CVCC Model: Learning-Based Computer Vision Color Constancy with RiR-DSN Architecture
Abstract
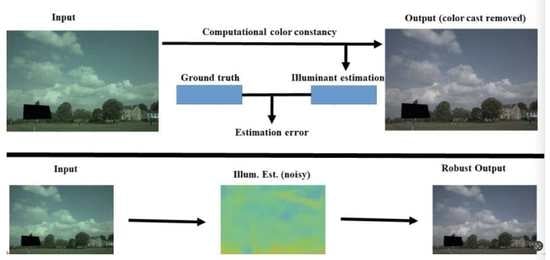
1. Introduction
2. Previous Works
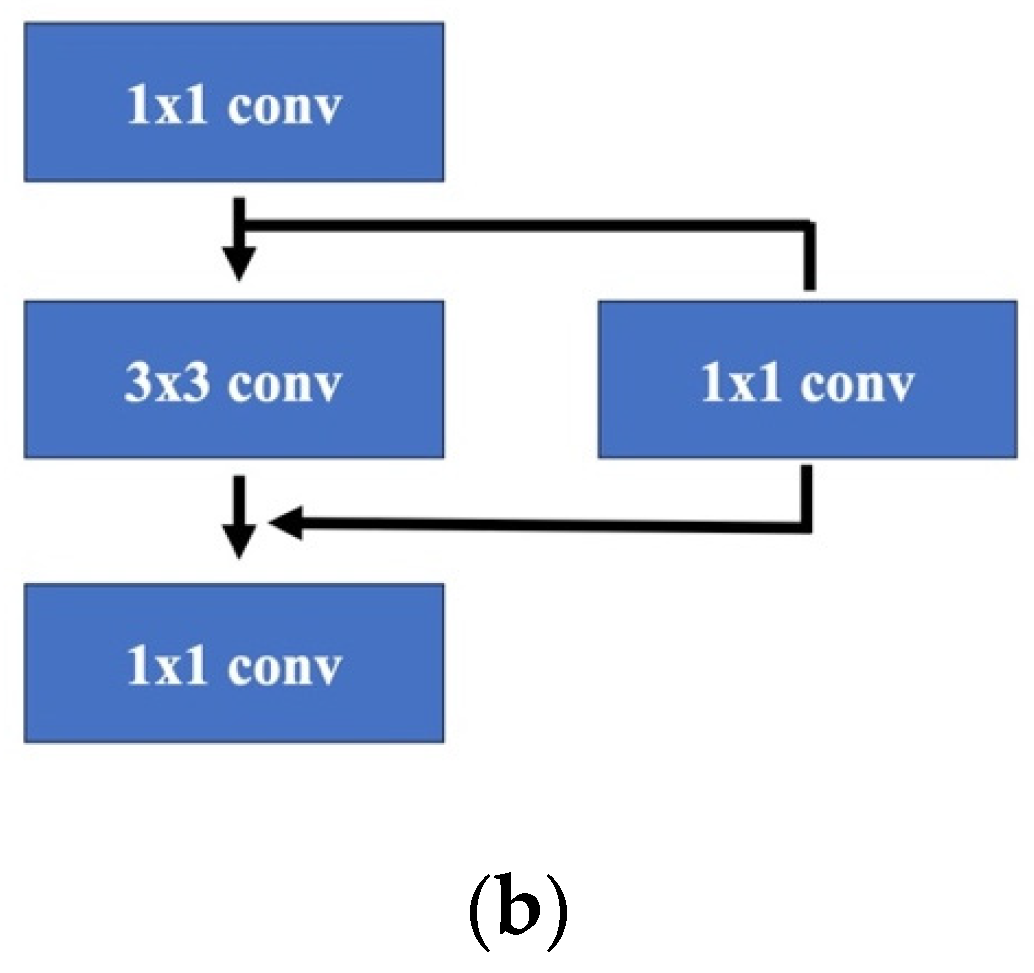
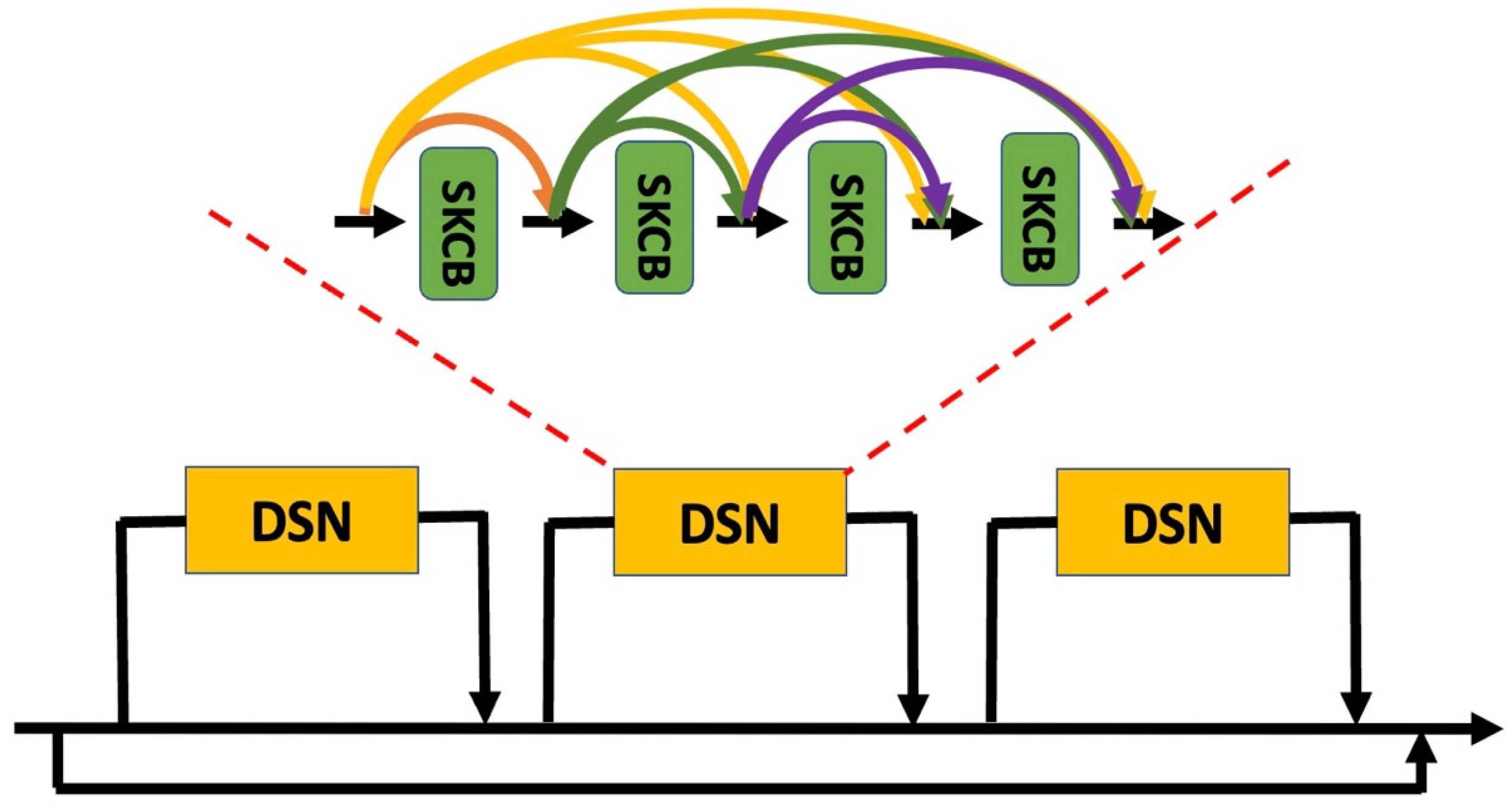
3. The Proposed Method
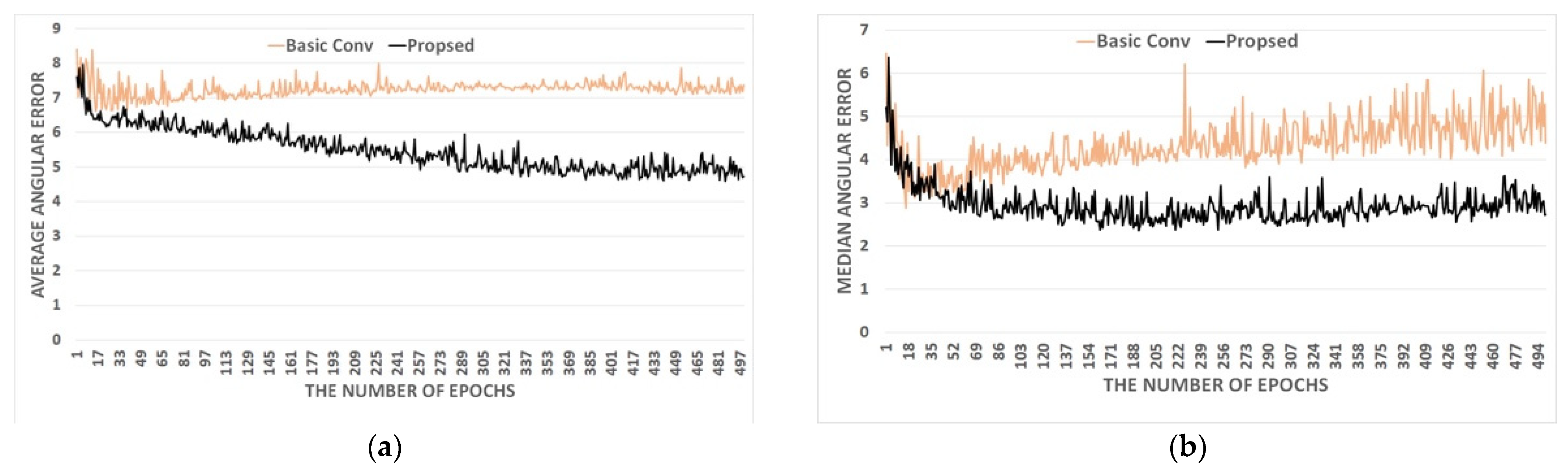
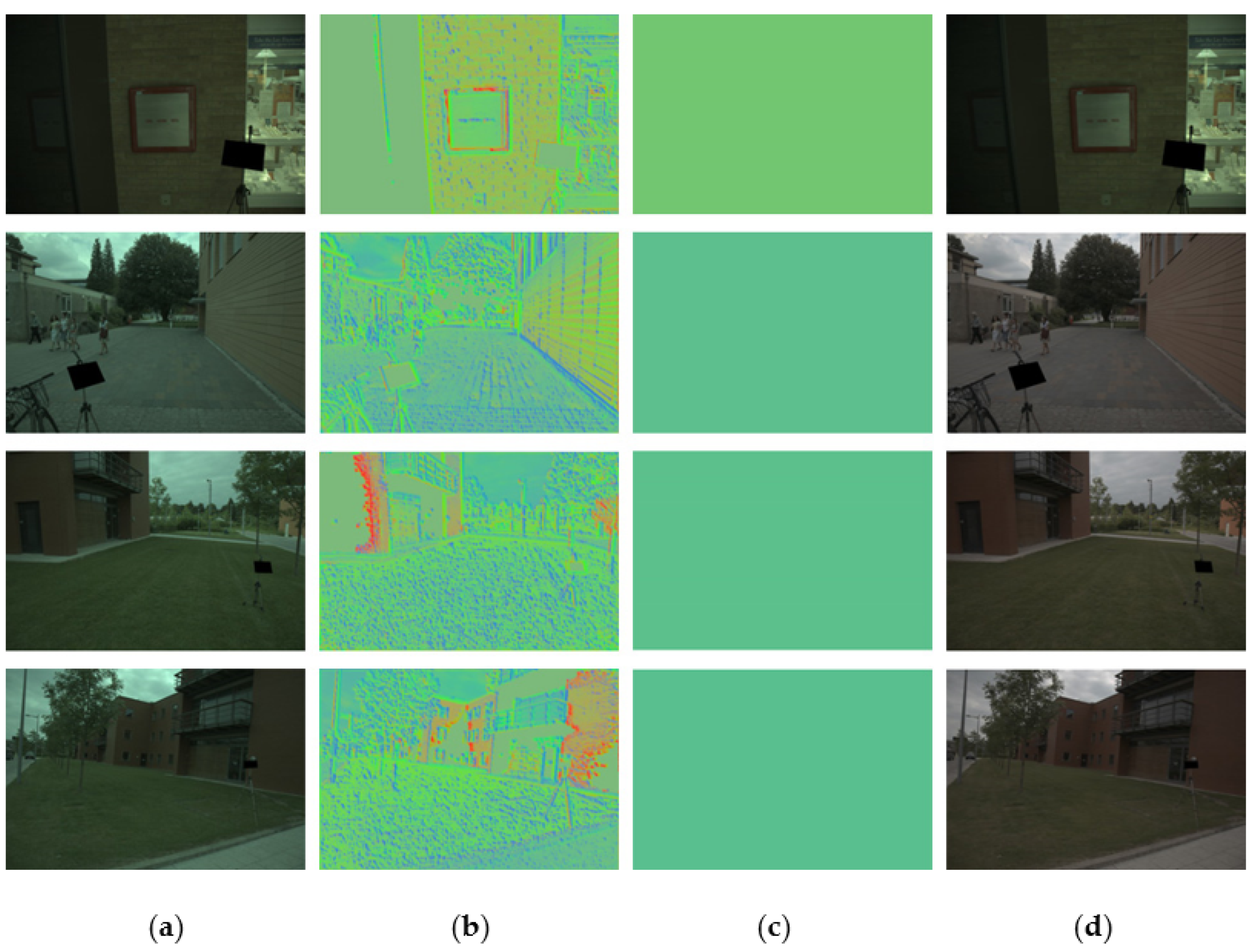
4. Experimental Results and Evaluations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebner, M. Color Constancy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Alsam, A. Colour constant image sharpening. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 4545–4548. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, K. Practical Colour Constancy; Simon Fraser University: Burnaby, BC, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Buchsbaum, G. A spatial processor model for object colour perception. J. Frankl. Inst. 1980, 310, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, E.H. The Retinex theory of color vision. Sci. Am. 1977, 237, 108–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banic, N.; Loncaric, S. Improving the white patch method by subsampling. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 605–609. [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson, G.D.; Trezzi, E. Shade of gray and color constancy. In Proceedings of the IS&T/SID Color Imaging Conference, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 9 November 2004; pp. 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Weijer, J.V.; Gevers, T.; Gijsenij, A. Edege-based color constancy. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsenij, A.; Gevers, T.; Van de Weijer, J. Improving color constancy by photometric edge weighting. IEEE Trans. Patten Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, D.A. A novel algorithm for color constancy. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1990, 5, 5–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.D. Color in perspective. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1996, 18, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.; Hordley, S. Improving gamut mapping color constancy. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlayson, G.; Xu, R. Convex programming color constancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Color and Photometric Methods in Computer Vision, Online, 1 October 2003; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mosny, M.; Funt, B. Cubical gamut mapping colour constancy. In Proceedings of the IS&T’s European Conference on Colour in Graphics, Imaging and Vision, Burnaby, BC, Canada, 14–17 June 2010; pp. 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Gijsenij, A.; Gevers, T.; van De Weijer, J. Generalized gamut mapping using image derivative structure for color constancy. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 86, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.D.; Hordley, S.D.; Xu, R. Convex programming color constancy with a diagonal-offset model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Genova, Italy, 14 September 2005; pp. 948–951. [Google Scholar]
- Gijsenij, A.; Gevers, T. Color constancy using natural image statistics and scene semantics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, S.; Wandell, B.A. Standard surface-reflectance model and illuminant estimation. J. Opt. Soc. Amer. A Opt. Image Sci. 1989, 6, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healey, G. Estimating spectral reflectance using high lights. Image Vis. Comput. 1991, 9, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.T.; Nishino, K.; Ikeuchi, K. Color constancy through inverse- intensity chromaticity space. J. Opt. Soc. Amer. A Opt. Image Sci. 2004, 21, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlayson, G.D.; Schaefer, G. Solving for colour constancy using a constrained dichromatic reflection model. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2001, 42, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, J.T. Convolutional color constancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, S.; Cusano, C.; Schettini, R. Color constancy using CNNs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Fourure, D.; Emonet, R.; Fromont, E.; Muselet, D.; Tre, A.; Wolf, C. Mixed pooling neural networks for color constancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3997–4001. [Google Scholar]
- Drew, M.S.; Joze, H.R.V.; Finlayson, G.D. Specularity, the Zeta-image, and information-theoretic illuminant estimation. In Proceedings of the ECCV, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; pp. 411–420. [Google Scholar]
- Joze, H.R.V.; Drew, M.S. Exemplar-based color constancy and multiple illumination. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Lin, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, H. A new global-based video enhancement algorithm by fusing features of multiple region-of- interests. In Proceedings of the Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Tainan, Taiwan, 6–9 November 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhang, C.; Xu, C.N.; Xie, J. Intra-and-inter- constraint-based video enhancement based on piecewise tone mapping. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2013, 23, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.B.; Yang, K.F.; Li, C.Y.; Li, Y.J. Color constancy using double- opponency. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1973–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-S.; Gao, S.-B.; Li, R.-X.; Du, X.-Y.; Li, C.-Y.; Li, Y.-J. Areti- nal mechanism inspired color constancy model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarinia, A.; Parraga, C.A. Colour constancy beyond the classical receptive field. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 2081–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, M.V.; McDonagh, S.; Maggioni, M.; Leonardis, A.; Perez-Pellitero, E. Model-based Image Signal Processors Via Learnable Dictionaries. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.0321v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the NIPS, Red Hook, NY, USA, 3–6 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective Kernel Network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.0658v2. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1608.06993v5. [Google Scholar]
- Gehler, P.V.; Rother, C.; Blake, A.; Minka, T.; Sharp, T. Bayesian color constancy revisited. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, Alaska, 23–18 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ciurea, F.; Funt, B. A large image database for color constancy research. In Proceedings of the 11th Color Imaging Conference: Imaging Science and Technology, Rochester, NY, USA, 13 May 2003; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.04467 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the ICML, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariance shit. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, J.T.; Tsai, Y.-T. Fast Fourier color constancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 886–894. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Lin, S. FC4: Fully convolutional color constancy with confidence-weighted pooling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4085–4094. [Google Scholar]
- Koscevic, K.; Subasic, M.; Loncaric, S. Iterative convolutional neural network-based illumination estimation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26755–26765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Gu, S.; Zhang, L. Multi-domain learning for accurate and few-shot color constancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 3258–3267. [Google Scholar]
- Domislovic, I.; Vrsnak, D.; Subasic, M.; Loncaric, S. One-Net: Convolutional color constancy simplified. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2022, 159, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Price, B.; Cohen, S.; Brown, M.S. Effective learning-based illuminant estimation using simple features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1000–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, K. Improvements to gamut mapping colour constancy algorithms. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 390–403. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Hirakawa, K.; Zickler, T. Color constancy with spatio-spectral statistics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Pertuz, S.; Nikkanen, J.; Kämäräinen, J.-K.; Matas, J. Revisiting Gray Pixel for Statistical Illumination Estimation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.08326. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1803.08326 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Bianco, S.; Cusano, C. Quasi-unsupervised color constancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Xu, H.; Ye, Z. Color constancy by Reweighting Image Feature Maps. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.09248v3. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1806.09248 (accessed on 1 June 2023). [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.H.; Kang, H.S.; Yun, B.J. CNN-based illumination estimation with semantic information. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-H.; Yun, B.-J. Deep learning-based computational color constancy with convoluted mixture of deep experts (CMoDE) fusion technique. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 188309–188320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-H.; Yun, B.-J. Learning-based illuminant estimation model with a persistent memory residual network (PMRN) architecture. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 29960–29969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method (s) | Mean | Median | Trimean | Worst-25% | Best-25% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics-Based Approach | |||||
| WP [5] | 9.69 | 7.48 | 8.56 | 20.49 | 1.72 |
| GW [4] | 7.71 | 4.29 | 4.98 | 20.19 | 1.01 |
| SoG [7] | 2.59 | 1.73 | 1.93 | 6.19 | 0.46 |
| First GE [8] | 2.41 | 1.52 | 1.72 | 5.89 | 0.45 |
| Second GE [8] | 2.50 | 1.59 | 1.78 | 6.08 | 0.48 |
| Learning-Based Approach | |||||
| FFCC [42] | 1.38 | 0.74 | 0.89 | 3.67 | 0.19 |
| FC4 (sque.) [43] | 1.35 | 0.93 | 1.01 | 3.24 | 0.30 |
| VGG-16 [44] | 1.34 | 0.83 | 0.97 | 3.20 | 0.28 |
| MDLCC [45] | 1.24 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 2.91 | 0.26 |
| One-net [46] | 1.21 | 0.72 | 0.83 | 3.05 | 0.21 |
| Ours | 1.13 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 2.55 | 0.18 |
| Method (s) | Mean | Median | Trimean | Best-25% | Worst-25% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVR [28] | 13.17 | 11.28 | 11.83 | 4.42 | 25.02 |
| BS [37] | 6.77 | 4.70 | 5.00 | - | - |
| NIS [17] | 5.24 | 3.00 | 4.35 | 1.21 | 11.15 |
| EM [47] | 4.42 | 3.48 | 3.77 | 1.01 | 9.36 |
| CNN [23] | 4.80 | 3.70 | - | - | - |
| Ours | 2.87 | 1.59 | 1.66 | 0.47 | 5.98 |
| Method (s) | Mean | Median | Trimean | Best-25% | Worst-25% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GW [4] | 4.57 | 3.63 | 3.85 | 1.04 | 9.64 |
| PG [48] | 3.76 | 2.99 | 3.10 | 1.14 | 7.70 |
| WP [5] | 3.64 | 2.84 | 2.95 | 1.17 | 7.48 |
| 1st GE [8] | 3.21 | 2.51 | 2.65 | 0.93 | 6.61 |
| 2nd GE [8] | 3.12 | 2.42 | 2.54 | 0.86 | 6.55 |
| BS [37] | 3.04 | 2.28 | 2.40 | 0.67 | 6.69 |
| SoG [7] | 2.93 | 2.24 | 2.41 | 0.66 | 6.31 |
| SSS [49] | 2.92 | 2.08 | 2.17 | 0.46 | 6.50 |
| DGP [50] | 2.80 | 2.00 | 2.22 | 0.55 | 6.25 |
| QU [51] | 2.39 | 1.69 | 1.89 | 0.48 | 5.47 |
| CNN [23] | 1.88 | 1.47 | 1.54 | 0.38 | 4.90 |
| 3-H [52] | 1.67 | 1.20 | 1.30 | 0.38 | 3.78 |
| FFCC [42] | 1.55 | 1.22 | 1.23 | 0.32 | 3.66 |
| FC4 (sque.) [43] | 1.54 | 1.13 | 1.20 | 0.32 | 3.59 |
| Ours | 1.45 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 0.30 | 3.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.-H. CVCC Model: Learning-Based Computer Vision Color Constancy with RiR-DSN Architecture. Sensors 2023, 23, 5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115341
Choi H-H. CVCC Model: Learning-Based Computer Vision Color Constancy with RiR-DSN Architecture. Sensors. 2023; 23(11):5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115341
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Ho-Hyoung. 2023. "CVCC Model: Learning-Based Computer Vision Color Constancy with RiR-DSN Architecture" Sensors 23, no. 11: 5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115341
APA StyleChoi, H.-H. (2023). CVCC Model: Learning-Based Computer Vision Color Constancy with RiR-DSN Architecture. Sensors, 23(11), 5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115341