Efficiency-Oriented Model Predictive Control: A Novel MPC Strategy to Optimize the Global Process Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries of Efficiency-Oriented MPC
2.1. Optimization Margin and Optimization Efficiency
2.2. The Relationship between the Global Process Performance and the Terminal Truncation Term
2.3. Understand Optimization Efficiency by Standard Optimal Control and MPC
2.4. Classes of Process Systems
3. Efficiency-Oriented Model Predictive Control Algorithm
3.1. Periodic Approximation Technique
3.2. Efficiency-Oriented MPC Type I
3.2.1. Recursive Feasibility of EfiMPC1
3.2.2. Closed-Loop Stability of EfiMPC1
3.3. Zone Control-Based Optimization Perspective
3.4. Efficiency-Oriented MPC Type II
4. A CSTR Case Study
4.1. Application to a Chemical Process Example
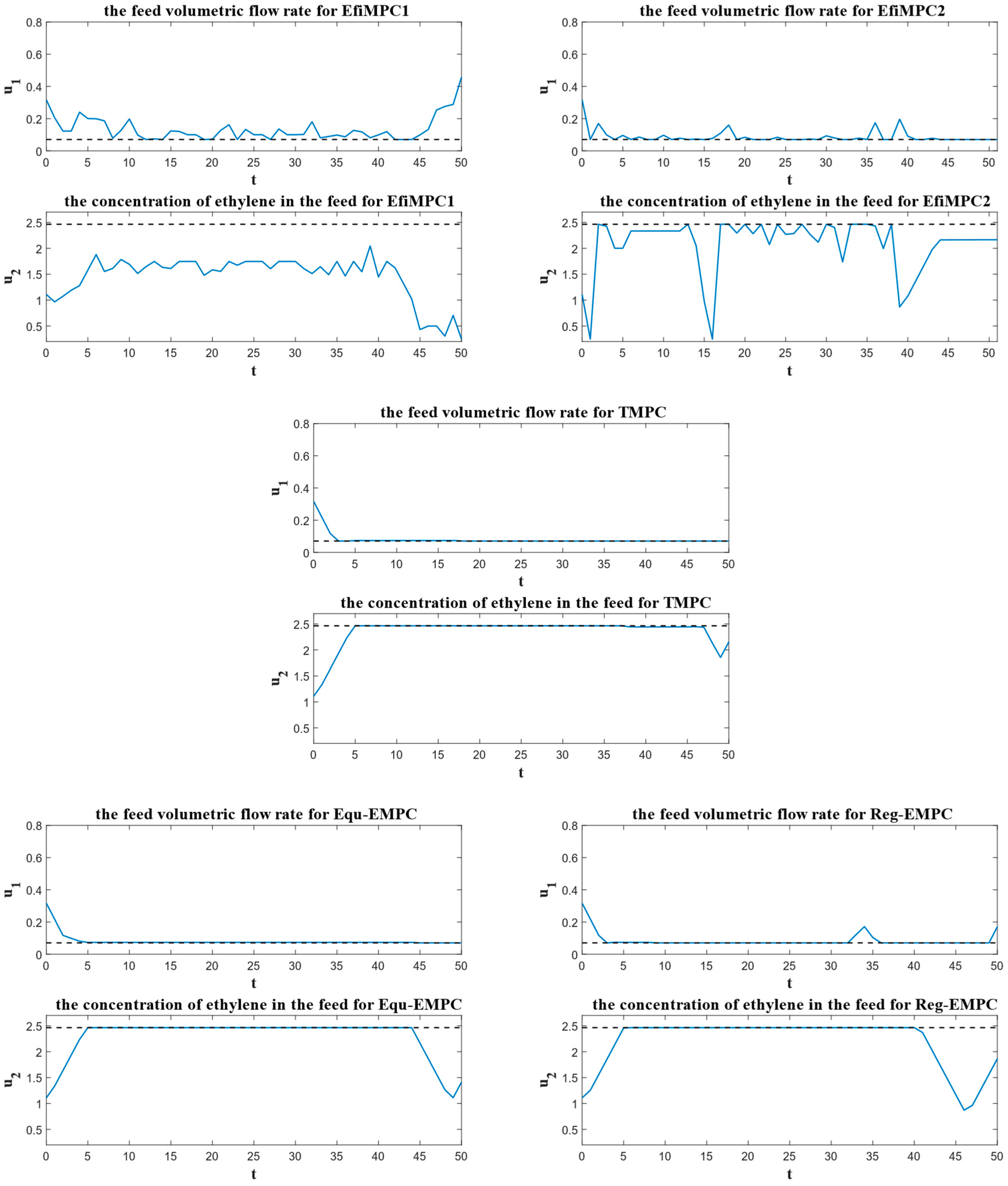
4.2. Simulation Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamnabhi-Lagarrigue, F.; Annaswamy, A.; Engell, S.; Isaksson, A.; Khargonekar, P.; Murray, R.; Van, P. Systems & control for the future of humanity, research agenda: Current and future roles, impact and grand challenges. Annu. Rev. Control 2017, 43, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Amrit, R.; Rawlings, J.; Angeli, D. Economic optimization using model predictive control with a terminal cost. Annu. Rev. Control 2011, 35, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.; Durand, H.; Christofides, P. A tutorial review of economic model predictive control methods. J. Process Control 2014, 24, 1156–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejjari, F.; Khoury, B.; Puig, V.; Quevedo, J.; Pascual, J.; de Campos, S. Economic Linear Parameter Varying Model Predictive Control of the Aeration System of a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sensors 2022, 22, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, I.J.; Yusoff, S.H.; Gunawan, T.S.; Zabidi, S.A.; Hanifah, M.S.B.A.; Sapihie, S.N.M.; Pranggono, B. Analysis of Model Predictive Control-Based Energy Management System Performance to Enhance Energy Transmission. Energies 2024, 17, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seborg, D.; Edgar, T.; Mellichamp, D.; Doyle, F., III. Process Dynamics and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cimini, G.; Bernardini, D.; Levijoki, S.; Bemporad, A. Embedded model predictive control with certified real-time optimization for synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2020, 29, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Huang, W.; Yin, X.; Khosravi, M.; Li, Q.; Wan, S.; Qi, L. Security-aware dynamic scheduling for real-time optimization in cloud-based industrial applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 4219–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untrau, A.; Sochard, S.; Marias, F.; Reneaume, J.M.; Le Roux, G.A.; Serra, S. Dynamic Real-Time Optimization of a solar thermal plant during daytime. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 172, 108184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.; Sajjad, K.; Hafeez, G.; Murawwat, S.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.A. Real-time energy optimization and scheduling of buildings integrated with renewable microgrid. Appl. Energy 2023, 335, 120640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Souza, G.; Odloak, D.; Zanin, A. Real time optimization (RTO) with model predictive control (MPC). Comput. Chem. Eng. 2010, 34, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetola, V.; Guay, M. Integration of real-time optimization and model predictive control. J. Process Control 2010, 20, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, J.B.; Mayne, D.; Diehl, M. Model Predictive Control: Theory, Computation, and Design; Nob Hill Publishing: Madison, WI, USA, 2017; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Meduri, A.; Shah, P.; Viereck, J.; Khadiv, M.; Havoutis, I.; Righetti, L. Biconmp: A nonlinear model predictive control framework for whole body motion planning. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 905–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Li, D.; Lin, S. Model predictive control-status and challenges. Acta Autom. Sin. 2013, 39, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.; Müller, M.; Allgöwer, F. Periodic optimal control of nonlinear constrained systems using economic model predictive control. J. Process Control 2020, 92, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldea, M.; Daoutidis, P. Control of integrated process networks—A multi-time scale perspective. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2007, 31, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, M.; Nikolaou, M.; Jones, J.; Nicholson, D. RTO: An overview and assessment of current practice. J. Process Control 2011, 21, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Chen, B.; He, X.; Stuart, P. Application of steady-state detection method based on wavelet transform. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2003, 27, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charitopoulos, V.; Papageorgiou, L.; Dua, V. Multi Set-Point Explicit Model Predictive Control for Nonlinear Process Systems. Processes 2021, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, J.; Bonné, D.; Jorgensen, J.; Venkat, A.; Jorgensen, S. Unreachable setpoints in model predictive control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 53, 2209–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engell, S. Feedback control for optimal process operation. J. Process Control 2007, 17, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Edgar, T.; Porter, J.; Bernaden, J.; Sarli, M. Smart manufacturing, manufacturing intelligence and demand-dynamic performance. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2012, 47, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budman, H.; Silveston, P. Control of periodically operated reactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 4942–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegler, L. Technology advances for dynamic real-time optimization. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2009, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sheha, M.; Powell, K. Dynamic real-time optimization of air-conditioning systems in residential houses with a battery energy storage under different electricity pricing structures. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2018, 44, 2527–2532. [Google Scholar]
- Weigert, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Esche, E.; Repke, J. Enabling Dynamic Real-Time Optimization under Uncertainty using Data-Driven Chance Constraints. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2020, 48, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Du, Q.; Zu, B.; Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Gu, X.; Jiao, K. Enabling real-time optimization of dynamic processes of proton exchange membrane fuel cell: Data-driven approach with semi-recurrent sliding window method. Appl. Energy 2021, 303, 117659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, D.; Amrit, R.; Rawlings, J. On average performance and stability of economic model predictive control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 57, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuk, A.; Trodden, P. Feedback-Optimizing Model Predictive Control for Constrained Linear Systems. IFAC-Pap. 2021, 54, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risbeck, M.; Rawlings, J. Economic model predictive control for time-varying cost and peak demand charge optimization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2019, 65, 2957–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulwasser, T.; Bonvin, D. On the design of economic NMPC based on approximate turnpike properties. In Proceedings of the 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Osaka, Japan, 14 December 2015; pp. 4964–4970. [Google Scholar]
- Grüne, L. Economic receding horizon control without terminal constraints. Automatica 2013, 49, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Angeli, D.; Allgöwer, F. On necessity and robustness of dissipativity in economic model predictive control, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüne, L. Dissipativity and optimal control: Examining the Turnpike Phenomenon. IEEE Control Syst. 2022, 42, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussi, A.; Zero, E.; Sacile, R.; Trinchero, D.; Fossa, M. Smart Sensors and Smart Data for Precision Agriculture: A Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, B.K.; Maurya, N.; Sharma, M. Advancements in Sensor-Based Technologies for Precision Agriculture: An Exploration of Interoperability, Analytics and Deployment Strategies. Eng. Proc. 2023, 58, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, A.; Zha, S.; Zhuo, X.; Ge, S. Application of Deep Learning and Intelligent Sensing Analysis in Smart Home. Sensors 2024, 24, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, N.P.; Damarla, S.K.; Kim, J.W.; Tulsyan, A.; Amjad, F.; Wang, K.; Gopaluni, R.B. Machine learning for industrial sensing and control: A survey and practical perspective. Control Eng. Pract. 2024, 145, 105841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartin, D. KG-RAG: Bridging the Gap Between Knowledge and Creativity. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.12035. [Google Scholar]
- Faulwasser, T.; Kellett, C. On continuous-time infinite horizon optimal control—Dissipativity, stability, and transversality. Automatica 2021, 134, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, D. An apologia for stabilising terminal conditions in model predictive control. Int. J. Control 2013, 86, 2090–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Malo, P.; Deb, K. A review on bilevel optimization: From classical to evolutionary approaches and applications. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2017, 22, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Min, H. Getting a suitable terminal cost and maximizing the terminal region for MPC. Math. Probl. Eng. 2010, 2010, 853679. [Google Scholar]
- Morari, M.; Arkun, Y.; Stephanopoulos, G. Studies in the synthesis of control structures for chemical processes: Part I: Formulation of the problem. Process decomposition and the classification of the control tasks. Analysis of the optimizing control structures. AIChE J. 1980, 26, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Luo, X. Economic Optimization in the Non-Steady-State Periodic Orbit under Zone Model Predictive Control for the Chemical Process: A Case Study of a Heavy-Oil Fractionator. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 9141–9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Xu, F.; Luo, X. Economic optimization for process transition based on redundant control variables in the framework of zone model predictive control. Energy 2022, 241, 122942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, H.; Ellis, M.; Christofides, P. Economic model predictive control designs for input rate-of-change constraint handling and guaranteed economic performance. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2016, 92, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, R.; Kennedy, J.; Blackwell, T. Particle swarm optimization. Swarm Intell. 2007, 1, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.; Mirjalili, S.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Mirjalili, S. Salp Swarm Algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.; Taghian, S.; Mirjalili, S. An improved grey wolf optimizer for solving engineering problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, G.; Liang, G.; Luo, F.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z. Integrated optimization algorithm: A metaheuristic approach for complicated optimization. Inf. Sci. 2022, 586, 424–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, L. Optimal Stochastic Process Optimizer: A New Metaheuristic Algorithm With Adaptive Exploration-Exploitation Property. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 108640–108664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgülşen, F.; Adomaitis, R.; Çinar, A. A numerical method for determining optimal parameter values in forced periodic operation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1992, 47, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfani, F.; Carberry, J. An exploratory kinetic study of ethylene oxidation over an unmoderated supported silver catalyst. La Chim. L’Ind. 1970, 52, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| s | s | ||
| s | |||
| [0.99, 1.5, 0.3, 1.0] | [0.9956, 1.7511, 0.2511, 1.0043] |
| Strategy | Closed-Loop Performance | Optimization Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| EfiMPC1 | −1.010810535 | 0.9446 |
| EfiMPC2 | −0.983458174 | 0.9191 |
| TMPC | −0.906837645 | 0.8513 |
| Equ-EMPC | −0.922916531 | 0.8651 |
| Reg-EMPC | −0.942180054 | 0.8819 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J. Efficiency-Oriented Model Predictive Control: A Novel MPC Strategy to Optimize the Global Process Performance. Sensors 2024, 24, 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175732
Xu J. Efficiency-Oriented Model Predictive Control: A Novel MPC Strategy to Optimize the Global Process Performance. Sensors. 2024; 24(17):5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175732
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiahong. 2024. "Efficiency-Oriented Model Predictive Control: A Novel MPC Strategy to Optimize the Global Process Performance" Sensors 24, no. 17: 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175732
APA StyleXu, J. (2024). Efficiency-Oriented Model Predictive Control: A Novel MPC Strategy to Optimize the Global Process Performance. Sensors, 24(17), 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24175732






