Compression Garments Reduce Soft Tissue Vibrations and Muscle Activations during Drop Jumps: An Accelerometry Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
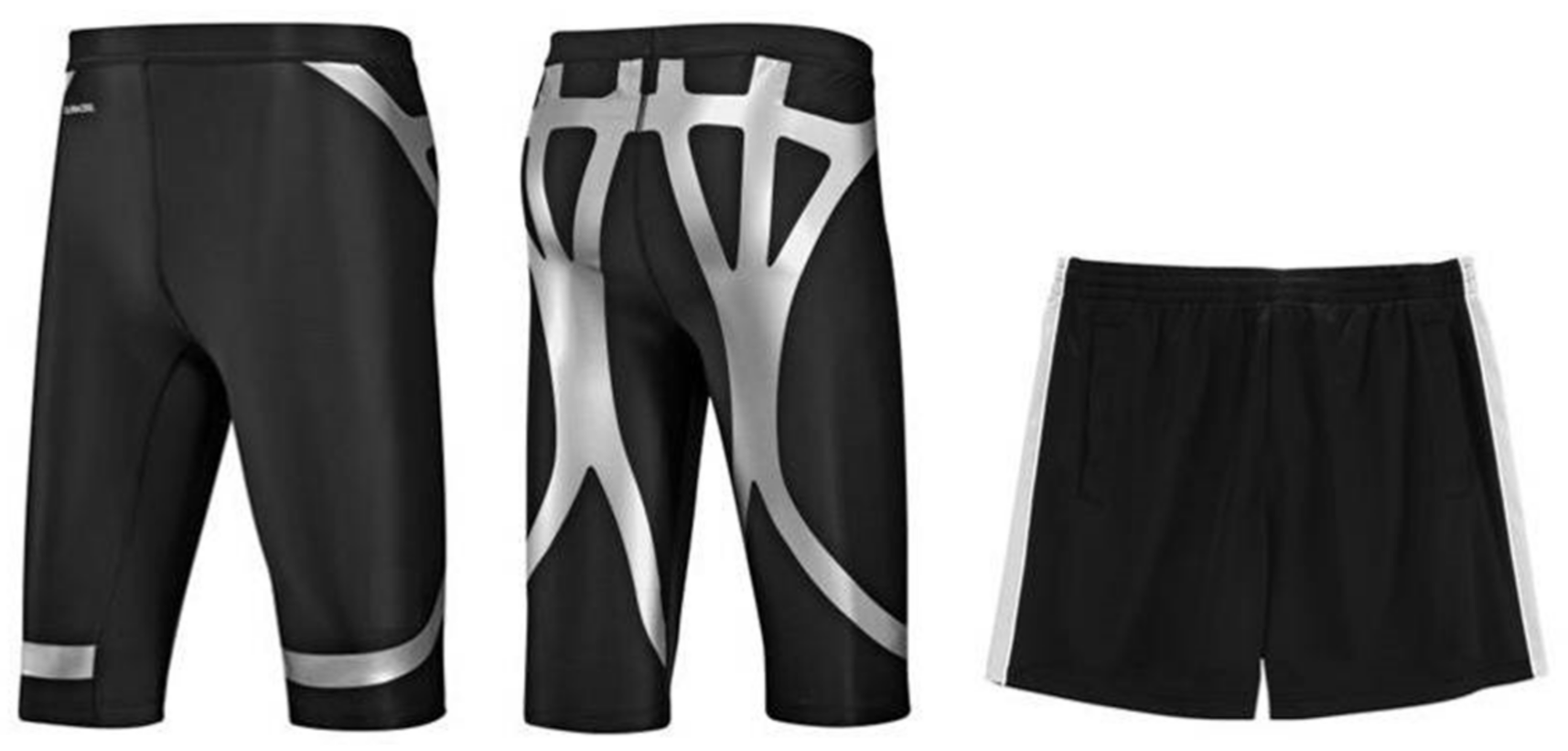
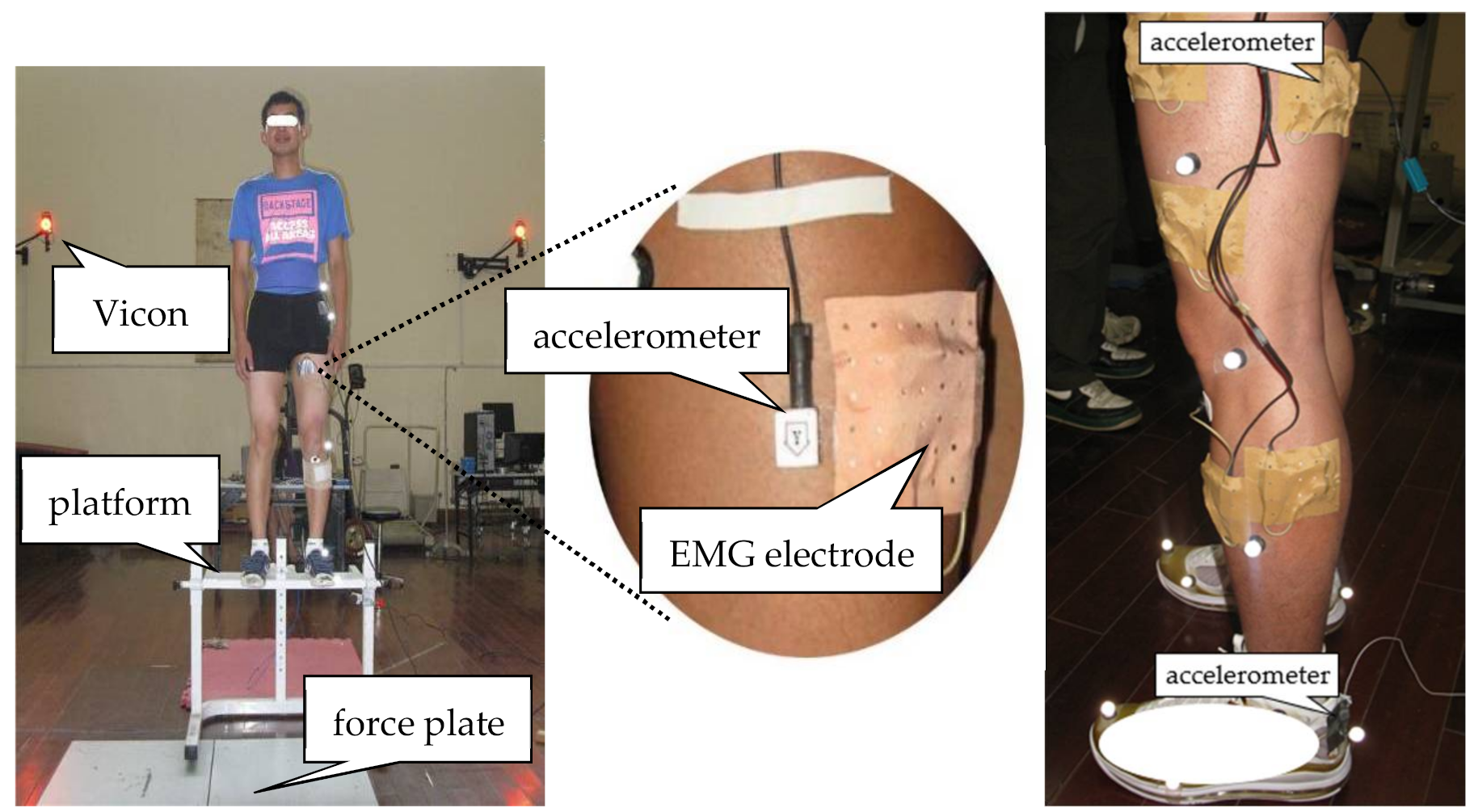
2. Methods
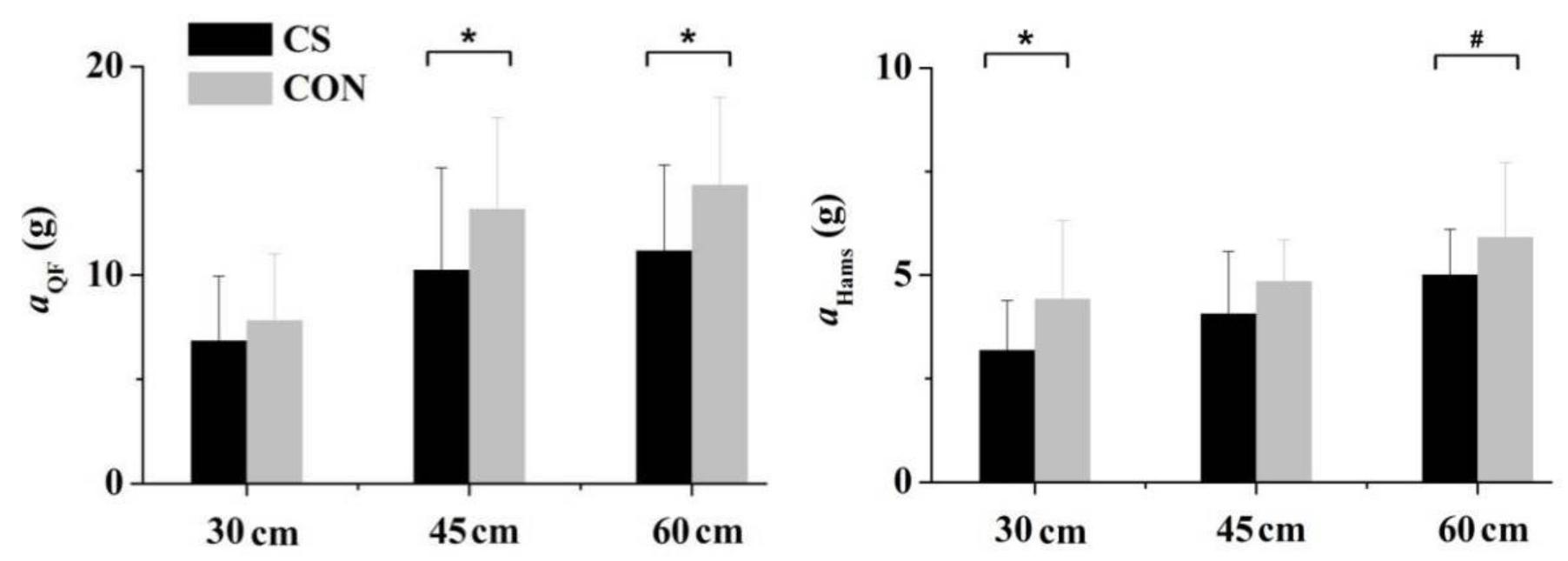
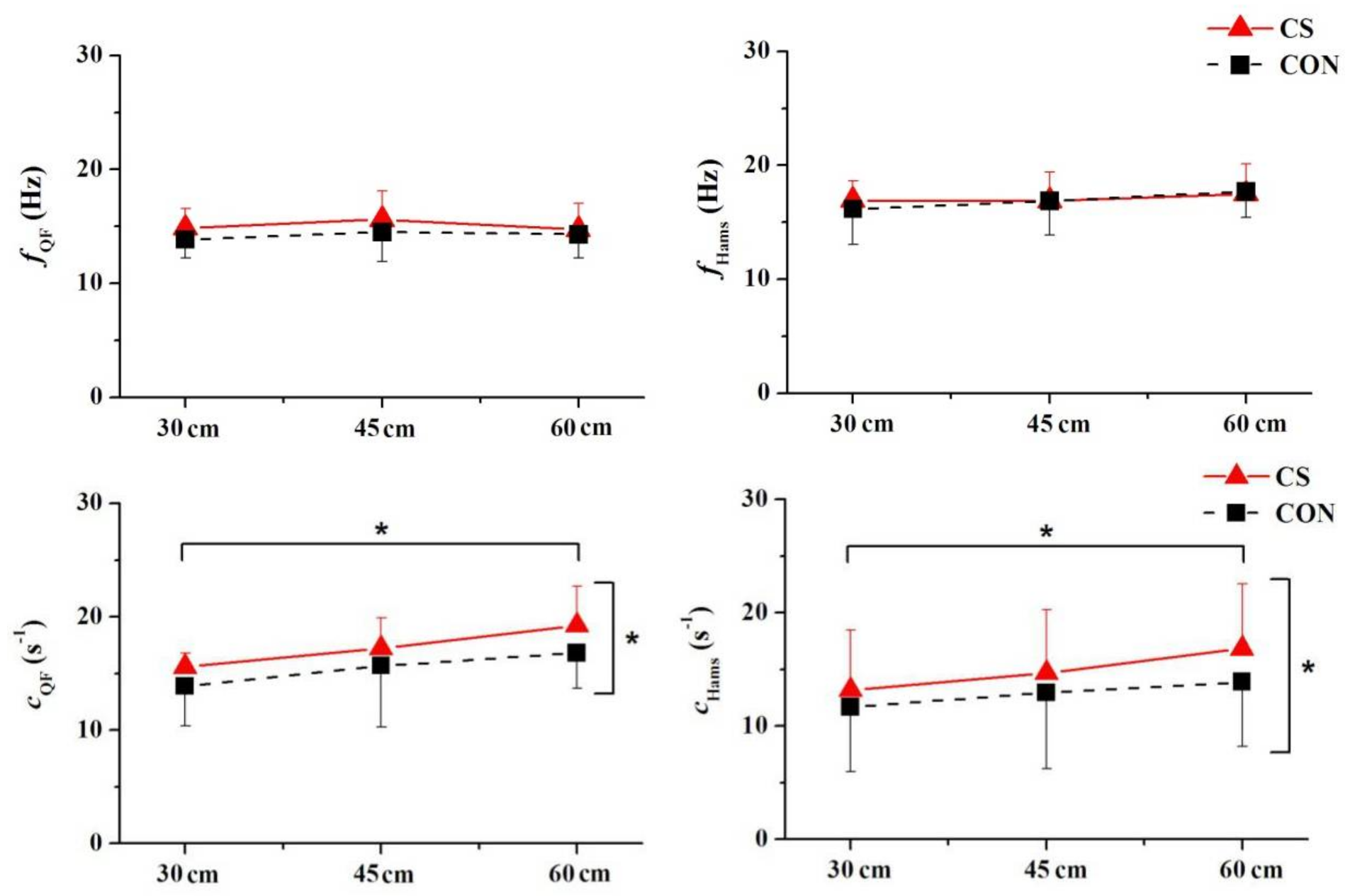
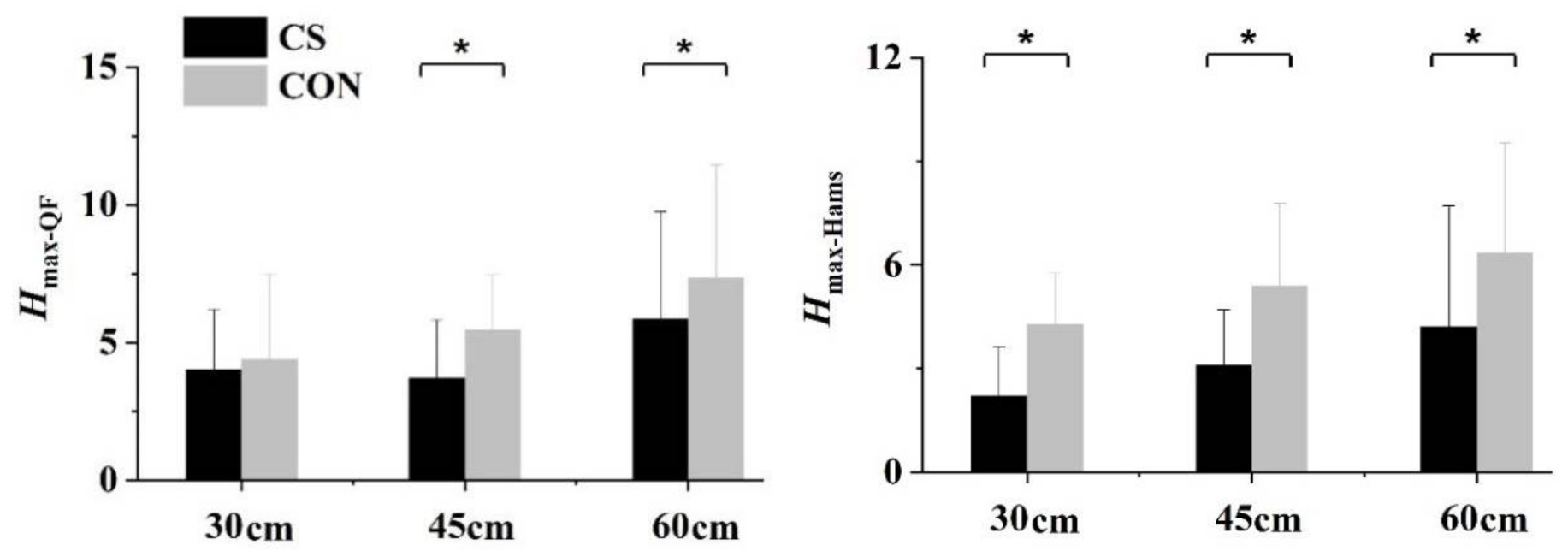
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schinkel-Ivy, A.; Burkhart, T.A.; Andrews, D.M. Leg tissue mass composition affects tibial acceleration response following impact. J. Appl. Biomech. 2012, 28, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martinez, A.; Lam, C.K.; von Tscharner, V.; Nigg, B.M. Soft tissue vibration dynamics after an unexpected impact. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e13990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakeling, J.M.; Nigg, B.M.; Rozitis, A.I. Muscle activity damps the soft tissue resonance that occurs in response to pulsed and continuous vibrations. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 93, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, K.A.; Nigg, B.M. Quantification of the input signal for soft tissue vibration during running. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 1877–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigg, B.M.; Wakeling, J.M. Impact forces and muscle tuning: A new paradigm. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2001, 29, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Effects of footwear on impact forces and soft tissue vibrations during drop jumps and unanticipated drop landings. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broatch, J.R.; Brophy-Williams, N.; Phillips, E.J.; O’Bryan, S.J.; Halson, S.L.; Barnes, S.; Bishop, D.J. Compression Garments Reduce Muscle Movement and Activation during Submaximal Running. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 52, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coza, A.; Nigg, B.M.; Dunn, J.F. Effects of vibrations on gastrocnemius medialis tissue oxygenation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittweger, J.; Schiessl, H.; Felsenberg, D. Oxygen uptake during whole-body vibration exercise: Comparison with squatting as a slow voluntary movement. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 86, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigg, B.M.; Stefanyshyn, D.; Cole, G.; Stergiou, P.; Miller, J. The effect of material characteristics of shoe soles on muscle activation and energy aspects during running. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, M.T.; Challis, J.H. The influence of soft tissue movement on ground reaction forces, joint torques and joint reaction forces in drop landings. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zange, J.; Haller, T.; Muller, K.; Liphardt, A.M.; Mester, J. Energy metabolism in human calf muscle performing isometric plantar flexion superimposed by 20-Hz vibration. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 105, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, B.K.; Kwon, Y.H.; Newton, R.U.; Shim, J.; Popper, E.M.; Rogers, R.A.; Bolt, L.R.; Robertson, M.; Kraemer, W.J. Evaluation of a lower-body compression garment. J. Sports Sci. 2003, 21, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Bush, J.A.; Triplett-McBride, N.T.; Koziris, L.P.; Mangino, L.C.; Fry, A.C.; McBride, J.M.; Johnston, J.; Volek, J.S.; Young, C.A. Compression Garments: Influence on Muscle Fatigue. J. Strength Cond. Res. 1998, 12, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.; Scurr, J.; Wood, L. A protocol for monitoring soft tissue motion under compression garments during drop landings. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1821–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. Shoe cushioning reduces impact and muscle activation during landings from unexpected, but not self-initiated, drops. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigward, S.M.; Ota, S.; Powers, C.M. Predictors of frontal plane knee excursion during a drop land in young female soccer players. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2008, 38, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.K., 3rd; Kernozek, T.W.; Miller, E.J.; Torry, M.R.; Reuteman, P. Influences of hip external rotation strength on knee mechanics during single-leg drop landings in females. Clin. Biomech. 2008, 23, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, K.A.; Nigg, B.M. Soft tissue vibrations within one soft tissue compartment. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horita, T.; Komi, P.V.; Nicol, C.; Kyrolainen, H. Interaction between pre-landing activities and stiffness regulation of the knee joint musculoskeletal system in the drop jump: Implications to performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 88, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komi, P.V.; Bosco, C. Utilization of stored elastic energy in leg extensor muscles by men and women. Med. Sci. Sports 1978, 10, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, W.; Liu, Y. Changes in Lower-Limb Biomechanics, Soft Tissue Vibrations, and Muscle Activation During Unanticipated Bipedal Landings. J. Hum. Kinet. 2019, 67, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, K.A.; Nigg, B.M. Muscle tuning during running: Implications of an un-tuned landing. J. Biomech. Eng. 2006, 128, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.M.; Piersol, A.G. Harris’ Shock and Vibration Handbook, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Hao, W.; Mei, Q.; Xiao, X.; Li, X.; Sun, W. Strategies of elite Chinese gymnasts in coping with landing impact from backward somersault. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, M.; Li, L. Approach run increases preactivation and eccentric phases muscle activity during drop jumps from different drop heights. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2010, 20, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, X.; Wei, S. Effects of local elastic compression on muscle strength, electromyographic, and mechanomyographic responses in the lower extremity. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2012, 22, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannop, J.W.; Worobets, J.T.; Madden, R.; Stefanyshyn, D.J. Influence of Compression and Stiffness Apparel on Vertical Jump Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Bush, J.A.; Newton, R.U.; Duncan, N.D.; Sebastianelli, W.J. Influence of a compression garment on repetitive power output production before and after different types of muscle fatigue. J. Sports Med. Train. 1998, 8, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Bush, J.A.; Bauer, J.A.; Tripleft-McBride, N.; Paxton, N.J.; Clemson, A.; Koziris, L.P.; Mangino, L.C.; Fry, A.C.; Newton, R.U. Influence of compression garments on vertical jump performance in NCAA Division I volleyball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 1996, 10, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Xiang, T.Y. Effect of jump performance on different compression garments. In Proceedings of the ISBS-Conference Proceedings Archive, Limerick, Ireland, 14–18 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zamporri, J.; Aguinaldo, A. The Effects of a Compression Garment on Lower Body Kinematics and Kinetics During a Drop Vertical Jump in Female Collegiate Athletes. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2018, 6, 2325967118789955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Britto, M.A.; Lemos, A.L.; Dos Santos, C.S.; Stefanyshyn, D.J.; Carpes, F.P. Effect of a Compressive Garment on Kinematics of Jump-Landing Tasks. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 2480–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coza, A.; Nigg, B.M. Compression Apparel Effects on Soft Tissue Vibrations; University Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nigg, B.M. Impact Forces, Soft-Tissue Vibrations, and Muscle Tuning; Topline Printing Inc.: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wakeling, J.M.; Uehli, K.; Rozitis, A.I. Muscle fibre recruitment can respond to the mechanics of the muscle contraction. J. R. Soc. Interface 2006, 3, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.C.; Tseng, L.W.; Chen, F.C.; Wang, L.C.; Yang, W.W.; Lin, Y.J.; Liu, C. Effects of compression garments on surface EMG and physiological responses during and after distance running. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Drop Height | Shorts Group | Hip Joint | Knee Joint | Jump Height (cm) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θcont (°) | θmax-flx (°) | θmax-ext (°) | θRoM (°) | ωcont (°/s) | ωmax-flx (°/s) | ωmax-ext (°/s) | θcont (°) | θmax-flx (°) | θmax-ext (°) | θRoM (°) | ωcont (°/s) | ωmax-flx (°/s) | ωmax-ext (°/s) | |||
| DJ30 | CS | 37.4 * ±9.9 | 68.6 ±7.9 | 13.5 * ±6.8 | 55.0 ±5.0 | 180.2 ±55.2 | 281.8 ±81.0 | 380.0 ±595 | 156.2 ±7.7 | 83.5 ±13.5 | 3.6 ±4.2 | 79.9 ±12.7 | 346.8 ±59.3 | 559.1 ±55.4 | 756.5 ±87.2 | 36.8 ±5.4 |
| CON | 43.8 ±11.9 | 73.9 ±8.7 | 18.0 ±5.9 | 55.8 ±7.7 | 180.5 ±66.5 | 266.4 ±89.1 | 405.2 ±56.3 | 155.3 ±6.8 | 80.1 ±10.7 | 4.6 ±4.9 | 75.4 ±8.5 | 330.2 ±60.2 | 533.0 ±76.0 | 744.9 ±98.3 | 37.2 ±4.6 | |
| DJ45 | CS | 33.2 * ±9.6 | 68.0 * ±6.0 | 10.6 * ±8.6 | 57.3 ±7.0 | 173.0 ±39.4 | 301.5 ±86.9 | 382.2 * ±57.5 | 155.2 ±6.3 | 87.0 ±13.8 | 4.1 ±5.0 | 82.8 ±12.6 | 400.4 ±63.7 | 590.7 ±52.9 | 765.3 ±93.2 | 37.8 ±7.2 |
| CON | 42.0 ±14.2 | 76.9 ±7.5 | 16.8 ±5.5 | 60.0 ±8.8 | 187.3 ±58.0 | 314.6 ±68.8 | 412.8 ±43.8 | 155.1 ±4.4 | 86.0 ±11.5 | 5.8 ±3.0 | 80.1 ±9.1 | 373.0 ±58.3 | 587.6 ±66.6 | 761.7 ±73.1 | 38.7 ±5.4 | |
| DJ60 | CS | 33.7 * ±8.9 | 71.9 * ±8.0 | 13.5 * ±6.3 | 58.3 ±6.8 | 177.3 ±54.7 | 308.8 * ±94.9 | 393.6 * ±53.6 | 153.6 ±5.5 | 92.2 ±16.3 | 4.6 ±4.6 | 87.5 ±14.6 | 397.7 ±69.7 | 593.6 ±64.8 | 782.3 ±98.2 | 38.9 ±7.9 |
| CON | 40.4 ±9.6 | 78.7 ±8.8 | 16.7 ±6.0 | 62.0 ±5.2 | 182.8 ±55.4 | 372.9 ±85.3 | 424.5 ±48.4 | 154.6 ±5.1 | 87.8 ±13.8 | 3.5 ±3.4 | 84.2 ±12.7 | 396.5 ±63.0 | 597.4 ±93.7 | 776.3 ±79.8 | 39.2 ±5.7 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Fu, W. Compression Garments Reduce Soft Tissue Vibrations and Muscle Activations during Drop Jumps: An Accelerometry Evaluation. Sensors 2021, 21, 5644. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165644
Deng L, Yang Y, Yang C, Fang Y, Zhang X, Liu L, Fu W. Compression Garments Reduce Soft Tissue Vibrations and Muscle Activations during Drop Jumps: An Accelerometry Evaluation. Sensors. 2021; 21(16):5644. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165644
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Liqin, Yang Yang, Chenhao Yang, Ying Fang, Xini Zhang, Li Liu, and Weijie Fu. 2021. "Compression Garments Reduce Soft Tissue Vibrations and Muscle Activations during Drop Jumps: An Accelerometry Evaluation" Sensors 21, no. 16: 5644. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165644
APA StyleDeng, L., Yang, Y., Yang, C., Fang, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, L., & Fu, W. (2021). Compression Garments Reduce Soft Tissue Vibrations and Muscle Activations during Drop Jumps: An Accelerometry Evaluation. Sensors, 21(16), 5644. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165644






