PT-Symmetric LC Passive Wireless Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PT Symmetry
2.1. PT Symmetry in Quantum Mechanics
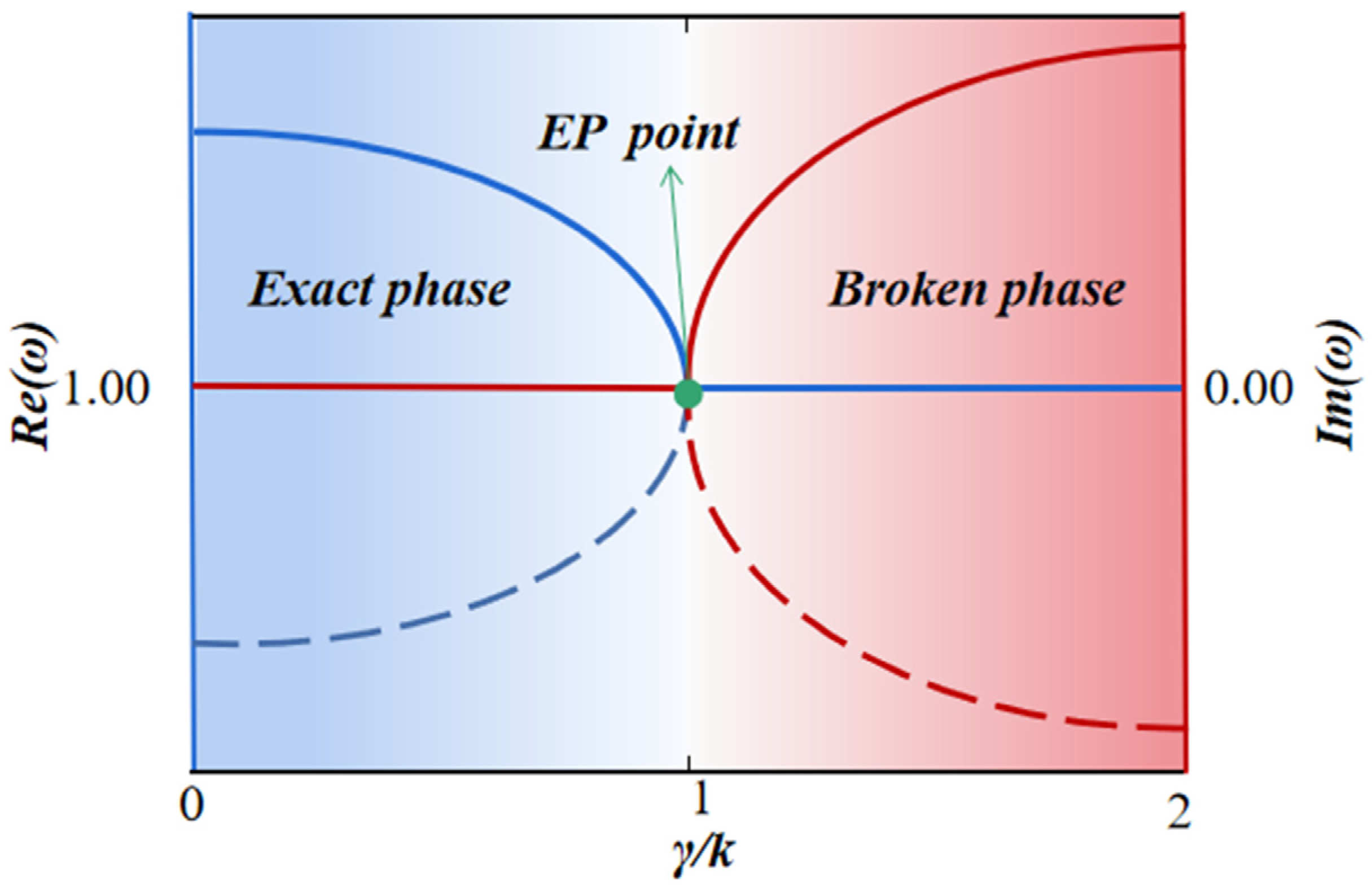
- . The eigenvalues are real-valued numbers, and the system is in the PT-symmetric exact phase;
- , the eigenvalues will merge. This point is described as the exceptional point (EP), at which the eigenstates are also merged;
- . The eigenvalue is a complex conjugate, and the system is in the PT-symmetric broken phase.
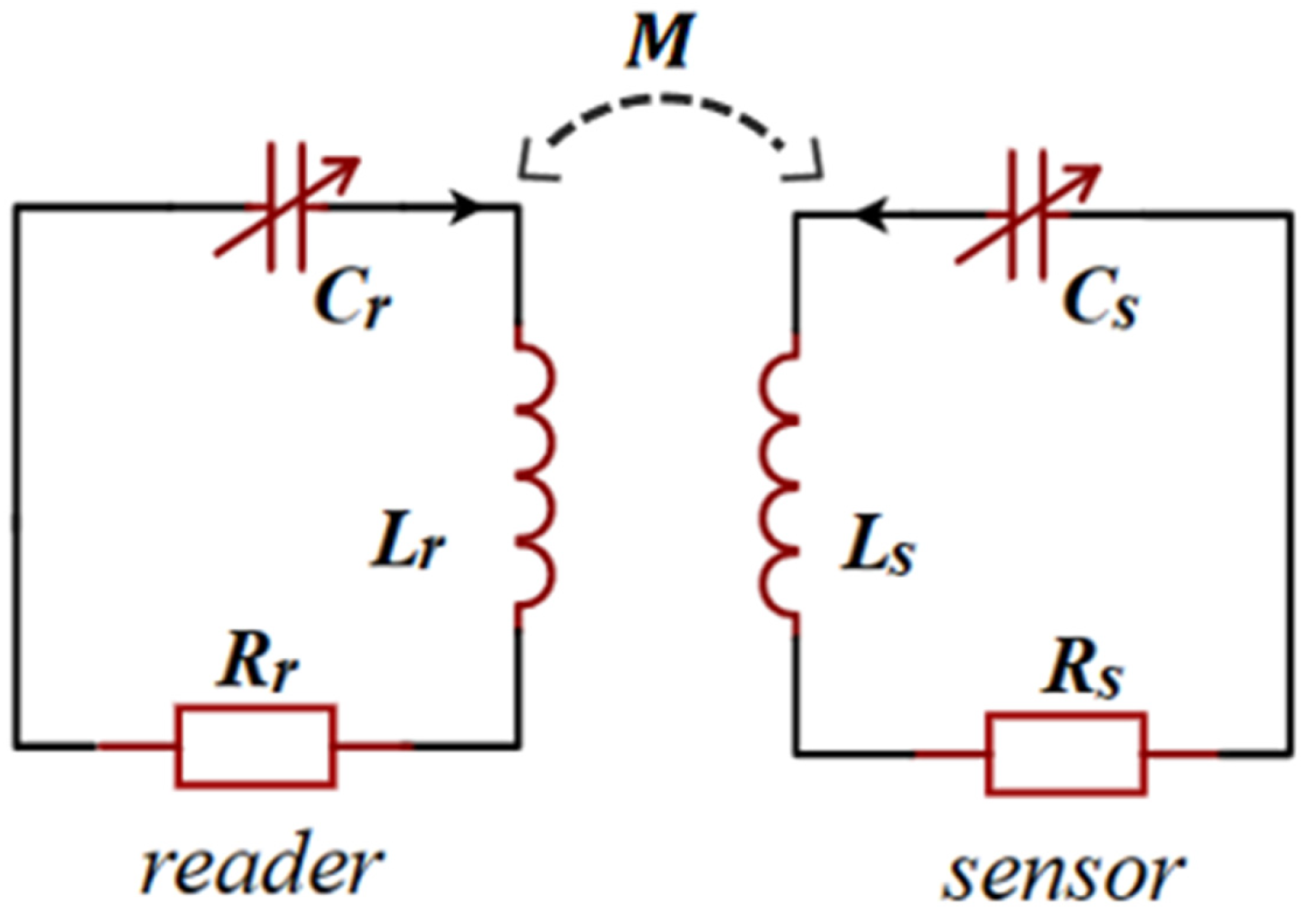
2.2. PT Symmetry in LC Sensors
- , The eigenvalues are real-valued numbers, and the system is in the PT-symmetric exact phase. The whole system will maintain equilibrium, and the total energy is also conserved;
- , this special point is the EP point. The system is still in the PT-symmetric phase, but the eigenvalues and eigenstates coalesce. In the following sections, we will see that the abrupt nature of phase transition results in intriguing phenomena;
- , The eigenvalues are a pair of conjugate complex numbers, and the system is in the PT-symmetric broken phase. In this region, the whole system is not in an equilibrium state, and the total energy is not conserved, which is exactly the opposite of the exact phase.
3. PT-Symmetric LC Sensing Systems
3.1. PT-Symmetric LC Sensors in Exact Phase
3.1.1. High Q-Factor and Deep Reflection Dips
3.1.2. The Multi-Parameter Sensitive Measurement
3.1.3. Generalized Parity–Time Symmetry
3.2. PT-Symmetric LC Sensors Based on Exceptional Points (EPs)
3.2.1. PT-Symmetric LC Sensors with Enhanced Sensitivity
3.2.2. LC Sensors Based on High-Order PT-Symmetric EP and DEP
3.2.3. Noise and Precision of LC Sensors Based on the EPs
3.2.4. Solutions to Overcome Noise Effect
3.3. PT-Symmetric LC Sensors in Broken Phase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, C.C. Miniature Passive Pressure Transensor for Implanting in Eye. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1967, BM14, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.-A.; Dong, L.; Wang, L.-F. LC Passive Wireless Sensors Toward a Wireless Sensing Platform: Status, Prospects, and Challenges. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2016, 25, 822–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutry, C.M.; Beker, L.; Kaizawa, Y.; Vassos, C.; Tran, H.; Hinckley, A.C.; Pfattner, R.; Niu, S.; Li, J.; Claverie, J.; et al. Biodegradable and Flexible Arterial-Pulse Sensor for the Wireless Monitoring of Blood Flow. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannoor, M.S.; Tao, H.; Clayton, J.D.; Sengupta, A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Naik, R.R.; Verma, N.; Omenetto, F.G.; McAlpine, M.C. Graphene-Based Wireless Bacteria Detection on Tooth Enamel. Nat. Commun. 2013, 3, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-J.; Rodger, D.C.; Saati, S.; Humayun, M.S.; Tai, Y.-C. Microfabricated Implantable Parylene-Based Wireless Passive Intraocular Pressure Sensors. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, G.; Maleki, T.; Samuels, B.; Cantor, L.B.; Ziaie, B. A Minimally Invasive Implantable Wireless Pressure Sensor for Continuous IOP Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.L.; Ng, W.N.; Shao, R.; Pereles, B.D.; Ong, K.G. A Wireless, Passive Sensor for Quantifying Packaged Food Quality. Sensors 2007, 7, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, J. Temperature and Pressure Composite Measurement System Based on Wireless Passive LC Sensor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 9502811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Luo, T.; Wei, T.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Xiong, J. A Wireless Passive Pressure and Temperature Sensor via a Dual LC Resonant Circuit in Harsh Environments. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2017, 26, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, G.; Radovanovic, M.; Malesev, M.; Radonjanin, V. Monitoring of Water Content in Building Materials Using a Wireless Passive Sensor. Sensors 2010, 10, 4270–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.; Son, K.A.; Powers, R.A.; Del Castillo, L.Y.; Okojie, R. Harsh Environment Microtechnologies for NASA and Terrestrial Applications. In Proceeding of the 4th IEEE Conference on Sensors, Irvine, CA, USA, 31 October–3 November 2005; pp. 1253–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Wu, G.; Tan, Q.; Luo, T.; Tang, S.; Shen, D.; Li, C.; Xiong, J. Modeling, Simulation and Coupling Experiment for Integrated Passive Wireless Multi-Parameters Ceramic Sensor. Sens. Rev. 2016, 36, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, S.K.; Mahajan, A.; Raghuwanshi, S.K. An Inductive-Capacitive-Circuit-Based Micro-Electromechanical System Wireless Capacitive Pressure Sensor for Avionic Applications: Preliminary Investigations, Theoretical Modelling and Simulation Examination of Newly Proposed Methodology. Meas. Control 2019, 52, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhori, A.H.; Kim, T.; Kim, W.S. Enhanced RF Response of 3D-Printed Wireless LC Sensors Using Dielectrics with High Permittivity. Flex. Print. Electron. 2023, 8, 015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, J.I.; Perez, N.; De No, J.; Mendizabal, J. Implementation of Simultaneous Multi-Parameter Monitoring Based in LC-Type Passive Wireless Sensing with Partial Overlapping and Decoupling Coils. Sensors 2019, 19, 5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhar, I.; Mandal, N. A Review on Advanced Wireless Passive Temperature Sensors. Measurement 2022, 187, 110255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvan, M.; Barekatain, M. The Sensors Are Innovative in Internet of Things. In Proceeding of the 8th International Wireless Internet Conference (WICON), Lisbon, Portugal, 13–14 November 2014; pp. 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Harpster, T.J.; Hauvespre, S.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Najafi, K. A Passive Humidity Monitoring System for In Situ Remote Wireless Testing of Micropackages. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2002, 11, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurs, A.; Karalis, A.; Moffatt, R.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Fisher, P.; Soljacic, M. Wireless Power Transfer via Strongly Coupled Magnetic Resonances. Science 2007, 317, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, D.A.; Mitrosbaras, C.; Unigarro, E.A.; Segura-Quijano, F. Passive Resonators for Wireless Passive Sensor Readout Enhancement. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 133502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.-F.; Huang, Q.-A. Extending the Remote Distance of LC Passive Wireless Sensors via Strongly Coupled Magnetic Resonances. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 125021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, L.-F.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Q.-A. A Cyclic Scanning Repeater for Enhancing the Remote Distance of LC Passive Wireless Sensors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 2016, 63, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, L.-F.; Huang, Q.-A. A Passive Wireless Adaptive Repeater for Enhancing the Readout of LC Passive Wireless Sensors. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2016, 26, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-Z.; Wang, L.-F.; Zhou, B.-B.; Huang, Q.-A. An Impedance Matching Method for LC Passive Wireless Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13833–13841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-B.; Deng, W.-J.; Wang, L.-F.; Dong, L.; Huang, Q.-A. Enhancing the Remote Distance of LC Passive Wireless Sensors by Parity-Time Symmetry Breaking. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 13, 064022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, C.M.; Boettcher, S. Real Spectra in Non-Hermitian Hamiltonians Having PT Symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 5243–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnok, A.; Nefedkin, N.; Alu, A. Parity-Time Symmetry and Exceptional Points [Electromagnetic Perspectives]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2021, 63, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Salamo, G.J.; Duchesne, D.; Morandotti, R.; Volatier-Ravat, M.; Aimez, V.; Siviloglou, G.A.; Christodoulides, D.N. Observation of PT-Symmetry Breaking in Complex Optical Potentials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 093902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyablovsky, A.A.; Vinogradov, A.P.; Pukhov, A.A.; Dorofeenko, A.V.; Lisyansky, A.A. PT-Symmetry in Optics. Phys.-Uspekhi 2014, 57, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, S.K.; Rotter, S.; Nori, F.; Yang, L. Parity-Time Symmetry and Exceptional Points in Photonics. Nat. Mater 2019, 18, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ramezani, H.; Shi, C.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X. PT-Symmetric Acoustics. Phys. Rev. X 2014, 4, 031042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, C.; Song, H. Theoretical Realization and Application of Parity-Time-Symmetric Oscillators in a Quantum Regime. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 031042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Ozdemir, S.K.; Geng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.-Y.; Peng, B.; Yang, L.; Nori, F. Optomechanically-Induced Transparency in Parity-Time-Symmetric Microresonators. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerjan, A.; Raman, A.; Fan, S. Exceptional Contours and Band Structure Design in Parity-Time Symmetric Photonic Crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 203902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Chan, C.T. Coalescence of Exceptional Points and Phase Diagrams for One-Dimensional PT-Symmetric Photonic Crystals. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 235310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Hu, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X. Fully Integrated Parity-Time-Symmetric Electronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Liu, F.; Li, J. Effective Spontaneous PT-Symmetry Breaking in Hybridized Metamaterials. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 053824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Hahn, C.; Yoon, J.W.; Song, S.H. Observation of an Anti-PT-Symmetric Exceptional Point and Energy-Difference Conserving Dynamics in Electrical Circuit Resonators. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.D.; Ge, L.; Stone, A.D. PT-Symmetry Breaking and Laser-Absorber Modes in Optical Scattering Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 093902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, F.; Bender, N.; Ramezani, H.; Moravvej-Farshi, M.K.; Christodoulides, D.N.; Kottos, T. Optical Isolation via PT-Symmetric Nonlinear Fano Resonances. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 9574–9584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, H.; Kottos, T.; El-Ganainy, R.; Christodoulides, D.N. Unidirectional Nonlinear PT-Symmetric Optical Structures. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 043803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assawaworrarit, S.; Yu, X.; Fan, S. Robust Wireless Power Transfer Using a Nonlinear Parity-Time-Symmetric Circuit. Nature 2017, 546, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, C.M.; Brody, D.C.; Jones, H.F. Complex Extension of Quantum Mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 270401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, C.M.; Brody, D.C.; Jones, H.F. Must a Hamiltonian be Hermitian? Am. J. Phys. 2003, 71, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, J.; Lin, Z.; Lee, J.M.; Ramezani, H.; Ellis, F.M.; Kottos, T. PT-Symmetric Electronics. J. Phys. A-Math. Theor. 2012, 45, 444029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, J.; Li, A.; Zheng, M.C.; Ellis, F.M.; Kottos, T. Experimental Study of Active LRC Circuits with PT Symmetries. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 040101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvanoff, M.; Venkataraman, J. A Feasibility Study of Tissue Characterization Using LC Sensors. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Sakhdari, M.; Hajizadegan, M.; Cui, Q.; Cheng, M.M.-C.; El-Ganainy, R.; Alù, A. Generalized Parity–Time Symmetry Condition for Enhanced Sensor Telemetry. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhdari, M.; Hajizadegan, M.; Li, Y.; Cheng, M.M.-C.; Hung, J.C.H.; Chen, P.-Y. Ultrasensitive, Parity–Time-Symmetric Wireless Reactive and Resistive Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 9548–9555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Huang, Y.; Yin, W.; Hao, X.; Ma, X.; Dong, T. Ultrahigh-Resolution Wireless Capacitance Readout Based on a Single Real Mode in a Perturbed PT-Symmetric Electronic Trimer Sandwich. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2022, 22, 064020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.-Y.; Wang, L.-F.; Huang, J.-Q.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Q.-A. Simultaneous Remote Sensing of Temperature and Humidity by LC-Type Passive Wireless Sensors. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2015, 24, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-B. Study on LC Passive Wireless Sensing Methods Based on PT Symmetry. Ph.D. Dissertation, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hajizadegan, M.; Sakhdari, M.; Liao, S.; Chen, P.-Y. High-Sensitivity Wireless Displacement Sensing Enabled by PT-Symmetric Telemetry. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 3445–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Qiu, C.-W.; Ho, J.S. Sensitive Readout of Implantable Microsensors Using a Wireless System Locked to An Exceptional Point. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-B.; Wang, L.-F.; Dong, L.; Huang, Q.-A. Observation of the Perturbed Eigenvalues of PT-Symmetric LC Resonator Systems. J. Phys. Commun. 2021, 5, 045010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Sakhdari, M. High-Order PT-Symmetric Telemetric Sensors with Singularity-Enhanced Sensitivity. In Proceeding of the IEEE-Antennas-and-Propagation-Society International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation /USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 2011–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Yang, M.; Alsaab, N.; Chen, P.-Y. A Wireless, Zero-Power and Multiplexed Sensor for Wound Monitoring. In Proceeding of the IEEE Sensors Conference, Dallas, TX, USA, 30 October–2 November 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sakhdari, M.; Hajizadegan, M.; Zhong, Q.; Christodoulides, D.N.; El-Ganainy, R.; Chen, P.Y. Experimental Observation of PT Symmetry Breaking near Divergent Exceptional Points. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 193901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhdari, M.; Ye, Z.; Farhat, M.; Chen, P.-Y. Generalized Theory of PT-Symmetric Radio-Frequency Systems With Divergent Exceptional Points. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 9396–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbein, W. No Exceptional Precision of Exceptional-Point Sensors. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 023805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, R.; Mann, S.A.; Alù, A. Limitations of Sensing at an Exceptional Point. ACS Photonics 2022, 9, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Li, H.; Kottos, T.; Alu, A. Enhanced Sensing and Nondegraded Thermal Noise Performance Based on PT-Symmetric Electronic Circuits with a Sixth-Order Exceptional Point. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 213901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononchuk, R.; Cai, J.; Ellis, F.; Thevamaran, R.; Kottos, T. Exceptional-Point Based Accelerometers with Enhanced Signal-to-Noise Ratio. Nature 2022, 607, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Ye, Z.; Alsaab, N.; Farhat, M.; Chen, P.Y. In-Vitro Demonstration of Ultra-Reliable, Wireless and Batteryless Implanted Intracranial Sensors Operated on Loci of Exceptional Points. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2022, 16, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Kwon, H.; Miri, M.-A.; Kallos, E.; Cano-Garcia, H.; Tong, M.S.; Alu, A. Noninvasive Glucose Sensor Based on Parity-Time Symmetry. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 11, 044049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Su, X.; Feng, C.; Zang, F.; Dong, L.; Shi, Y. Wireless Sensing for Monitoring of Coal Gangue Mixing Based on PT Symmetry. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 66401–66408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.-Y.; Dong, L.; Huang, Q.-A. PT-Symmetric LC Passive Wireless Sensing. Sensors 2023, 23, 5191. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115191
Chen D-Y, Dong L, Huang Q-A. PT-Symmetric LC Passive Wireless Sensing. Sensors. 2023; 23(11):5191. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115191
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Dong-Yan, Lei Dong, and Qing-An Huang. 2023. "PT-Symmetric LC Passive Wireless Sensing" Sensors 23, no. 11: 5191. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115191
APA StyleChen, D.-Y., Dong, L., & Huang, Q.-A. (2023). PT-Symmetric LC Passive Wireless Sensing. Sensors, 23(11), 5191. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23115191









