Multi-Focus Images Fusion for Fluorescence Imaging Based on Local Maximum Luminosity and Intensity Variance
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A block-based image fusion method for multi-focus fluorescent imaging is proposed, and it is based on the local maximum luminosity, variance of intensity, and an information filling method. This method benefits from the architecture of fluorescence microscopy.
- A method of information filling for neighboring blocks is proposed to deal with the blocking effect introduced by the common block-based method.
- The depth information of each pixel can be obtained, and it can be used to reconstruct the 3D surface of these objects within source images.
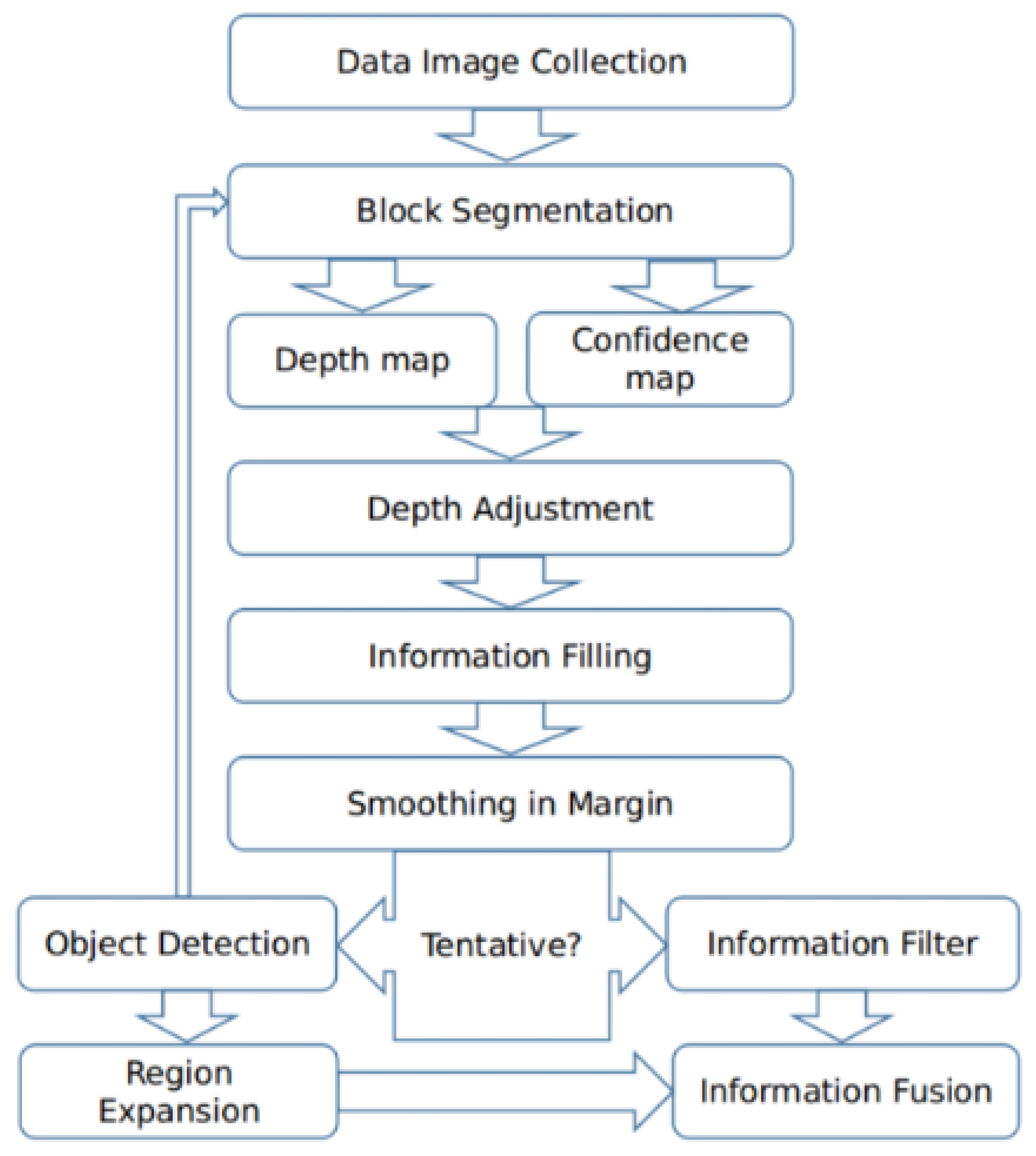
2. Our Method
2.1. Image Collection and Block Segmentation
2.2. Rough Construction of Depth Map
2.3. Depth Adjustment
| Algorithm 1 Adjust |
|
2.4. Information Filling
| Algorithm 2 Information filling. |
|
2.5. Optional Step
3. Experiments
3.1. Fusion Performance
3.2. Computation Time
3.3. Depth Map
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lichtman, J.W.; Conchello, J.A. Fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renz, M. Fluorescence microscopy—A historical and technical perspective. Cytom. Part A 2013, 83, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.; Amos, W.; Fordham, M. An evaluation of confocal versus conventional imaging of biological structures by fluorescence light microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoué, S. Foundations of confocal scanned imaging in light microscopy. In Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, S.; Wang, C.; Chawla, M.K.; Nguyen, M.; Baggett, B.K.; Utzinger, U.; Barnes, C.A.; Liang, R. High resolution, high speed, long working distance, large field of view confocal fluorescence microscope. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tian, L.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H. Rendering distortion estimation model for 3D high efficiency depth coding. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 940737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsovsky, C.; Shelton, R.; Carrasco-Zevallos, O.; Applegate, B.E.; Maitland, K.C. Chromatic confocal microscopy for multi-depth imaging of epithelial tissue. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Coole, J.B.; Tan, M.T.; Zhao, X.; Badaoui, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Williams, M.D.; Gillenwater, A.M. Deep learning extended depth-of-field microscope for fast and slide-free histology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33051–33060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, N.; Xin, B.; Xing, W.; Zhang, Z. A novel multi-focus image fusion method of nonwovens based on GHM multiwavelet transform technology. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 2870–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C. The Fusion of Multi-Focus Images Based on the Complex Shearlet Features-Motivated Generative Adversarial Network. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 5439935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Dong, C.; Guo, M.; Wang, Z.; Mu, X. Multi-focus image fusion based on area-based standard deviation in dual tree contourlet transform domain. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Graphic and Image Processing (ICGIP 2017), Qingdao, China, 14–16 October 2017; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; pp. 878–885. [Google Scholar]
- De, I.; Chanda, B. A simple and efficient algorithm for multifocus image fusion using morphological wavelets. Signal Process. 2006, 86, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Hu, J. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Yan, J.; Qu, X. High quality multi-focus image fusion using self-similarity and depth information. Opt. Commun. 2015, 338, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Sim, T. Defocus map estimation from a single image. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, K.; Kim, K. Design of a long-pass filter with effects on fluorescence image observation for surgical fluorescence microscope applications. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, F.C.; Young, I.T.; Ligthart, G. A comparison of different focus functions for use in autofocus algorithms. Cytom. J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 1985, 6, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlangen, S.; Ihme, M.; Rahlves, M.; Roth, B. Autofocusing system for spatial light modulator-based maskless lithography. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leray, A.; Odin, C.; Le Grand, Y. Out-of-focus fluorescence collection in two-photon microscopy of scattering media. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 6139–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, M.; Efstathiou, G.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D. The evolution of large-scale structure in a universe dominated by cold dark matter. Astrophys. J. 1985, 292, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| De | GFF | SSS | SSSDI | Ours | Ours (with Optional Step) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Set 1 () | 3.48 | 4.38 | 254.67 | 2212.07 | 1.51 | 17.17 |
| Set 2 () | 2.97 | 3.12 | 111.67 | 1555.05 | 0.89 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, H.; Wu, K.; Gu, C.; Ma, D. Multi-Focus Images Fusion for Fluorescence Imaging Based on Local Maximum Luminosity and Intensity Variance. Sensors 2024, 24, 4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24154909
Cheng H, Wu K, Gu C, Ma D. Multi-Focus Images Fusion for Fluorescence Imaging Based on Local Maximum Luminosity and Intensity Variance. Sensors. 2024; 24(15):4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24154909
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Hao, Kaijie Wu, Chaochen Gu, and Dingrui Ma. 2024. "Multi-Focus Images Fusion for Fluorescence Imaging Based on Local Maximum Luminosity and Intensity Variance" Sensors 24, no. 15: 4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24154909
APA StyleCheng, H., Wu, K., Gu, C., & Ma, D. (2024). Multi-Focus Images Fusion for Fluorescence Imaging Based on Local Maximum Luminosity and Intensity Variance. Sensors, 24(15), 4909. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24154909






