Analysing All-Optical Random Bit Sequences Using Gap-Based Approaches †
Abstract
1. Introduction
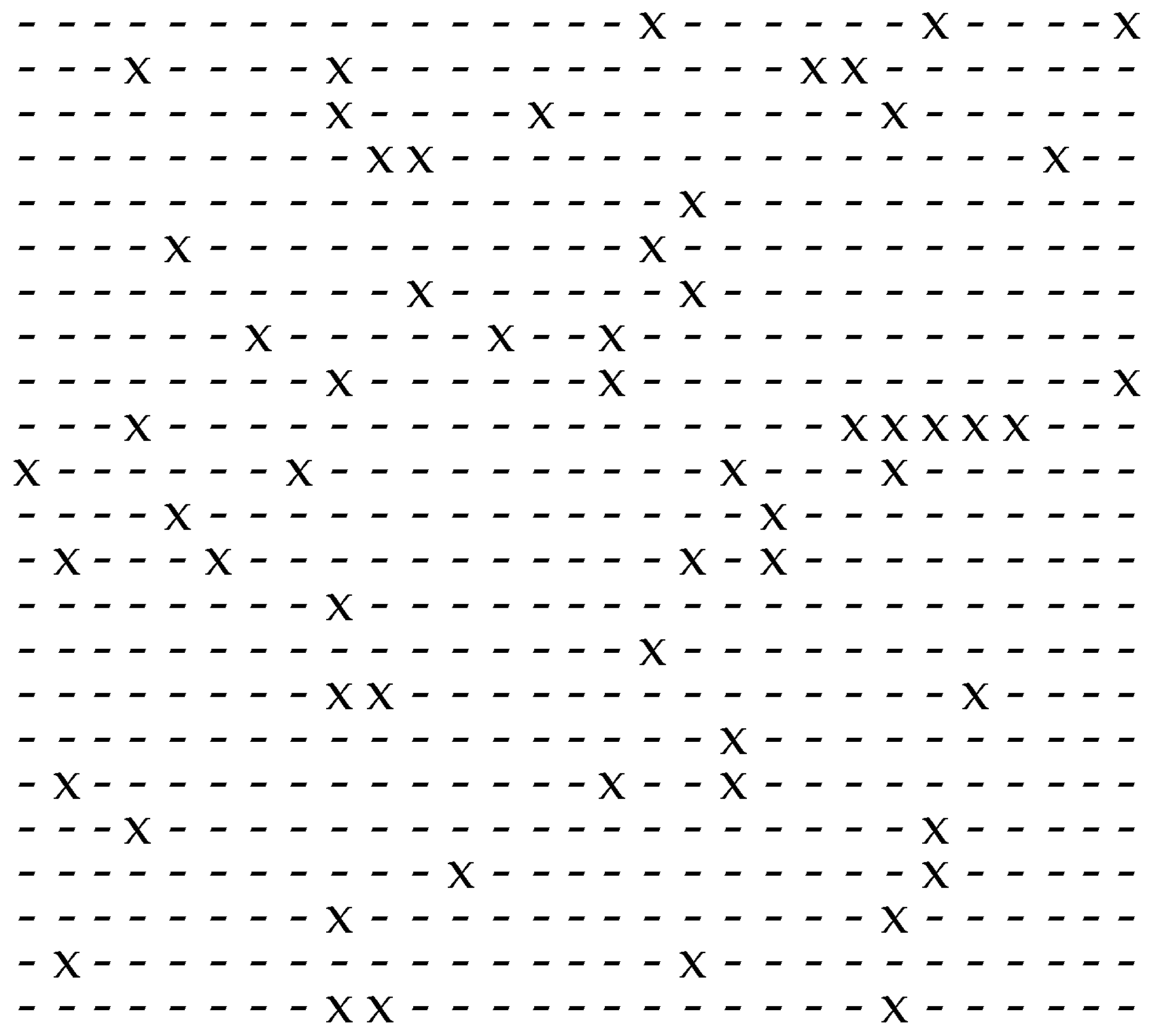
2. Gap-Based Modelling of Binary Sequences
2.1. Introduction and Principles
2.2. Mathematical Description
3. Generation of Binary Sequences
3.1. Introduction
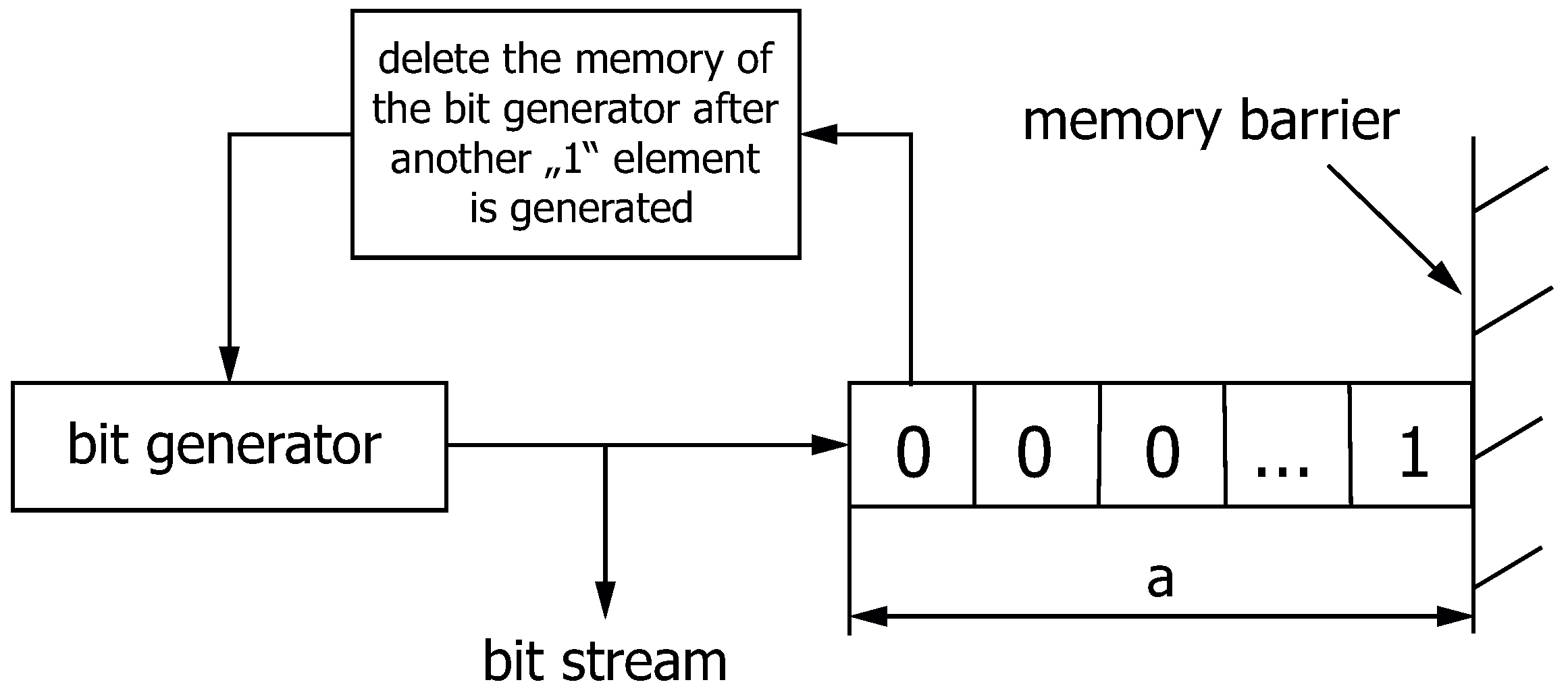
3.2. All-Optically Generated Bit Sequences
3.2.1. Simulation Setup
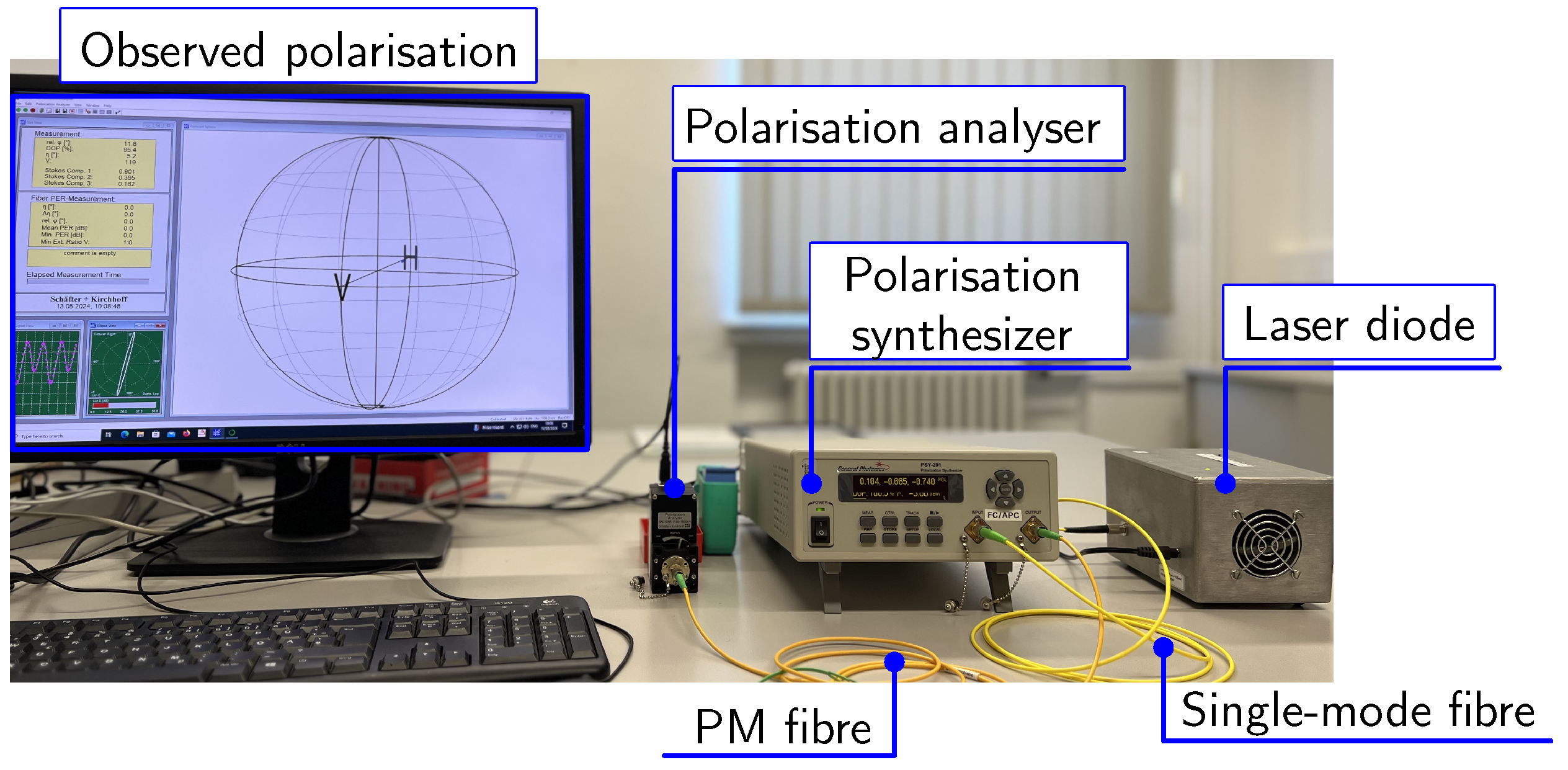
3.2.2. Experimental Setup
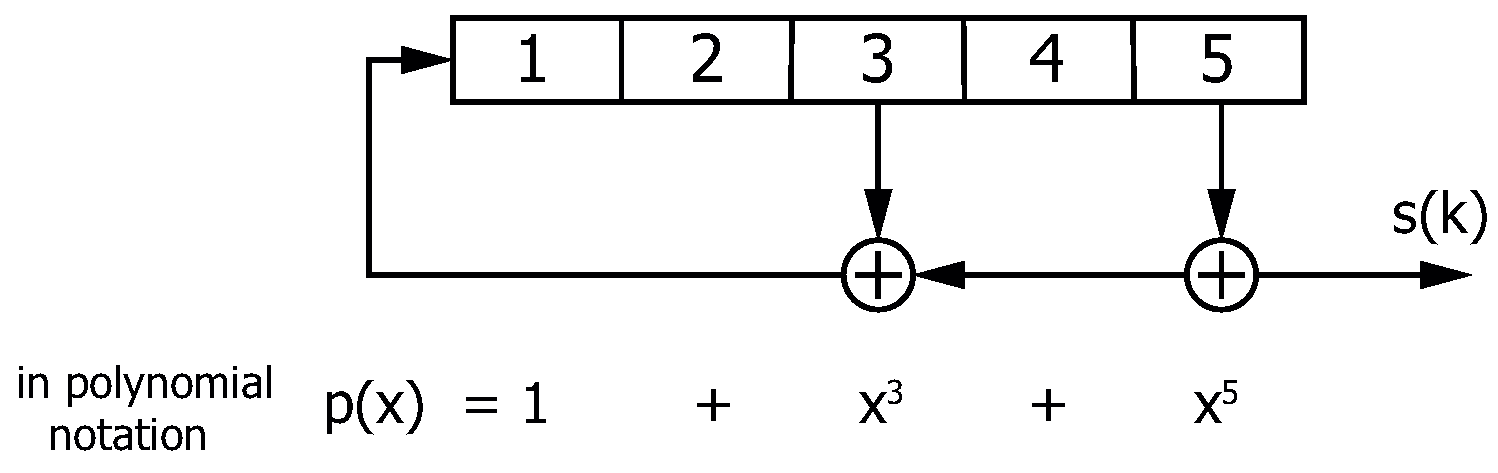
3.3. m-Sequences and Gold Sequences
3.4. Cryptographic Primitives
4. Criteria for the Evaluation of Bit Sequences
5. Results
5.1. Introduction
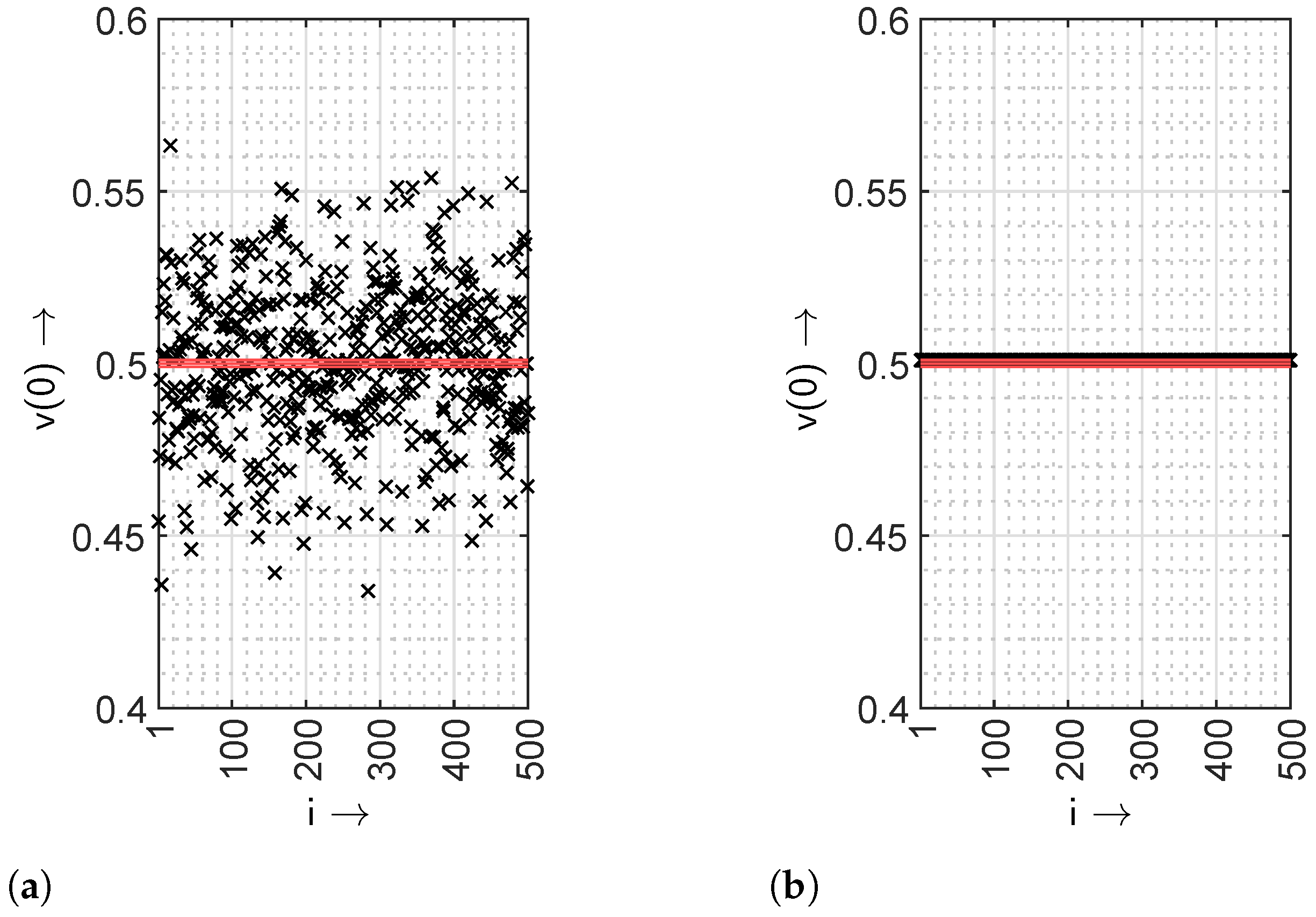
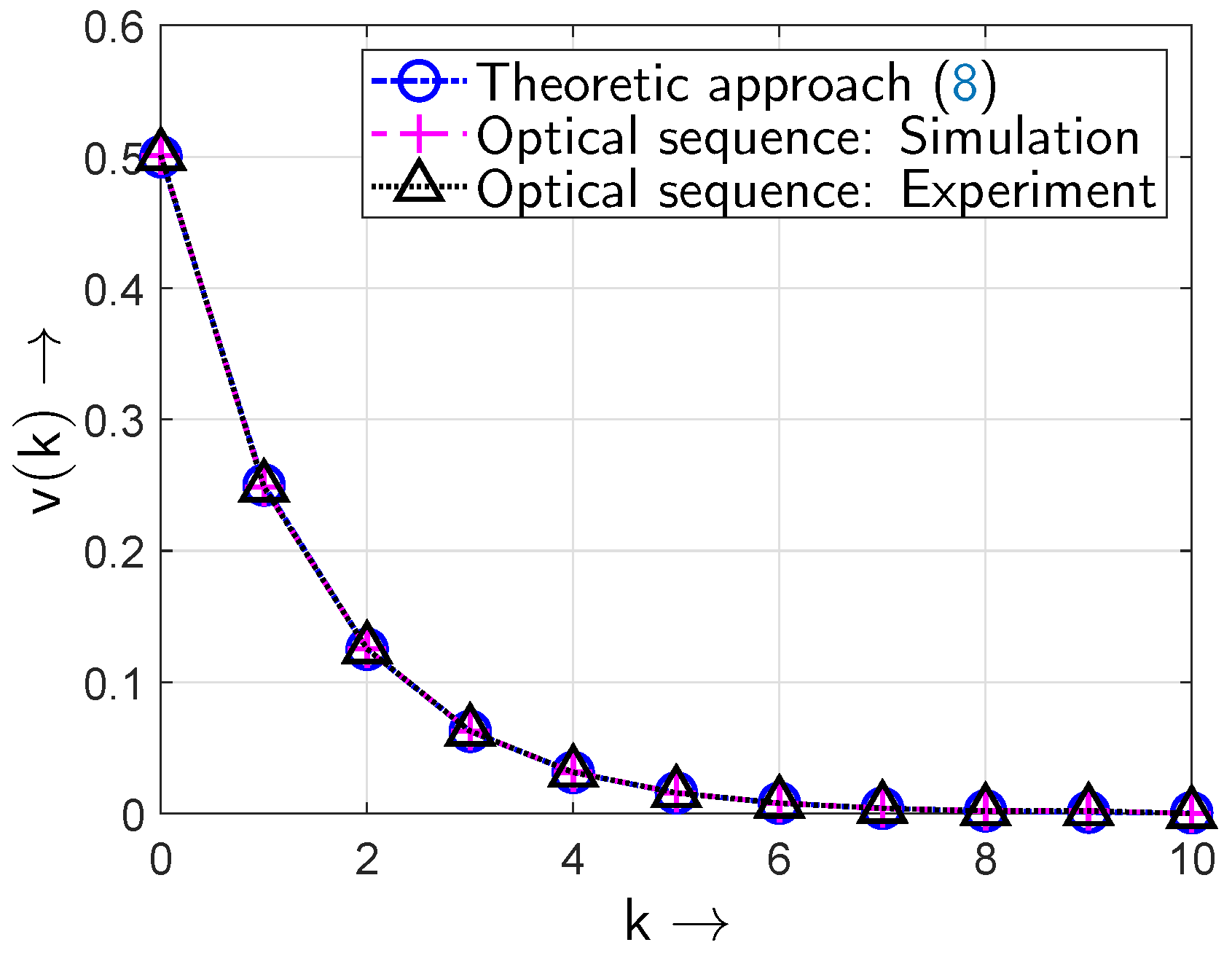
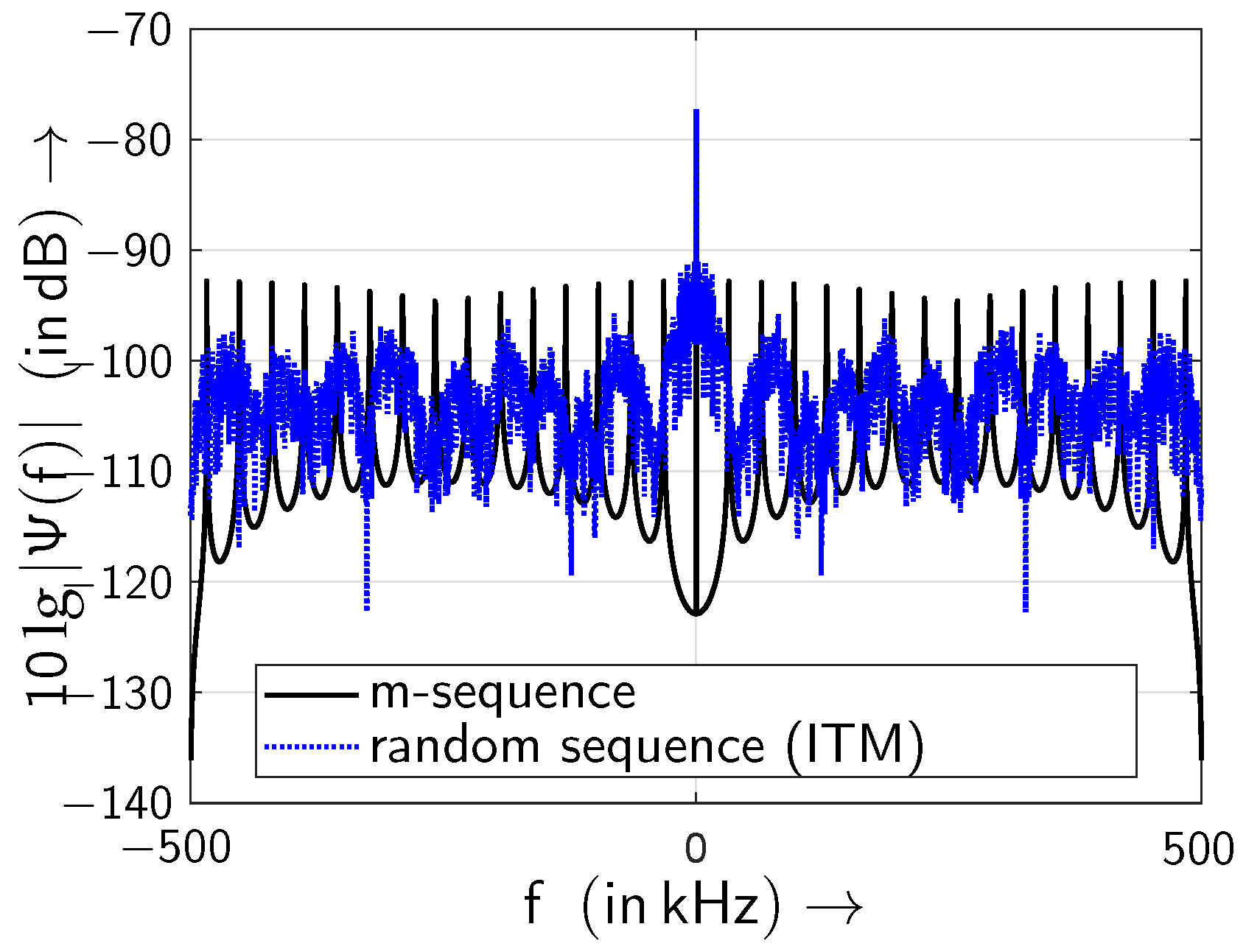
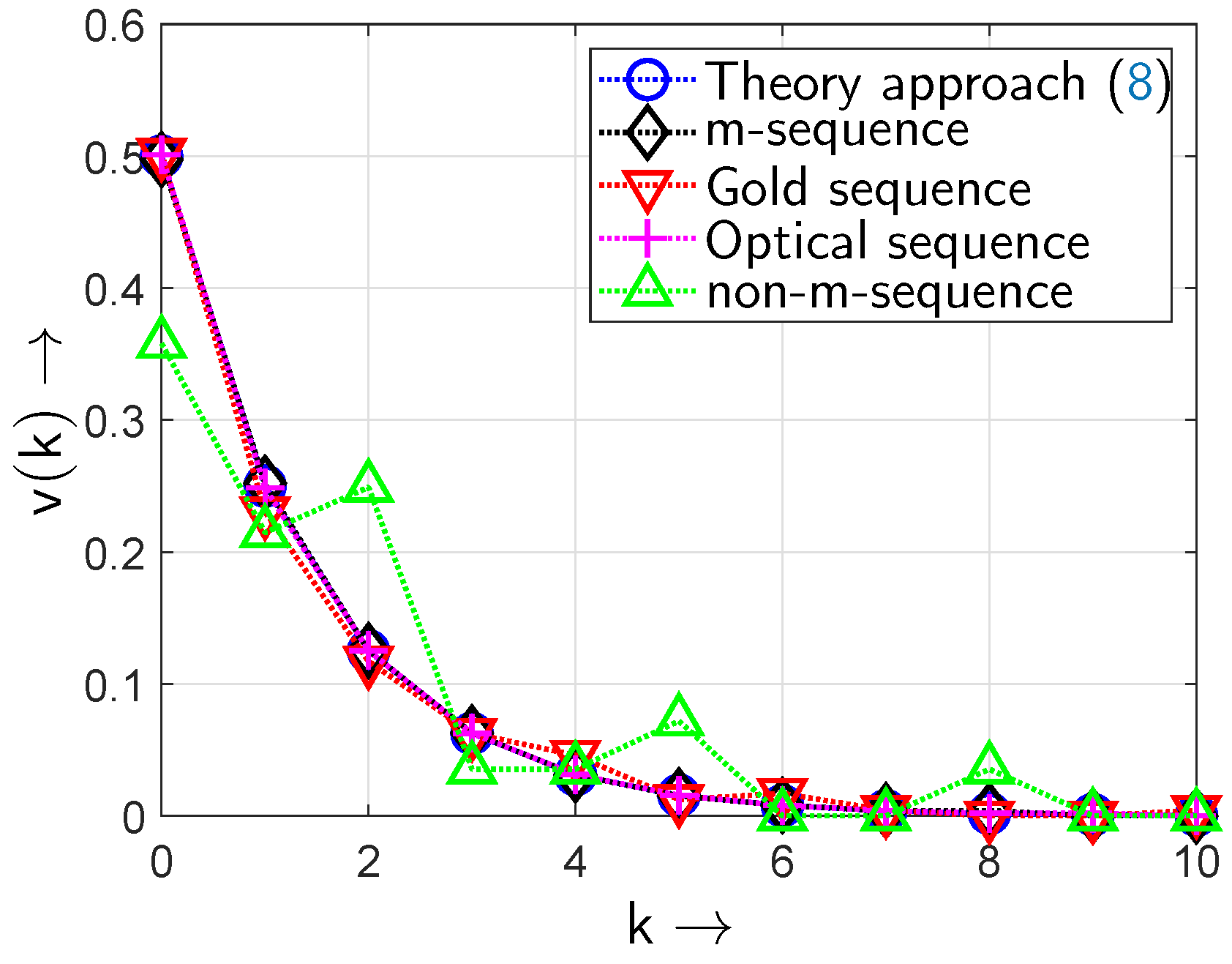
5.2. Results from the All-Optical Setup
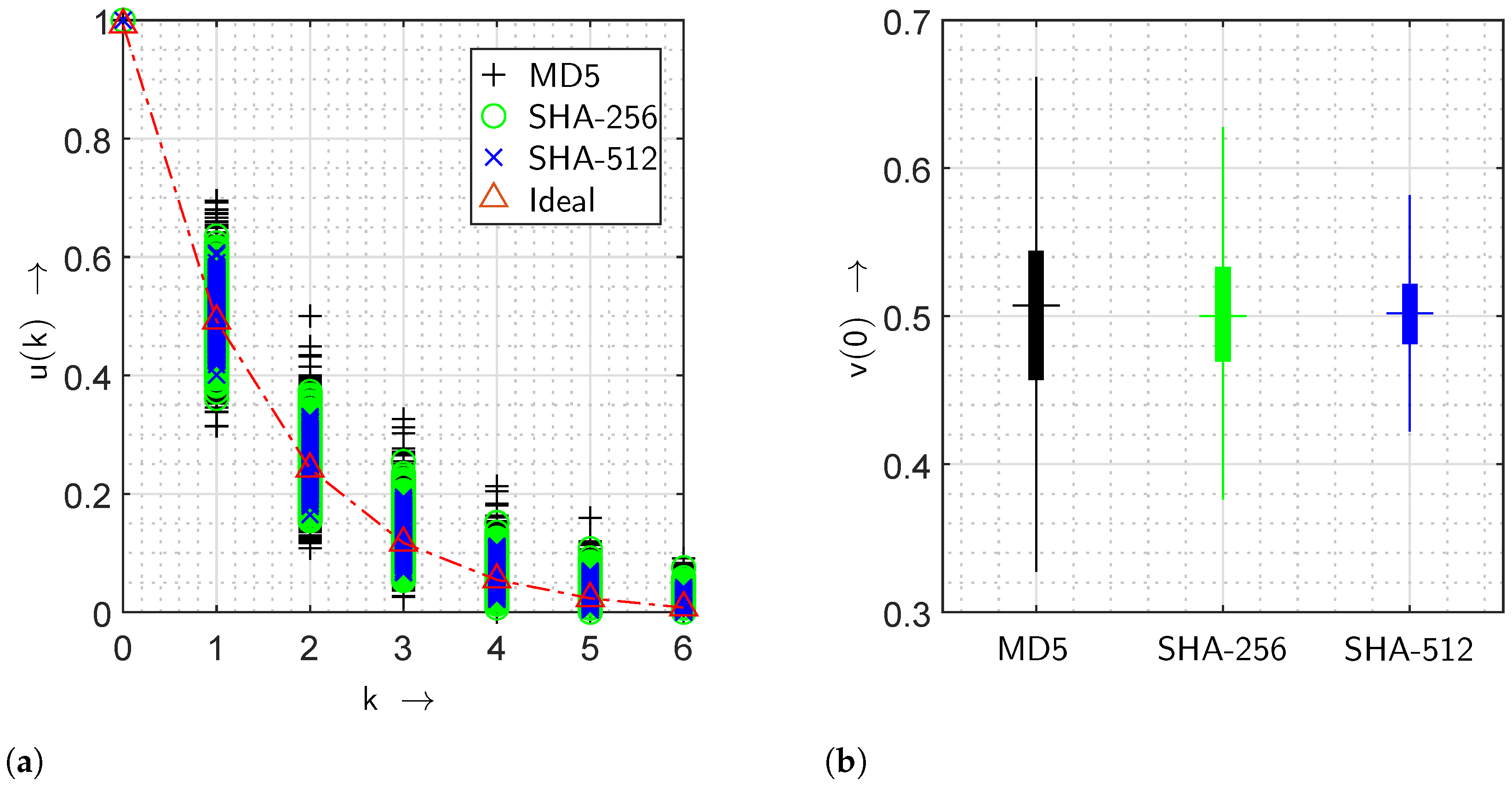
5.3. Results from Cryptographic Primitives
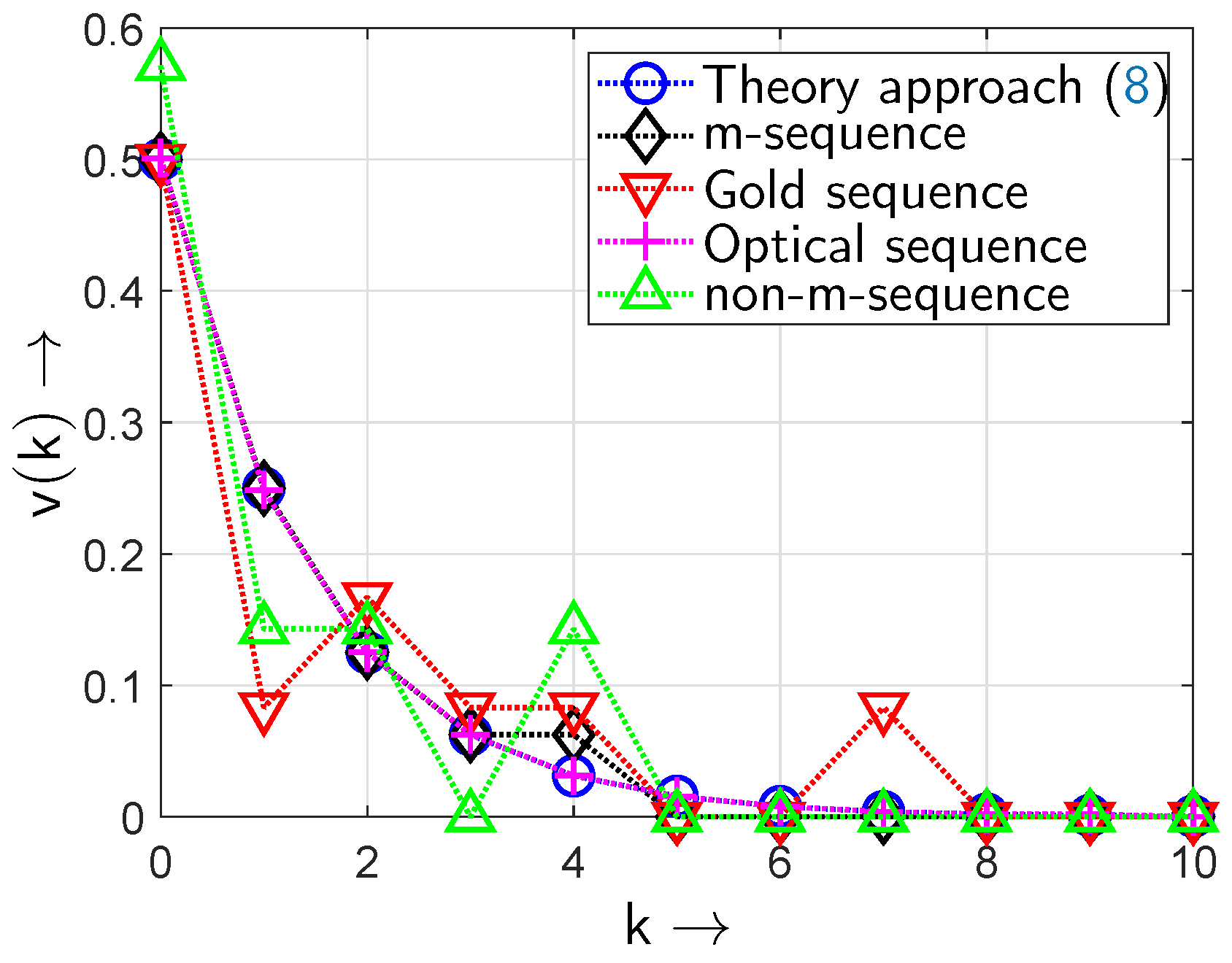
5.4. Results from Deterministic Algorithms
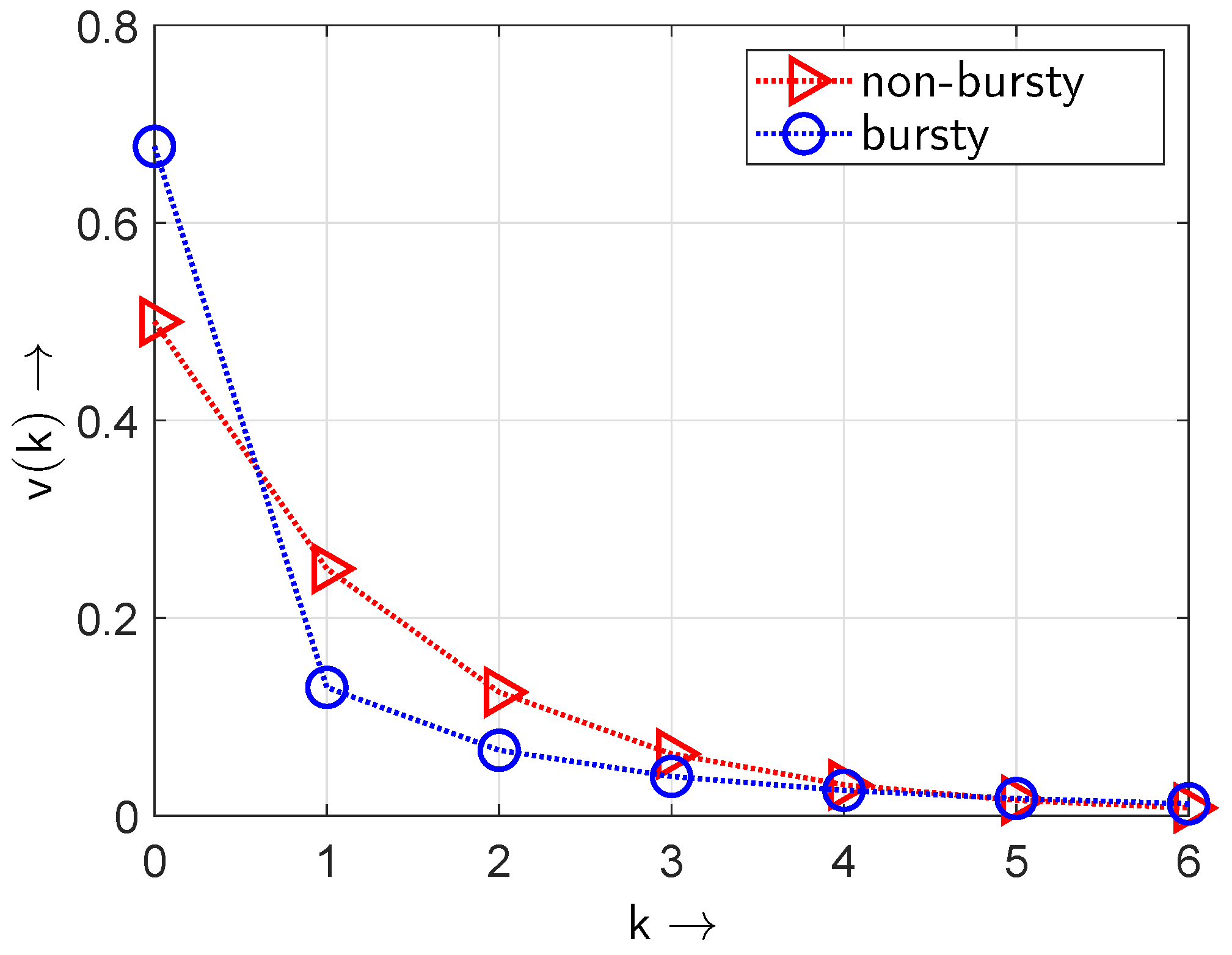
5.5. Burstiness Level
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BOP | Bit occurrence probability |
| DOP | Degree of polarisation |
| IID | Independently and identically distributed |
| ITM | Inverse transform method |
| LD | Laser diode |
| MLS | Maximum length sequence |
| MMF | Multi-mode fibre |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| PMF | Polarisation-maintaining fibre |
| PSD | Power spectral density |
| QKD | Quantum key distribution |
| SEQ | Sequence |
| SMF | Single-mode fibre |
| SOP | State of polarisation |
| VOA | Variable optical attenuator |
References
- Price, R.; Green, P.E. A Communication Technique for Multipath Channels. Proc. IRE 1958, 46, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, B.; Harris, F. Digital Communications—Fundamentals and Applications, 3rd ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Giroto de Oliveira, L.; Nuss, B.; Alabd, M.B.; Diewald, A.; Pauli, M.; Zwick, T. Joint Radar-Communication Systems: Modulation Schemes and System Design. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2022, 70, 1521–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroto de Oliveira, L.; Antes, T.; Nuss, B.; Bekker, E.; Bhutani, A.; Diewald, A.; Alabd, M.B.; Li, Y.; Pauli, M.; Zwick, T. Doppler Shift Tolerance of Typical Pseudorandom Binary Sequences in PMCW Radar. Sensors 2022, 22, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götten, M.; Lochmann, S.; Ahrens, A.; Lindner, E.; Van Roosbroeck, J. 2000 Serial FBG Sensors Interrogated with a Hybrid CDM-WDM Scheme. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golomb, S.W.; Gong, G. Signal Design for Good Correlation: For Wireless Communication, Cryptography, and Radar; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursell, M. The Importance of Systems. In Trust in Computer Systems and the Cloud; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 93–150. [Google Scholar]
- Simion, E. Entropy and Randomness: From Analogic to Quantum World. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 74553–74561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.S.; Barker, E.N.; Kelsey, J.N.; McKay, K.N.; Baish, M.N.; Boyle, M.N. Recommendation for the Entropy Sources Used for Random Bit Generation; Special Publication 800-90B; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Peter, M.; Schindler, W. A Proposal for Functionality Classes for Random Number Generators; Anwendungshinweise und Interpretationen (AIS) 20/31; Federal Office for Information Security of Germany: Bonn, Germany, 2023.
- Forney, G.D. Coding and its application in space communications. IEEE Spectr. 1970, 7, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, E.; Jabbari, B. Spreading codes for direct sequence CDMA and wideband CDMA cellular networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 1998, 36, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuna, M. A novel secure chaos-based pseudo random number generator based on ANN-based chaotic and ring oscillator: Design and its FPGA implementation. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2020, 105, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, G. (Ed.) Optical Fiber Sensors: Advanced Techniques and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Glišić, B. Performance and Health Monitoring of Civil Structures and Infrastructure Using Long-Gauge and Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Trento, Italy, 10–14 July 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braghin, F.; Cazzulani, G.; Cinquemani, S.; Resta, F. Potential of FBG Sensors for Vibration Control in Smart Structures. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM), Vicenza, Italy, 27 February–1 March 2013; pp. 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2014, 560, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekert, A.K. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 67, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana, B.; Krithika, S. Implementation of BB84 Quantum Key Distribution using OptSim. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd International Conference on Electronics and Communication Systems (ICECS), Coimbatore, India, 26–27 February 2015; pp. 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Buhari, A.; Zukarnain, Z.A.; Subramaniam, S.K.; Zainuddin, H.; Saharudin, S. An efficient modeling and simulation of quantum key distribution protocols using OptiSystem™. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Symposium on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Bandung, Indonesia, 23–26 September 2012; pp. 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Rohde, M.; Ali, A. Quantum Cryptography and Simulation: Tools and Techniques. In ICCSP 2020, Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Cryptography, Security and Privacy, Nanjing, China, 10–12 January 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaergaard, M.; Schwartz, M.E.; Braumüller, J.; Krantz, P.; Wang, J.I.J.; Gustavsson, S.; Oliver, W.D. Superconducting Qubits: Current State of Play. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2020, 11, 369–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OptiWave Systems Inc. OptiSystem Design Software; OptiWave Systems Inc.: Nepean, ON, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lo, H.K.; Pan, J.W. Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazirani, U.; Vidick, T. Fully device independent quantum key distribution. Commun. ACM 2019, 62, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Miranskyy, A.; Rjaibi, W.; Stager, G.; Gray, M.; Peck, J. Making existing software quantum safe: A case study on IBM Db2. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2023, 161, 107249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassham, L.E.; Rukhin, A.L.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.R.; Smid, M.E.; Barker, E.B.; Leigh, S.D.; Levenson, M.; Vangel, M.; Banks, D.L.; et al. SP 800-22 Rev. 1a. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Technical report; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2010.
- Ahrens, A.; Lange, C.; Singh, J.; Grote, O. A New Gap-based Approach for Analysing All-Optical Random Bit Sequences. In Proceedings of the 25th International Microwave and Radar Conference (MIKON 2024), Wrocław, Poland, 1–4 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Hao, T.; Li, W.; Li, M. Tb/s Fast Random Bit Generation Based on a Broadband Random Optoelectronic Oscillator. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2021, 33, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazwani, S.; Khan, S.; Siddiqi, M.U.; Al-Khateeb, K.A.; Habaebi, M.H.; Shahid, Z. Randomness Analysis of Pseudo Random Noise Generator Using 24-Bits LFSR. In Proceedings of the 2014 5th International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Modelling and Simulation, Langkawi, Malaysia, 27–29 January 2014; pp. 772–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, A. A new digital radio-channel model suitable for the evaluation and simulation of channel effects. In Proceedings of the IEE Seminar Speech Coding for Algorithms for Radio Channels, London, UK, 17 April 2000; number 2000/012. pp. 2/1–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köpke, A.; Willig, A.; Karl, H. Chaotic Maps as Parsimonious Bit Error Models of Wireless Channels. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2003. Twenty-Second Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37428), San Francisco, CA, USA, 30 March–3 April 2003; Volume 1, pp. 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, H. Calculation of Error Structures in Binary Channels with Memory; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, E.N. Capacity of a Burst-Noise Channel. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1960, 39, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulis, A.; Pillai, S.U. Probability, Random Variables, and Stochastic Processes, 4th ed.; McGraw Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Weisstein, E.W. The CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Blitzstein, J.K.; Hwang, J. Introduction to Probability, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- The Mathworks. Matlab; The Mathworks: Natick, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chipman, R.A.; Lam, W.S.T.; Young, G. Polarized Light and Optical Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. An Overview and Analysis of Hybrid Encryption: The Combination of Symmetric Encryption and Asymmetric Encryption. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Computing and Data Science (CDS), Stanford, CA, USA, 28–29 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preneel, B. Cryptographic hash functions. Eur. Trans. Telecommun. 1994, 5, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.I.; Barabási, A.L. Burstiness and Memory in Complex Systems. Explor. Front. Phys. (EPL) 2008, 81, 48002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.H. Secure Hash Standard; Technical Report; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2015.
- Dang, Q.H. Recommendation for Applications Using Approved Hash Algorithms; Technical Report; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.M. Simulation, 5th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA; London, UK; Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, C.; Ahrens, A. On the Undetected Error Probability for Shortened Hamming Codes on Channels with Memory. In Cryptography and Coding; Honary, B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 9–19. [Google Scholar]
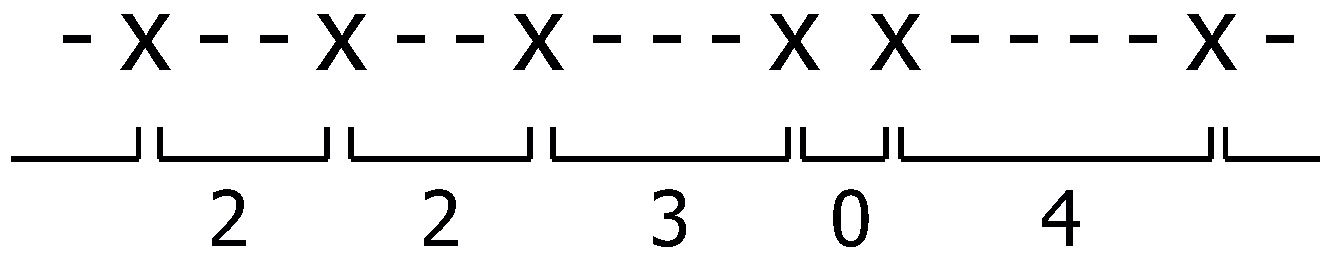

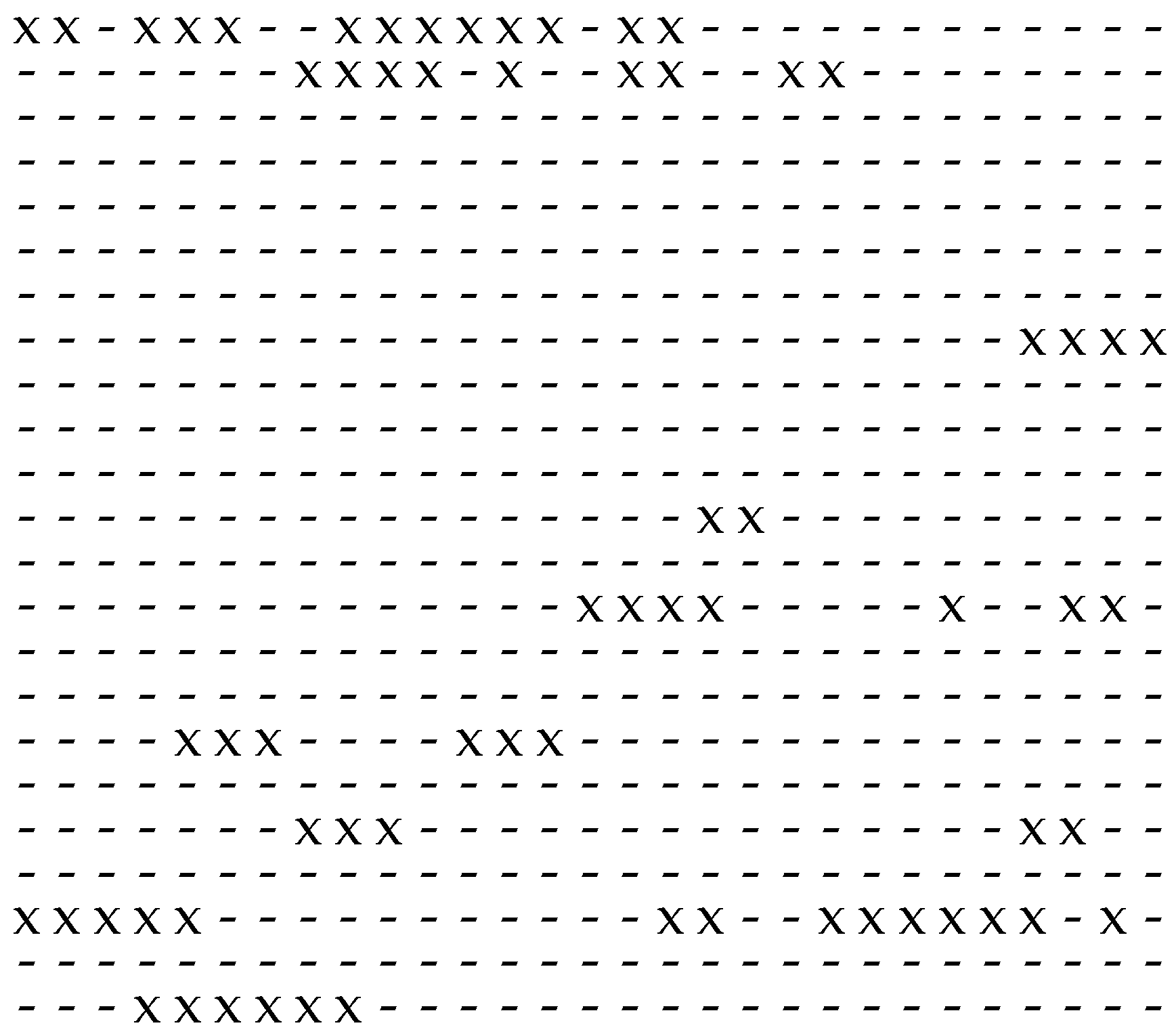

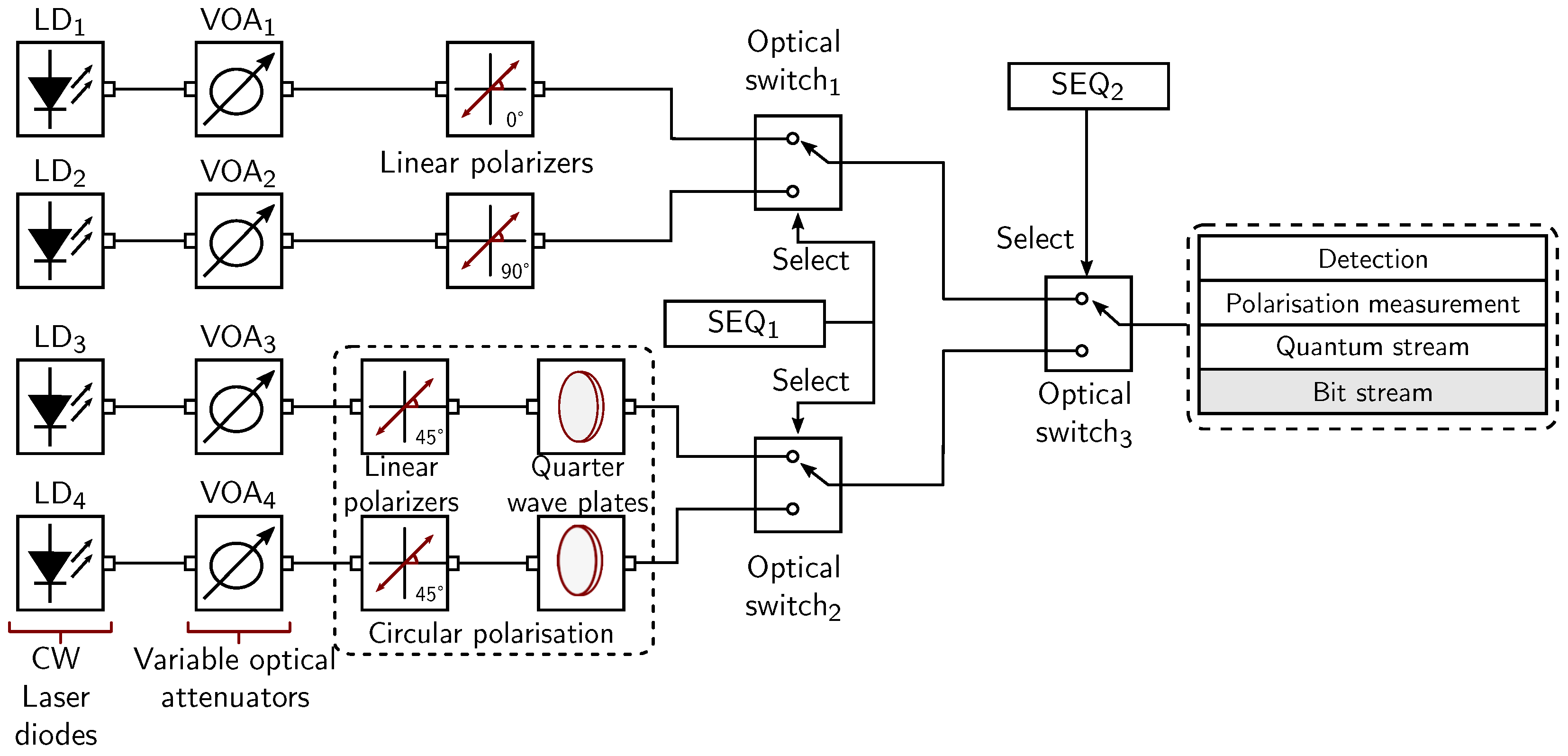
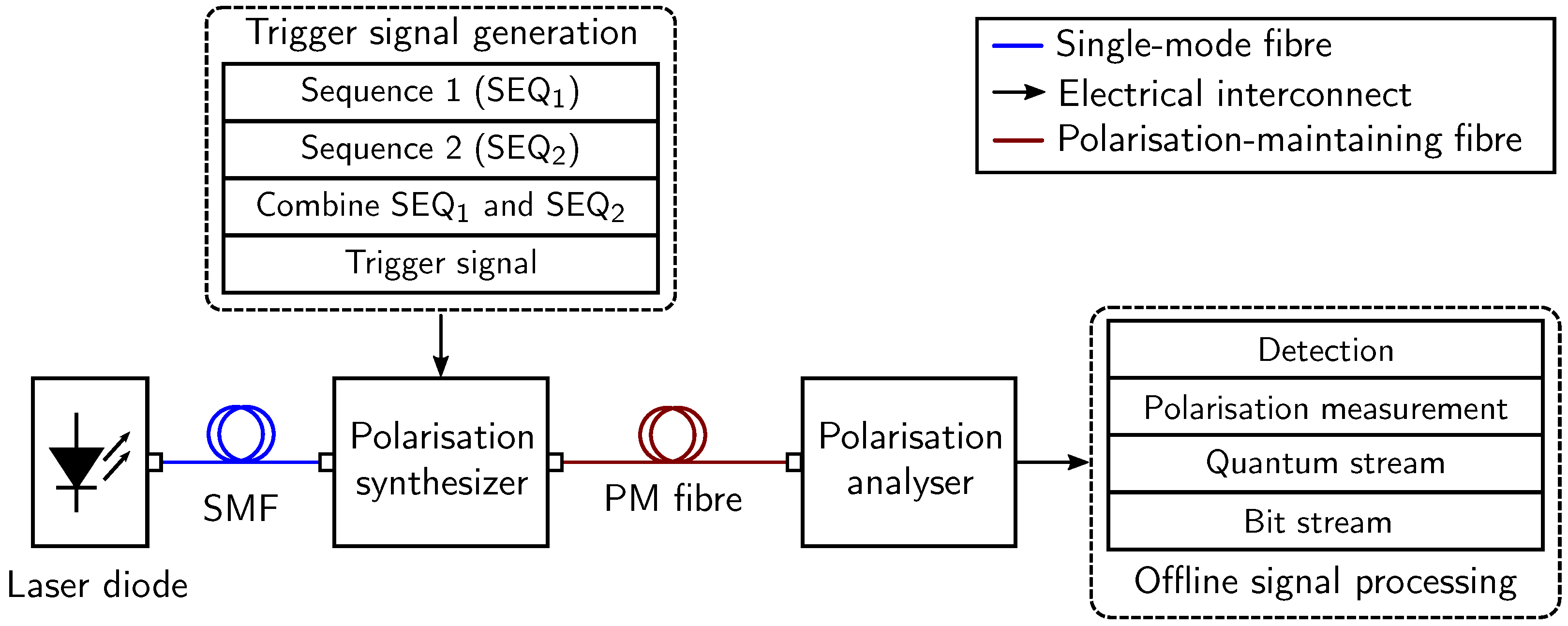

| Types of Polarisation | SEQ1 Select | SEQ2 Select |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | 0 | 0 |
| Vertical | 1 | 0 |
| Right circular | 1 | 1 |
| Left circular | 0 | 1 |
| Cryptographic Hash Algorithms | Length of Digest (in Bits) |
|---|---|
| MD5 | 128 |
| SHA-256 | 256 |
| SHA-512 | 512 |
| m-Sequence | Sequence (ITM) | Gold Sequence | Optical Sequence | Non-m-Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1218 | 0.1846 | 0.1408 | 0.1689 | 0.1717 |
| Primitive Polynomial p(x) | Burstiness Level B |
|---|---|
| 0.1641 | |
| 0.1777 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lange, C.; Ahrens, A.; Singh, J.; Grote, O. Analysing All-Optical Random Bit Sequences Using Gap-Based Approaches. Sensors 2024, 24, 4474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144474
Lange C, Ahrens A, Singh J, Grote O. Analysing All-Optical Random Bit Sequences Using Gap-Based Approaches. Sensors. 2024; 24(14):4474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144474
Chicago/Turabian StyleLange, Christoph, Andreas Ahrens, Jasmeet Singh, and Olaf Grote. 2024. "Analysing All-Optical Random Bit Sequences Using Gap-Based Approaches" Sensors 24, no. 14: 4474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144474
APA StyleLange, C., Ahrens, A., Singh, J., & Grote, O. (2024). Analysing All-Optical Random Bit Sequences Using Gap-Based Approaches. Sensors, 24(14), 4474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24144474







