Driver Identification Using Statistical Features of Motor Activity and Genetic Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
Related Work
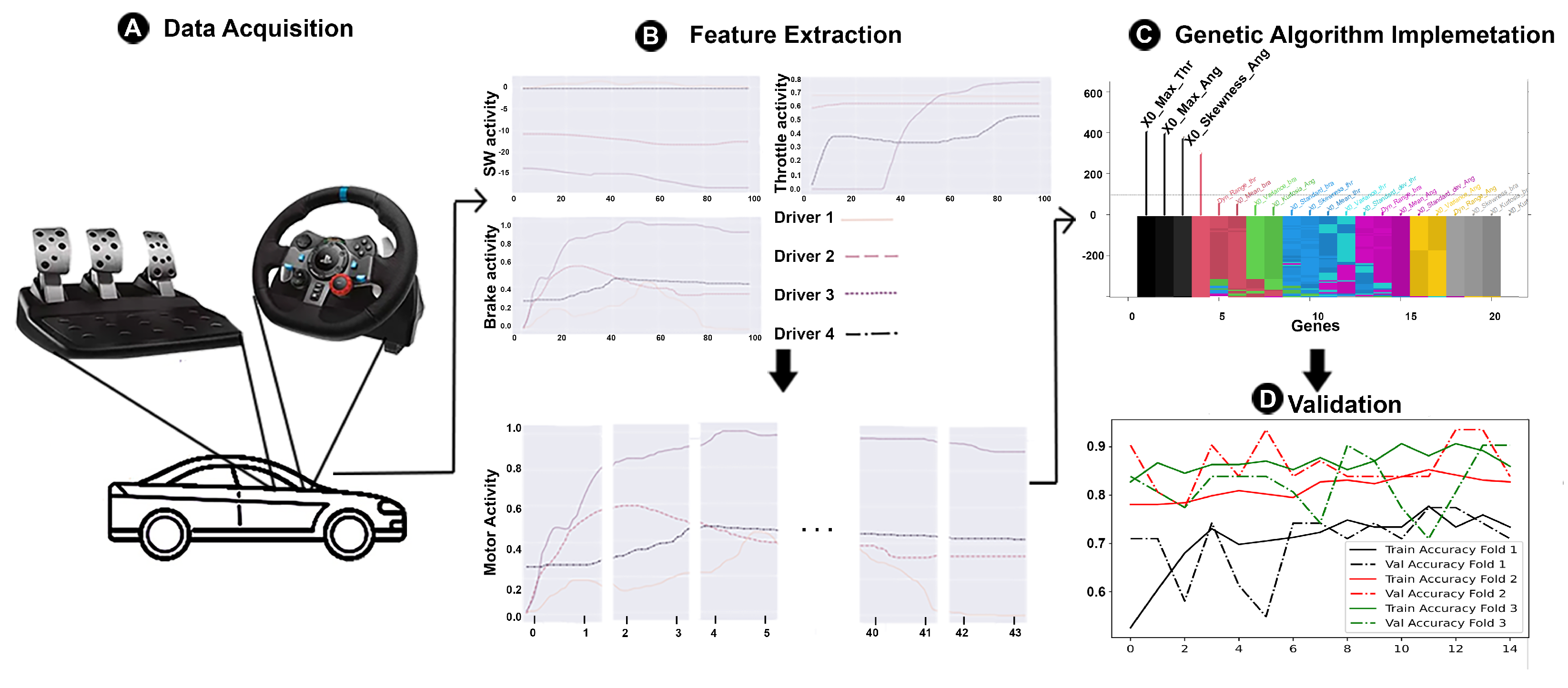
2. Materials and Methods
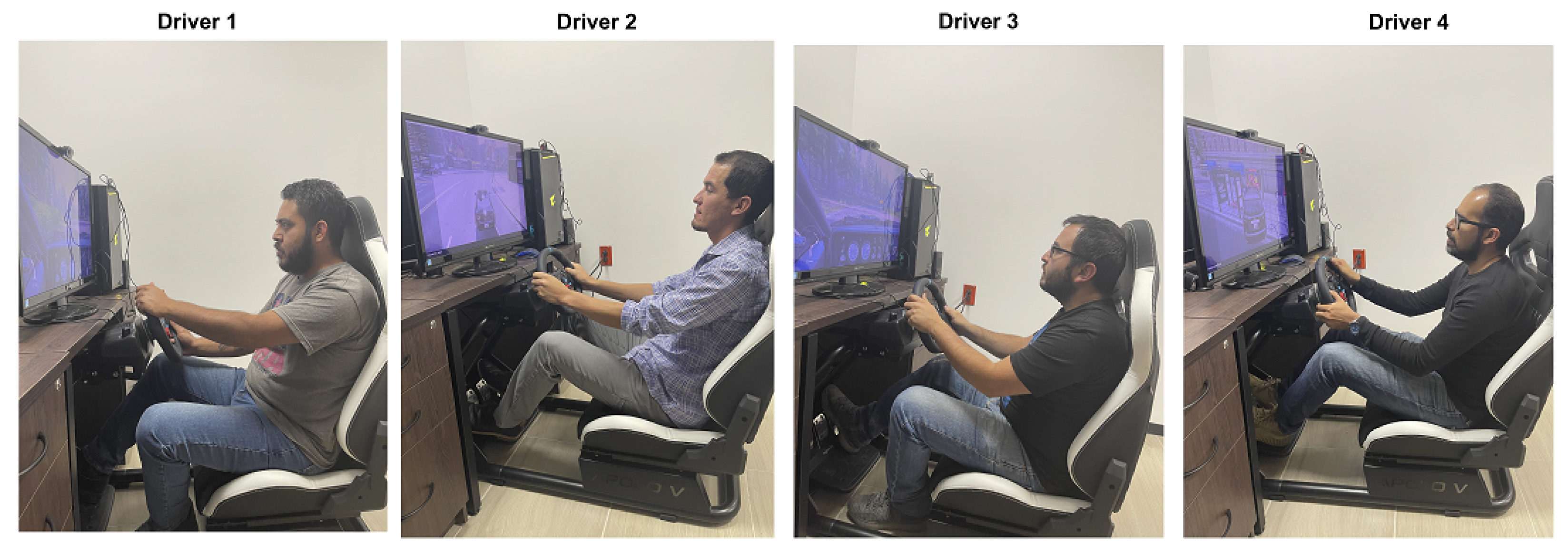
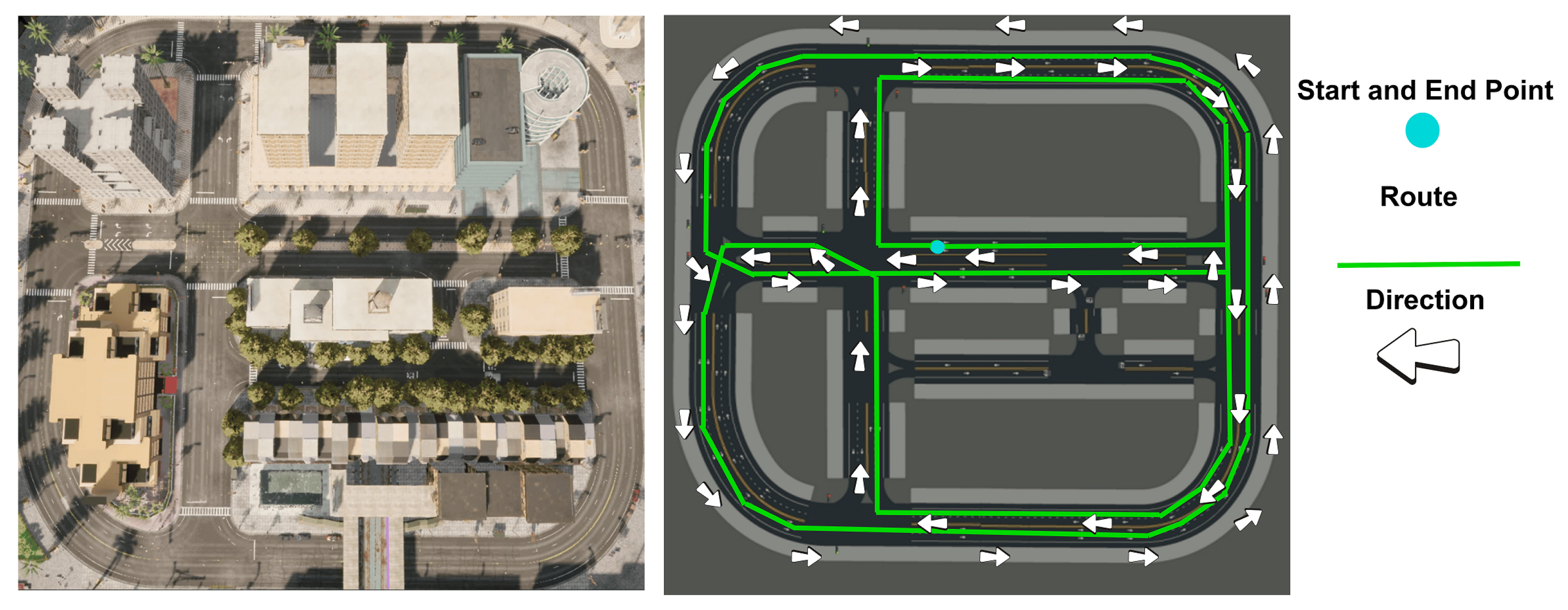
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Feature Extraction
2.3. Genetic Algorithm Implementation
2.4. Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator
2.5. Recursive Feature Elimination
2.6. Validation
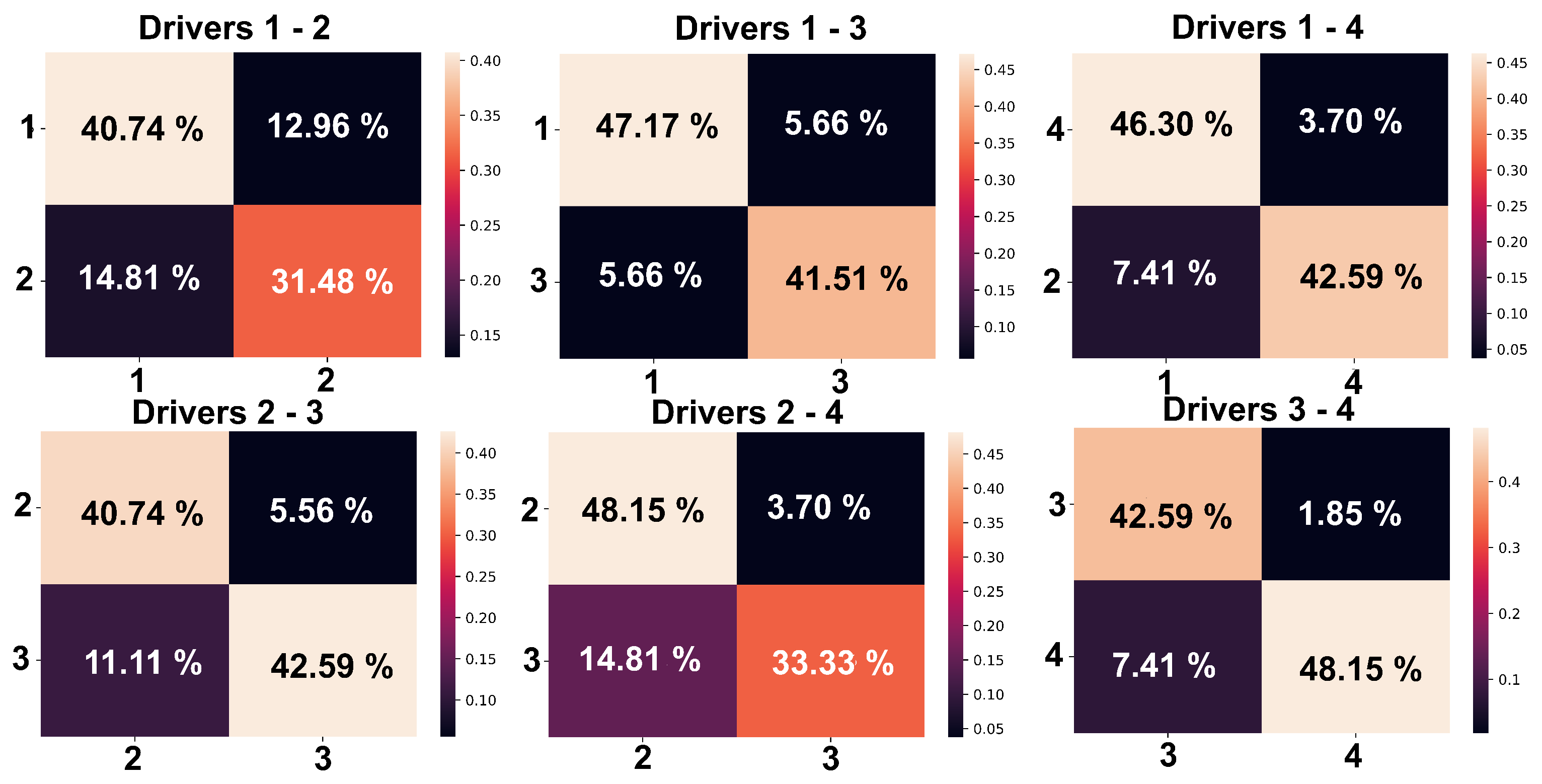
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Musa, A.; Pipicelli, M.; Spano, M.; Tufano, F.; De Nola, F.; Di Blasio, G.; Gimelli, A.; Misul, D.A.; Toscano, G. A Review of Model Predictive Controls Applied to Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems. Energies 2021, 14, 7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdennour, N.; Ouni, T.; Amor, N.B. Driver identification using only the CAN-Bus vehicle data through an RCN deep learning approach. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2021, 136, 103707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzini, S.; Berrada, I.; Ghogho, M. Who is behind the wheel? Driver identification and fingerprinting. J. Big Data 2018, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwak, J.; Hirao, A.; Shino, M. An Investigation of Early Detection of Driver Drowsiness Using Ensemble Machine Learning Based on Hybrid Sensing. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya-Padilla, J.M.; Romero-González, J.S.; Galvan-Tejada, C.E.; Galvan-Tejada, J.I.; Luna-GarcÃa, H.; Arceo-Olague, J.G.; Gamboa-Rosales, N.K.; Sifuentes-Gallardo, C.; Martinez-Torteya, A.; De la Rosa, J.I.; et al. In-Vehicle Alcohol Detection Using Low-Cost Sensors and Genetic Algorithms to Aid in the Drinking and Driving Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr Azadani, M.; Boukerche, A. Siamese Temporal Convolutional Networks for Driver Identification Using Driver Steering Behavior Analysis. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 18076–18087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, Z.; Khan, S.; Gai, K. Zero-to-Stable Driver Identification: A Non-Intrusive and Scalable Driver Identification Scheme. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Chan, C.Y. Enhancing Localization Accuracy of MEMS-INS/GPS/In-Vehicle Sensors Integration During GPS Outages. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.; Ramanandan, A.; Chen, A.; Farrell, J.A.; Barth, M. Real-Time Computer Vision/DGPS-Aided Inertial Navigation System for Lane-Level Vehicle Navigation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2012, 13, 899–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q. Technology review - Biometrics-Technology, Application, Challenge, and Computational Intelligence Solutions. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2007, 2, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahabi, S.; Pouryayevali, S.; Hatzinakos, D. Posture-invariant ECG recognition with posture detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, South Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; Volume 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugiglando, U.; Massaro, E.; Santi, P.; Milardo, S.; Abida, K.; Stahlmann, R.; Netter, F.; Ratti, C. Driving Behavior Analysis through CAN Bus Data in an Uncontrolled Environment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Xiong, S. Few-shot driver identification via meta-learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 203, 117299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júnior, J.F.; Carvalho, E.; Ferreira, B.V.; De Souza, C.; Suhara, Y.; Pentland, A.; Pessin, G. Driver behavior profiling: An investigation with different smartphone sensors and machine learning. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraqi, H.M.; Abouelnaga, Y.; Saad, M.H.; Moustafa, M.N. Driver distraction identification with an ensemble of convolutional neural networks. J. Adv. Transp. 2019, 2019, 4125865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhu, M.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y. Identification of significant factors in fatal-injury highway crashes using genetic algorithm and neural network. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 111, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Wu, Y.; Lian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Meng, L. Energy management of hybrid electric vehicles: A review of energy optimization of fuel cell hybrid power system based on genetic algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya-Padilla, J.M.; Galván-Tejada, C.E.; López-Monteagudo, F.E.; Alonso-González, O.; Moreno-Báez, A.; Martínez-Torteya, A.; Galván-Tejada, J.I.; Arceo-Olague, J.G.; Luna-García, H.; Gamboa-Rosales, H. Speed Bump Detection Using Accelerometric Features: A Genetic Algorithm Approach. Sensors 2018, 18, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchegiani, L.; Posner, I. Long-Term Driving Behaviour Modelling for Driver Identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, T.; Jin, J.; Lee, C.; Lim, S. Real-time Driver Identification using Vehicular Big Data and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Kim, D.H. Lightweight Driver Behavior Identification Model with Sparse Learning on In-Vehicle CAN-BUS Sensor Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, C.; Tigga, A.; Gadekallu, T.; Hakak, S.; Alazab, M. Driver Identification Using Optimized Deep Learning Model in Smart Transportation. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2022, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, P. Driver identification using 1D convolutional neural networks with vehicular CAN signals. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 14, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadani, M.N.; Boukerche, A. Driver Identification Using Vehicular Sensing Data: A Deep Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 29 March–1 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, A.; Yan, X.; Homaifar, A. Driver Identification Based on Vehicle Telematics Data using LSTM-Recurrent Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 31st International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 November 2019; pp. 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, B.I.; Han, M.L.; Kim, H.K. Driver Identification Based on Wavelet Transform Using Driving Patterns. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 2400–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfardus, A.; Rawat, D.B. Intrusion Detection System for CAN Bus In-Vehicle Network based on Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 12th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 1–4 December 2021; pp. 0944–0949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapaksha, S.; Kalutarage, H.; Al-Kadri, M.O.; Madzudzo, G.; Petrovski, A.V. Keep the Moving Vehicle Secure: Context-Aware Intrusion Detection System for In-Vehicle CAN Bus Security. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Cyber Conflict: Keep Moving! (CyCon), Tallinn, Estonia, 31 May–3 June 2022; Volume 700, pp. 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- hyun Baek, S.; Jang, J.W. Implementation of integrated OBD-II connector with external network. Inf. Syst. 2015, 50, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, M.; Cimitile, M.; Martinelli, F.; Mercaldo, F. Driver Identification: A Time Series Classification Approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, A.E.; Bouhoute, A.; Berrada, I. Improving Driver Identification for the Next-Generation of In-Vehicle Software Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 7406–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J. An Experimental Study Towards Driver Identification for Intelligent and Connected Vehicles. In Proceedings of the ICC 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fu, Y.; Yu, F.R.; Luan, T.H.; Zhang, Y. Vehicle Position Correction: A Vehicular Blockchain Networks-Based GPS Error Sharing Framework. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 898–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Chakravarty, T.; Ghose, A.; Banerjee, T.; Balamuralidhar, P. Investigations on Driver Unique Identification from Smartphone’s GPS Data Alone. J. Adv. Transp. 2018, 2018, 9702730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidecker, F.; Gruhl, C.; Sick, B. Novelty Based Driver Identification on RR Intervals from ECG Data. In Pattern Recognition. ICPR International Workshops and Challenges; Del Bimbo, A., Cucchiara, R., Sclaroff, S., Farinella, G.M., Mei, T., Bertini, M., Escalante, H.J., Vezzani, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 407–421. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Li, F.; Hu, X.; He, L.; Niu, W.; Lu, S.; Zhang, T. Multi-mode energy management strategy for fuel cell electric vehicles based on driving pattern identification using learning vector quantization neural network algorithm. J. Power Sources 2018, 389, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Ros, G.; Codevilla, F.; Lopez, A.; Koltun, V. CARLA: An Open Urban Driving Simulator. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Conference on Robot Learning, Mountain View, CA, USA, 13–15 November 2017; Levine, S., Vanhoucke, V., Goldberg, K., Eds.; Proceedings of Machine Learning Research. 2017; Volume 78, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Azadani, M.N.; Boukerche, A. Performance Evaluation of Driving Behavior Identification Models through CAN-BUS Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván-Tejada, C.E.; Galván-Tejada, J.I.; Celaya-Padilla, J.M.; Delgado-Contreras, J.R.; Magallanes-Quintanar, R.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L.; Garza-Veloz, I.; López-Hernández, Y.; Gamboa-Rosales, H. An Analysis of Audio Features to Develop a Human Activity Recognition Model Using Genetic Algorithms, Random Forests, and Neural Networks. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2016, 2016, 1784101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, V.; Falciani, F. GALGO: An R package for multivariate variable selection using genetic algorithms. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1154–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, A.K.; Dash, M.; Sabut, S.K. Automated segmentation and classification of brain stroke using expectation-maximization and random forest classifier. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene Selection for Cancer Classification using Support Vector Machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, F.; Luo, L. Structure damage detection based on random forest recursive feature elimination. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2014, 46, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caelen, O. A Bayesian interpretation of the confusion matrix. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 2017, 81, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluyver, T.; Ragan-Kelley, B.; Pérez, F.; Granger, B.; Bussonnier, M.; Frederic, J.; Kelley, K.; Hamrick, J.; Grout, J.; Corlay, S.; et al. Jupyter Notebooks—A publishing format for reproducible computational workflows. In Positioning and Power in Academic Publishing: Players, Agents and Agendas; Loizides, F., Schmidt, B., Eds.; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Barandas, M.; Folgado, D.; Fernandes, L.; Santos, S.; Abreu, M.; Bota, P.; Liu, H.; Schultz, T.; Gamboa, H. TSFEL: Time Series Feature Extraction Library. SoftwareX 2020, 11, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadharshini, G.; Ferni Ukrit, M. An empirical evaluation of importance-based feature selection methods for the driver identification task using OBD data. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; West, N.P.; Chen, P.Y.; Thang, M.W.C.; Price, G.; Cripps, A.W.; Cox, A.J. Selection of microbial biomarkers with genetic algorithm and principal component analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, B.I.; Woo, J.; Kim, H.K. Know your master: Driver Profiling-based Anti-theft method. In Proceedings of the PST 2016, Auckland, New Zealand, 12–14 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Romera, E.; Bergasa, L.M.; Arroyo, R. Need data for driver behaviour analysis? Presenting the public UAH-DriveSet. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–4 November 2016; pp. 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneegass, S.; Pfleging, B.; Broy, N.; Heinrich, F.; Schmidt, A. A Data Set of Real World Driving to Assess Driver Workload. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Automotive User Interfaces and Interactive Vehicular Applications, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 28–30 October 2013; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2013. AutomotiveUI ’13. pp. 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardi, N.; Zanella, M.; Reghenzani, F.; Raspa, N.; Brandolese, C. An Unsupervised Approach for Automotive Driver Identification. In Proceedings of the Workshop on INTelligent Embedded Systems Architectures and Applications, Turin, Italy, 4 October 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2018. INTESA ’18. pp. 51–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Sustainable Systems, University of Michigan. Personal Transportation Factsheet; Center for Sustainable Systems, University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.; Lv, C.; Wang, H.; Cao, D.; Velenis, E.; Wang, F.Y. Driver Activity Recognition for Intelligent Vehicles: A Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 5379–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, M.; Hallac, D.; Sodnik, J.; Leskovec, J. Driver2vec: Driver Identification from Automotive Data. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.05234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Chen, B.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L. Driver identification in intelligent vehicle systems using machine learning algorithms. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 13, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Number | Motor Activity Acceleration | Motor Activity Brake | Motor Activity SWA | Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.679932302 | 0 | −0.243051659 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.672789414 | 0 | 0.301507503 | 0 |
| 3 | 0.669198607 | 0 | −0.104604312 | 0 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 1 | 0 | 0.5495534057 | −1.439965432 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.392749183 | −0.079991518 | 1 |
| 3 | 0.524402881 | 0 | −0.590714625 | 1 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 1 | 0 | 0.898714153 | 2.221737421 | 2 |
| 2 | 0.476545161 | 0 | −1.892375448 | 2 |
| 3 | 0.402442758 | 0 | 3.758628905 | 2 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 1 | 0.840223762 | 0 | 8.276900048 | 3 |
| 2 | 0.639982157 | 0 | −16.88071172 | 3 |
| 2 | 0.639982157 | 0 | −16.88071172 | 3 |
| Driver | Validation Metrics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
| 1 | 0.69 | 0.83 | 0.71 |
| 2 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.71 |
| Accuracy | 72.2% | ||
| 1 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| 3 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| Accuracy | 88.68% | ||
| 1 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.89 |
| 4 | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.88 |
| Accuracy | 88.89% | ||
| 2 | 0.79 | 0.88 | 0.83 |
| 3 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.84 |
| Accuracy | 83.33% | ||
| 2 | 0.76 | 0.93 | 0.84 |
| 4 | 0.90 | 0.69 | 0.78 |
| Accuracy | 81.48% | ||
| 3 | 0.85 | 0.96 | 0.90 |
| 4 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.91 |
| Accuracy | 90.74% | ||
| Driver Set | Features | AUC | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | “X0_Mean_Ang”, “X0_Max_bra”, “X0_Mean_thr”, “X0_Max_thr” | 0.817 (0.702–0.931) | 0.9423 | 0.9231 | 0.9231 | 0.9412 |
| 1-3 | “X0_Mean_Ang”, “X0_Kurtosis_Ang”, “X0_Kurtosis_bra”, “X0_Max_thr” | 0.885 (0.790–0.979) | 0.9615 | 0.9615 | 0.9615 | 0.9615 |
| 1-4 | “X0_Mean_bra”, “X0_Skewness_bra”, “X0_Standard_bra”, “Dyn_Range_thr” | 0.816 (0.692–0.940) | 0.7115 | 0.9615 | 0.9615 | 0.7692 |
| 2-3 | “X0_Mean_Ang”, “X0_Standard_dev_Ang”, “X0_Mean_thr”, “X0_Max_thr” | 0.925 (0.858–0.991) | 0.9423 | 0.9231 | 0.9231 | 0.9412 |
| 2-4 | “X0_Mean_Ang”, “X0_Kurtosis_Ang”, “X0_Mean_bra”, “X0_Variance_thr” | 0.815 (0.699–0.932) | 0.8846 | 1 | 1 | 0.8966 |
| 3-4 | “X0_Mean_Ang”, “X0_Skewness_Ang”, “X0_Kurtosis_Ang”, “X0_Mean_bra”, “X0_Mean_thr”, “X0_Max_thr” | 0.949 (0.877–1) | 0.9231 | 1 | 1 | 0.9286 |
| Driver Set | Features | AUC | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | “X0_Mean_Ang”, “X0_Max_Ang”, “X0_Mean_thr”, “X0_Max_thr” | 0.71 (0.566–0.854) | 0.8269 | 0.8462 | 0.8462 | 0.8302 |
| 1-3 | “X0_Variance_Ang”, “X0_Mean_thr”, “X0_Max_thr”, “Dyn_Range_thr” | 0.902 (0.825–0.98) | 0.9231 | 0.8462 | 0.8462 | 0.9167 |
| 1-4 | “X0_Standard_dev_Ang”, “X0_Max_Ang”, “X0_Mean_thr”, “X0_Max_thr” | 0.904 (0.827–0.981) | 0.9615 | 0.9615 | 0.9615 | 0.9615 |
| 2-3 | “Dyn_Range_Ang”, “X0_Mean_thr”, “X0_Max_thr”, “Dyn_Range_thr” | 0.922 (0.837–1) | 0.9231 | 0.8462 | 0.8462 | 0.9167 |
| 2-4 | “X0_Mean_Ang”, “X0_Max_Ang”, “X0_Mean_thr”, “X0_Max_thr” | 0.831 (0.718–0.945) | 0.9038 | 0.9615 | 0.9615 | 0.9091 |
| 3-4 | “Dyn_Range_Ang”, “X0_Max_bra”, “X0_Mean_thr”, “X0_Max_thr” | 0.962 (0.894–1) | 0.9615 | 1 | 1 | 0.963 |
| Title | Technique | Validation Metric | Result | Features | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Driver2vec: Driver Identification from Automotive Data [60] (2020) | temporal convolutional networks, embedding separation power of triplet loss and classification accuracy of gradient boosting decision trees | Accuracy | 83.1% | 31 | 10 s |
| Novelty Based Driver Identification on RR Intervals from ECG Data [35] (2021) | Combined Approach to Novelty Detection in Intelligent Embedded Systems (CANDIES), Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), one-class SVM classification | precision, recall, score | Unknown, driver 1: 56.8%, 76.6%, 59.8%; Unknown, driver 1/2: 43.5%, 64%, 47.7%; Unknown, driver 1/2/3: 37.83%, 56.12%, 42.38% | 9 | 1 min |
| Driver identification in intelligent vehicle systems using machine learning algorithms [61] (2018) | K-nearest neighbor (KNN) algorithm, random forests (RFs) algorithm, multilayer perceptron algorithm (MLP), Adaboost algorithm, ensemble | accuracy, recall, precision | Best performance model Random Forest: 93.7%, 93.7%, 93.4% | 4 | 100 records per sec |
| Driver Activity Recognition for Intelligent Vehicles: A Deep Learning Approach [59] (2019) | deep convolutional neural networks (CNN), Gaussian mixture model | accuracy | 81.6% accuracy using the AlexNet, 78.6% and 74.9% accuracy using the GoogLeNet and ResNet50 | pre-trained sets | - |
| This Work in 1-2 drivers dataset | Genetic Algorithm with GALGO-rf | Accuracy | 72.2% | 4 | 2 s |
| This Work in 1-3 drivers dataset | Genetic Algorithm with GALGO-rf | Accuracy | 88.68% | 4 | 2 s |
| This Work in 1-4 drivers dataset | Genetic Algorithm with GALGO-rf | Accuracy | 88.89% | 4 | 2 s |
| This Work in 2-3 drivers dataset | Genetic Algorithm with GALGO-rf | Accuracy | 83.33% | 4 | 2 s |
| This Work in 2-4 drivers dataset | Genetic Algorithm with GALGO-rf | Accuracy | 81.48% | 4 | 2 s |
| This Work in 3-4 drivers dataset | Genetic Algorithm with GALGO-rf | Accuracy | 90.74% | 3 | 2 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espino-Salinas, C.H.; Luna-García, H.; Celaya-Padilla, J.M.; Morgan-Benita, J.A.; Vera-Vasquez, C.; Sarmiento, W.J.; Galván-Tejada, C.E.; Galván-Tejada, J.I.; Gamboa-Rosales, H.; Villalba-Condori, K.O. Driver Identification Using Statistical Features of Motor Activity and Genetic Algorithms. Sensors 2023, 23, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020784
Espino-Salinas CH, Luna-García H, Celaya-Padilla JM, Morgan-Benita JA, Vera-Vasquez C, Sarmiento WJ, Galván-Tejada CE, Galván-Tejada JI, Gamboa-Rosales H, Villalba-Condori KO. Driver Identification Using Statistical Features of Motor Activity and Genetic Algorithms. Sensors. 2023; 23(2):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020784
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspino-Salinas, Carlos H., Huizilopoztli Luna-García, José M. Celaya-Padilla, Jorge A. Morgan-Benita, Cesar Vera-Vasquez, Wilson J. Sarmiento, Carlos E. Galván-Tejada, Jorge I. Galván-Tejada, Hamurabi Gamboa-Rosales, and Klinge Orlando Villalba-Condori. 2023. "Driver Identification Using Statistical Features of Motor Activity and Genetic Algorithms" Sensors 23, no. 2: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020784
APA StyleEspino-Salinas, C. H., Luna-García, H., Celaya-Padilla, J. M., Morgan-Benita, J. A., Vera-Vasquez, C., Sarmiento, W. J., Galván-Tejada, C. E., Galván-Tejada, J. I., Gamboa-Rosales, H., & Villalba-Condori, K. O. (2023). Driver Identification Using Statistical Features of Motor Activity and Genetic Algorithms. Sensors, 23(2), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020784










