Selection of the Minimum Number of EEG Sensors to Guarantee Biometric Identification of Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
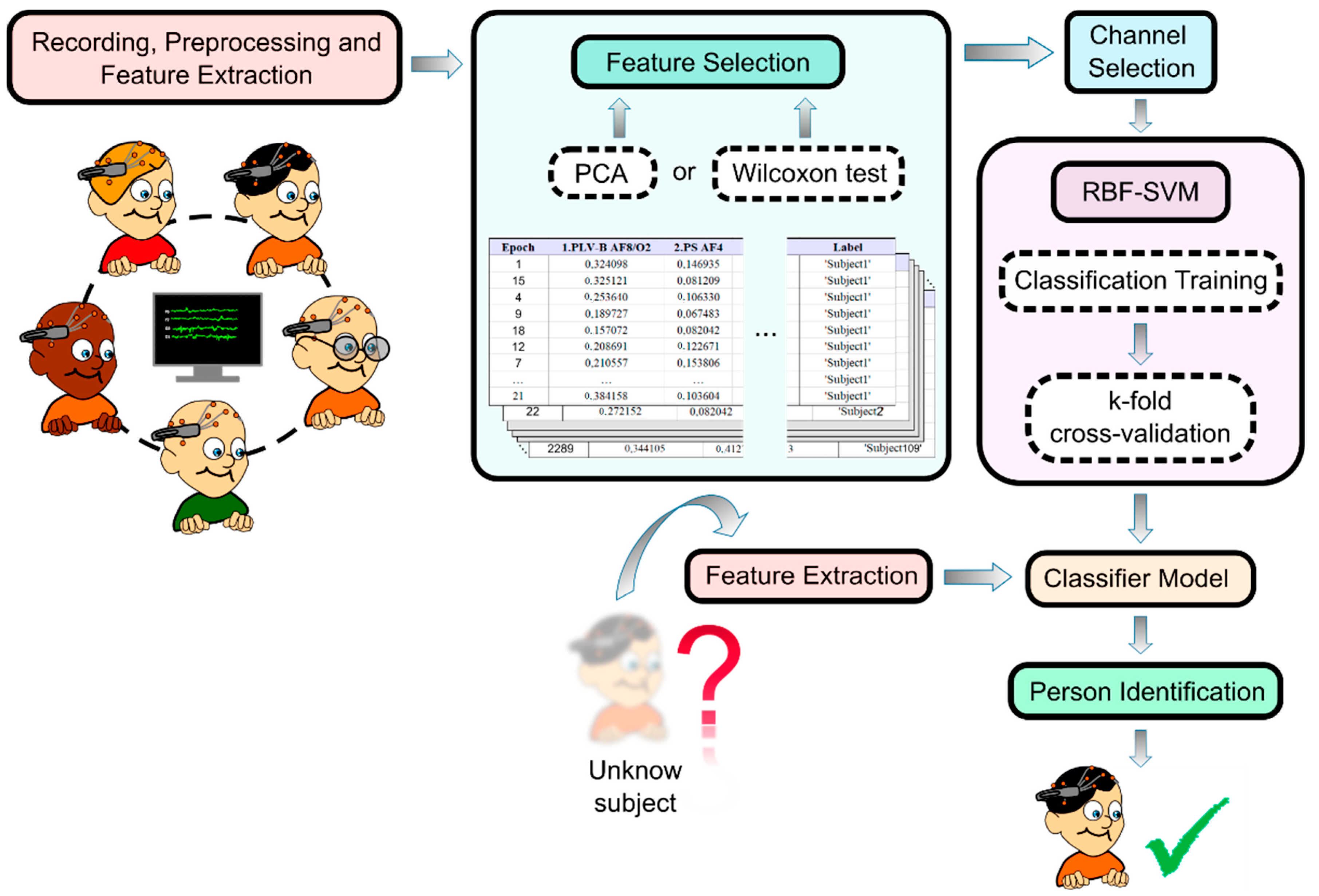
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Procedure
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Preprocessing
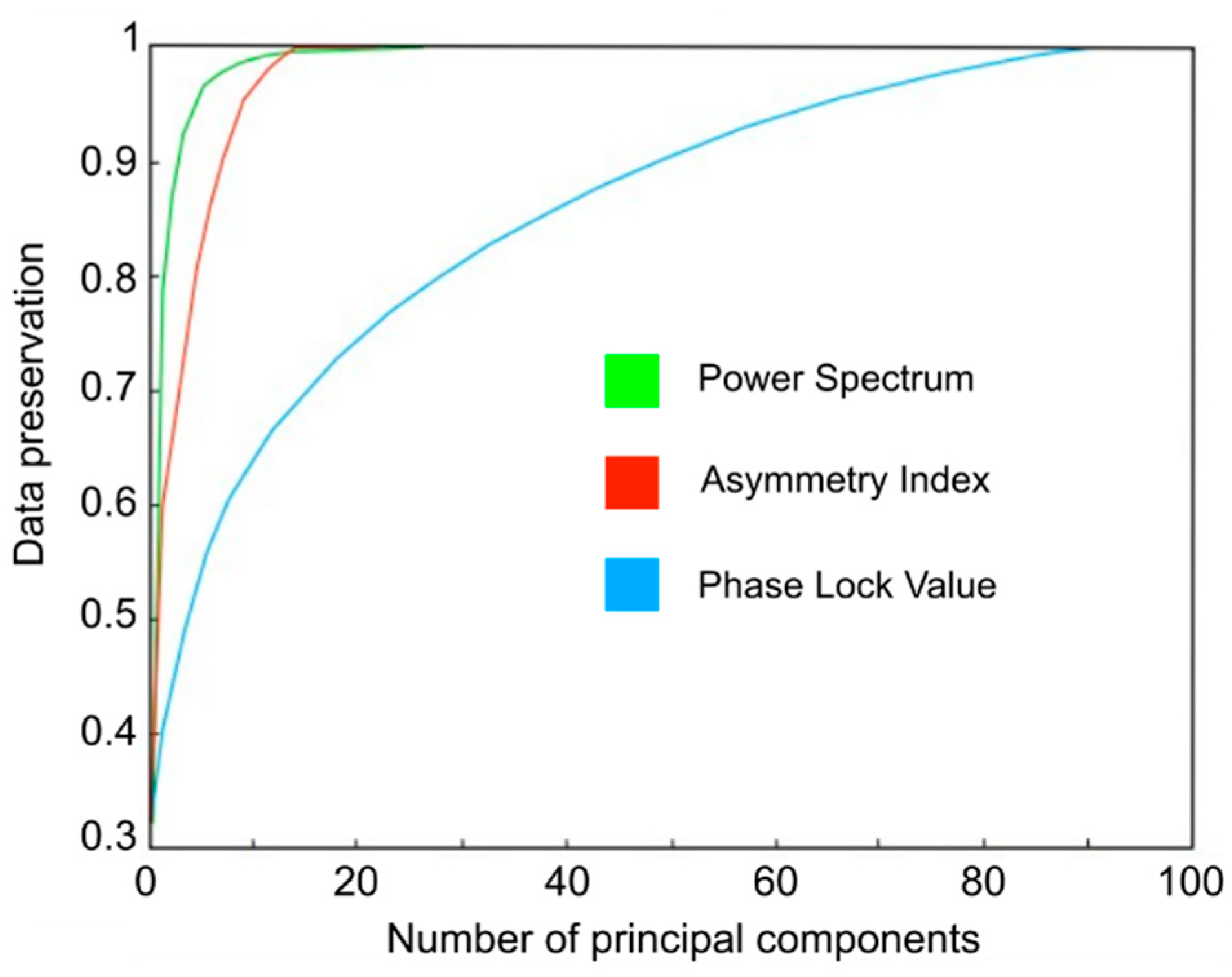
2.4. Feature Extraction
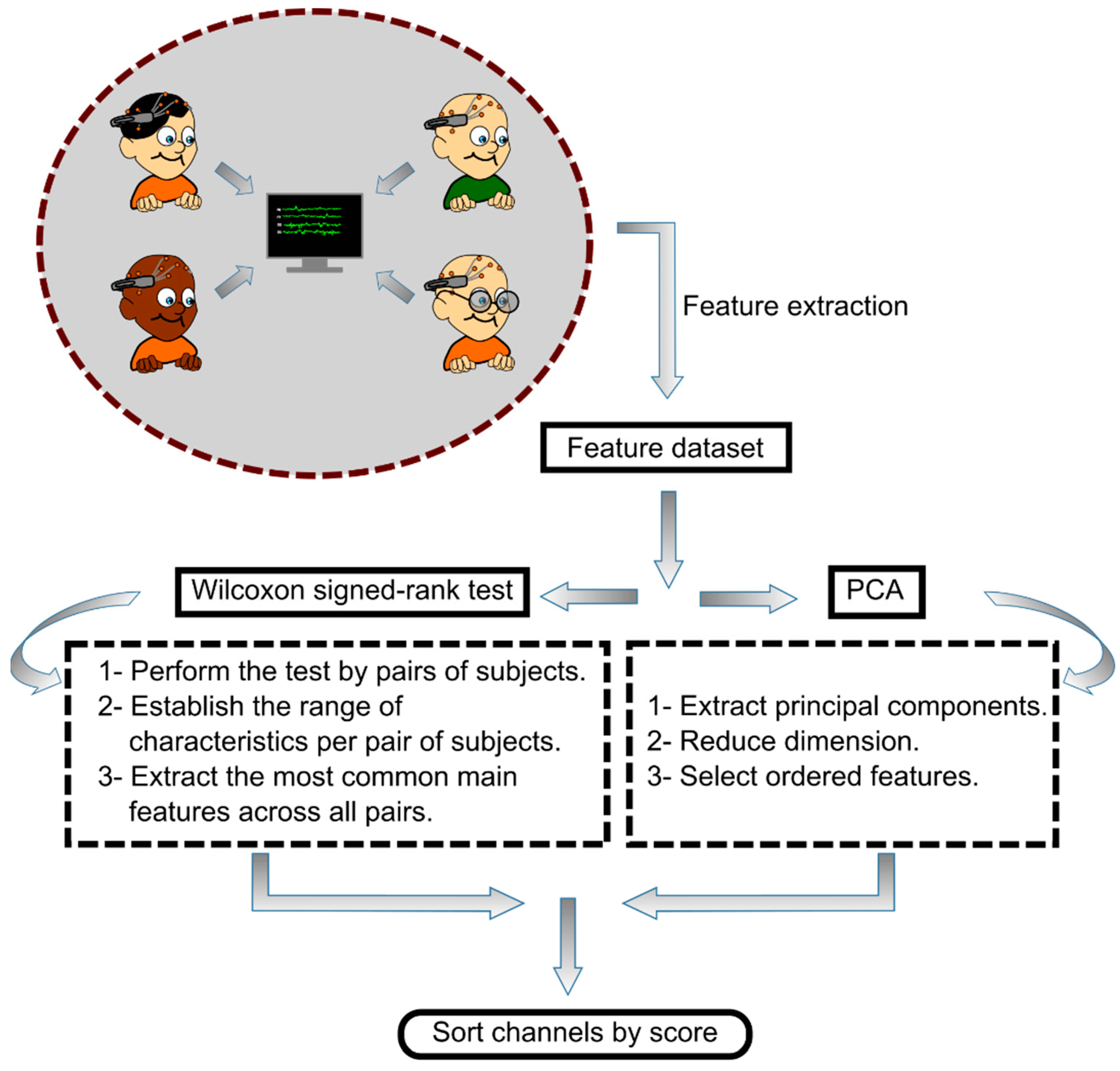
2.5. Feature Selection
2.6. Channel Selection
2.7. Classification. Support Vector Machine
2.8. Computation Setup
3. Results
3.1. Channel Selection Using PCA
| Features | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| = 2) | = 1) | = 1.2) | |
| 91 | O1–T8 | ||
| … | … | ||
| 14 | AF3 | F7–T7 | |
| 13 | F8 | P8–AF4 | |
| 12 | FC6 | F3–O2 | |
| 11 | T8 | T7–P7 | |
| 10 | T7 | F3–P8 | |
| 9 | AF4 | AF3–AF4 | |
| 8 | FC5 | AF3–F3 | |
| 7 | F7 | AF3–AF4 | F7–AF4 |
| 6 | F4 | F3–F4 | F3–P7 |
| 5 | P7 | T7–T8 | F3–F4 |
| 4 | F3 | FC5–FC6 | F3–T7 |
| 3 | O2 | O1–O2 | F4–AF4 |
| 2 | O1 | F7–F8 | F3–AF4 |
| 1 | P8 | P7–P8 | F3–FC5 |
| Weight for T8 | {, , …, } | ||
| Score for T8 | |||
| Order | Channel | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | T8 | 13.61 |
| 2 | F8 | 13.52 |
| 3 | FC6 | 12.39 |
| 4 | FC5 | 11.68 |
| 5 | O1 | 11.40 |
| 6 | O2 | 10.67 |
| 7 | F4 | 10.2 |
| 8 | F7 | 8.99 |
| 9 | AF3 | 8.53 |
| 10 | P7 | 8.51 |
| 11 | T7 | 8.38 |
| 12 | P8 | 7.18 |
| 13 | AF4 | 5.35 |
| 14 | F3 | 3.68 |
| Set of Channels | Set of Features | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 112 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 13 | 98 | 1.39 | 0.92 | 0.80 | 0.86 |
| 12 | 83 | 1.50 | 1.08 | 0.98 | 1.05 |
| 11 | 70 | 1.63 | 2.04 | 1.14 | 1.22 |
| 10 | 58 | 2.42 | 1.92 | 1.96 | 2.11 |
| 9 | 48 | 2.00 | 2.20 | 1.56 | 1.68 |
| 8 | 39 | 2.47 | 3.27 | 2.02 | 2.17 |
| 7 | 30 | 2.77 | 3.45 | 2.13 | 2.28 |
| 6 | 23 | 3.82 | 3.94 | 3.41 | 3.69 |
| 5 | 16 | 8.13 | 6.44 | 6.46 | 6.93 |
| 4 | 11 | 11.68 | 8.10 | 9.49 | 10.00 |
| 3 | 6 | 13.02 | 10.42 | 11.18 | 12.06 |
| 2 | 3 | 21.52 | 20.14 | 19.85 | 21.12 |
| 1 | 1 | 28.95 | 29.53 | 22.64 | 20.57 |
| Dataset | Set of Channels | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (13 subj.) | 4 | 11.68 | 8.10 | 9.49 | 10.00 |
| II (109 subj.) | 16 | 1.84 | 2.02 | 1.51 | 1.51 |
| II (109 subj.) | 64 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.45 | 0.52 |
3.2. Channel Selection by Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
| Features | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| = 2) | = 1) | = 1.2) | |
| 91 | AF–3F3 | ||
| … | … | ||
| 14 | F3–P8 | ||
| 13 | T7–F8 | ||
| 12 | AF3 | AF3–O1 | |
| 11 | F3 | F7–AF4 | |
| 10 | FC6 | F7–FC6 | |
| 9 | AF4 | F3–FC5 | |
| 8 | AF4 | AF3–AF4 | P7–AF4 |
| 7 | FC6 | F7–F8 | T7–T8 |
| 6 | F8 | F3–F4 | P7–F8 |
| 5 | AF4 | FC5–FC6 | P8–AF4 |
| 4 | O2 | T7–T8 | F7–FC6 |
| 3 | O2 | T7–T8 | F7–O2 |
| 2 | T7 | O1–O2 | F7–O1 |
| 1 | O1 | O1–O2 | P7–T8 |
| Weight for AF4 | {, , …, }; | ; | {, , …, } |
| Score for AF4 | |||
| Order | Channel | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AF3 | 14.58 |
| 2 | F3 | 13.79 |
| 3 | F7 | 11.50 |
| 4 | FC5 | 11.07 |
| 5 | T7 | 10.20 |
| 6 | F4 | 9.74 |
| 7 | AF4 | 9.64 |
| 8 | P7 | 9.55 |
| 9 | T8 | 8.24 |
| 10 | FC6 | 8.10 |
| 11 | F8 | 8.03 |
| 12 | O2 | 6.90 |
| 13 | O1 | 6.01 |
| 14 | P8 | 4.58 |
| Set of Channels | Set of Features | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 112 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 13 | 98 | 1.08 | 99.44 ± 1.07 | 99.42 ± 0.65 | 99.38 ± 0.70 |
| 12 | 83 | 1.43 | 99.44 ± 1.07 | 99.42 ± 0.84 | 99.38 ± 0.89 |
| 11 | 70 | 1.58 | 99.26 ± 1.51 | 99.23 ± 0.96 | 99.17 ± 1.03 |
| 10 | 58 | 1.20 | 99.24 ± 1.18 | 99.23 ± 0.81 | 99.17 ± 0.88 |
| 9 | 48 | 1.22 | 99.25 ± 1.52 | 99.23 ± 1.08 | 99.17 ± 1.17 |
| 8 | 39 | 2.47 | 97.73 ± 2.31 | 97.69 ± 1.75 | 97.50 ± 1.89 |
| 7 | 30 | .10 | 97.01 ± 3.67 | 96.92 ± 3.22 | 96.67 ± 3.47 |
| 6 | 23 | .73 | 95.31 ± 4.78 | 95.20 ± 4.20 | 94.80 ± 4.52 |
| 5 | 16 | 5.54 | 92.56 ± 7.04 | 92.36 ± 5.66 | 91.68 ± 6.14 |
| 4 | 11 | 90.58 6.05 | 90.81 ± 6.71 | 90.60 ± 5.69 | 89.81 ± 6.15 |
| 3 | 6 | 11.02 | 80.88 ± 11.10 | 80.57 ± 10.48 | 78.98 ± 11.33 |
| 2 | 3 | 18.51 | 59.63 ± 15.88 | 59.55 ± 16.93 | 57.17 ± 17.71 |
| 1 | 1 | 26.11 | 38.83 ± 24.88 | 38.63 ± 23.66 | 37.98 ± 23.25 |
| Dataset | Set of Channels | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (13 subj.) | 4 | 6.05 | 6.71 | 5.69 | 6.15 |
| II (109 subj.) | 16 | 1.41 | 1.45 | 1.12 | 1.02 |
| II (109 subj.) | 64 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.45 | 0.52 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thorpe, J.; van Oorschot, P.C.; Somayaji, A. Pass-Thoughts: Authenticating with Our Minds. In Proceedings of the New Security Paradigms Workshop, Schloss Dagstuhl, Germany, 19–22 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nandakumar, K.; Jain, A.K.; Nagar, A. Biometric Template Security. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2008, 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putte, T.; Keuning, J. Biometrical Fingerprint Recognition: Don’t Get Your Fingers Burned. In Smart Card Research and Advanced Applications; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, Y.N.; Singh, S.K. Vitality Detection from Biometrics: State-of-the-Art. In Proceedings of the 2011 World Congress on Information and Communication Technologies (WICT), Dijon, France, 21–23 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Galbally, J.; Marcel, S.; Fierrez, J. Biometric Antispoofing Methods: A Survey in Face Recognition. IEEE Access 2014, 2, 1530–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Behera, S.; Vatsa, M.; Singh, R. On Iris Spoofing Using Print Attack. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Rodríguez, J.; Martín-Chinea, K.; Gómez-González, J.F.; Pereda, E. Brainprint Based on Functional Connectivity and Asymmetry Indices of Brain Regions: A Case Study of Biometric Person Identification with Non-expensive Electroencephalogram Headsets. IET Biom. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, R.B.; Mahovsky, J.; Benedicenti, L.; Koles, Z. The Electroencephalogram as a Biometric. Can. Conf. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2001, 2, 1363–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, R.; Mandic, D.P. EEG Based Biometric Framework for Automatic Identity Verification. J. VLSI Signal Process. Syst. Signal Image Video Technol. 2007, 49, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo-Banos, M.; Alonso, J.B.; Ticay-Rivas, J.R.; Travieso, C.M. Electroencephalogram Subject Identification: A Review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 6537–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirvent Blasco, J.L.; Iáñez, E.; Úbeda, A.; Azorín, J.M. Visual Evoked Potential-Based Brain-Machine Interface Applications to Assist Disabled People. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 7908–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, D.J.; Wolpaw, J.R. Brain-Computer Interfaces for Communication and Control. Commun. ACM 2011, 54, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, S.; Singh, P.; Kaur, C. EEG Signal Analysis for BCI Interface: A Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Technologies (ACCT), Haryana, India, 21–22 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Collura, T.F. History and Evolution of Electroencephalographic Instruments and Techniques. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1993, 10, 476–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohi-Azizi, M.; Azimi, L.; Heysieattalab, S.; Aamidfar, M. Changes of the Brain’s Bioelectrical Activity in Cognition, Consciousness, and Some Mental Disorders. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2017, 31, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klonowski, W. Everything You Wanted to Ask about EEG but Were Afraid to Get the Right Answer. Nonlinear Biomed. Phys. 2009, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miladinović, A.; Ajčević, M.; Jarmolowska, J.; Marusic, U.; Colussi, M.; Silveri, G.; Battaglini, P.P.; Accardo, A. Effect of Power Feature Covariance Shift on BCI Spatial-Filtering Techniques: A Comparative Study. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 198, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.; Babiloni, F.; Chen, H. EEG Fingerprints: Phase Synchronization of EEG Signals as Biomarker for Subject Identification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 121165–121173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashenaei, R.; Asghar Beheshti, A.; Yousefi Rezaii, T. Stable EEG-Based Biometric System Using Functional Connectivity Based on Time-Frequency Features with Optimal Channels. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 77, 103790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; El-Fiqi, H.; Hu, J.; Abbass, H.A. Convolutional Neural Networks Using Dynamic Functional Connectivity for EEG-Based Person Identification in Diverse Human States. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 3359–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Mu, Z.; Wang, J. Phase Locking Analysis of Motor Imagery in Brain-Computer Interface. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, Sanya, China, 28–30 May 2008; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 478–481. [Google Scholar]
- Caramia, N.; Lotte, F.; Ramat, S. Optimizing Spatial Filter Pairs for EEG Classification Based on Phase-Synchronization. In Proceedings of the ICASSP, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Proceedings, Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, P.; Scarano, G.; Babiloni, F.; DeVico Fallani, F.; Colonnese, S.; Maiorana, E.; Forastiere, L. Brain Waves Based User Recognition Using the “Eyes Closed Resting Conditions” Protocol. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS), Iguacu Falls, Brazil, 29 November–2 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- David, O.; Cosmelli, D.; Friston, K.J. Evaluation of Different Measures of Functional Connectivity Using a Neural Mass Model. Neuroimage 2004, 21, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billinger, M.; Brunner, C.; Müller-Putz, G.R. Single-Trial Connectivity Estimation for Classification of Motor Imagery Data. J. Neural Eng. 2013, 10, 046006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J. Automatic Recognition of Epileptic EEG Patterns via Extreme Learning Machine and Multiresolution Feature Extraction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 5477–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, M.; Katebi, S.D.; Boostani, R.; Price, G.W. A New Approach for EEG Signal Classification of Schizophrenic and Control Participants. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.; Moore, P. EEG-Based Biometric Identification Using Local Probability Centers. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Killarney, Ireland, 12–17 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Friston, K.J. Functional and Effective Connectivity: A Review. Brain Connect. 2011, 1, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinowska, K.J.; Rakowski, F.; Kaminski, M.; de Vico Fallani, F.; del Percio, C.; Lizio, R.; Babiloni, C. Functional and Effective Brain Connectivity for Discrimination between Alzheimer’s Patients and Healthy Individuals: A Study on Resting State EEG Rhythms. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, P.; La Rocca, D. Brain Waves for Automatic Biometric-Based User Recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2014, 9, 782–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rocca, D.; Campisi, P.; Vegso, B.; Cserti, P.; Kozmann, G.; Babiloni, F.; de Vico Fallani, F. Human Brain Distinctiveness Based on EEG Spectral Coherence Connectivity. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2406–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.; Silva, G.F.A.; Papa, J.P.; Marana, A.N.; Yang, X.S. EEG-Based Person Identification through Binary Flower Pollination Algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 62, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike-Akino, T.; Mahajan, R.; Marks, T.K.; Wang, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Tuzel, O.; Orlik, P. High-Accuracy User Identification Using EEG Biometrics. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet. Circulation 2000, 101, E215–E220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, B.; Babiloni, F.; Borghini, G. Assessment of Driving Fatigue Based on Intra/Inter-Region Phase Synchronization. Neurocomputing 2017, 219, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalk, G.; McFarland, D.J.; Hinterberger, T.; Birbaumer, N.; Wolpaw, J.R. BCI2000: A General-Purpose Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) System. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Maris, E.; Schoffelen, J.M. FieldTrip: Open Source Software for Advanced Analysis of MEG, EEG, and Invasive Electrophysiological Data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 156869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Chinea, K.; Ortega, J.; Gómez-González, J.F.; Pereda, E.; Toledo, J.; Acosta, L. Effect of Time Windows in LSTM Networks for EEG-Based BCIs. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2022, 17, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, D.J.; Miner, L.A.; Vaughan, T.M.; Wolpaw, J.R. Mu and Beta Rhythm Topographies during Motor Imagery and Actual Movements. Brain Topogr. 2000, 12, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, D.J. Spectrum Estimation and Harmonic Analysis. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 1055–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, O.; Mari, Z.; Vorbach, S.; Hallett, M. Asymmetric Spatiotemporal Patterns of Event-Related Desynchronization Preceding Voluntary Sequential Finger Movements: A High-Resolution EEG Study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Prieto, J.; Bajo, R.; Pereda, E. Efficient Computation of Functional Brain Networks: Toward Real-Time Functional Connectivity. Front. Neuroinformatics 2017, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschini, M.; Pani, S.M.; Didaci, L.; Marcialis, G.L. Robustness of Functional Connectivity Metrics for EEG-Based Personal Identification over Task-Induced Intra-Class and Inter-Class Variations. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 125, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tǎutan, A.M.; Rossi, A.C.; de Francisco, R.; Ionescu, B. Dimensionality Reduction for EEG-Based Sleep Stage Detection: Comparison of Autoencoders, Principal Component Analysis and Factor Analysis. Biomed. Tech. 2021, 66, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artoni, F.; Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. Applying Dimension Reduction to EEG Data by Principal Component Analysis Reduces the Quality of Its Subsequent Independent Component Decomposition. Neuroimage 2018, 175, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.C.; Duan, R.N.; Lu, B.L. A Robust Principal Component Analysis Algorithm for EEG-Based Vigilance Estimation. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal Component Analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual Comparisons by Ranking Methods. Biom. Bull. 1945, 1, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Nie, D.; Lu, B.L. EEG-Based Emotion Recognition Using Frequency Domain Features and Support Vector Machines. In Neural Information Processing; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 7062. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Gao, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, B.; Lu, N.; Wang, J. Motor Imagery EEG Classification Based on Ensemble Support Vector Learning. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 193, 105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sercan Bayram, K.; Kızrak, M.A. Classification of EEG Signals by Using Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE INISTA, Albena, Bulgaria, 19–21 June 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albasri, A.; Abdali-Mohammadi, F.; Fathi, A. EEG Electrode Selection for Person Identification Thru a Genetic-Algorithm Method. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moctezuma, L.A.; Molinas, M. Multi-Objective Optimization for EEG Channel Selection and Accurate Intruder Detection in an EEG-Based Subject Identification System. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsy, J.C.; Vinod, A.P. EEG-based Biometric Identification Using Frequency-weighted Power Feature. IET Biom. 2020, 9, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyasseri, Z.A.A.; Alomari, O.A.; Papa, J.P.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Abdulkareem, K.H.; Mohammed, M.A.; Kadry, S.; Thinnukool, O.; Khuwuthyakorn, P. EEG Channel Selection Based User Identification via Improved Flower Pollination Algorithm. Sensors 2022, 22, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortega-Rodríguez, J.; Gómez-González, J.F.; Pereda, E. Selection of the Minimum Number of EEG Sensors to Guarantee Biometric Identification of Individuals. Sensors 2023, 23, 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094239
Ortega-Rodríguez J, Gómez-González JF, Pereda E. Selection of the Minimum Number of EEG Sensors to Guarantee Biometric Identification of Individuals. Sensors. 2023; 23(9):4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094239
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtega-Rodríguez, Jordan, José Francisco Gómez-González, and Ernesto Pereda. 2023. "Selection of the Minimum Number of EEG Sensors to Guarantee Biometric Identification of Individuals" Sensors 23, no. 9: 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094239
APA StyleOrtega-Rodríguez, J., Gómez-González, J. F., & Pereda, E. (2023). Selection of the Minimum Number of EEG Sensors to Guarantee Biometric Identification of Individuals. Sensors, 23(9), 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23094239







