Temporally and Spatially Resolved Reflected Overpressure Measurements in the Extreme Near Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
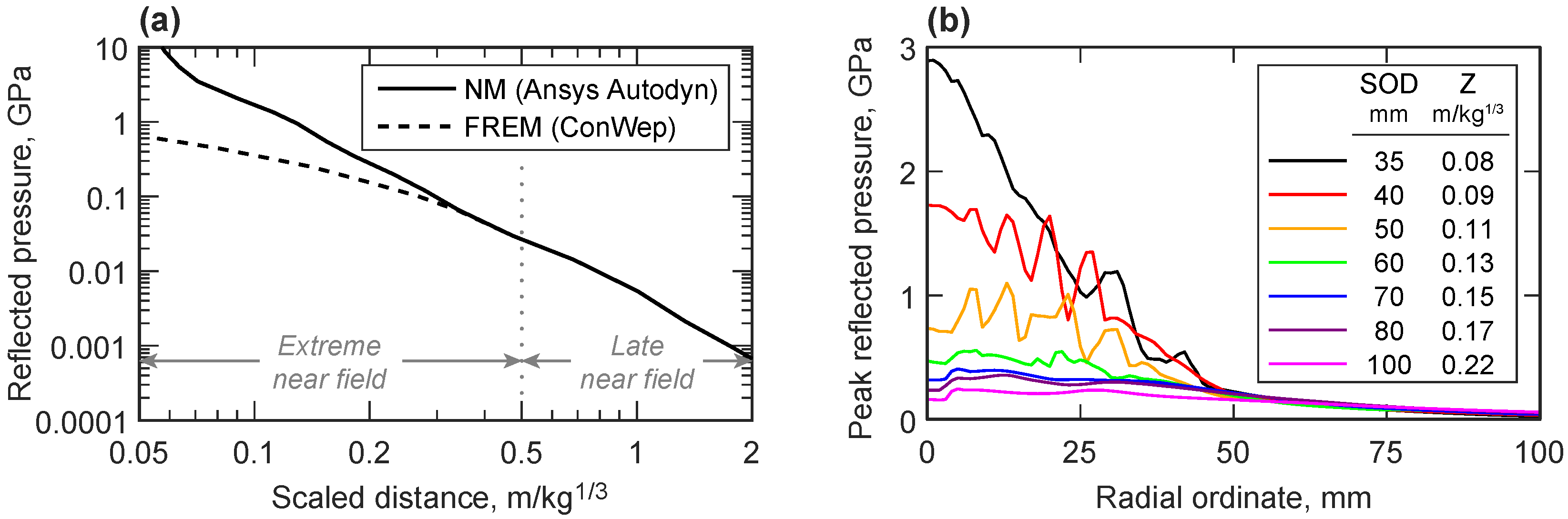
2.1. Expected Loading Profile
2.2. Test Frame
2.3. Hopkinson Pressure Bar Design
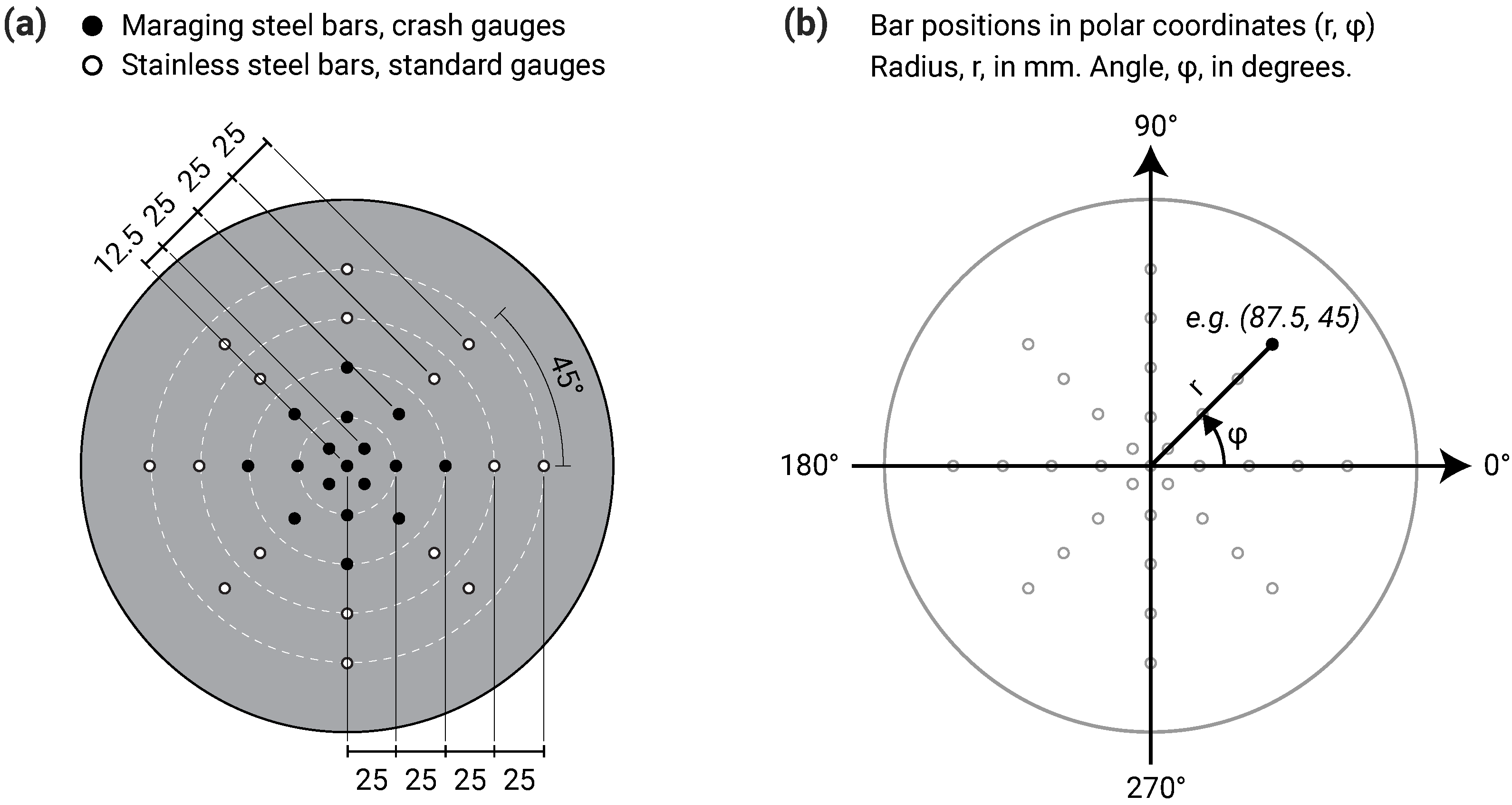
2.4. Hopkinson Pressure Bar Array
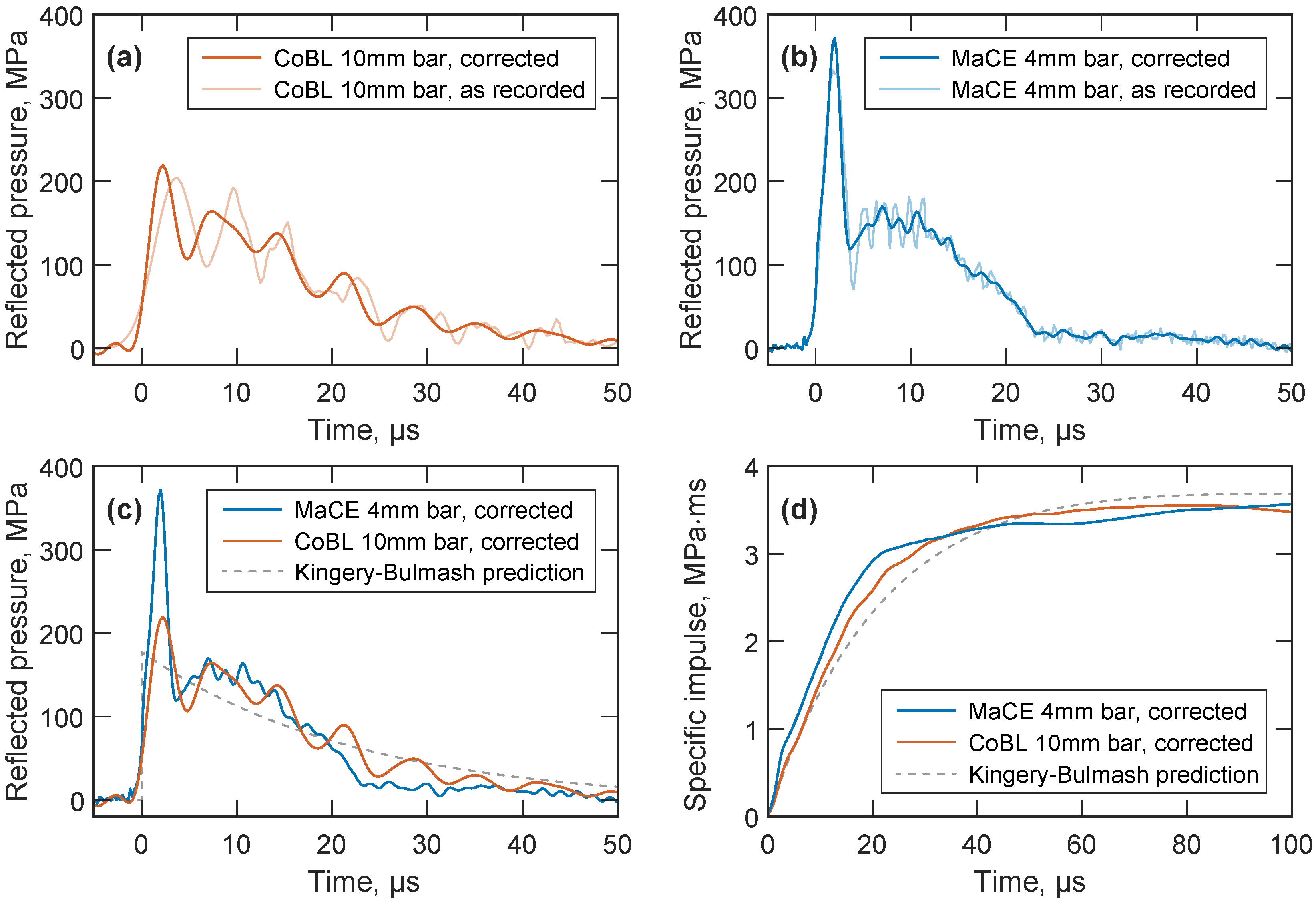
3. Experimental Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Institute for Economics & Peace. The 2022 Global Terrorism Index; Institute for Economics & Peace: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kingery, C.N.; Bulmash, G. Airblast Parameters from TNT Spherical Air Burst and Hemispherical Surface Burst; Technical Report ARBRL-TR-02555; U.S Army BRL, Aberdeen Proving Ground: Aberdeen, MD, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Granström, S. Loading Characteristics of Air Blasts from Detonating Charges; Technical Report 100; Transactions of the Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Rickman, D.D.; Murrell, D.W. Development of an Improved Methodology for Predicting Airblast Pressure Relief on a Directly Loaded Wall. J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 2007, 129, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyas, A.; Warren, J.; Bennett, T.; Fay, S. Prediction of clearing effects in far-field blast loading of finite targets. Shock Waves 2011, 21, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.E.; Tyas, A.; Fay, S.D.; Clarke, S.D.; Warren, J.A. Validation of Semi-Empirical Blast Pressure Predictions for Far Field Explosions—Is There Inherent Variability in Blast Wave Parameters? In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Protection of Structures against Hazards, Tianjin, China, 16–17 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rigby, S.E.; Tyas, A.; Bennett, T.; Clarke, S.D.; Fay, S.D. The Negative Phase of the Blast Load. Int. J. Prot. Struct. 2014, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalnot, M.; Pons, P.; Aubert, H. Frequency bandwidth of pressure sensors dedicated to blast experiments. Sensors 2022, 22, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, D.W. Conventional Weapons Program (ConWep); U.S Army Waterways Experimental Station: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Whittaker, A.; Cormie, D. Incident and Normally Reflected Overpressure and Impulse for Detonations of Spherical High Explosives in Free Air. J. Struct. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, M. Blast impulse at very near distance. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2008, 33, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.H.; Thomas, G.O.; Milne, A.; Hooper, G.; Tasker, D. Blast wave measurements close to explosive charges. Shock Waves 1992, 2, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, E. Reflected blast measurements near pancake charges. In Proceedings of the 24th DoD Explosives Safety Seminar, St. Louis, MO, USA, 28–30 August 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Crawford, R.; Mann, K.; Coleman, P.; Petersen, C. Evidence of higher Pochhammer-Chree modes in an unsplit Hopkinson bar. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1995, 6, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.; Fourney, W.; Leiste, H. Pressures on targets from buried explosions. Blasting Fragm 2010, 4, 165–192. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson, B. A method of measuring the pressure produced in the detonation of high explosives or by the impact of bullets. Philiosophical Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1914, 213, 437–456. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, S.D.; Fay, S.D.; Warren, J.A.; Tyas, A.; Rigby, S.E.; Elgy, I. A large scale experimental approach to the measurement of spatially and temporally localised loading from the detonation of shallow-buried explosives. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.; Rigby, S.; Fay, S.; Barr, A.; Tyas, A.; Gant, M.; Elgy, I. Characterisation of buried blast loading. Proc. R. Soc. A 2020, 476, 20190791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, S.; Tyas, A.; Clarke, S.; Fay, S.; Reay, J.; Warren, J.; Gant, M.; Elgy, I. Observations from Preliminary Experiments on Spatial and Temporal Pressure Measurements from Near-Field Free Air Explosions. Int. J. Prot. Struct. 2015, 6, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyas, A. Blast loading from high explosive detonation: What we know and what we don’t know. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Shock and Impact Loads on Structures, Guangzhou, China, 13–15 December 2019; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rigby, S.E.; Barr, A.D.; Clayton, M. A review of Pochhammer–Chree dispersion in the Hopkinson bar. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Eng. Comput. Mech. 2018, 171, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.; Fuller, B.; Tyas, A. Validation of near-field blast loading in LS-DYNA. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Protective Structures (ICPS5), Poznan, Poland, 19–23 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rigby, S.; Tyas, A.; Bennett, T. Single-degree-of-freedom response of finite targets subjected to blast loading—The influence of clearing. Eng. Struct. 2012, 45, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.E.; Tyas, A.; Bennett, T.; Warren, J.A.; Fay, S. Clearing effects on plates subjected to blast loads. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Eng. Comput. Mech. 2013, 166, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyas, A.; Woolford, S.; Farrimond, D.G.; Rigby, S.E.; Clarke, S.D.; Barr, A.D.; Hobbs, M.J.; Wilmott, J.R.; Whittaker, M.J.; Pope, D.J.; et al. Development of an ideal gas-based thermochemical model for the prediction of quasi-static pressures generated by the detonation of confined plastic explosives. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Protective Structures, Auburn, AL, USA, 14–17 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, M.J.; Barr, A.; Woolford, S.; Farrimond, D.; Clarke, S.D.; Tyas, A.; Willmott, J.R. High-Speed Infrared Radiation Thermometer for the Investigation of Early Stage Explosive Development and Fireball Expansion. Sensors 2022, 22, 6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speak, T.; Woolford, S.; Farrimond, D.; Christopher, I.; Barr, A.D.; Potius, P.; Tyas, A. Experimental Observation and Modelling of Contained Detonations of PE4: What is the Influence of Afterburn? In Proceedings of the 2022 International Explosives Conference, London, UK, 22–24 June 2022; RSC Publishing: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tyas, A.; Watson, A.J. An investigation of frequency domain dispersion correction of pressure bar signals. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2001, 25, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, A.; Rigby, S.; Clayton, M. Correction of higher mode Pochhammer—Chree dispersion in experimental blast loading measurements. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 139, 103526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrimond, D.; Woolford, S.; Rigby, S.E.; Tyas, A.; Clarke, S.D.; Barr, A.D.; Whittaker, M.; Pope, D. Far-field blast parameter characterisation of RDX and PETN based explosives. Int. J. Prot. Struct. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, A.D. dispersion.m—A MatLab script for phase angle and amplitude correction of pressure bar signals. FigShare 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.E.; Tyas, A. Blast.m. White Rose Research Online. 2014. Available online: https://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/77858/ (accessed on 12 January 2023).


| Strain Gauge | Max Strain, m (max MPa) | Active Length, mm | Resistance at 25 °C, | Nominal Gauge Factor | TCGF 1, %°C | TCR 2, %/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kyowa KSPB-2-120-E4 | 3000 (600) | 2.00 | 120 | 125 | −0.20 | 0.17 |
| Micron SS-027-013-500P | 3000 (600) | 0.33 | 540 | 155 | −0.32 | 0.43 |
| Micron SS-040-010-1100P | 9000 (1800) | 0.25 | 1100 | 200 | −0.41 | 0.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barr, A.D.; Rigby, S.E.; Clarke, S.D.; Farrimond, D.; Tyas, A. Temporally and Spatially Resolved Reflected Overpressure Measurements in the Extreme Near Field. Sensors 2023, 23, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020964
Barr AD, Rigby SE, Clarke SD, Farrimond D, Tyas A. Temporally and Spatially Resolved Reflected Overpressure Measurements in the Extreme Near Field. Sensors. 2023; 23(2):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020964
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarr, Andrew D., Sam E. Rigby, Sam D. Clarke, Dain Farrimond, and Andy Tyas. 2023. "Temporally and Spatially Resolved Reflected Overpressure Measurements in the Extreme Near Field" Sensors 23, no. 2: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020964
APA StyleBarr, A. D., Rigby, S. E., Clarke, S. D., Farrimond, D., & Tyas, A. (2023). Temporally and Spatially Resolved Reflected Overpressure Measurements in the Extreme Near Field. Sensors, 23(2), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020964






