mm-TPG: Traffic Policemen Gesture Recognition Based on Millimeter Wave Radar Point Cloud
Abstract
1. Introduction
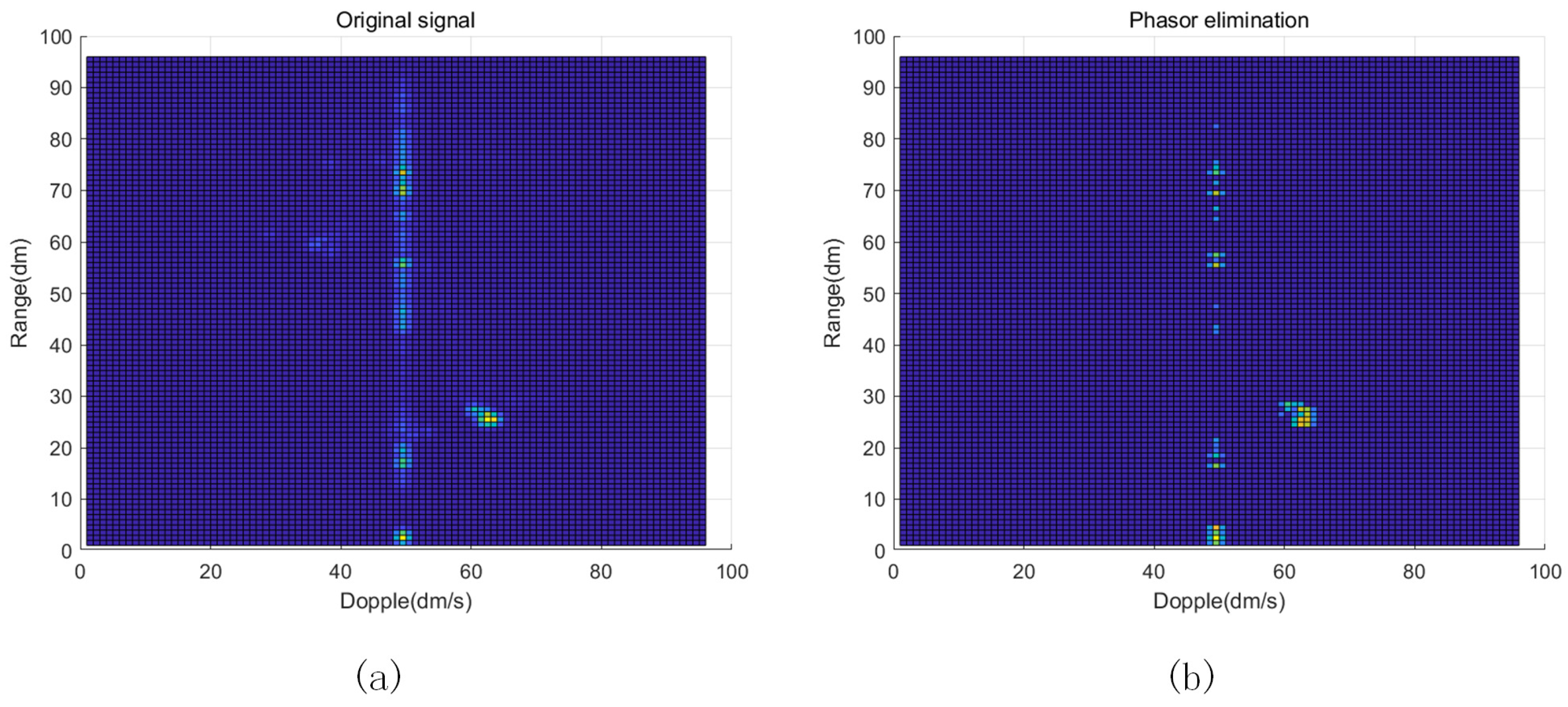
- A signal-noise removal method with double-threshold detection is proposed, which effectively solves the problem of noise and clutter in the data and achieves the enhancement of radar signal and echo information.
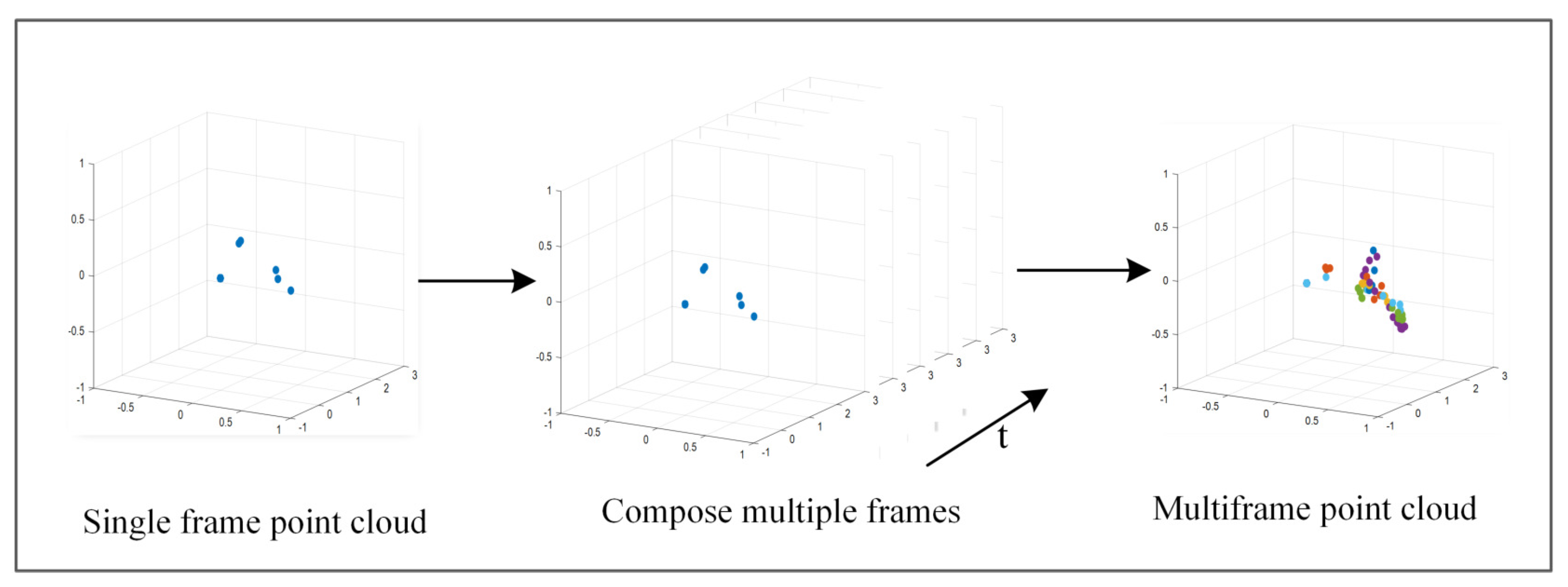
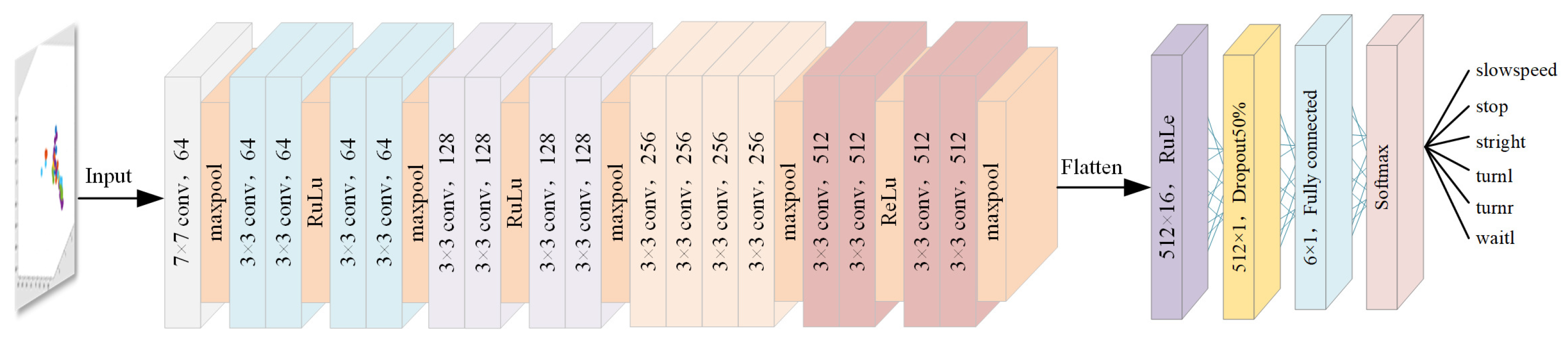
- A model that introduces multi-frame point cloud synthesis and combines ResNet18 with gated recurrent units, addresses the problem of the limited information capacity of single-frame point clouds, improves the efficiency of classification, and avoids the problem of gradient explosion.
- The mm-TPG system developed in this paper senses the command gestures of traffic police in a non-contact manner. Through extensive experiments, it is proved that the system is almost unaffected by personnel differences and has a comprehensive recognition rate of over 89% with strong robustness.
2. Related Works
- Millimeter-wave signals have higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths, providing higher spatial resolution and more detailed gesture data.
- Millimeter-wave point cloud data not only includes traditional features such as distance and angle but also directly indicates the spatial position of the target, making the gesture information more visualized.
- Millimeter-wave radar can obtain high-quality data even in harsh weather conditions, independent of weather and lighting conditions.
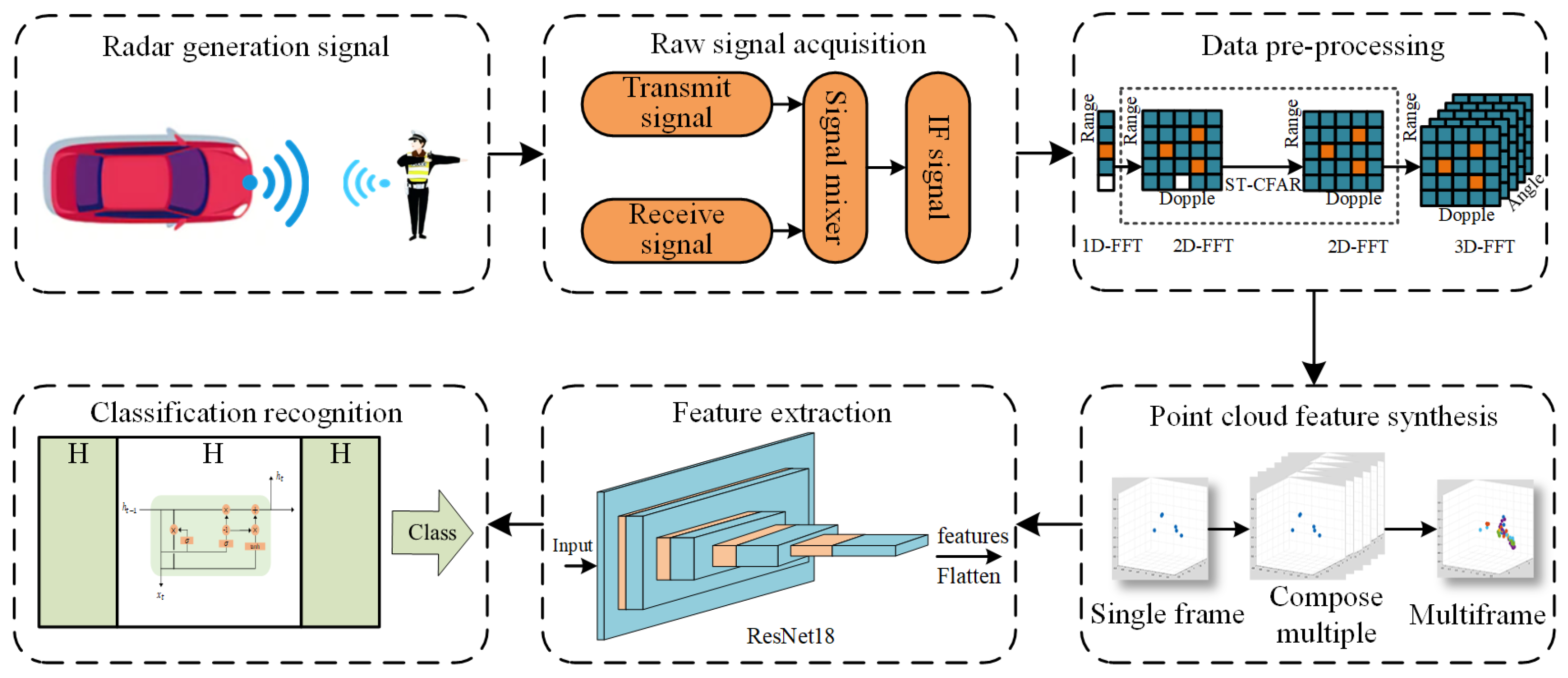
3. System Design
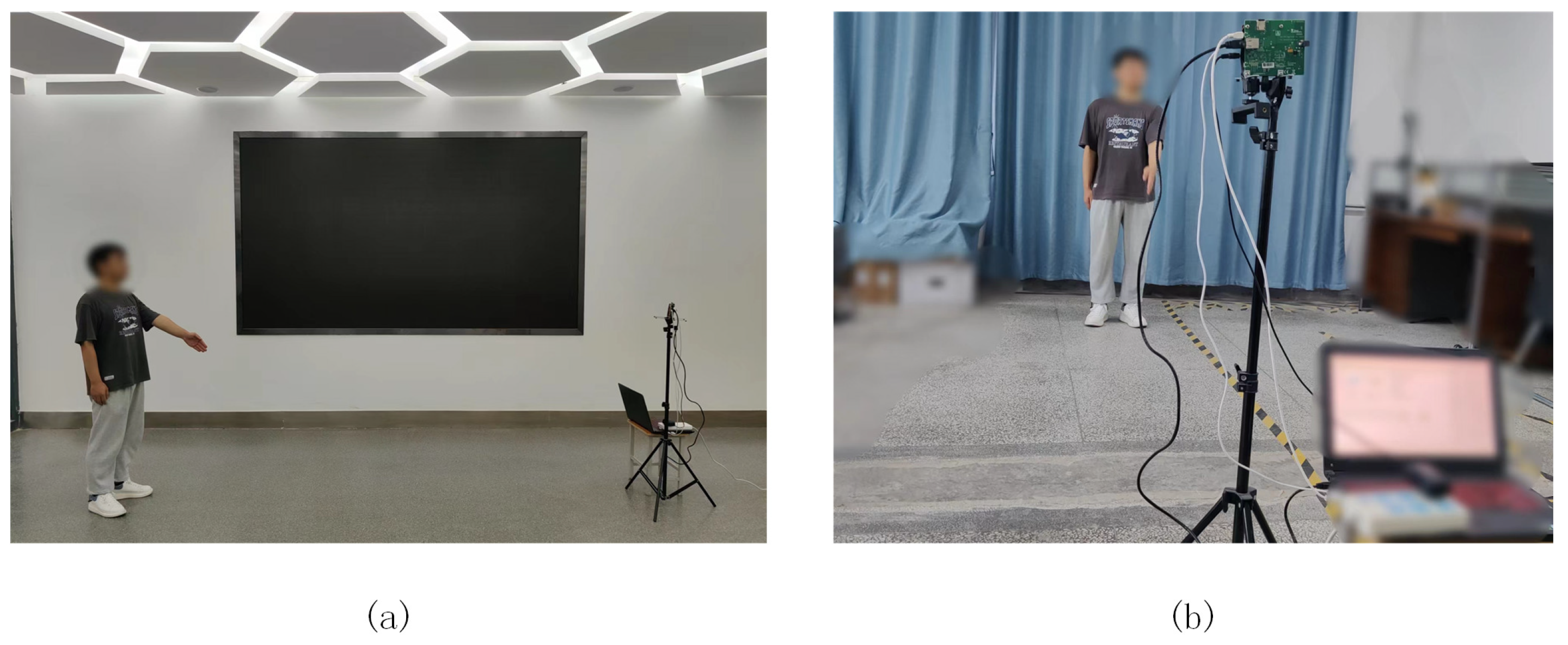
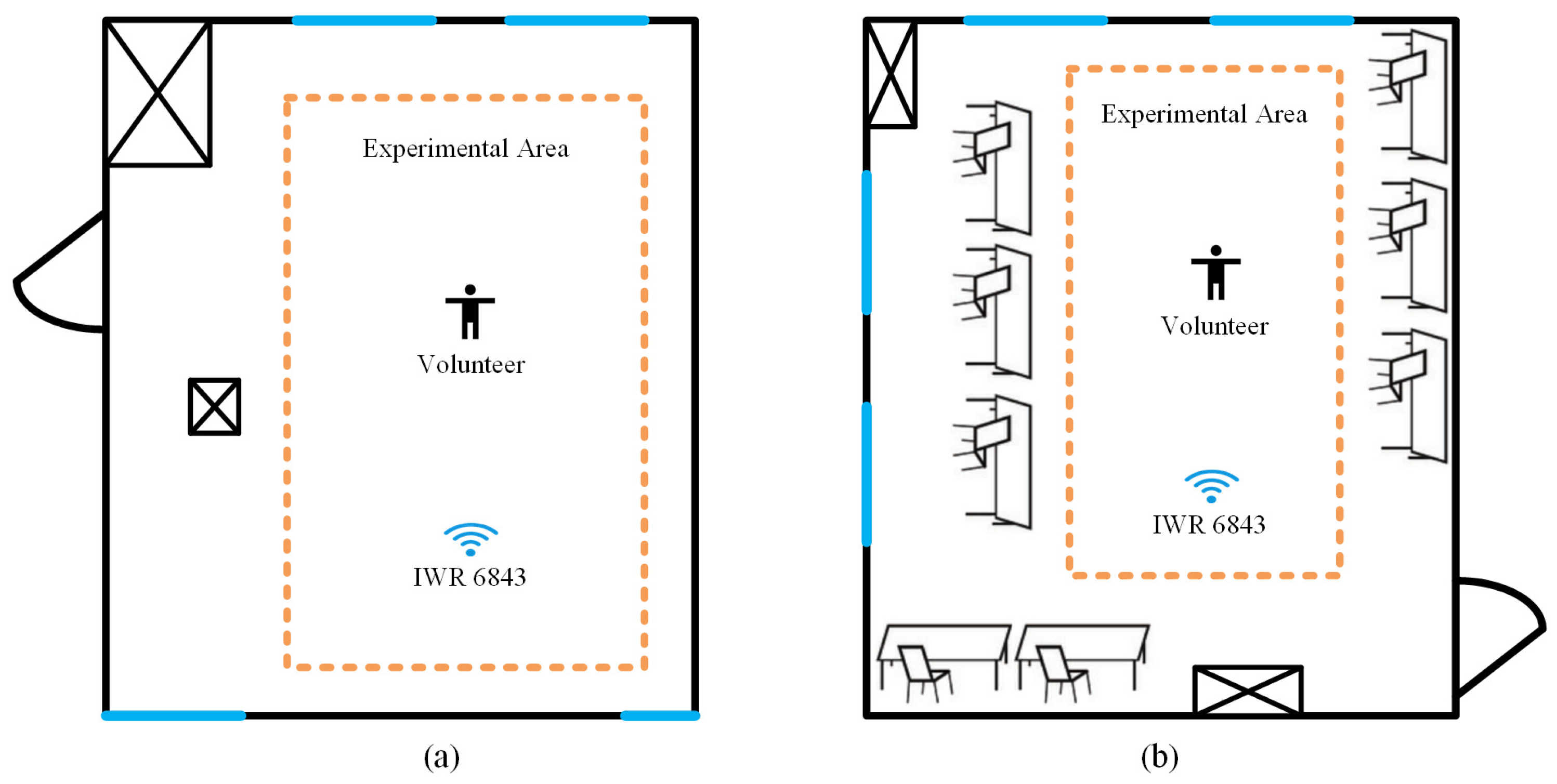
3.1. Experiment Setup
3.2. Overview
3.3. Raw Data Pre-Processing Module
3.4. Motion Feature Extraction Module
3.5. Classification Module
Point Cloud Gesture Classification Module Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Point cloud gesture classification |
 |
4. Experiments and Evaluation
4.1. Experimental Analysis
4.1.1. Effect of Different Distances on Experimental Results
- a
- Different distances
- b
- Different azimuth angles
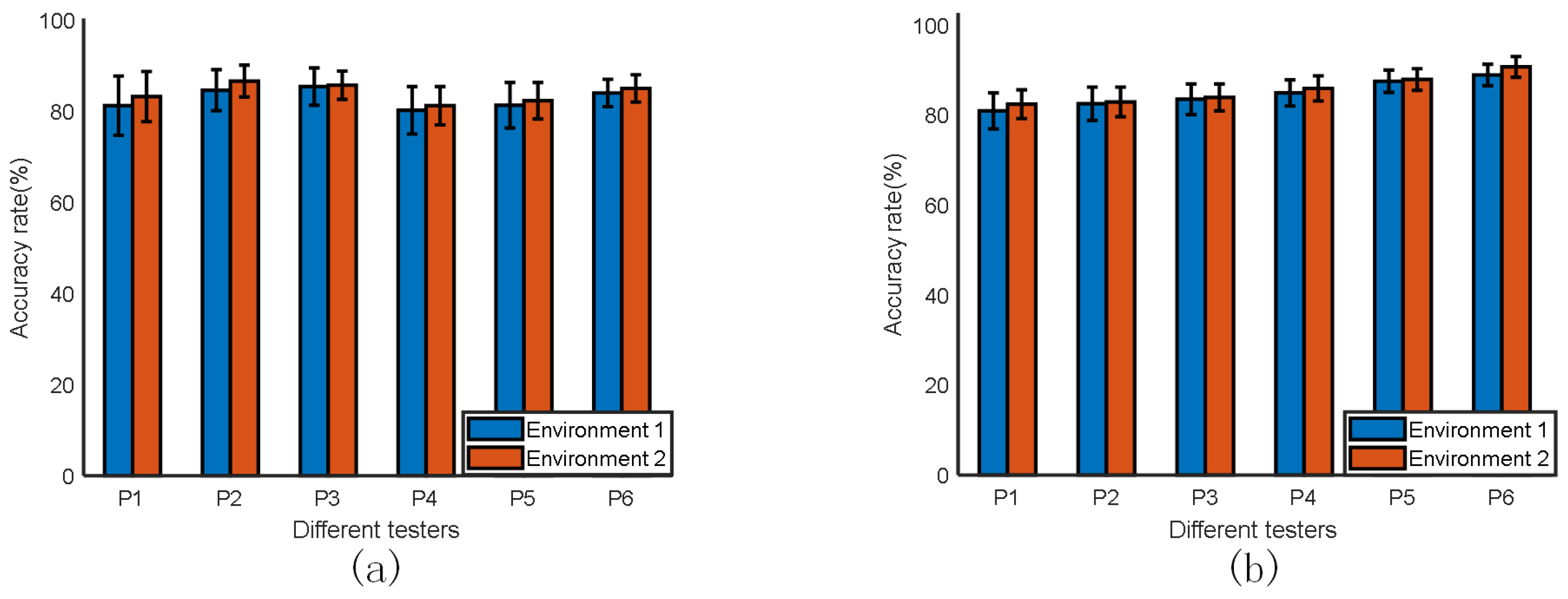
4.1.2. Influence of Different Subjects
4.1.3. Effect of Different Numbers of Synthesized Frames on the Experiment
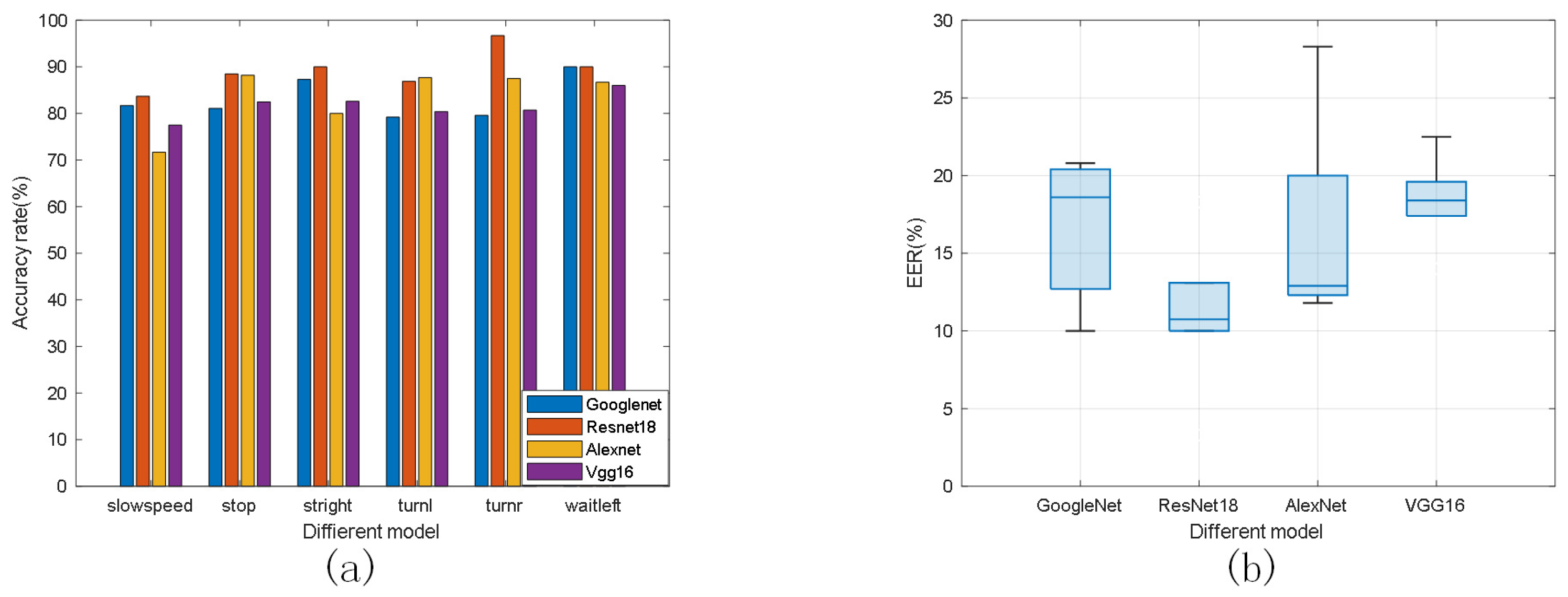
4.1.4. Comparison of Different Feature Extraction Models
4.1.5. Comparison with Other Existing Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FMCW | Frequency-Modulated Continuous Wave |
| SAE | Society of Automotive Engineers |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Units |
| CV | Computer Vision |
| GSE | Gesture Skeleton Extractor |
| RFID | Radio Frequency Identification |
| RSSI | Received Signal-Strength Indicator |
| CSI | Channel State Information |
| OMP | Orthogonal Matching Pursuit |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| MIMO | Multiple Input Multiple Output |
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array |
| MTI | Moving Target Indication |
| AoA | Angle of Arrival |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
References
- Ma, N.; Li, D.; He, W.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Future vehicles: Interactive wheeled robots. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 156101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Qin, F.; Bu, X.; Liang, X. A robust perception algorithm based on a radar and LiDAR for intelligent driving. J. Radars 2021, 10, 622–631. [Google Scholar]
- Tesla Vehicles Come Standard with Advanced Hardware to Support Autopilot Assisted Driving and Fully Autonomous Driving Capabilities. Available online: https://www.tesla.cn/autopilot (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Taxonomy and Definitions for Terms Related to Driving Automation Systems for On-Road Motor Vehicles. Available online: https://www.sae.org/standards/content/j3016 (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Zhu, P.; Zhou, H.; Cao, S.; Yang, P.; Xue, S. Control with gestures: A hand gesture recognition system using off-the-shelf smartwatch. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Big Data Computing and Communications (BIGCOM), Chicago, IL, USA, 7–9 August 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Savoie, P.; Cameron, J.A.; Kaye, M.E.; Scheme, E.J. Automation of the timed-up-and-go test using a conventional video camera. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, W.; Peng, D.; Liu, Y.; Liao, X.; Jiang, H. Adversarial wifi sensing for privacy preservation of human behaviors. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 24, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, Z.; Li, M.; Fang, D.; Nurmi, P.; Wang, Z. CrossSense: Towards cross-site and large-scale WiFi sensing. In Proceedings of the 24th annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, New Delhi, India, 29 October–2 November 2018; pp. 305–320. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, M.; Shaker, G.; De Almeida, J.C.M.; Morita, P.P.; Safavi-Naeini, S. Remote monitoring of human vital signs using mm-wave FMCW radar. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54958–54968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, A.; Ulaganathan, R.V.; Finke, T. Short-range millimetric-wave radar system for occupancy sensing application. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2018, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, J.; Pérez, R.; Biebl, E. Improved people counting algorithm for indoor environments using 60 GHz FMCW radar. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wachs, J.P.; Kölsch, M.; Stern, H.; Edan, Y. Vision-based hand-gesture applications. Commun. ACM 2011, 54, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautaray, S.S.; Agrawal, A. Vision based hand gesture recognition for human computer interaction: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2015, 43, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wu, H.; Min, W.; Xu, J.; Fu, Q.; Peng, C. Traffic police gesture recognition based on gesture skeleton extractor and multichannel dilated graph convolution network. Electronics 2021, 10, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Tang, J.; Wang, X. Gesture recognition of traffic police based on static and dynamic descriptor fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 8915–8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, S.; Sun, B. Extreme Learning Machine Based Hand Posture Recognition in Color-Depth Image; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 276–285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, H.; Alsheikh, M.A.; Li, T.; Hristov, R.; Kabelac, Z.; Katabi, D.; Torralba, A. RF-based 3D skeletons. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Budapest, Hungary, 20–25 August 2018; pp. 267–281. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelnasser, H.; Harras, K.; Youssef, M. A ubiquitous WiFi-based fine-grained gesture recognition system. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2018, 18, 2474–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Gruteser, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, H. E-eyes: Device-free location-oriented activity identification using fine-grained wifi signatures. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Maui, HI, USA, 7–11 September 2014; pp. 617–628. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, M.; Santra, A.; Fischer, G. Human target detection and localization with radars using deep learning. Deep. Learn. Appl. 2021, 2, 173–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Xing, G.; Roy, S.; Liu, H. Experiments with mmwave automotive radar test-bed. In Proceedings of the 2019 53rd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 3–6 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Pan, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, J. Capturing human pose using mmWave radar. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Austin, TX, USA, 23–27 March 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, B.; Ding, L.; Feng, Z.; Zhu, M.; Lei, T.; Xing, M.; Zhou, X. CNN-LRP: Understanding convolutional neural networks performance for target recognition in SAR images. Sensors 2021, 21, 4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Jung, J.; Lee, J.E.; Park, H.M.; Lee, S. DNN-based human face classification using 61 GHz FMCW radar sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 12217–12224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Abedi, H.; Shaker, G. Low-cost low-power in-vehicle occupant detection with mm-wave FMCW radar. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE SENSORS, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Toomajian, B. Hand gesture recognition using micro-Doppler signatures with convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 7125–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cao, S. Real-time human motion behavior detection via CNN using mmWave radar. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2018, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, P.; Gupta, S.; Kim, K.; Pulli, K. Short-range FMCW monopulse radar for hand-gesture sensing. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, USA, 10–15 May 2015; pp. 1491–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Dekker, B.; Jacobs, S.; Kossen, A.S.; Kruithof, M.C.; Huizing, A.G.; Geurts, M. Gesture recognition with a low power FMCW radar and a deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 European Radar Conference (EURAD), Nuremberg, Germany, 11–13 October 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Lei, P.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, M.L. Gesture action radar recognition method based on convolutional neural network. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2018, 44, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Geng, X.; Lin, Y.J. Comprehensive mpoint: A method for 3d point cloud generation of human bodies utilizing fmcw mimo mm-wave radar. Sensors 2021, 21, 6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xu, Z.; Yan, K.; Chien, Y.R.; Fang, S.H.; Wu, H.C. Noninvasive human activity recognition using millimeter-wave radar. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 3036–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Dou, Z.; Zou, W.; Zhang, A.; Li, Z. Activity Recognition Based on Millimeter-Wave Radar by Fusing Point Cloud and Range–Doppler Information. Signals 2022, 3, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H. Human Detection and Action Classification Based on Millimeter Wave Radar Point Cloud Imaging Technology. In Signal Processing Symposium (SPSympo); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.X. A millimetre-wave radar-based fall detection method using line kernel convolutional neural network. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13364–13370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv 2021, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.; Wang, Y. WiNum: A WiFi finger gesture recognition system based on CSI. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th International Conference on Information Technology: IoT and Smart City, Shanghai China, 20–23 December 2019; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar]










| Number of Frames | Preconditioning Time | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.029 | 52.90% |
| 2 | 0.042178 | 66.1% |
| 3 | 0.058164 | 74.60% |
| 4 | 0.07059 | 80.3% |
| 5 | 0.086115 | 88.2% |
| 6 | 0.101581 | 89.60% |
| 7 | 0.125181 | 87.10% |
| 8 | 0.135551 | 84.50% |
| 9 | 0.156078 | 78.60% |
| Project | Device | Algorithm | Feature | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al. | mmWave | CNN | micro-Doppler | 81% |
| Wi-Num | WiFi | GBDT | CSI | 80% |
| MMPointGNN | mmWave | PointNet | Pointcloud | 84% |
| mm-TPG (ours) | mmWave | ResNet+GRU | Pointcloud | 89% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dang, X.; Ke, W.; Hao, Z.; Jin, P.; Deng, H.; Sheng, Y. mm-TPG: Traffic Policemen Gesture Recognition Based on Millimeter Wave Radar Point Cloud. Sensors 2023, 23, 6816. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156816
Dang X, Ke W, Hao Z, Jin P, Deng H, Sheng Y. mm-TPG: Traffic Policemen Gesture Recognition Based on Millimeter Wave Radar Point Cloud. Sensors. 2023; 23(15):6816. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156816
Chicago/Turabian StyleDang, Xiaochao, Wenze Ke, Zhanjun Hao, Peng Jin, Han Deng, and Ying Sheng. 2023. "mm-TPG: Traffic Policemen Gesture Recognition Based on Millimeter Wave Radar Point Cloud" Sensors 23, no. 15: 6816. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156816
APA StyleDang, X., Ke, W., Hao, Z., Jin, P., Deng, H., & Sheng, Y. (2023). mm-TPG: Traffic Policemen Gesture Recognition Based on Millimeter Wave Radar Point Cloud. Sensors, 23(15), 6816. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23156816






