HRpI System Based on Wavenet Controller with Human Cooperative-in-the-Loop for Neurorehabilitation Purposes
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Contribution
2. The Problem Formulation
2.1. The Dynamics of the HRpI System
2.2. Problem Statement
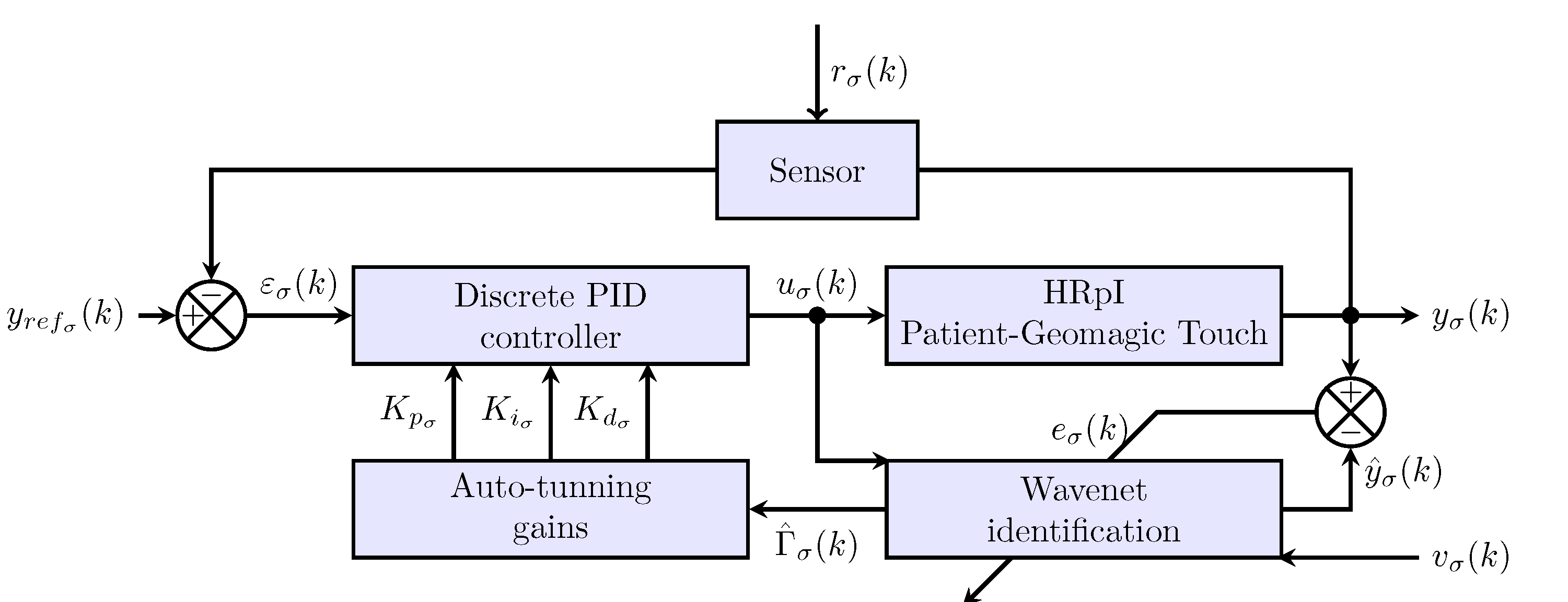
3. Adaptive Interaction System
3.1. Input-Output Dynamics of the HRpI
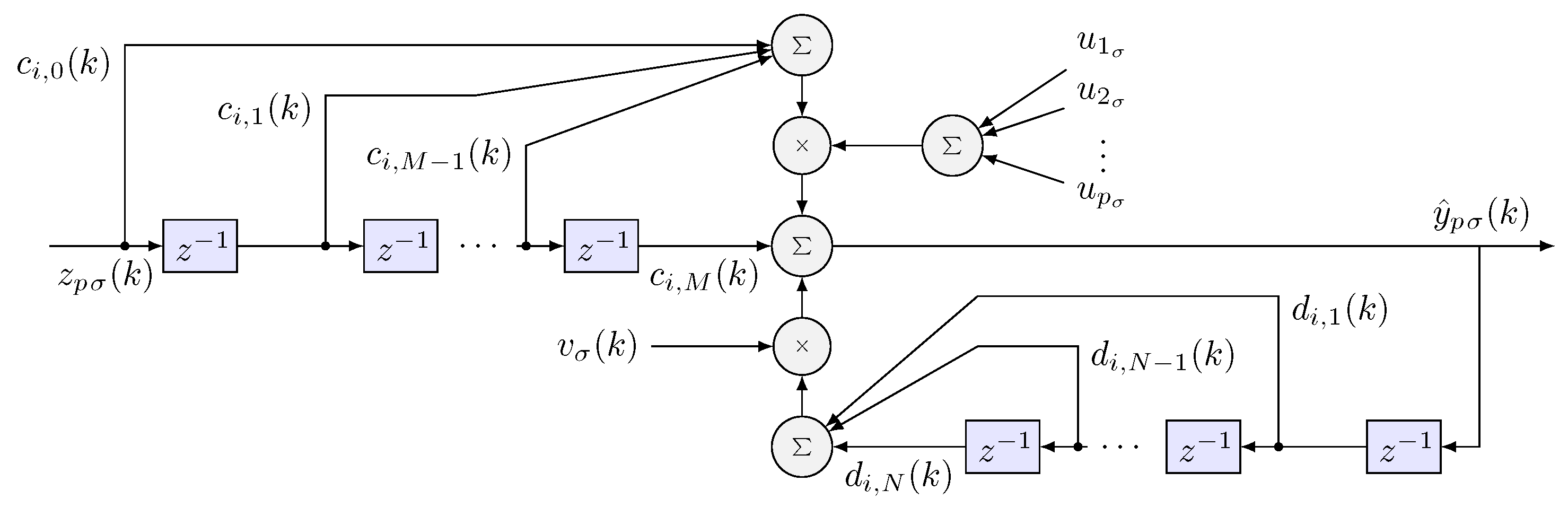
3.2. Wavenet Identification
Weavenet Learning
3.3. Discrete PID Controller for Each Haptic Device
3.4. Auto-Tuning PID Gains
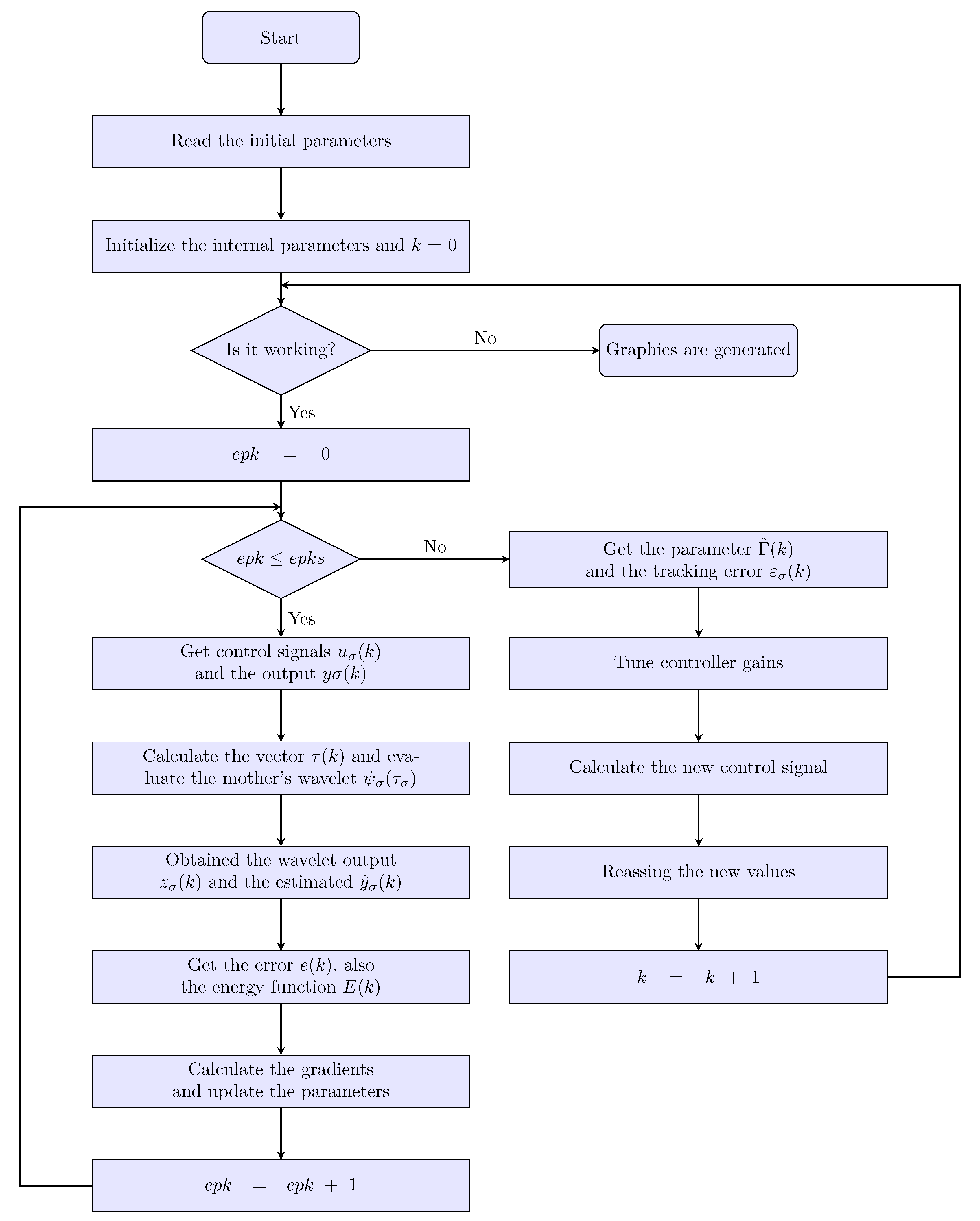
3.5. PID Wavenet Controller Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: PID Wavenet Controller |
|
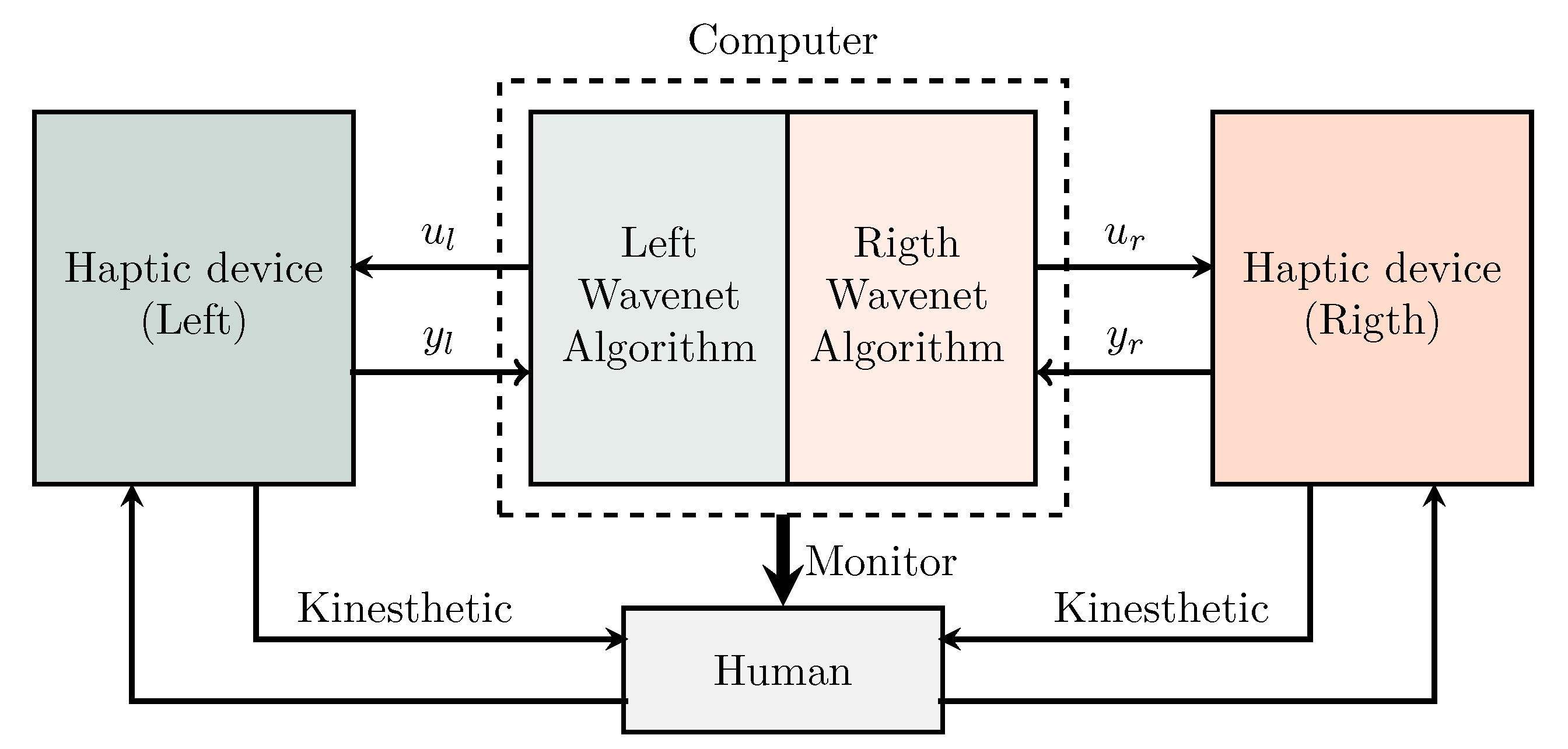
4. The Experimental System
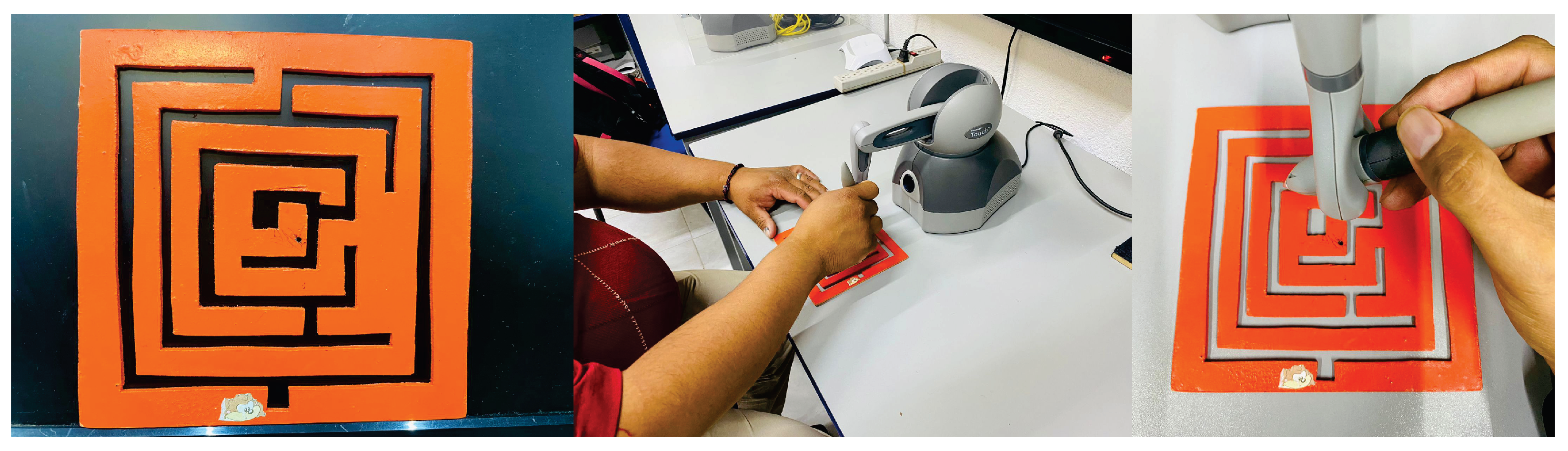
4.1. Experimental Platform
4.2. Design of Experiments
4.3. How the Haptic Control Occurs and How Human Is Guided Spatially
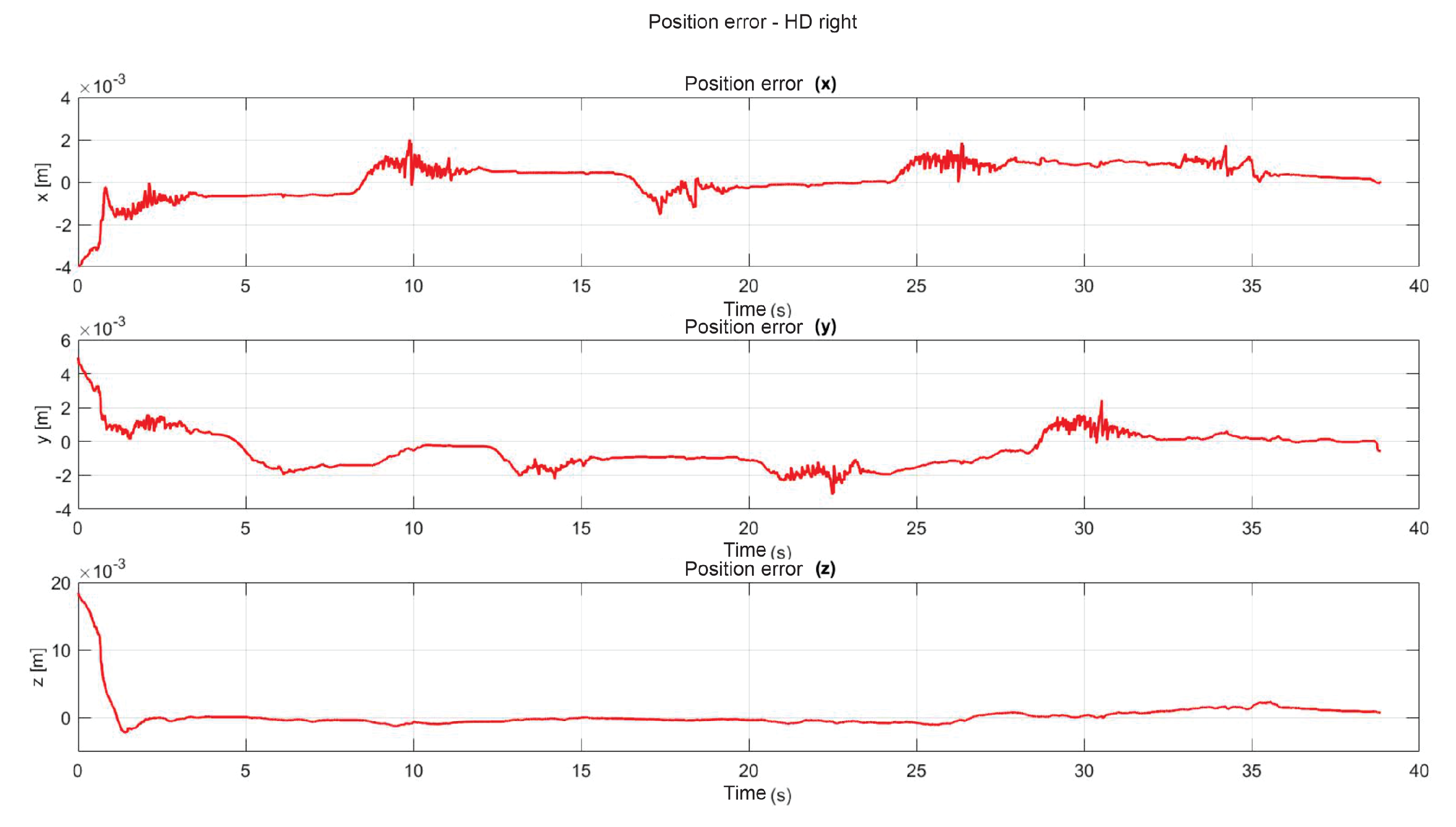
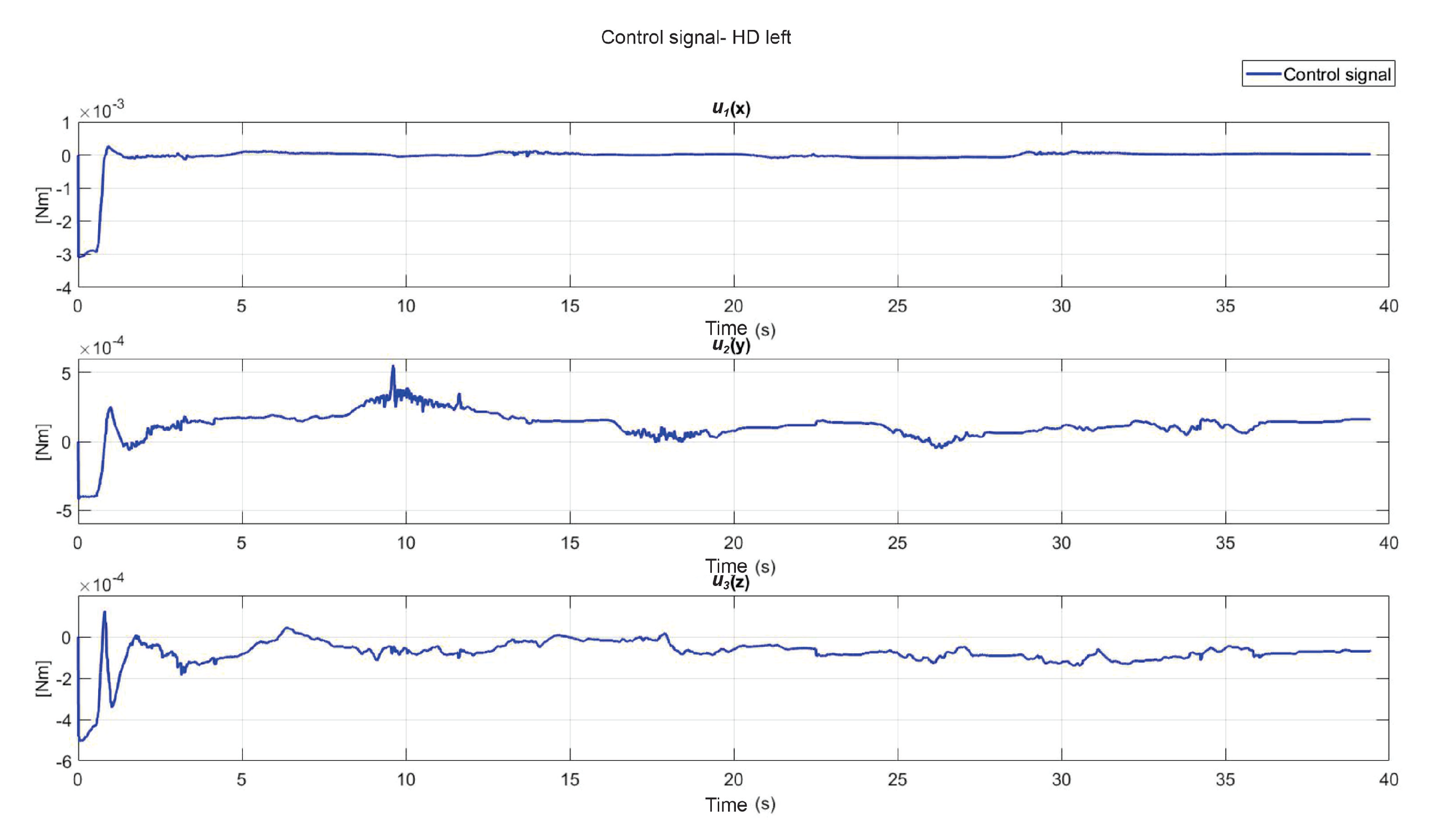
5. Experimental Results
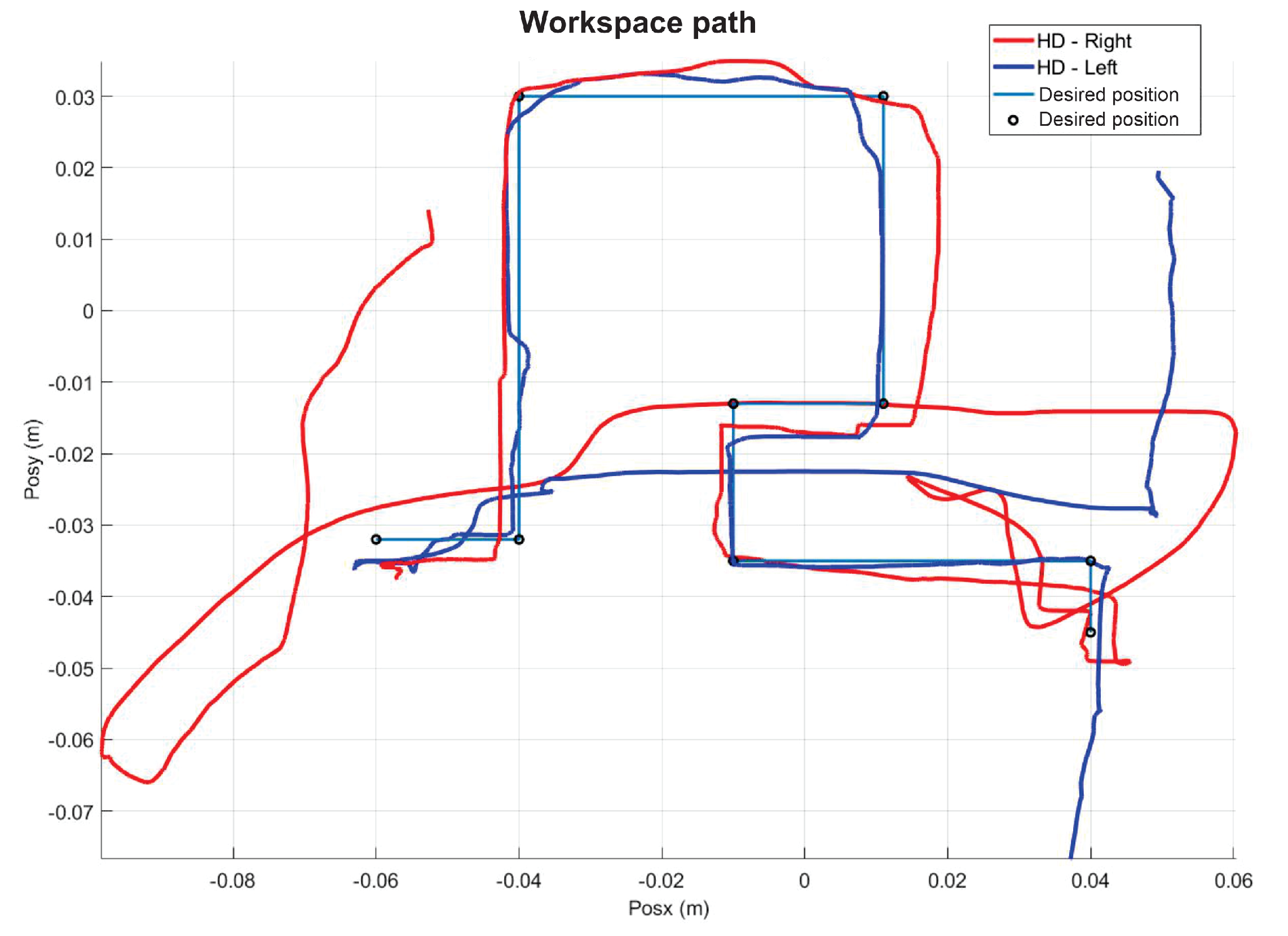
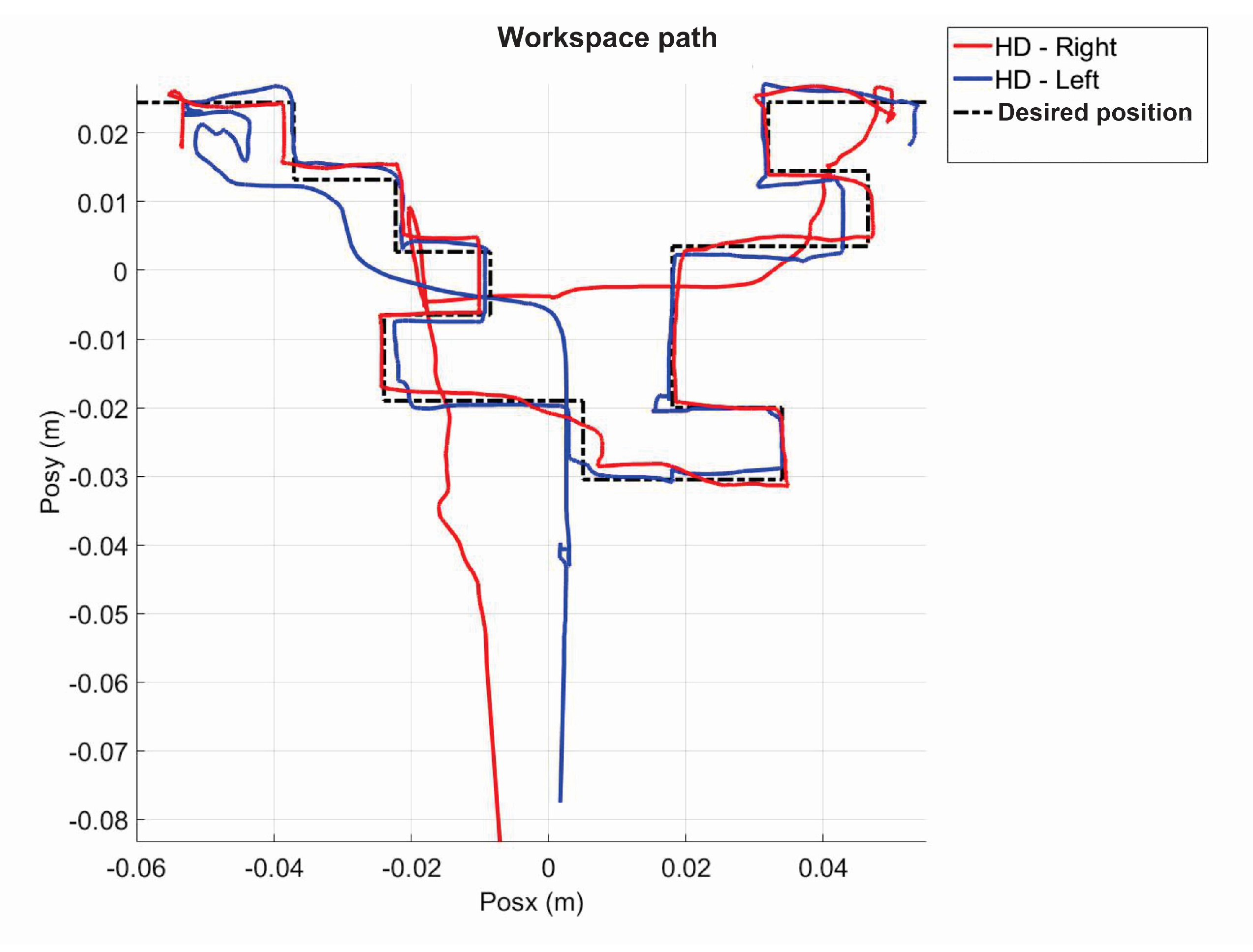
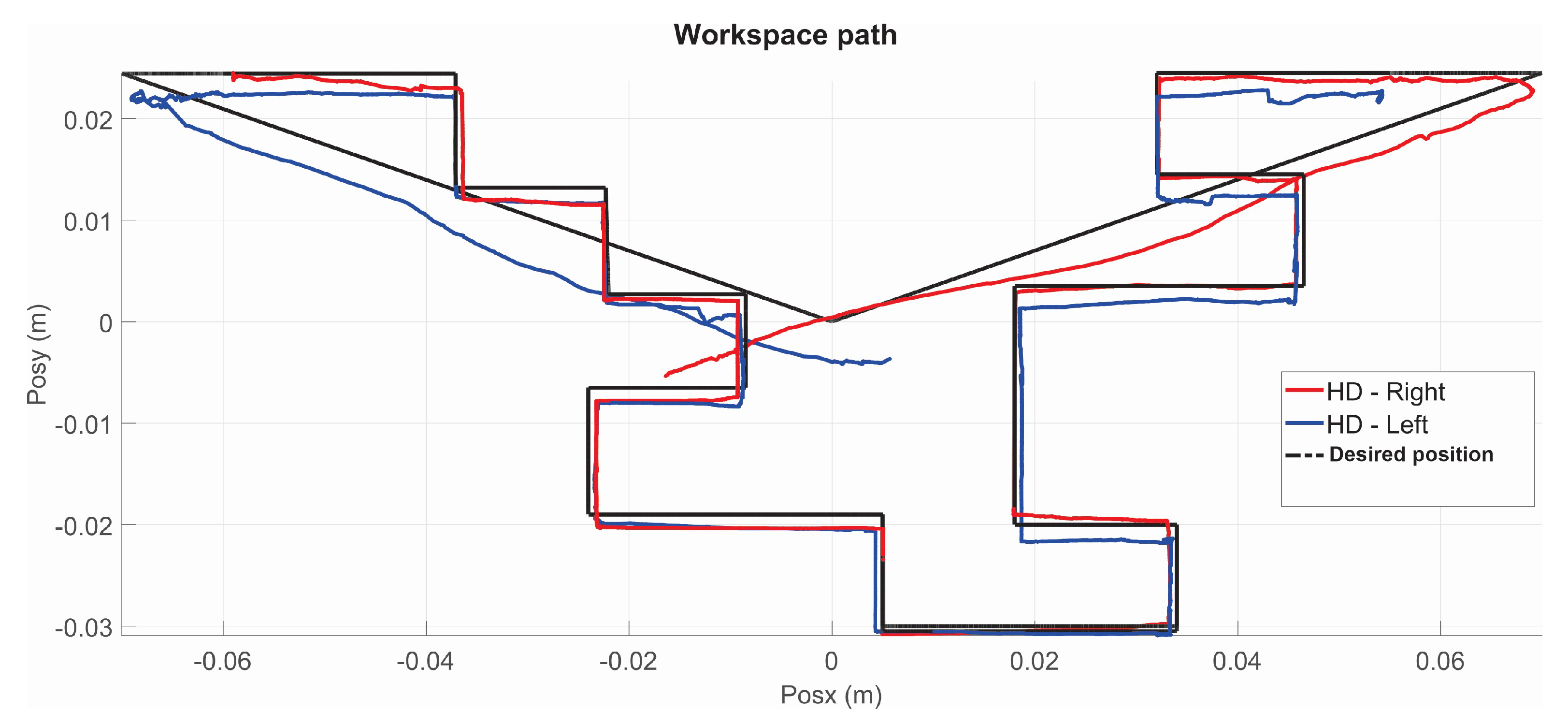
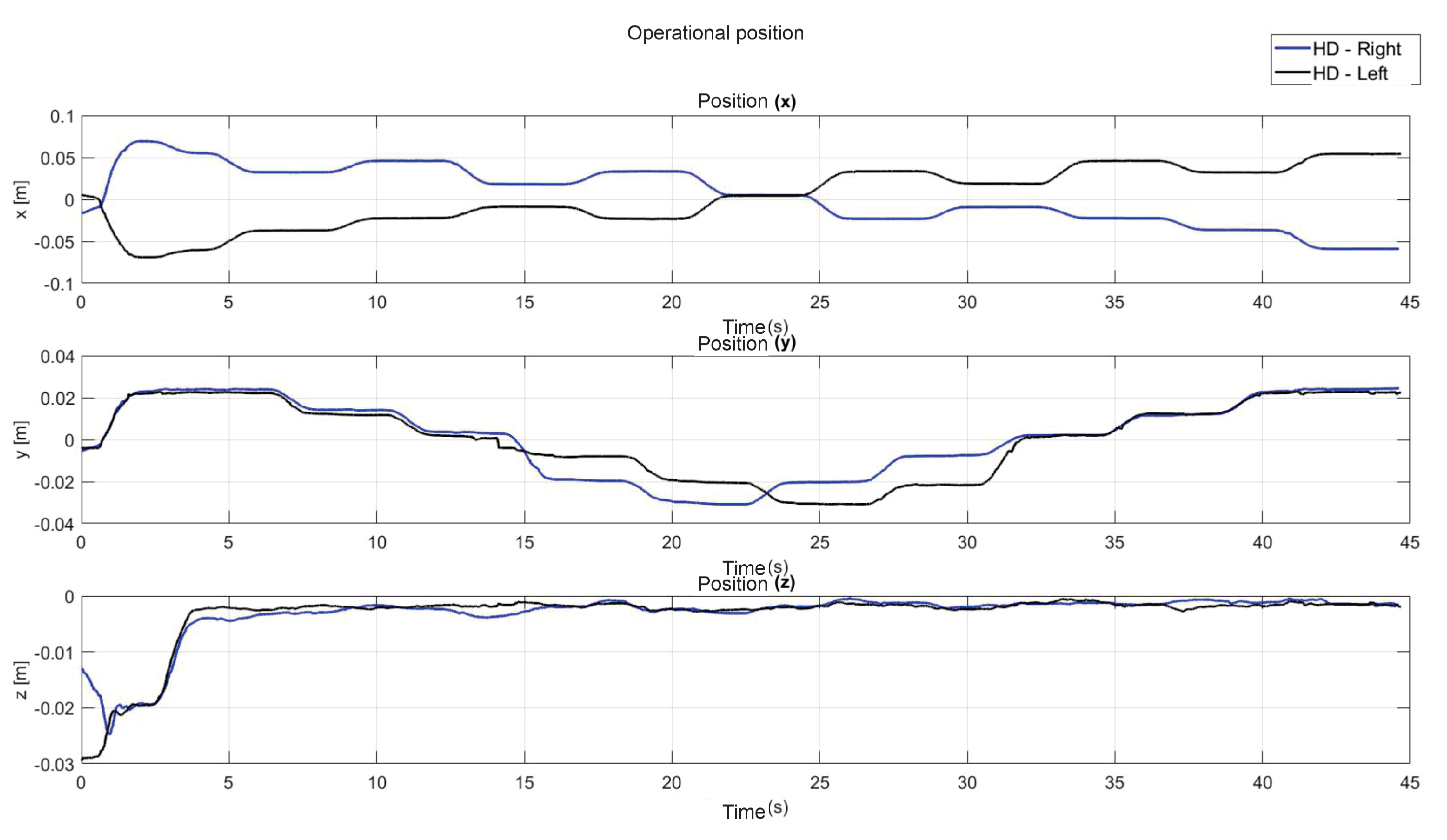
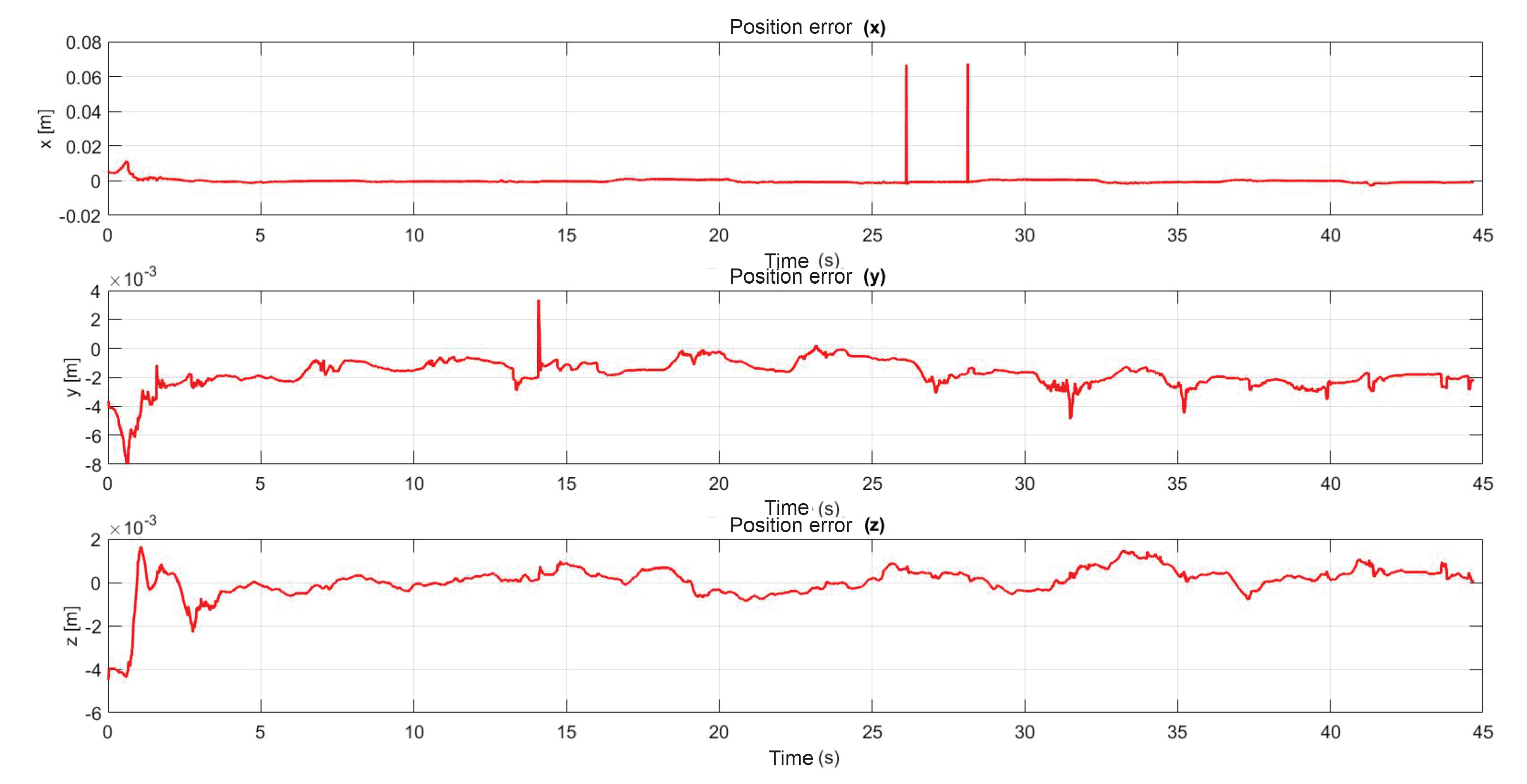
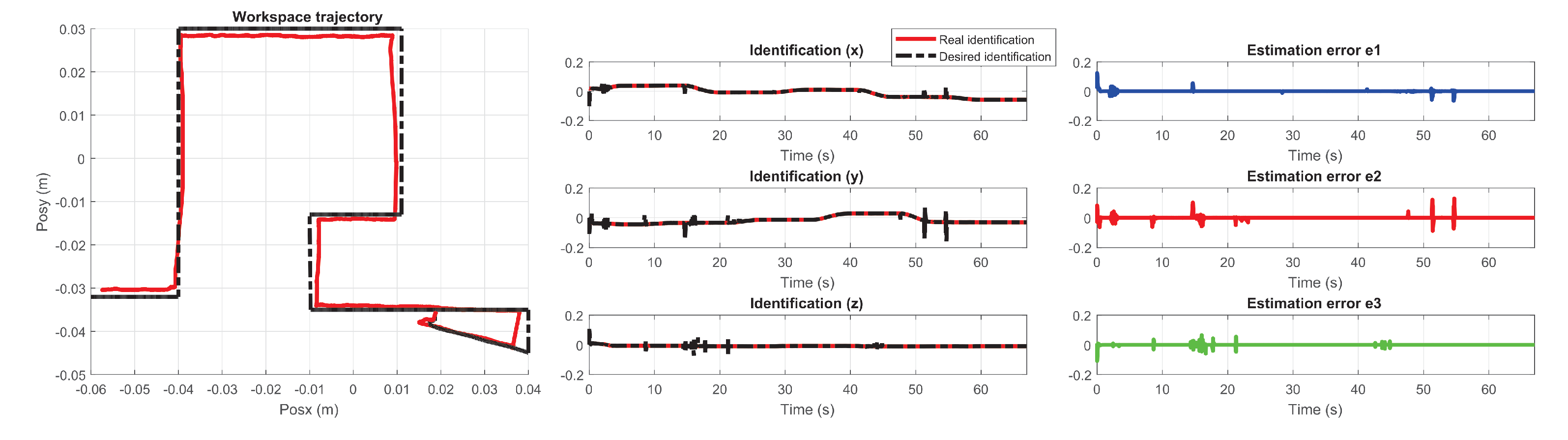
5.1. Experiment 1: Active Haptic Guidance with SCM and MCM
5.2. Experiment 2: Passive Haptic Guidance with SCM and MCM
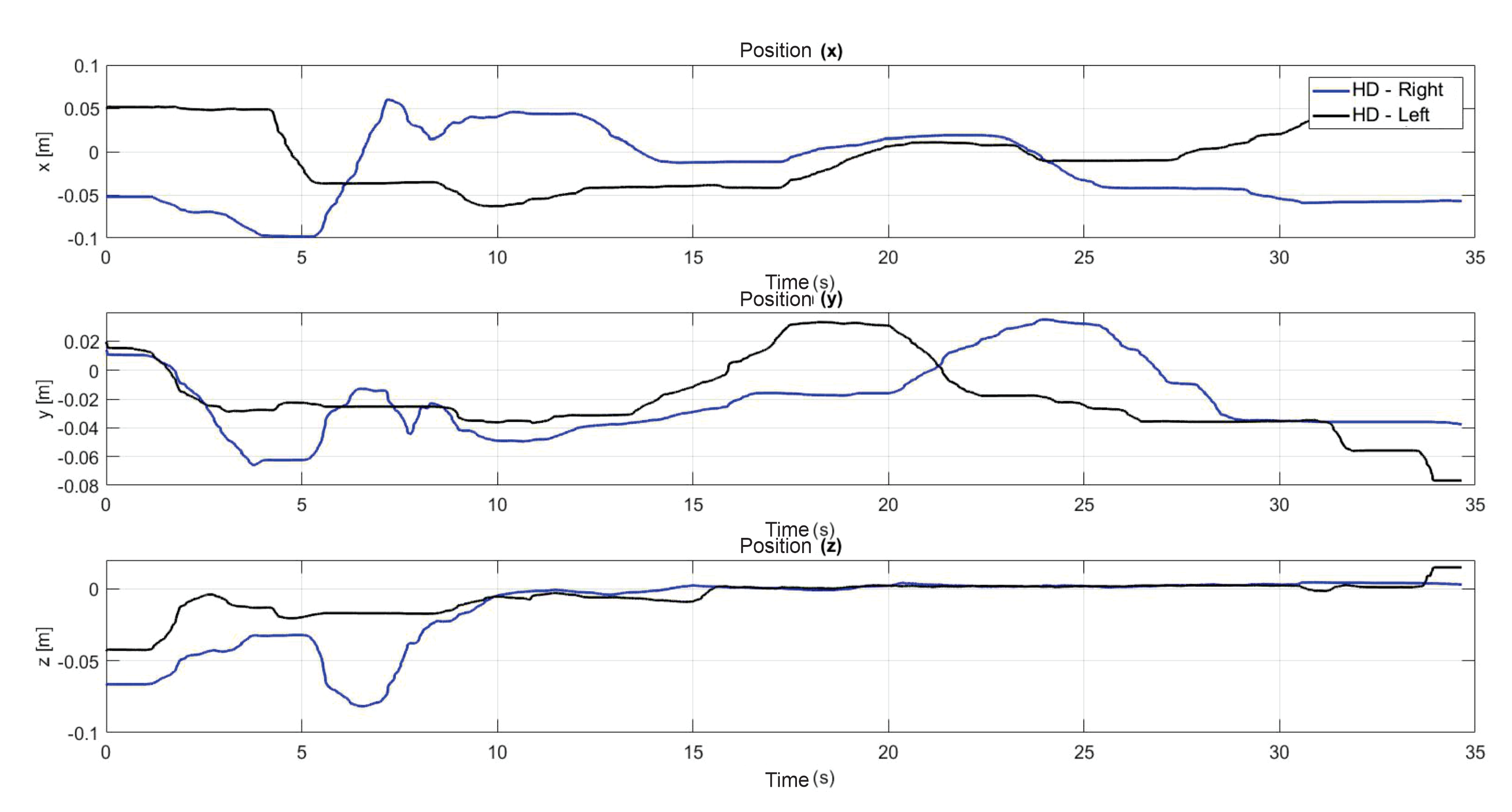
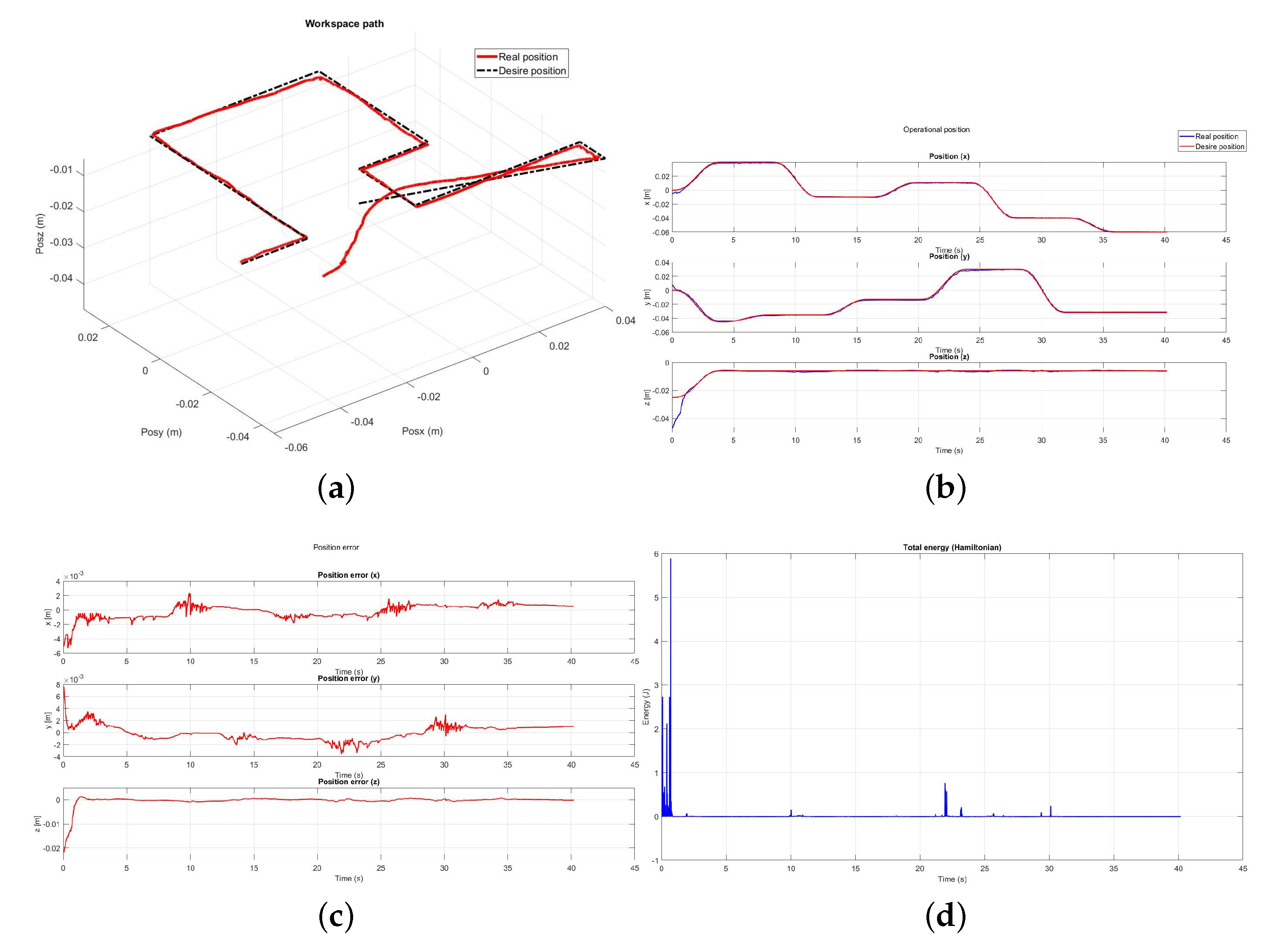
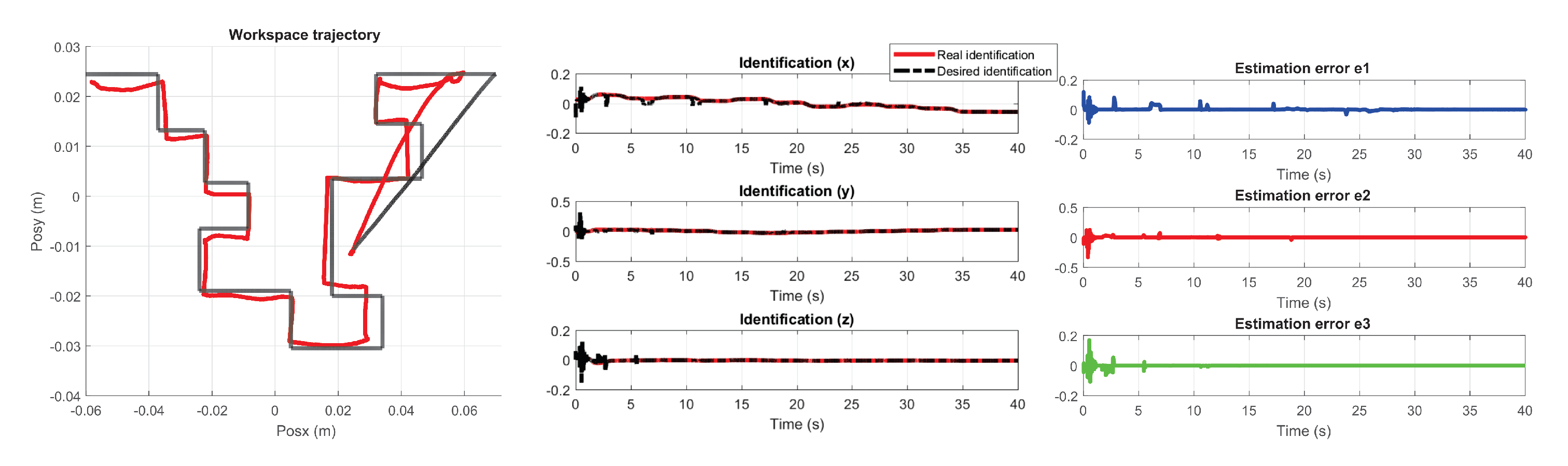
5.3. Exercise 1: Passive Haptic Guidance without User in the Loop
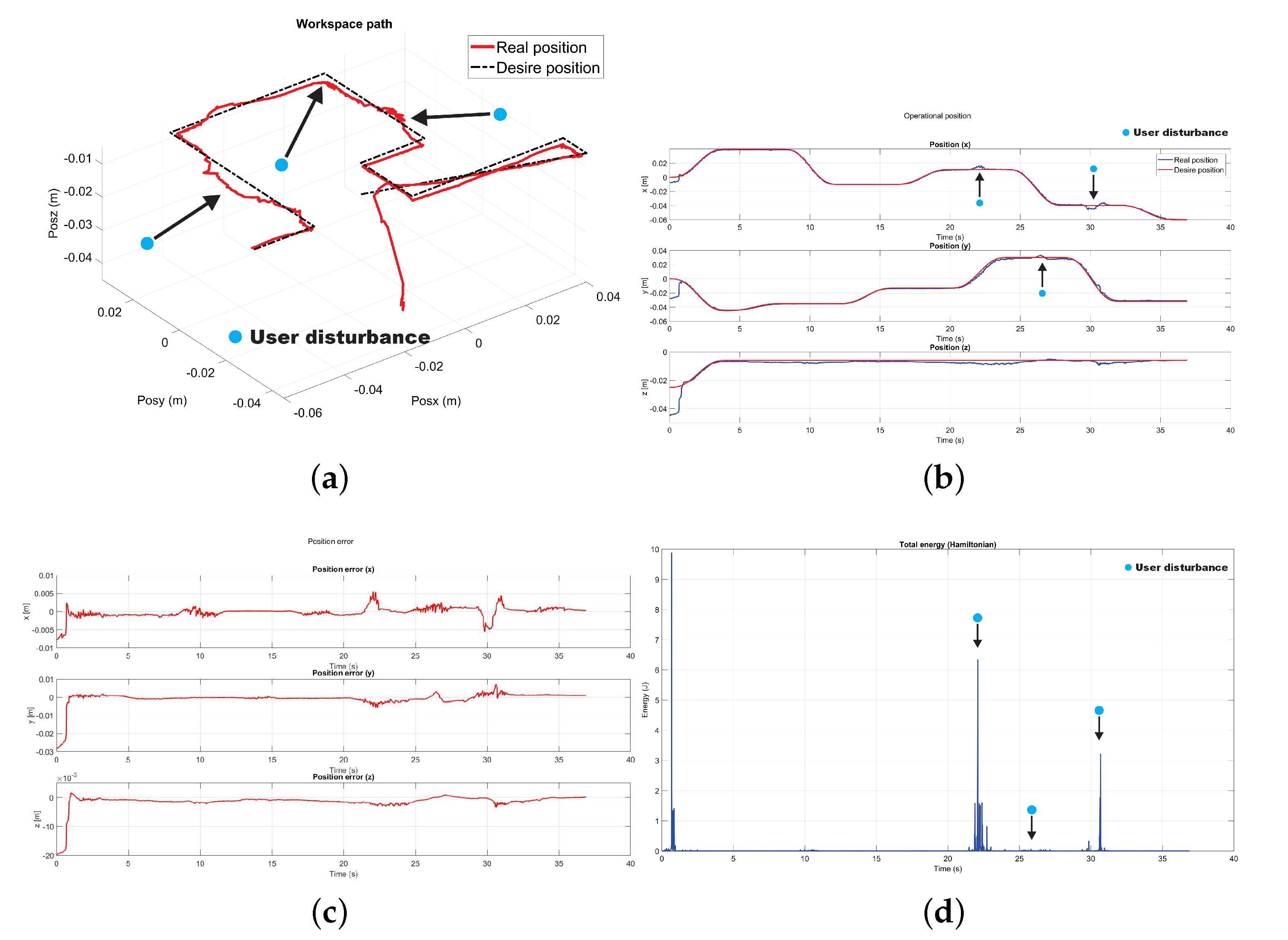
5.4. Exercise 1: Passive Haptic Guidance with User in the Loop and Disturbances
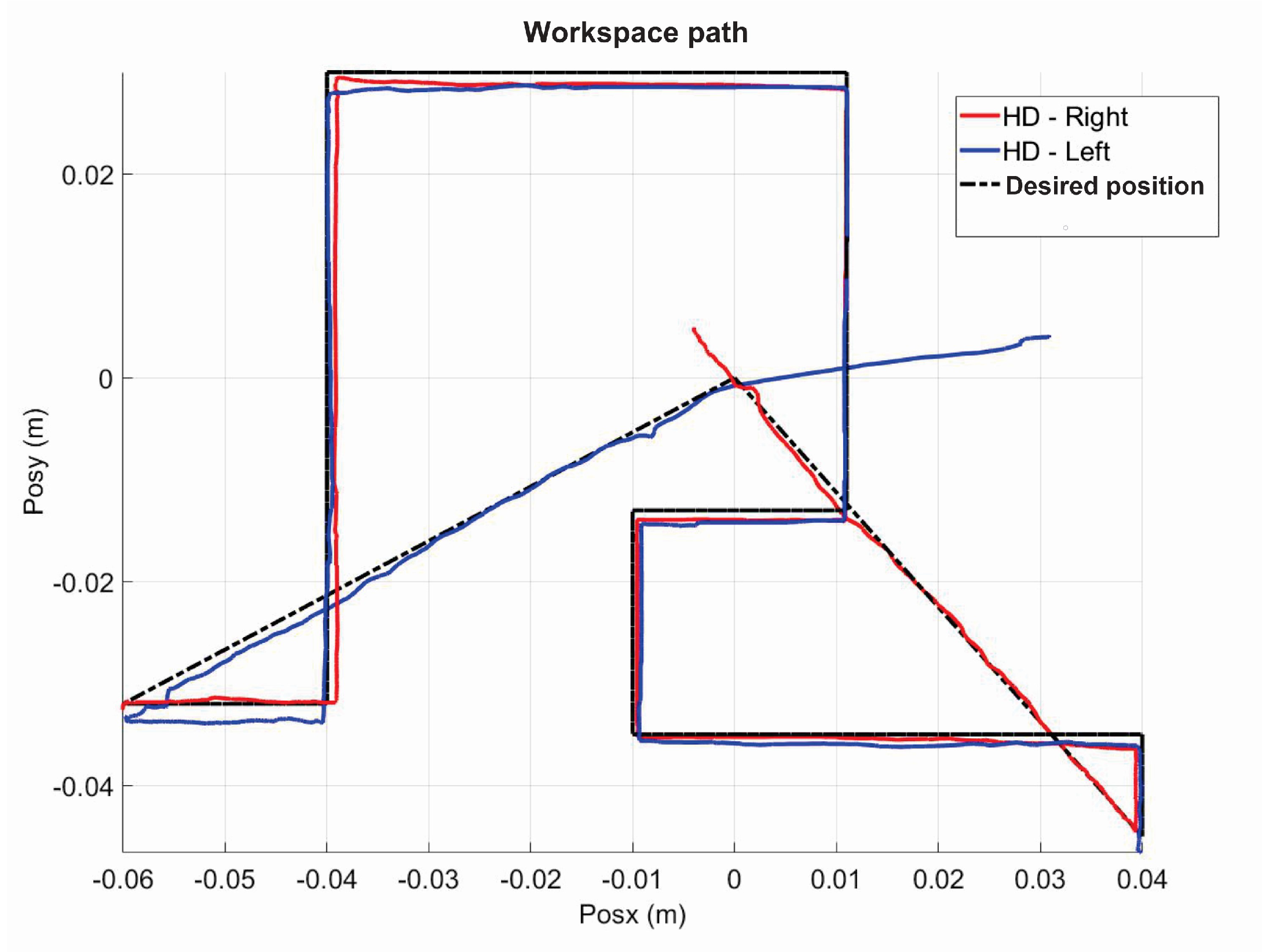
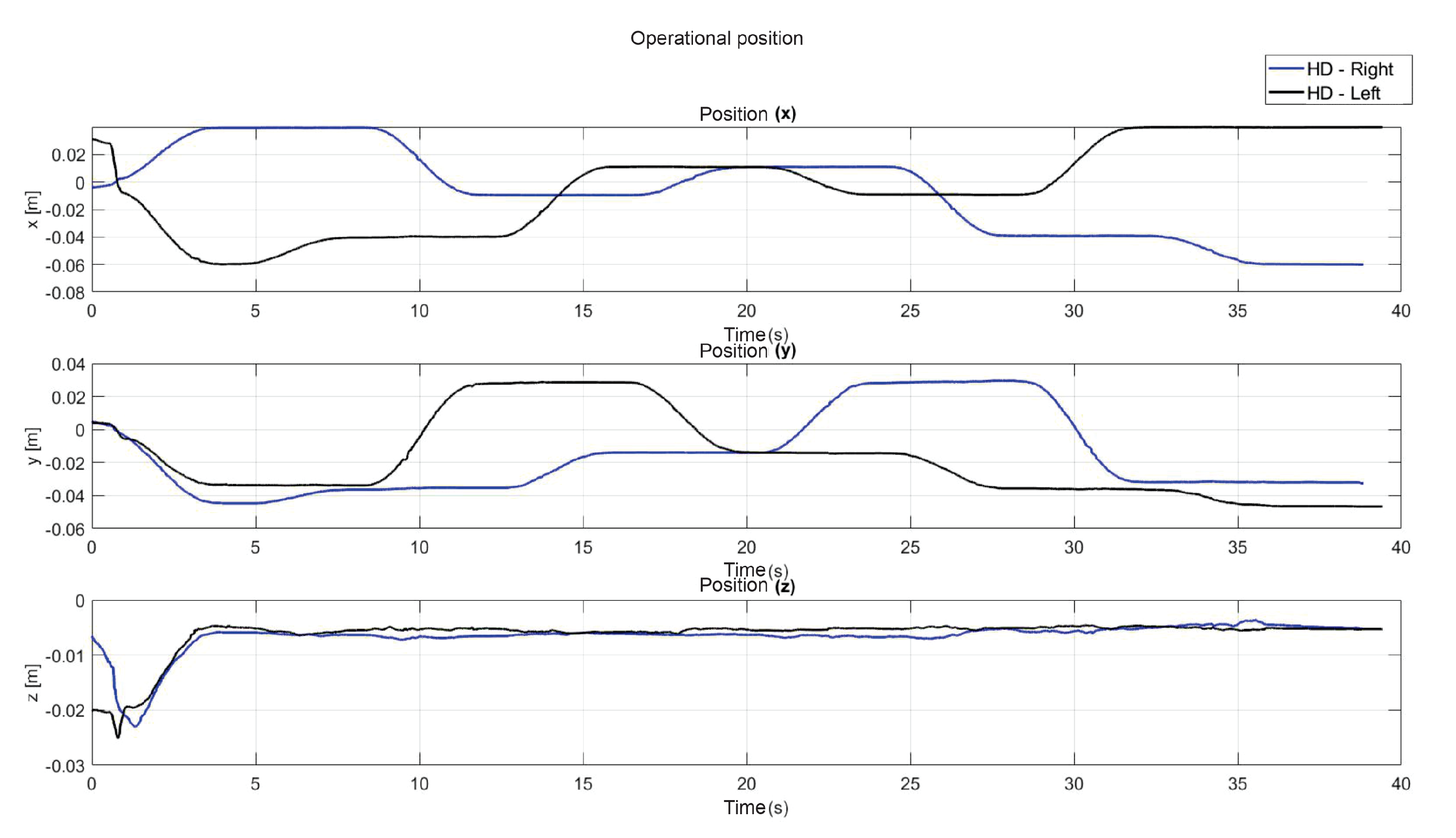
5.5. Exercise 2: Active Haptic Guidance
5.6. Exercise 3: Passive Haptic Guidance
5.7. PID Wavenet-IIR Parematers
6. Conclusions and Future Work
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winstein, C.J.; Stein, J.; Arena, R.; Bates, B.; Cherney, L.R.; Cramer, S.C.; Deruyter, F.; Eng, J.J.; Fisher, B.; Harvey, R.L.; et al. Guidelines for Adult Stroke Rehabilitation and Recovery: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2016, 47, e98–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, K.R.; Lang, C.E.; Boyd, L.A. Is more better? Using metadata to explore dose-response relationships in stroke rehabilitation. Stroke 2014, 45, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, S.; Wolf, S.L.; Fasoli, S.; Bohannon, R. Treatment interventions for the paretic upper limb of stroke survivors: A critical review. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2003, 17, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheis, M.T.; Himelstein, J.; Rizzo, A.A. Virtual reality and neuropsychology: Upgrading the current tools. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2002, 17, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.J.; Cavusoglu, M.C. Human-arm-and-hand-dynamic model with variability analyses for a stylus-based haptic interface. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 2012, 42, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, H.I.; Hogan, N.; Aisen, M.L.; Volpe, B.T. Robot-aided neurorehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1988, 6, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucar, L.; Orihuela-Espina, F.; Velazquez, R.; Reinkensmeyer, D.; Leder, R.; Hernandez-Franco, J. Gesture Therapy: An Upper Limb Virtual Reality-Based Motor Rehabilitation Platform. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-S.; Cho, S.; Ku, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.; Hwang, H.-J.; Paik, N.-J. Clinical Application of Virtual Reality for Upper Limb Motor Rehabilitation in Stroke: Review of Technologies and Clinical Evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Hernande, N.; Huerta-Cervantes, K.; Muñoz-Pepi, I.; Parra-Vega, V. Touch location and force sensing interactive system for upper limb motor rehabilitation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 14133–14152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.; Korner-Bitensky, N.; Levin, M. Virtual Reality in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review of its Effectiveness for Upper Limb Motor Recovery. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2007, 14, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Wu, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, B.; Wu, L.; Huang, X.; Jiang, S.; Huang, L. Evaluating the effect and mechanism of upper limb motor function recovery induced by immersive virtual-reality-based rehabilitation for subacute stroke subjects: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2019, 20, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses-González, J.D.; Domínguez-Ramírez, O.A.; Ramos-Velasco, L.E.; Castro-Espinoza, F.A.; Parra-Vega, V. An Adaptive Robotic Assistance Platform for Neurorehabilitation Therapy of Upper Limb. In Proceedings of the Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Guadalajara, Mexico, 22–27 October 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11289. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Hernandez, N.; Huerta-Cervantes, K.; Muñoz-Pepi, I.; Parra-Vega, V. Personalized Touch-Based Exergame System for Unilateral and Bilateral Rehabilitation Training. Games Health J. 2022, 11, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero Sanchez, C.; Francisco, J.M.; Vaillo, R.R.; Romero, A.R.; Coves, A.; Murillo, D.B. The role of motor variability in motor control and learning depends on the nature of the task and the individual’s capabilities. Eur. J. Hum. Mov. 2017, 38, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sveistrup, H. Motor rehabilitation using virtual reality. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2004, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, M. Virtual Environments for Motor Rehabilitation: Review. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2005, 8, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlozzi, N.E. Porteus Maze. In Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology; Kreutzer, J.S., DeLuca, J., Caplan, B., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- El Saddik, A. Chapter 2: Haptics: Haptics Applications, Haptic Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 21–43. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Andersson, K.; Wikander, J. Dynamic based control strategy for haptic devices. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE World Haptics Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 21–24 June 2011; pp. 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mugisha, S.; Guda, V.K.; Chevallereau, C.; Zoppi, M.; Molfino, R.; Chablat, D. Improving Haptic Response for Contextual Human Robot Interaction. Sensors 2022, 22, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanmahin, R.; Masoud, S.; Rickli, J.; Djuric, A. Human-robot interactions in manufacturing: A survey of human behavior modeling. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2022, 78, 102404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ro, P.I. Human Intention-Oriented Variable Admittance Control with Power Envelope Regulation in Physical Human-Robot Interaction. Mechatronics 2022, 84, 102802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgante, F.; Gaggioli, A.; Strambi, L.; Rusconi, M.L.; Riva, G. Computer-enhanced Route and Survey Spatial Knowledge Assessment in Clinical Neuropsychology. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Workshop on Virtual Rehabilitation, New York, NY, USA, 29–30 August 2006; pp. 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Huiyu, Z.; Huosheng, H. Inertial Motion Tracking of Human Arm Movements in Stroke Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Mechatronics and Automation, Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 29 July–1 August 2005; Volume 3, pp. 1306–1311. [Google Scholar]
- Arimoto, S. Control theory of nonlinear mechanical systems. In A Passivity-Based and Circuit-Theoretic Approach; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Ramirez, O.A.; Parra-Vega, V. Texture, roughness, and shape haptic perception of deformable virtual objects with constrained Lagrangian formulation. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2003) (Cat. No.03CH37453), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–31 October 2003; Volume 3, pp. 3106–3111. [Google Scholar]
- Spong, M.W.; Vidyasagar, M. Robot Dynamics and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jarillo-Silva, A.; Dominguez-Ramirez, O.A.; Parra-Vega, V. Haptic training method for a therapy on upper limb. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Yantai, China, 16–18 October 2010; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Zamora, J.D.; Martinez-Teran, G.; Dominguez-Ramirez, O.A.; Ramos-Velasco, L.; Parra-Vega, V.; Saucedo-Ugalde, I. Wavenet control of a CyberForce system with human dynamic on passive haptic guidance tasks. In Proceedings of the 2015 CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON), Santiago, Chile, 28–30 October 2015; pp. 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Turijan-Rivera, J.A.; Ruiz-Sanchez, F.J.; Dominguez-Ramirez, O.A.; Parra-Vega, V. Modular platform for haptic guidance in paediatric rehabilitation of upper limb neuromuscular disabilities. In Converging Clinical and Engineering Research on Neurorehabilitation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 923–928. [Google Scholar]
- Parra-Vega, V.; Arimoto, S.; Liu, Y.H.; Hirzinger, G.; Akella, P. Dynamic sliding PID control for tracking of robot manipulators: Theory and experiments. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2003, 19, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Yamanaka, Y.; Ohkawa, F.; Katoh, R. Digital control of a robot manipulator disturbed by unknown external forces. In Proceeding of The Society if Instruments and control Engineers, Tokushima, Japan, 29–31 July 1997; pp. 1115–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Mareels, I.; Penfold, H.B.; Evans, R.J. Controlling nonlinear time-varying systems via Euler approximations. Automatica 1992, 28, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.U.; Narendra, K.S. Control of nonlinear dynamical systems using neural networks: Controllability and stabilization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1933, 4, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Kalman Filtering and Neural Networks; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 47. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Velasco, L.E.; Domínguez-Ramírez, O.A.; Parra-Vega, V. Wavenet fuzzy PID controller for nonlinear MIMO systems: Experimental validation on a high-end haptic robotic interface. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 40, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jarillo-Silva, A.; Domínguez-Ramírez, O.A.; Parra-Vega, V.; Ordaz-Oliver, J.P. Phantom omni haptic device: Kinematic and manipulability. In Proceedings of the 2009 Electronics, Robotics and Automotive Mechanics Conference (CERMA), Cuernavaca, Mexico, 22–25 September 2009; pp. 193–198. [Google Scholar]





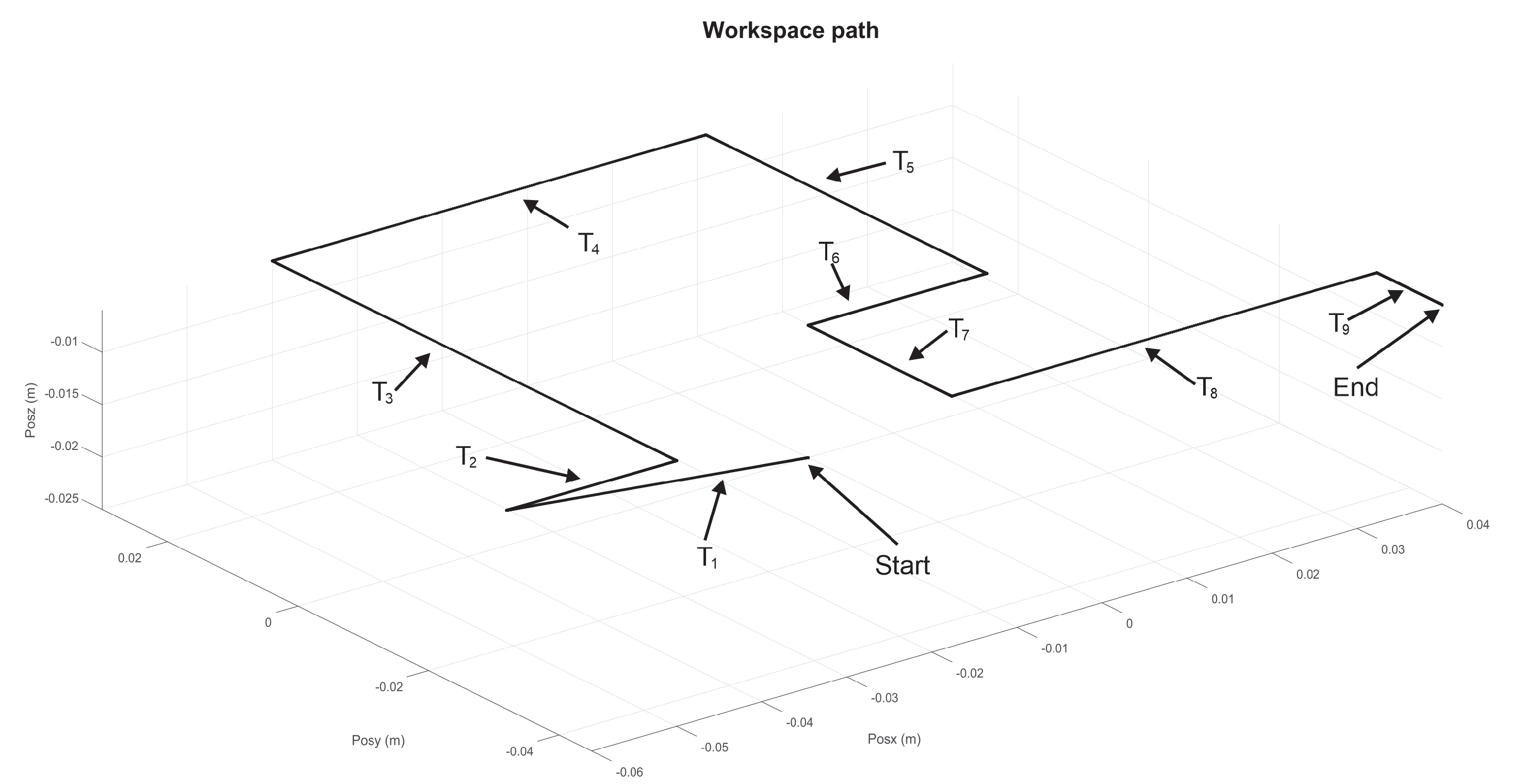
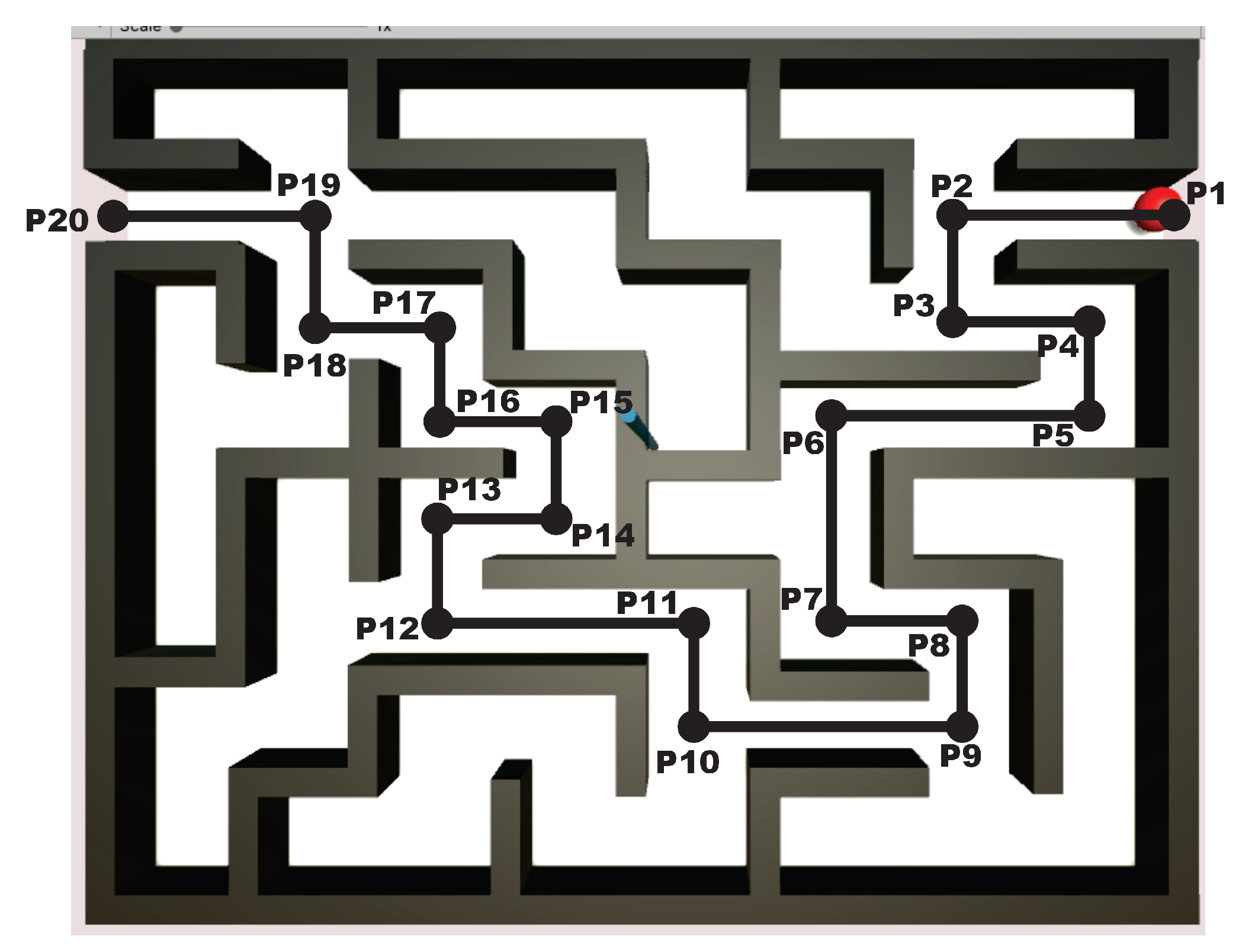
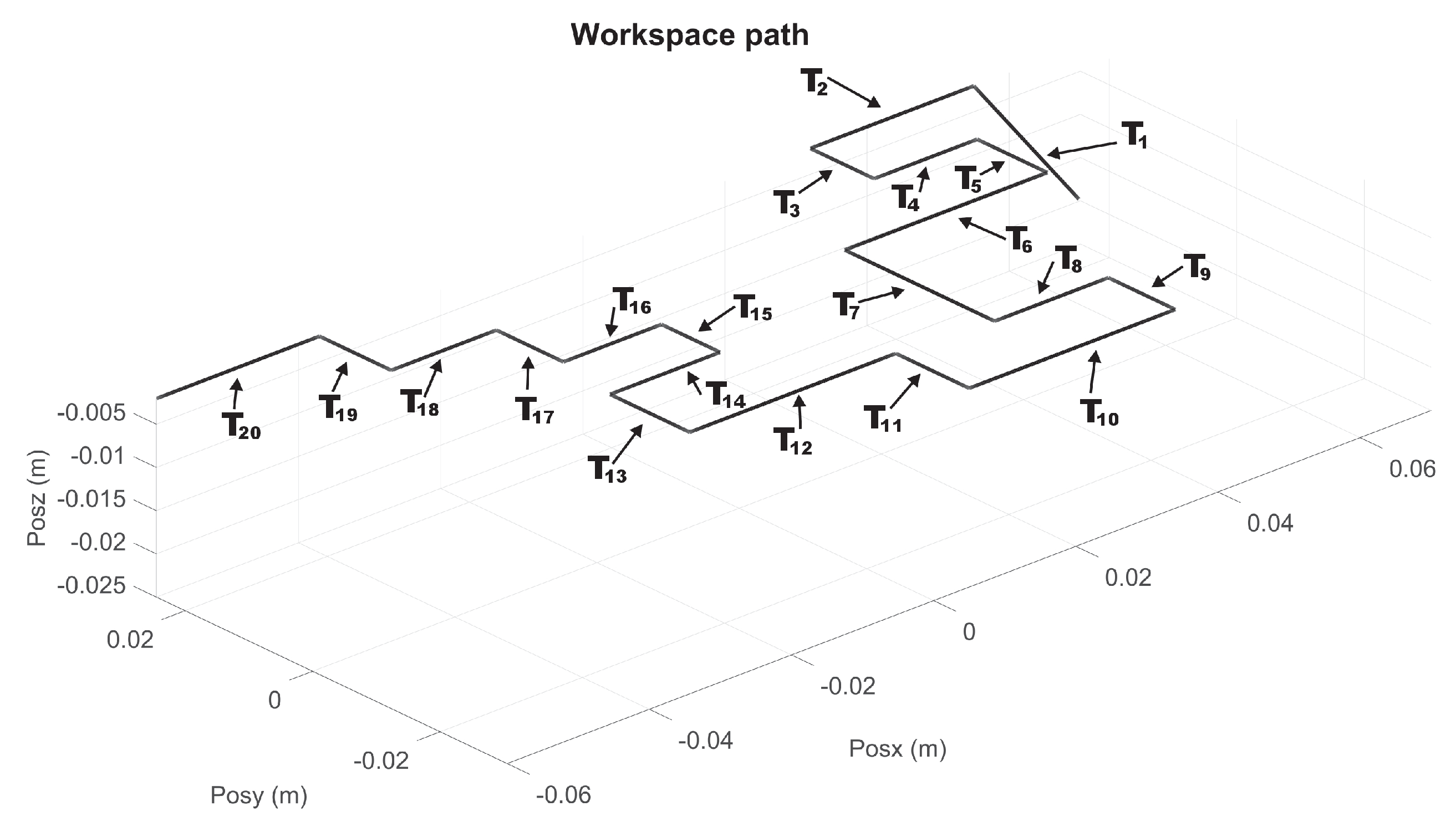
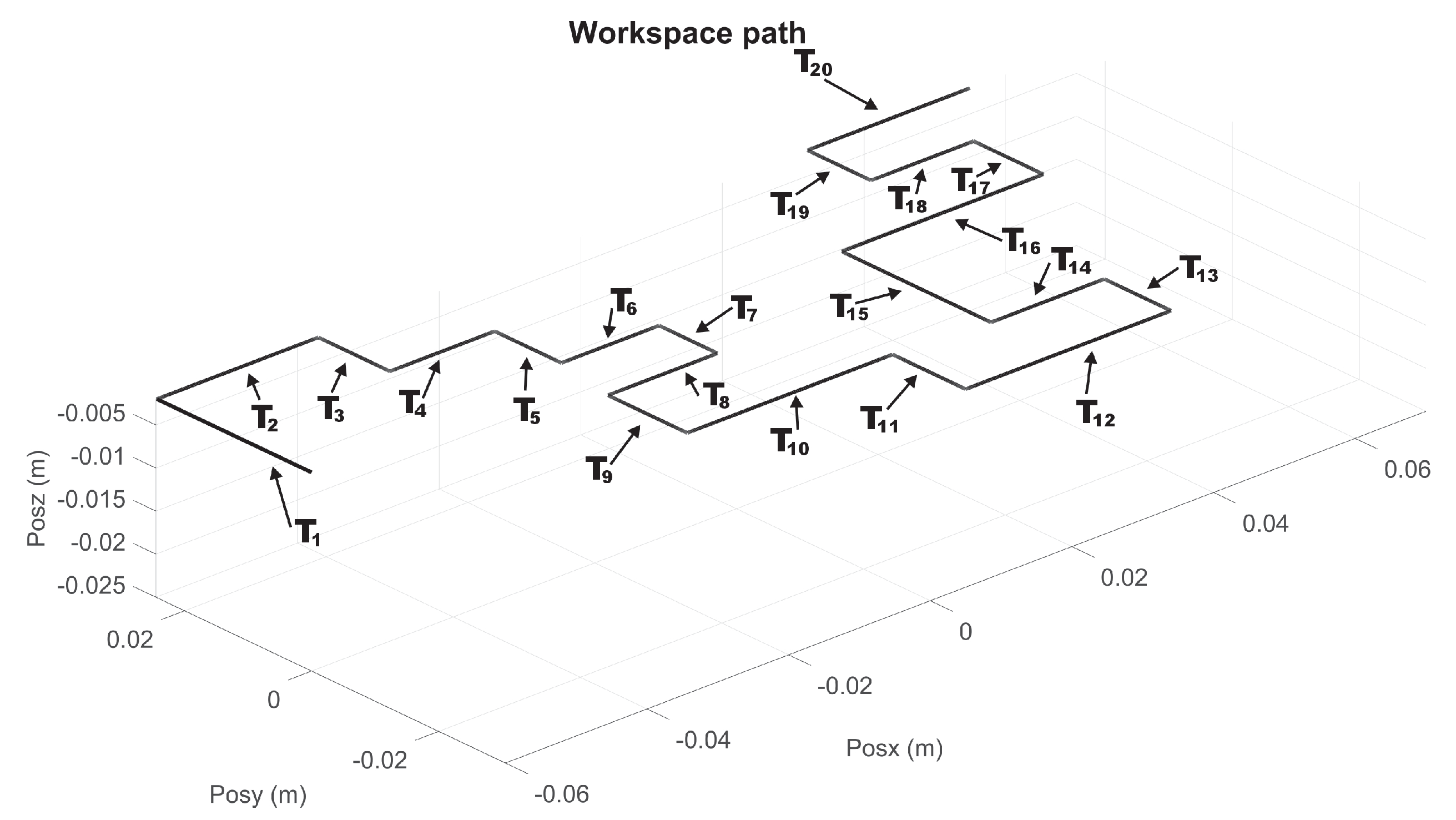









| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurons, L | 3 | 0.5 | |||
| Feed-back, M | 3 | 0.5 | |||
| Feed-forward, N | 2 | 0.5 | |||
| Epocs, | 50 | 0.5 | |||
| 0.5 | |||||
| 0.5 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramirez-Zamora, J.D.; Dominguez-Ramirez, O.A.; Ramos-Velasco, L.E.; Sepulveda-Cervantes, G.; Parra-Vega, V.; Jarillo-Silva, A.; Escotto-Cordova, E.A. HRpI System Based on Wavenet Controller with Human Cooperative-in-the-Loop for Neurorehabilitation Purposes. Sensors 2022, 22, 7729. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207729
Ramirez-Zamora JD, Dominguez-Ramirez OA, Ramos-Velasco LE, Sepulveda-Cervantes G, Parra-Vega V, Jarillo-Silva A, Escotto-Cordova EA. HRpI System Based on Wavenet Controller with Human Cooperative-in-the-Loop for Neurorehabilitation Purposes. Sensors. 2022; 22(20):7729. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207729
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamirez-Zamora, Juan Daniel, Omar Arturo Dominguez-Ramirez, Luis Enrique Ramos-Velasco, Gabriel Sepulveda-Cervantes, Vicente Parra-Vega, Alejandro Jarillo-Silva, and Eduardo Alejandro Escotto-Cordova. 2022. "HRpI System Based on Wavenet Controller with Human Cooperative-in-the-Loop for Neurorehabilitation Purposes" Sensors 22, no. 20: 7729. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207729
APA StyleRamirez-Zamora, J. D., Dominguez-Ramirez, O. A., Ramos-Velasco, L. E., Sepulveda-Cervantes, G., Parra-Vega, V., Jarillo-Silva, A., & Escotto-Cordova, E. A. (2022). HRpI System Based on Wavenet Controller with Human Cooperative-in-the-Loop for Neurorehabilitation Purposes. Sensors, 22(20), 7729. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207729







