influence of the functionalization of graphene nanoplatelets in the elastic properties of a modified polyethylene [125], or a more recent study by D. Shin for graphene-modified PET [126].
- (ii)
- Non-linear behavior and strength predictions of CNMs, as the approach proposed by J. Nafar Dastgerdi introducing interfacial damage/debonding processes in CNTs-reinforced polymers [127] or the model developed by W. Azoti and A. Elmarakbi applied to a graphene platelets GPL-reinforced polymer PA6 composite (Generalized Mori-Tanaka) [128].

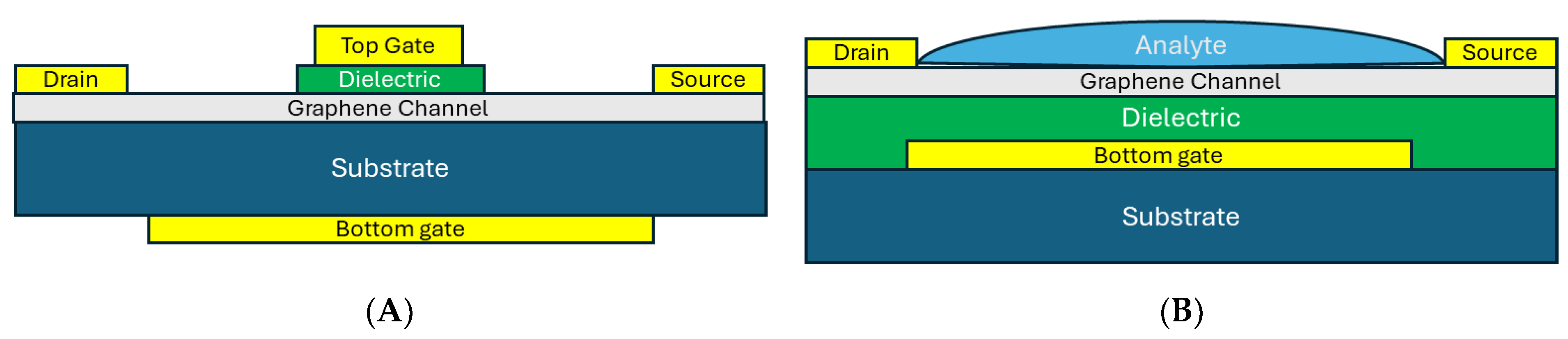
5. CNM Devices—Graphene Field Effect Transistors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. What Makes a Material Function?—Let me Compute the Ways—Modelling in FP7 NMP Programme Materials Projects, 4th ed.; Rosso, L., Baas, A., Eds.; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017; Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2777/951455 (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Perala, R.S.; Chandrasekar, N.; Balaji, R.; Alexander, P.S.; Humaidi NZ, N.; Hwang, M.T. A comprehensive review on graphene-based materials: From synthesis to contemporary sensor applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2024, 159, 100805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Qiang, H.; Wei, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Luo, N. A review on the laser-induced synthesis of graphene and its applications in sensors. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 11644–11668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeshina, M.A.; Ogunleye, A.M.; Lee, H.; Mareddi, B.; Kim, H.; Park, J. Graphene–Liquid Crystal Synergy: Advancing Sensor Technologies across Multiple Domains. Materials 2024, 17, 4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aftab, S.; Koyyada, G.; Mukhtar, M.; Kabir, F.; Nazir, G.; Memon, S.A.; Aslam, M.; Assiri, M.A.; Kim, J.H. Laser-Induced Graphene for Advanced Sensing: Comprehensive Review of Applications. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 4536–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owais, T.; Khater, M.; Al-Qahtani, H. Graphene-Based MEMS Devices for Gas Sensing Applications: A Review. Micro Nanostruct. 2024, 195, 207954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, X.; Chandra, B.; Tulevski, G.; Wu, Y.; Freitag, M.; Zhu, W.; Avouris, P.; Xia, F. Tunable Infrared Plasmonic Devices Using Graphene/Insulator Stacks. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Diaz, J.S.; Moldovan, C.; Capdevila, S.; Romeu, J.; Bernard, L.S.; Magrez, A.; Ionescu, A.M.; Perruisseau-Carrier, J. Self-Biased Reconfigurable Graphene Stacks for Terahertz Plasmonics. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescato, Y.; Giannini, V.; Yang, J.; Huang, M.; Maier, S.A. Graphene Sandwiches as a Platform for Broadband Molecular Spectroscopy. ACS Photonics 2014, 1, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Z.-Y.; Fischetti, M.V. Theory of Interfacial Plasmon-Phonon Scattering in Supported Graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 165422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Low, T.; Zhu, W.; Wu, Y.; Freitag, M.; Li, X.; Guinea, F.; Avouris, P.; Xia, F. Damping Pathways of Mid-Infrared Plasmons in Graphene Nanostructures. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z.; Andreev, G.O.; Bao, W.; Zhang, L.M.; McLeod, A.S.; Wang, C.; Stewart, M.K.; Zhao, Z.; Dominguez, G.; Thiemens, M.; et al. Infrared Nanoscopy of Dirac Plasmons at the Graphene–SiO2 Interface. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4701–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despoja, V.; Djordjević, T.; Karbunar, L.; Radović, I.; Mišković, Z.L. Ab Initio Study of the Electron Energy Loss Function in a Graphene-Sapphire-Graphene Composite System. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 075433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Yuan, K.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, K. Broadband High-Efficiency near-Infrared Graphene Phase Modulators Enabled by Metal–Nanoribbon Integrated Hybrid Plasmonic Waveguides. Nanophotonics 2022, 11, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Tang, L.; Nong, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, H.; Wei, X. Electrically Tunable Graphene Metamaterial with Strong Broadband Absorption. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 075703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiga, K.; Komiyama, T.; Fuse, Y.; Fukidome, H.; Sato, A.; Otsuji, T.; Uchino, T. Electrical Transport Properties of Gate Tunable Graphene Lateral Tunnel Diodes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 59, SIID03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirdel, M.; Mansouri-Birjandi, M.A. A Broadband Graphene Modulator Based on Plasmonic Valley-Slot Waveguide. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2020, 52, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirdel, M.; Mansouri-Birjandi, M.A. Broadband Graphene Modulator Based on a Plus-Shaped Plasmonic Slot Waveguide. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 8174–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X. Double-Layer Graphene Optical Modulator. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.F.; Mišković, Z.L. Friction Force on Slow Charges Moving over Supported Graphene. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 134017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinković, T.; Radović, I.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L. Probing the Plasmon-Phonon Hybridization in Supported Graphene by Externally Moving Charged Particles. Plasmonics 2015, 10, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despoja, V.; Radović, I.; Karbunar, L.; Kalinić, A.; Mišković, Z.L. Wake Potential in Graphene-Insulator-Graphene Composite Systems. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 035443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinić, A.; Radović, I.; Karbunar, L.; Despoja, V.; Mišković, Z.L. Wake Effect in Interactions of Ions with Graphene-Sapphire-Graphene Composite System. Phys. E 2021, 126, 114447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinić, A.; Despoja, V.; Radović, I.; Karbunar, L.; Mišković, Z.L. Stopping and Image Forces Acting on a Charged Particle Moving near a Graphene-Al2O3-Graphene Heterostructure. Phys. Rev. B 2022, 106, 115430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radović, I.; Hadžievski, L.J.; Bibić, N.; Mišković, Z.L. Dynamic-Polarization Forces on Fast Ions and Molecules Moving over Supported Graphene. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 76, 042901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radović, I.; Hadžievski, L.J.; Mišković, Z.L. Polarization of Supported Graphene by Slowly Moving Charges. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 075428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbs, G.; Huang, D.; Echenique, P.M. Comparing the Image Potentials for Intercalated Graphene with a Two-Dimensional Electron Gas with and without a Gated Grating. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 035410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.F.; Borka, D.; Radović, I.; Hadžievski, L.J.; Mišković, Z.L. Dynamic Polarization of Graphene by Moving External Charges: Random Phase Approximation. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 195405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radović, I.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L. Wake Effect in Doped Graphene Due to Moving External Charge. Phys. Lett. A 2011, 375, 3720–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbs, G.; Roslyak, O.; Huang, D.; Balassis, A. Spectroscopic Characterization of Gapped Graphene in the Presence of Circularly Polarized Light. J. Mod. Opt. 2011, 58, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borka, D.; Radović, I.; Mišković, Z.L. Dynamic Polarization of Graphene by Moving External Charges: Comparison with 2D Electron Gas. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2011, 269, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despoja, V.; Dekanić, K.; Šunjić, M.; Marušić, L. Ab Initio Study of Energy Loss and Wake Potential in the Vicinity of a Graphene Monolayer. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 165419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radović, I.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L. Dynamic Polarization of Graphene by External Correlated Charges. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 125442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radović, I.; Borka Jovanović, V.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L. Interactions of Slowly Moving Charges with Graphene: The Role of Substrate Phonons. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2012, 279, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radović, I.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L. Wake Effect in Interactions of Dipolar Molecules with Doped Graphene. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 377, 2614–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinković, T.; Radović, I.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L. Wake Effect in the Interaction of Slow Correlated Charges with Supported Graphene Due to Plasmon–Phonon Hybridization. Phys. Lett. A 2015, 379, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Lin, X.; Gao, F.; Xu, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, B. Caustic Graphene Plasmons with Kelvin Angle. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 081404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, A.J.; Peres, N.M.R.; Smirnov, G.; Mortensen, N.A. Hydrodynamic Model Approach to the Formation of Plasmonic Wakes in Graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 195438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolomeisky, E.B.; Straley, J.P. Kelvin-Mach Wake in a Two-Dimensional Fermi Sea. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 226801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W. Pseudomagnetic Field Modulation of Stopping Power for a Charged Particle Moving above Graphene. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 072107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qu, G.-F.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Zhu, Z.-S.; Shi, M.-G.; Zhou, M.-L.; Liu, D.; Xu, Z.-X.; Song, M.-J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Interaction of H2+ Molecular Beam with Thin Layer Graphene Foils. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 093401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Mišković, Z.L.; Radović, I.; Li, C.-Z.; Song, Y.-H. Interactions of Moving Charge with Supported Graphene in the Presence of Strain-Induced Pseudomagnetic Field. Eur. Phys. J. D 2020, 74, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.-J.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Mišković, Z.L.; Radović, I.; Li, C.-Z.; Song, Y.-H. The Effects of Pseudomagnetic Fields on Plasmon–Phonon Hybridization in Supported Graphene Probed by a Moving Charged Particle. Plasmonics 2021, 16, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preciado Rivas, M.R.; Moshayedi, M.; Mišković, Z.L. On the Role of the Energy Loss Function in the Image Force on a Charge Moving over Supported Graphene. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 130, 173103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylnikov, D.A.; Kashchenko, M.A.; Kapralov, K.N.; Ghazaryan, D.A.; Vdovin, E.E.; Morozov, S.V.; Novoselov, K.S.; Bandurin, D.A.; Chernov, A.I.; Svintsov, D.A. Infrared Photodetection in Graphene-Based Heterostructures: Bolometric and Thermoelectric Effects at the Tunneling Barrier. Npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2024, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, H.; Sakr, M.A.S.; Teleb, N.H.; Abd-Elkader, O.H.; Zhilong, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Highly Efficient Spin Field-Effect Transistor Based on Nanographene and hBN Heterostructures: Spintronic and Quantum Transport Properties. Chin. J. Phys. 2024, 90, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanin, Y.N.; Vdovin, E.E.; Morozov, S.V.; Novoselov, K.S. Coulomb Correlation Gap at Magnetic Tunneling Between Graphene Layers. JETP Lett. 2023, 118, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of AAB-Stacked Single-Crystal Graphene/hBN/Graphene Trilayer van Der Waals Heterostructures by In Situ CVD. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2201324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, B.; Ou, H.; Li, B.; Zhou, K.; Song, J.; Luo, Z.; Cheng, Q. Enhanced Near-Field Radiative Heat Transfer between Graphene/hBN Systems. Small 2022, 18, 2108032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Deng, A.; Shen, P.; Luo, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, T.; Huang, X.; Dong, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; et al. Direct Imaging of Interlayer-Coupled Symmetric and Antisymmetric Plasmon Modes in Graphene/hBN/Graphene Heterostructures. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 14628–14635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-B.; Yoon, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Yang, S.; Seo, S.-Y.; Cha, S.; Jeong, H.-W.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Lee, G.-H.; et al. Deep-Ultraviolet Electroluminescence and Photocurrent Generation in Graphene/hBN/Graphene Heterostructures. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Ren, B.; Song, J.; Jiang, Y. Tuning of Mid-Infrared Absorption through Phonon-Plasmon-Polariton Hybridization in a Graphene/hBN/Graphene Nanodisk Array. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 2288–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Zhou, X.; Tao, L.; Yu, W.; Liu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, C.; Shang, N.; Xie, J.; Liu, K.; et al. Sandwiched Graphene/hBN/Graphene Photonic Crystal Fibers with High Electro-Optical Modulation Depth and Speed. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 14472–14478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golenić, N.; de Gironcoli, S.; Despoja, V. Optically Driven Plasmons in Graphene/hBN van Der Waals Heterostructures: Simulating s-SNOM Measurements. Nanophotonics 2024, 13, 2765–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golenić, N.; de Gironcoli, S.; Despoja, V. Tailored Plasmon Polariton Landscape in Graphene/Boron Nitride Patterned Heterostructures. Npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2024, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.W.; Bourgeois, M.R.; Walton, C.; Masiello, D.J. Probing the Polarization of Low-Energy Excitations in 2D Materials from Atomic Crystals to Nanophotonic Arrays Using Momentum-Resolved Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 7748–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govyadinov, A.A.; Konečná, A.; Chuvilin, A.; Vélez, S.; Dolado, I.; Nikitin, A.Y.; Lopatin, S.; Casanova, F.; Hueso, L.E.; Aizpurua, J.; et al. Probing Low-Energy Hyperbolic Polaritons in van Der Waals Crystals with an Electron Microscope. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslyak, O.; Gumbs, G.; Huang, D. Energy Loss Spectroscopy of Epitaxial versus Free-Standing Multilayer Graphene. Phys. E 2012, 44, 1874–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borka Jovanović, V.; Radović, I.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L. High-Energy Plasmon Spectroscopy of Freestanding Multilayer Graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 155416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsmuth, P.; Hambach, R.; Kinyanjui, M.K.; Guzzo, M.; Benner, G.; Kaiser, U. High-Energy Collective Electronic Excitations in Free-Standing Single-Layer Graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 075433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsmuth, P.; Hambach, R.; Benner, G.; Kaiser, U. Plasmon Bands in Multilayer Graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 235434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjević, T.; Radović, I.; Despoja, V.; Lyon, K.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L. Analytical Modeling of Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy of Graphene: Ab Initio Study versus Extended Hydrodynamic Model. Ultramicroscopy 2018, 184, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radović, I.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L. Theoretical Modeling of Experimental HREEL Spectra for Supported Graphene. Phys. Lett. A 2014, 378, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politano, A.; Radović, I.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L.; Chiarello, G. Interband Plasmons in Supported Graphene on Metal Substrates: Theory and Experiments. Carbon 2016, 96, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politano, A.; Radović, I.; Borka, D.; Mišković, Z.L.; Yu, H.K.; Farías, D.; Chiarello, G. Dispersion and Damping of the Interband π Plasmon in Graphene Grown on Cu (111) Foils. Carbon 2017, 114, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despoja, V.; Radović, I.; Politano, A.; Mišković, Z.L. Insights on the Excitation Spectrum of Graphene Contacted with a Pt Skin. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z. Polymer-Integrated Acoustic Graphene Plasmon Resonator for Sensitive Detection of CO2 Gas. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2024, 57, 335102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, Z. Understanding and Probing of Sub-Femtometer Resolutions Utilizing Acoustic Plasmon Resonances in Graphene-Dielectric-Metal Hybrid-Structures. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 162, 109305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marušić, L.; Kalinić, A.; Radović, I.; Jakovac, J.; Mišković, Z.L.; Despoja, V. Resolving the Mechanism of Acoustic Plasmon Instability in Graphene Doped by Alkali Metals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Graphene and Graphene-like 2D Materials for Optical Biosensing and Bioimaging: A Review. 2d Mater. 2015, 2, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.Y.; Cubukcu, E. Graphene nanophotonic sensors. 2D Mater. 2015, 2, 032005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.P. Introduction to Molecular Dynamics Simulation; NIC Series; John von Neumann Institute for Computing: Jülich, Germany, 2004; ISBN 978-3-00-012641-3. [Google Scholar]
- Torkaman-Asadi, M.A.; Kouchakzadeh, M.A. Atomistic Simulations of Mechanical Properties and Fracture of Graphene: A Review. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 210, 111457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; McLean, B.; Hedman, D.; Ding, F. A Comprehensive Assessment of Empirical Potentials for Carbon Materials. APL Mater. 2021, 9, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, S.J.; Tutein, A.B.; Harrison, J.A. A Reactive Potential for Hydrocarbons with Intermolecular Interactions. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 112, 6472–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tersoff, J. Empirical Interatomic Potential for Carbon, with Applications to Amorphous Carbon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 61, 2879–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.G.; van Duin, A.C.T.; Ganesh, P. Development of a ReaxFF Potential for Carbon Condensed Phases and Its Application to the Thermal Fragmentation of a Large Fullerene. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deringer, V.L.; Csányi, G. Machine Learning Based Interatomic Potential for Amorphous Carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 094203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Tadmor, E.B. Hybrid Neural Network Potential for Multilayer Graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 195419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, P.; Deringer, V.L.; Gasparotto, P.; Csányi, G.; Michaelides, A. An Accurate and Transferable Machine Learning Potential for Carbon. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 034702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, D.P.; Moore, J.H.; Browning, N.J.; Batatia, I.; Horton, J.T.; Kapil, V.; Witt, W.C.; Magdău, I.-B.; Cole, D.J.; Csányi, G. MACE-OFF23: Transferable Machine Learning Force Fields for Organic Molecules. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.15211. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.; Fasano, M.; Nejad, S.M.; Thielemann, H.C.; Chiavazzo, E.; Asinari, P. 3 Modeling Carbon-Based Smart Materials. In Carbon-Based Smart Materials; Charitidis, C.A., Koumoulos, E.P., Dragatogiannis, D.A., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 33–80. ISBN 978-3-11-047913-3. [Google Scholar]
- Sáenz Ezquerro, C.; Laspalas, M.; García Aznar, J.M.; Castelar Ariza, S.; Chiminelli, A. Molecular Modelling of Graphene Nanoribbons on the Effect of Porosity and Oxidation on the Mechanical and Thermal Properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 13295–13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S. A Review on Enhancement of Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Polymer Composites Reinforced by Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Sheet: Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 160, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, L.; Wang, J. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Mechanical Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystals—Graphene Layered Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, J.-L.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, F.-C.; Zhao, Y.-P. A Comparative Study of Young’s Modulus of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube by CPMD, MD and First Principle Simulations. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2009, 46, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirca, M.; To, A.C. Mechanics of CNT Network Materials. In Advanced Computational Nanomechanics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 29–70. ISBN 978-1-119-06892-1. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.P. Nanoindentation of Graphene-Reinforced Silica Aerogel: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Molecules 2019, 24, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Zhou, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Coiled Carbon Nanotube Pull-Out from Matrix. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz Ezquerro, C.; Laspalas, M.; Chiminelli, A.; Serrano, F.; Valero, C. Interface Characterization of Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites: A Molecular Dynamics Approach. Fibers 2018, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Nejad, S.; Srivastava, R.; Bellussi, F.M.; Chávez Thielemann, H.; Asinari, P.; Fasano, M. Nanoscale Thermal Properties of Carbon Nanotubes/Epoxy Composites by Atomistic Simulations. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 159, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigdeli, M.B.; Fasano, M. Thermal Transmittance in Graphene Based Networks for Polymer Matrix Composites. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 117, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, M.; Bozorg Bigdeli, M.; Vaziri Sereshk, M.R.; Chiavazzo, E.; Asinari, P. Thermal Transmittance of Carbon Nanotube Networks: Guidelines for Novel Thermal Storage Systems and Polymeric Material of Thermal Interest. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellussi, F.M.; Sáenz Ezquerro, C.; Laspalas, M.; Chiminelli, A. Effects of Graphene Oxidation on Interaction Energy and Interfacial Thermal Conductivity of Polymer Nanocomposite: A Molecular Dynamics Approach. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.J.; Hu, L.; Keblinski, P. Thermal Conductivity of Graphene Ribbons from Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics: Effect of Ribbon Width, Edge Roughness, and Hydrogen Termination. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 203112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.S.; Machado, W.S. The Effects of Computational Time Parameter in the Thermal Conductivity of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Comput. Condens. Matter 2018, 15, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casto, A.; Vittucci, M.; Vialla, F.; Crut, A.; Bellussi, F.M.; Fasano, M.; Vallée, F.; Del Fatti, N.; Banfi, F.; Maioli, P. Experimental Optical Retrieval of the Thermal Boundary Resistance of Carbon Nanotubes in Water. Carbon 2024, 229, 119445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, B. Interfacial Thermal Resistance: Past, Present, and Future. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2022, 94, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casto, A.; Bellussi, F.M.; Diego, M.; Del Fatti, N.; Banfi, F.; Maioli, P.; Fasano, M. Water Filling in Carbon Nanotubes with Different Wettability and Implications on Nanotube/Water Heat Transfer via Atomistic Simulations. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 205, 123868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J. Parametrizing Nonbonded Interactions from Wetting Experiments via the Work of Adhesion: Example of Water on Graphene Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 28470–28481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellussi, F.M.; Roscioni, O.M.; Rossi, E.; Cardellini, A.; Provenzano, M.; Persichetti, L.; Kudryavtseva, V.; Sukhorukov, G.; Asinari, P.; Sebastiani, M.; et al. Wettability of Soft PLGA Surfaces Predicted by Experimentally Augmented Atomistic Models. MRS Bull. 2023, 48, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.; Bellussi, F.M.; Morciano, M.; Asinari, P.; Fasano, M. Method for Predicting the Wettability of Micro-Structured Surfaces by Continuum Phase-Field Modelling. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamane, S.S.; Gaikwad, P.S.; Radue, M.S.; Gowtham, S.; Odegard, G.M. Wetting Simulations of High-Performance Polymer Resins on Carbon Surfaces as a Function of Temperature Using Molecular Dynamics. Polymers 2021, 13, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, J.; Hao, X.; Zhang, C.; Wei, N.; Zhang, C. Wetting Properties of Defective Graphene Oxide: A Molecular Simulation Study. Molecules 2018, 23, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffo, R.; Di Natale, F.; Minale, M.; Sirignano, M.; Parisi, A.; Carotenuto, C. Analysis of Carbon Nanoparticle Coatings via Wettability. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Chen, W.; Ren, Y.; Chu, L.Y. Exploring dielectric spectra of polymer through molecular dynamics simulations. Mol. Simul. 2022, 48, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolis, G.D.; Dineva, P.S.; Rangelov, T.; Sfyris, D. Mechanical Models and Numerical Simulations in Nanomechanics: A Review across the Scales. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2021, 128, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmiela, S.; Sauceda, H.E.; Müller, K.-R.; Tkatchenko, A. Towards Exact Molecular Dynamics Simulations with Machine-Learned Force Fields. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Z.; Li, X. Comparative Study of Boundary Conditions for Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Solids at Low Temperature. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 224111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, J.; Takase, N.; Mori, K.; Sakai, T. Molecular Dynamics Simulation for the Quantitative Prediction of Experimental Tensile Strength of a Polymer Material. Compos. Part C Open Access 2020, 2, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccotti, G.; Dellago, C.; Ferrario, M.; Hernández, E.R.; Tuckerman, M.E. Molecular Simulations: Past, Present, and Future (a Topical Issue in EPJB). Eur. Phys. J. B 2022, 95, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Srivastava, R.; Koutroumanis, N.; Semitekolos, D.; Chiavazzo, E.; Pappas, P.-N.; Galiotis, C.; Asinari, P.; Charitidis, C.A.; Fasano, M. Mesoscopic Modeling and Experimental Validation of Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene Nanocomposites Reinforced By Graphene-Based Fillers. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 9969–9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebara, Y.; El Moumen, A.; Kanit, T.; Madani, S.; Imad, A. Modeling of the effect of particles size, particles distribution and particles number on mechanical properties of polymer-clay nano-composites: Numerical homogenization versus experimental results. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 86, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, A.; Fu, X.; Zhang, P. Relationship between the structure and thermal properties of polypropylene/graphene nanoplatelets composites for different platelet-sizes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 183, 107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.; Inam, F. Modeling and simulation of graphene based polymer nanocomposites: Advances in the last decade. Graphene 2016, 5, 96–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, Y.; Adhikari, S.; Flores, E.S. Advances in finite element modelling of graphene and associated nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2020, 140, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshelby, J.D. The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1957, 241, 376–396. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T.; Tanaka, K. Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions. Acta Metall. 1973, 21, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Z. Analytical Micromechanics Models for Elastoplastic Behavior of Long Fibrous Composites: A Critical Review and Comparative Study. Materials 2018, 11, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahei-El-Din, Y.A. 1.17 Multiscale Mechanics of Composite Materials and Structures. In Comprehensive Composite Materials II; Beaumont, P.W.R., Zweben, C.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 426–450. ISBN 978-0-08-100534-7. [Google Scholar]
- Elmasry, A.; Azoti, W.; El-Safty, S.A.; Elmarakbi, A. A Comparative Review of Multiscale Models for Effective Properties of Nano- and Micro-Composites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 132, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrieh, M.M.; Esmkhani, M.; Shokrieh, Z.; Zhao, Z. Stiffness Prediction of Graphene Nanoplatelet/Epoxy Nanocomposites by a Combined Molecular Dynamics–Micromechanics Method. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 92, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laspalas, M.; Chiminelli, A.; Sáenz-Ezquerro, C.; Serrano, F.; Valero, C. Analysis of the Elastic Properties of CNTs and Their Effect in Polymer Nanocomposites. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 188, 01018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, D. Effect of Functionalization on the Elastic Behavior of Graphene Nanoplatelet-PE Nanocomposites with Interface Consideration Using a Multiscale Approach. Mech. Mater. 2019, 132, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Jeon, I.; Yang, S. Multiscale Modeling Assessment of the Interfacial Properties and Critical Aspect Ratio of Structurally Defected Graphene in Polymer Nanocomposites for Defect Engineering. Eur. J. Mech.—A/Solids 2022, 96, 104728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafar Dastgerdi, J.; Marquis, G.; Salimi, M. Micromechanical Modeling of Nanocomposites Considering Debonding and Waviness of Reinforcements. Compos. Struct. 2014, 110, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoti, W.; Elmarakbi, A. Constitutive Modelling of Ductile Damage Matrix Reinforced by Platelets-like Particles with Imperfect Interfaces: Application to Graphene Polymer Nanocomposite Materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 113, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajari, A.R.; Ghajar, R.; Shokrieh, M.M. Multiscale Modeling of the Viscoelastic Properties of CNT/Polymer Nanocomposites, Using Complex and Time-Dependent Homogenizations. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2018, 142, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh-Aghdam, M.K. Evaluating the Effective Creep Properties of Graphene-Reinforced Polymer Nanocomposites by a Homogenization Approach. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 209, 108791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Ji, M. Model-Based Dielectric Constant Estimation of Polymeric Nanocomposite. Polymers 2022, 14, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.J.; Kinloch, I.A.; Gong, L.; Novoselov, K.S. The Mechanics of Graphene Nanocomposites: A Review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 1459–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weon, J.-I.; Sue, H.-J. Effects of Clay Orientation and Aspect Ratio on Mechanical Behavior of Nylon-6 Nanocomposite. Polymer 2005, 46, 6325–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.M.; Hinder, S.J.; Taylor, A.C. Graphene Nanoplatelet-Modified Epoxy: Effect of Aspect Ratio and Surface Functionality on Mechanical Properties and Toughening Mechanisms. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 8764–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasvand Zarasvand, K.; Golestanian, H. Investigating the Effects of Number and Distribution of GNP Layers on Graphene Reinforced Polymer Properties: Physical, Numerical and Micromechanical Methods. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 139, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Li, W.; Zhao, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Dong, P.; Zheng, S. Micromechanical Modeling for the Temperature-Dependent Yield Strength of Polymer-Matrix Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 220, 109265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doghri, I.; Ouaar, A. Homogenization of Two-Phase Elasto-Plastic Composite Materials and Structures: Study of Tangent Operators, Cyclic Plasticity and Numerical Algorithms. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 1681–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Doghri, I.; Noels, L. An Incremental-Secant Mean-Field Homogenization Method with Second Statistical Moments for Elasto-Plastic Composite Materials. Philos. Mag. 2015, 95, 3348–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, G.J. Transformation Field Analysis of Inelastic Composite Materials. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1997, 437, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, G.J.; Benveniste, Y. On Transformation Strains and Uniform Fields in Multiphase Elastic Media. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1997, 437, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, I.A.L.; Sinapius, M. Multiscale Modelling and Simulation of Polymer Nanocomposites Using Transformation Field Analysis (TFA). Compos. Struct. 2019, 209, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontefisso, A.; Mishnaevsky, L. Nanomorphology of Graphene and CNT Reinforced Polymer and Its Effect on Damage: Micromechanical Numerical Study. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 96, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanit, T.; Forest, S.; Galliet, I.; Mounoury, V.; Jeulin, D. Determination of the Size of the Representative Volume Element for Random Composites: Statistical and Numerical Approach. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2003, 40, 3647–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Liu, Y.J. Square Representative Volume Elements for Evaluating the Effective Material Properties of Carbon Nanotube-Based Composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2004, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Chen, X.L. Evaluations of the Effective Material Properties of Carbon Nanotube-Based Composites Using a Nanoscale Representative Volume Element. Mech. Mater. 2003, 35, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwał, M.; Muc, A. Transversely Isotropic Properties of Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 88, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwał, M. Numerical Evaluation of Effective Material Constants for CNT-Based Polymeric Nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 849, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.; Reda, H.; Chazirakis, A.; Harmandaris, V. Investigating the Mechanical Performance of Graphene Reinforced Polymer Nanocomposites via Atomistic and Continuum Simulation Approaches. Polymer 2023, 286, 126379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Sáenz Ezquerro, C.; Srivastava, R.; Asinari, P.; Laspalas, M.; Chiminelli, A.; Fasano, M. Atomistic to Mesoscopic Modelling of Thermophysical Properties of Graphene-Reinforced Epoxy Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malagù, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Lyulin, A.; Benvenuti, E.; Simone, A. Diameter-Dependent Elastic Properties of Carbon Nanotube-Polymer Composites: Emergence of Size Effects from Atomistic-Scale Simulations. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 131, 260–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Lu, Z. Numerical Analysis of Elastic–Plastic Properties of Polymer Composite Reinforced by Wavy and Random CNTs. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 95, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasvand Zarasvand, K.; Golestanian, H. Determination of Nonlinear Behavior of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Polymer: Experimental, numerical, and micromechanical. Mater. Des. 2016, 109, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, W.; Zhang, R.; Guo, R. Two-Scale Modeling of Composites Damage with Voronoi Cell Finite Element Method for Microscale Computation. Compos. Struct. 2022, 291, 115659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Lee, K.; Moorthy, S. Multiple Scale Analysis of Heterogeneous Elastic Structures Using Homogenization Theory and Voronoi Cell Finite Element Method. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1995, 32, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, E.J.; Bednarcyk, B.A.; Waas, A.M.; Arnold, S.M. Progressive Failure of a Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Composite Using the Method of Cells: Discretization Objective Computational Results. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, M.A.A.; Pindera, M.-J. Finite-Volume Enabled Transformation Field Analysis of Periodic Materials. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 2013, 9, 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, M.A.A.; Pindera, M.-J. Generalized FVDAM Theory for Elastic–Plastic Periodic Materials. Int. J. Plast. 2016, 77, 90–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, F.E.; Aydin, R.C.; Cyron, C.J.; Huber, N.; Kalidindi, S.R.; Klusemann, B. A review of the application of machine learning and data mining approaches in continuum materials mechanics. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Vu-Bac, N.; Zhuang, X.; Fu, X.; Rabczuk, T. Stochastic full-range multiscale modeling of thermal conductivity of Polymeric carbon nanotubes composites: A machine learning approach. Compos. Struct. 2022, 289, 115393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.A.; Pinho, S.T.; Tagarielli, V.L. Application of machine learning to predict the multiaxial strain-sensing response of CNT-polymer composites. Carbon 2019, 146, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Andersson, M.A.; Stake, J. A 200 GHz CVD Graphene FET Based Resistive Subharmonic Mixer. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–27 May 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jenkins, K.A.; Valdes-Garcia, A.; Farmer, D.B.; Zhu, Y.; Bol, A.A.; Dimitrakopoulos, C.D.; Zhu, W.; Xia, F.; Avouris, P.H.; et al. State-of-the-Art Graphene High-Frequency Electronics. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3062–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-M.; Jenkins, K.; Farmer, D.; Valdes-Garcia, A.; Avouris, P.; Sung, C.-Y.; Chiu, H.-Y.; Ek, B. Development of Graphene FETs for High Frequency Electronics. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), Baltimore, MD, USA, 1–9 December 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibpour, O.; Vukusic, J.; Stake, J. A 30-GHz Integrated Subharmonic Mixer Based on a Multichannel Graphene FET. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwierz, F. Graphene Transistors: Status, Prospects, and Problems. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1567–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szunerits, S.; Rodrigues, T.; Bagale, R.; Happy, H.; Boukherroub, R.; Knoll, W. Graphene-Based Field-Effect Transistors for Biosensing: Where Is the Field Heading To? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 2137–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T. Flexible Sensing Electronics for Wearable/Attachable Health Monitoring. Small 2017, 13, 1602790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Infectious Diseases: From Methods to Devices. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prattis, I.; Hui, E.; Gubeljak, P.; Kaminski Schierle, G.S.; Lombardo, A.; Occhipinti, L.G. Graphene for Biosensing Applications in Point-of-Care Testing. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Haick, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, C.; Lee, S.; Yokota, T.; Someya, T. Skin Bioelectronics towards Long-Term, Continuous Health Monitoring. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3759–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Li, K.; Liu, B.; Tu, J.; Li, T.; Li, Y.-T.; Zhang, G.-J. A pH-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor for Monitoring of Cancer Cell External Acid Environment. Talanta 2023, 252, 123764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnaji, N.; Wasfi, A.; Awwad, F. The Design of a Point of Care FET Biosensor to Detect and Screen COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Hao, Z.; Qi, T.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, X. An Integrated Flexible and Reusable Graphene Field Effect Transistor Nanosensor for Monitoring Glucose. J. Mater. 2020, 6, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, S.; Schwierz, F. Modeling of the Steady State Characteristics of Large-Area Graphene Field-Effect Transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 034506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selberherr, S. Analysis and Simulation of Semiconductor Devices; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1984; ISBN 978-3-7091-8754-8. [Google Scholar]
- Landauer, G.M.; Jiménez, D.; González, J.L. An Accurate and Verilog-A Compatible Compact Model for Graphene Field-Effect Transistors. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2014, 13, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasi, G.; Romano, V. A Full Coupled Drift-Diffusion-Poisson Simulation of a GFET. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2020, 87, 105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoh, I.J.; Kazmierski, T.J.; Al-Hashimi, B.M. A dual-gate graphene FET model for circuit simulation—SPICE implementation. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2013, 12, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmai, B.; Silva, V.; Mendes, P.M. 2D Electronics Based on Graphene Field Effect Transistors: Tutorial for Modelling and Simulation. Micromachines 2021, 12, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuente-Zapico, E.; Martínez-Mazon, P.; Carlos Galdón, J.; Márquez, C.; Navarro, C.; Donetti, L.; Sampedro, C.; Gamiz, F. Simulation of BioGFET Sensors Using TCAD. Solid State Electron. 2023, 208, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multi Project Wafer Runs. Available online: https://graphene-flagship.eu/industrialisation/pilot-line/multi-project-wafer-runs/ (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Venkatesan, K.R.; Koo, B.; Khafagy, K.H.; Chattopadhyay, A. Multiscale modeling of carbon nanotube-reinforced polymer with coarse-grain molecular dynamics informed morphology. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 223, 109412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, U.; Gulsen, H. A novel computational multi-scale modeling of randomly-distributed-graphene/epoxy nanocomposites with interfacial interactions. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2023, 285, 112553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeowa, C.; Muthu, S.J. Multiscale Modeling and Characterization of Graphene Epoxy Nanocomposite. Polymers 2024, 16, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, H.; Yazdani, H. Atomistic simulation and machine learning predictions of mechanical response in nanotube-polymer composites considering filler morphology and aggregation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2025, 246, 113399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Weng, G.J.; Su, Y. A multiscale study of the filler-size and temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity of graphene-polymer nanocomposites. Carbon 2021, 175, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, X.; Cao, B.; Fu, Y. Mesoscopic simulation of thermal conductivities of 3D carbon nanotubes, graphene and their epoxy resin based composites. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 172, 107273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, K.; Zbyrad, P.; Uhl, T.; Staszewski, W.J.; Packo, P. Multiscale electro-mechanical modeling of carbon nanotube composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 135, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talamadupula, K.K.; Seidel, G.D. Statistical analysis of effective electro-mechanical properties and percolation behavior of aligned carbon nanotube/polymer nanocomposites via computational micromechanics. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 197, 110616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, X.; Fu, Y.; Gong, S.; Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Lei, X.; Zhu, Z. A multi-scale model to predict the electromagetic interference shielding performance of (Fe/Cu)@ CNT/SA/PDMS flexible composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 927, 167043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. Theoretical estimation on electrical conductivity, synergy effect and piezoresistive behavior for nanocomposites with hybrid carbon nanotube/graphene based on modified Bethe lattice method. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 202, 110986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talamadupula, K.K.; Seidel, G. Computational Micromechanics Investigation of Percolation and Effective Electro-Mechanical Properties of Carbon Nanotube/Polymer Nanocomposites using Stochastically Generated Realizations: Effects of Orientation and Waviness. Polymers 2022, 14, 5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | CNM | Matrix | Analyzed Properties | Models | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical properties | |||||
| Venkatesan et al. (2022) | CNT | Epoxy | Elastic modulus, tensile strength, failure strain, damage index | CGMD + FEM | [182] |
| Caliskan and Gulsen (2023) | GNP | Epoxy | Elastic modulus, tensile strength | MD + FEM | [183] |
| Ekeowa and Muthu (2024) | Gr functionalized | Epoxy | Young’s modulus, Poisson ratio, tensile strength, interphase properties | MD + FEM | [184] |
| Ghasemi and Yazdani (2025) | CNT | PVC | Young’s modulus, Poisson ratio, shear modulus | MD + CGMD + ML | [185] |
| Thermal properties | |||||
| Wang et al. (2021) | Gr | Epoxy | Thermal conductivity, Kapitza resistance | MD + EMT | [186] |
| Yang et al. (2022) | CNT, Gr | Epoxy | Thermal conductivity | SPH + DPD | [187] |
| Muhammad et al. (2023) | Gr | Epoxy | Thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity, glass transition temperature, elastic moduli | MD + CGMD + FEM | [149] |
| Muhammad et al. (2023) | Gr, GO, rGO | PP | Thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity, glass transition temperature, elastic moduli | CGMD + FEM + EMT | [112] |
| Electromagnetic/sensing properties | |||||
| Grabowski et al. (2017) | CNT | Epoxy | Electrical resistivity, Young’s modulus, Poisson ratio | MD + FEM (micro and macro) | [188] |
| Talamadupula and Seidel (2021) | CNT | Epoxy | Piezoresistive coefficients, electrical conductivity, elastic moduli | Tunneling model + FEM | [189] |
| Wu et al. (2022) | Fe/Cu particles on CNT | PDMS + Sodium alginate | Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness, electrical conductivity, and dielectric and magnetic losses | EMT + percolation network + propagation matrix | [190] |
| Liu et al. (2022) | CNT, GNP | Epoxy | Piezoresistive coefficients, electrical conductivity | Bethe lattice method, excluded volume theory | [191] |
| Talamadupula and Seidel (2022) | CNT | Epoxy | Piezoresistive coefficients, electrical conductivity, elastic moduli | Tunneling model + FEM | [192] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiminelli, A.; Radović, I.; Fasano, M.; Fantoni, A.; Laspalas, M.; Kalinić, A.; Provenzano, M.; Fernandes, M. Modeling Carbon-Based Nanomaterials (CNMs) and Derived Composites and Devices. Sensors 2024, 24, 7665. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237665
Chiminelli A, Radović I, Fasano M, Fantoni A, Laspalas M, Kalinić A, Provenzano M, Fernandes M. Modeling Carbon-Based Nanomaterials (CNMs) and Derived Composites and Devices. Sensors. 2024; 24(23):7665. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237665
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiminelli, Agustίn, Ivan Radović, Matteo Fasano, Alessandro Fantoni, Manuel Laspalas, Ana Kalinić, Marina Provenzano, and Miguel Fernandes. 2024. "Modeling Carbon-Based Nanomaterials (CNMs) and Derived Composites and Devices" Sensors 24, no. 23: 7665. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237665
APA StyleChiminelli, A., Radović, I., Fasano, M., Fantoni, A., Laspalas, M., Kalinić, A., Provenzano, M., & Fernandes, M. (2024). Modeling Carbon-Based Nanomaterials (CNMs) and Derived Composites and Devices. Sensors, 24(23), 7665. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237665









