ECG Classification Using an Optimal Temporal Convolutional Network for Remote Health Monitoring
Abstract
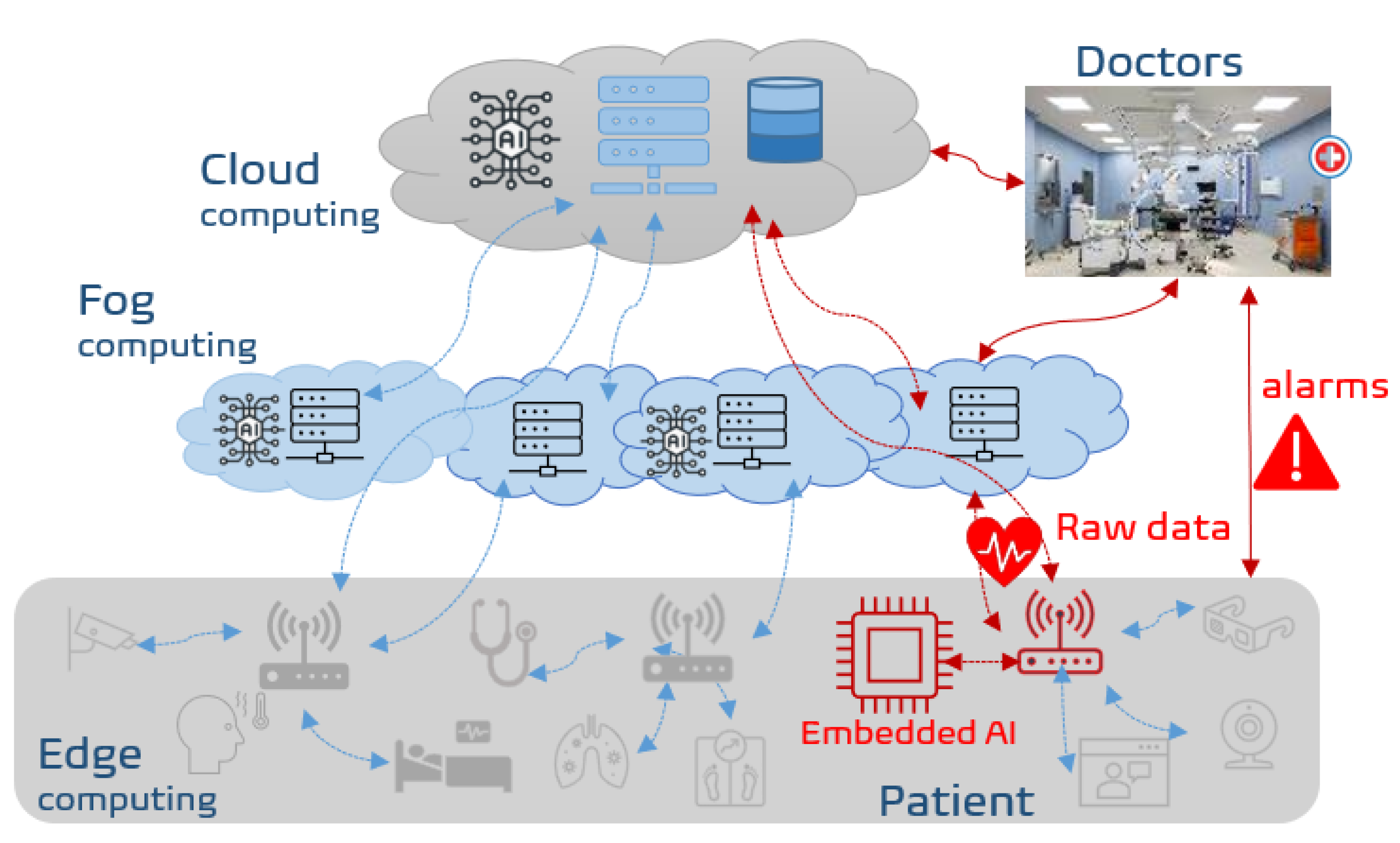
:1. Introduction
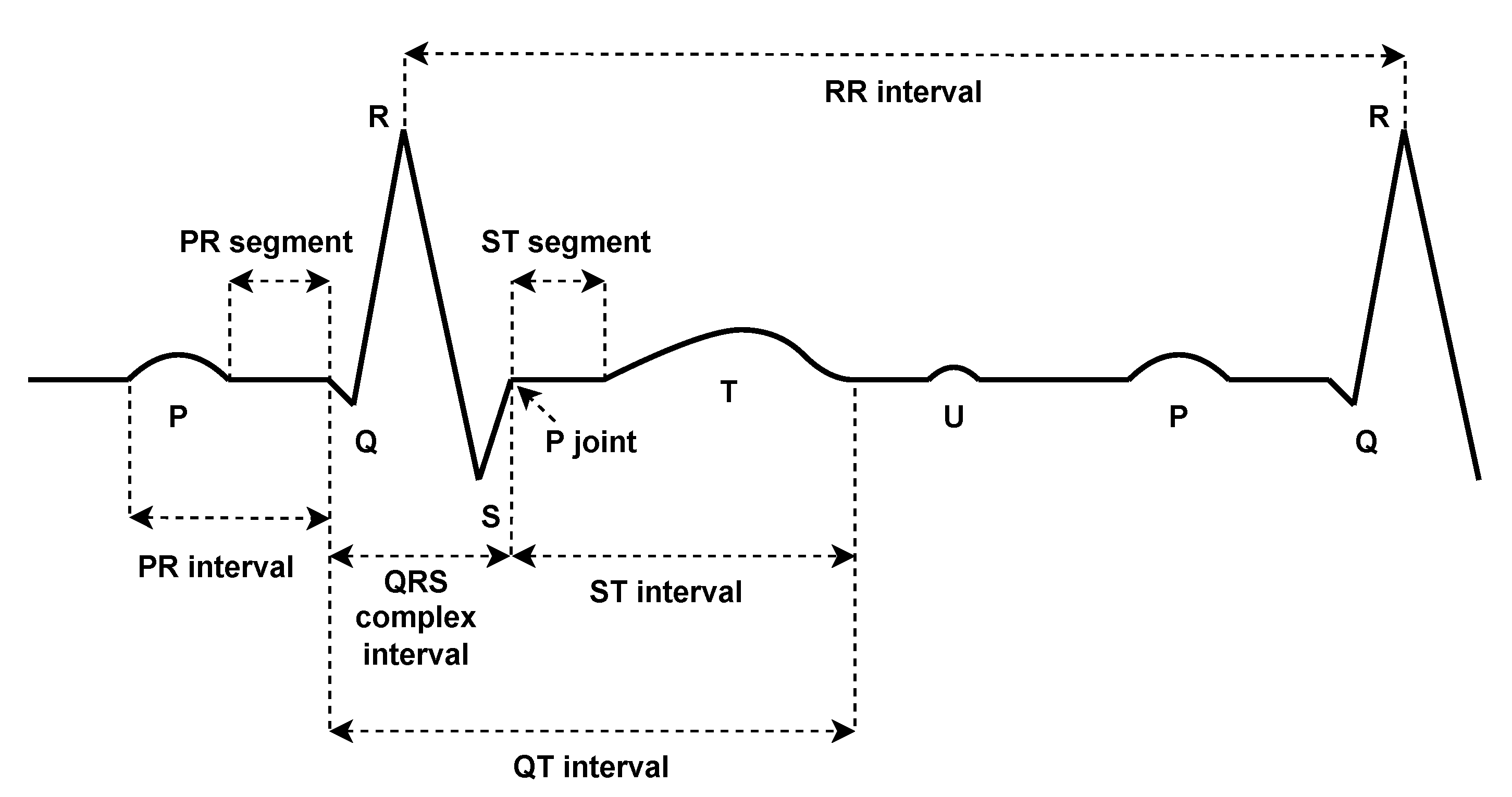
2. Background and Related Work
3. Method
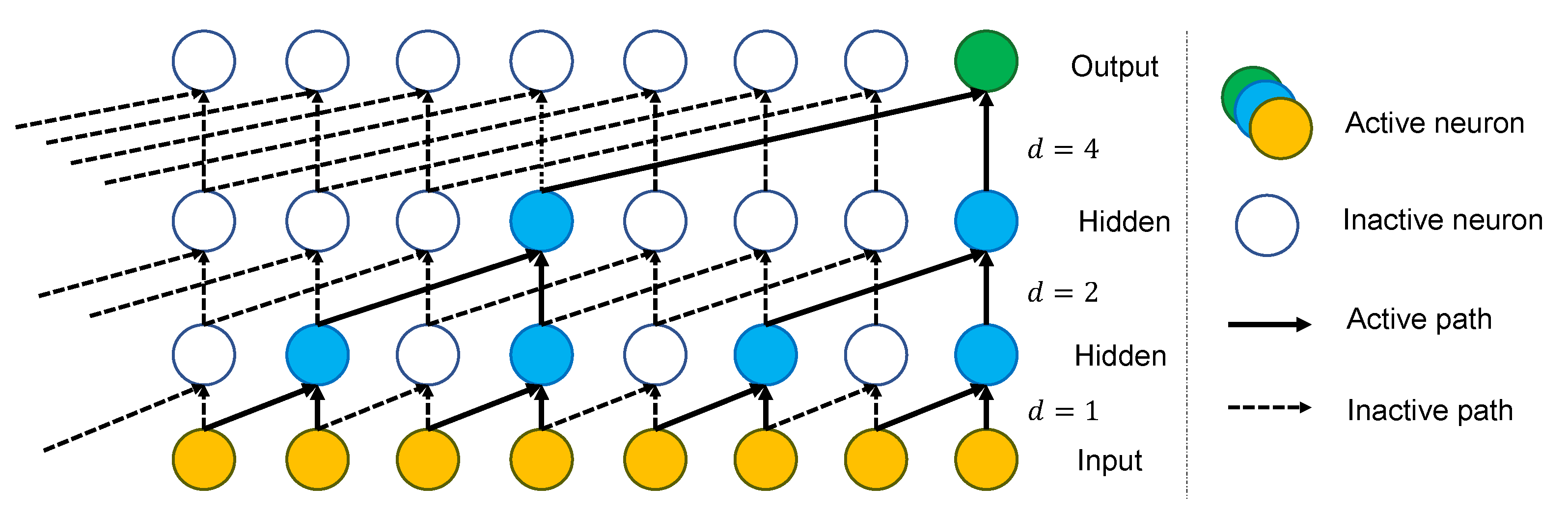
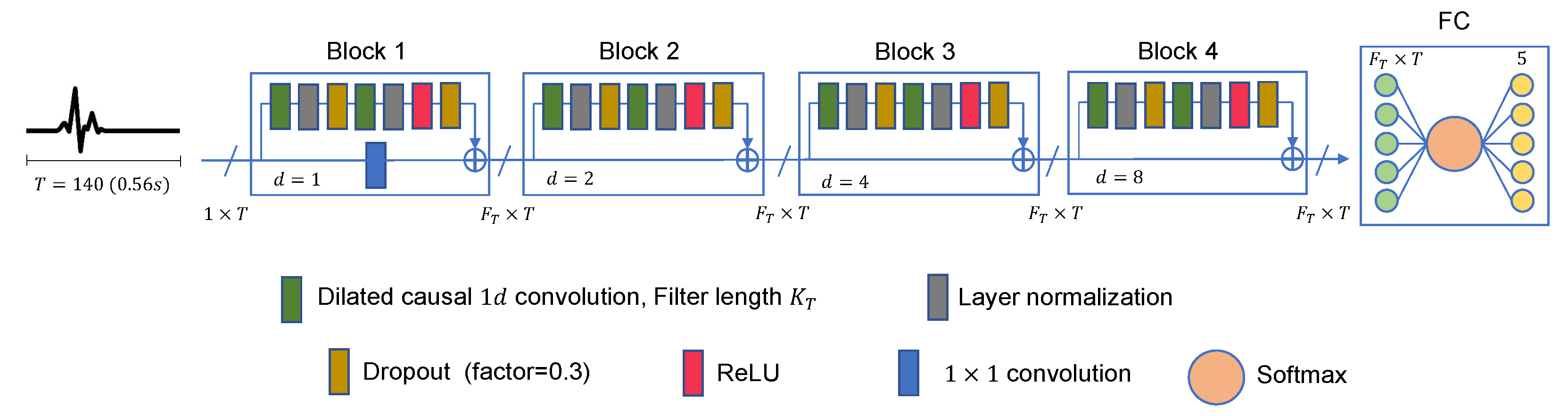
3.1. Proposed Architecture
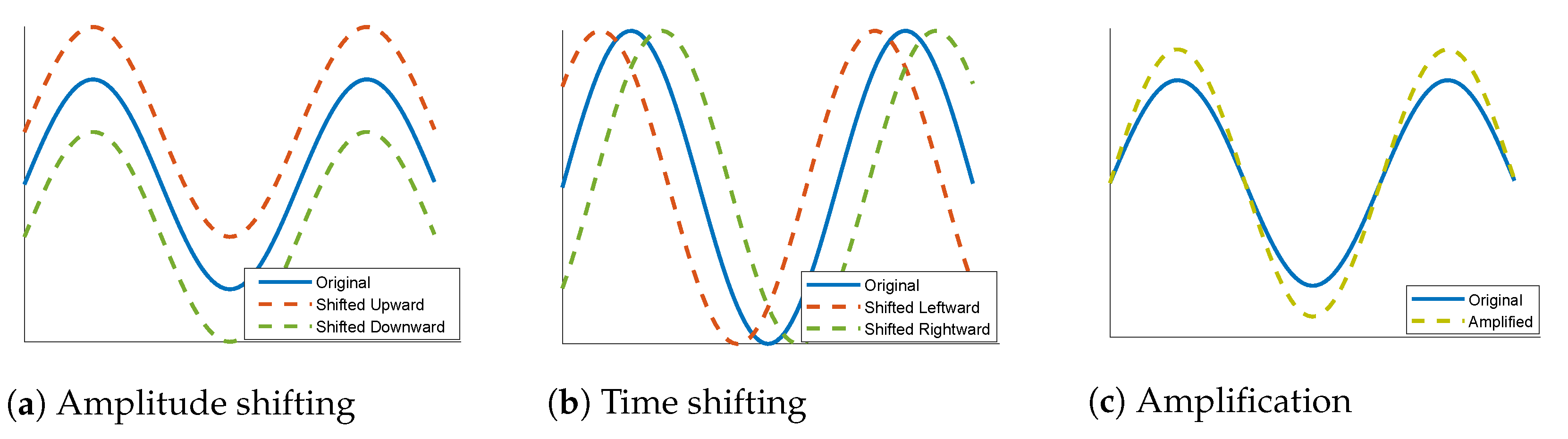
3.2. Data Augmentation
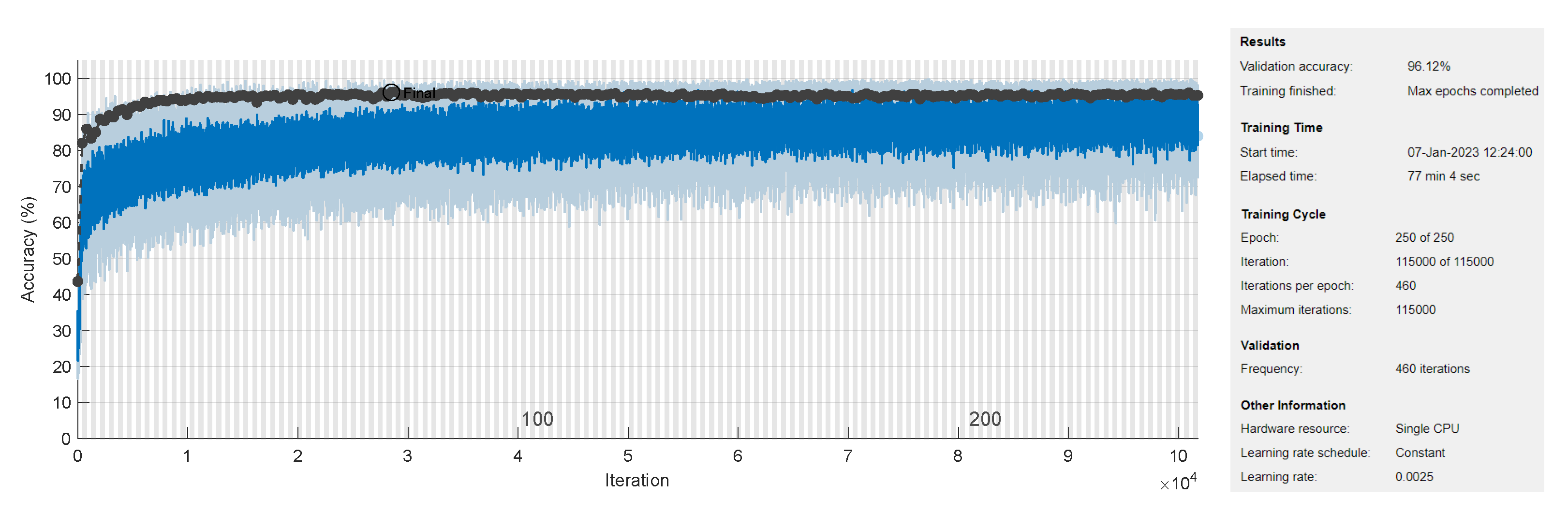
3.3. Training Process
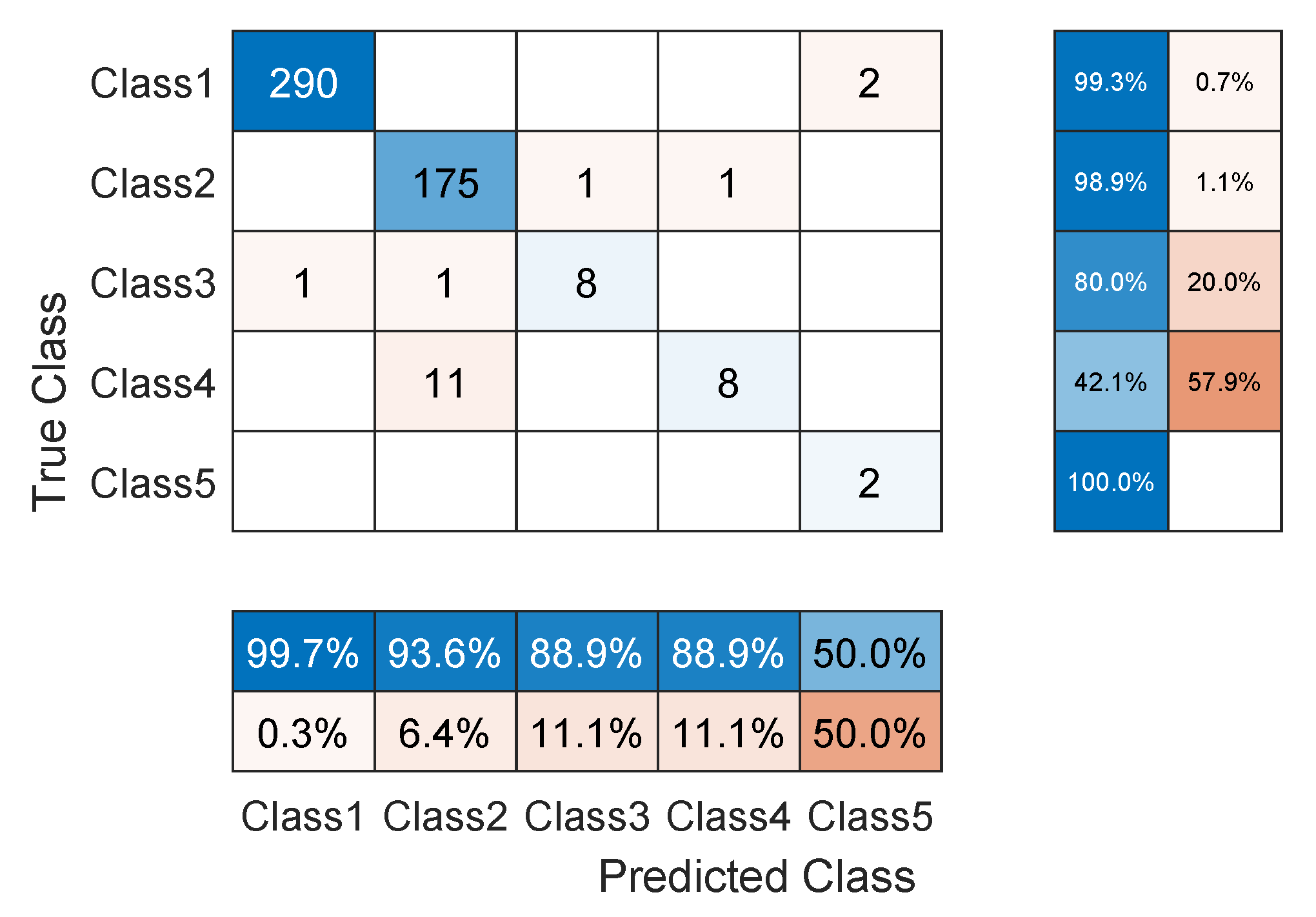
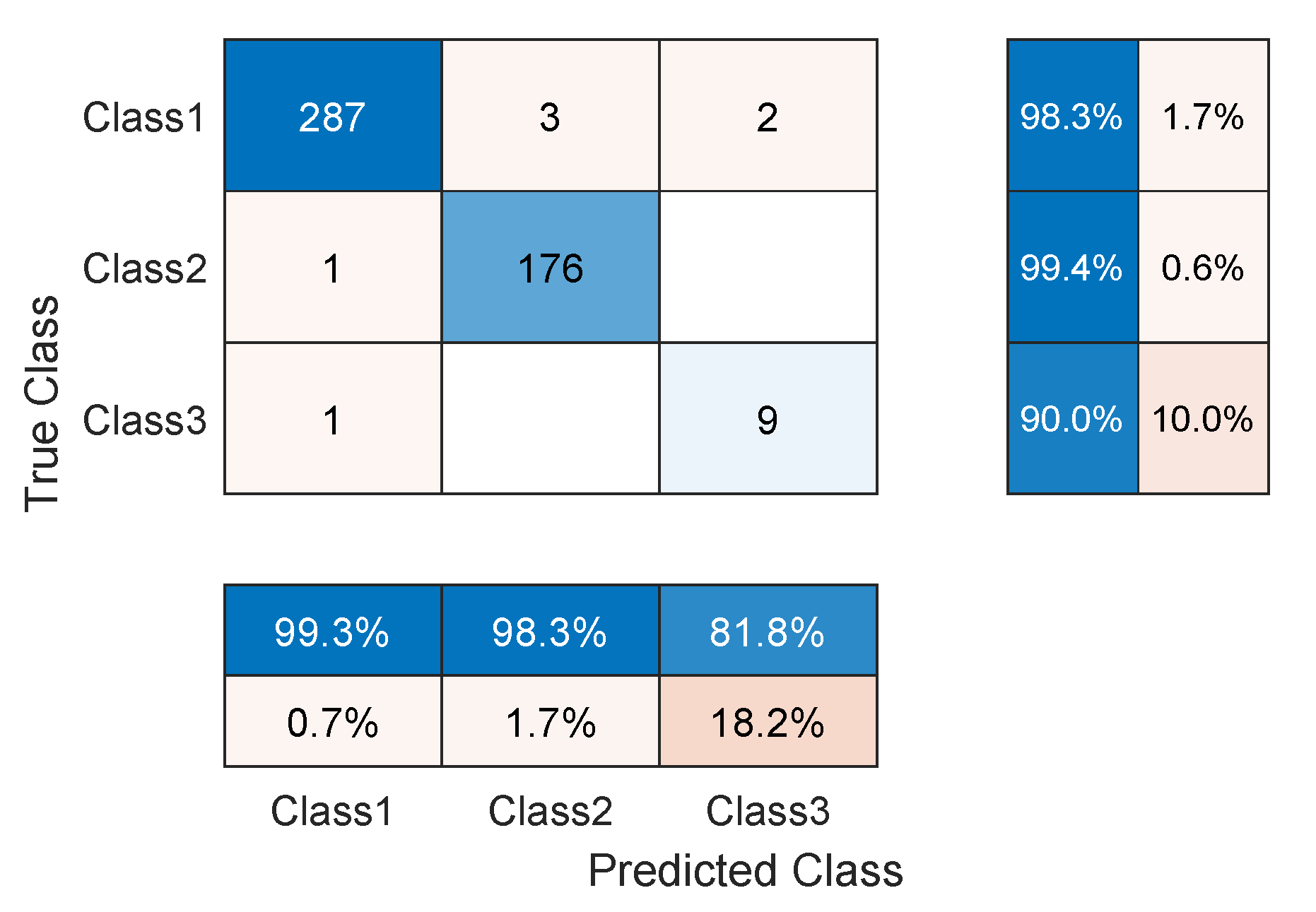
3.4. Network Evaluation
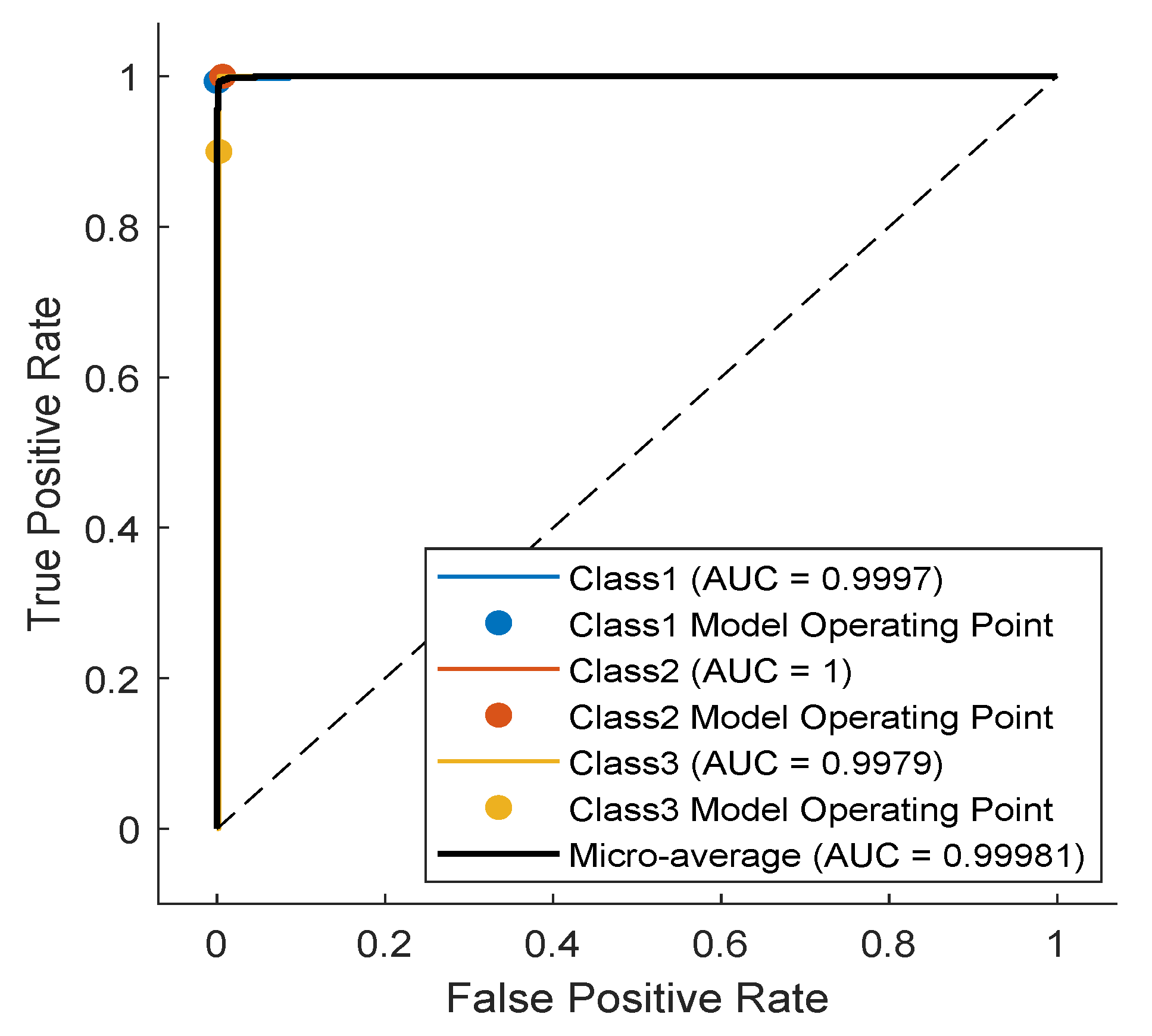
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, M.; Lu, Y.; Yang, W.; Wong, S.Y. A Study on Arrhythmia via ECG Signal Classification Using the Convolutional Neural Network. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 564015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.; Oh, S.Y.; Pusic, M. Accuracy of Physicians’ Electrocardiogram Interpretations: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schläpfer, J.; Wellens, H.J. Computer-Interpreted Electrocardiograms: Benefits and Limitations. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, M.J.; Ahmed, S.; Riaz, K. Exploiting Cross-Correlation Between ECG signals to Detect Myocardial Infarction. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology (IBCAST), Islamabad, Pakistan, 14–18 January 2020; pp. 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar, M.; Sabamoniri, S. An ECG-based feature selection and heartbeat classification model using a hybrid heuristic algorithm. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2018, 13, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, O.; Kareem, M.; Ali, A.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Acharya, U.R. Automated Arrhythmia Detection Based on RR Intervals. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khafif, S.H.; El-Brawany, M.A. Artificial Neural Network-Based Automated ECG Signal Classifier. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.H.; Ribeiro, M.H.; Paixão, G.M.M.; Oliveira, D.M.; Gomes, P.R.; Canazart, J.A.; Ferreira, M.P.S.; Andersson, C.R.; Macfarlane, P.W.; Meira, W.; et al. Automatic diagnosis of the 12-lead ECG using a deep neural network. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Seo, S.Y.; Song, C.G.; Kim, K.S. Assessment of Electrocardiogram Rhythms by GoogLeNet Deep Neural Network Architecture. J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 2019, 2826901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, E.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ji, Z.; Ganchev, I. ECG Heartbeat Classification Based on an Improved ResNet-18 Model. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 6649970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatnejad, S.; Oveisi, M.; Hashemi, M. LSTM-Based ECG Classification for Continuous Monitoring on Personal Wearable Devices. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Park, S.J. Big-ECG: Cardiographic Predictive Cyber-Physical System for Stroke Management. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 123146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Keogh, E. Time Series Classification. Available online: http://www.timeseriesclassification.com/description.php?Dataset=ECG5000 (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Baim, D.S.; Colucci, W.S.; Monrad, E.S.; Smith, H.S.; Wright, R.F.; Lanoue, A.; Gauthier, D.F.; Ransil, B.J.; Grossman, W.; Braunwald, E. Survival of patients with severe congestive heart failure treated with oral milrinone. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1986, 7, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikipedia Contributors. Electrocardiography—Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. 2022. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Electrocardiography&oldid=1120710988 (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Chen, B.; Li, Y.; Cao, X.; Sun, W.; He, W. Removal of Power Line Interference From ECG Signals Using Adaptive Notch Filters of Sharp Resolution. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 150667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, P.C.; Uplane, M.D. High Frequency Electromyogram Noise Removal from Electrocardiogram Using FIR Low Pass Filter Based on FPGA. Procedia Technol. 2016, 25, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, F.P.; Romaguera, L.V.; V’azquez-Seisdedos, C.R.; Filho, C.F.F.C.; Costa, M.G.F.; Neto, J.E. Baseline wander removal methods for ECG signals: A comparative study. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.11359. [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam, S.R.; Ling, B.W.K.; Georgakis, A. Motion artifact suppression in the ECG signal by successive modifications in frequency and time. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ruan, Q. Continuous wavelet transforms. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 31 August–4 September 2004; Volume 1, pp. 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, S. Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT). In Digital Signal Processing and Spectral Analysis for Scientists; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 645–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyagarajan, K. Discrete Fourier Transform. In Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Using MATLAB with Application to Digital Communications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 151–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, W.; Burge, M. The Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). In Digital Image Processing: An Algorithmic Introduction Using Java; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H. The Tutorial: S Transform; National Taiwan University: Taipei, Taiwan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Sarkar, U.; Taraphder, S.; Datta, S.; Swain, D.; Saikhom, R.; Panda, S.; Laishram, M. Principal Component Analysis. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2017, 7, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia Contributors. Pan–Tompkins Algorithm—Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. 2022. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/30809 (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Wikipedia Contributors. Daubechies Wavelet—Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. 2022. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Daubechies_wavelet (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Tharwat, A. Independent Component Analysis: An Introduction. Appl. Comput. Inform. 2018, 17, 222–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Z-Score. 2010. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9780470479216.corpsy1047 (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Lee, D.; In, J.; Lee, S. Standard deviation and standard error of the mean. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2015, 68, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.C.; Balas, V.; Perescu-Popescu, L.; Mastorakis, N. Multilayer perceptron and neural networks. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. 2009, 8, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, Y.; Yun, W.; Jung, S.; Kim, J. Quantum Neural Networks: Concepts, Applications, and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2021 Twelfth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 17–20 August 2021; pp. 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, C.; Behera, A.K.; Dehuri, S.; Cho, S.B. Radial basis function neural networks: A topical state-of-the-art survey. Open Comput. Sci. 2016, 6, 33–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.C.; Yang, D.L. An efficient Fuzzy C-Means clustering algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, San Jose, CA, USA, 29 November–2 December 2001; pp. 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogheneovo, E.; Nlerum, P. Iterative Dichotomizer 3 (ID3) Decision Tree: A Machine Learning Algorithm for Data Classification and Predictive Analysis. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2020, 7, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A. Support vector machine—A survey. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2012, 2, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Aliev, R.; Guirimov, B. Type-2 Fuzzy Clustering. In Type-2 Fuzzy Neural Networks and Their Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali, Y.; Story, B. Competitive probabilistic neural network. Integr. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2017, 24, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallali, A.; Kachouri, A.; Samet, M. A Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmia Using WT, HRV, and Fuzzy C-Means Clustering. Signal Process. Int. J. (SPJI) 2011, 5, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Dallali, A.; Kachouri, A.; Samet, M. Fuzzy C-means clustering, neural network, WT, and HRV for classification of cardiac arrhythmia. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2011, 6, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Khazaee, A. Heart Beat Classification Using Particle Swarm Optimization. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2013, 5, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwa, A.; Lal, M.; Dixit, S.; Varadwaj, P. Clasification Of Arrhythmic ECG Data Using Machine Learning Techniques. Int. J. Interact. Multimed. Artif. Intell. 2011, 1, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korürek, M.; Doğan, B. ECG beat classification using particle swarm optimization and radial basis function neural network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 7563–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.N.; Chou, K.T. Integration of independent component analysis and neural networks for ECG beat classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 34, 2841–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, S.; Saini, J. ECG classification and abnormality detection using cascade forward neural network. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Si, Y.; Xu, T.; Saibiao, J. Deep Convolutional Neural Network Based ECG Classification System Using Information Fusion and One-Hot Encoding Techniques. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia Contributors. One-Hot—Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. 2022. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/One-hot (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Zeiler, M.D. ADADELTA: An Adaptive Learning Rate Method. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, J.; Randazzo, V.; Cirrincione, G.; Pasero, E. 1-D Convolutional Neural Network for ECG Arrhythmia Classification. In Progresses in Artificial Intelligence and Neural Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, J.; Kiros, J.; Hinton, G. Layer Normalization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.06450. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.; Koltun, V. An Empirical Evaluation of Generic Convolutional and Recurrent Networks for Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01271. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T. A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, T.R.; Fahlman, S.E.; Craw, S.; Andritsos, P.; Tsaparas, P.; Silva, R.; Drummond, C.; Ling, C.X.; Sheng, V.S.; Drummond, C.; et al. Confusion Matrix. In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rodrigues, N.; Taguchi, Y.h. Incremental Dilations Using CNN for Brain Tumor Classification. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y.; Park, S.; Sim, K.B. Optimal hyperparameter tuning of convolutional neural networks based on the parameter-setting-free harmony search algorithm. Optik 2018, 172, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingolfsson, T.M.; Wang, X.; Hersche, M.; Burrello, A.; Cavigelli, L.; Benini, L. ECG-TCN: Wearable Cardiac Arrhythmia Detection with a Temporal Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Circuits and Systems (AICAS), Washington, DC, USA, 3–7 May 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, F.; Majumdar, S.; Darabi, H.; Chen, S. LSTM Fully Convolutional Networks for Time Series Classification. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Keogh, E.; Hu, B.; Begum, N.; Bagnall, A.; Mueen, A.; Batista, G. The UCR Time Series Classification Archive. 2015. Available online: https://www.cs.ucr.edu/~eamonn/time_series_data/ (accessed on 8 April 2002).

| Exp | #Blocks | #Filters | Filter Size | #Parms | Data Augmentation Factor | Epoch Size | F1 Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 16 | 10.2 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 3 | 16 | 6 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 5 | 16 | 15.4 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 4 | 8 | 2.7 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 4 | 32 | 39.9 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 4 | 16 | 14.9 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 4 | 32 | 58.4 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 3 | 16 | 8.6 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 3 | 16 | 12.2 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 3 | 32 | 23.3 K | class3:24, class4:12, class5:24 | 460 | ||||
| 4 | 16 | 10.2 K | class3:24, class4:24, class5:24 | 566 | ||||
| 4 | 16 | 10.2 K | class3:24, class4:06, class5:24 | 407 |
| Class | Data Augmentation Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude Shift | Time Shift | Amplification | |
| PVC | |||
| SP | |||
| UB | |||
| Class | Count | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testing Set | Before Augmentation | After Augmentation | |||
| Training Set | Total | Training Set | Total | ||
| N | 292 | 2627 | 2919 | 2627 | 2919 |
| Ron-T PVC | 177 | 1590 | 1767 | 1590 | 1767 |
| PVC | 10 | 86 | 96 | 2150 | 2160 |
| SP | 19 | 175 | 194 | 2287 | 2306 |
| UB | 20 | 2 | 24 | 550 | 552 |
| Total | 500 | 4500 | 5000 | 9204 | 9704 |
| Architecture | Accuracy (%) | F1 Score (%) | #Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCN [57] | 94.2 | 89.0 | 14.88 K |
| LSTM-FCN [58] | 94.1 | 72.5 | 404.74 K |
| CCN [58] | 93.4 | 81.5 | 266.37 K |
| LSTM [58] | 93.1 | 68.9 | 138.37 K |
| 1-NN (L2 dist.) [59] | 92.5 | 54.9 | 70 K |
| Our TCN | 96.12 | 84.13 | 10.2 K |
| Our TCN (First 3 classes) | 98.54 | 94.51 | 10.2 K |
| Our TCN (Without Data Augmentation) | 93.4 | 70.18 | 10.2 K |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, A.R.; Jovanovic, S.; Ramzan, N.; Rabah, H. ECG Classification Using an Optimal Temporal Convolutional Network for Remote Health Monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031697
Ismail AR, Jovanovic S, Ramzan N, Rabah H. ECG Classification Using an Optimal Temporal Convolutional Network for Remote Health Monitoring. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031697
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Ali Rida, Slavisa Jovanovic, Naeem Ramzan, and Hassan Rabah. 2023. "ECG Classification Using an Optimal Temporal Convolutional Network for Remote Health Monitoring" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031697
APA StyleIsmail, A. R., Jovanovic, S., Ramzan, N., & Rabah, H. (2023). ECG Classification Using an Optimal Temporal Convolutional Network for Remote Health Monitoring. Sensors, 23(3), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031697








