CNN-Based Suppression of False Contour and Color Distortion in Bit-Depth Enhancement †
Abstract
1. Introduction
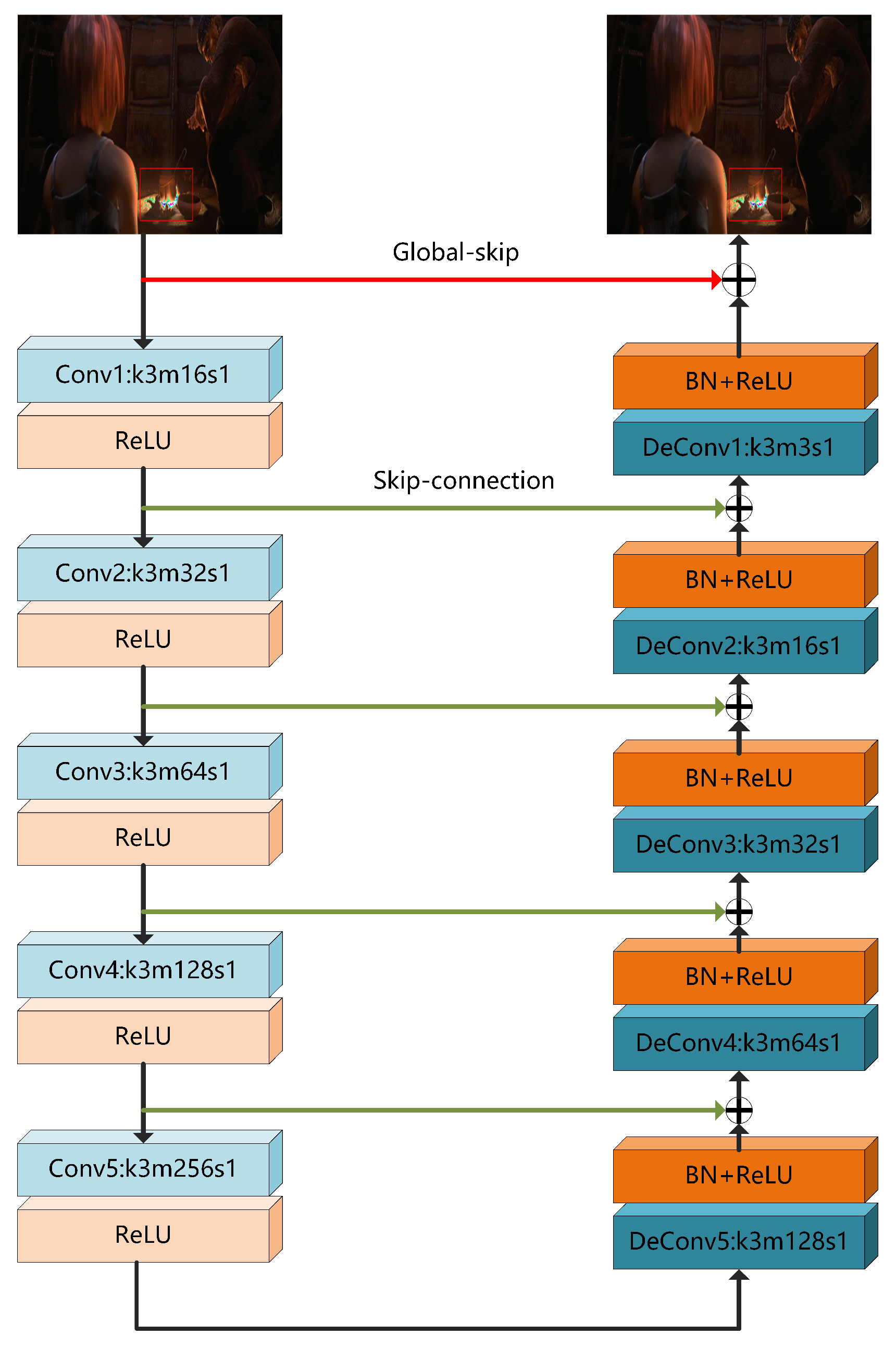
- An auto-encoder of convolution-combined-with-deconvolution structure is proposed for BDE, and it is superior to pure convolution and pure deconvolution. With the help of the global skip connection, the color distortion is well suppressed.
- The mechanism of color distortion is analyzed in detail. It has been experimentally proved that the value of the restored image can be confined into a reasonable range by applying a global skip connection to suppress the color distortion. Moreover, it has been also proved by experimental results that global skip is effective under different network structures.
- A deep BDE algorithm BE-AUTO is proposed. It can effectively suppress false contours and color distortion under the constraint of , and obtain state-of-the-art experimental results both in objective and subjective performance.
2. Related Work
- We make an in-depth analysis of the causes of color distortion, and based on numerical interval estimation and estimation error analysis, theoretical support is provided for the final solution;
- Experiments are made to verify that the global skip connection has similar color distortion suppression effect for different network structures;
- The test set is extended. We add 3 test sets to make a sufficient comparison of different scale BDE in natural and synthetic images between our algorithm and the related;
- The latest related algorithms and 4 visual comparison figures are added to fully reflect the merits of our algorithm.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Problem Model
3.1.1. Quantization and Bit-Depth Variation
3.1.2. Key Problems to Be Solved
3.1.3. Mathematical Modeling
3.2. Loss Function
3.3. BDE Model
4. Experiments and Discussion
4.1. Experiment Settings
4.1.1. Data Sets
4.1.2. Algorithms to be Compared
4.1.3. Training Details
4.2. Results and Discussion
4.2.1. Objective Performance Evaluation
- (1)
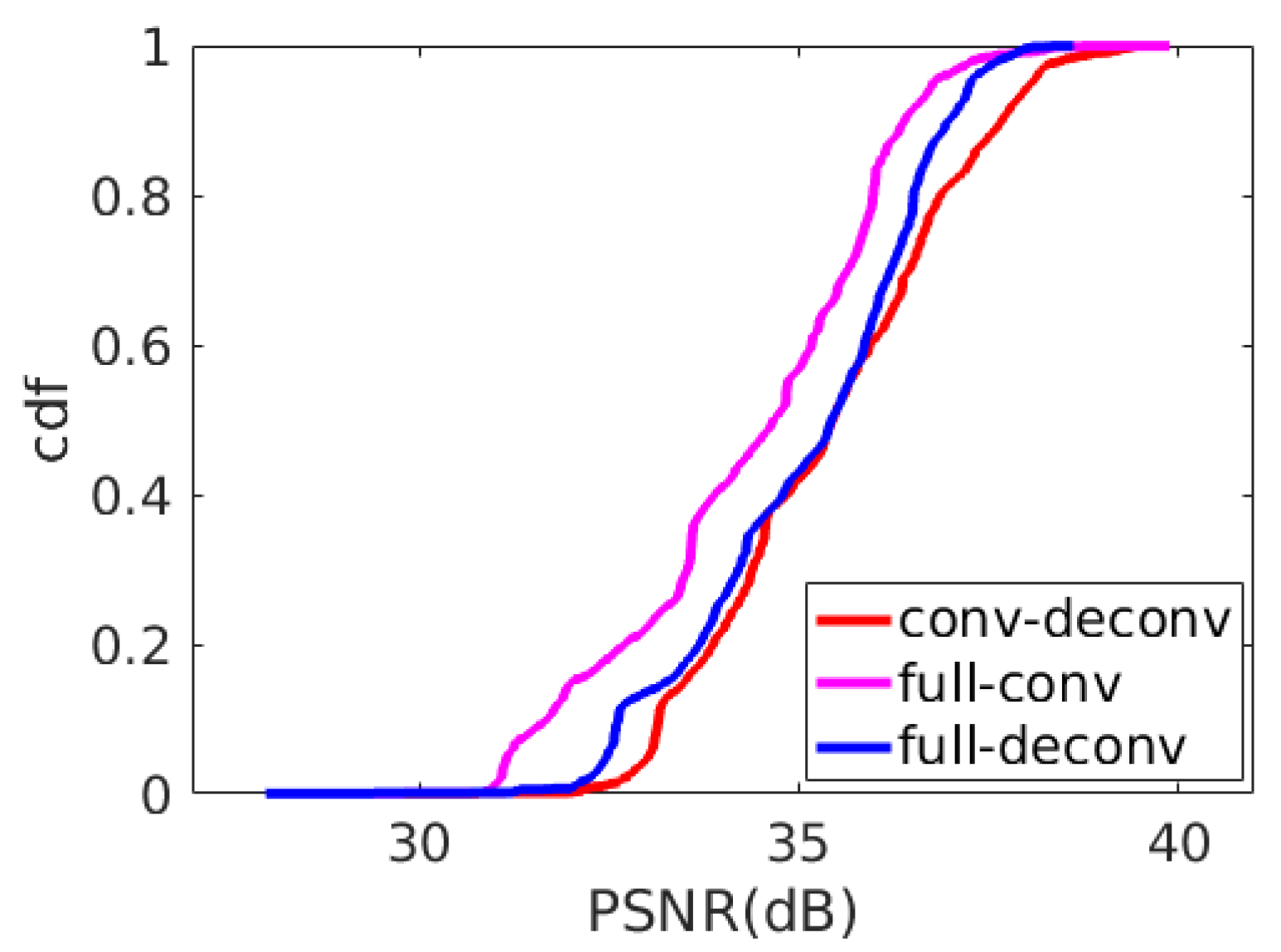
- The use of convolution for encoding and deconvolution for decoding can better extract features and perform better reconstruction.
- (2)
- The addition of the global skip connection allows the network output to remain well within the desired range, thereby avoiding color distortion and not interfering with the false contour suppression.
- (3)
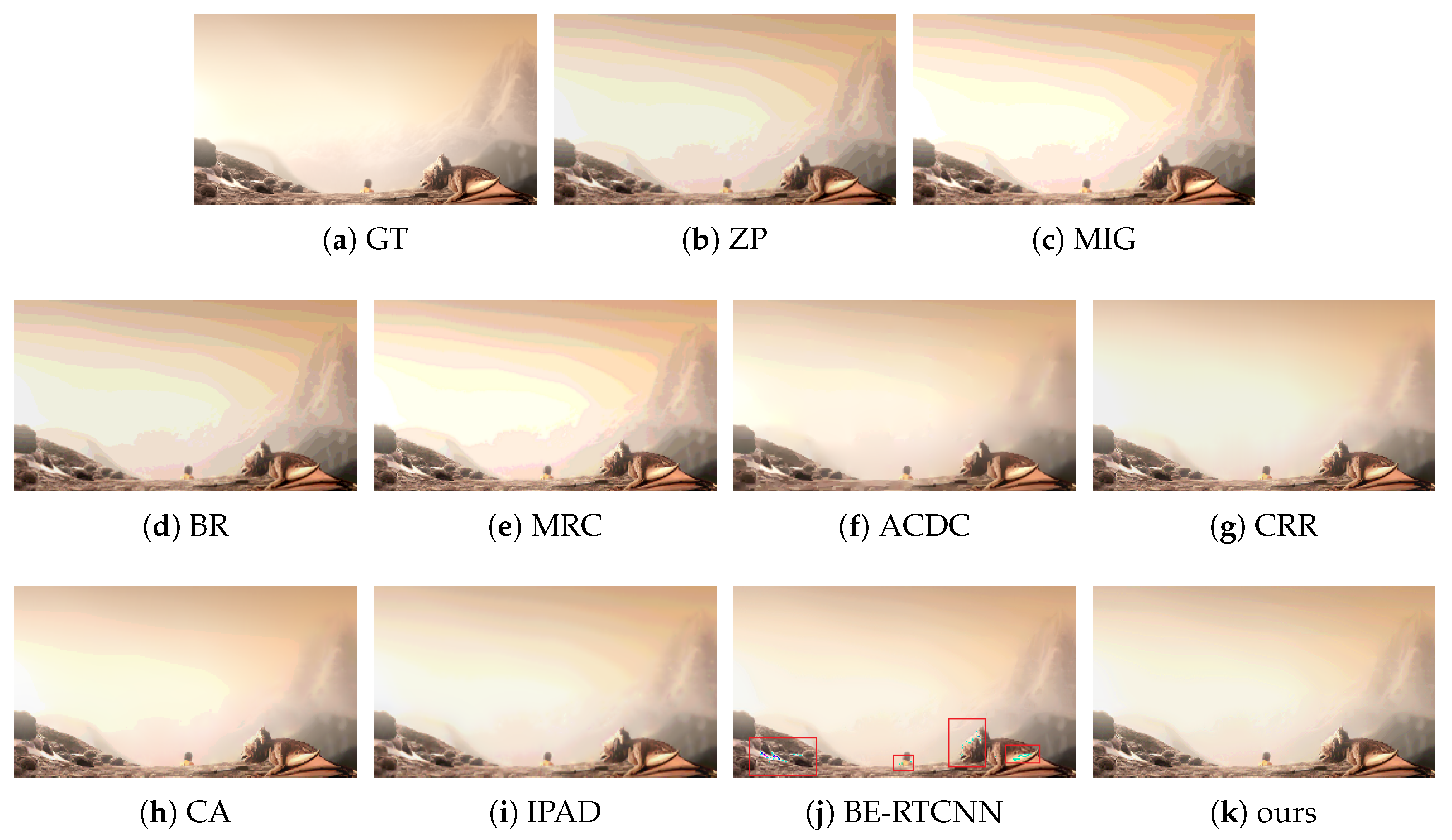
- has an incomparable inhibitory effect on false contours relative to , which is fully discussed in BE-RTCNN [15].
4.2.2. Subjective Performance Evaluation
4.2.3. Run Time Comparison
4.3. Ablation Analysis
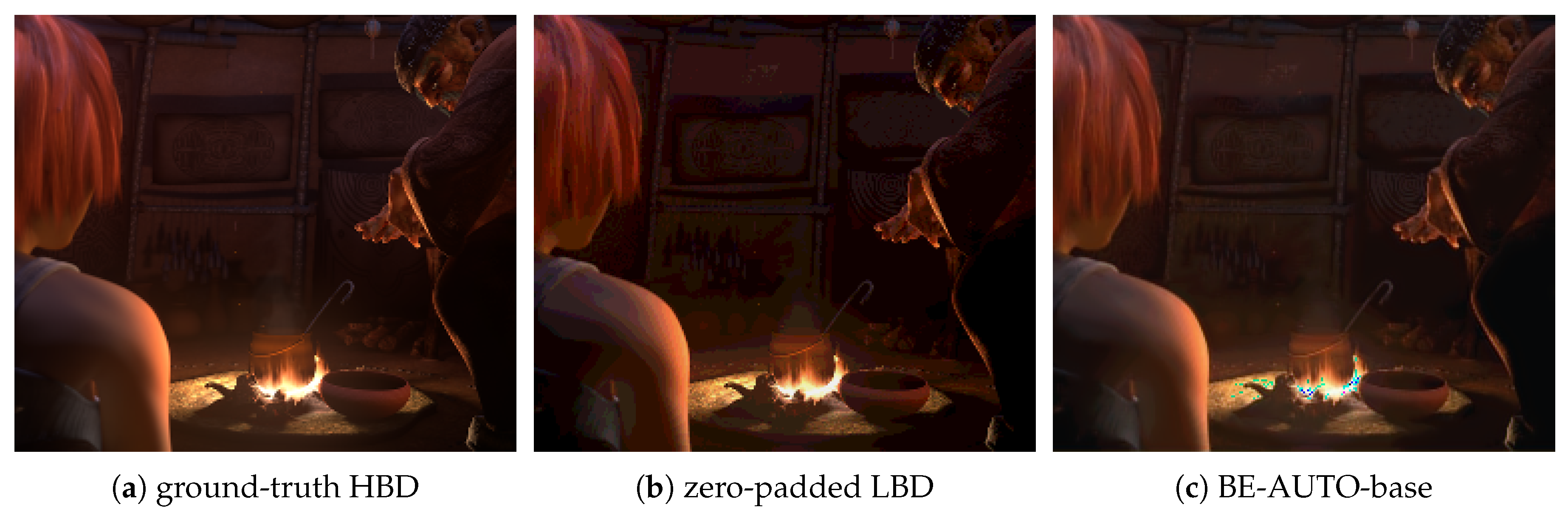
4.3.1. Analysis of Color Distortion
4.3.2. Color Distortion Reasons
4.3.3. Non-Triviality of Color Distortion Problem
4.3.4. Effect of Global Skip Connections
4.3.5. Convolution vs. Deconvolution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehmood, I.; Ullah, A.; Muhammad, K.; Deng, D.J.; Meng, W.; Al-Turjman, F.; Sajjad, M.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Efficient Image Recognition and Retrieval on IoT-Assisted Energy-Constrained Platforms From Big Data Repositories. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 9246–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Xu, J.; Qiao, H.; Zhou, M.; Liang, B. Visual IoT: Enabling internet of things visualization in smart cities. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Internet of Business. Opinion: The Visual Internet of Things–Why IoT Needs Visual Data. 2013. Available online: https://internetofbusiness.com/opinion-the-visual-internet-of-things-why-iot-needs-visual-data/ (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D. Hybrid Cross Deep Network for Domain Adaptation and Energy Saving in Visual Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 6026–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Xie, Y. Low-cost and confidentiality-preserving data acquisition for internet of multimedia things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 5, 3442–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkiadakis, A.; Charalampidis, P.; Tragos, E. Adaptive compressive sensing for energy efficient smart objects in IoT applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 4th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Vehicular Technology, Information Theory and Aerospace & Electronic Systems (VITAE), Aalborg, Denmark, 11–14 May 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Da Xu, L.; Wang, X. Compressed sensing signal and data acquisition in wireless sensor networks and internet of things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2012, 9, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.M.; Allstot, E.G.; Gangopadhyay, D.; Allstot, D.J. Compressed sensing system considerations for ECG and EMG wireless biosensors. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Yang, B.; Li, L.; Yang, Y. Secure and Traceable Image Transmission Scheme Based on Semitensor Product Compressed Sensing in Telemedicine System. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 2432–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Ulichney, R.; Cheung, S. Pixel Bit-Depth Increase by Bit Replication. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 1998, 3300, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, G.; Jakhetiya, V.; Jaiswal, S.; Au, O.; Tiwari, A.; Dei, W. Bit-depth expansion using Minimum Risk Based Classification. In Proceedings of the 2012 Visual Communications and Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 27–30 November 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong Cheng, C.; Au, O.; Liu, C.H.; Yue Yip, K. Bit-depth Expansion by Contour Region Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 24–27 May 2009; pp. 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhai, G.; Liu, A.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, C.W. IPAD: Intensity Potential for Adaptive De-Quantization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4860–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Bit-Depth Enhancement via Convolutional Neural Network. In Digital TV and Wireless Multimedia Communication; Zhai, G., Zhou, J., Yang, X., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 255–264. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, J.; Zhai, G.; Jing, P. Photo-realistic image bit-depth enhancement via residual transposed convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 2019, 347, 200–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, R.; Jia, W.; Zuo, W.; Liu, X.; Gao, W. Deep Reconstruction of Least Significant Bits for Bit-Depth Expansion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2847–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4681–4690. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, Y.; Kanamori, Y.; Mitani, J. Deep Reverse Tone Mapping. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Jing, P.; Yu, J.; Su, Y. Improving Bit-depth Expansion via Context-aware MMSE Optimization (CAMO). IEEE Access 2018, 6, 46396–46406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Lee, S.; Choe, W. Bit Depth Expansion via Estimation of Bit Value Expectation. Electron. Imaging 2016, 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, C.; He, T.; Wang, J.; Hoai, M. Gif2video: Color dequantization and temporal interpolation of gif images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–21 June 2019; pp. 1419–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.S.; Yuan, X.; Choi, G.S. LISR: Image Super-resolution under Hardware Constraints. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.10136. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, A.; Nishiyama, J. Bit-length expansion by inverse quantization process. In Proceedings of the 2012 20th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Bucharest, Romania, 27–31 August 2012; pp. 1543–1547. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, P.; Su, Y.; Jing, P.; Yang, X. Spatiotemporal Symmetric Convolutional Neural Network for Video Bit-Depth Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 2397–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Au, O.; Tang, K.; Guo, Y. Image de-quantization via spatially varying sparsity prior. In Proceedings of the 2012 19th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 September–3 October 2012; pp. 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, S.; Watanabe, H.; Ikai, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Chujoh, T.; Ito, N. Joint super-resolution and bit depth extension by DNN. In International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT); International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 11049, p. 1104925. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, P.; Cheung, G.; Florencio, D.; Zhang, C.; Au, O. Image bit-depth enhancement via maximum-a-posteriori estimation of graph AC component. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing ICIP, Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; Volume 25, pp. 4052–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Cheung, G.; Florencio, D.; Zhang, C.; Au, O.C. Image Bit-Depth Enhancement via Maximum A Posteriori Estimation of AC Signal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 2896–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Au, O.; Tang, K.; Guo, Y.; Fang, L. From 2D Extrapolation to 1D Interpolation: Content Adaptive Image Bit-Depth Expansion. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 9–13 July 2012; pp. 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 391–407. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kwon Lee, J.; Mu Lee, K. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1646–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Mu Lee, K. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Rcognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Cnference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Su, Y.; Jing, P.; Yang, X. BE-CALF: Bit-depth enhancement by concatenating all level features of DNN. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 4926–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Cai, L.; Fu, Z.; Li, X. CNN-based bit-depth enhancement by the suppression of false contour and color distortion. In Proceedings of the 2019 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Lanzhou, China, 18–21 November 2019; pp. 1145–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Deep image prior. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 9446–9454. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Gallo, O.; Frosio, I.; Kautz, J. Loss Functions for Neural Networks for Image Processing. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.08861. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Krishnan, D.; Taylor, G.W.; Fergus, R. Deconvolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2528–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. In Proceedings of the 32Nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; Volume 37, pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Glorot, X.; Bordes, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks. In Proceedings of the fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistic, Ft. Lauderdale, FL, USA, 11–13 April 2011; pp. 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Kodak. Kodak Lossless True Color Image Suite. 2013. Available online: http://r0k.us/graphics/kodak/ (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- X.Foundation. Xiph.Org. 2016. Available online: https://www.xiph.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Bychkovsky, V.; Paris, S.; Chan, E.; Durand, F. Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011, Providence, RI, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Agustsson, E.; Timofte, R. NTIRE 2017 Challenge on Single Image Super-Resolution: Dataset and Study. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 28 July 2017; pp. 1122–1131. [Google Scholar]



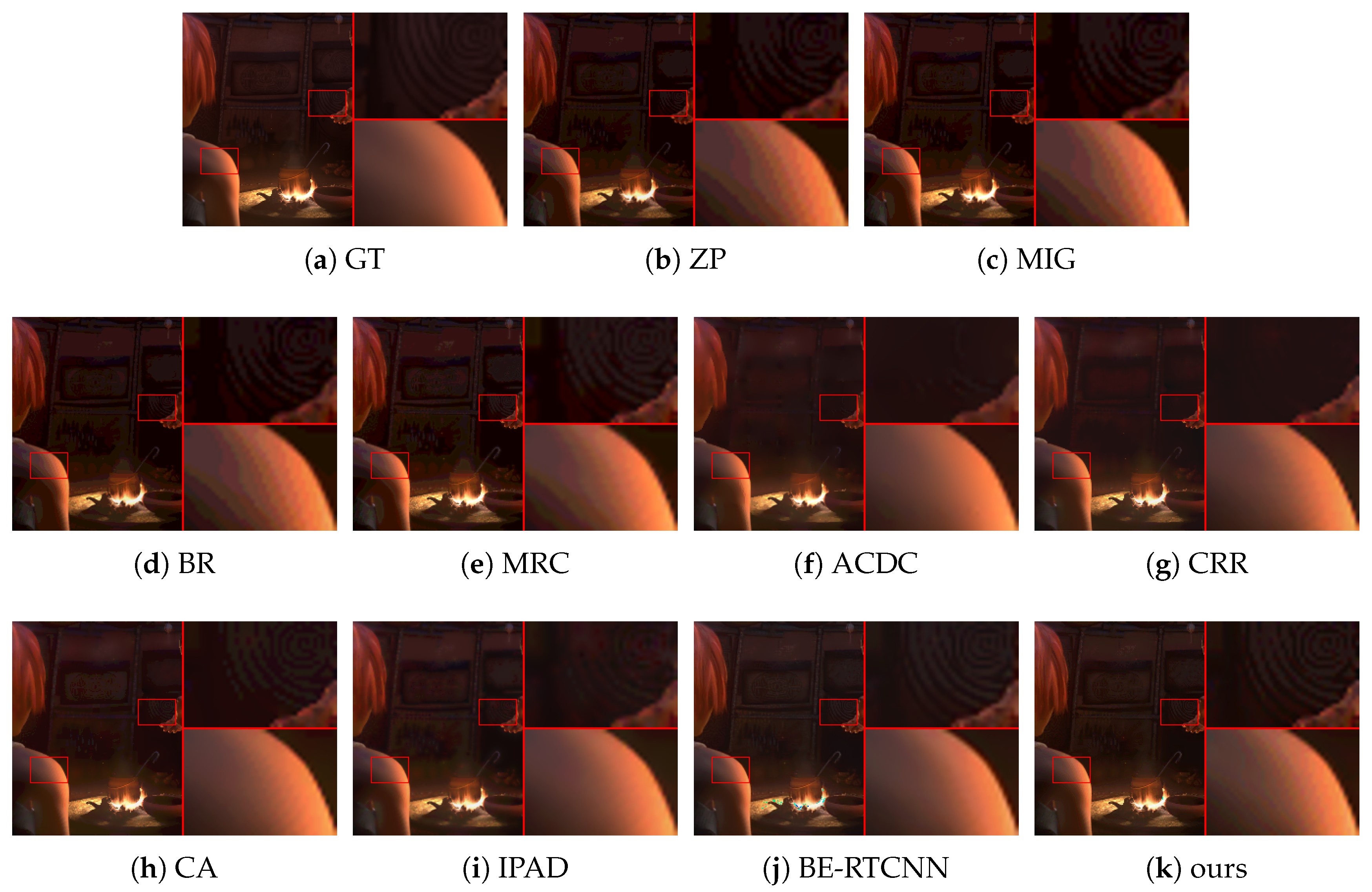

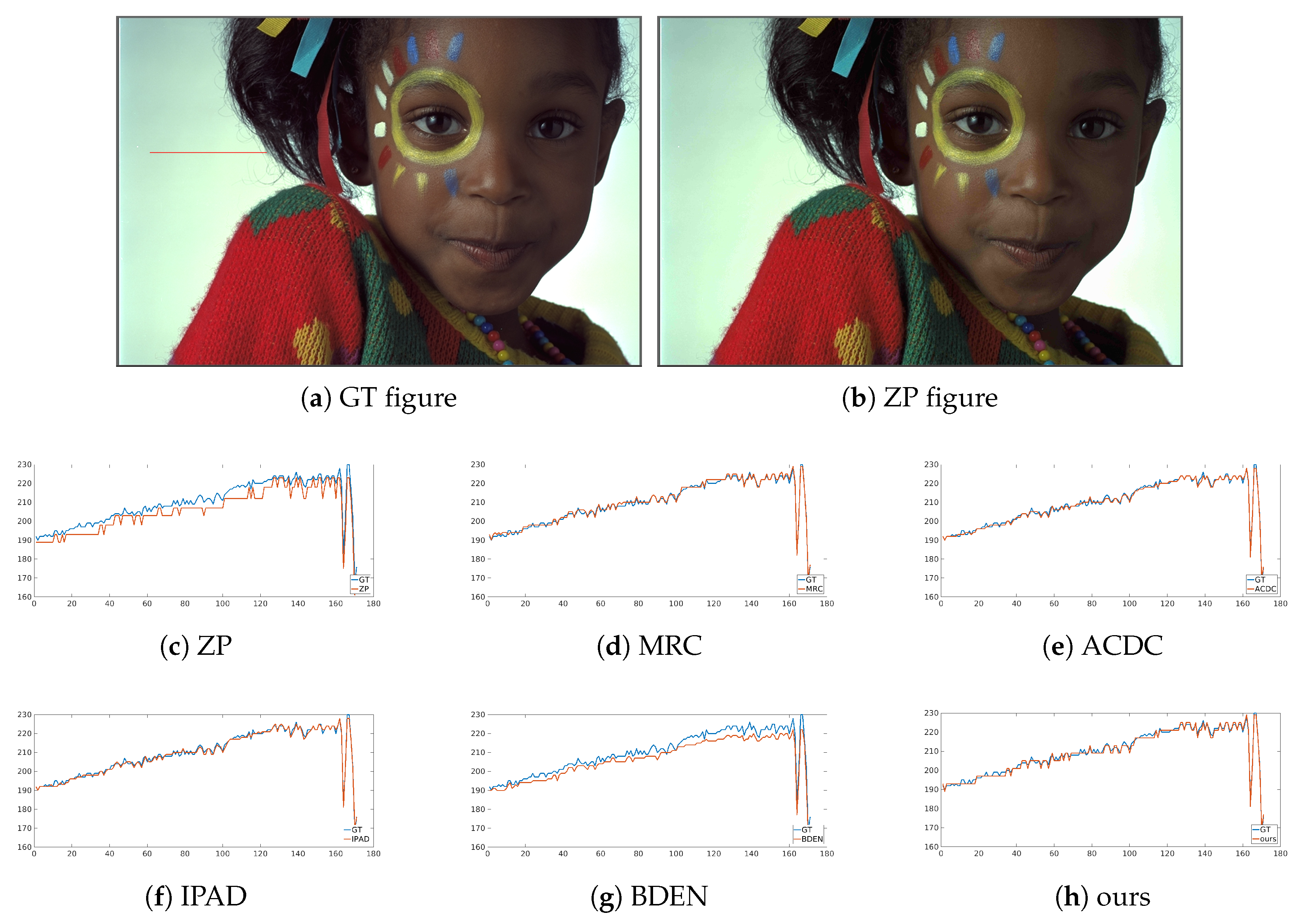

| Dataset | ZP | MIG | BR [10] | MRC [11] | ACDC [28] | CRR [12] | CA [29] | IPAD [13] | BE-RTCNN [15] | BDEN [16] | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sintel-8 | 29.7141 | 31.6352 | 32.1936 | 33.0923 | 33.3474 | 31.3352 | 34.9920 | 34.4867 | 35.2994 | - | 36.2270 |
| fiveK-40 | 28.8342 | 31.3927 | 31.9534 | 33.6832 | 34.8084 | 33.8474 | 35.2481 | 35.5903 | 34.3688 | - | 36.0413 |
| BDE-set | 42.7506 | 45.4445 | 44.3908 | 47.0334 | 47.0099 | 45.0150 | 45.9547 | 45.5052 | - | - | 47.1877 |
| Kodak | 42.5077 | 45.5028 | 45.1540 | 47.1177 | 47.1001 | 45.1564 | 46.0462 | 45.5074 | - | 46.4550 | 47.2576 |
| Algorithm | ZP | MIG | BR [10] | MRC [11] | ACDC [28] | CRR [12] | CA [29] | IPAD [13] | BE-RTCNN [15] | BDEN [16] | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run time | 0.0005 | 0.0012 | 0.0041 | 90.4498 | 332.0405 | 15.9587 | 24.476 | 7.2593 | 1.9025 | 2.6334 | 1.1031 |
| img_idx | img1 | img2 | img3 | img4 | img5 | img6 | img7 | img8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| range | [−1.16,1.21] | [−0.94,0.76] | [−1.14,1.18] | [−1.18,1.01] | [−1.21,1.05] | [−1.17,1.04] | [−1.18,0.97] | [−1.29,1.18] |
| BDEN | BE-RTCNN | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|
| without global skip | 415.62 | 495.34 | 761.04 |
| with global skip | 53.13 | 26.36 | 20.27 |
| average PSNR | 34.3741 | 35.1176 | 35.4293 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, C.; Cai, L.; Huang, X.; Fu, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, X. CNN-Based Suppression of False Contour and Color Distortion in Bit-Depth Enhancement. Sensors 2021, 21, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020416
Peng C, Cai L, Huang X, Fu Z, Xu J, Li X. CNN-Based Suppression of False Contour and Color Distortion in Bit-Depth Enhancement. Sensors. 2021; 21(2):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020416
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Changmeng, Luting Cai, Xiaoyang Huang, Zhizhong Fu, Jin Xu, and Xiaofeng Li. 2021. "CNN-Based Suppression of False Contour and Color Distortion in Bit-Depth Enhancement" Sensors 21, no. 2: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020416
APA StylePeng, C., Cai, L., Huang, X., Fu, Z., Xu, J., & Li, X. (2021). CNN-Based Suppression of False Contour and Color Distortion in Bit-Depth Enhancement. Sensors, 21(2), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020416





