Nafion Modified Titanium Nitride pH Sensor for Future Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. pH Measurements
2.2. Response Time, Drift Rate, and Hysteresis
2.3. Measurements of Real Samples
3. Results and Analysis
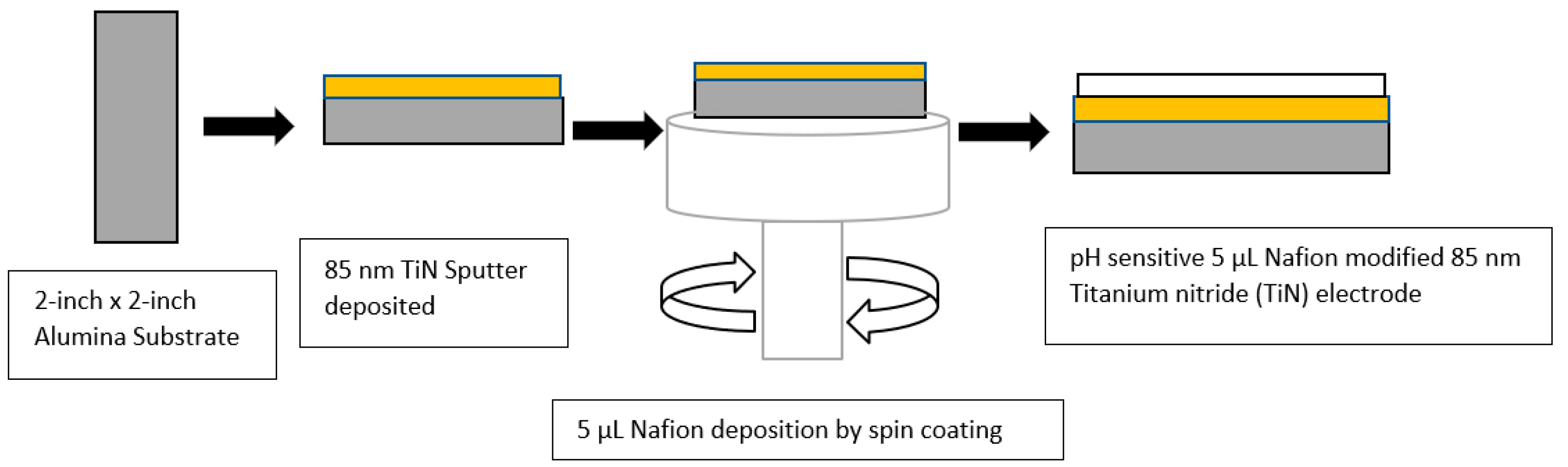
3.1. Deposition Parameters
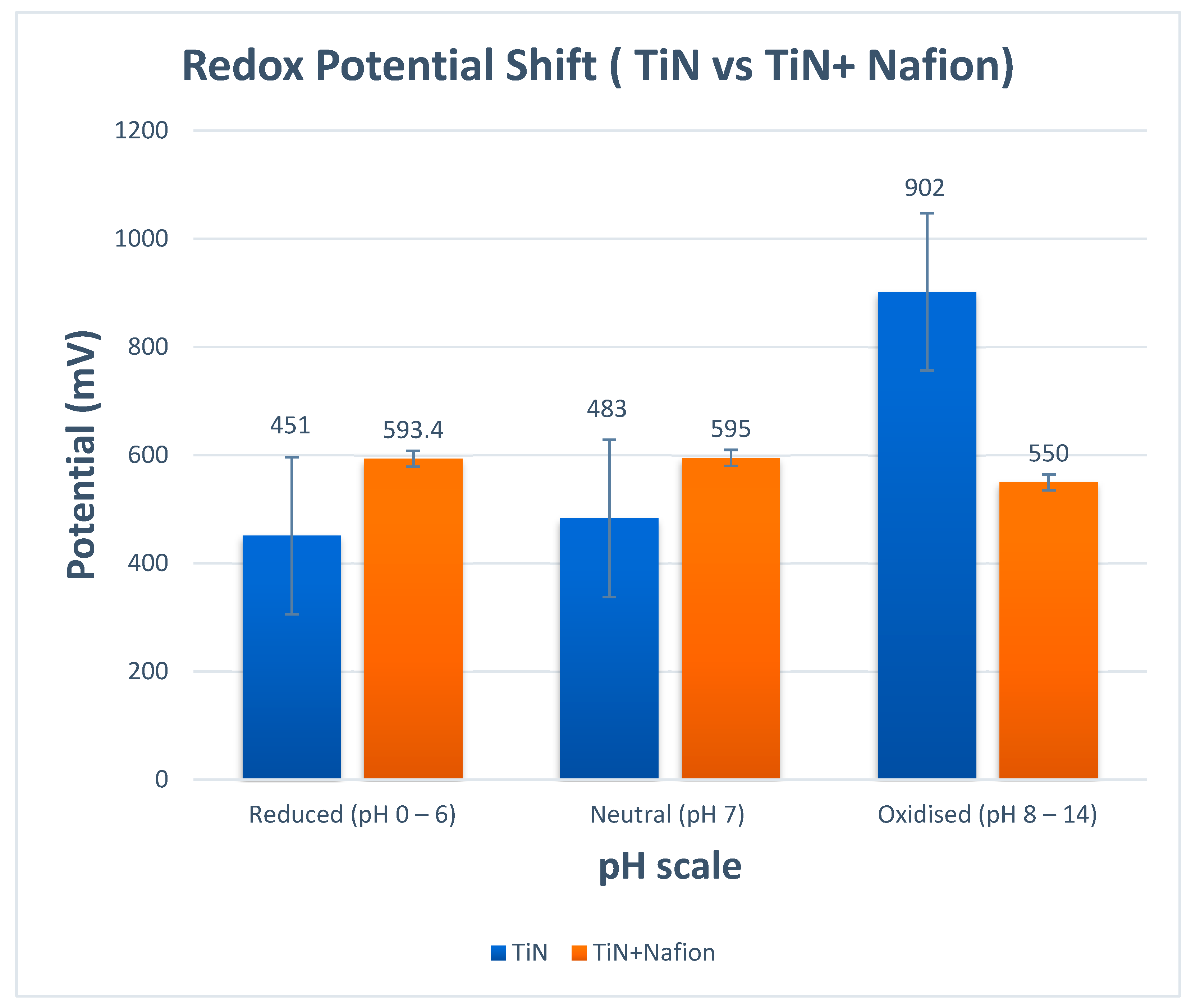
3.2. Sensing Properties
3.3. Drift Rate
3.4. Hysteresis
3.5. Real Samples Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurzweil, P. Metal Oxides and Ion-Exchanging Surfaces as pH Sensors in Liquids: State-of-the-Art and Outlook. Sensors 2009, 9, 4955–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, D.; Sardarinejad, A.; Alameh, K. Recent Developments in R.F. Magnetron Sputtered Thin Films for pH Sensing Applications—An Overview. Coatings 2014, 4, 756–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddle, P. pH meters and their electrodes: Calibration, maintenance and use. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 202–205. Available online: https://www.ibms.org/includes/act_download.php?download=2013-apr-ph-meters.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2022).
- Cheng, K.; Zhu, D. On calibration of pH meters. Sensors 2005, 5, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.; Baldwin, R. Self-calibrating microfabricated iridium oxide pH electrode array for remote monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Journet, B.; Takhedmit, H.; Lissorgues, G. Porous Titanium Nitride electrodes on miniaturised pH sensor for foetal health monitoring application. In Proceedings of the 2022 Symposium on Design, Test, Integration and Packaging of MEMS/MOEMS (DTIP), Pont-a-Mousson, France, 11–13 July 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, W.; Shylendra, S.; Brouwer, S.; Wajrak, M.; Alameh, K. Application of ruthenium oxide pH sensitive electrode to samples with high redox interference. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Cvejin, K.; Kulawik, J.; Zaraska, K.; Szwagierczak, D.; Socha, R. Fabrication of thick film sensitive RuO2-TiO2 and Ag/AgCl/KCl reference electrodes and their application for pH measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Cvejin, K.; Kulawik, J.; Zaraska, K.; Szwagierczak, D.; Stojanovic, G. Sensing of RuO2–SnO2 thick film pH sensors studied by potentiometric method and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 759, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, S.; Okada, H.; Takamatsu, S.; Itoh, T. Valve-actuator-integrated reference electrode for an ultra-long-life rumen pH sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonsdale, W.; Wajrak, M.; Alameh, K. Manufacture and application of RuO2 solid-state metaloxide pH sensor to common beverages. Talanta 2018, 180, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Sun, X.; He, S. Iridium Oxide Enabled Sensors Applications. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, P.; Mukherjee, R.; Kare, S.P.O.; Das, S. Impedimetric blood pH sensor based on MoS2. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102088–102095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazouskaya, M.; Scheler, O.; Mikli, V.; Uppuluri, K.; Zaraska, K.; Tamm, M. Nafion protective membrane enables using ruthenium oxide electrodes for pH measurement in milk. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 107511–107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, W.; Wajrak, M.; Alameh, K. RuO2 pH Sensor with Super-Glue-Inspired Reference Electrode. Sensors 2017, 17, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitanda, I.; Kiryu, H.; Itagaki, M. Improvement in the long-term stability of screen-printed planar type solid-state Ag/AgCl reference electrode by introducing poly(dimethylsiloxane) liquid junction. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 58, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fog, A.; Buck, R.P. Electronic semiconducting oxides as pH sensors. Sens. Actuators 1984, 5, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinlen, P.; Heider, J.; Hubbard, D. A solid-state pH sensor based on a Nafion-coated iridium oxide indicator electrode and a polymer-based silver chloride reference electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 22, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalupczok, S.; Kurzweil, P.; Hartmann, H. Impact of Various Acids and Bases on the Voltammetric Response of Platinum Group Metal Oxides. Int. J. Electrochem. 2018, 2018, 1697956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E. Hydrophobic Membranes as Liquid Junction-Free Reference Electrodes. Electroanalysis 1999, 11, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul Shylendra, S.; Lonsdale, W.; Wajrak, M.; Nur-E-Alam, M.; Alameh, K. Titanium Nitride Thin Film Based Low-Redox-Interference Potentiometric pH Sensing Electrodes. Sensors 2021, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.V.; Schroeder, J.L.; Ni, X.; Kildishev, A.V.; Sands, T.D.; Boltasseva, A. Titanium nitride as a plasmonic material for visible and near-infrared wavelengths. Opt. Mater. Express 2012, 2, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-H.; Chou, J.-C. Fabrication and Characterization of a Ruthenium Nitride Membrane for Electrochemical pH Sensors. Sensors 2009, 9, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-H.; Lau, K.-W.; Yu, G.-P. Effect of nitrogen flow rate on structure and properties of nanocrystalline TiN thin films produced by unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 191, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabah, F.A.; Ahmed, N.M.; Hassan, Z.; Almessiere, M.A. Study effects of thin film thickness on the behavior of CuS EGFET implemented as pH sensor. DJNB 2016, 11, 787–793. [Google Scholar]
- Nur-E-Alam, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Basher, M.K.; Vasiliev, M.; Alameh, K. Optical and Chromaticity Properties of Metal-Dielectric Composite-Based Multilayer Thin-Film Structures Prepared by RF Magnetron Sputtering. Coatings 2020, 10, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, W.M.; Gumarov, A.I.; Vakhitov, I.R.; Yanilkin, I.V.; Kiiamov, A.G.; Kharintsev, S.S.; Nikitin, S.I.; Tagirov, L.R.; Yusupov, R.V. Electrical properties of titanium nitride films synthesized by reactive magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 927, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Huang, B.R.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chen, K.H.; Chen, L.C. Amorphous boron carbon nitride as a pH sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 2676–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, K.A.; Noh, N.I.; Herman, S.H.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Zolkapli, M.; Abdullah, W.F. pH sensing characteristics of silicon nitride thin film and silicon nitride-based ISFET sensor. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 4th Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium, IEEE, Shah Alam, Malaysia, 19–20 August 2013; pp. 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, Y.-L.; Chou, J.-C.; Lei, Z.-C.; Sun, T.-P.; Chung, W.-Y.; Hsiung, S.-K. Titanium Nitride Membrane Application to Extended Gate Field Effect Transistor pH Sensor Using VLSI Technology. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 40, 6311–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhanov, D.I.; Knizhnik, A.A.; Safonov, A.A.; Bagatur’yants, A.A.; Stoker, M.W.; Korkin, A.A. Structure and electronic properties of zirconium and hafnium nitrides and oxynitrides. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 044108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Lu, Y.-S.; Hong, Y.-L.; Gwo, S.; Yeh, J.A. Highly Sensitive pH Sensing Using an Indium Nitride Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyachandran, Y.L.; Narayandass, S.K.; Mangalaraj, D.; Areva, S.; Mielczarski, J.A. Properties of titanium nitride films prepared by direct current magnetron sputtering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 445–446, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengauer, W. The Reactivity of Some Transition Metal Nitrides and Carbides; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, B.M.; Hector, A.L.; Jura, M.; Owen, J.R.; Whittam, J. Effect of oxidative surface treatments on charge storage at titanium nitride surfaces for supercapacitor applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4550–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitanda, I.; Komoda, M.; Hoshi, Y.; Itagaki, M. An instantly usable paper-based screen-printed solid-state KCl/Ag/AgCl reference electrode with long-term stability. Analyst 2015, 140, 6481–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.-J.; Santos, M.P. dos Characterization of titanium nitride films prepared by d.c. reactive magnetron sputtering at different nitrogen pressures. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1997, 90, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babinova, R.V.; Smirnov, V.V.; Useenov, A.S.; Kravchuk, K.S.; Gladkikh, E.V.; Shapovalov, V.I.; Mylnikov, I.L. Mechanical properties of titanium nitride films obtained by reactively sputtering with hot target. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 872, 012035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgrabik, C.M.; Hu, E.L. Optimization of sputtered titanium nitride as a tunable metal for plasmonic applications. Opt. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patan, M.K. Titanium nitride as an electrode material for high charge density applications. Theses 2007, 394, 9159350. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Wang, H.; Lu, S.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Q.; Liang, D.; Xiang, Y. Titanium nitride as an electrocatalyst for V(II)/V(III)redox couples in all-vanadium redox flow batteries. Electrochem. Acta 2015, 182, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umapathi, R.; Ghoreishian, S.; Sonwal, S.; Rani, G.; Huh, Y. Portable electrochemical sensing methodologies for on-site detection of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 453, 214305–214336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Application Matrix | pH Sensitive Material | Fabrication Method | Sensitivity (mV/h) | pH Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redox matrix | RuO2 | RF sputtering | −56.6 | 2–12 | [7] |
| Biological and environmental application | RuN | Magnetron sputtering | −58.3 | 1–12 | [23] |
| Phosphate buffer solution | Br-C-N | Dual gun sputtering | −46 | 1–13 | [28] |
| Aquaculture | SiN | ISFET package | −53.6 | 4–10 | [29] |
| Chemical applications | InN | ISFET | −58.2 | 2–12 | [32] |
| Chemical application | IrO2 + Nafion | Cryogenic sputtering | −60.2 | 2–12 | [21] |
| Fresh Orange juice | TiN | RF Magnetron sputtering | −59.1 | 2–12 | [21] previous work |
| Common drinks with redox species | TiN + Nafion | RF Magnetron sputtering | −56.6 | 2–12 | * This work |
| Resistivity (ohm) | Sputter Target | Gas Ratio (Ar:N2) | Sputter Pressure (mTorr) | Nafion Thickness (µL) | Sensitivity (mV/pH) | Hysteresis (mV) | R2 | Drift (mV/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.6 | Ti | 9:1 | 2 | 5 | −56.4 ± 1.2 | 2.3 ± 1.2 | 0.9997 | 4.6 ± 1.2 |
| 4.1 | Ti | 9:1 | 2 | 10 | −59.3 ± 3.2 | 84.7 ± 3.4 | 0.9341 | 78.48 ± 2.5 |
| 4.8 | Ti | 9:1 | 2 | 15 | −56.2 ± 2.8 | 52.63 ± 1.2 | 0.9818 | 165.4 ± 6.7 |
| 4.9 | Ti | 9:1 | 2 | 20 | −53.4 ± 4.2 | 55.17 ± 4.7 | 0.9698 | 210.56 ± 2.7 |
| 5.6 | Ti | 9:1 | 2 | 25 | −53.1 ± 1.2 | 71.30 ± 7.8 | 0.9519 | 222.84 ± 3.8 |
| pH | Reaction Time (min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 60 | 120 | 240 | |
| 2 | 36.16 mV/h | 15.22 mV/h | 9.32 mV/h | 6.20 mV/h |
| 4 | 18.26 mV/h | 12.54 mV/h | 10.33 mV/h | 7.88 mV/h |
| 7 | 15.33 mV/h | 12.45 mV/h | 9.44 mV/h | 4.22 mV/h |
| 10 | 42.56 mV/h | 34.88 mV/h | 19.73 mV/h | 12.45 mV/h |
| 12 | 22.43 mV/h | 9.36 mV/h | 7.11 mV/h | 4.26 mV/h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shylendra, S.P.; Wajrak, M.; Alameh, K.; Kang, J.J. Nafion Modified Titanium Nitride pH Sensor for Future Biomedical Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020699
Shylendra SP, Wajrak M, Alameh K, Kang JJ. Nafion Modified Titanium Nitride pH Sensor for Future Biomedical Applications. Sensors. 2023; 23(2):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020699
Chicago/Turabian StyleShylendra, Shimrith Paul, Magdalena Wajrak, Kamal Alameh, and James Jin Kang. 2023. "Nafion Modified Titanium Nitride pH Sensor for Future Biomedical Applications" Sensors 23, no. 2: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020699
APA StyleShylendra, S. P., Wajrak, M., Alameh, K., & Kang, J. J. (2023). Nafion Modified Titanium Nitride pH Sensor for Future Biomedical Applications. Sensors, 23(2), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020699







