Load Prediction in Double-Channel Residual Self-Attention Temporal Convolutional Network with Weight Adaptive Updating in Cloud Computing
Abstract
1. Introduction
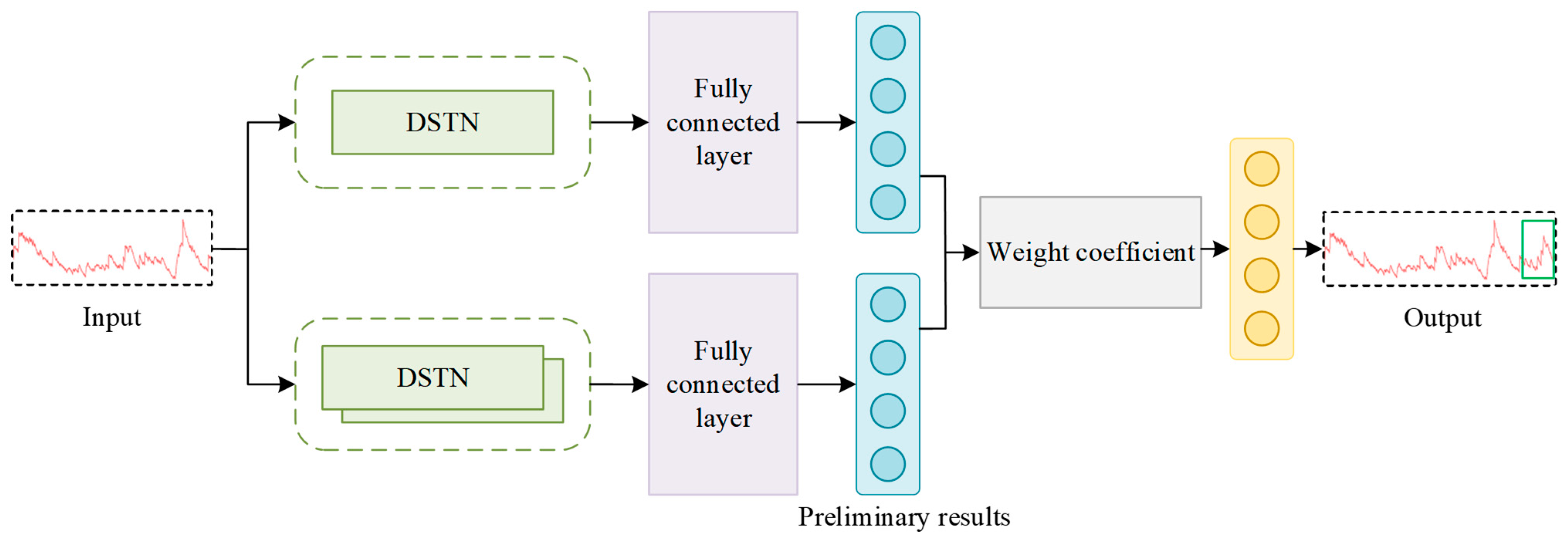
2. DSTNW Network
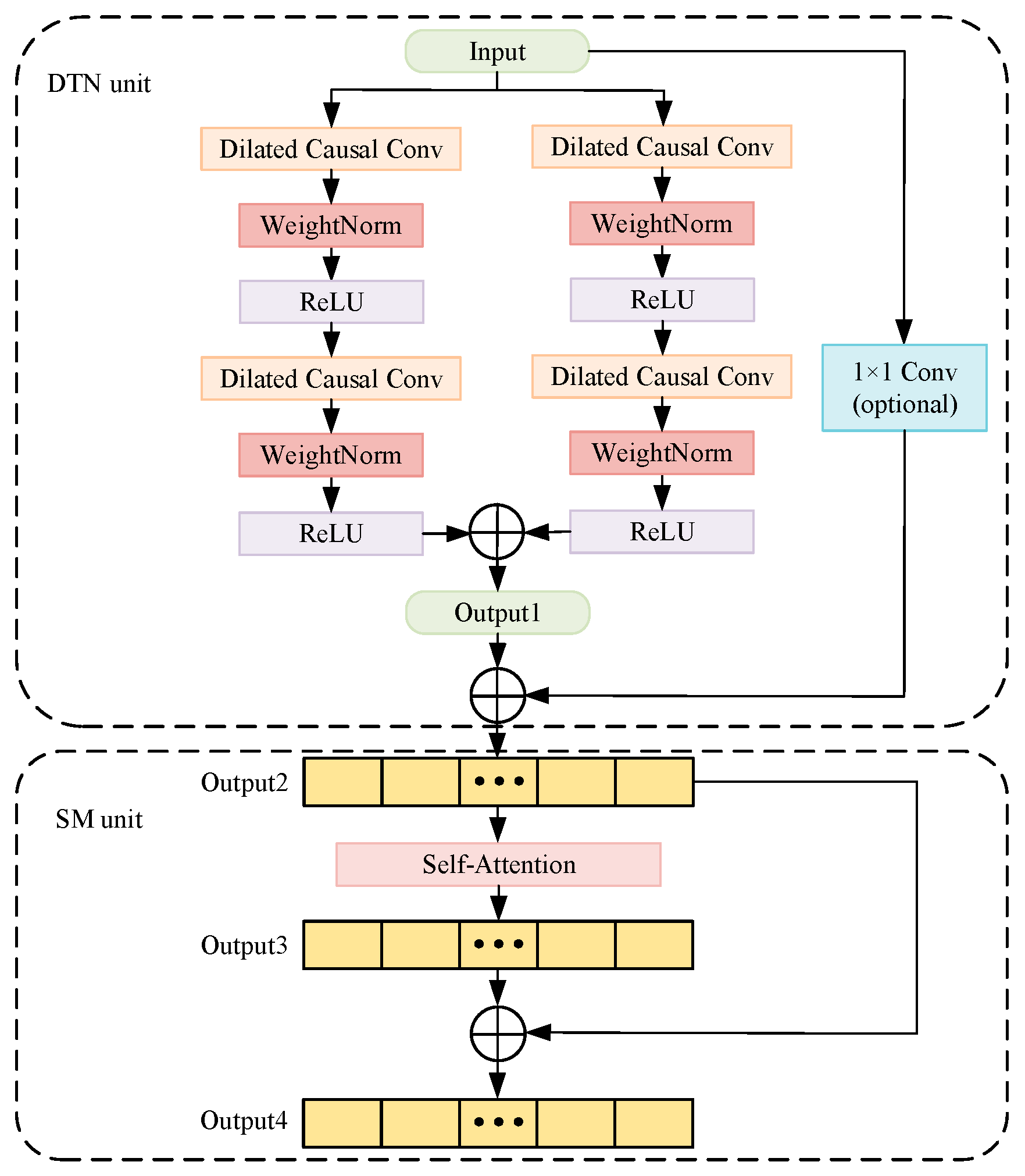
2.1. DSTN
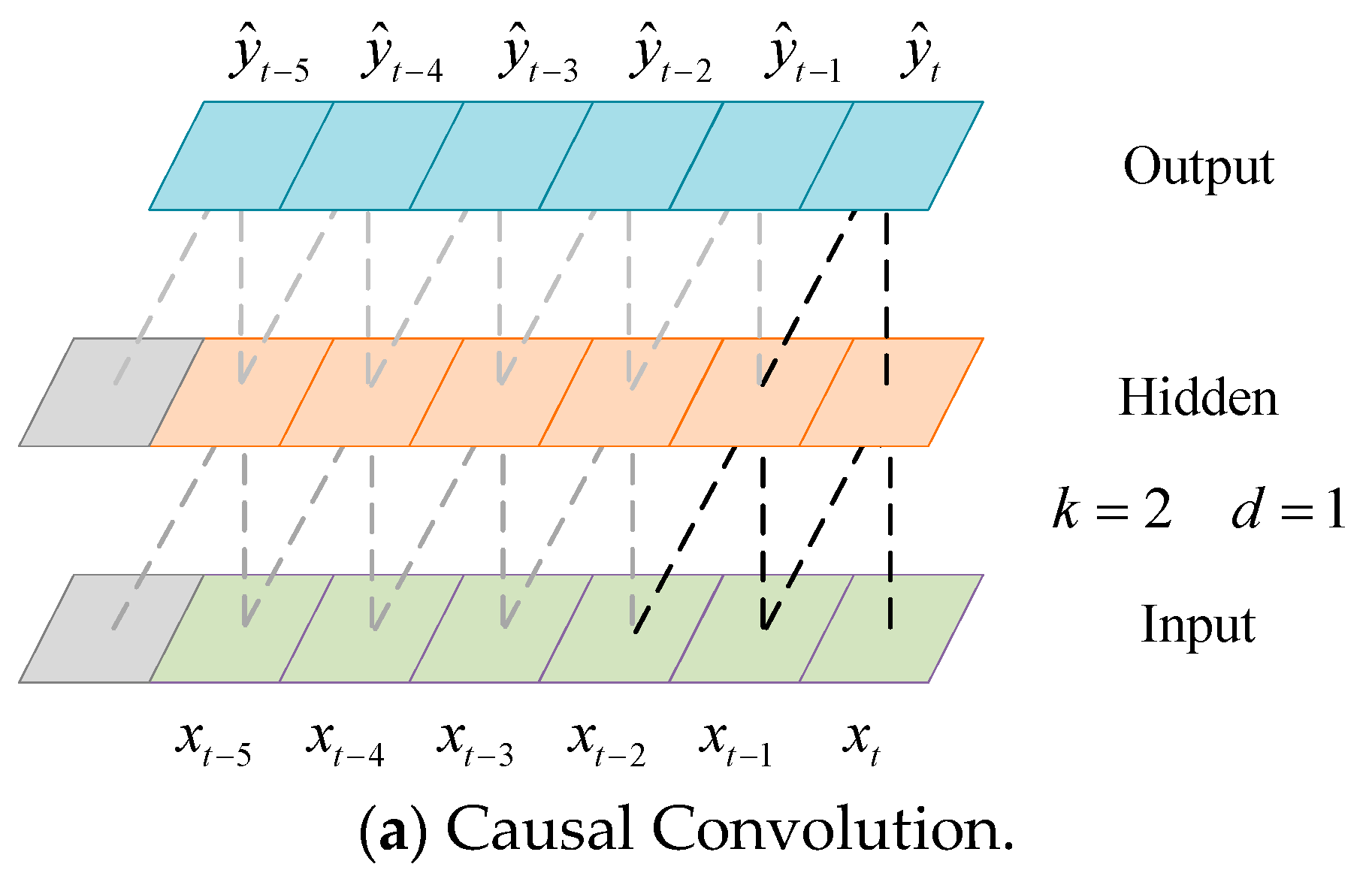
2.1.1. DTN Unit
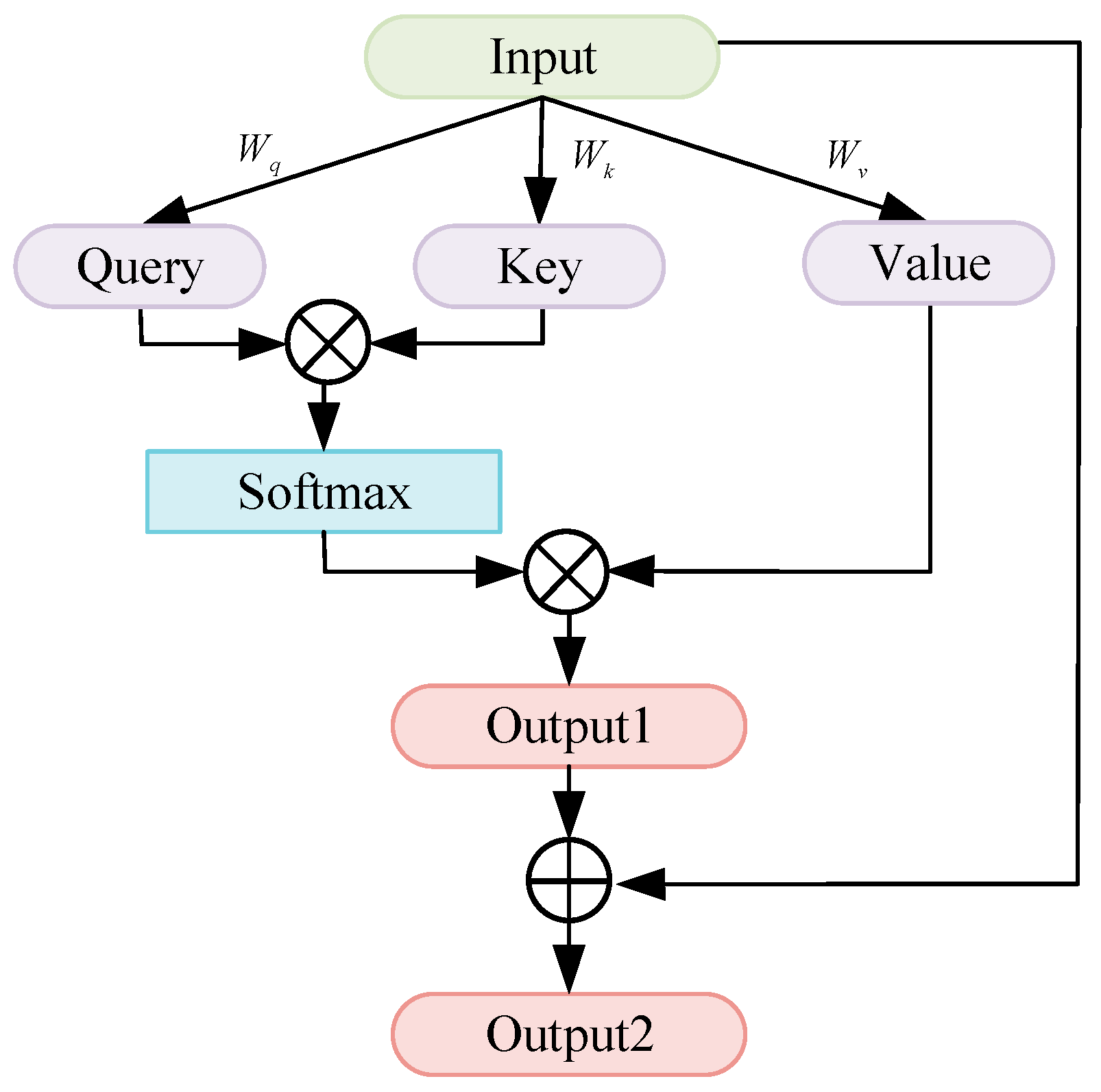
2.1.2. SM Unit
2.2. Adaptive Weight Update Strategy
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Datasets and Implements
| Algorithm 1 Training process |
| Input: Epoch, number of trainings iterations. LR, learning rate. Series, load series. Label, ground truth of the prediction. |
| 1: Normseries←(Series-Seriesmin)/(Seriesmax-Seriesmin) 2: Series Input←Preprocess(Normseries) 3: For i in Epoch do: 4: Prediction←Model.Forward(Series Input) 5: MSELOSS←MSE(Prediction, Label) 6: Model.Backward(MSELOSS, LR) 7: End For |
3.2. Parameter Analyses
3.2.1. Network Layer
3.2.2. Time Step
3.3. Ablation Experiment
3.4. Comparisons with Some State-of-the-Art Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi, J.; Li, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, M. Integrated deep learning method for workload and resource prediction in cloud systems. Neurocomputing 2021, 424, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Du, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Li, K. AEML: An acceleration engine for multi-GPU load-balancing in distributed heterogeneous environment. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2021, 71, 1344–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam, C.; Faramarz, S. ARIMA: Predictive consolidation of virtual machines applying ARIMA method. J. Supercomput. 2021, 77, 2172–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaval, B.; Deshpande, A. Short-term load forecasting using method of multiple linear regression. New Approaches Eng. Res. 2021, 14, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Kaur, P.; Sood, S. Energy efficient IoT-based cloud framework for early flood prediction. Nat. Hazards 2021, 109, 2053–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediger, V.; Akar, S. ARIMA forecasting of primary energy demand by fuel in Turkey. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, I.; Valenzuela, O.; Rojas, F.; Guillen, A.; Herrera, L.; Pomares, H.; Marquez, L.; Pasadas, M. Soft-computing techniques and ARMA model for time series prediction. Neurocomputing 2008, 71, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapankevych, N.; Sankar, R. Time series prediction using support vector machines: A survey. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2009, 4, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, O.; Tapak, L.; Abbasi, H.; Maryanaji, Z. Application of random forest time series, support vector regression and multivariate adaptive regression splines models in prediction of snowfall. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 134, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.; Lall, U. Climate informed monthly streamflow forecasts for the Brazilian hydropower network using a periodic ridge regression model. J. Hydrol. 2010, 380, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, W. Forecasting macroeconomic time series: LASSO-based approaches and their forecast combinations with dynamic factor models. Int. J. Forecast. 2014, 30, 996–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L. Support vector machines experts for time series forecasting. Neurocomputing 2003, 51, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Shang, Y.; Cheng, B.; Mao, Z.; Liu, C.; Niu, L.; Chen, J. A cost-aware auto-scaling approach using the workload prediction in service clouds. Inf. Syst. Front. 2014, 16, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.U.; Mostafa, R.R.; Mohammed, A.; Sihag, P.; Qadir, A. Support vector regression (SVR) and grey wolf optimization (GWO) to predict the compressive strength of GGBFS-based geopolymer concrete. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 2909–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Qin, K. A CNN-BiLSTM-AM method for stock price prediction. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 4741–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherstinsky, A. Fundamentals of recurrent neural network (RNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) network. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2020, 404, 132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Shao, H.; Ma, X.; de Silva, C.W. A stacked GRU-RNN-based approach for predicting renewable energy and electricity load for smart grid operation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 7050–7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, E.; Maswood, M.M.S.; Das, S.; Alharbi, A.G. BHyPreC: A novel Bi-LSTM based hybrid recurrent neural network model to predict the CPU workload of cloud virtual machine. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 131476–131495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; Wong, W.K.; Woo, W.C. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Conference, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, F.; Majumdar, S.; Darabi, H.; Harford, S. Multivariate LSTM-FCNs for time series classification. Neural Netw. 2019, 116, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Lv, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z. Fault analysis of wind power rolling bearing based on EMD feature extraction. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2022, 130, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, J. Multilevel wavelet decomposition network for interpretable time series analysis. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 2437–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, H.; Luo, P.; Peng, Y.; Li, Q. Ultra-short-term railway traction load prediction based on DWT-TCN-PSO_SVR combined model. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 135, 107595–107605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xia, K.; Fan, S. Oil logging reservoir recognition based on TCN and SA-BiLSTM deep learning method. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 121, 105950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Guan, Y. A cloud computing load prediction hybrid model with adaptive weight strategy. Signal Image Video Process. 2022, 17, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limouni, T.; Yaagoubi, R.; Bouziane, K.; Guissi, K.; Baali, E.H. Accurate one step and multistep forecasting of very short-term PV power using LSTM-TCN model. Renew. Energy 2023, 205, 1010–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Dou, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, R.; Xing, K. A novel hybrid LMD-ETS-TCN approach for predicting landslide displacement based on GPS time series analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Mei, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, F. Multivariate temporal convolutional network: A deep neural networks approach for multivariate time Series forecasting. Electronics 2019, 8, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Qian, S.; Zhang, J. Machine remaining life prediction based on multi-layer self-attention and temporal convolution network. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 1409–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Song, L.; Woźniak, M.; Liu, S. Self-attention negative feedback network for real-time image super-resolution. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 6179–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wu, C.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, L. Spatial-temporal injection network: Exploiting auxiliary losses for action recognition with apparent difference and self-attention. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z. Fisher: An efficient container load prediction model with deep neural network in clouds. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Melbourne, Australia, 11–13 December 2018; pp. 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; John, P.; Lu, L.; Yan, W. RVLBPNN: A workload forecasting model for smart cloud computing. Sci. Program. 2016, 2016, 5635673. [Google Scholar]



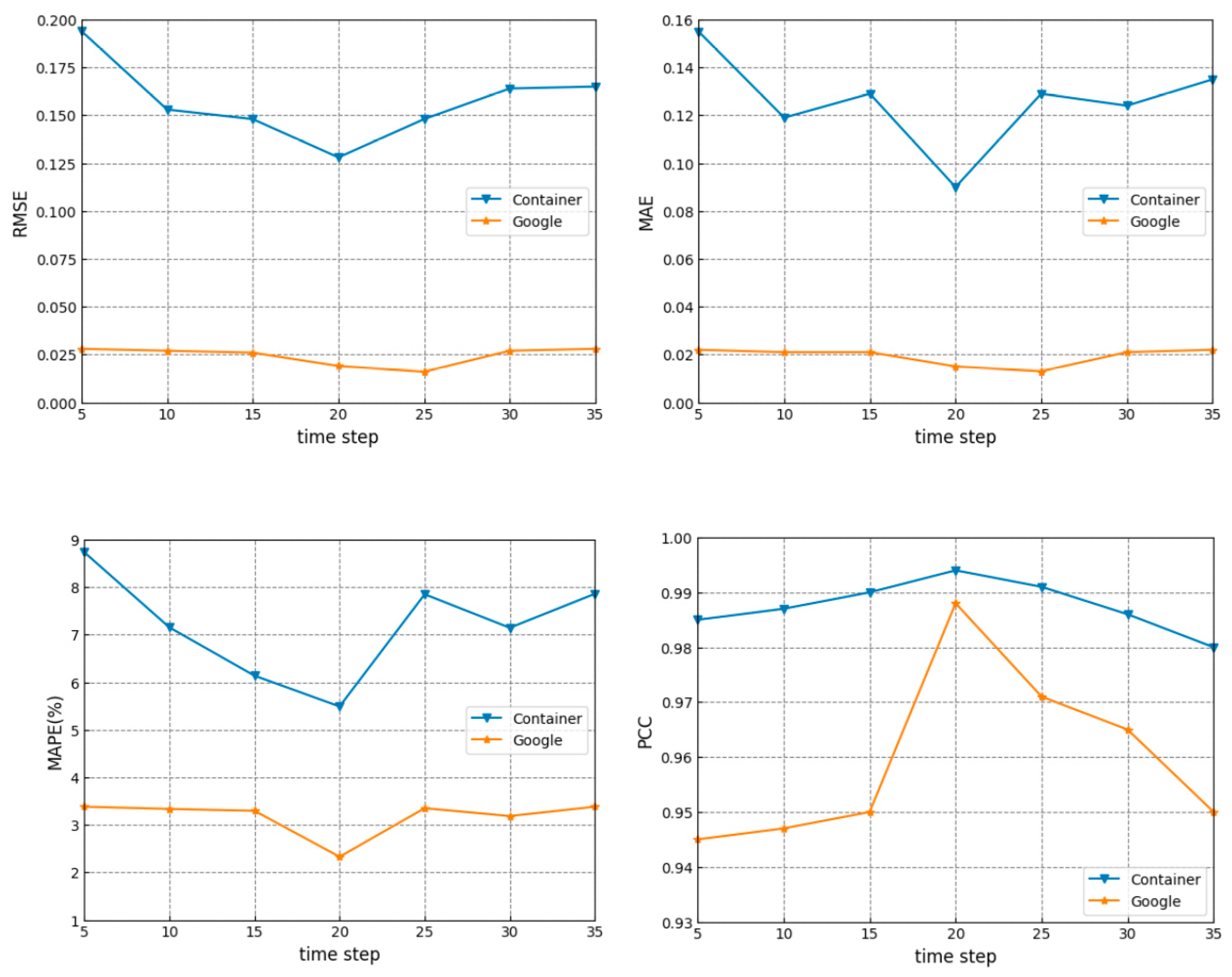

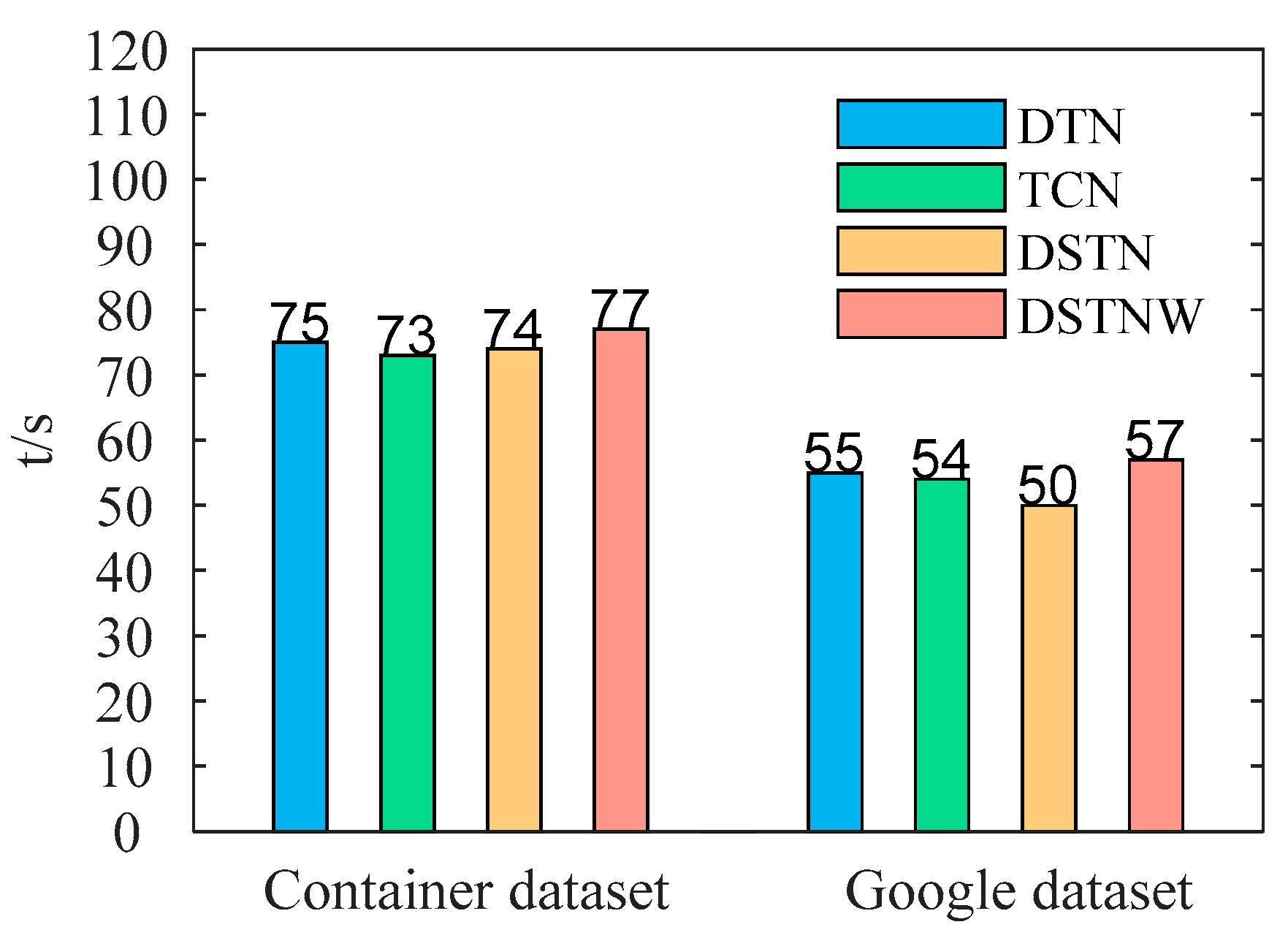
| Methods | Container [34] | Google [35] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE↓ | MAE↓ | MAPE↓ | PCC↑ | RMSE↓ | MAE↓ | MAPE↓ | PCC↑ | |
| TCN [26] | 0.164 | 0.124 | 7.146% | 0.988 | 0.027 | 0.021 | 3.186% | 0.945 |
| DTN | 0.148 | 0.129 | 6.138% | 0.987 | 0.026 | 0.021 | 3.297% | 0.950 |
| TCN-SM | 0.153 | 0.119 | 7.154% | 0.985 | 0.027 | 0.021 | 3.336% | 0.947 |
| DSTN | 0.148 | 0.129 | 7.850% | 0.990 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 2.329% | 0.971 |
| DSTNW | 0.128 | 0.090 | 5.491% | 0.994 | 0.020 | 0.013 | 2.312% | 0.988 |
| Methods | Container [34] | Google [35] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE↓ | MAE↓ | MAPE↓ | PCC↑ | RMSE↓ | MAE↓ | MAPE↓ | PCC↑ | |
| ARIMA [3] | 0.194 | 0.155 | 10.235% | 0.975 | 0.029 | 0.023 | 3.502% | 0.948 |
| LSTM [18] | 0.168 | 0.129 | 8.413% | 0.976 | 0.028 | 0.022 | 3.383% | 0.944 |
| TCN [26] | 0.164 | 0.124 | 7.146% | 0.988 | 0.027 | 0.021 | 3.186% | 0.945 |
| Ours | 0.128 | 0.090 | 5.491% | 0.994 | 0.020 | 0.013 | 2.312% | 0.988 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.; Guan, Y. Load Prediction in Double-Channel Residual Self-Attention Temporal Convolutional Network with Weight Adaptive Updating in Cloud Computing. Sensors 2024, 24, 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103181
Lin J, Guan Y. Load Prediction in Double-Channel Residual Self-Attention Temporal Convolutional Network with Weight Adaptive Updating in Cloud Computing. Sensors. 2024; 24(10):3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103181
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jiang, and Yepeng Guan. 2024. "Load Prediction in Double-Channel Residual Self-Attention Temporal Convolutional Network with Weight Adaptive Updating in Cloud Computing" Sensors 24, no. 10: 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103181
APA StyleLin, J., & Guan, Y. (2024). Load Prediction in Double-Channel Residual Self-Attention Temporal Convolutional Network with Weight Adaptive Updating in Cloud Computing. Sensors, 24(10), 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24103181





