Detecting of Barely Visible Impact Damage on Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Using Diffusion Ultrasonic Improved by Time-Frequency Domain Disturbance Sensitive Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
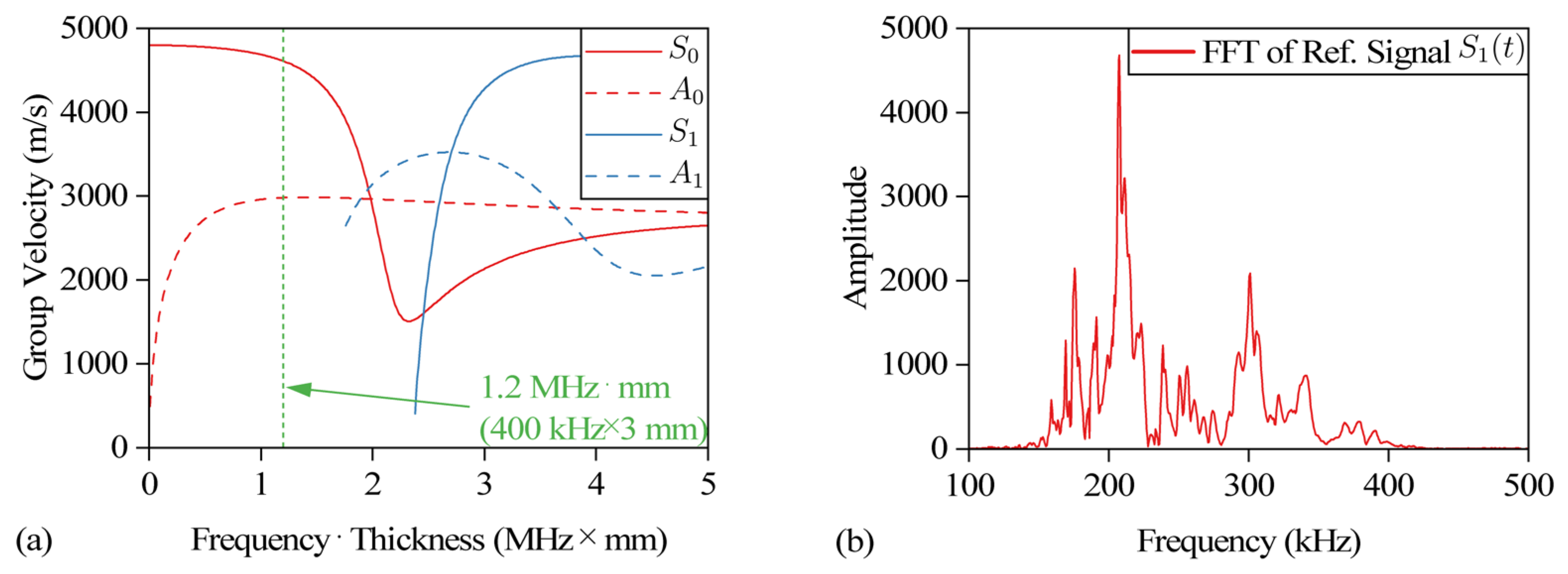
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
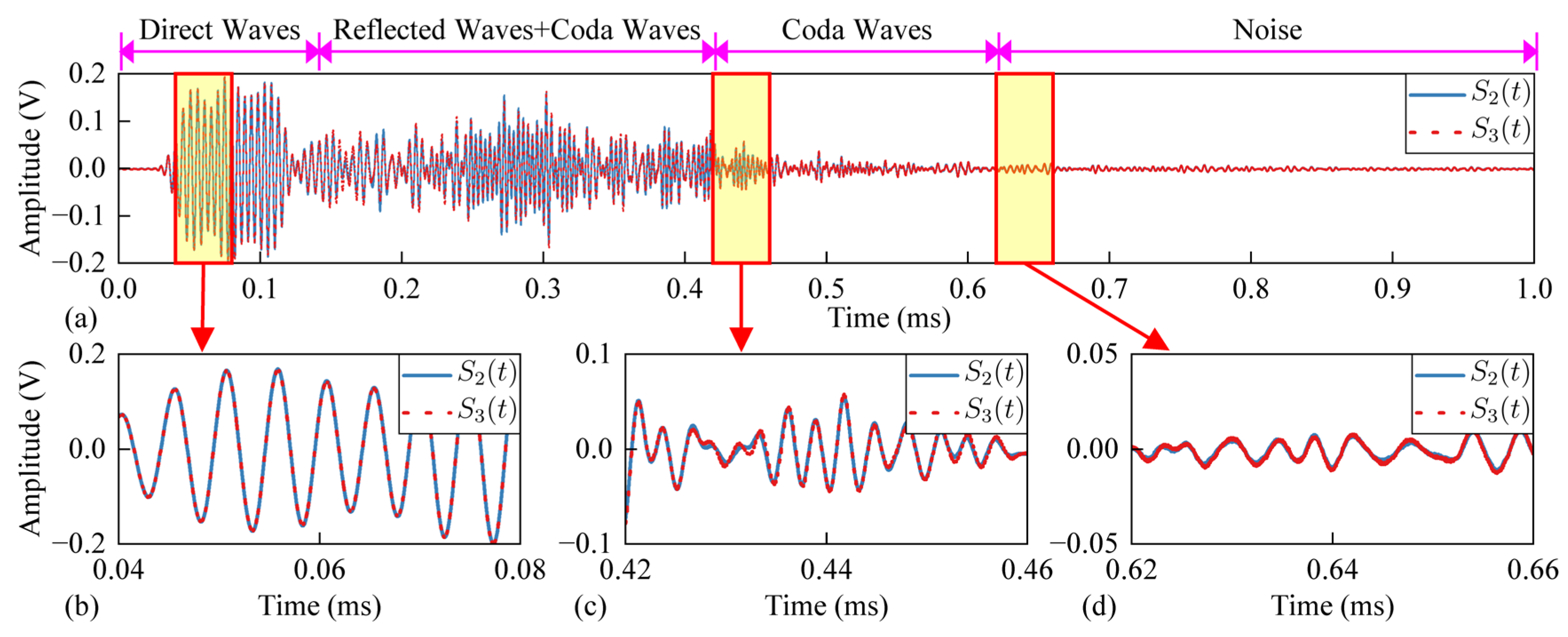
3.1. Time Domain Decorrelation
3.2. Frequency Domain Decorrelation
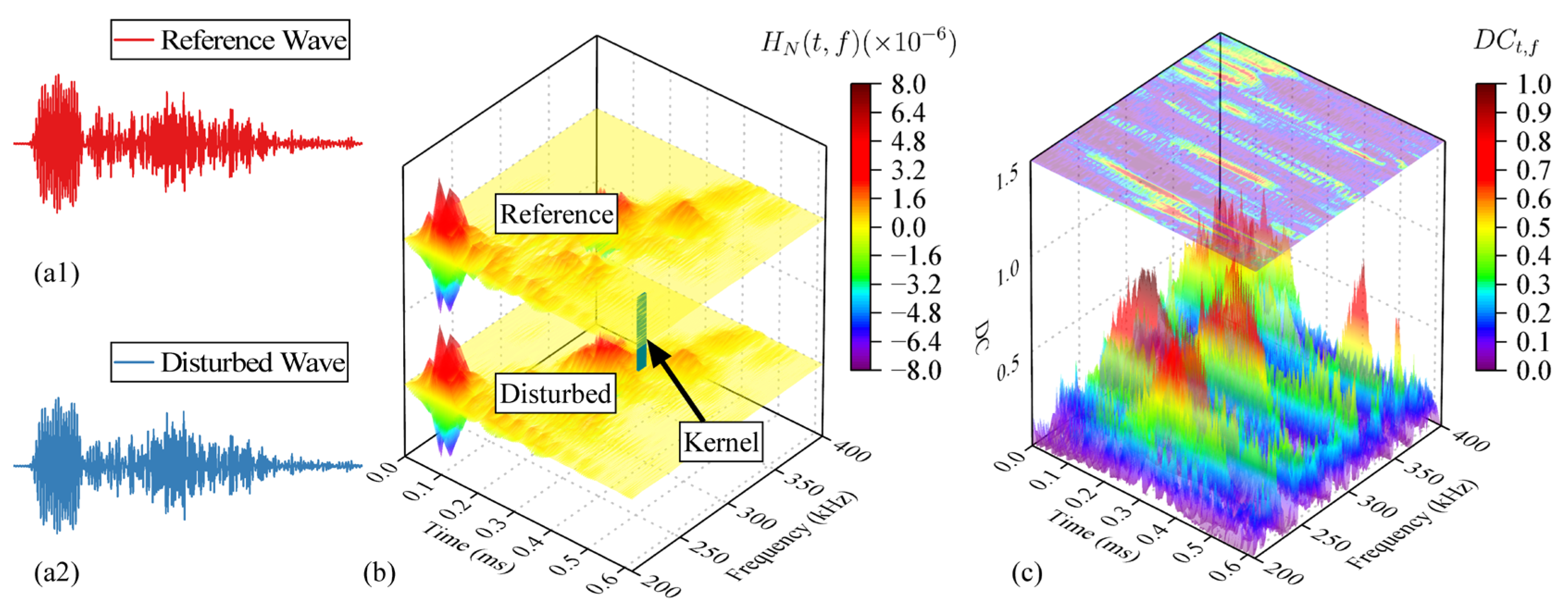
3.3. Time-Frequency Domain Decorrelation
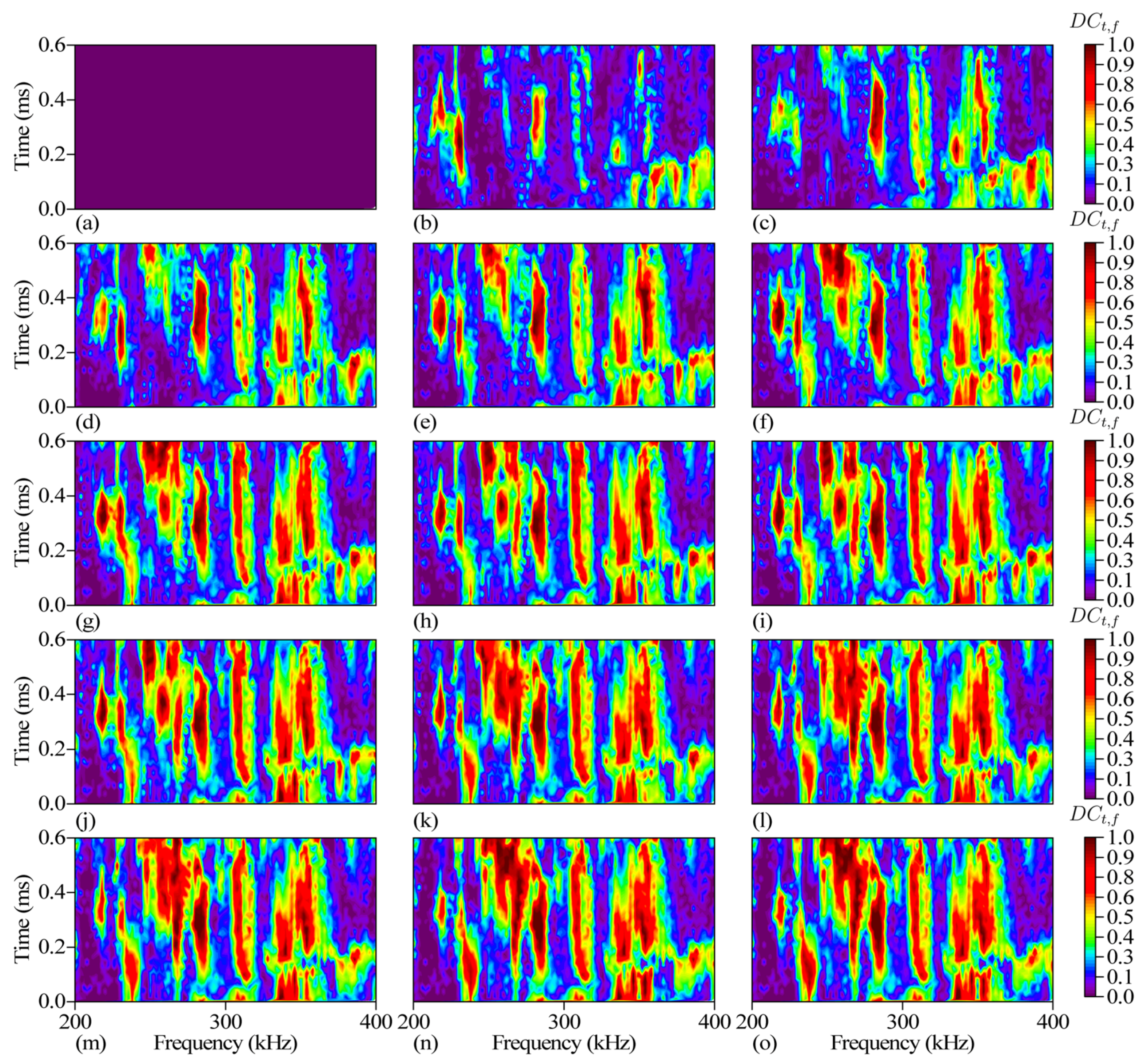
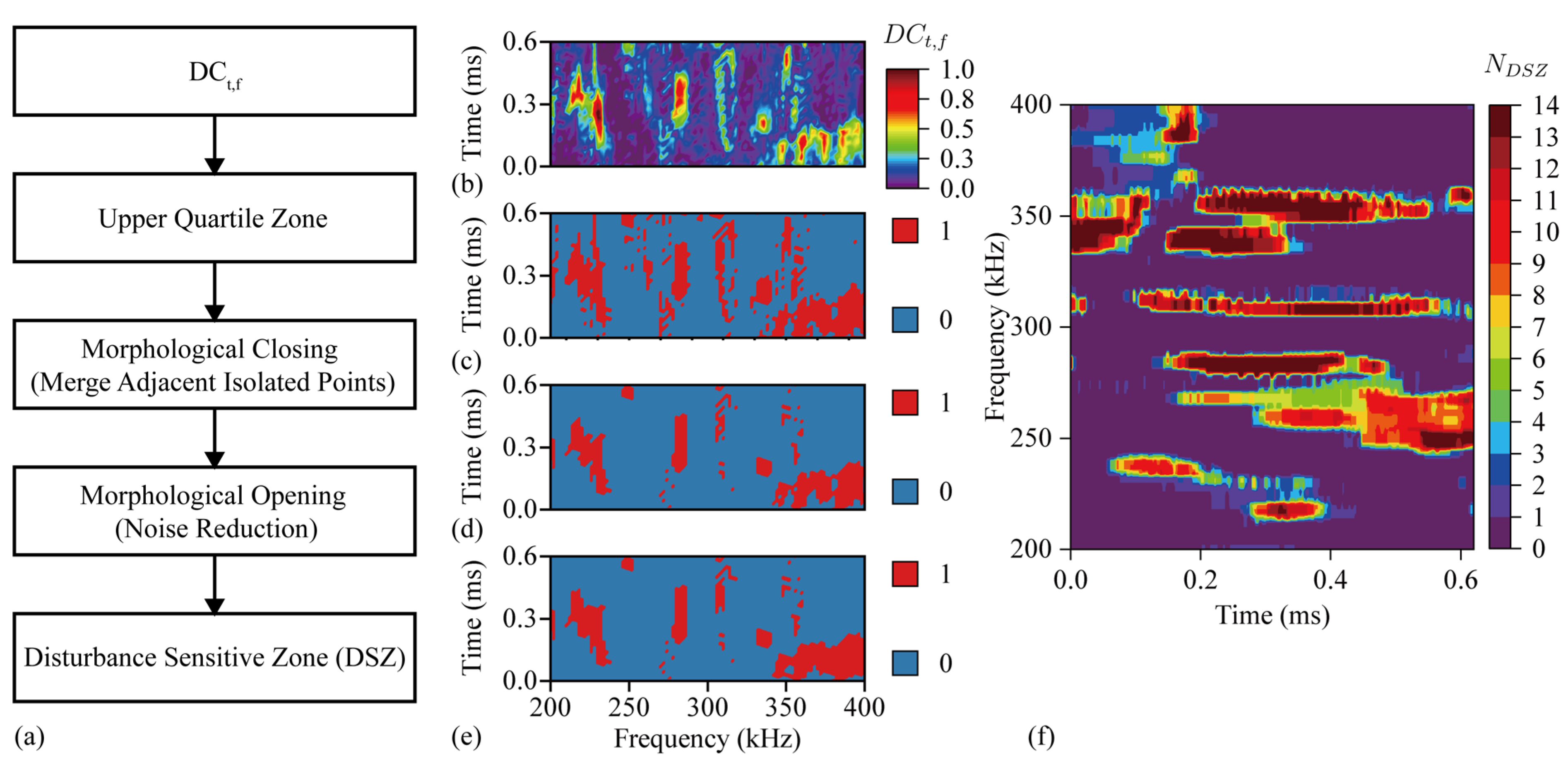
3.4. Disturbance Sensitive Zone
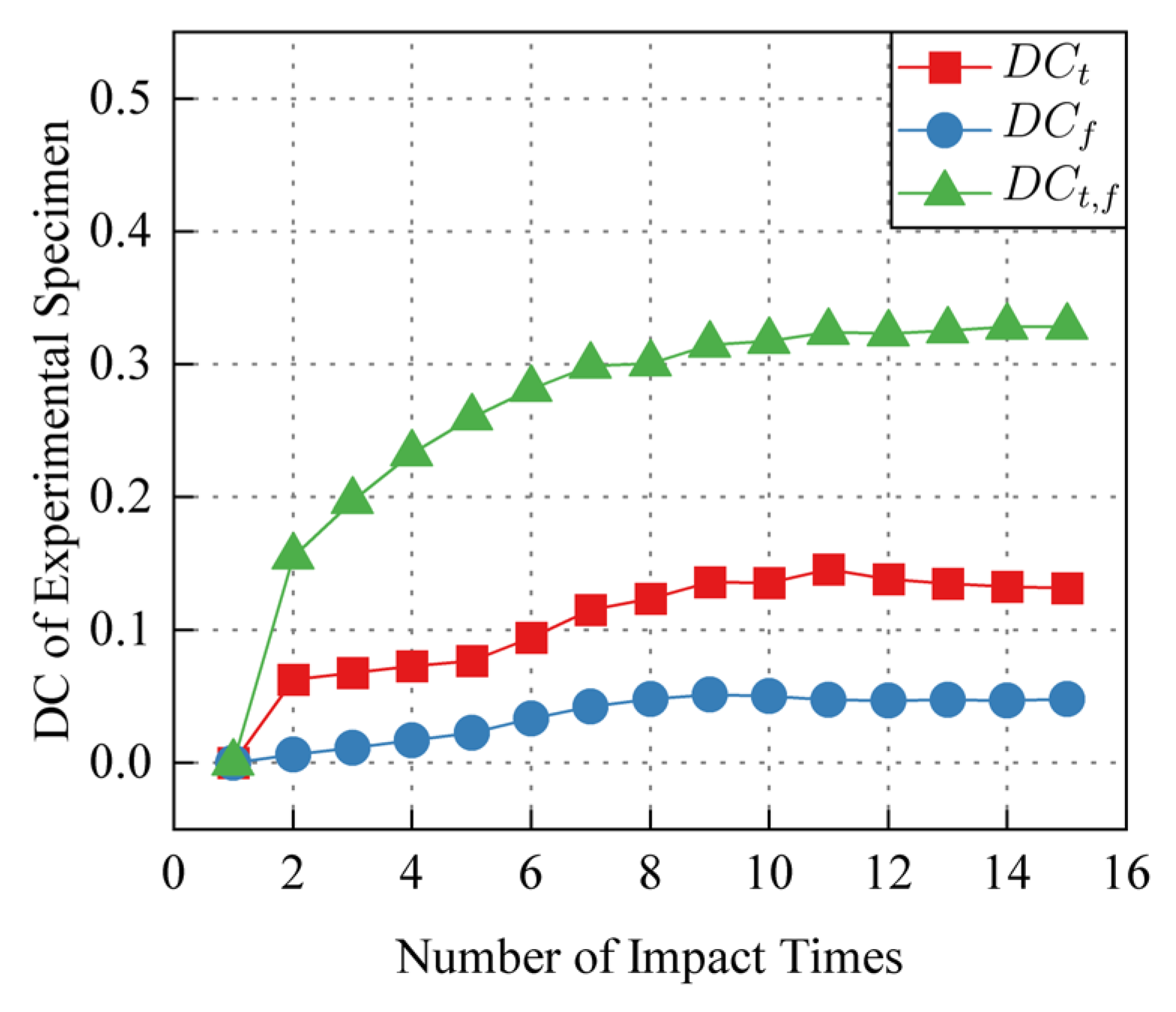
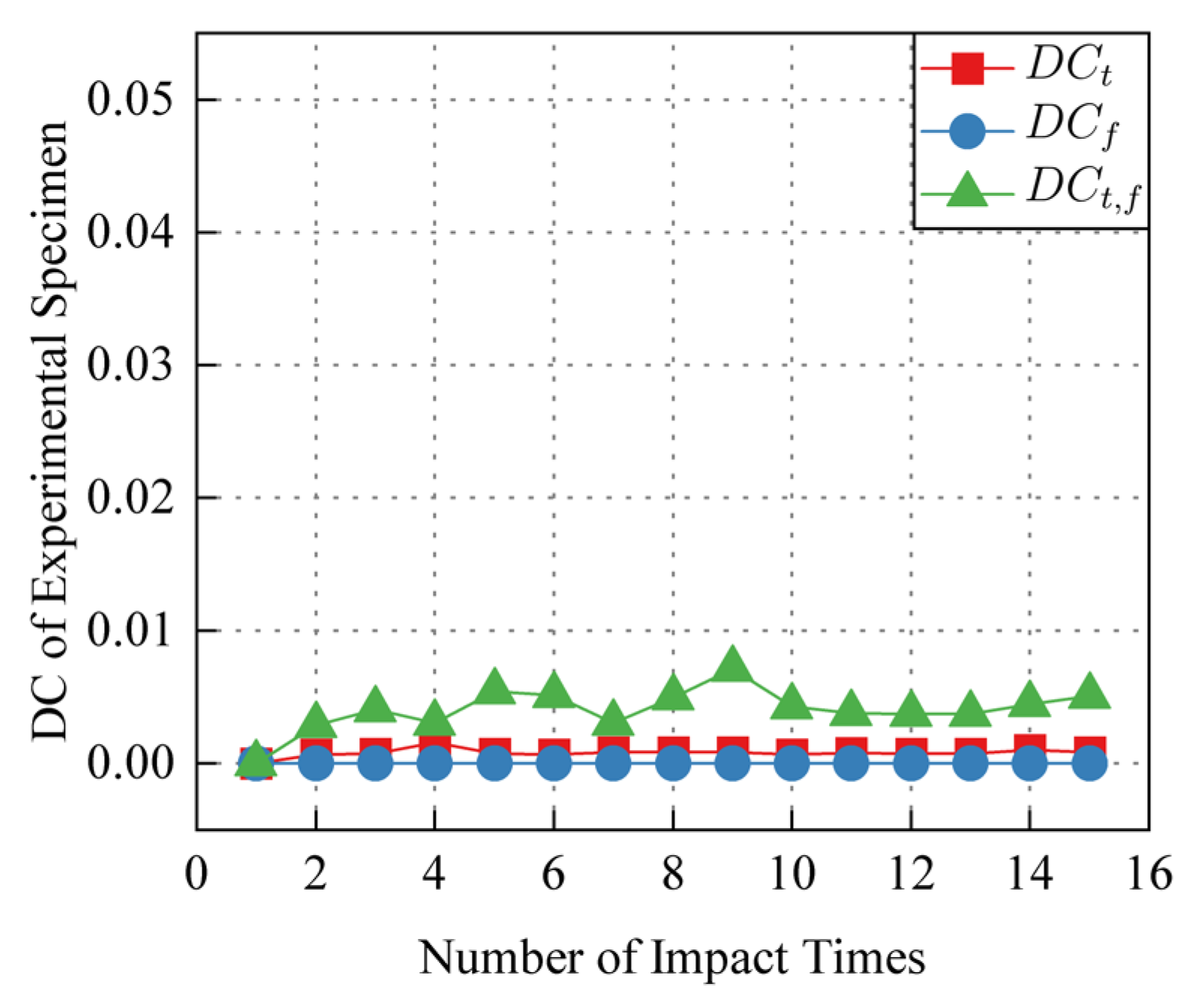
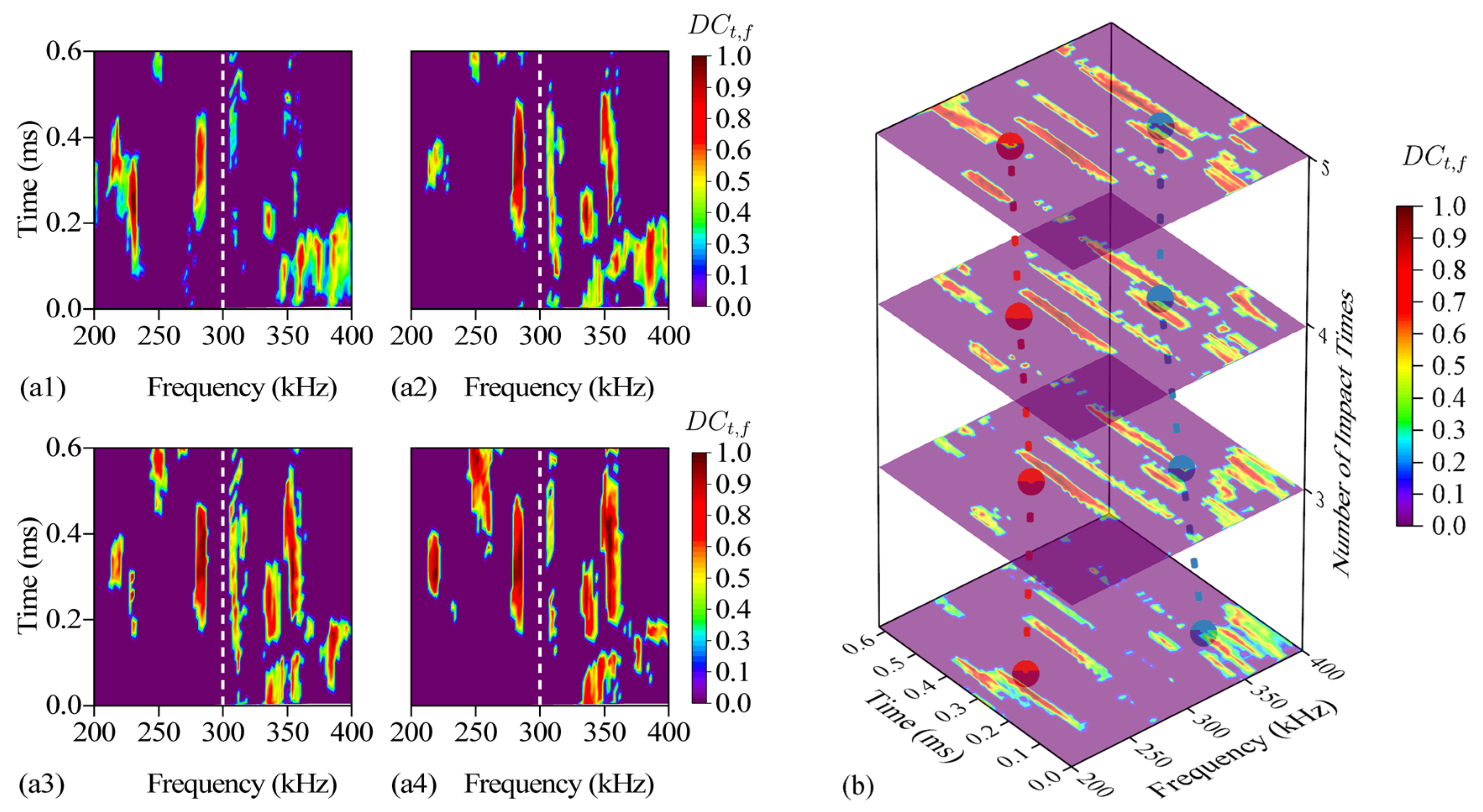
3.5. DC Improving by Prior DSZ
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spytek, J.; Pieczonka, L.; Stepinski, T.; Ambrozinski, L. Mean Local Frequency-Wavenumber Estimation through Synthetic Time-Reversal of Diffuse Lamb Waves. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 156, 107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtczak, E.; Rucka, M.; Skarżyński, Ł. Monitoring the Fracture Process of Concrete during Splitting Using Integrated Ultrasonic Coda Wave Interferometry, Digital Image Correlation and X-ray Micro-Computed Tomography. NDT E Int. 2022, 126, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomarède, P.; Chehami, L.; Declercq, N.F.; Meraghni, F.; Dong, J.; Locquet, A.; Citrin, D.S. Application of Ultrasonic Coda Wave Interferometry for Micro-Cracks Monitoring in Woven Fabric Composites. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2019, 38, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, L.; Hua, J.; Lin, J.; Mal, A. Application of Lamb Wave and Its Coda Waves to Disbond Detection in an Aeronautical Honeycomb Composite Sandwich. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 146, 107063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalvier, A.; Cetrangolo, G.; Martinho, L.; Kubrusly, A.; Blasina, F.; Perez, N. Monitoring of Compressive Stress Changes in Concrete Pillars Using Cross Correlation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Glasgow, UK, 16–19 October 2019; IEEE: Glasgow, UK, 2019; pp. 2465–2468. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Z. Implementation of Coda Wave Interferometry Using Taylor Series Expansion. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2015, 34, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, X.; Yuan, H.; Tang, W.; Guan, X. An Ultrasonic Coda Wave Method for Stress Loss Prediction in Pre-Stressed Strongly Heterogeneous Multi-Layer Structures. NDT E Int. 2023, 138, 102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederleithinger, E.; Wang, X.; Herbrand, M.; Müller, M. Processing Ultrasonic Data by Coda Wave Interferometry to Monitor Load Tests of Concrete Beams. Sensors 2018, 18, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hei, C.; Luo, M.; Gong, P.; Song, G. Quantitative Evaluation of Bolt Connection Using a Single Piezoceramic Transducer and Ultrasonic Coda Wave Energy with the Consideration of the Piezoceramic Aging Effect. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 027001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.L.; Chiu, W.K.; Rajic, N. Integrity Assessment of Composite Repair Patch Using Propagating Lamb Waves. Compos. Struct. 2002, 58, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.H.; Duczek, S.; Gabbert, U. Damage Localization in Plates Using Mode Conversion Characteristics of Ultrasonic Guided Waves. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2013, 33, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, C.; Snieder, R. Time-Lapse Traveltime Change of Singly Scattered Acoustic Waves. Geophys. J. Int. 2006, 165, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanu, C.; Snieder, R. Time-lapse Imaging of a Localized Weak Change with Multiply Scattered Waves Using Numerical-based Sensitivity Kernel. JGR Solid Earth 2015, 120, 5595–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larose, E.; Obermann, A.; Digulescu, A.; Planès, T.; Chaix, J.-F.; Mazerolle, F.; Moreau, G. Locating and Characterizing a Crack in Concrete with Diffuse Ultrasound: A Four-Point Bending Test. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Larose, E.; Moreau, L.; d’Ozouville, G. Three-Dimensional in-Situ Imaging of Cracks in Concrete Using Diffuse Ultrasound. Struct. Health Monit. 2018, 17, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrate, S. Impact on Laminated Composite Materials. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1991, 44, 155–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yu, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; Tu, D. A Loading Assisted Diffuse Wave Inspection of Delamination in a Unidirectional Composite. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 177, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, D.; Pascoe, J.-A.; Alderliesten, R. Investigating Apparent Plateau Phases in Fatigue after Impact Damage Growth in CFRP with Ultrasound Scan and Acoustic Emissions. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 177, 107957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrieh, M. Multiaxial Fatigue Behaviour of Unidirectional Plies Based on Uniaxial Fatigue Experiments—II. Experimental Evaluation. Int. J. Fatigue 1997, 19, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Ji, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yao, W. Characterization of Fatigue Damages in Composite Laminates Using Lamb Wave Velocity and Prediction of Residual Life. Compos. Struct. 2017, 166, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhuo, L.; Hao, W.; Xie, W. Characterization of Impact Fatigue Damage in CFRP Composites Using Nonlinear Acoustic Resonance Method. Compos. Struct. 2020, 253, 112804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yuan, F. Group Velocity and Characteristic Wave Curves of Lamb Waves in Composites: Modeling and Experiments. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1370–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
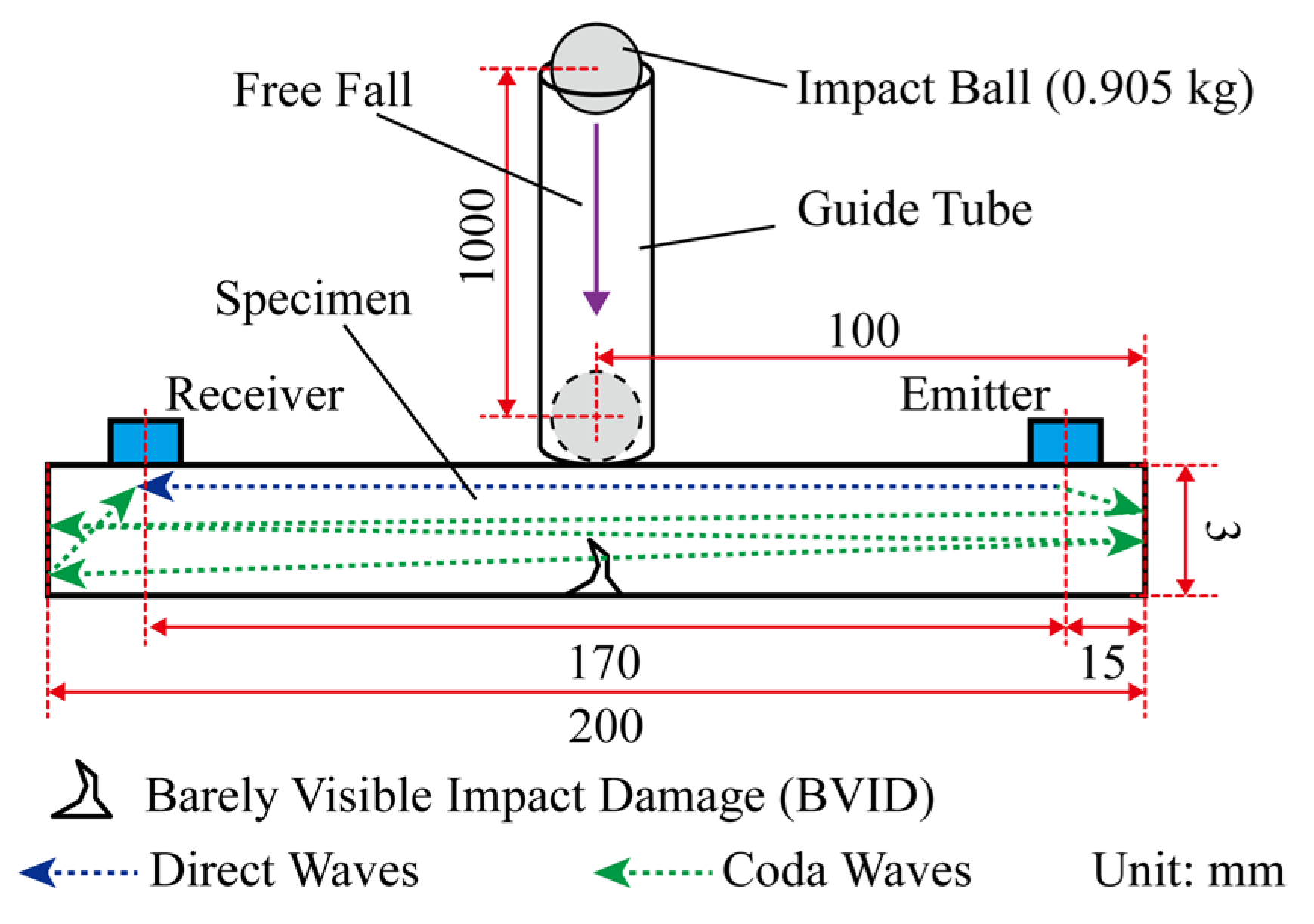

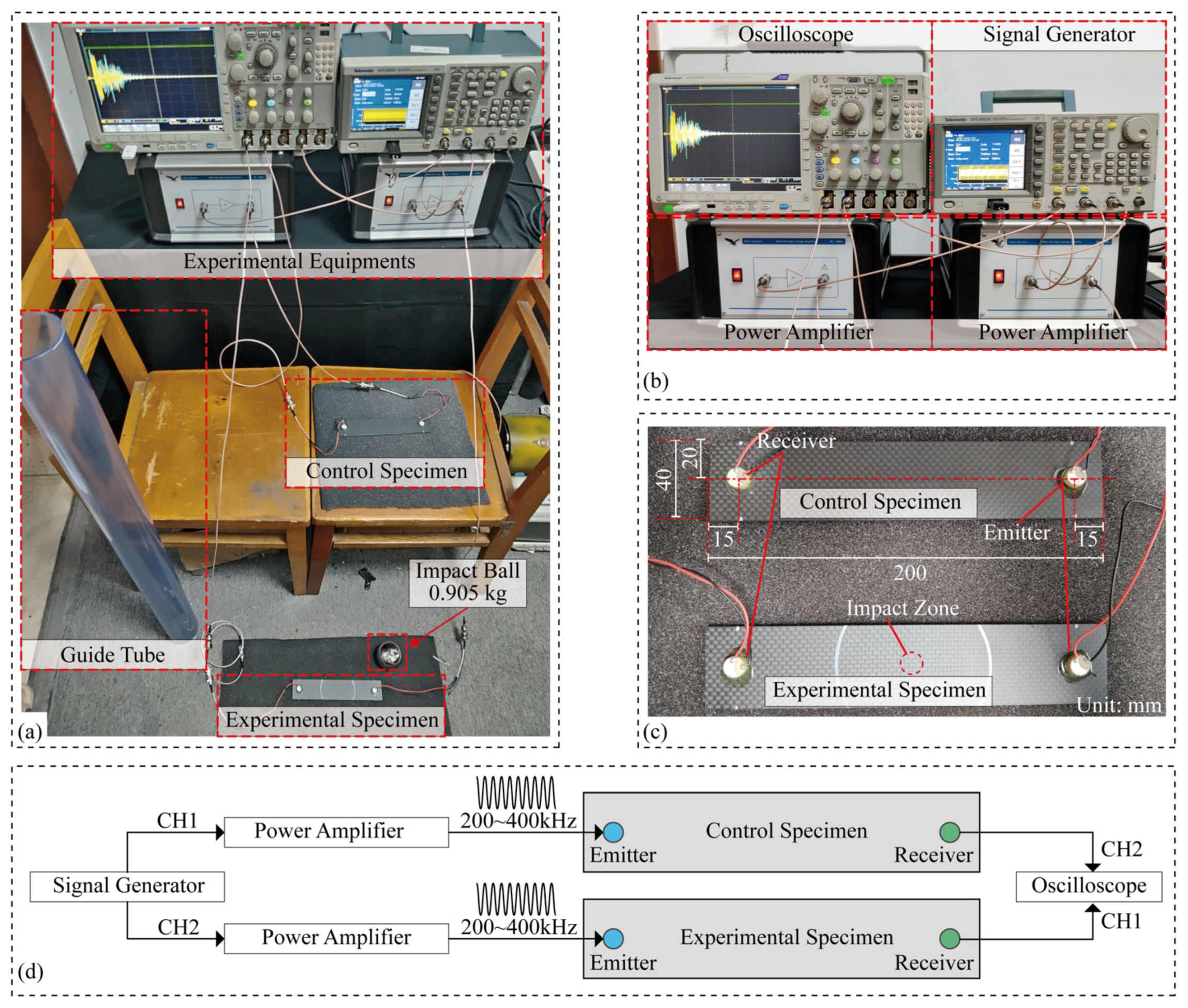



| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Model | T300 |
| Number of fiber filaments | 3 K |
| Filament Diameter | 7 um |
| Density | 1.76 g/cm3 |
| Size | 200 × 40 × 3 mm |
| Number of Impact | DCt | DCf | DCt,f | DCt,f|DSZ2-15 | Increase Rate IR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 9.88314 × 10−4 | 1.31597 × 10−6 | 0.00436 | 0.00469 | 7.5688% |
| 18 | 8.40645 × 10−4 | 2.88991 × 10−6 | 0.00548 | 0.00609 | 11.1314% |
| 19 | 8.26131 × 10−4 | 4.10172 × 10−6 | 0.00606 | 0.00668 | 10.2310% |
| 20 | 9.84513 × 10−4 | 8.63983 × 10−6 | 0.00869 | 0.00973 | 11.9678% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Li, F.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Xia, H.; Xu, Z. Detecting of Barely Visible Impact Damage on Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Using Diffusion Ultrasonic Improved by Time-Frequency Domain Disturbance Sensitive Zone. Sensors 2024, 24, 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103201
Ma Y, Li F, Wu J, Liu Z, Xia H, Xu Z. Detecting of Barely Visible Impact Damage on Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Using Diffusion Ultrasonic Improved by Time-Frequency Domain Disturbance Sensitive Zone. Sensors. 2024; 24(10):3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103201
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yuqi, Fangyuan Li, Jianbo Wu, Zhaoting Liu, Hui Xia, and Zhaoyuan Xu. 2024. "Detecting of Barely Visible Impact Damage on Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Using Diffusion Ultrasonic Improved by Time-Frequency Domain Disturbance Sensitive Zone" Sensors 24, no. 10: 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103201
APA StyleMa, Y., Li, F., Wu, J., Liu, Z., Xia, H., & Xu, Z. (2024). Detecting of Barely Visible Impact Damage on Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer Using Diffusion Ultrasonic Improved by Time-Frequency Domain Disturbance Sensitive Zone. Sensors, 24(10), 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103201





