The Minimum AC Signal Model of Bipolar Transistor in Amplification Region for Weak Signal Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Minimum AC Signal Model
2.1. The Non-Equilibrium Carrier Theory
2.2. The Limit Small Voltage Signal Theory
2.3. The Minimum Signal Model
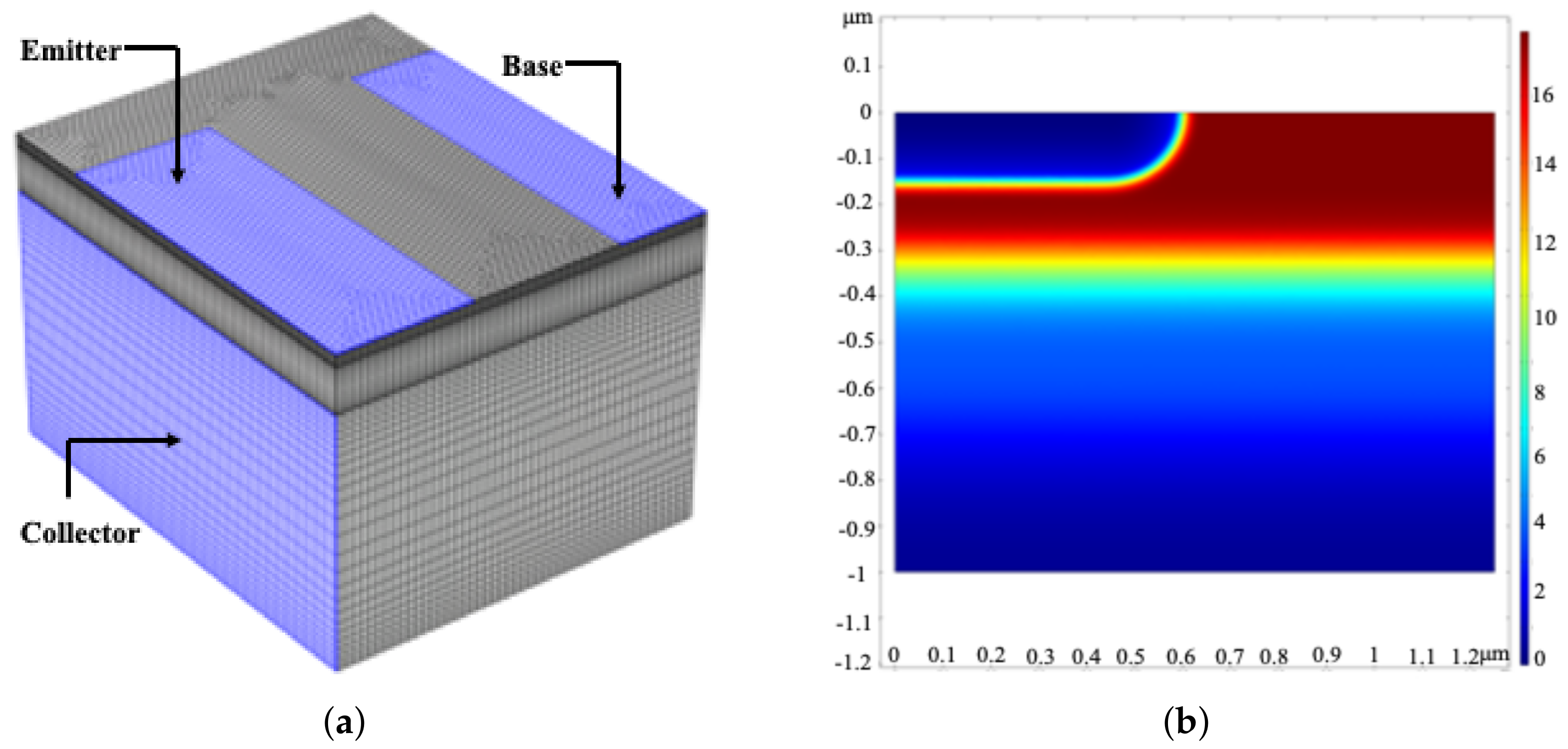
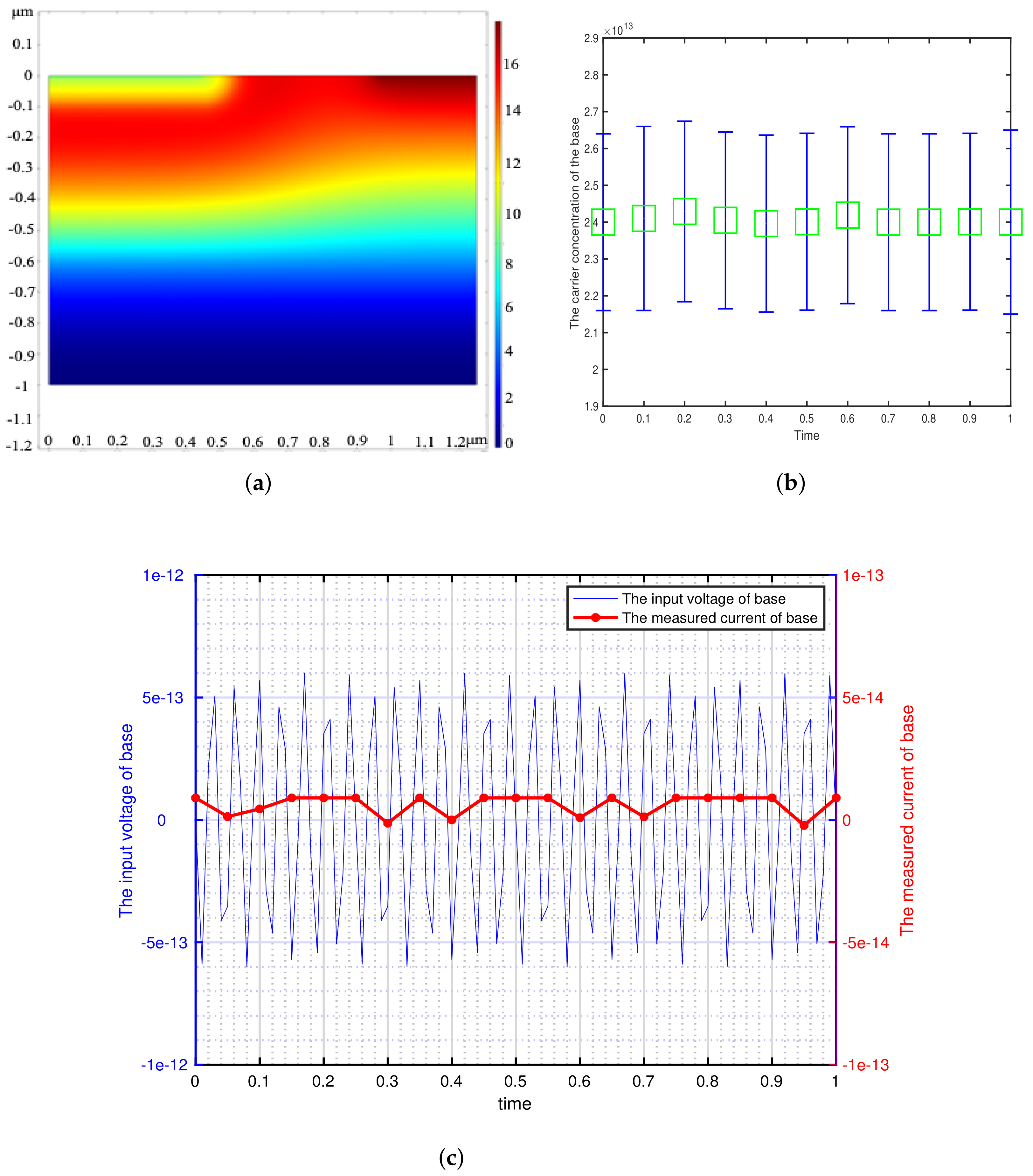
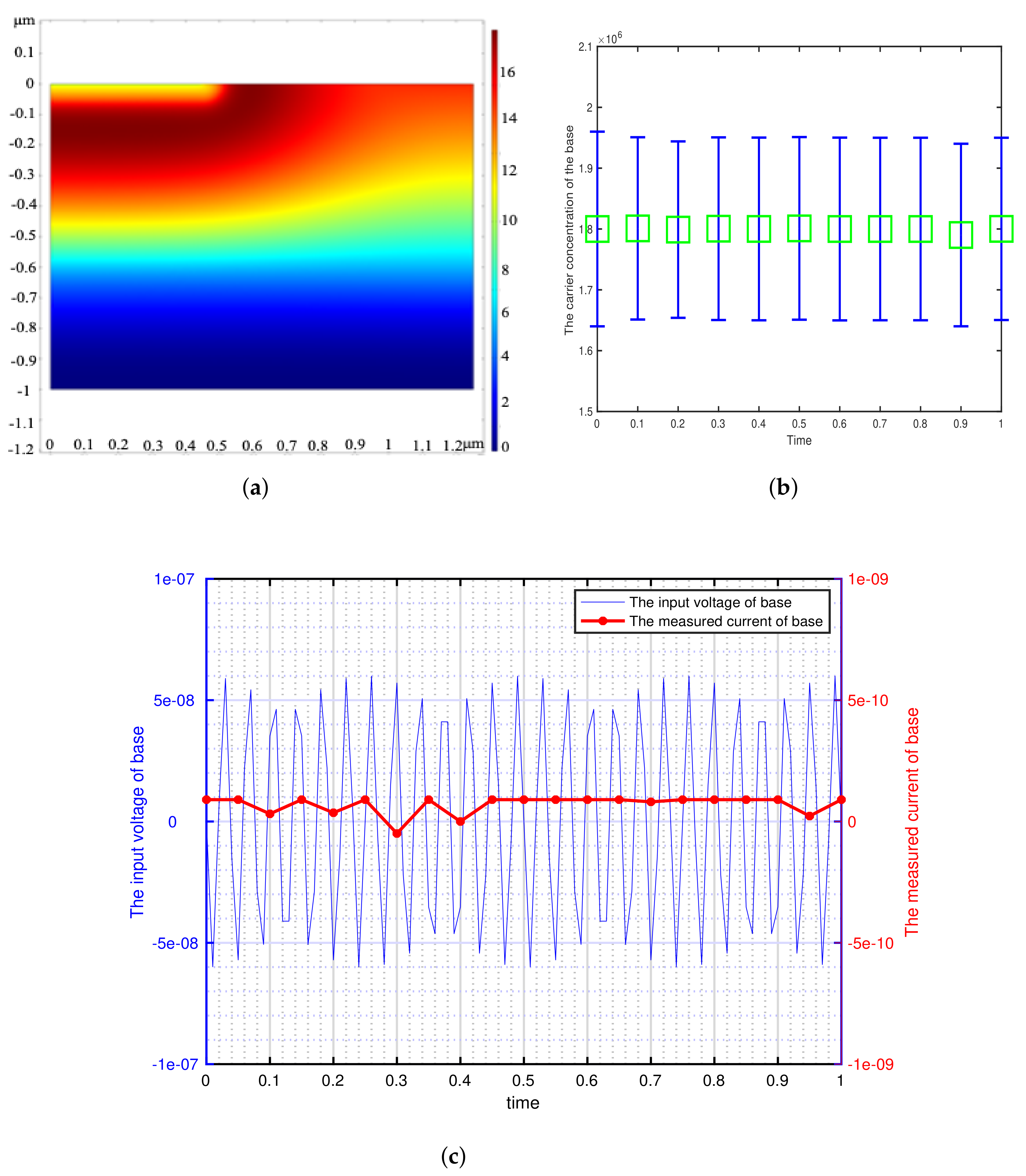
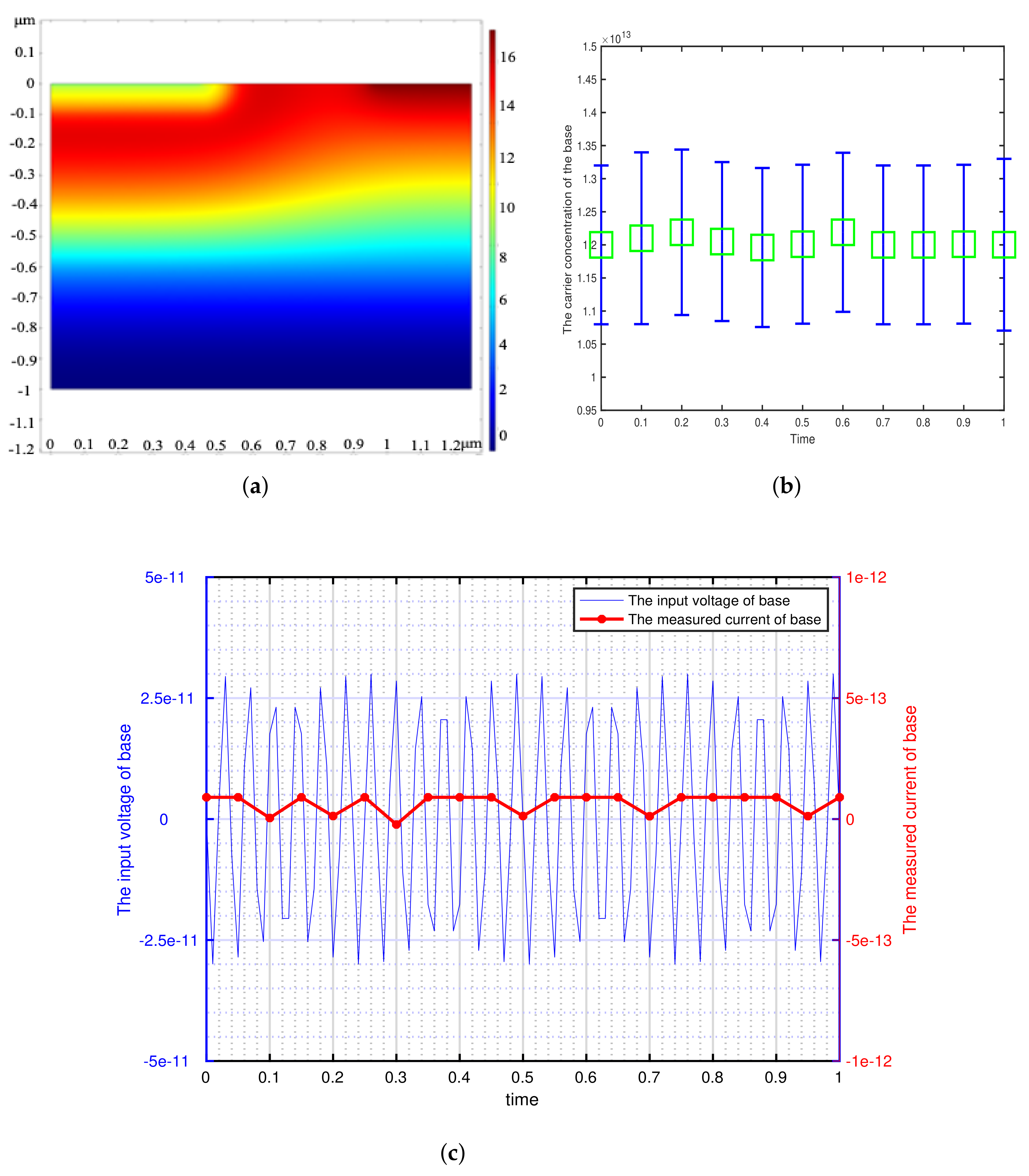
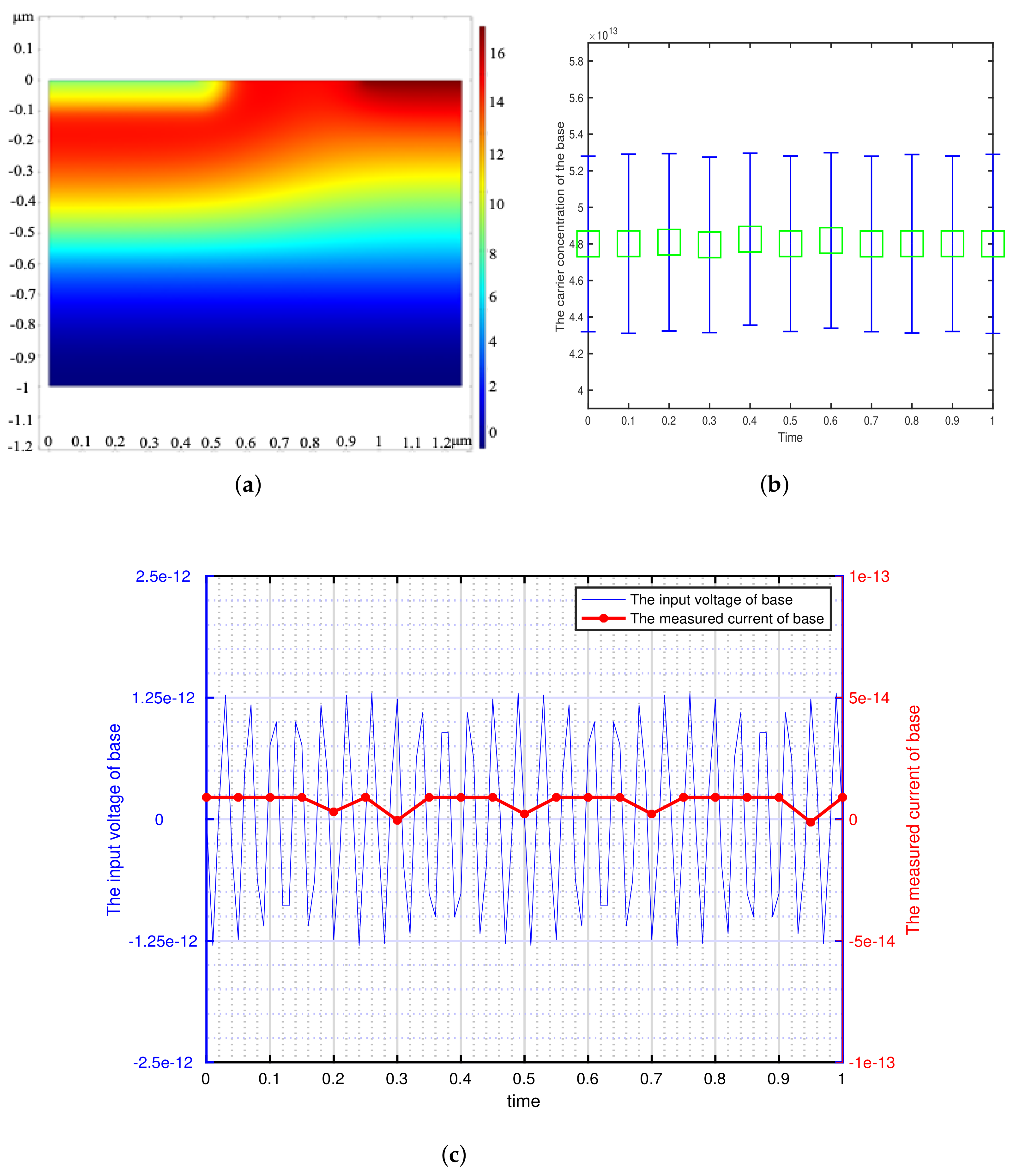
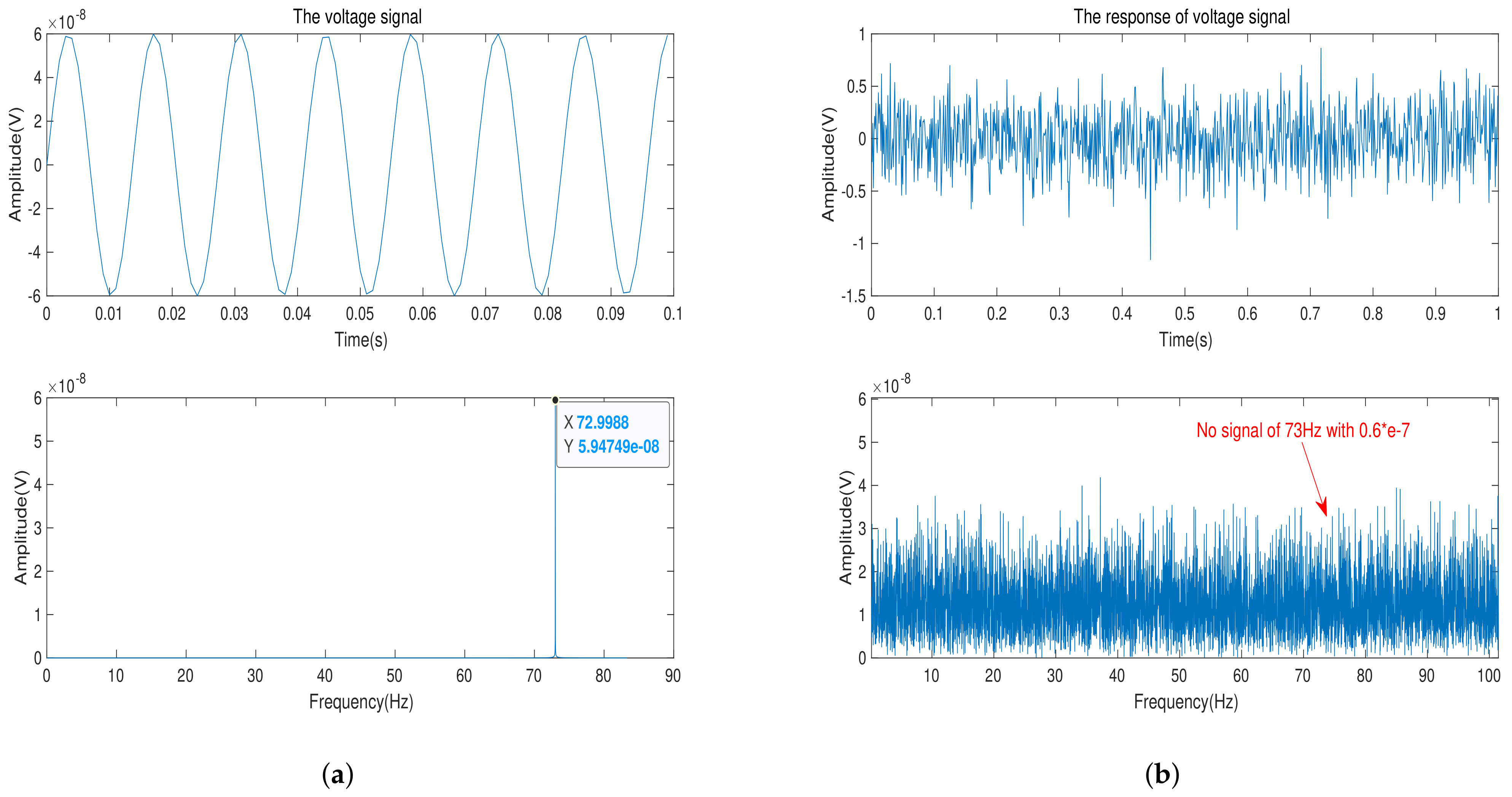
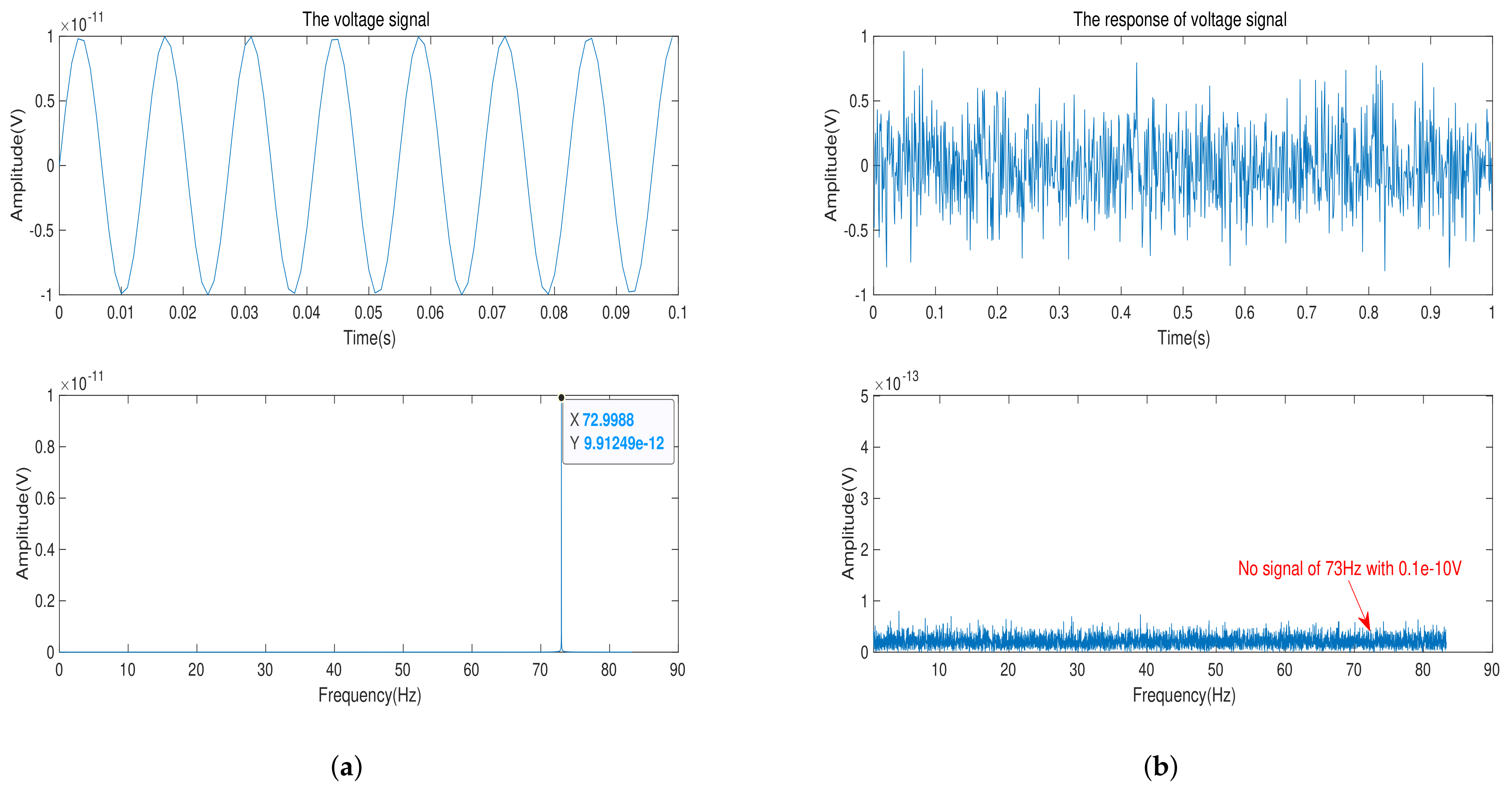
3. Simulation and Experiment
3.1. The Simulation of Model
3.2. The Experiment of Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Assaf, J. Bulk and surface damages in complementary bipolar junction transistors produced by high dose irradiation. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 016103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, A.; Skorobogatov, P. Modeling of the bipolar transistor under different pulse ionizing radiations. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 798, 012161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Prediction of thermal conductivity and phonon spectral of silicon material with pores for semiconductor device. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2021, 11, 413034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.; Shin, W.; Hong, S. Comparison of the characteristics of semiconductor gas sensors with different transducers fabricated on the same substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 3070, 129661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumcenco, D.; Giannini, E. Growth of van der Waals magnetic semiconductor materials. J. Cryst. Growth 2020, 548, 125799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, A. Review of semiconductor materials for monolithic microwave millimeter wave integrated circuits. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 37, 1567–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; He, Z.; Li, D. Measurement of Material Gain Transparency of Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers. Bandaoti Guangdian/Semicond. Optoelectron. 2018, 39, 780–784. [Google Scholar]
- Romstad, F.; Borri, P.; Langbein, W. Measurement of pulse amplitude and phase distortion in a semiconductor optical amplifier: From pulse compression to breakup. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2002, 12, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendler, A.; Dhler, M.; Ventura, C. A reliability-based approach to determine the minimum detectable damage for statistical damage detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 154, 107561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojkov, I.; Layden, D.; Cappellaro, P. Bias in error-corrected quantum sensing. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.05817. [Google Scholar]
- Babajanyan, A.; Minasyan, B.; Odabashyan, L. Noninvasive in Vivo Evaluation of Mouse-Blood Glycemia with a Microwave Spiral Sensor. J. Contemp. Phys. 2021, 56, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabashyan, L.; Margaryan, N.; Ohanyan, G. Detection of Iron Nanoparticles in Aqueous Solutions by Microwave Sensor. J. Contemp. Phys. 2020, 55, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, S.; Tyberkevych, V.; Jia, L. Low Power Microwave Signal Detection With a Spin-Torque Nano-Oscillator in the Active Self-Oscillating Regime. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gervasoni, G.; Carminati, M.; Ferrari, G. Switched ratiometric lock-in amplifier enabling sub-ppm measurements in a wide frequency range. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhi, S. Sensitive detection of cardiac troponin T based on superparamagnetic bead-labels using a flexible micro-fluxgate sensor. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 52327–52336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melkikh, A. Quantum system: Wave function, entanglement and the uncertainty principle. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 35, 2150222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campaioli, F. Tightening Time-Energy Uncertainty Relations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08384. [Google Scholar]
- Northington, M. Uncertainty Principles for Fourier Multipliers. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 2020, 26, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoui, Y.; Hitzer, E.; Fahlaoui, S. Heisenberg’s and Hardy’s Uncertainty Principles for Special Relativistic Space-Time Fourier Transformation. Adv. Appl. Clifford Algebr. 2020, 30, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Saha, A. Generalized uncertainty principle in resonant detectors of gravitational waves. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 195006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiao, C. An optimal measurement strategy to beat the quantum uncertainty in correlated system. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2020, 3, 2000039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Li, S.; Wu, S. Small-Signal Stability Analysis for Power System Frequency Regulation with Renewable Energy Participation. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5556062. [Google Scholar]
- Quandu, L.; Chunliu, D. Amplification Circuit Analysis base on Bipolar Junction Transistor. J. Chengdu Univ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 34, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, B.; Yang, Y. Simulation Study on Dynamic and Static Characteristics of Novel SiC Gate-Controlled Bipolar-Field-Effect Composite Transistor. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2020, 8, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroter, M.; Pawlak, A. Analysis of the Transistor Tetrode-Based Determination of the Base Resistance Components of Bipolar Transistors—A Review. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 65, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J. An Improved Small-Signal Equivalent Circuit Model Considering Channel Current Magnetic Effect. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2018, 28, 804–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cheng, Q.; Yan, S. Transistor Model Building for a Microwave Power Hetero junction Bipolar Transistor. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2015, 16, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goradia, C.; Vaughn, J.; Baraona, C. Theoretical results on the tandem junction solar cell based on its Ebers-Moll transistor model. In Proceedings of the 14th Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–10 January 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, C. A Modefied Ebers-Moll Transisitor Model for RF-Interference Analysis. IEEE Trans. 1979, 21, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Jitsumatsu, Y.; Nishi, T. An Upper Bound for the Number of Solutions of a Piecewise-linear Equation Related to Two-transistor Circuits. Fundam. Constants 2001, 6, 103–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.; Perry, P.A.; Brazil, T.J. A new large-signal AlGaAs/GaAs HBT model including self-heating effects, with corresponding parameter-extraction procedure. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1995, 43, 1433–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyotaka, Y.; Hitomi, K.; Ai, T. Finding All Solutions of Transistor Circuits Using Linear Programming. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 1998, 81, 1310–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, A.; Agrawal, A.; Gupta, M. Extraction of small-signal model parameters of silicon MOSFET for RF applications. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JasinSki, J.; Majkusiak, B. Small-signal admittance model as a characterization tool of the MOS tunnel diode. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 2013, 31, 01A111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, C.; Garcia, X.; Zurek, E. Statistical model of a signal of Raman spectroscopy: Detection. In Proceedings of the Symposium of Signals, Images and Artificial Vision—2013: STSIVA-2013, Bogota, Colombia, 11–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Maity, S.; Pandit, S. Study of G-S/D underlap for enhanced analog performance and RF/circuit analysis of UTB InAs-OI-Si MOSFET using NQS small signal model. Superlattices Microstruct. 2016, 101, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cai, T.; Lai, C. Model-based detector and extraction of weak signal frequencies from chaotic data. Chaos 2008, 18, 013104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundstrom, M. An Ebers-Moll model for the heterostructure bipolar transistor. Solid-State Electron. 1986, 29, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, J.; Zutic, I. The Ebers—Moll model for magnetic bipolar transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 133506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaeger, R.; Brodersen, A. Self consistent bipolar transistor models for computer simulation. Solid-State Electron. 1978, 21, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| The Name of Semiconductor Material | Si | Ge | GaAs | Impurity Ge-1 | Impurity Ge-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The carrier lifetime (s) | |||||
| The minimum perceived voltage (v) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Miao, Q.; Su, X.; Wu, B.; Song, K. The Minimum AC Signal Model of Bipolar Transistor in Amplification Region for Weak Signal Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 7102. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217102
Huang L, Miao Q, Su X, Wu B, Song K. The Minimum AC Signal Model of Bipolar Transistor in Amplification Region for Weak Signal Detection. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7102. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217102
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Lidong, Qiuyan Miao, Xiruo Su, Bin Wu, and Kaichen Song. 2021. "The Minimum AC Signal Model of Bipolar Transistor in Amplification Region for Weak Signal Detection" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7102. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217102
APA StyleHuang, L., Miao, Q., Su, X., Wu, B., & Song, K. (2021). The Minimum AC Signal Model of Bipolar Transistor in Amplification Region for Weak Signal Detection. Sensors, 21(21), 7102. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217102






