RF-EMF Exposure near 5G NR Small Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
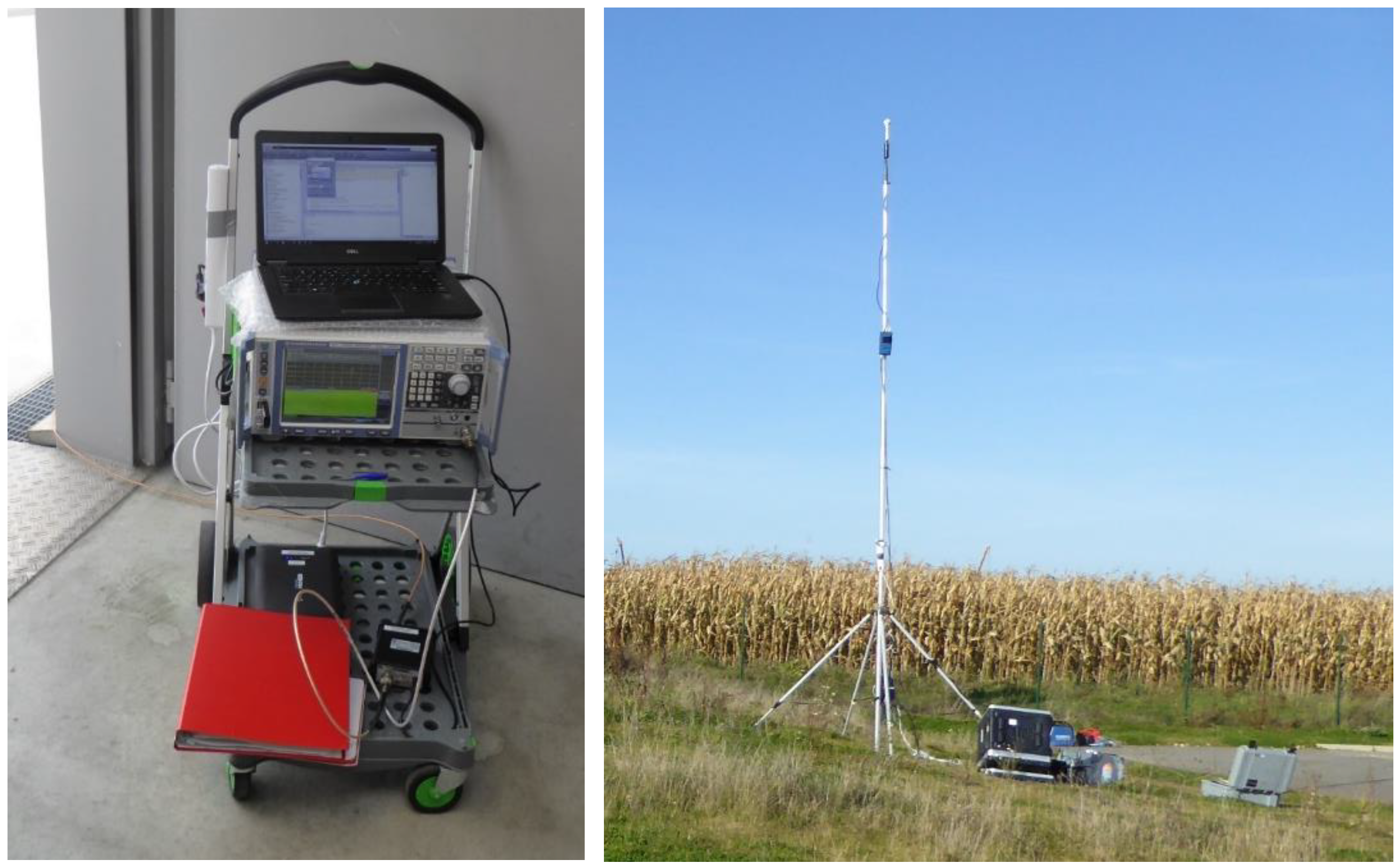
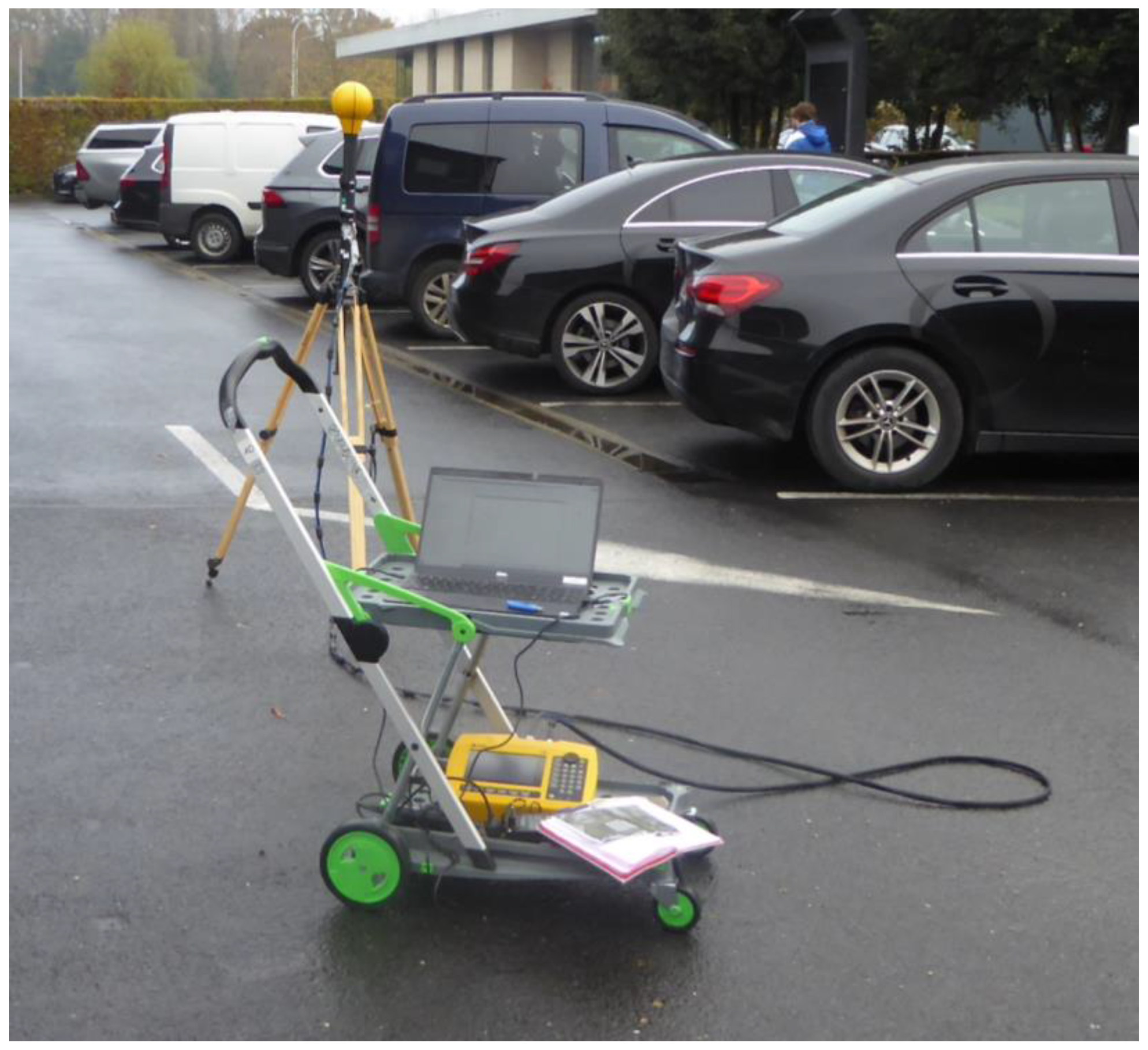
2.1. Measurement Equipment
2.2. Measurement Method
2.3. 5G NR Base Station Sites
2.4. Typical Exposures
2.4.1. The Worst-Case User
2.4.2. The Typical User
2.4.3. The Non-User
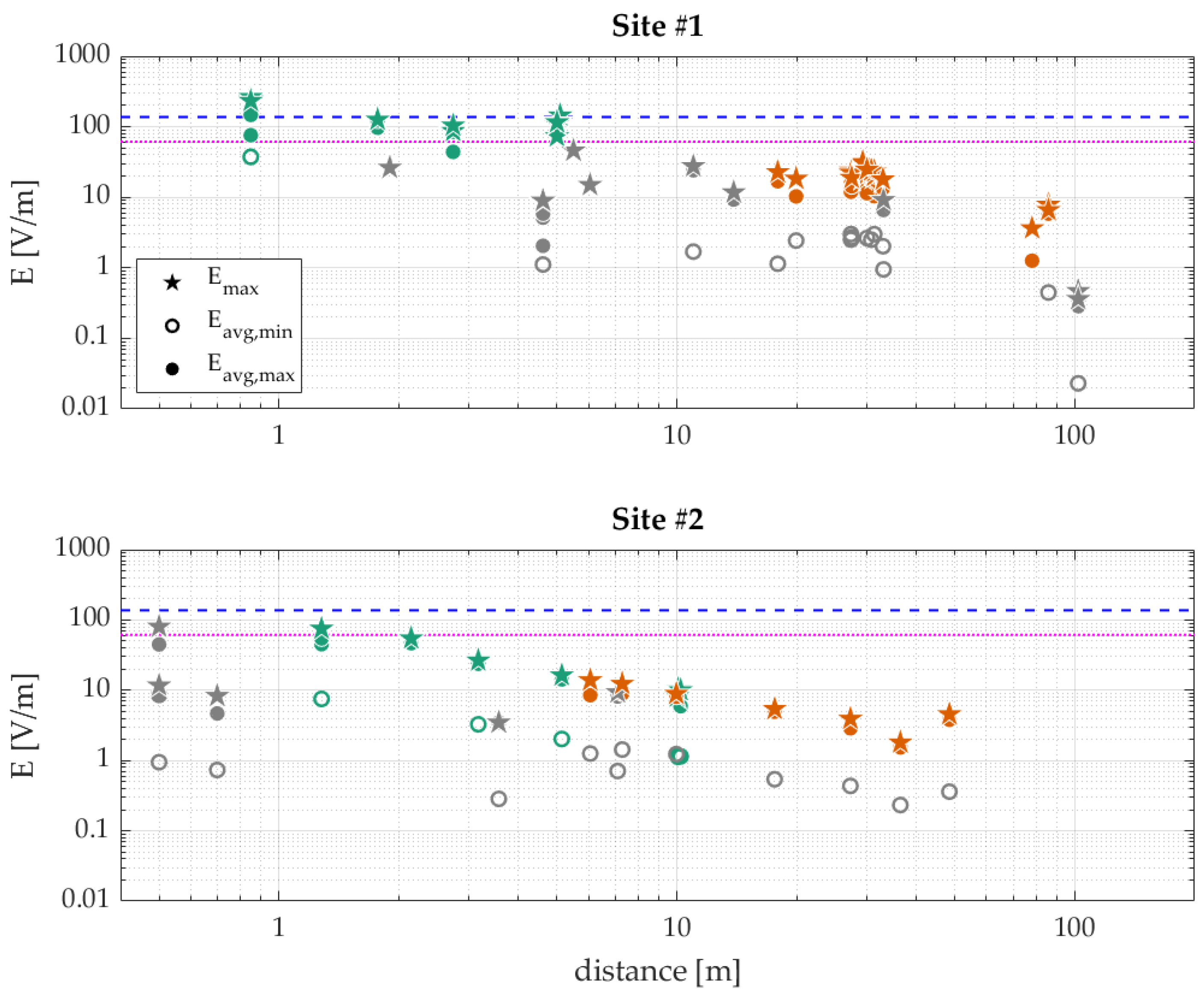
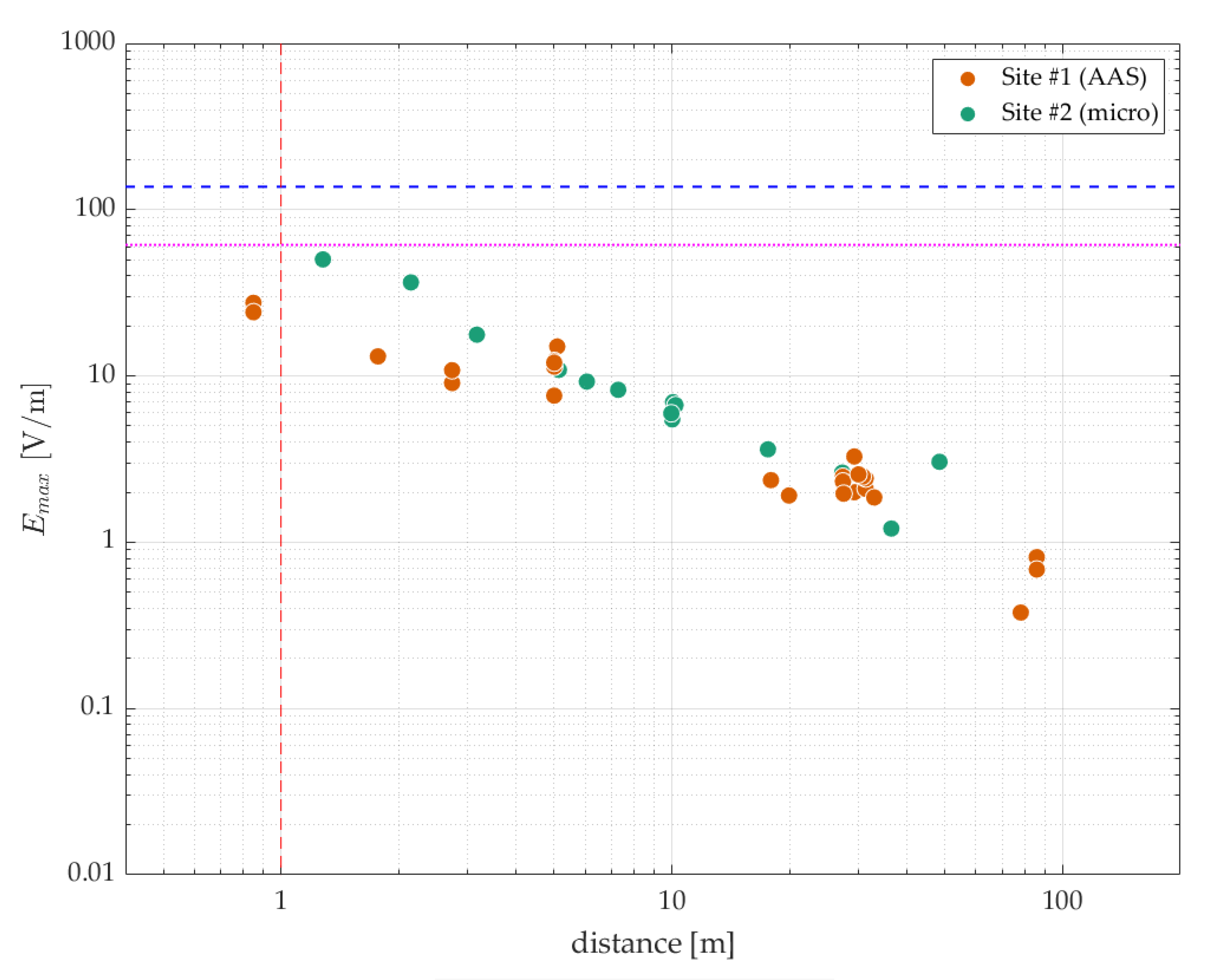
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). TS 45.022 V15.0.0 [2018-06], GSM/EDGE Radio Link Management in Hierarchical Networks. Available online: http://www.3gpp.org/ftp//Specs/archive/45_series/45.022/45022-f00.zip (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- IEC 62232:2022; Determination of RF Field Strength, Power Density and SAR in the Vicinity of Base Stations for the Purpose of Evaluating Human Exposure. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Forge, S.; Horvitz, R.; Blackman, C.; Bohlin, E. Light Deployment Regime for Small-Area Wireless Access Points (SAWAPs), A Study Prepared for the European Commission; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursianis, A.; Vanias, P.; Samaras, T. Measurements for Assessing the Exposure from 3G Femtocells. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2012, 150, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Plets, D.; Thielens, A.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Impact of a Small Cell on the RF-EMF Exposure in a Train. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 2639–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Plets, D.; Verloock, L.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Assessment and Comparison of Total RF-EMF Exposure in Femtocell and Macrocell Base Station Scenarios. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 162, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wyk, M.J.; Visser, J.C.; Le Roux, C.W. Measurement of EMF exposure around small cell base station sites. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2019, 184, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA). Electromagnetic Energy (EME) Measurements Near Small Cell Base Stations. 2020. Available online: https://www.acma.gov.au/sites/default/files/2020-07/EME-measurements-near-small-cell-base-stations.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- El-Hajj, A.M.; Naous, T. Radiation Analysis in a Gradual 5G Network Deployment Strategy. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 3rd 5G World Forum (5GWF), Bangalore, India, 10–12 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aerts, S.; Verloock, L.; Van Den Bossche, M.; Colombi, D.; Martens, L.; Tornevik, C.; Joseph, W. In-Situ Measurement Methodology for the Assessment of 5G NR Massive MIMO Base Station Exposure at Sub-6 GHz Frequencies. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 184658–184667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adda, S.; Aureli, T.; D’Elia, S.; Franci, D.; Grillo, E.; Migliore, M.D.; Pavoncello, S.; Schettino, F.; Suman, R. A Theoretical and Experimental Investigation on the Measurement of the Electromagnetic Field Level Radiated by 5G Base Stations. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 101448–101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaraviglio, L.; Lodovisi, C.; Franci, D.; Pavoncello, S.; Aureli, T.; Blefari-Melazzi, N.; Alouini, M.S. Massive Measurements of 5G Exposure in a Town: Methodology and Results. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021, 2, 2029–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprez, K.; Verloock, L.; Colussi, L.; Aerts, S.; Van den Bossche, M.; Kamer, J.; Bolte, J.; Martens, L.; Plets, D.; Joseph, W. In-situ 5G NR base station exposure of the general public: Comparison of assessment methods. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2022, 198, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qahtan Wali, S. RF-EMF Measurement for 5G over C-Band and Mm-Wave Frequency Band: Exposure Assessment and Procedures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1254, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombi, D.; Ghasemifard, F.; Joshi, P.; Xu, B.; Paola, C.D.; Tornevik, C. Methods and Practices for In Situ Measurements of RF EMF Exposure from 5G Millimeter Wave Base Stations. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2022, 64, 1986–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, M.D.; Franci, D.; Pavoncello, S.; Aureli, T.; Merli, E.; Lodovisi, C.; Chiaraviglio, L.; Schettino, F. Application of the Maximum Power Extrapolation Procedure for Human Exposure Assessment to 5G Millimeter Waves: Challenges and Possible Solutions. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 103438–103446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP). Guidelines for Limiting Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 2020, 118, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, S.; Deprez, K.; Colombi, D.; Van den Bossche, M.; Verloock, L.; Martens, L.; Törnevik, C.; Joseph, W. In Situ Assessment of 5G NR Massive MIMO Base Station Exposure in a Commercial Network in Bern, Switzerland. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhantsov, S.; Thielens, A.; Aerts, S.; Verloock, L.; Torfs, G.; Martens, L.; Demeester, P.; Joseph, W. Ray-Tracing-Based Numerical Assessment of the Spatiotemporal Duty Cycle of 5G Massive MIMO in an Outdoor Urban Environment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, I.; Blackman, C.; Chamberlin, K.; DeSalles, A.; Dasdag, S.; Fernández, C.; Hardell, L.; Héroux, P.; Kelley, E.; Kesari, K.; et al. Scientific evidence invalidates health assumptions underlying the FCC and ICNIRP exposure limit determinations for radiofrequency radiation: Implications for 5G. Environ. Health 2022, 21, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Class | EIRP [dBm] | Product Installation Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| E2 | ≤33 | […] Compliance with the exposure limits is generally obtained at zero distance or within a few centimeters. |
| E10 | ≤40 | […] the lowest radiating part of the antenna(s) is at a minimum height of 2.2 m above the general public walkway. |
| E100 | ≤50 | […] (a) the lowest radiating part of the antenna(s) is at a minimum height of 2.5 m above the general public walkway; (b) the minimum distance to areas accessible to the general public in the main lobe direction is Dm; (c) there are no pre-existing RF sources with EIRP above 10 W installed within a distance of 5 Dm meters in the main lobe direction (as determined by considering the half power beam width) and within Dm meters in other directions. If Dm is not available, a value of 2 m can be used or 1 m if all product transmit frequencies are equal to or above 1500 MHz. |
| E+ | >50 | […] |
| Site #1 | Site #2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency band | n78 (FR1) | n78 (FR1) |
| Channel center frequency | 3.775 GHz | 3.430 GHz |
| Channel bandwidth | 50 MHz | 40 MHz |
| Subcarrier spacing | 30 kHz | 30 kHz |
| Maximum number of resource blocks (NRB) | 133 | 106 |
| Number of antenna elements (per polarization) | 96 | 4 |
| MIMO | 64T64R | 4T2R |
| Advanced Antenna System (AAS)? | Yes | No |
| Transmit power | 49.7 dBm (92.5 W) | 43 dBm (20 W) |
| Maximum gain (array gain + antenna element gain) | 25 dBi | 10.5 dBi |
| EIRP | 74.7 dBm (29.5 kW) | 53.5 dBm (112 W) |
| Height | 5.5 m | 4.5 m |
| Size of radio unit | 795 mm × 470 mm × 190 mm | 295 mm × 270 mm × 20 mm |
| Technology duty cycle factor (fTDC) | 0.743 | 0.743 |
| Variable | Site #1 | Site #2 |
|---|---|---|
| Number of active users | 10 | 10 |
| Typical usage (connection time) | 10 s | 10 s |
| Number of antenna elements | 100 | 4 |
| MaMIMO/beamforming scheme | Codebook ‘grid of beams’ | n/a |
| DCsite,95 | 0.20 | 0.96 |
| User Type | Electric-Field Level E (V/m) and Exposure Ratio R (-) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workers | General Public | |||
| AAS | E100 (1) | AAS | E100 | |
| Worst-case user (maximum exposure, with base station at maximized downlink traffic capacity) | 21.6 (0.03) | 30.0 (0.05) | 12.8 (0.04) | 36.6 (0.36) |
| Worst-case user (worst-case exposure, extrapolated Emax) | 27.5 (0.04) | 53.6 (0.15) | 13.1 (0.05) | 50.8 (0.68) |
| Typical user (performing a video call) | 7.8 (0.003) | 16.5 (0.02) | 4.2 (0.005) | 15.5 (0.06) |
| Non-user without other users (no induced downlink traffic, Eavg,min) | 3.9 (0.0008) | 5.7 (0.002) | 2.4 (0.002) | 5.0 (0.007) |
| Non-user in mature network (based on maximum exposure, with base station at maximized downlink traffic capacity, and a 95th percentile spatiotemporal duty cycle to account for spatiotemporal dispersion of power) | 9.7 (0.005) | 29.4 (0.05) | 5.7 (0.009) | 35.9 (0.34) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aerts, S.; Deprez, K.; Verloock, L.; Olsen, R.G.; Martens, L.; Tran, P.; Joseph, W. RF-EMF Exposure near 5G NR Small Cells. Sensors 2023, 23, 3145. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063145
Aerts S, Deprez K, Verloock L, Olsen RG, Martens L, Tran P, Joseph W. RF-EMF Exposure near 5G NR Small Cells. Sensors. 2023; 23(6):3145. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063145
Chicago/Turabian StyleAerts, Sam, Kenneth Deprez, Leen Verloock, Robert G. Olsen, Luc Martens, Phung Tran, and Wout Joseph. 2023. "RF-EMF Exposure near 5G NR Small Cells" Sensors 23, no. 6: 3145. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063145
APA StyleAerts, S., Deprez, K., Verloock, L., Olsen, R. G., Martens, L., Tran, P., & Joseph, W. (2023). RF-EMF Exposure near 5G NR Small Cells. Sensors, 23(6), 3145. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063145








