Mapping Pharmacologically Evoked Neurovascular Activation and Its Suppression in a Rat Model of Tremor Using Functional Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.1.1. Animal Handling
2.1.2. Surgery and Tremor Induction
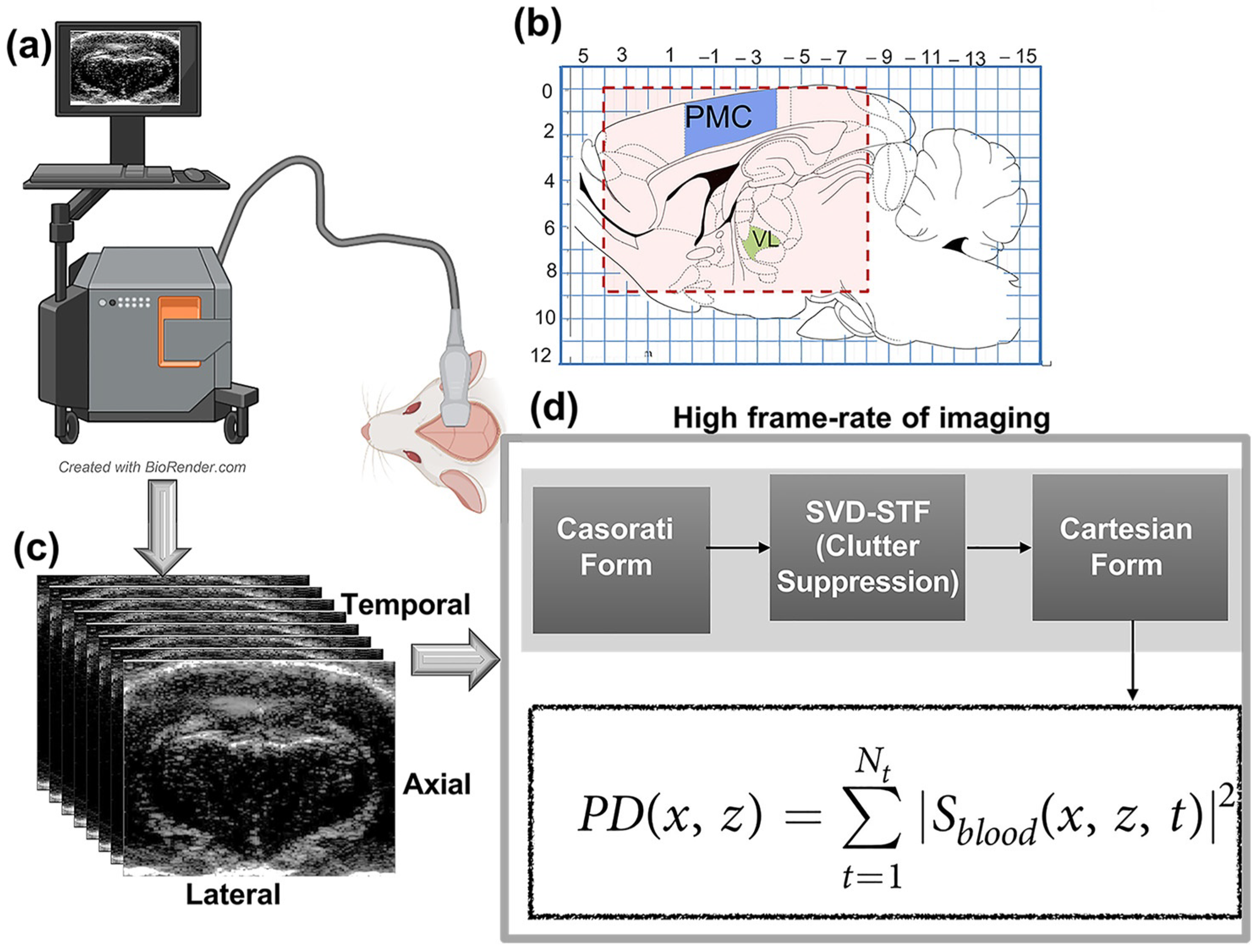
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Functional Image Processing and Estimation of microDoppler Image
2.4. Electrophysiology Data Acquisition and Processing
2.5. Statistical Tests
3. Results
3.1. fUS Reveals Correlated Brain Activity Corresponding to Harmaline-Evoked Tremor
3.2. Characterization of Putative Spatiotemporal Changes in Brain Activity Corresponding to Tremor Suppression Using Beta-Adrenergic Blocker
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welton, T.; Cardoso, F.; Carr, J.A.; Chan, L.-L.; Deuschl, G.; Jankovic, J.; Tan, E.-K. Essential tremor. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, V. Essential tremor: Diagnosis and management. BMJ 2019, 366, l4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Lo, S.E.; Louis, E.D. Common misdiagnosis of a common neurological disorder: How are we misdiagnosing essential tremor? Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, S.; Nederveen, A.J.; Booij, J.; van Rootselaar, A.-F. Neuroimaging essentials in essential tremor: A systematic review. NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 5, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, I.; Lee, J.; Knight, E.; Cheng, L.; il Kang, S.; Jang, D.P.; Chang, S.-Y. Development of harmaline-induced tremor in a swine model. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2018, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, H. Rodent models of tremor. Cerebellum 2007, 6, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Cortez, J.; Chang, S.-Y. Thalamo-cortical network is associated with harmaline-induced tremor in rodent model. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 358, 114210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handforth, A. Harmaline tremor: Underlying mechanisms in a potential animal model of essential tremor. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2012, 2, 02-92-769-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.W. Diagnosis and Treatment of Essential Tremor. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2022, 28, 1333–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.C.; Thu Le, A.; Handforth, A. Harmaline-induced tremor as a potential preclinical screening method for essential tremor medications. Mov. Disord. 2005, 20, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lei, D.; Suo, X.; Li, N.; Lu, Z.; Li, J.; Peng, J.; Gong, Q.; Peng, R. Resting-state fMRI study on drug-naive patients of essential tremor with and without head tremor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrasiabi, M.; Noroozian, N. Advantages and Limitations of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) of the Human Visual Brain; Horizons in Neuroscience Research Series; Costa, A., Villalba, E., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sorger, B.; Goebel, R. Real-time fMRI for brain-computer interfacing. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 168, 289–302. [Google Scholar]
- Demené, C.; Deffieux, T.; Pernot, M.; Osmanski, B.-F.; Biran, V.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Sieu, L.-A.; Bergel, A.; Franqui, S.; Correas, J.-M. Spatiotemporal clutter filtering of ultrafast ultrasound data highly increases Doppler and fUltrasound sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 2271–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesnik, M.; Blaize, K.; Deffieux, T.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Sahel, J.-A.; Fink, M.; Picaud, S.; Tanter, M. 3D functional ultrasound imaging of the cerebral visual system in rodents. Neuroimage 2017, 149, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provost, J.; Papadacci, C.; Arango, J.E.; Imbault, M.; Fink, M.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Tanter, M.; Pernot, M. 3D ultrafast ultrasound imaging in vivo. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffieux, T.; Demene, C.; Pernot, M.; Tanter, M. Functional ultrasound neuroimaging: A review of the preclinical and clinical state of the art. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 50, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, E.; Montaldo, G.; Osmanski, B.-F.; Cohen, I.; Fink, M.; Tanter, M. Functional ultrasound imaging of the brain: Theory and basic principles. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2013, 60, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanter, M.; Fink, M. Ultrafast imaging in biomedical ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.-K.; Haselden, W.D.; Goulam Houssen, Y.; Pouzat, C.; Rungta, R.L.; Demené, C.; Tanter, M.; Drew, P.J.; Charpak, S.; Boido, D. Transfer functions linking neural calcium to single voxel functional ultrasound signal. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paz, J.M.M.; Macé, E. Functional ultrasound imaging: A useful tool for functional connectomics? NeuroImage 2021, 245, 118722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macé, E.; Montaldo, G.; Cohen, I.; Baulac, M.; Fink, M.; Tanter, M. Functional ultrasound imaging of the brain. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, A.; Mace, E.; Brunner, C.; Heidmann, M.; Rossier, J.; Montaldo, G. Chronic assessment of cerebral hemodynamics during rat forepaw electrical stimulation using functional ultrasound imaging. Neuroimage 2014, 101, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhauer, M.; Lidouren, F.; Remy-Jouet, I.; Mongardon, N.; Adam, C.; Bruneval, P.; Hocini, H.; Levy, Y.; Blengio, F.; Carli, P. Hypothermic total liquid ventilation is highly protective through cerebral hemodynamic preservation and sepsis-like mitigation after asphyxial cardiac arrest. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, e420–e430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, R.; Kruizinga, P.; Mastik, F.; Belau, M.; de Jong, N.; Bosch, J.G.; Scheffer, W.; Maret, G. 3D functional ultrasound imaging of pigeons. Neuroimage 2018, 183, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, A.; Dussaux, C.; Martel, G.; Brunner, C.; Mace, E.; Montaldo, G. Real-time imaging of brain activity in freely moving rats using functional ultrasound. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demene, C.; Baranger, J.; Bernal, M.; Delanoe, C.; Auvin, S.; Biran, V.; Alison, M.; Mairesse, J.; Harribaud, E.; Pernot, M. Functional ultrasound imaging of brain activity in human newborns. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbault, M.; Chauvet, D.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Capelle, L.; Tanter, M. Intraoperative functional ultrasound imaging of human brain activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloukey, S.; Vincent, A.J.; Satoer, D.D.; Mastik, F.; Smits, M.; Dirven, C.M.; Strydis, C.; Bosch, J.G.; van der Steen, A.F.; De Zeeuw, C.I. Functional ultrasound (fUS) during awake brain surgery: The clinical potential of intra-operative functional and vascular brain mapping. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranger, J.; Demene, C.; Frerot, A.; Faure, F.; Delanoë, C.; Serroune, H.; Houdouin, A.; Mairesse, J.; Biran, V.; Baud, O. Bedside functional monitoring of the dynamic brain connectivity in human neonates. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, M.; Fatemi, M.; Alizad, A. Background removal and vessel filtering of noncontrast ultrasound images of microvasculature. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Lee, J.; Chantigian, S.; Fatemi, M.; Chang, S.-Y.; Alizad, A. Imaging the response to deep brain stimulation in rodent using functional ultrasound. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 05LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Fatemi, M.; Alizad, A. Adaptive background noise bias suppression in contrast-free ultrasound microvascular imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 245015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tort, A.B.; Komorowski, R.; Eichenbaum, H.; Kopell, N. Measuring phase-amplitude coupling between neuronal oscillations of different frequencies. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 104, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nahab, F.B.; Hallett, M. Current role of functional MRI in the diagnosis of movement disorders. Neuroimaging Clin. 2010, 20, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, J.-Y.; Suo, X.-L.; Li, N.-N.; Lei, D.; Lu, Z.-J.; Wang, L.; Peng, J.-X.; Duan, L.-R.; Gong, Q.-Y.; Peng, R. Altered spontaneous brain activity in essential tremor with and without resting tremor: A resting-state fMRI study. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2021, 34, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contarino, M.F.; Groot, P.F.; van der Meer, J.N.; Bour, L.J.; Speelman, J.D.; Nederveen, A.J.; van den Munckhof, P.; Tijssen, M.A.; Schuurman, P.R.; van Rootselaar, A.-F. Is there a role for combined EMG-fMRI in exploring the pathophysiology of essential tremor and improving functional neurosurgery? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Luft, F.; de Boer, L.; Buijink, A.; Mugge, W.; Schouten, A.; Heida, T.; Bour, L.; van Rootselaar, A. Closing the loop: Novel quantitative fMRI approach for manipulation of the sensorimotor loop in tremor. NeuroImage 2022, 262, 119554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtbernd, F.; Shah, N.J. Imaging the pathophysiology of essential tremor—A systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 680254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jo, H.J.; Kim, I.; Lee, J.; Min, H.-K.; In, M.-H.; Knight, E.J.; Chang, S.-Y. Mapping BOLD activation by pharmacologically evoked tremor in swine. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.L.; Luh, W.M.; Liu, T.T.; Martinez, A.; Obata, T.; Wong, E.C.; Frank, L.R.; Buxton, R.B. Nonlinear temporal dynamics of the cerebral blood flow response. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2001, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Brown, G.G. Measurement of cerebral perfusion with arterial spin labeling: Part 1. Methods. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2007, 13, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmanski, B.-F.; Pezet, S.; Ricobaraza, A.; Lenkei, Z.; Tanter, M. Functional ultrasound imaging of intrinsic connectivity in the living rat brain with high spatiotemporal resolution. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, T.-H.H.; Chen, J.-H.; Yen, C.-T. Repeated BOLD-fMRI imaging of deep brain stimulation responses in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaize, K.; Arcizet, F.; Gesnik, M.; Ahnine, H.; Ferrari, U.; Deffieux, T.; Pouget, P.; Chavane, F.; Fink, M.; Sahel, J.-A. Functional ultrasound imaging of deep visual cortex in awake nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14453–14463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizeux, A.; Gesnik, M.; Ahnine, H.; Blaize, K.; Arcizet, F.; Picaud, S.; Sahel, J.-A.; Deffieux, T.; Pouget, P.; Tanter, M. Functional ultrasound imaging of the brain reveals propagation of task-related brain activity in behaving primates. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, S.L.; Maresca, D.; Christopoulos, V.N.; Griggs, W.S.; Demene, C.; Tanter, M.; Shapiro, M.G.; Andersen, R.A. Single-trial decoding of movement intentions using functional ultrasound neuroimaging. Neuron 2021, 109, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Nawar, N.; Webb, J.; Fatemi, M.; Alizad, A. Impact of imaging cross-section on visualization of thyroid microvessels using ultrasound: Pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabut, C.; Correia, M.; Finel, V.; Pezet, S.; Pernot, M.; Deffieux, T.; Tanter, M. 4D functional ultrasound imaging of whole-brain activity in rodents. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiran, E.; Ferrier, J.; Deffieux, T.; Gennisson, J.-L.; Pezet, S.; Lenkei, Z.; Tanter, M. Transcranial functional ultrasound imaging in freely moving awake mice and anesthetized young rats without contrast agent. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, C.; Grillet, M.; Urban, A.; Roska, B.; Montaldo, G.; Macé, E. Whole-brain functional ultrasound imaging in awake head-fixed mice. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3547–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Moto Cortex | Ventrolateral Thalamus | |
|---|---|---|
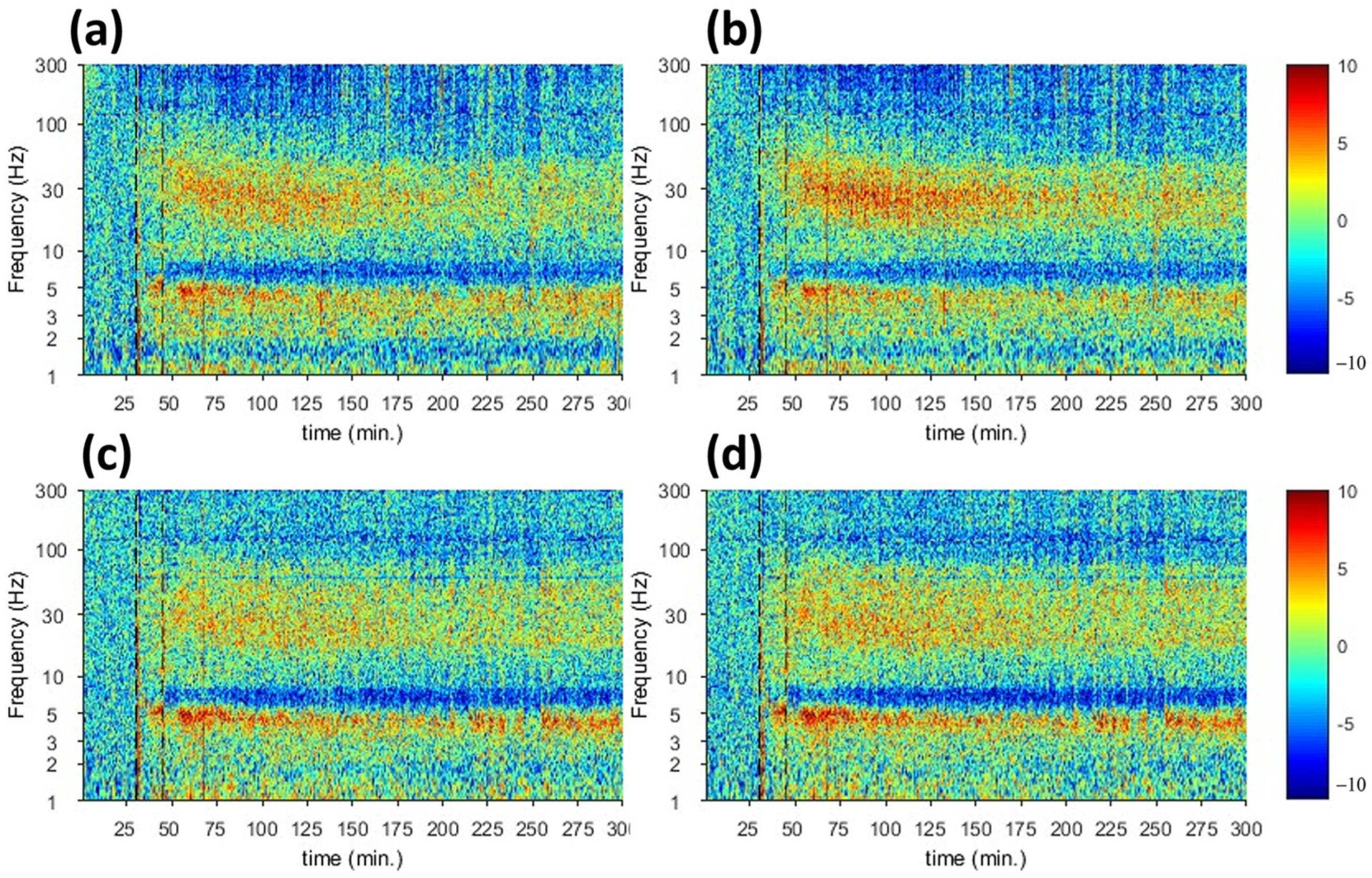
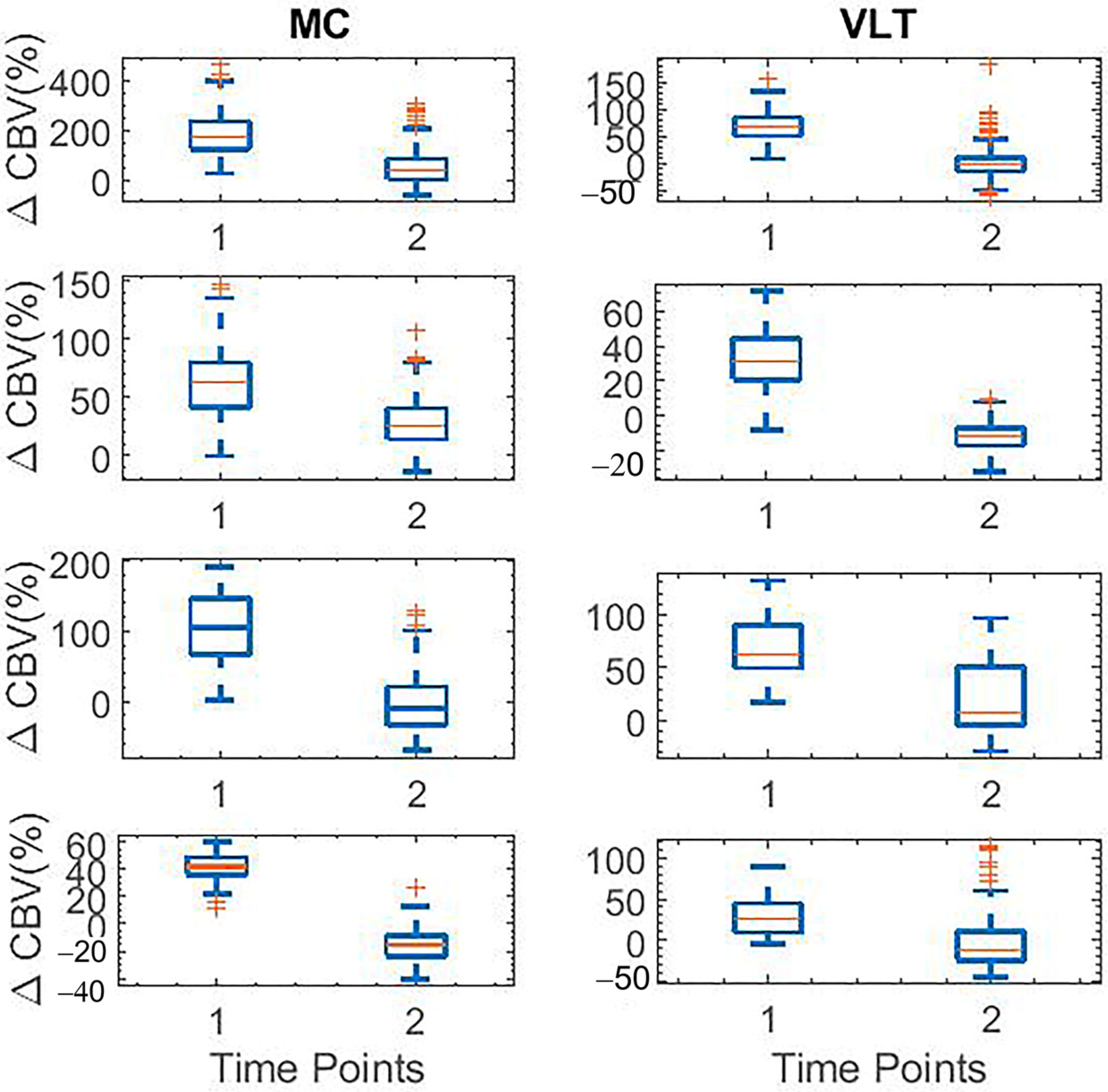
| fUS | Harmaline-induced activities start at t = 30 and decrease at t = 140 | Harmaline-induced activities start at t = 30 and decrease at t = 140 |
| Electrophysiology | Increase in the spectrogram signal at t = 45 and decrease in t = 145 | Increase in the spectrogram signal at t = 45 and decrease in t = 175 |
| Moto Cortex | Ventrolateral Thalamus | |
|---|---|---|
| fUS | Suppression of harmaline-induced activities start at t = 30 and increase again with peak at t = 110 | Suppression of harmaline-induced activities start at t = 30 and increase again with peak at t = 110 |
| Electrophysiology | Low spectrogram signal at t = 45 and increase signal in t = 120 | Low spectrogram signal at t = 45 and increase signal in t = 120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nayak, R.; Lee, J.; Sotoudehnia, S.; Chang, S.-Y.; Fatemi, M.; Alizad, A. Mapping Pharmacologically Evoked Neurovascular Activation and Its Suppression in a Rat Model of Tremor Using Functional Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study. Sensors 2023, 23, 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156902
Nayak R, Lee J, Sotoudehnia S, Chang S-Y, Fatemi M, Alizad A. Mapping Pharmacologically Evoked Neurovascular Activation and Its Suppression in a Rat Model of Tremor Using Functional Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study. Sensors. 2023; 23(15):6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156902
Chicago/Turabian StyleNayak, Rohit, Jeyeon Lee, Setayesh Sotoudehnia, Su-Youne Chang, Mostafa Fatemi, and Azra Alizad. 2023. "Mapping Pharmacologically Evoked Neurovascular Activation and Its Suppression in a Rat Model of Tremor Using Functional Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study" Sensors 23, no. 15: 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156902
APA StyleNayak, R., Lee, J., Sotoudehnia, S., Chang, S.-Y., Fatemi, M., & Alizad, A. (2023). Mapping Pharmacologically Evoked Neurovascular Activation and Its Suppression in a Rat Model of Tremor Using Functional Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study. Sensors, 23(15), 6902. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156902








