Reflectometers for Absolute and Relative Reflectance Measurements in the Mid-IR Region at Vacuum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Primary Reflectometer
3. Relative Reflectometer
4. Overall Measurement System
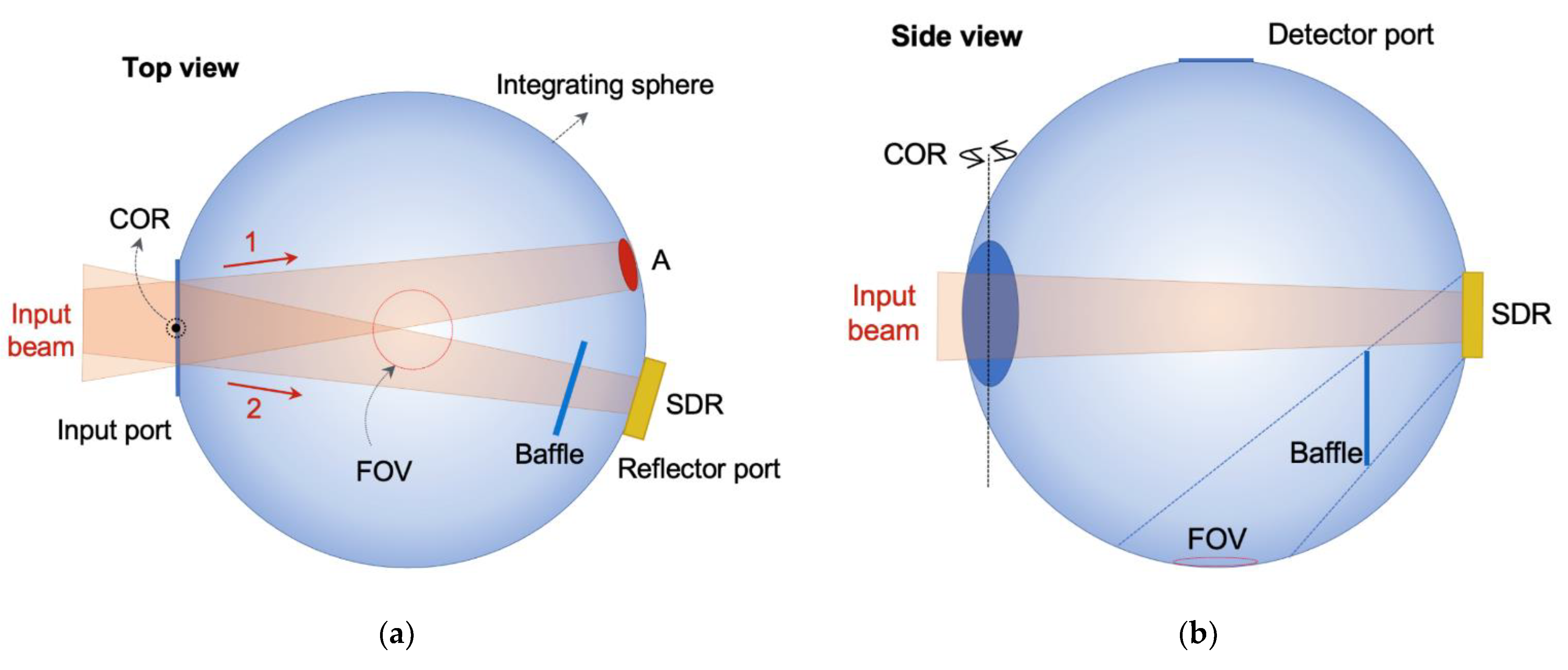
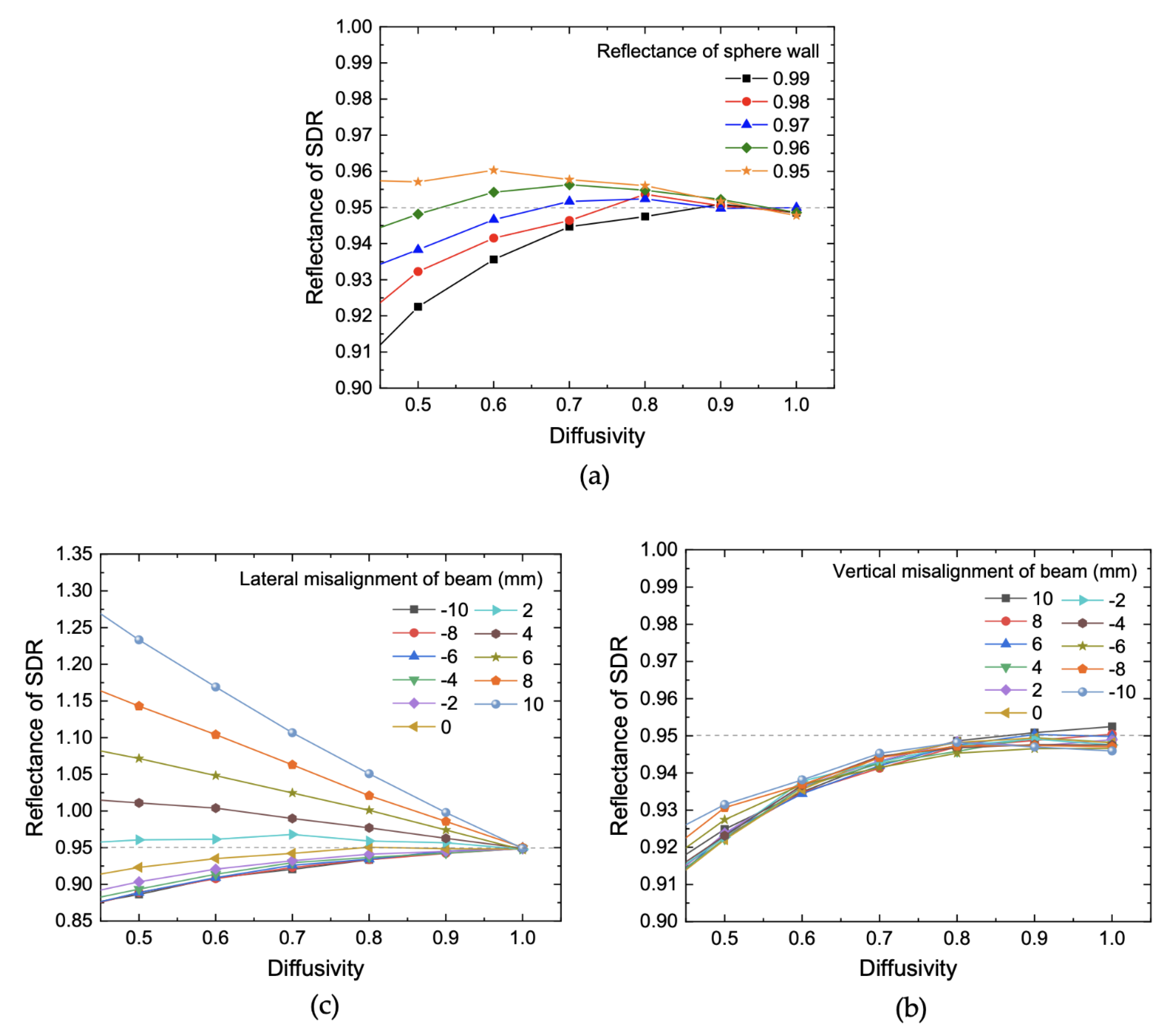
5. Ray-Tracing Simulation about Systematic Uncertainty of Primary Reflectometer
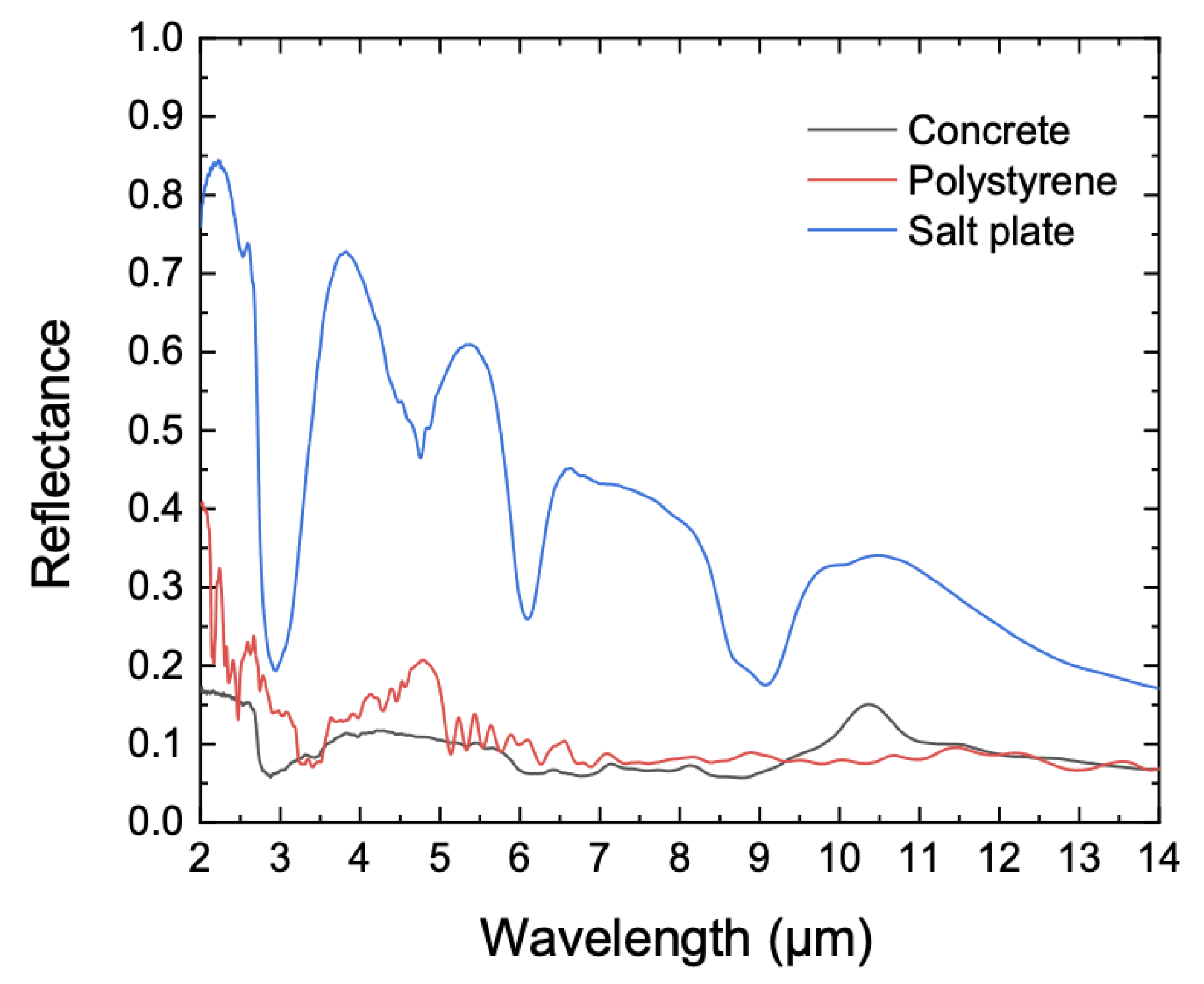
6. Reflectance Measurements and Uncertainty Evaluation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wood, B.E.; Pipes, J.G.; Smith, A.M.; Roux, J.A. Hemi-ellipsoidal mirror infrared reflectometer: Development and operation. Appl. Opt. 1976, 15, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebielec, G.; Mccarty, G.W.; Stuczynski, T.I. Near- and mid-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for measuring soil metal content. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 2069, 2056–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, D.B. Mid-infrared reflectance spectra (23–22 μm) of sulfur, gold, KBr, MgO, and halon. Appl. Opt. 1986, 25, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Liu, D.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L. Vanadium dioxide nanopowders with tunable emissivity for adaptive infrared camouflage in both thermal atmospheric windows. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 175, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A. Detection of forests using mid-IR reflectance: An application for aerosol studies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitcolin, F.; Vermote, E. Land surface reflectance, emissivity and temperature from MODIS middle and thermal infrared data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, J.W.; D’Aria, D.M.; Wald, A. Measurements of thermal infrared spectral reflectance of frost, snow, and ice. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Raman, A.; Wang, K.X.; Anoma, M.A.; Fan, S. Radiative cooling of solar cells. Optica 2014, 1, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, I.; Silverman, T.J.; Deceglie, M.G.; Podraza, N.J. Emissivity of solar cell cover glass calculated from infrared reflectance measurements. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 190, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, G.; Shen, X.; Yan, X.; Cheng, C. Low infrared emissivity of polyurethane/Cu composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 6077–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, J.W.; Prahl, S.A.; van Wieringen, N.; Beek, J.F.; Sterenborg, H.J.C.M.; van Gemert, M.J.C. Double-integrating-sphere system for measuring the optical properties of tissue. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gindele, K.; Köhl, M.; Mast, M. Spectral reflectance measurements using an integrating sphere in the infrared. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.K.; Gier, J.T.; Nelson, K.E.; Roddick, R.D. Integrating sphere for imperfectly diffuse samples*. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1961, 51, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerlaut, G.A.; Anderson, T.E. Multiple-integrating sphere spectrophotometer for measuring absolute spectral reflectance and transmittance. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisdal, B.J. Reflectance of perfect diffuse and specular samples in the integrating sphere. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1965, 55, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, T.A.; Johnson, T.J.; Tonkyn, R.G.; Forland, B.M.; Myers, T.L.; Brauer, C.S.; Su, Y.-F.; Bernacki, B.E.; Hanssen, L.; Gonzalez, G. Methods for quantitative infrared directional-hemispherical and diffuse reflectance measurements using an FTIR and a commercial integrating sphere. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, L. Integrating-sphere system and method for absolute measurement of transmittance, reflectance, and absorptance of specular samples. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, J.A.; Clarke, F.J.J. Correction methods for integrating sphere measurement of hemispherical reflectance. Anal. Spectrosc. Libr. 1987, 2, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffer, D.; Oppenheim, U.P.; Devir, A.D. Absolute reflectometer for the mid infrared region. Appl. Opt. 1990, 29, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devir, A.D.; Sheffer, D.; Clement, D.; Oppenheim, U.P. Absolute reflectometer for the 0.8–2.5-μm region. Appl. Opt. 1987, 26, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.P.; Griffiths, P.R. Diffuse reflectance measurements by infrared fourier transform spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1978, 50, 1906–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, W. Calibration of reflectance standards. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. Sect. A Phys. Chem. 1976, 80A, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, L.M.; Snail, K.A. Integrating spheres for mid- and near-infrared reflection spectroscopy. In Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy; Griffiths, P.R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2001; Volume 80A, ISBN 0471988472. [Google Scholar]
- Balling, B. A Comparative Study of the Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function of Several Surfaces as a Mid-wave Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Standard. Ph.D. Thesis, Air Force Institute of Technology, Dayton, OH, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chunnilall, C.J.; Theocharous, E. Infrared hemispherical reflectance measurements in the 2.5 µm to 50 µm wavelength region using a Fourier transform spectrometer. Metrologia 2012, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstern, J.B.; Pitcher, B.W. Analysis of H2O in silicate glass using attenuated total reflectance (ATR) micro-FTIR spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 2013, 1, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M. An almost “perfectly” diffuse, “perfect” reflector for far-infrared reflectance calibration. In Proceedings of SPIE; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992; Volume 1753. [Google Scholar]
- Sapritsky, V.I.; Prokhorov, A.V. Calculation of the effective emissivities of specular-diffuse cavities by the Monte Carlo method. Metrologia 1992, 29, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, L.M. Effects of non-Lambertian surfaces on integrating sphere measurements. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, L.M.; Kaplan, S. Infrared diffuse reflectance instrumentation and standards at NIST. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 380, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Description | Uncertainty Components | Standard Uncertainty | Sensitivity Coefficient | Contribution | DOF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISW reflectance | ur(RSDR)ISW | 1.6% | Standard | Ray-tracing simulation | 0.2% | ∞ |
| Vertical shift | ur (RSDR)vertical | 1 mm | Square | Ray-tracing simulation | 0.1% | ∞ |
| Horizontal shift | ur (RSDR)horizontal | 1 mm | Square | Ray-tracing simulation | 0.5% | ∞ |
| ISW diffusivity | ur (RSDR)diffusivity | 0.1 | Standard | Ray-tracing simulation | 0.5% | ∞ |
| Light source power drift | ur (P1)source | 0.5% | Standard | 0.95 | 0.47% | ∞ |
| ur (P2)source | 0.47% | |||||
| MCT linearity | ur (P1)linear | 0.58% | Square | 0.95 | 0.55% | ∞ |
| ur (P2)linear | 0.55% | |||||
| MCT sensitivity drift | ur (P1)sensitivity | 0.87% | Square | 0.95 | 0.82% | ∞ |
| ur (P2)sensitivity | 0.82% | |||||
| Repeatability | ur (P1)rep | 1% | t | 0.95 | 0.95% | 4 |
| ur (P2)rep | 0.95% | |||||
| Overall Uncertainty | Standard | 2.18% | 55.5 |
| Description | Uncertainty Components | Standard Uncertainty | Sensitivity Coefficient | Contribution (Relative) | DOF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDR reflectance uncertainty | ur(RSDR) | 2.07% | Standard | 1 | 2.07% | ∞ |
| Light source power drift | ur(PA)source | 0.5% | Standard | 1 | 0.5% | ∞ |
| ur(PB)source | 0.5% | |||||
| MCT linearity | ur(PA)linear | 0.58% | Square | 1 | 0.58% | ∞ |
| ur(PB)linear | 0.58% | |||||
| MCT sensitivity drift | ur(PA)sensitivity | 0.87% | Square | 1 | 0.87% | ∞ |
| ur(PB)sensitivity | 0.87% | |||||
| Repeatability | ur (PA)rep | 1% | t | 1 | 1% | 4 |
| ur (PB)rep | 1% | |||||
| Overall Uncertainty | Standard | 2.99 | 159.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gene, J.; Jeon, M.Y.; Lim, S.D. Reflectometers for Absolute and Relative Reflectance Measurements in the Mid-IR Region at Vacuum. Sensors 2021, 21, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041169
Gene J, Jeon MY, Lim SD. Reflectometers for Absolute and Relative Reflectance Measurements in the Mid-IR Region at Vacuum. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041169
Chicago/Turabian StyleGene, Jinhwa, Min Yong Jeon, and Sun Do Lim. 2021. "Reflectometers for Absolute and Relative Reflectance Measurements in the Mid-IR Region at Vacuum" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041169
APA StyleGene, J., Jeon, M. Y., & Lim, S. D. (2021). Reflectometers for Absolute and Relative Reflectance Measurements in the Mid-IR Region at Vacuum. Sensors, 21(4), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041169








