Experimental Guesswork with Quantum Side Information Using Twisted Light
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
3. Experiment
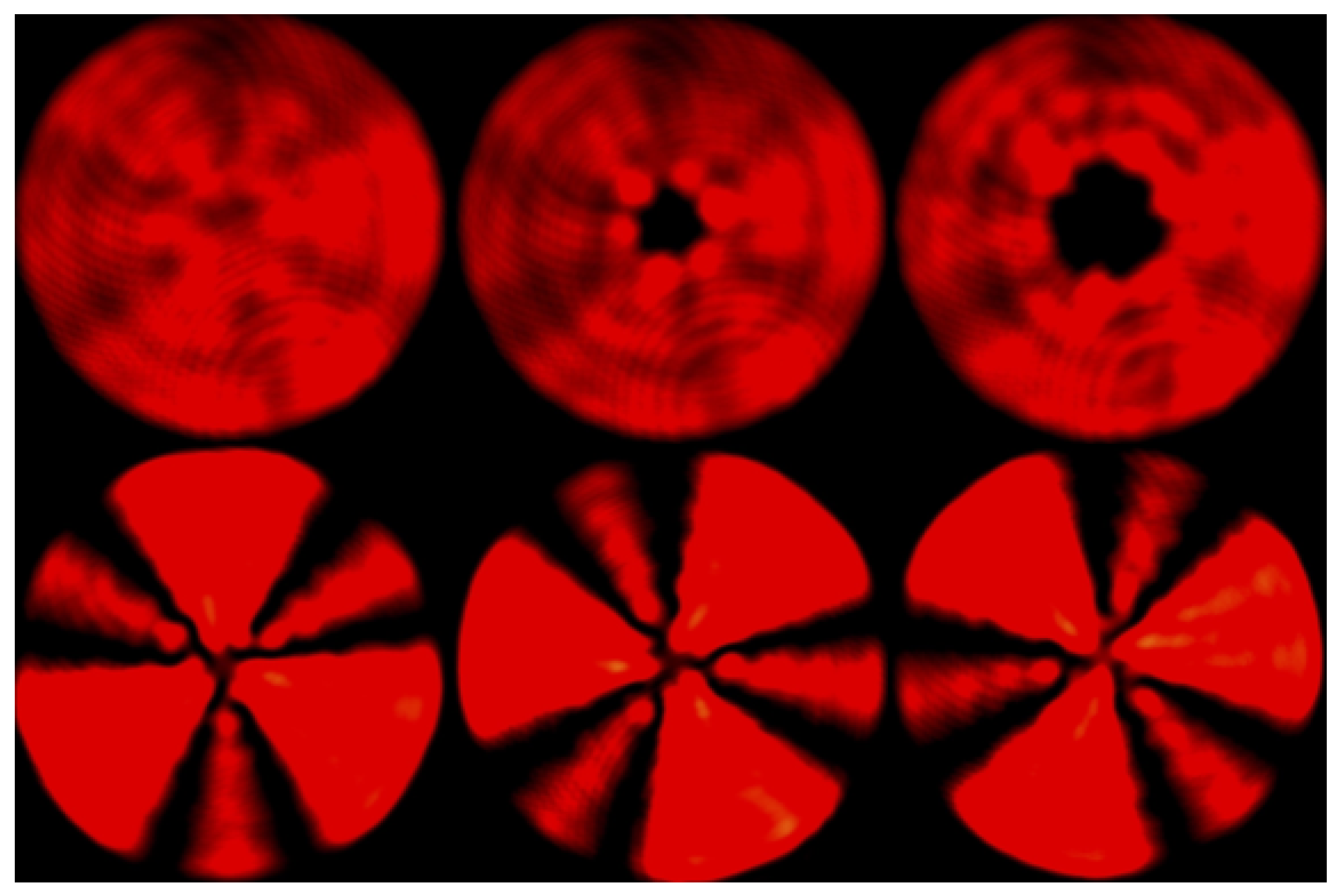
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Experimental Determination of Guesswork
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Guesswork Calculation with a Standard Basis Measurement
Appendix A.1. d = 2
Appendix A.2. General Dimension d
Appendix B. Guesswork Calculation with the Optimal Projective Measurement
Appendix B.1. Guesswork Calculation for d = 3 with the Numerically Determined Measurement
| 0.4809 | 0.0120 | 0.0071 | |
| 0.0075 | 0.0024 | 0.4901 | |
| 0.0116 | 0.4857 | 0.0028 | |
| 0.2574 | 0.1170 | 0.1257 | |
| 0.1347 | 0.1482 | 0.2171 | |
| 0.1079 | 0.2348 | 0.1572 |
Appendix B.2. Guesswork Calculation for d = 4 with the Numerically Determined Measurement
Appendix C. Alphabet of Input State Beams Used

References
- Massey, J. Guessing and entropy. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Trondheim, Norway, 27 June–1 July 1994; p. 204. [Google Scholar]
- Arikan, E. An inequality on guessing and its application to sequential decoding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1996, 42, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y. Minimum Guesswork Discrimination between Quantum States. Quantum Inf. Comput. 2015, 15, 737–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, E.P.; Katariya, V.; Datta, N.; Wilde, M.M. Guesswork with Quantum Side Information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2022, 68, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Arno, M.; Buscemi, F.; Koshiba, T. Guesswork of a Quantum Ensemble. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2022, 68, 3139–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Arno, M.; Buscemi, F.; Koshiba, T. Classical computation of quantum guesswork. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.01666. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Arno, M. Quantum guesswork. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.06783. [Google Scholar]
- Avirmed, B.; Niinomi, K.; Dall’Arno, M. Adversarial guesswork with quantum side information. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.12633. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, S. Structured light techniques and applications. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J. Structured-light 3D surface imaging: A tutorial. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2011, 3, 128–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, M.P.; Speirits, F.C.; Barnett, S.M.; Padgett, M.J. Detection of a spinning object using light’s orbital angular momentum. Science 2013, 341, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Boyd, R. Quantum imaging technologies. La Rivista del Nuovo Cimento 2014, 37, 273–332. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Lei, J.; Romero, J. Quantum digital spiral imaging. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseini, M.; Magaña-Loaiza, O.S.; O’Sullivan, M.N.; Rodenburg, B.; Malik, M.; Lavery, M.P.; Padgett, M.J.; Gauthier, D.J.; Boyd, R.W. High-dimensional quantum cryptography with twisted light. New J. Phys. 2015, 17, 033033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Loaiza, O.S.; Mirhosseini, M.; Cross, R.M.; Rafsanjani, S.M.H.; Boyd, R.W. Hanbury Brown and Twiss interferometry with twisted light. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H.; Forbes, A.; Berry, M.V.; Dennis, M.R.; Andrews, D.L.; Mansuripur, M.; Denz, C.; Alpmann, C.; Banzer, P.; Bauer, T.; et al. Roadmap on structured light. J. Opt. 2016, 19, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Magaña-Loaiza, O.S.; Mirhosseini, M.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, B.; Gao, L.; Rafsanjani, S.M.H.; Long, G.L.; Boyd, R.W. Digital spiral object identification using random light. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milione, G.; Wang, T.; Han, J.; Bai, L. Remotely sensing an object’s rotational orientation using the orbital angular momentum of light. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2017, 15, 030012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Loaiza, O.S.; León-Montiel, R.d.J.; Perez-Leija, A.; U’Ren, A.B.; You, C.; Busch, K.; Lita, A.E.; Nam, S.W.; Mirin, R.P.; Gerrits, T. Multiphoton quantum-state engineering using conditional measurements. npj Quantum Inf. 2019, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, B.; Leach, J.; Romero, J.; Franke-Arnold, S.; Ritsch-Marte, M.; Barnett, S.; Padgett, M. Holographic ghost imaging and the violation of a Bell inequality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 083602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegman, A.E. Lasers; University Science Books: Melville, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, L.; Beijersbergen, M.W.; Spreeuw, R.; Woerdman, J. Orbital angular momentum of light and the transformation of Laguerre-Gaussian laser modes. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 45, 8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, D.; Romero, J.; Leach, J.; Dudley, A.; Forbes, A.; Padgett, M.J. Characterization of High-Dimensional Entangled Systems via Mutually Unbiased Measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 143601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, V.; Cardano, F.; Karimi, E.; Nagali, E.; Santamato, E.; Marrucci, L.; Sciarrino, F. Test of mutually unbiased bases for six-dimensional photonic quantum systems. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.; O’Sullivan, M.; Rodenburg, B.; Mirhosseini, M.; Leach, J.; Lavery, M.P.J.; Padgett, M.J.; Boyd, R.W. Influence of atmospheric turbulence on optical communications using orbital angular momentum for encoding. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 13195–13200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, 10–12 December 1984; pp. 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, T.; Ohtake, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Inoue, T.; Fukuchi, N. Mode purities of Laguerre–Gaussian beams generated via complex-amplitude modulation using phase-only spatial light modulators. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhusal, N.; Lohani, S.; You, C.; Hong, M.; Fabre, J.; Zhao, P.; Knutson, E.M.; Glasser, R.T.; Magaña-Loaiza, O.S. Spatial Mode Correction of Single Photons Using Machine Learning. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2021, 4, 2000103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A.; Kermani, M.M.; Azarderakhsh, R. Fault Detection Architectures for Inverted Binary Ring-LWE Construction Benchmarked on FPGA. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari-Kermani, M.; Azarderakhsh, R.; Aghaie, A. Reliable and Error Detection Architectures of Pomaranch for False-Alarm-Sensitive Cryptographic Applications. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 2015, 23, 2804–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaie, A.; Mozaffari Kermani, M.; Azarderakhsh, R. Fault Diagnosis Schemes for Low-Energy Block Cipher Midori Benchmarked on FPGA. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 2017, 25, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Azarderakhsh, R. Curve448 on 32-Bit ARM Cortex-M4. In Proceedings of the Information Security and Cryptology—ICISC 2020, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2–4 December 2020; Hong, D., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bisheh-Niasar, M.; Azarderakhsh, R.; Mozaffari-Kermani, M. Cryptographic Accelerators for Digital Signature Based on Ed25519. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 2021, 29, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedemann, S.R. Hyperspherical Parameterization of Unitary Matrices. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.5904. [Google Scholar]



| Dimension | Theoretical Value | Experimental Value |
|---|---|---|
| Standard basis measurement | ||
| d = 2 | 1.75 | |
| d = 3 | 2 | |
| d = 4 | 2.25 | |
| Optimized projective measurement | ||
| d = 2 | 1.709 | |
| d = 3 | 1.9425 | |
| d = 4 | 2.1429 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katariya, V.; Bhusal, N.; You, C. Experimental Guesswork with Quantum Side Information Using Twisted Light. Sensors 2023, 23, 6570. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23146570
Katariya V, Bhusal N, You C. Experimental Guesswork with Quantum Side Information Using Twisted Light. Sensors. 2023; 23(14):6570. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23146570
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatariya, Vishal, Narayan Bhusal, and Chenglong You. 2023. "Experimental Guesswork with Quantum Side Information Using Twisted Light" Sensors 23, no. 14: 6570. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23146570
APA StyleKatariya, V., Bhusal, N., & You, C. (2023). Experimental Guesswork with Quantum Side Information Using Twisted Light. Sensors, 23(14), 6570. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23146570