A Blanket Accommodative Sleep Posture Classification System Using an Infrared Depth Camera: A Deep Learning Approach with Synthetic Augmentation of Blanket Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Recruitment
2.2. Hardware Setup
2.3. Experimental Procedure
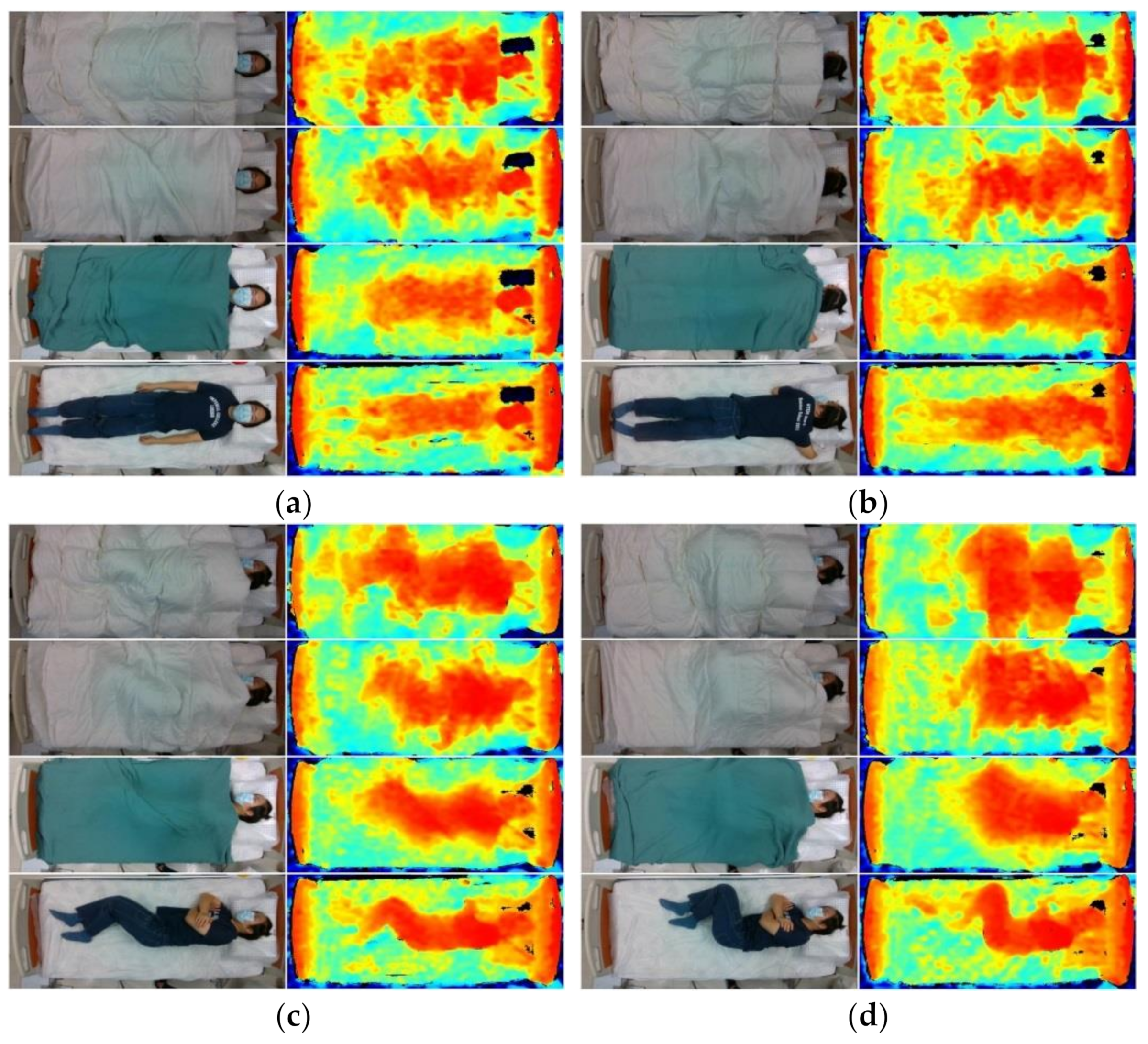
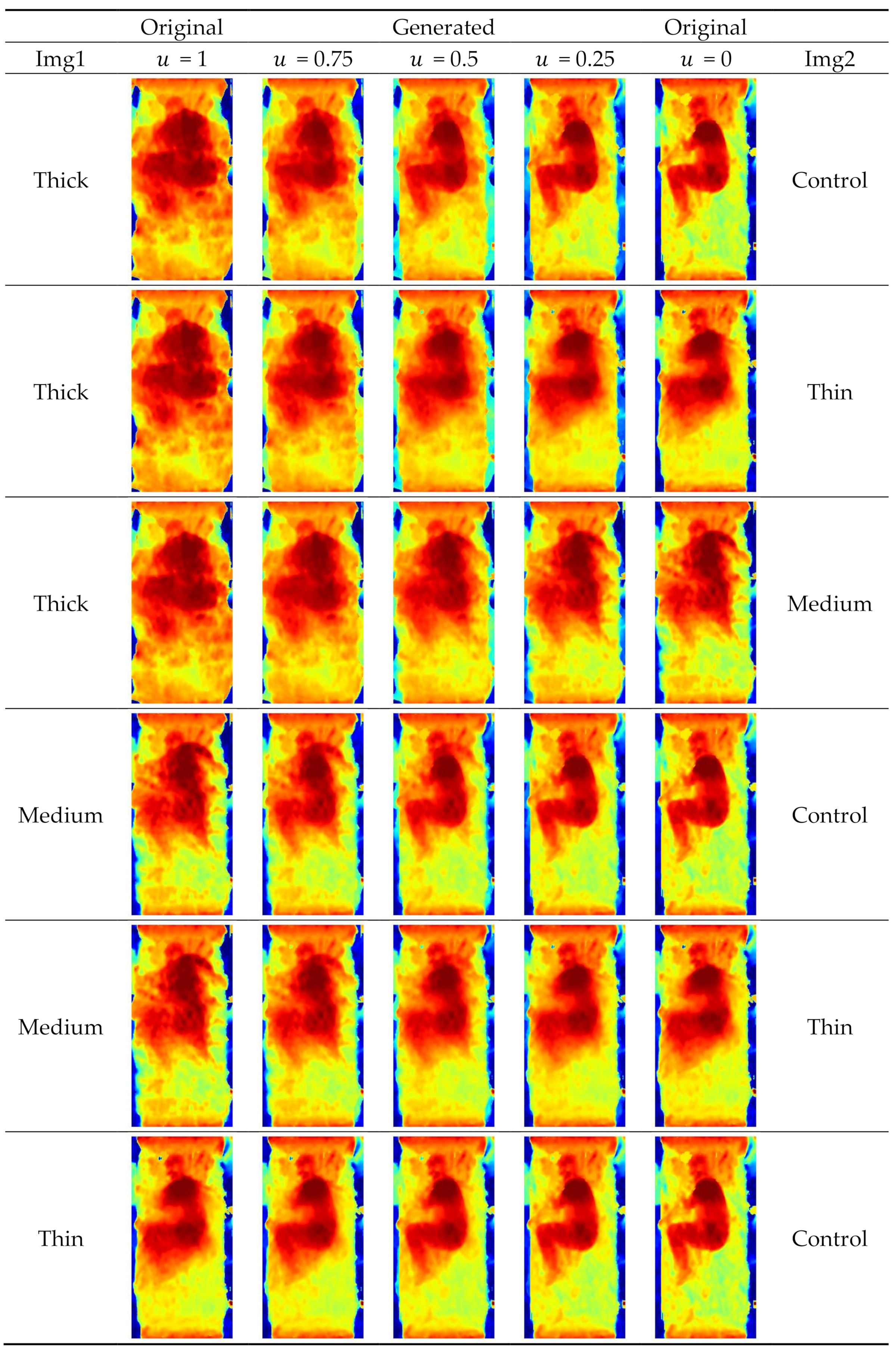
2.4. Data Pre-Processing and Augmentation
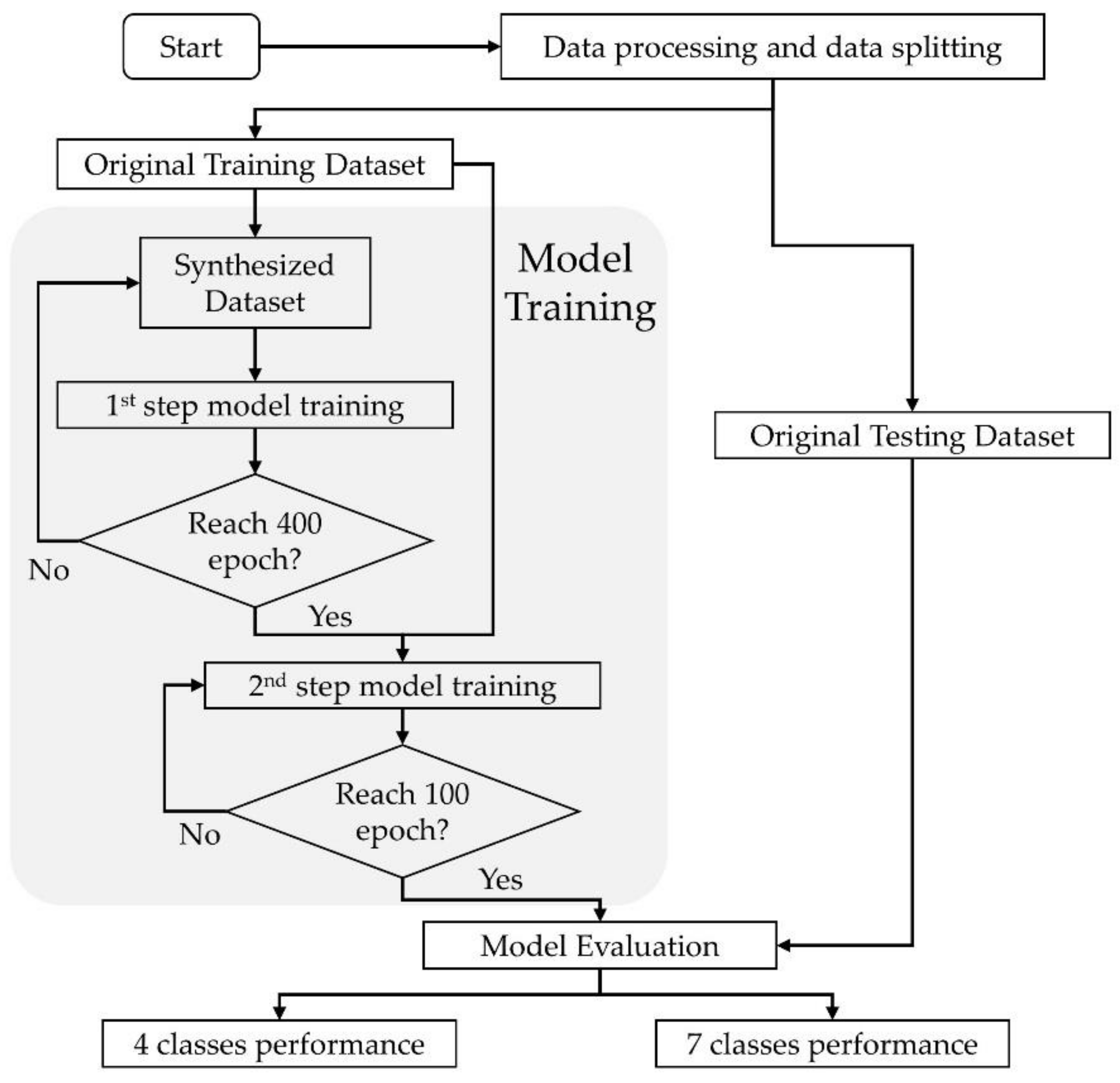
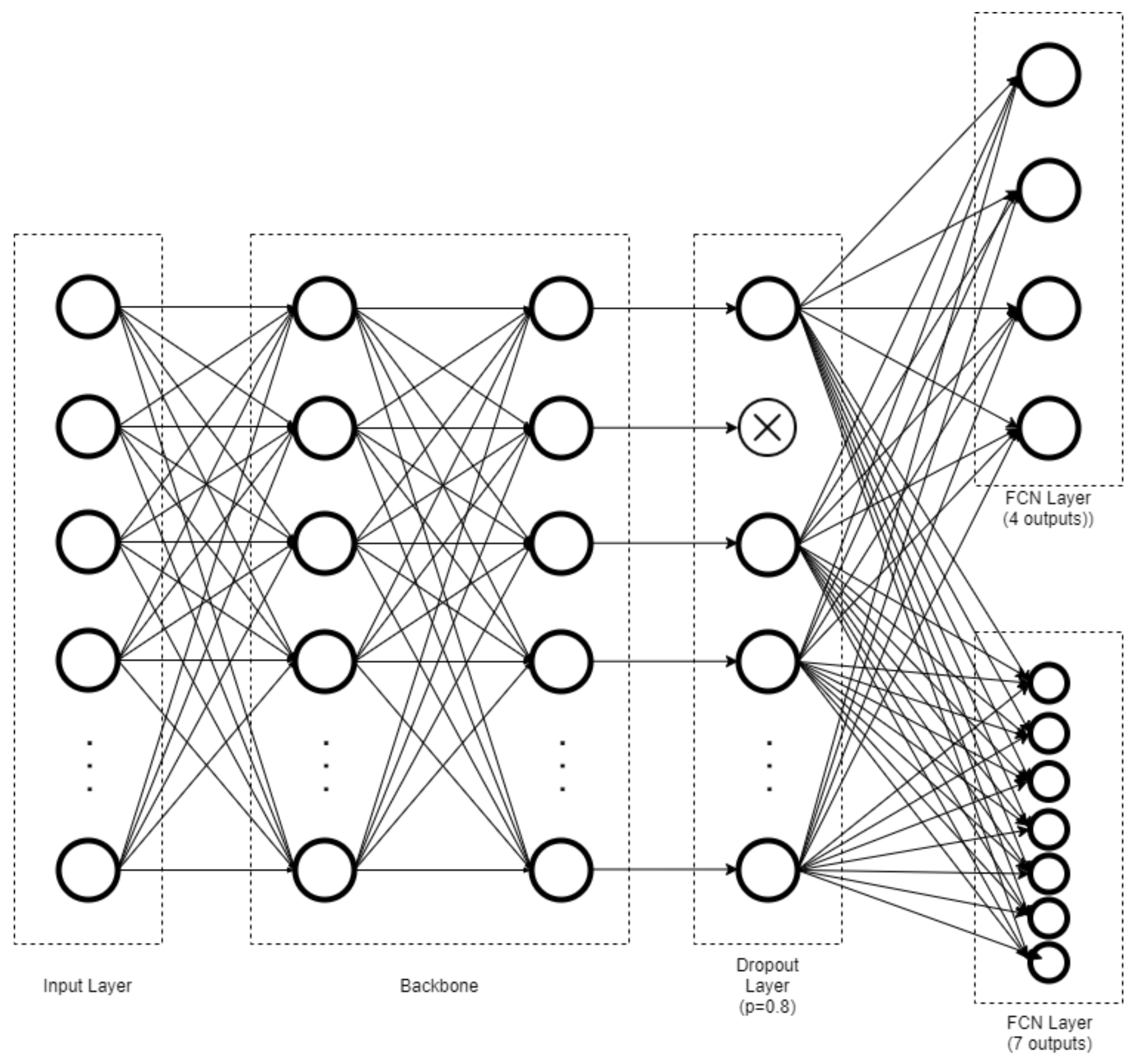
2.5. Model Training and Architecture
2.6. Model Evaluation
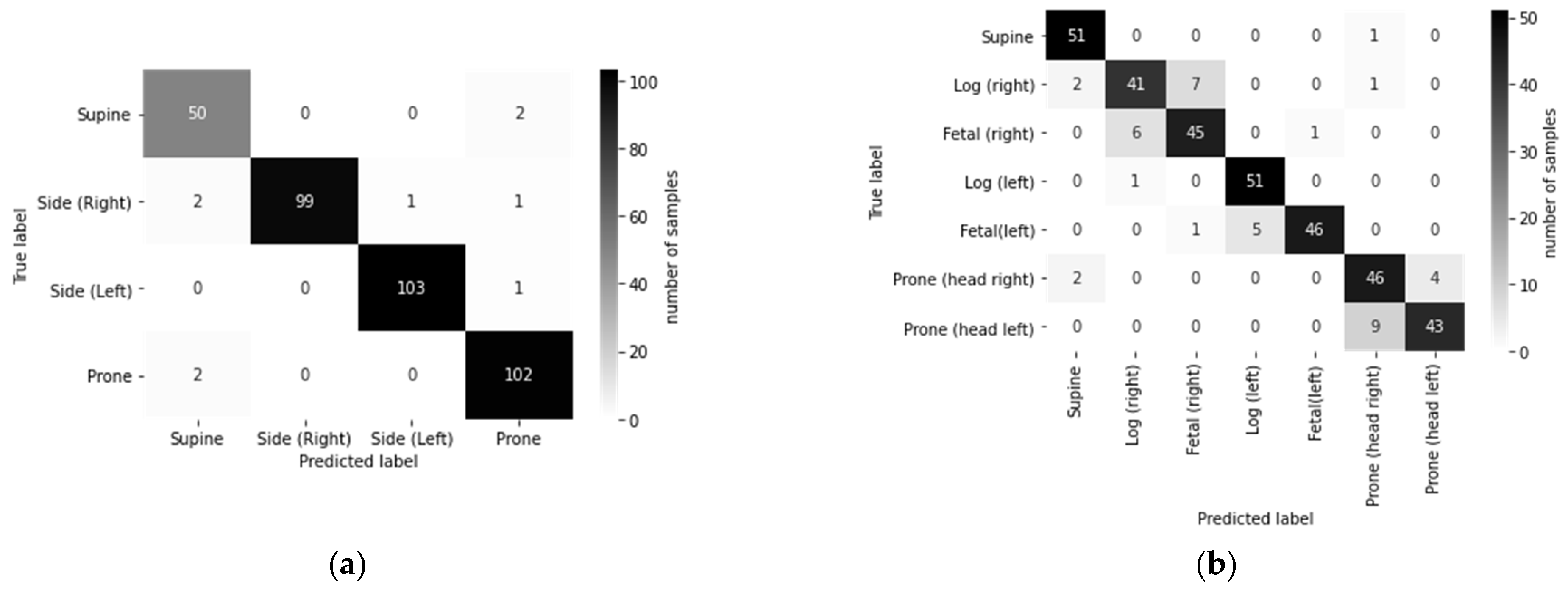
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| 0 | Requie: a Stepsize |
| 1 | Exponential decay rates for the moment estimates |
| 2 | : Initial parameter vector |
| 3 | ← 0 (Initial 1st moment vector) |
| 4 | ← 0 (Initial 2nd moment vector) |
| 5 | t ←0 : (Initial time step) |
| 6 | not converged do |
| 7 | t ← t+1 |
| 8 | Feature_vector ← BackboneNetwork(x) (Extract feature vector using CNN ) |
| 9 | DropoutFeatureVector ← Dropout(Feature_vector) (Dropout layer) |
| 10 | ← fullyConnectedNetwork1(DropoutFeatureVector) (Predict Coarse Classification) |
| 11 | ← fullyConnectedNetwork2(DropoutFeatureVector) (Predict Fine Classificatoin) |
| 12 | (Compute Loss) |
| 13 | ← (Get gradients w.r.t. stochastic objective at timestep t) |
| 14 | ← (Update biased first moment estimate) |
| 15 | ← (Update biased second raw moment estimate) |
| 16 | ← (Compute bias-correced first moment estimate) |
| 17 | ←(Update parameters) |
| 18 | end while |
| 19 | (Resulting parameters) |
References
- Lin, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, A.; Li, Y.; Gu, C.; Li, C.; Xu, W. SleepSense: A noncontact and cost-effective sleep monitoring system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 11, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.; Power, N.; Graham, E.; Deschênes, S.S.; Schmitz, N. The association between sleep and diabetes outcomes—A systematic review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 161, 108035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorona, R.D.; Winn, M.P.; Babineau, T.W.; Eng, B.P.; Feldman, H.R.; Ware, J.C. Overweight and obese patients in a primary care population report less sleep than patients with a normal body mass index. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spiegel, K.; Knutson, K.; Leproult, R.; Tasali, E.; Cauter, E.V. Sleep loss: A novel risk factor for insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, M.A.; Booth, S.A.; Omar, O.; Ostlundh, L.; Arora, T. The relationship between sleep duration and mood in adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2020, 52, 101311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hombali, A.; Seow, E.; Yuan, Q.; Chang, S.H.S.; Satghare, P.; Kumar, S.; Verma, S.K.; Mok, Y.M.; Chong, S.A.; Subramaniam, M. Prevalence and correlates of sleep disorder symptoms in psychiatric disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 279, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Guo, L.; Huo, J.; Zhou, G. Prevalence of sleep disturbances in Chinese adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. TagSheet: Sleeping posture recognition with an unobtrusive passive tag matrix. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; pp. 874–882. [Google Scholar]
- Dreischarf, M.; Shirazi-Adl, A.; Arjmand, N.; Rohlmann, A.; Schmidt, H. Estimation of loads on human lumbar spine: A review of in vivo and computational model studies. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-H.; Ko, M.-S. Effect of sleep posture on neck muscle activity. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canivet, C.; Östergren, P.-O.; Choi, B.; Nilsson, P.; Af Sillen, U.; Moghadassi, M.; Karasek, R.; Isacsson, S.-O. Sleeping problems as a risk factor for subsequent musculoskeletal pain and the role of job strain: Results from a one-year follow-up of the Malmö Shoulder Neck Study Cohort. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2008, 15, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cary, D.; Briffa, K.; McKenna, L. Identifying relationships between sleep posture and non-specific spinal symptoms in adults: A scoping review. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e027633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cary, D.; Collinson, R.; Sterling, M.; Briffa, K. Examining the relationship between sleep posture and morning spinal symptoms in the habitual environment using infrared cameras. J. Sleep Disord. Treat. Care 2016, 5, 1000173. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.-Y.; Eum, S.-H. Implement the system of the Position Change for Obstructive sleep apnea patient. J. Korea Inst. Inf. Commun. Eng. 2017, 21, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Cheyne, J.A. Situational factors affecting sleep paralysis and associated hallucinations: Position and timing effects. J. Sleep Res. 2002, 11, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.A.; Orr, W.C.; Crawley, J.A.; Traxler, B.; McCullough, J.; Brown, K.A.; Roth, T. Effect of esomeprazole on nighttime heartburn and sleep quality in patients with GERD: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltisberg, D.; Arnrich, B.; Tröster, G. Sleep quality monitoring with the smart bed. In Pervasive Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 211–227. [Google Scholar]
- Sprigle, S.; Sonenblum, S. Assessing evidence supporting redistribution of pressure for pressure ulcer prevention: A review. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2011, 48, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, C.A.; Moore, J.S.S.; McLaws, M.-L. Two-Hourly Repositioning for Prevention of Pressure Ulcers in the Elderly: Patient Safety or Elder Abuse? J. Bioethical Inq. 2019, 16, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, J.C.-W.; Tam, E.W.-C.; Mak, A.H.-Y.; Chan, T.T.-C.; Lai, W.P.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-P. Night-time monitoring system (eNightLog) for elderly wandering behavior. Sensors 2021, 21, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, T.; Ohshima, N.; Kunisawa, N.; Murayama, R.; Okano, S.; Mori-Okamoto, J. Characteristic features of the nocturnal sleeping posture of healthy men. Sleep Biol. Rhythm. 2003, 1, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Kumar, A.; Nadeem, M.; Maaz, I. CNN-Based Smart Sleep Posture Recognition System. IoT 2021, 2, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Rhuma, A.; Naqvi, S.M.; Wang, L.; Chambers, J. A posture recognition-based fall detection system for monitoring an elderly person in a smart home environment. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2012, 16, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Masek, M.; Lam, C.P.; Tranthim-Fryer, C.; Jansen, B.; Baptist, K. Sleep monitor: A tool for monitoring and categorical scoring of lying position using 3D camera data. SoftwareX 2018, 7, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, E.; Dickerson, R.F.; Stankovic, J.A. Monitoring body positions and movements during sleep using wisps. In Proceedings of the Wireless Health 2010, WH 2010, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–7 October 2010; pp. 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, B.; Wu, M.; Bugos, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.R. Smars: Sleep monitoring via ambient radio signals. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 2019, 20, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Xu, W.; Huang, M.-C.; Alshurafa, N.; Sarrafzadeh, M.; Raut, N.; Yadegar, B. A dense pressure sensitive bedsheet design for unobtrusive sleep posture monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), San Diego, CA, USA, 18–22 March 2013; pp. 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Pino, E.J.; De la Paz, A.D.; Aqueveque, P.; Chávez, J.A.; Morán, A.A. Contact pressure monitoring device for sleep studies. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 4160–4163. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, W.; Niu, S.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric active sensor array for self-powered static and dynamic pressure detection and tactile imaging. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8266–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, G.; Lina, J.-M.; Kaddoum, G. Artificial neural network for in-bed posture classification using bed-sheet pressure sensors. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mingliang, S.; Lu, K. A Method to Recognize Sleeping Position Using an CNN Model Based on Human Body Pressure Image. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Power, Intelligent Computing and Systems (ICPICS), Shenyang, China, 12–14 July 2019; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, A.; Dong, J.; Zhou, H. Self-supervised learning from multi-sensor data for sleep recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 93907–93921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Kwak, K.-C. Posture Recognition Using Ensemble Deep Models under Various Home Environments. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viriyavit, W.; Sornlertlamvanich, V. Bed Position Classification by a Neural Network and Bayesian Network Using Noninvasive Sensors for Fall Prevention. J. Sens. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-W.; Wang, S.-K.; Wan, B.-T.; Song, W.W. A novel multi-label classification algorithm based on K-nearest neighbor and random walk. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2020, 16, 1550147720911892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallmann, S.; Chen, L. Computational sleep behavior analysis: A survey. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 142421–142440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buslaev, A.; Iglovikov, V.I.; Khvedchenya, E.; Parinov, A.; Druzhinin, M.; Kalinin, A.A. Albumentations: Fast and flexible image augmentations. Information 2020, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Luong, M.-T.; Hovy, E.; Le, Q.V. Self-training with noisy student improves imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10687–10698. [Google Scholar]
- Artstein, R.; Poesio, M. Inter-coder agreement for computational linguistics. Comput. Linguist. 2008, 34, 555–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, A.; Dong, B.; Lv, X.; Zhu, T.; Hu, F.; Yang, X. A non-contact sleep posture sensing strategy considering three dimensional human body models. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 14–17 October 2016; pp. 414–417. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, T.; Martinez, M.; Benz, A.; Stiefelhagen, R. Sleep position classification from a depth camera using bed aligned maps. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Fallmann, S.; Van Veen, R.; Chen, L.; Walker, D.; Chen, F.; Pan, C. Wearable accelerometer based extended sleep position recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 19th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Dalian, China, 12–15 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, R.; Ostadabbas, S.; Faezipour, M.; Farshbaf, M.; Nourani, M.; Tamil, L.; Pompeo, M. Bed posture classification for pressure ulcer prevention. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 7175–7178. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, S.M.; Alnowami, M.; Khan, S.; Dijk, D.-J.; Hilton, A.; Wells, K. Sleep posture classification using a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ostadabbas, S.; Pouyan, M.B.; Nourani, M.; Kehtarnavaz, N. In-bed posture classification and limb identification. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS) Proceedings, Lausanne, Switzerland, 22–24 October 2014; pp. 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, M. Effect of pillow height on the biomechanics of the head-neck complex: Investigation of the cranio-cervical pressure and cervical spine alignment. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, D.W.-C.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Tan, Q.; Chen, T.L.-W.; Zhang, M. Sleeping mattress determinants and evaluation: A biomechanical review and critique. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Performance | 4-Posture Coarse Classification | 7-Posture Fine-Grained Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 97.5% | 89.0% |
| Recall | 97.3% | 89.0% |
| Precision | 97.0% | 88.9% |
| F1 score | 97.1% | 88.9% |
| Cohen’s kappa coefficient | 0.970 | 0.891 |
| Posture/Blanket | Thick | Medium | Thin | Control | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-posture coarse-grained classification | |||||
| Supine | 92.3% | 92.9% | 96.0% | 96.3% | 94.3% |
| Side (right) | 95.8% | 98.0% | 100% | 98.0% | 98.0% |
| Side (left) | 98.1% | 98.0% | 100% | 100% | 99.0% |
| Prone | 94.3% | 96.2% | 98.1% | 100% | 97.1% |
| Overall | 95.1% | 96.3% | 98.5% | 98.6% | 97.1% |
| 7-posture fine-grained classification | |||||
| Supine | 92.9% | 96.3% | 96.0% | 96.3% | 95.3% |
| Log (right) | 72.0% | 83.3% | 88.9% | 87.0% | 82.8% |
| Fetal (right) | 81.5% | 83.3% | 84.6% | 92.9% | 85.7% |
| Log (left) | 92.3% | 92.9% | 96.3% | 96.3% | 94.4% |
| Fetal (left) | 96.0% | 88.0% | 91.7% | 96.0% | 92.9% |
| Prone (head right) | 75.0% | 78.6% | 89.7% | 92.9% | 84.4% |
| Prone (head left) | 81.5% | 83.3% | 91.7% | 91.7% | 86.9% |
| Overall | 84.4% | 86.5% | 91.3% | 93.3% | 88.9% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tam, A.Y.-C.; So, B.P.-H.; Chan, T.T.-C.; Cheung, A.K.-Y.; Wong, D.W.-C.; Cheung, J.C.-W. A Blanket Accommodative Sleep Posture Classification System Using an Infrared Depth Camera: A Deep Learning Approach with Synthetic Augmentation of Blanket Conditions. Sensors 2021, 21, 5553. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165553
Tam AY-C, So BP-H, Chan TT-C, Cheung AK-Y, Wong DW-C, Cheung JC-W. A Blanket Accommodative Sleep Posture Classification System Using an Infrared Depth Camera: A Deep Learning Approach with Synthetic Augmentation of Blanket Conditions. Sensors. 2021; 21(16):5553. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165553
Chicago/Turabian StyleTam, Andy Yiu-Chau, Bryan Pak-Hei So, Tim Tin-Chun Chan, Alyssa Ka-Yan Cheung, Duo Wai-Chi Wong, and James Chung-Wai Cheung. 2021. "A Blanket Accommodative Sleep Posture Classification System Using an Infrared Depth Camera: A Deep Learning Approach with Synthetic Augmentation of Blanket Conditions" Sensors 21, no. 16: 5553. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165553
APA StyleTam, A. Y.-C., So, B. P.-H., Chan, T. T.-C., Cheung, A. K.-Y., Wong, D. W.-C., & Cheung, J. C.-W. (2021). A Blanket Accommodative Sleep Posture Classification System Using an Infrared Depth Camera: A Deep Learning Approach with Synthetic Augmentation of Blanket Conditions. Sensors, 21(16), 5553. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165553








