Algorithm Analysis and Optimization of a Digital Image Correlation Method Using a Non-Probability Interval Multidimensional Parallelepiped Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Methodology
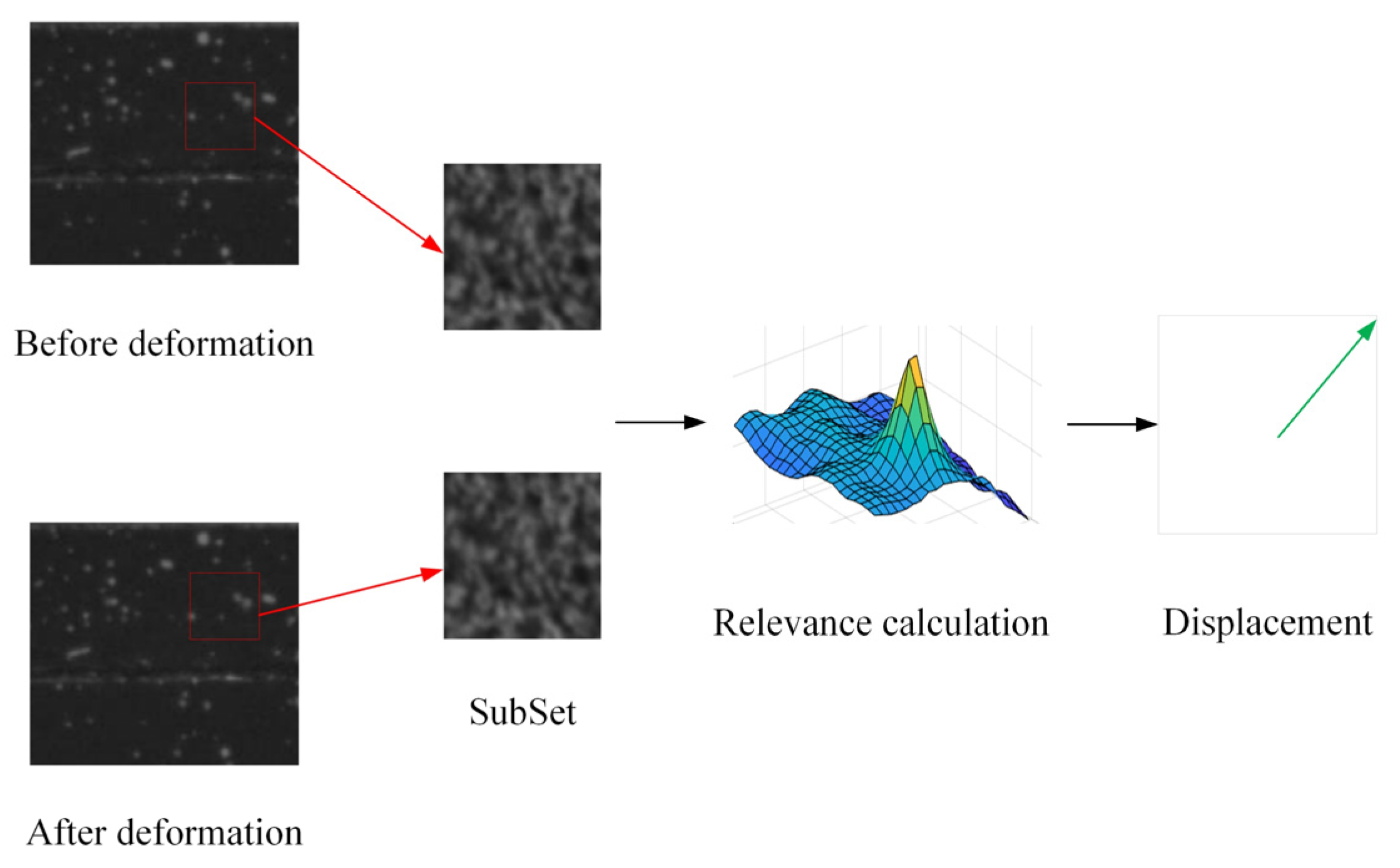
2.1. IC-GN-PC Method
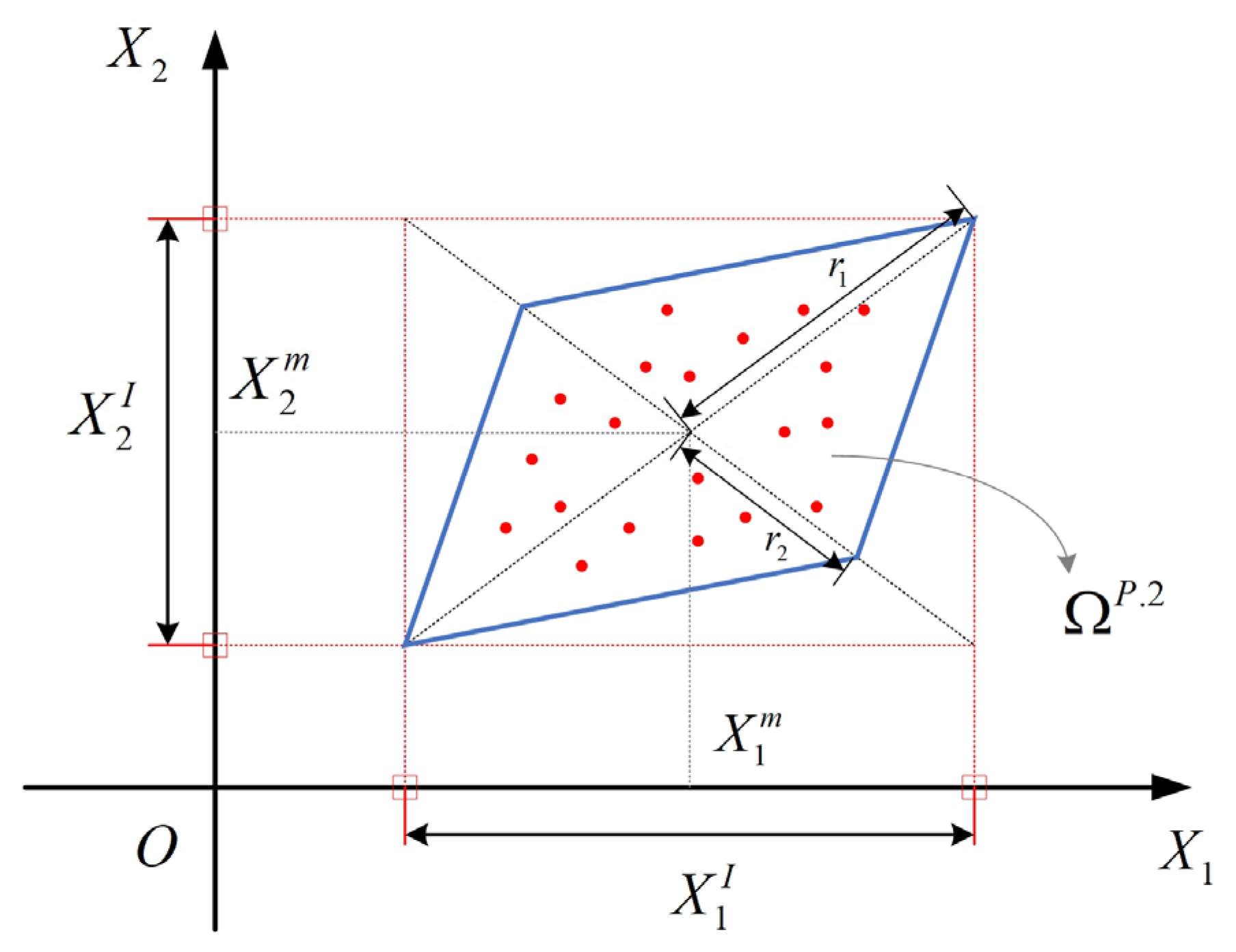
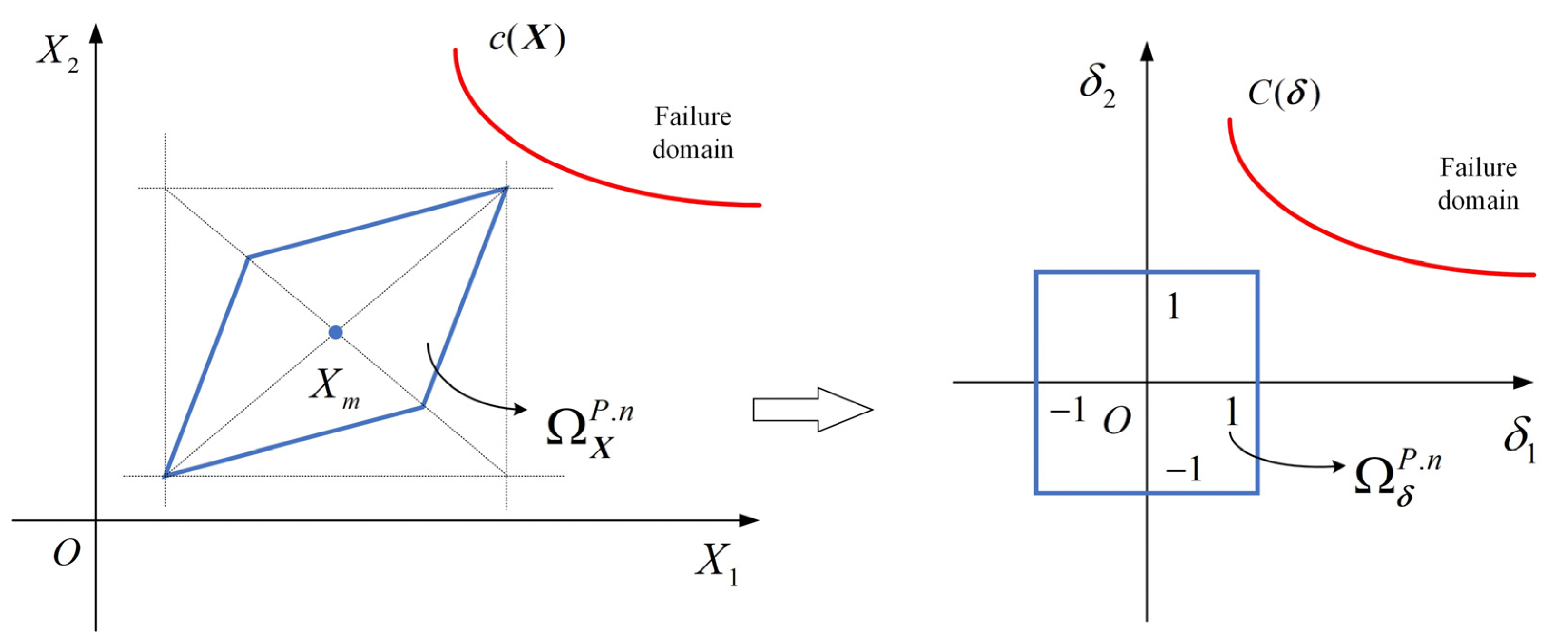
2.2. Non-Probabilistic Reliability Analysis
2.3. Parameter Interval Optimization
- Computing the n reliability indexes η1P, η2P, … ηmP under corresponding reliability requirements according to Section 2.2;
- Adjusting the interval median of a parameter so that the reliability index ηiP reaches a minimum value but not less than 1. Repeating this operation for each reliability index, and obtaining the optimal interval of the parameter by taking the intersections of the aforementioned intervals. If all the reliability requirements cannot be satisfied for a parameter, then its optimal interval is empty;
- Doing step (2) for all the parameters to obtain the optimized parameter intervals for the instanced algorithm.
3. Analysis and Discussion
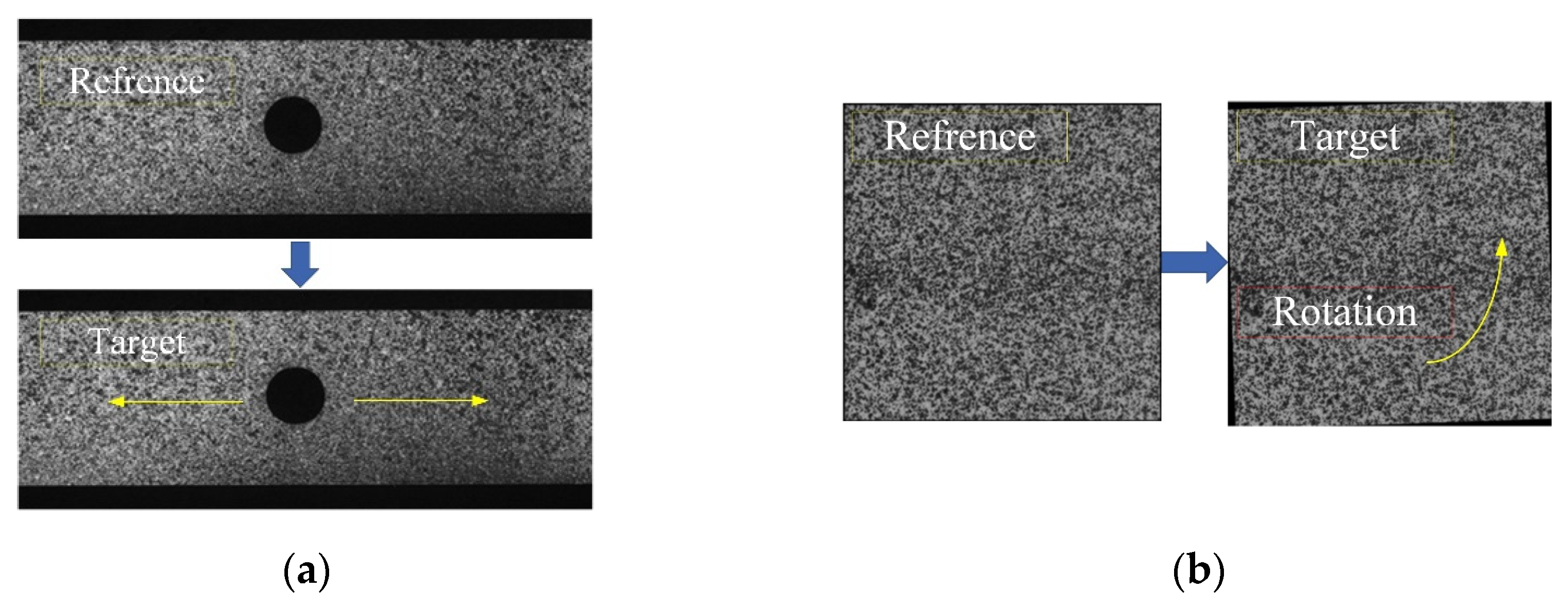
3.1. Presentation of the IC-GN-PC Method
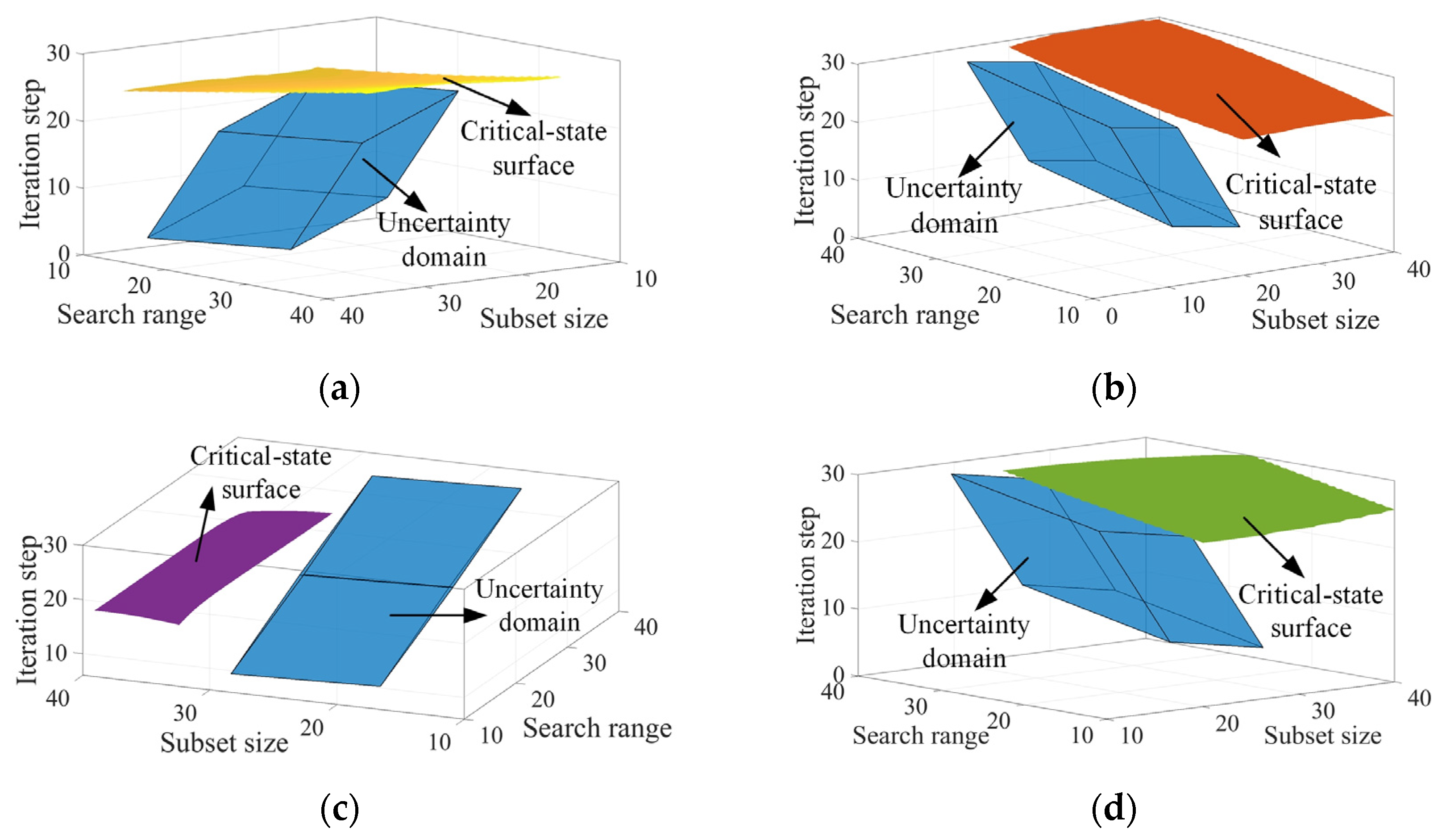
3.2. Reliability Analysis and Optimization of Parameter Intervals
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farahani, B.V.; Tavares, P.J.; Belinha, J.; Moreira, P.M.G.P. A fracture mechanics study of a compact tension specimen: Digital image correlation, finite element and meshless methods. Int. Conf. Struct. Integr. 2017, 5, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qambela, C.J.; Heyns, P.S.; Inglis, H.M. Damage detection for laminated composites using full-field digital image correlation. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2021, 40, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Zhang, X.; Fatikow, S. 3D robust digital image correlation for vibration measurement. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Stinville, J.C.; Francis, T.; Polonsky, A.T.; Torbet, C.; Charpagne, M.; Chen, Z.; Balbus, G.; Bourdin, F.; Valle, V.; Callahan, P.; et al. Time-resolved digital image correlation in the scanning electron microscope for analysis of time-dependent mechanisms. Exp. Mech. 2020, 61, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Liang, J.; Li, X. In situ scanning–digital image correlation for high-temperature deformation measurement of nickel-based single crystal superalloy. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 084008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Pan, B. Calibration-free single camera stereo-digital image correlation for small-scale underwater deformation measurement. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 10509–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G.M. Deformation measurement in the presence of discontinuities with digital image correlation: A review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 137, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Li, H.Q.; Tong, J.W.; Ruan, J.T. Statistical analysis of the effect of intensity pattern noise on the displacement measurement precision of digital image correlation using self-correlated images. Exp. Mech. 2007, 47, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Sutton, M.A.; Bruck, H.A.; Schreier, H.W. Quantitative error assessment in pattern matching: Effects of intensity pattern noise, interpolation, strain and image contrast on motion measurements. Strain 2009, 45, 160–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecompte, D.; Smits, A.; Bossuyt, S.; Sol, H.; Vantomme, J.; Van Hemelrijck, D.; Habraken, A. Quality assessment of speckle patterns for digital image correlation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2006, 44, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Gao, Z. Quality assessment of speckle patterns for DIC by consideration of both systematic errors and random errors. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 86, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, H.W.; Sutton, M.A. Systematic errors in digital image correlation due to under matched subset shape functions. Exp. Mech. 2002, 42, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Su, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, Q. Effects of various shape functions and subset size in local deformation measurements using DIC. Exp. Mech. 2015, 55, 1575–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.X.; Dai, X.J.; He, X.Y. Noise robustness and parallel computation of the inverse compositional Gauss-Newton algorithm in digital image correlation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2015, 71, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Xie, H.M.; Xu, B.Q.; Dai, F.L. Performance of sub-pixel registration algorithms in digital image correlation. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Schreier, H.W.; Braasch, J.R.; Sutton, M.A. Systematic errors in digital image correlation caused by intensity interpolation. Opt. Eng. 2000, 39, 2915–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, L.; Wang, Z.; Vo, M.; Hoang, T.; Ma, J. Accuracy enhancement of digital image correlation with B-spline interpolation. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 3070–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Xu, X.; Wu, X. Fourier-based interpolation bias prediction in digital image correlation. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 19242–19260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reu, P.L.; Sweatt, W.; Miller, T.; Fleming, D. Camera System Resolution and its Influence on Digital Image Correlation. Exp. Mech. 2015, 55, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulmy, J.P.; Jegou, S.; Barrallier, L. Towards an image quality criterion to optimize digital image correlation. Use of an analytical model to optimize acquisition conditions. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2022, 148, 107792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiong, C.; Lei, X.; Huang, Y.; Lv, W.; Zhu, F. Optimized super-resolution promotes accuracy for projection speckle three-dimensional digital image correlation. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 115601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcaen, R.; Reu, P.; Lava, P.; Debruyne, D. Stereo-DIC uncertainty quantification based on simulated images. Exp. Mech. 2016, 57, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcaen, R.; Wittevrongel, L.; Reu, P.L.; Lava, P.; Debruyne, D. Stereo-DIC calibration and speckle image generator based on FE formulations. Exp. Mech. 2017, 57, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, Q.C.; Gao, Z.R. Statistical model for speckle pattern optimization. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 30259–30275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alefeld, G.; Mayer, G. Interval analysis: Theory and applications. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2000, 121, 421–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Debnath, A.K.; Pedrycz, W. A variable and a fixed ordering of intervals and their application in optimization with interval-v1alued functions. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2020, 121, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elishakoff, I.; Elisseeff, P.; Glegg, S.A.L. Non-probabilistic convex-theoretic modeling of scatter in material properties. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhaim, Y. Convex models of uncertainty in radial pulse buckling of shells. J. Appl. Mech. 1993, 60, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Han, X.; Lu, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, Y. Correlation analysis of non-probabilistic convex model and corresponding structural reliability technique. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 2528–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.X.; Qiu, Z.P. Non-probabilistic convex models and interval analysis method for dynamic response of a beam with bounded uncertainty. Appl. Math. Model. 2010, 34, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.P.; Elishakoff, I.; Starnes, J.H. Derivation of multi-dimensional ellipsoidal convex model for experimental data. Math. Comput. Model. 1996, 24, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Kang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Li, A. Continuum topology optimization with non-probabilistic reliability constraints based on multi-ellipsoid convex model. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2009, 39, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, Q.F.; Han, X.; Liu, J.; Hu, D.A. Multidimensional parallelepiped model-a new type of non-probabilistic convex model for structural uncertainty analysis. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2015, 103, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.Y.; Jiang, C.; Han, X. An improved multidimensional parallelepiped non-probabilistic model for structural uncertainty analysis. Appl. Math. Model. 2016, 40, 4727–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Shangguan, W.B.; Zhao, K. Effective correlation analysis algorithms for uncertain structures based on multidimensional parallelepiped model. Appl. Math. Model. 2023, 120, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelides, C.P. Stability of elastic bars on uncertain foundations using a convex model. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1996, 33, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryba, L.; Yoshikawa, N. Bounds analysis of a beam based on the convex model of uncertain foundation. J. Sound Vib. 1998, 212, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzerli, S.; Pantelides, C.P. Optimum structural design via convex model superposition. Comput. Struct. 2000, 74, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Bi, R.G.; Lu, G.Y.; Han, X. Structural reliability analysis using non-probabilistic convex model. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 254, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xia, Y. Interval Uncertainty-Oriented Optimal Control Method for Spacecraft Attitude Control. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 5460–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Bai, Z.F. A bivariate subinterval method for dynamic analysis of mechanical systems with interval uncertain parameters. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2023, 125, 107377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Xia, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, A.; Yang, Y. A prediction–correction method for fast and accurate initial displacement field estimation in digital image correlation. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reu, P.L.; Toussaint, E.; Jones, E.; Bruck, H.A.; Iadicola, M.; Balcaen, R.; Turner, D.Z.; Siebert, T.; Lava, P.; Simonsen, M.D.I.C. DIC challenge: Developing images and guidelines for evaluating accuracy and resolution of 2D analyses. Exp. Mech. 2017, 58, 1067–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Li, K.; Tong, W. Fast, robust and accurate digital image correlation calculation without redundant computations. Exp. Mech. 2013, 53, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Selected Algorithm Parameters | Marginal Interval | Interval Median | Interval Radius |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subset size | [20, 40] | 30 | 10 |
| Search range | [10, 40] | 25 | 15 |
| Iteration steps | [6, 30] | 18 | 12 |
| Serial | Subset Size | Search Range | Iteration Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 | 25 | 24 |
| 2 | 28 | 23 | 12 |
| 3 | 39 | 30 | 18 |
| 4 | 36 | 31 | 23 |
| 5 | 40 | 39 | 29 |
| 6 | 33 | 18 | 19 |
| 7 | 20 | 31 | 18 |
| 8 | 37 | 30 | 9 |
| 9 | 39 | 15 | 9 |
| 10 | 34 | 13 | 12 |
| 11 | 35 | 25 | 27 |
| 12 | 35 | 33 | 12 |
| 13 | 28 | 20 | 26 |
| 14 | 33 | 28 | 12 |
| 15 | 23 | 16 | 29 |
| p1(1:9) | 29.79 | 24.81 | 27.69 | 26.04 | 27.10 | 25.86 | 27.61 | 26.00 | 25.93 |
| p1(10:18) | 25.83 | 23.72 | 21.27 | 26.82 | 29.36 | 26.85 | 26.57 | 26.87 | 24.38 |
| p1(19:27) | 24.65 | 22.54 | 26.82 | 23.45 | 25.41 | 24.89 | 25.72 | 27.95 | 26.23 |
| p2(1:9) | 31.06 | 29.42 | 23.91 | 23.70 | 27.92 | 23.68 | 45.55 | 23.64 | 28.03 |
| p2(10:18) | 29.65 | 27.82 | 21.26 | 21.42 | 25.83 | 21.96 | 43.24 | 21.36 | 26.57 |
| p2(19:27) | 28.45 | 31.42 | 22.64 | 26.56 | 26.54 | 20.34 | 46.94 | 24.54 | 26.81 |
| t1(1:9) | −0.41 | −1.90 | −1.52 | −1.62 | −1.41 | −1.11 | −0.79 | −0.95 | −1.62 |
| t1(10:18) | 7.93 | 7.31 | 9.28 | 6.64 | 6.76 | 5.14 | 6.07 | 4.28 | 7.35 |
| t1(19:27) | 17.64 | 14.92 | 20.87 | 14.55 | 14.35 | 11.31 | 12.22 | 9.36 | 14.25 |
| t2(1:9) | −0.77 | −0.73 | −0.57 | −0.70 | −0.87 | −0.78 | −0.99 | −0.47 | −0.72 |
| t2(10:18) | 4.97 | 4.96 | 4.36 | 4.02 | 4.01 | 3.76 | 4.10 | 2.55 | 3.61 |
| t2(19:27) | 10.15 | 12.36 | 10.16 | 9.44 | 8.16 | 7.90 | 7.40 | 6.00 | 8.16 |
| Serial | PSNR of DIC | Predicted PSNR | PSNR Relative Error (%) | Computational Time of DIC | Predicted Time | Computational Time Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26.9392 | 26.6837 | 0.95 | 8.2749 | 8.3711 | 1.16 |
| 2 | 26.8975 | 26.6194 | 1.03 | 4.5103 | 4.5795 | 1.53 |
| 3 | 26.1781 | 26.3895 | 0.80 | 5.8767 | 5.9538 | 1.31 |
| 4 | 26.8704 | 26.4790 | 1.45 | 7.8004 | 7.6921 | 1.38 |
| 5 | 26.3277 | 26.2404 | 0.33 | 9.1381 | 9.0499 | 1.01 |
| 6 | 26.5841 | 26.4656 | 0.44 | 7.3573 | 7.3795 | 0.30 |
| 7 | 26.4474 | 26.6595 | 0.80 | 6.1410 | 6.2133 | 1.17 |
| 8 | 26.5605 | 26.4556 | 0.39 | 3.4255 | 3.4233 | 0.06 |
| 9 | 26.2544 | 26.3843 | 0.49 | 3.6621 | 3.6962 | 0.93 |
| 10 | 26.2734 | 26.3359 | 0.23 | 4.9886 | 4.9128 | 1.51 |
| 11 | 26.0813 | 26.5140 | 1.65 | 9.6197 | 9.6565 | 0.38 |
| 12 | 26.7937 | 26.4904 | 1.13 | 4.0818 | 4.0763 | 0.13 |
| 13 | 26.8975 | 26.5856 | 1.15 | 8.8906 | 8.9476 | 0.64 |
| 14 | 26.5841 | 26.5646 | 0.07 | 4.9111 | 4.8519 | 1.05 |
| 15 | 26.7866 | 26.6796 | 0.39 | 10.5578 | 10.5490 | 0.08 |
| Serial | PSNR of DIC | Predicted PSNR | PSNR Relative error (%) | Computational Time of DIC | Predicted Time | Computational Time Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26.6656 | 27.0654 | 1.49 | 5.5700 | 5.5069 | 1.13 |
| 2 | 25.2075 | 25.3182 | 0.43 | 2.7996 | 2.8250 | 0.90 |
| 3 | 27.0882 | 26.5753 | 1.90 | 3.7305 | 3.7123 | 0.48 |
| 4 | 24.9728 | 25.2890 | 1.26 | 4.6776 | 4.6315 | 0.98 |
| 5 | 24.2411 | 24.5181 | 1.14 | 4.9305 | 4.9775 | 0.85 |
| 6 | 28.4261 | 28.1620 | 0.93 | 4.4975 | 4.4672 | 0.67 |
| 7 | 31.0711 | 30.9611 | 0.35 | 3.9062 | 3.8675 | 0.98 |
| 8 | 24.5835 | 25.0092 | 1.73 | 2.2204 | 2.1918 | 1.28 |
| 9 | 26.5893 | 26.3208 | 1.01 | 2.4378 | 2.4121 | 1.05 |
| 10 | 27.4022 | 27.2739 | 0.46 | 3.2079 | 3.1819 | 0.81 |
| 11 | 27.6861 | 27.6310 | 0.19 | 5.9777 | 5.8887 | 1.48 |
| 12 | 25.9449 | 26.3268 | 1.47 | 2.4908 | 2.5233 | 1.30 |
| 13 | 25.2075 | 25.6269 | 1.66 | 5.6671 | 5.7626 | 1.68 |
| 14 | 25.6900 | 25.7379 | 0.18 | 2.6208 | 2.6688 | 1.83 |
| 15 | 25.5279 | 25.8053 | 1.08 | 6.4818 | 6.5849 | 1.59 |
| Selected Algorithm Parameters | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimized Interval | ηPP1 | Optimized Interval | ηPT1 | Optimized Interval | ηPP2 | Optimized Interval | ηPT2 | |
| Subset size | [16, 36] | 1.06 | [12, 30] | 1.02 | [13, 33] | 1.04 | [13, 33] | 1.01 |
| Search range | [2, 32] | 1.05 | [26, 56] | 1.02 | [0, 30] * | 0.73 | [16, 46] | 1.02 |
| Iteration step | ** | 0.79 | [3, 27] | 1.03 | ** | 0.53 | [4, 28] | 1.08 |
| Case | Sample | Subset Size | Search Range | Iteration Steps | PSNR | Computational Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 1 | 22 | 27 | 15 | 26.80 | 5.54 s |
| 2 | 18 | 26 | 21 | 26.63 | 7.85 s | |
| 3 | 27 | 30 | 18 | 26.73 | 6.32 s | |
| Case 2 | 4 | 25 | 20 | 13 | 30.39 | 3.10 s |
| 5 | 28 | 18 | 24 | 29.22 | 5.92 s | |
| 6 | 30 | 30 | 20 | 27.79 | 4.52 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Ao, X.; Xia, H.; Huang, S.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Du, C. Algorithm Analysis and Optimization of a Digital Image Correlation Method Using a Non-Probability Interval Multidimensional Parallelepiped Model. Sensors 2024, 24, 6460. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196460
Zhu X, Liu J, Ao X, Xia H, Huang S, Zhu L, Li X, Du C. Algorithm Analysis and Optimization of a Digital Image Correlation Method Using a Non-Probability Interval Multidimensional Parallelepiped Model. Sensors. 2024; 24(19):6460. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196460
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xuedong, Jianhua Liu, Xiaohui Ao, Huanxiong Xia, Sihan Huang, Lijian Zhu, Xiaoqiang Li, and Changlin Du. 2024. "Algorithm Analysis and Optimization of a Digital Image Correlation Method Using a Non-Probability Interval Multidimensional Parallelepiped Model" Sensors 24, no. 19: 6460. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196460
APA StyleZhu, X., Liu, J., Ao, X., Xia, H., Huang, S., Zhu, L., Li, X., & Du, C. (2024). Algorithm Analysis and Optimization of a Digital Image Correlation Method Using a Non-Probability Interval Multidimensional Parallelepiped Model. Sensors, 24(19), 6460. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24196460







