A Systematic Review of International Affective Picture System (IAPS) around the World
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods

| Ref. | Country | Year | N | Age Group | Age | Occupation | Stimuli | Sets | Ratings | Sensors | PPT | SAM | MRS | Written Language |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [46] | Argentina | 2016 | 125 (84 ♀ 41 ♂) | Adults | 21.6 ± 5.13 | Uni. Students | 59 | 19 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [47] | Argentina | 2020 | 646 (342 ♀ 304 ♂) | Adults | 25.86 ± 7.52 | Uni. Students | 412 | 3, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 15 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [48] | Argentina | 2015 | 524 (278 ♀ 246 ♂) | Adults | 23.32 ± 6.69 | Uni. Students | 358 | 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 14 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [49] | Argentina | 2022 | 141 (67 ♀ 74 ♂) | Children and Adolescents | 11.16 ± 2.16 | School Students | 60 | N.R. | VA | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [50] | Argentina | 2017 | 141 (67 ♀ 74 ♂) | Children and Adolescents | 11.16 ± 2.16 | School Students | 60 | N.R. | VA | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [51] | Belgium | 2001 | 80 (50 ♀ 30 ♂) | Adults | 19.16 ± 1.87 | Uni. Students | 60 | N.R. | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [52] | Bosnia | 2013 | 72 (55 ♀ 22 ♂) | Adults | N.R. | Uni. Students | 60 | N.R. | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [53] | Brazil | 2019 | 30 (13 ♀ 17 ♂) | Adults | 44.6 ± N.R. | Medical Doctors | 36 | N.R. | VA | - | Individual | Paper | - | Portuguese |
| [54] | Brazil | 2008 | 448 (269 ♀ 179 ♂) | Adults | 24.2 ± 7.8 | Uni. Students | 240 | 13 - 16 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [55] | Brazil | 2016 | 100 ♀ | Adults | 25.07 ± 7.175 | Uni. Students | 105 (80 IAPS) | N.R. | VA, Categorical | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [56] | Brazil | 2008 | 48 (42 ♀ 6 ♂) | Elderly | 68.65 ± 6.7 | Third Age Open Uni. Students | 71 | N.R. | VA | - | N.R. | Paper | - | Portuguese |
| [57] | Brazil | 2011 | 187 (111 ♀ 76 ♂) | Elderly | 68.3 ± 6.99 | N.R. | 702 | N.R. | VA | - | Group | Paper | - | Portuguese |
| [58] | Brazil | 2008 | 448 (269 ♀ 179 ♂) | Adults | 24.2 ± 7.8 | Uni. Students | 240 | 13–16 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | Portuguese |
| [59] | Brazil | 2018 | 161 (69 ♀ 92 ♂) | Adolescents | 15 ± 2.2 | School Students | 182 | N.R. | VA | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [60] | Brazil | 2005 | 1062 (698 ♀ 364 ♂) | Adults | 22.8 ± 4.6 | Uni. Students | 707 | 1-12 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [61] | Brazil | 2007 | 24 (12 ♀ 12 ♂) | Adults | N.R. | Uni. Students | 32 | N.R. | VA | Facial EMG, SCL, HR, and peripheral temp. | Individual | N.R. | - | English |
| [62] | Chile | 2010 | 135 (88 ♀ 47 ♂) | Adults | 20.13 ± 2.29 | Uni. Students | 188 | N.R. | VA | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [63] | Chile | 2016 | 60 (30 ♀ 30 ♂) | Adults | 22.3 ± 3.2 | Uni. Students and 3 Finished High School | 146 | N.R. | VAD, Categorical | - | Individual | Paper | - | English |
| [64] | Chile | 2011 | 208 (124 ♀ 84 ♂) | Adults | 19 ± 1.2 | Uni. Students | 119 | 7;14 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [65] | China | 2015 | 120 (53 ♀ 67 ♂) | Adults | 21.35 ± 1.58 | Uni. Students | 816 | N.R. | VA | - | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [66] | China | 2017 | 493 (274 ♀ 219 ♂) | Adults | 19.66 ± 2.01 | Uni. Students | 108 | N.R. | Emotion intension 9-point (0–8) | - | Individual | N.A. | - | English |
| [67] | China | 2016 | 126 (86 ♀ 40 ♂) | Elderly | 67.3 ± 4.96 | N.R. | 942 | All sets (excluding erotic) | VA | - | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [68] | Colombia | 2019 | 1222 (699 ♀ 523 ♂) | Adults | 20.39 ± 2.60 | Uni. Students | 240 | 15–18 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [69] | Colombia | 2019 | 447 (295 ♀ 149 ♂, 3 N.R.) | Adults | 20.36 ± 2.74 | Uni. Students | 200 | N.R. | Categorical | - | Individual | N.A. | - | English |
| [70] | Colombia | 2011 | 404 (229 ♀ 175 ♂) | Adults | 22.3 ± 5.2 | Uni. Students | 248 | 13, 14, 19, 20 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [71] | Finland | 2010 | 25 ♀ | Adults | N.R. | Uni. Students | 48 | N.R. | VA | HRV, Eye Tracking, Facial Expressions | Individual | Oral Report | - | English |
| [72] | Finland | 2013 | 14 ♂ | Adults | N.R. | Uni. Students | 48 | N.R. | VA | HRV, Eye Tracking, Facial Expressions | Individual | Oral Report | - | English |
| [73] | Finland | 2008 | 5 ♀ | Adults | N.R. | Uni. Students | 48 | N.R. | VA | HRV, Eye Tracking, Facial Expressions | Individual | Oral Report | - | English |
| [74] | Finland | 2010 | 25 ♀ | Adults | N.R. | Uni. Students | 48 | N.R. | VA | HRV, Eye Tracking, Facial Expressions | Individual | Oral Report | - | English |
| [75] | Finland | 2013 | 44 (25 ♀ 19 ♂) | Adults | N.R. | Uni. Students | 48 | N.R. | VA | HRV, Eye Tracking, Facial Expressions | Individual | Oral Report | - | English |
| [76] | Germany | 2006 | 27 (Sex N.R.) | Adults and Elderly | 49.3 ± 4.62 | N.R. | 702 (54 rated) | N.R. | VA | EEG | Individual | N.R. | - | English |
| [77] | Germany | 2011 | 41 ♀ | Adults | 30.0 ± 7.6 | Uni. Students and others (N.R.) | 120 (20 IAPS) | N.R. | VAD | - | N.R. | N.R. | - | English |
| [78] | Germany | 2009 | 156 (95 ♀ 61 ♂) | Adults and Elderly | 41.9 ± N.R. | Uni. Students and others (N.R.) | 172 | N.R. | VA | - | Individual | Paper | - | English |
| [79] | Germany | 2011 | 104 (53 ♀ 51 ♂) | Adults and Elderly | 46 ± 3.9 | Uni. Students and others (N.R.) | 172 | N.R. | VA, Categorical | - | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [80] | Germany | 2012 | 191 (95 ♀ 96 ♂) | Adults | 23.6 ± 2.8 | Uni. Students, Workers and others (N.R.) | 298 | N.R. | VA, Categorical | - | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [81] | Germany | 2008 | 106 (52 ♀ 54 ♂) | Adults and Elderly | 47.42 ± 3.485 | N.R. | 504 | N.R. | VA | - | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [82] | Hungary | 2010 | 187 (146 ♀ 41 ♂) | Adults | 19.91 ± 1.34 | Uni. Students | 239 | N.R. | VAD | - | Group | N.R. | - | English |
| [83] | India | 2013 | 80 (36 ♀ 44 ♂) | Adults | 23.7 ± 2.67 | Uni. Students | 100 | N.R. | VAD | - | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [84] | Israel | 2011 | 38 (20 ♀ 18 ♂) | Adults | 24.2 ± 2.9 | Uni. Students | 629 | N.R. | VA | - | N.R. | N.R. | - | English |
| [85] | Japan | 2019 | 62 (30 ♀ 32 ♂) | Adults and Elderly | 44.72 ± 3.26 | Uni. Students and others (N.R.) | 120 | N.R. | VA | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [86] | Lithuania | 2015 | 103 (82 ♀ 21 ♂) | Adults | 18–24 y | Uni. Students | 60 | 20 | VAD | - | N.R. | Paper | - | English |
| [87] | Malaysia | 2017 | 72 (46 ♀ 18 ♂) | Adults | 19.2 ± 1.68 | N.R. | 166 images (83 IAPS) | N.R. | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [88] | Mexico | 2003 | 804 (Sex N.R.) | Adults | 20.10 ± 3.69 | Uni. Students | 459 (266 IAPS) | N.R. | VAD + 2 subscale | - | Group | Paper | Valence rating inverted and Arousal was changed | Spanish |
| [89] | Mexico | 2002 | 41 (21 ♀ 20 ♂) | Adults | 24.8 ± 5.96 | Uni. Students | 700 | N.R. | VA | - | Individual | Computer | 5 point | Spanish |
| [90] | Mexico | 2018 | 408 (220 ♀ 188 ♂) | Adults | 19.81 ± 2.58 | Uni. Students | 238 | 13, 14, 19, 20 | VAD | - | N.R. | N.R. | - | Spanish |
| [91] | Morocco | 2020 | 100 (69 ♀ 41 ♂) | Adults | 19.56 ± 1.21 | Uni. Students | 20 | N.R. | V | - | N.R. | N.R. | - | English |
| [92] | Morocco | 2018 | 120 (69 ♀ 51 ♂) | Adults | 19.47 ± 0.67 | Uni. Students | 102 | 3;11 | VAD | - | N.R. | Paper | - | English |
| [93] | Portugal | 2015 | 2000 (1.419 ♀ 581 ♂) | Adults | 21.57 ± 5.67 | Uni. Students | 1182 | All | VAD | - | Individual | Paper | - | English |
| [94] | Serbia | 2019 | 158 (73 ♀ 85 ♂) | Adults | 19-21 y | Uni. Students | 60 | N.R. | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [95] | South Africa | 2022 | 150 (75 ♀ 75 ♂) | Adults | 21.6 ± 2.85 | Uni. Students and others (N.R.) | 340 | N.R. | VA | - | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [96] | Republic of Korea | 2017 | 30 (15 ♀ 15 ♂) | Adults | 23.8 ± 3.1 | N.R. | 15 | N.R. | VAD | HRV | N.R. | N.R. | - | English |
| [97] | Republic of Korea | 2009 | 104 (Sex N.R.) | Adults and Elderly | 47.95 ± 3.65 | N.R. | 156 | N.R. | V | - | Individual | N.R. | 7 point | English |
| [98] | Spain | 2001 | 715 (434 ♀ 281 ♂) | Adults | 20.51 ± 3.40 | Uni. Students | 352 | 8-14 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [99] | Spain | 2008 | 45 (25 ♀ 20 ♂) | Adults | 27.2 ± 9.5 | Uni. Students | 120 | N.R. | VAD, Categorical | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [100] | Spain | 1999 | 1102 (673 ♀ 429 ♂) | Adults | 20.28 ± N.R. | Uni. Students | 480 | 1-8 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [101] | Spain | 2013 | 811 (521 ♀ 290 ♂) | Adults | 20.52 ± 3.73 | Uni. Students | 358 | 15–20 | VAD | - | Group | Paper | - | Spanish |
| [102] | Spain/ Switzerland | 2015 | 847 (541 ♀ 306 ♂) | Adults | 22.91 ± 6.11 | Uni. Students | 60 | N.R. | VA | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [103] | Turkey | 2010 | 219 (59 ♀ 160 ♂) | Adults | 21.17 ± N.R. | Elite Athletes | 224 | N.R. | VA | - | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [104] | UK | 2006 | 659 (340 ♀ 319 ♂) | Children | 7–11 y | School Students | 27 | N.R. | VA | - | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [105] | US | 2001 | 206 (106 ♀ 100 ♂) | Children, Adolescents and Adults | ≥7 y | Uni. and School Students | 60 | N.R. | VAD | Facial EMG, HR, SCL | N.R. and Group | Paper & Computer | - | English |
| [106] | US | 2005 | 66 (32 ♀ 34 ♂) | Adults and Elderly | 18–71 | Uni. Students and Retired | 45 | N.R. | VA | EEG, Facial EMG, HR | Individual | Computer | 21-point | English |
| [107] | US | 1995 | 60 (30 ♀ 30 ♂) | Adults | N.R. | Uni. Students | 114 | 1–2 | VAD, Categorical | Facial EMG | Group | Paper | - | English |
| [108] | US | 2007 | 1302 (N.R.) | Adults | ≥18 y | Uni. Students | 703 | N.R. | VA and Categorical/ Dimensional | - | Group | Paper | 9-point | English |
| [109] | US | 2014 | 13 (7 ♀ 6 ♂) | Adults | Median 34 y | N.R. | 60 | N.R. | VA | EEG (RREP) | Individual | Paper | - | English |
| [110] | US | 2005 | 42 (23 ♀ 19 ♂) | Adults and Elderly | 43.14 ± 3.96 | Uni. Students | 90 | N.R. | VA | - | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [111] | US | 1998 | 509 (275 ♀ 234 ♂) | Adults | N.R. | Uni. Students | 472 | 1–8 | VAD and BEAM | - | N.R. | Paper | - | English |
| [112] | US | 2005 | 140 (70 ♀ 70 ♂) | Adults | 19.02 ± N.R. | Uni. Students | 390 | N.R. | Categorical | - | Individual | N.A. | N.A. | English |
| [113] | US | 2000 | 46 (24 ♀ 22 ♂) | Adults and Elderly | 47.4 ± N.R. | Uni. Students and others (N.R.) | 27 | N.R. | VA | Facial EMG | Individual | Computer | - | English |
| [114] | US | 2004 | 34 (16 ♀ 18 ♂) | Adults and Elderly | 50.91 ± 4.05 | N.R. | 64 | N.R. | A (Not SAM) | fMRI | Individual | N.A. | Rating 1–4 in Arousal | English |
3. Findings
3.1. Localization
3.1.1. Argentina
3.1.2. Belgium
3.1.3. Bosnia
3.1.4. Brazil
3.1.5. Chile
3.1.6. China
3.1.7. Colombia
3.1.8. Finland
3.1.9. Germany
3.1.10. Hungary
3.1.11. India
3.1.12. Israel
3.1.13. Japan
3.1.14. Lithuania
3.1.15. Malaysia
3.1.16. Mexico
3.1.17. Morocco
3.1.18. Portugal
3.1.19. Serbia
3.1.20. South Africa
3.1.21. Republic of Korea
3.1.22. Spain
3.1.23. Spain/Switzerland
3.1.24. Turkey
3.1.25. United Kingdom
3.1.26. United States
3.2. Participants’ Characterization
3.3. Studies Timeline
3.4. Stimuli Characterization
3.4.1. Stimuli Presentation
3.4.2. Rating
3.4.3. Physiology
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A | Arousal |
| ANT | Animal Naming Task |
| APSD | Antisocial Process Screening Device |
| AUDIT-C | Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test Consumption |
| BDI | Beck Depression Inventory |
| BEAMs | Bivariate Evaluation and Ambivalence Measures |
| CDT | Clock Drawing Test |
| CES–D | 20-item Center for Epidemiologic Studies—Depression Scale |
| CV | Computer Vision |
| DAST-10 | Drug Abuse Screening Test |
| DSM | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders |
| EBIR | Emotional based image retrieval |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| ERP | Event-Related Potentials |
| FEDA | Experienced Attention Deficits Self-Rating Inventory |
| FFPI | Five Factor Personality Inventory |
| fMRI | Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| FTP | Future Time Limit |
| GDS | Geriatric Depression Scale |
| HIS | Hachinski Ischemic Score |
| HRV | Heart Rate Variability |
| IADL | Instrumental Activities of Daily Living |
| IAPS | International Afective Picture System |
| IVE | Impulsiveness, Venturesomeness and Empathy |
| K-WAIS | Korean Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale |
| K-WPSI | Korean Wahler Physical Symptoms Inventory |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| MRS | Modified Rating Scale |
| N.A. | Not Applicable |
| N.D. | No Difference |
| N.R | Not Reported |
| PANAS | Positive and Negative Affect Schedule |
| PANAS-X | Expanded version of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule |
| PBR | Population Reference Bureau |
| PC-PTSD | Primary Care Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Screen |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Health Questionnaire for Depression-9 |
| PPT | Picture Presentation Type |
| RREP | Respiratory Related Evoked Potential |
| SAM | Self Assessment Manikin |
| SCL | Skin Conductance Level |
| SDQ | Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire |
| SDS | Self Depression Scale |
| SEEDs | Standardized Emotion Elicitation Databases |
| SHPMSQ | Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire |
| SPSRQ | Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire |
| STAI | State Trait Anxiety Inventory |
| US | United States |
| V | Valence |
| VA | Valence–Arousal |
| VAD | Valence–Arousal–Dominance |
| WAIS | Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale |
| WHD | Waterloo Handedness Questionnaire |
| WST | Wortschatztest [Vocabulary test] |
| ZKPQ | Zuckerman–Kuhlman Personality Questionnaire |
References
- Frijda, N.H.; Mesquita, B. The Analysis of Emotions. In What Develops in Emotional Development? Mascolo, M.F., Griffin, S., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, K.R. What are emotions? And how can they be measured? Soc. Sci. Inf. 2005, 44, 695–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P. An argument for basic emotions. Cogn. Emot. 1992, 6, 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutchik, R. A General Psychoevolutionary Theory of Emotion. In Theories of Emotion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980; pp. 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.A. A circumplex model of affect. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1980, 39, 1161–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crone, D.L.; Bode, S.; Murawski, C.; Laham, S.M. The Socio-Moral Image Database (SMID): A novel stimulus set for the study of social, moral and affective processes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, B.; Lozano, S.; Banaji, M.R. Introducing the Open Affective Standardized Image Set (OASIS). Behav. Res. Methods 2017, 49, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchewka, A.; Żurawski, L.; Jednoróg, K.; Grabowska, A. The Nencki Affective Picture System (NAPS): Introduction to a novel, standardized, wide-range, high-quality, realistic picture database. Behav. Res. Methods 2014, 46, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.; Leite, J.; Galdo-Álvarez, S.; Gonçalves, O.F. The Emotional Movie Database (EMDB): A Self-Report and Psychophysiological Study. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2012, 37, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baveye, Y.; Dellandrea, E.; Chamaret, C.; Chen, L. LIRIS-ACCEDE: A Video Database for Affective Content Analysis. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 6, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, L.M.; Andrewes, D.G. A New Set of Standardised Verbal and Non-verbal Contemporary Film Stimuli for the Elicitation of Emotions. Brain Impair. 2012, 13, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin, P.; Fillion-Bilodeau, S.; Gosselin, F. The Montreal Affective Voices: A validated set of nonverbal affect bursts for research on auditory affective processing. Behav. Res. Methods 2008, 40, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.A.; James, T.W. Affective auditory stimuli: Characterization of the International Affective Digitized Sounds (IADS) by discrete emotional categories. Behav. Res. Methods 2008, 40, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfi, A.M.; Kacirek, K. The famous melodies stimulus set. Behav. Res. Methods 2021, 53, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Affective Norms for English Words (ANEW): Instruction Manual and Affective Ratings; Technical Report C-1; The Center for Research in Psychophysiology, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Grühn, D. An English Word Database of EMOtional TErms (EMOTE). Psychol. Rep. 2016, 119, 290–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syssau, A.; Monnier, C. Children’s emotional norms for 600 French words. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popic, D.; Pacozzi, S.G.; Martarelli, C.S. Database of virtual objects to be used in psychological research. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, D. A standardized set of 3-D objects for virtual reality research and applications. Behav. Res. Methods 2018, 50, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tromp, J.; Klotzsche, F.; Krohn, S.; Akbal, M.; Pohl, L.; Quinque, E.M.; Belger, J.; Villringer, A.; Gaebler, M. OpenVirtualObjects: An Open Set of Standardized and Validated 3D Household Objects for Virtual Reality-Based Research, Assessment, and Therapy. Front. Virtual Real. 2020, 1, 611091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Measuring emotion: The self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 1994, 25, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, P.J.; Bradley, M.M.; Cuthbert, B.N. International Affective Picture System (IAPS): Technical Manual and Affective Ratings; NIMH Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2008; Volume 1, p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Measuring Emotion: Behavior, Feeling, and Physiology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, M.M.; Miccoli, L.; Escrig, M.A.; Lang, P.J. The pupil as a measure of emotional arousal and autonomic activation. Psychophysiology 2008, 45, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, S.; Matsuda, G.; Hiraki, K. Negative emotion modulates prefrontal cortex activity during a working memory task: A NIRS study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.R.; Lebel, R.M.; Dolcos, F.; Wilman, A.H.; Silverstone, P.H.; Pazderka, H.; Fujiwara, E.; Wild, T.C.; Carroll, A.M.; Hodlevskyy, O.; et al. Effects of emotional context on impulse control. NeuroImage 2012, 63, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genet, J.J.; Malooly, A.M.; Siemer, M. Flexibility is not always adaptive: Affective flexibility and inflexibility predict rumination use in everyday life. Cogn. Emot. 2013, 27, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, A.M.; McMillan, K.M.; Laird, A.R.; Bullmore, E. N-back working memory paradigm: A meta-analysis of normative functional neuroimaging studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. B 2015, 25, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, L.; Lipszyc, J.; Dupuis, A.; Thayapararajah, S.W.; Schachar, R. Response Inhibition and Psychopathology: A Meta-Analysis of Go/No-Go Task Performance. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2014, 123, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, I.; Gade, M.; Schuch, S.; Philipp, A.M. The role of inhibition in task switching: A review. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2010, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.T.; Cho, S.W.; Khang, H.S.; Lee, B.C.; Choi, I.G.; Lyoo, I.K.; Ham, B.J. The neural substrates of affective processing toward positive and negative affective pictures in patients with major depressive disorder. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, R.; Tulen, J.; Vanbeveren, N.; Vansteenis, H.; Mulder, P.; Hengeveld, M. Physiological responsivity to emotional pictures in schizophrenia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2005, 39, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yao, X.; Yang, J.; Jia, G.; Ding, G.; Chua, T.S.; Schuller, B.W.; Keutzer, K. Affective Image Content Analysis: Two Decades Review and New Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3094362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Peacock, R. Effectiveness and efficiency of search methods in systematic reviews of complex evidence: Audit of primary sources. BMJ 2005, 331, 1064–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Winter, B.; Schürkens, A.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Herpertz, S. Validierung und Normierung von kindgerechten, standardisierten Bildmotiven aus dem International Affective Picture System: Untersuchung an einer deutschen Feldstichprobe von Kindern im Alter zwischen sechs und zwölf Jahren. Z.-Kinder-Jugendpsychiatrie Psychother. 2004, 32, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, A.O.; Vaitl, D. Emotionsinduktion durch visuelle Reize: Validierung einer Stimulationsmethode auf drei Reaktionsebenen. [Induction of emotions via visual stimuli: Validation of an induction method on 3 response levels.]. Psychol. Rundsch. 1993, 44, 143–161. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, S.K.; Tam, W.C.C.; Hua, M.S.; Chen, W.L.; Chang, C.S. The International Affective Picture System: A Validation Study for Young Adults in Taiwan. Chin. J. Psychol. 2012, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, A.; Zhou, R. Native Research of International Affective Picture System: Assessment in University Students. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 2009, 17, 687–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chiang, S. The International Affective Picture System (IAPS)—-Comparison of Evaluating Method in Young Adults Sample. Adv. Psychol. 2014, 4, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanov, A.Y.; Marchenko, O.P.; Mashanlo, A.S. Approbation of standard measures of emotional pictures from IAPS system on Russian sample. Eksperimental’na Psihol. (Exp. Psychol. (Russia)) 2011, 4, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Vasanov, A.Y.; Marchenko, O.P.; Sevostyanova, M.S. Selection of culture-specific emotion evocative pictures for experimental studies. Eksperimental’na Psihol. (Exp. Psychol. (Russia)) 2013, 6, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.; Yi, I.; Sohn, J. A comparative study using International Affective Picture System. Korea Sci. 1997, 29, 220–223. [Google Scholar]
- Bungener, C.; Bonnet, P.; Fiori-Duharcourt, N. Validation of 120 images of the IAPS in a French population aged from 20 to 88 years. Geriatr. Psychol. Neuropsychiatr. Viellissement 2016, 14, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, N. Is international affective picture system (IAPS) appropriate for using in Iranian culture, comparing to the original normative rating based on a North American sample. Eur. Psychiatry 2017, 41, S520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, M.E.; Rovella, A.T.; Brusasca, M.C.; Leporati, J.L. Validación argentina de la serie 19 del Sistema Internacional de Imágenes Afectivas (IAPS). Rev. Evaluar 2016, 16, 15709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrazabal, N.; Tonini, F. Datos normativos del Sistema Internacional de Imágenes Afectivas (IAPS) en una muestra argentina. Segunda parte. Rev. Argent. Cienc. Comport. 2020, 12, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrazabal, N.; Aranguren, M.; Zaldua, E.; Di Giuliano, N. Datos normativos del Sistema Internacional de Imágenes Afectivas (IAPS) en una muestra argentina. Rev. Argent. Cienc. Comport. 2015, 7, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, L.; Bakker, L.; Rubiales, J.; Funes, N. Procesamiento emocional en niños y adolescentes según sexo. CES Psicol. 2022, 15, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, L.; Bakker, L.; Rubiales, J.; González, R. Estudio de validación del International Affective Picture System en niños y adolescentes argentinos. Rev. Psicol. 2017, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuere, B.; Crombez, G.; Koster, E. The International Affective Picture System a Flemish Validation Study. Psychol. Belg. 2001, 41, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drace, S.; Efendic, E.; Kusturica, M.; Landzo, L. Cross-cultural validation of the “International affective picture system” (IAPS) on a sample from Bosnia and Herzegovina. Psihologija 2013, 46, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelhano, L.M.; Wahba, L. Respostas Emocionais de Médicos aos Estímulos Afetivos do International Affective Picture System (IAPS). Rev. Bras. Educ. Medica 2019, 43, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaitis, C.; Ribeiro, R.L.; Bueno, O.F.A. Brazilian norms for the International Affective Picture System (IAPS): Comparison of the affective ratings for new stimuli between Brazilian and North-American subjects. J. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2008, 57, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, J.; de Oliveira, L.; Pereira, M.G.; David, I.; Souza, G.G.L.; Sobral, A.P.; Machado-Pinheiro, W.; Mocaiber, I. The Perception of Aversiveness of Surgical Procedure Pictures Is Modulated by Personal/Occupational Relevance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, W.G.a.; Bertolucci, P.; Ribeiro, R.L.; Bueno, O.F.A. Um estudo dos relatos afetivos subjetivos a estímulos do International Affective Picture System em uma amostra geriátrica brasileira. Rev. Psiquiatr. Rio Gd. Sul 2008, 30, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pôrto, W.G.a.; Bertolucci, P.H.F.; Bueno, O.F.A. The paradox of age: An analysis of responses by aging Brazilians to International Affective Picture System (IAPS). Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2010, 33, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasaitis, C.; Ribeiro, R.L.; Freire, M.V.; Bueno, O.F.A. Atualização das normas brasileiras para o International Affective Picture System (IAPS). Rev. Psiquiatr. Rio Gd. Sul 2008, 30, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.; Ribeiro, R.L.; Santos, F.H.; Len, C.A. Classification of the International Affective Picture System (IAPS) images for teenagers of the city of São Paulo. Psychol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.L.; Pompéia, S.; Bueno, O.F.A. Comparison of Brazilian and American norms for the International Affective Picture System (IAPS). Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2005, 27, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.L.; Teixeira-Silva, F.; Pompéia, S.; Bueno, O.F.A. IAPS includes photographs that elicit low-arousal physiological responses in healthy volunteers. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufey Domínguez, M.; Fernández Tapia, A.M.; Mayol Troncoso, R. Adding support to cross-cultural emotional assessment: Validation of the international affective picture system in a chilean sample. Univ. Psychol. 2010, 10, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.P.; Quezada, V.E.; Antivilo, A. Identifying Fear-evoking Pictures from the International Affective Picture System (IAPS) in a Chilean Sample. Ter. Psicol. 2016, 34, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.R. International Affective Picture System (IAPS) in Chile: A cross-cultural adaptation and validation study. Ter. Psicológica 2011, 29, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, D.; Peterson, B.S.; Hu, J.; Cao, L.; Wei, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y.; Hu, S. Affective reactions differ between Chinese and American healthy young adults: A cross-cultural study using the international affective picture system. BMC Psychiatry 2015, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhu, R.; Shen, C.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W. Selecting pure-emotion materials from the International Affective Picture System (IAPS) by Chinese university students: A study based on intensity-ratings only. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Wang, D. Applicability of the International Affective Picture System in Chinese older adults: A validation study: Cross-cultural validity of the IAPS. PsyCh J. 2016, 5, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantiva, C.; Barrera-Valencia, M.; Cadavid-Ruiz, N.; Calderón-Delgado, L.; Gelves-Ospina, M.; Herrera, E.; Mejía-Orduz, M.; Montoya-Arenas, D.; Suárez-Pico, P. Inducción de estados afectivos a través de imágenes. Segunda validación colombiana del Sistema Internacional de Imágenes Afectivas (IAPS). Rev. Latinoam. Psicol. 2019, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Torre, S.B.; Jiménez-Leal, W.; Caicedo Mera, J.C.; Martínez Cotrina, J.; Aponte Canencio, D. Emotional Categorization of the International Affective Picture System in a Colombian Sample. Psykhe 2019, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, C.A.G.; Muñoz, P.G.; Castellar, J.V. Validación colombiana del sistema internacional de imágenes afectivas: Evidencias del origen transcultural de la emoción. Acta Colomb. Psicol. 2011, 14, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Rantanen, A.; Laukka, S.J.; Lehtihalmes, M.; Seppänen, T. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) reflecting from oral reports of negative experience. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 5, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantanen, A.; Siipo, A.; Seppänen, T.; Väyrynen, E.; Lehtihalmes, M.; Laukka, S.J. Heart Rate Variability (HRV) of Male Subjects Related to Oral Reports of Affective Pictures. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 84, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukka, S.J.; Rantanen, A.; Zhao, G.; Taini, M.; Heikkilä, J. Affective pictures and emotion analysis of facial expressions with local binary pattern operator: Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the EHTI’08: The First Finnish Symposium on Emotions and Human-Technology Interaction, Tampere, Finland, 30 May 2008; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Laukka, S.J.; Rantanen, A.; Juntunen, T.; Rinkinen, A.K. Oral reporting of affective pictures related to viewing distance. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 5, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukka, S.J.; Haapala, M. Oral Reporting of Affective Pictures Related to the Viewing Distance: Gender Differences. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 84, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, M.J.; Mühlberger, A.; Kenntner-Mabiala, R.; Pauli, P. Is emotion processing affected by advancing age? An event-related brain potential study. Brain Res. 2006, 1096, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, G.A.; Arntz, A.; Domes, G.; Reiss, N.; Siep, N. Positive erotic picture stimuli for emotion research in heterosexual females. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 190, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, A.; Freund, A.M. Changes in the sensitivity to appetitive and aversive arousal across adulthood. Psychol. Aging 2009, 24, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streubel, B.; Kunzmann, U. Age differences in emotional reactions: Arousal and age-relevance count. Psychol. Aging 2011, 26, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barke, A.; Stahl, J.; Kröner-Herwig, B. Identifying a subset of fear-evoking pictures from the IAPS on the basis of dimensional and categorical ratings for a German sample. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 2012, 43, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grühn, D.; Scheibe, S. Age-related differences in valence and arousal ratings of pictures from the International Affective Picture System (IAPS): Do ratings become more extreme with age? Behav. Res. Methods 2008, 40, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deák, A.; Csenki, L.; Révész, G. Hungarian ratings for the International Affective Picture System (IAPS): A cross-cultural comparison. Empir. Text Cult. Res. 2010, 4, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lohani, M.; Gupta, R.; Srinivasan, N. Cross-Cultural Evaluation of the International Affective Picture System on an Indian Sample. Psychol. Stud. 2013, 58, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon-Singer, H.; Kofman, O.; Tzelgov, J.; Henik, A. Using international emotional picture sets in countries suffering from violence: Using International Emotional Picture Sets. J. Trauma. Stress 2011, 24, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, D.; Masumoto, K.; Sato, S.; Gondo, Y. Age-Related Differences in the International Affective Picture System (IAPS) Valence and Arousal Ratings among Japanese Individuals. Exp. Aging Res. 2019, 45, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mačiukaitė, L.; Kuzinas, A.; Rukšėnas, O. The universality of the international affective picture system: Ratings from a sample of Lithuanian students. Int. J. Psychol. Biopsychosoc. Approach 2015, 16, 111–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.A.; Reza, F. Rating of Affective Pictures of Low and High Arousal Domain among Malaysian Population. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2017, 7, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chayo-Dichy, R.; García, A.E.V.; García, N.A.; Castillo-Parra, G.; Ostrosky-Solis, F. Valencia, activación, dominancia y contenido moral, ante estímulos visuales con contenido emocional y moral: Un estudio en población mexicana. Rev. Esp. Neuropsicol. 2003, 5, 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Parra, G.; De Jesús, A.I.; Ostrosky-Solís, J.; Ostrosky-Solís, F. Valencia, Activación y Tiempos de Reacción ante Estímulos Visuales con Contenido Emocional: Un Estudio en Población Mexicana. [Affective valence, arousal and reaction time: A study with Mexican population.]. Rev. Mex. Psicol. 2002, 19, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Romo-González, T.; González-Ochoa, R.; Gantiva, C.; Campos-Uscanga, Y. Valores normativos del sistema internacional de imágenes afectivas en población mexicana: Diferencias entre Estados Unidos, Colombia y México. Univ. Psychol. 2018, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandadi, L.; Chamkal, N.; Ahami, A.O.T. Rating of the valence of twenty negatives images from IAPS by a sample of Moroccan nurse students. Acta Neuropsychol. 2020, 18, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandadi, L.; Chamkal, N.; Ahami, A. Effect of Clinical Traineeship on the Emotional Dimensions (Valence and Arousal) among Nurses Student. Int. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. J. 2018, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.P.; Pinheiro, A.P.; Costa, A.; Frade, C.S.; Comesaña, M.; Pureza, R. Adaptation of the International Affective Picture System (IAPS) for European Portuguese. Behav. Res. Methods 2015, 47, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabovac, B.; Deák, A. Validation of the International Affective Picture System (IAPS) in Serbia: Comparison of a Serbian and a Hungarian Sample. Primenj. Psihol. 2019, 12, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestadt, A.E.; Kantor, K.; Thomas, K.G.F.; Lipinska, G. A South African adaptation of the international affective picture system: The influence of socioeconomic status and education level on picture ratings. Behav. Res. Methods 2022, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, O.S.; Kim, M.J.; Ryu, Y.H.; Park, J.E. Is heart rate variability (HRV) an adequate tool for evaluating human emotions?—A focus on the use of the International Affective Picture System (IAPS). Psychiatry Res. 2017, 251, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Scheibe, S.; Samanez-Larkin, G.R.; Tsai, J.L.; Carstensen, L.L. Replicating the positivity effect in picture memory in Koreans: Evidence for cross-cultural generalizability. Psychol. Aging 2009, 24, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, J.; Sánchez, M.; Ramírez, I.; Fernández, M.C.; Cobos, P.; Rodríguez, S.; Muñoz, M.A.; Tormo, M.P.; Herrero, M.; Segarra, P.; et al. El Sistema Internacional de Imágenes Afectivas (IAPS): Adaptación española: II. [The International Affective Picture System (IAPS): Spanish adaptation: II.]. Rev. Psicol. Gen. Apl. 2001, 54, 635–657. [Google Scholar]
- Javela, J.J.; Mercadillo, R.E.; Ramírez, J.M. Anger and Associated Experiences of Sadness, Fear, Valence, Arousal, and Dominance Evoked by Visual Scenes. Psychol. Rep. 2008, 103, 663–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moltó, J.; Montañés, S.; Poy, R.; Segarra, P.; Ramírez, I.; Hernández, M.; Sánchez, M.; Fernández, M.; Vila, J. Un método para el estudio experimental de las emociones: El International Affective Picture System (IAPS). Adaptación española. Rev. Psicol. Gen. Apl. Rev. Fed. Esp. Asoc. Psicol. 1999, 52, 55–87. [Google Scholar]
- Moltó, J.; Segarra, P.; López, R.; Esteller, A.; Fonfría, A.; Pastor, M.C.; Poy, R. Adaptación eapañola del “International Affective Picture System” (IAPS). Tercera parte. An. Psicol. 2013, 29, 965–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluja, A.; Rossier, J.; Blanch, A.; Blanco, E.; Martí-Guiu, M.; Balada, F. Personality effects and sex differences on the International Affective Picture System (IAPS): A Spanish and Swiss study. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2015, 77, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tok, S.; Koyuncu, M.; Dural, S.; Catikkas, F. Evaluation of International Affective Picture System (IAPS) ratings in an athlete population and its relations to personality. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2010, 49, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, C.; van Goozen, S.; Goodyer, I. Children’s subjective emotional reactivity to affective pictures: Gender differences and their antisocial correlates in an unselected sample of 7-11-year-olds. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2006, 47, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManis, M.H.; Bradley, M.M.; Berg, W.K.; Cuthbert, B.N.; Lang, P.J. Emotional reactions in children: Verbal, physiological, and behavioral responses to affective pictures. Psychophysiology 2001, 38, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.P.; Hillman, C.H.; Duley, A.R. Influences of Age on Emotional Reactivity During Picture Processing. J. Gerontol. Ser. Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2005, 60, P49–P56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson Davis, W.; Rahman, M.A.; Smith, L.J.; Burns, A.; Senecal, L.; McArthur, D.; Halpern, J.A.; Perlmutter, A.; Sickels, W.; Wagner, W. Properties of human affect induced by static color slides (IAPS): Dimensional, categorical and electromyographic analysis. Biol. Psychol. 1995, 41, 229–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libkuman, T.M.; Otani, H.; Kern, R.; Viger, S.G.; Novak, N. Multidimensional normative ratings for the International Affective Picture System. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenivesse, C.; Chan, P.Y.; Tsai, H.W.; Wheeler-Hegland, K.; Silverman, E.; von Leupoldt, A.; Similowski, T.; Davenport, P. Negative emotional stimulation decreases respiratory sensory gating in healthy humans. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2014, 204, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backs, R.W.; da Silva, S.P.; Han, K. A Comparison of Younger and Older Adults’ Self-Assessment Manikin Ratings of Affective Pictures. Exp. Aging Res. 2005, 31, 421–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.A.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Lang, P.J. Eliciting Affect Using the International Affective Picture System: Trajectories through Evaluative Space. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 1998, 24, 855–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikels, J.A.; Fredrickson, B.L.; Larkin, G.R.; Lindberg, C.M.; Maglio, S.J.; Reuter-Lorenz, P.A. Emotional category data on images from the international affective picture system. Behav. Res. Methods 2005, 37, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reminger, S.L.; Kaszniak, A.W.; Dalby, P.R. Age-Invariance in the Asymmetry of Stimulus-Evoked Emotional Facial Muscle Activity. Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2000, 7, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, M.; Canli, T.; English, T.; Whitfield, S.; Wais, P.; Ochsner, K.; John, D.G.; Carstensen, L.L. Amygdala Responses to Emotionally Valenced Stimuli in Older and Younger Adults. Psychol. Sci. 2004, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.; Sinha, V.K. Event-related potential: An overview. Ind. Psychiatry J. 2009, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polich, J. Updating P300: An integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2128–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, P.W.; Friedman, W.A.; Thompson, F.; Franzen, O. Respiratory-related cortical potentials evoked by inspiratory occlusion in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 60, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Leupoldt, A.; Keil, A.; Chan, P.Y.S.; Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J.; Davenport, P.W. Cortical sources of the respiratory-related evoked potential. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010, 170, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radloff, L.S. The CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 1977, 1, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K.; Kivlahan, D.R.; McDonell, M.B.; Fihn, S.D.; Bradley, K.A.; Ambulatory Care Quality Improvement Project. The AUDIT alcohol consumption questions (AUDIT-C): An effective brief screening test for problem drinking. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertesz, A. Western Aphasia Battery Test Manual; Psychological Corporation: Woodland Hills, CA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Frick, P.J.; Hare, R.D. Antisocial process screening device. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Ward, C.H.; Mendelson, M.; Mock, J.; Erbaugh, J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, K.I. Clock-drawing: Is it the ideal cognitive screening test? Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2000, 15, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-IV; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, H.A. The drug abuse screening test. Addict. Behav. 1982, 7, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslow, T.; Arolt, V.; Junghanns, K. Differential validity of the questionnaire for experiences of attention deficit: Concurrent validation results of schizophrenic and depressive patients. Z. Klin. Psychol. Psychiatr. Psychother. 1998, 46, 152–165. [Google Scholar]
- Somer, O.; Korkmaz, M.; Tatar, A. Development of five factor personality inventory. Turk. J. Psychol. 2002, 17, 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, F.R.; Carstensen, L.L. Time counts: Future time perspective, goals, and social relationships. Psychol. Aging 2002, 17, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesavage, J.A.; Brink, T.L.; Rose, T.L.; Lum, O.; Huang, V.; Adey, M.; Leirer, V.O. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: A preliminary report. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1982, 17, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachinski, V.C.; Iliff, L.D.; Zilhka, E.; Du Boulay, G.H.; McAllister, V.L.; Marshall, J.; Russell, R.W.R.; Symon, L. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch. Neurol. 1975, 32, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eysenck, S.B.; Eysenck, H.J. Impulsiveness and venturesomeness: Their position in a dimensional system of personality description. Psychol. Rep. 1978, 43, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.P.; Brody, E.M. Assessment of older people: Self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist 1969, 9, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahler, H. Wahler Physical Symptom Checklist (WPSI); WPS: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Yeom, T.; Park, Y.; Oh, K.; Lee, Y. Korean version Wechsler adult intelligence scale. Seoul Korean Guid. 1992, 4, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B. The Patient Health Questionnaire-2: Validity of a two-item depression screener. Med. Care 2003, 41, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, R.P.; Gusman, D. The primary care PTSD screen (PC-PTSD): Development and operating characteristics. Prim. Care Psychiatry 2003, 9, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, D.; Clark, L.A.; Tellegen, A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1988, 54, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.; Clark, L.A. The PANAS-X: Manual for the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule-Expanded Form; University of Iowa: Iowa City, IA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zung, W.W. A self-rating depression scale. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1965, 12, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrubia, R.; Avila, C.; Moltó, J.; Caseras, X. The Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire (SPSRQ) as a measure of Gray’s anxiety and impulsivity dimensions. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2001, 31, 837–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, E. A short portable mental status questionnaire for the assessment of organic brain deficit in elderly patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1975, 23, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielberger, C.D. Manual for the State-Trait Anxietry, Inventory; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, R. Psychometric properties of the strengths and difficulties questionnaire. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2001, 40, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenhuis, R.E.; Bryden, M. Different dimensions of hand preference that relate to skilled and unskilled activities. Cortex 1989, 25, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale–Third Edition (WAIS-III) [Database Record]; APA PsycTests; APA: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.H.; Metzler, P. Wortschatztest [Vocabulary Test]; Beltz Test: Weinheim, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, M.; Kuhlman, D.M.; Joireman, J.; Teta, P.; Kraft, M. A comparison of three structural models for personality: The big three, the big five, and the alternative five. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1993, 65, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Unmasking the Face: A Guide to Recognizing Emotions from Facial Clues; Prentice-Hall: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Population Reference Bureau. Global Aging and the Demographic Divide; Population Reference Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, G.; Cope, C.; Michalski, D.; Christidis, P.; Lin, L.; Conroy, J. Data Point: Women Outnumber Men in Psychology Graduate Programs. Monit. Psychol. 2018, 49, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen, L.L.; Pasupathi, M.; Mayr, U.; Nesselroade, J.R. Emotional experience in everyday life across the adult life span. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2000, 79, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, S.T.; Mather, M.; Carstensen, L.L. Aging and emotional memory: The forgettable nature of negative images for older adults. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2003, 132, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, M.; Carstensen, L.L. Aging and motivated cognition: The positivity effect in attention and memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.M.; Codispoti, M.; Cuthbert, B.N.; Lang, P.J. Emotion and motivation I: Defensive and appetitive reactions in picture processing. Emotion 2001, 1, 276–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvat, M.; Kukolja, D.; Ivanec, D. Comparing affective responses to standardized pictures and videos: A study report. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.07398. [Google Scholar]
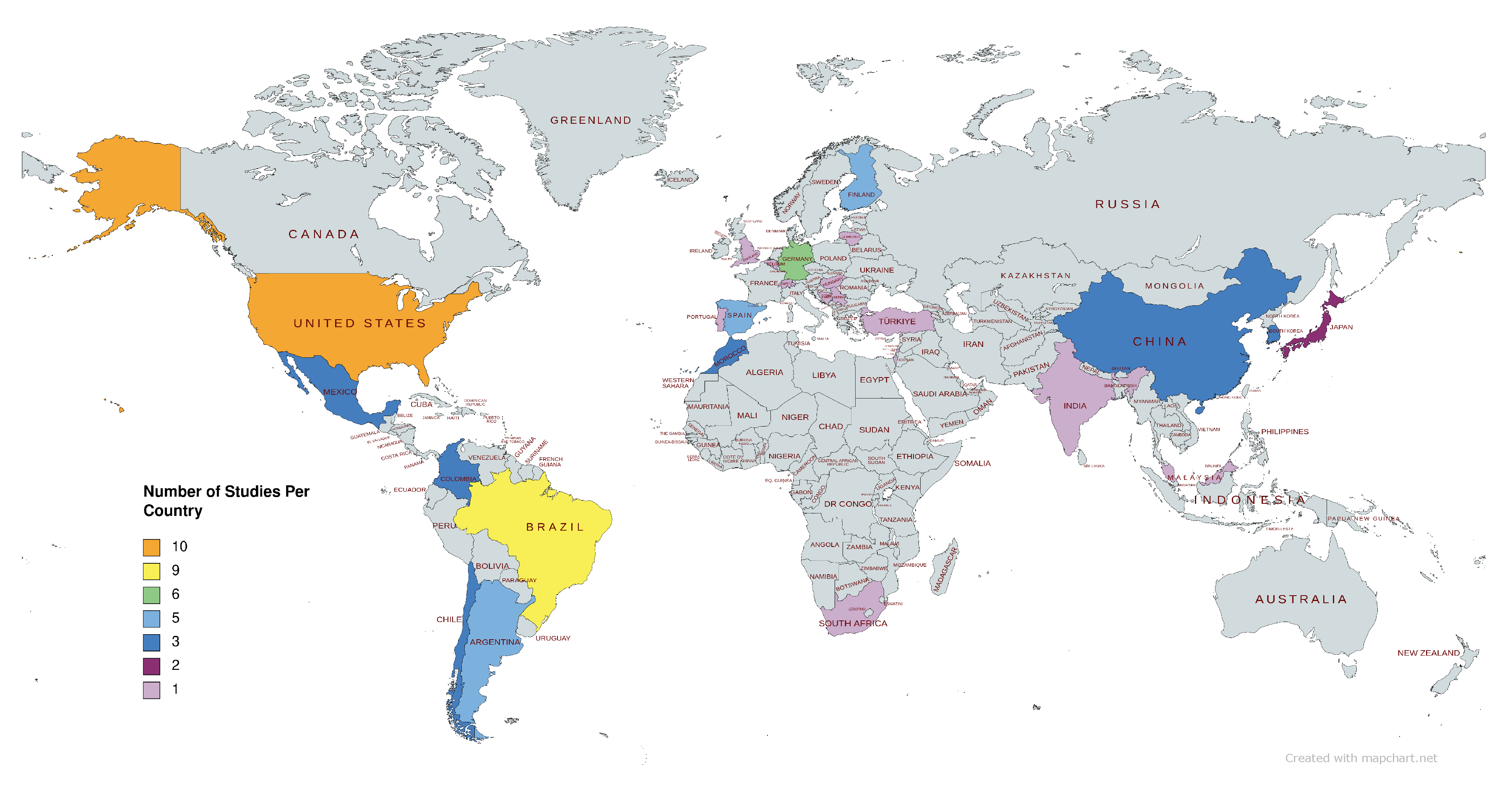
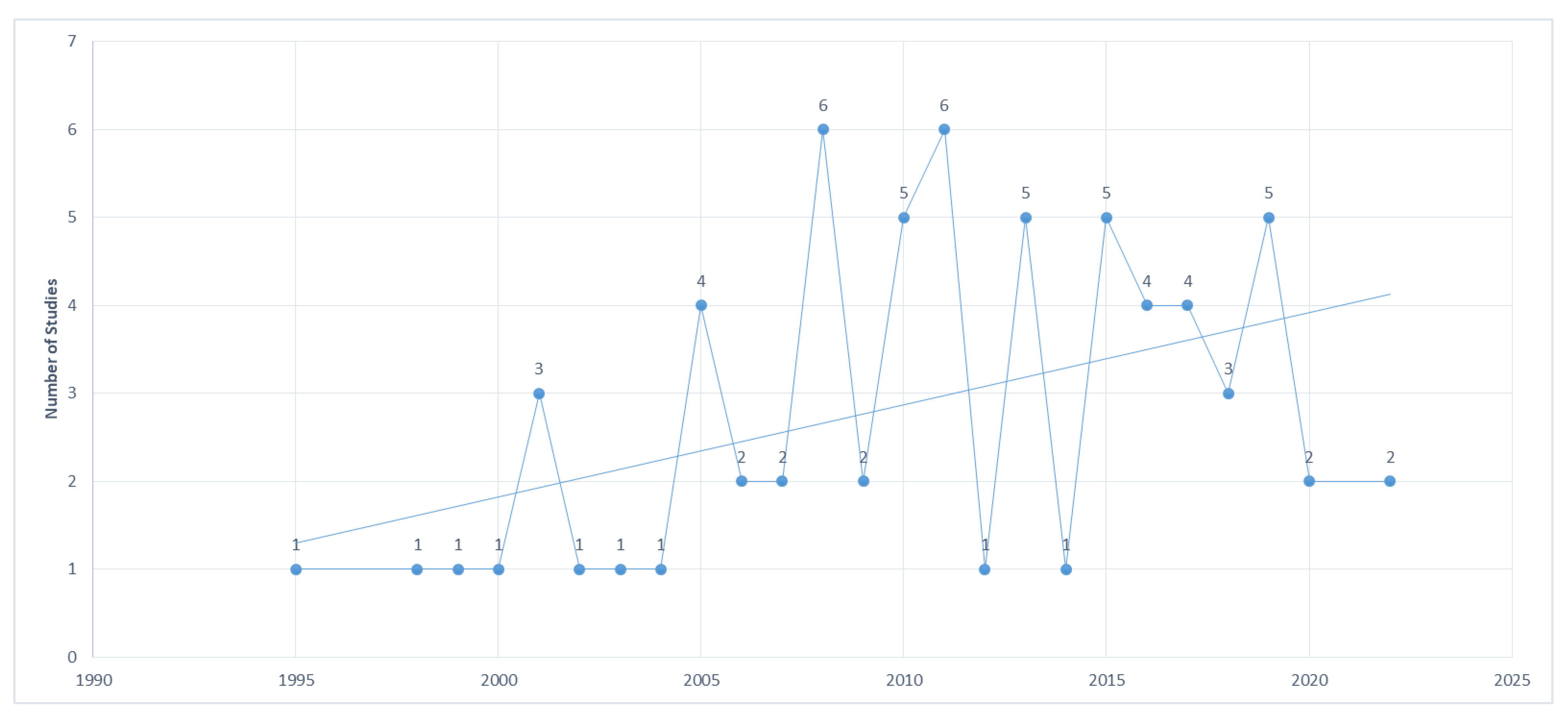

| Country | Reference | Valence | Arousal | Dominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belgium | [51] | N.D. | N.D. | Lower |
| Bosnia | [52] | N.D. | Higher | N.D. |
| Brazil | [54,60] | N.D. | Higher | N.D. |
| Brazil | [56,57] | N.D. | N.D. | - |
| Chile | [62] | Lower | Higher | - |
| Chile | [64] | N.D. | Lower | Higher |
| China | [65] | Lower | Higher | - |
| Colombia | [68] | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Colombia | [70] | N.D. | Higher | Higher |
| Germany | [80] | N.D. | Lower | - |
| Hungary | [82] | N.D. | N.D. | Higher |
| India | [83] | N.D. | Higher | Higher |
| Israel | [84] | Lower | N.D. | - |
| Lithuania | [86] | N.D. | Lower | N.D. |
| Malaysia | [87] | N.D. | Higher | N.D. |
| Mexico | [89] | N.D. | N.D. | - |
| Mexico | [90] | Higher | Lower | Higher |
| Morocco | [91,92] | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Portugal | [93] | Lower | Higher | Lower |
| Serbia | [94] | N.D. | Higher | N.D. |
| Republic of Korea | [97] | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Spain | [98,100,101] | N.D. | Higher | Lower |
| Spain | [99] | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Turkey | [103] | N.D. | N.D. | - |
| United States | [108] | N.D. | Lower | - |
| Country | Reference | Instruments |
|---|---|---|
| Brazil | [56] | IADL, HIS, CDT |
| Brazil | [57] | IADL, HIS |
| China | [67] | CDT, GDS |
| Finland | [71] | STAI, TAS-20 |
| Finland | [72] | STAI, TAS-20 |
| Finland | [73] | STAI, TAS-20 |
| Finland | [74] | STAI, TAS-20 |
| Finland | [75] | STAI, TAS-20 |
| Germany | [76] | SDS, MMSE, FEDA, PANAS |
| Germany | [78] | MMSE, STAI, WAIS |
| Germany | [79] | PANAS-X |
| Germany | [81] | WAIS, WST, PANAS |
| South Africa | [95] | PHQ-9, PC-PTSD, AUDIT-C, DAST-10 |
| Republic of Korea | [97] | K-WAIS, K-WPSI, CES–D, PANAS, FTP |
| Spain | [102] | ZKPQ, IVE, SPSRQ |
| Turkey | [103] | FFPI |
| UK | [104] | SDQ, APSD, Questionnaires based on DSM |
| US | [106] | BDI, MMSE |
| US | [109] | STAI |
| US | [113] | WHD, MMSE, BDI |
| US | [114] | SHPMSQ, WAIS, ANT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Branco, D.; Gonçalves, Ó.F.; Badia, S.B.i. A Systematic Review of International Affective Picture System (IAPS) around the World. Sensors 2023, 23, 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083866
Branco D, Gonçalves ÓF, Badia SBi. A Systematic Review of International Affective Picture System (IAPS) around the World. Sensors. 2023; 23(8):3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083866
Chicago/Turabian StyleBranco, Diogo, Óscar F. Gonçalves, and Sergi Bermúdez i Badia. 2023. "A Systematic Review of International Affective Picture System (IAPS) around the World" Sensors 23, no. 8: 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083866
APA StyleBranco, D., Gonçalves, Ó. F., & Badia, S. B. i. (2023). A Systematic Review of International Affective Picture System (IAPS) around the World. Sensors, 23(8), 3866. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23083866







