Identifying Patient–Ventilator Asynchrony on a Small Dataset Using Image-Based Transfer Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
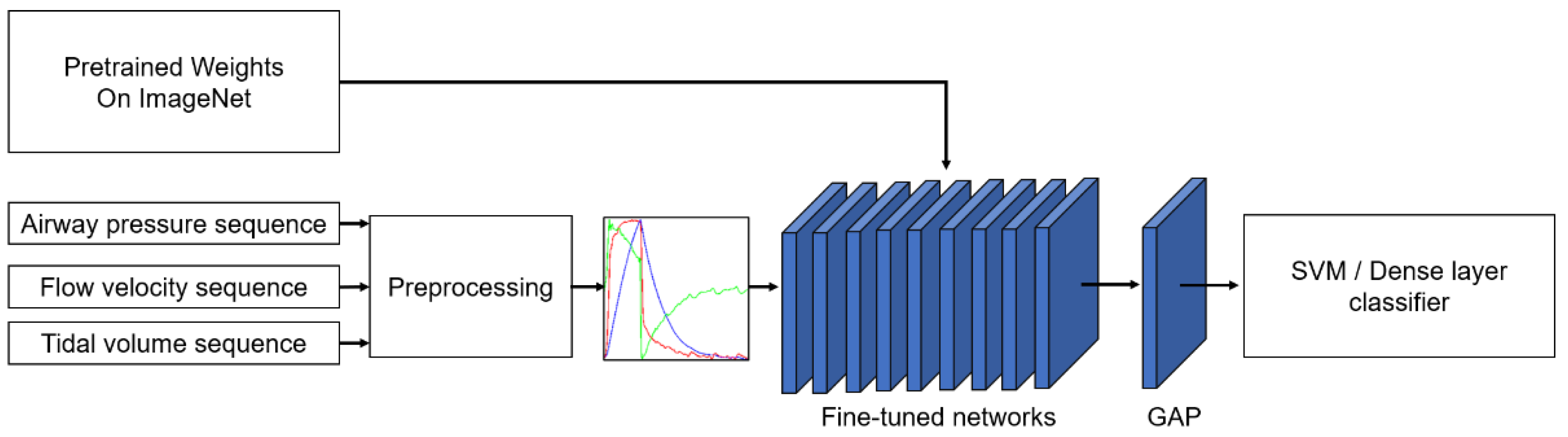
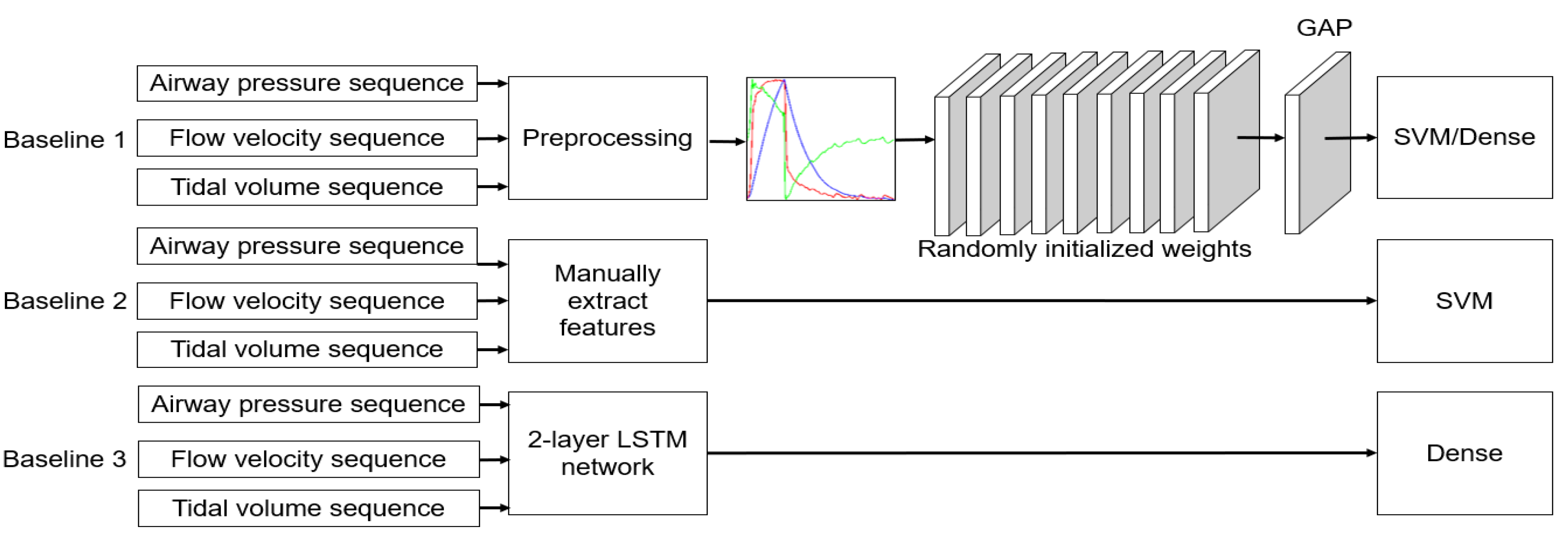
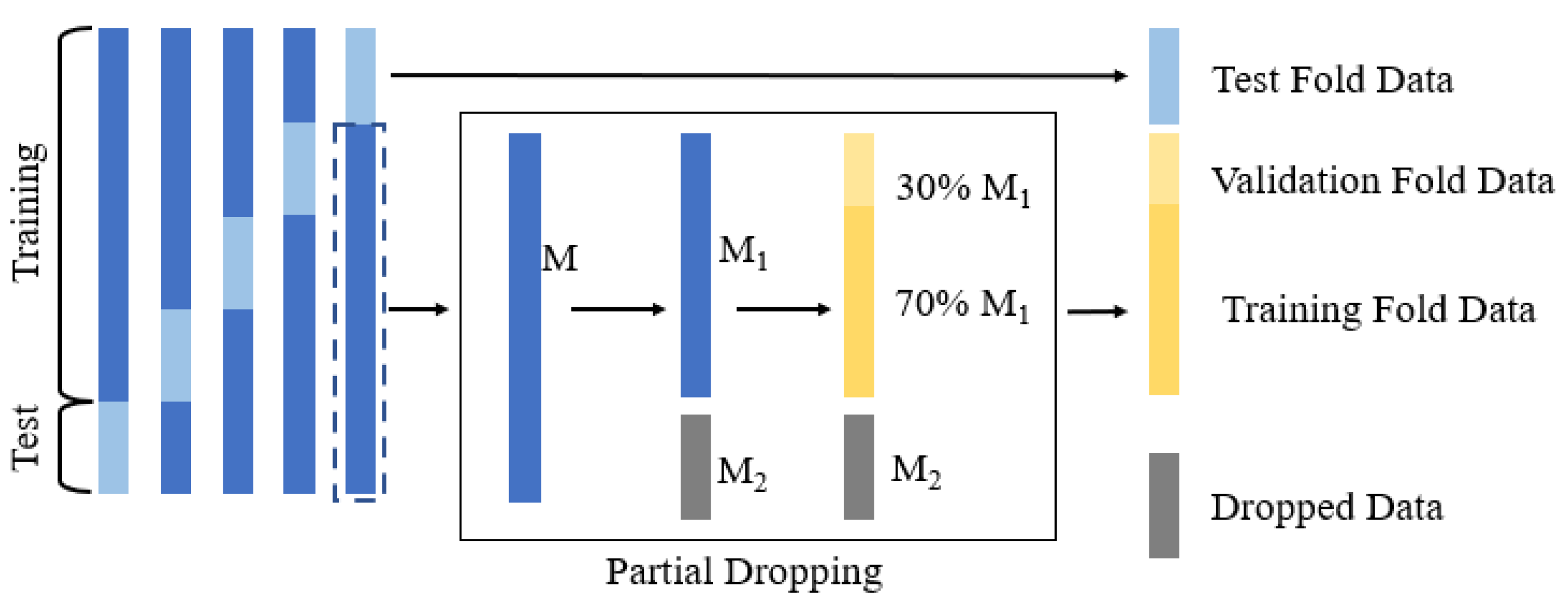
2.1. Overview of the Method
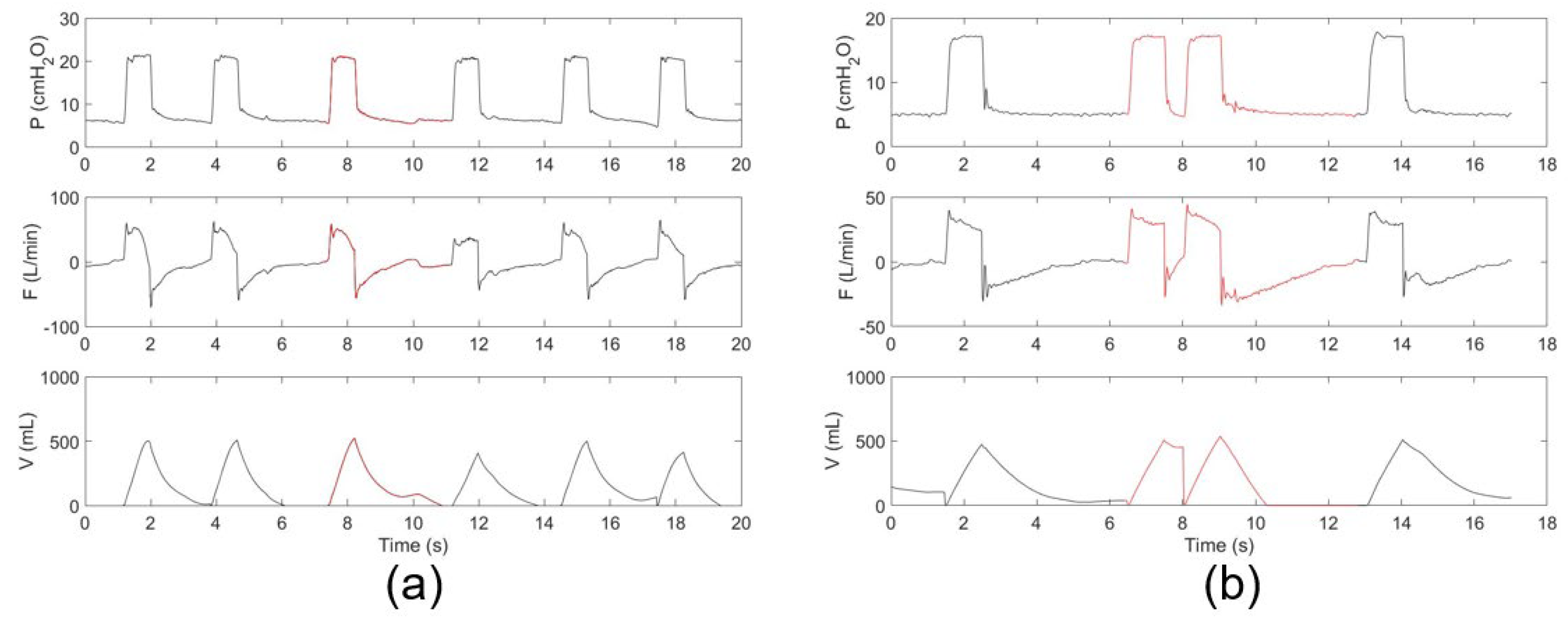
2.2. Data Collection and Annotation
2.3. Preprocessing
- (1)
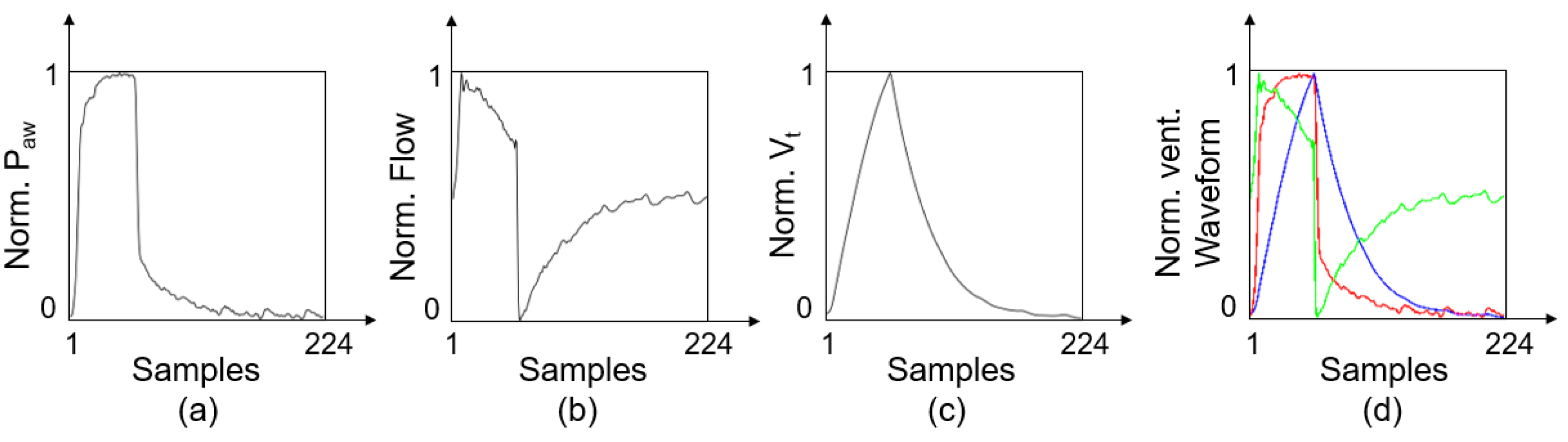
- Standardization. First, the P, F, and V of each breath were interpolated and resampled to a uniform length of 224. Then, each respiratory sequence was normalized according to Equation (1), where denotes the normalized data, denotes the original data, and and are the maximum and minimum values of the original data set, respectively.
- (2)
- Dimensional Transformation. Each 1D respiratory sequence was plotted in a 224 224 grayscale image, as shown in Figure 3.
- (3)
- Multichannel Fusion. The Pdiag, Fdiag and Vdiag were treated as three respective channels and combined into an RGB image.
2.4. Pretrained Models for Feature Extraction
2.5. Performance Evaluation
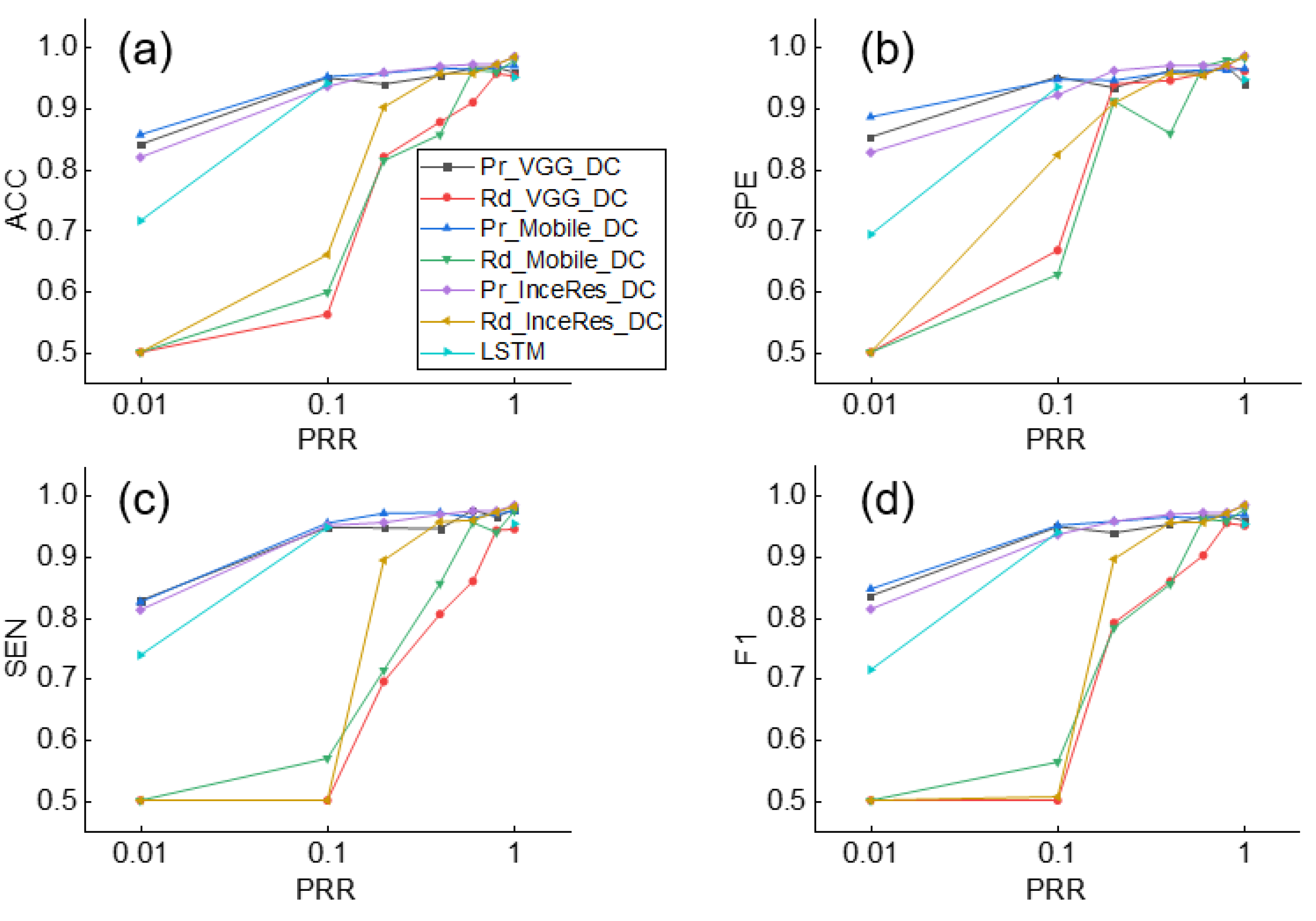
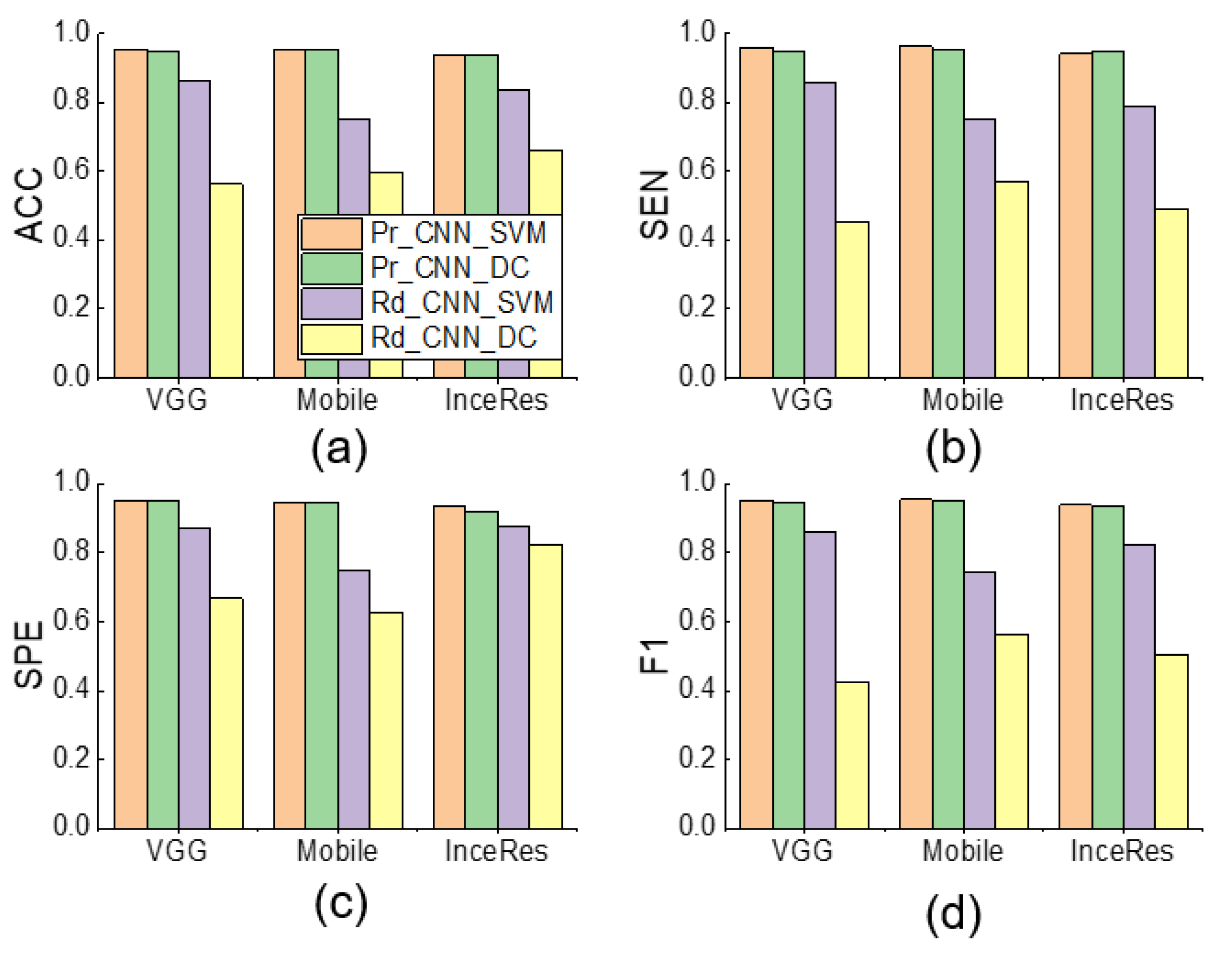
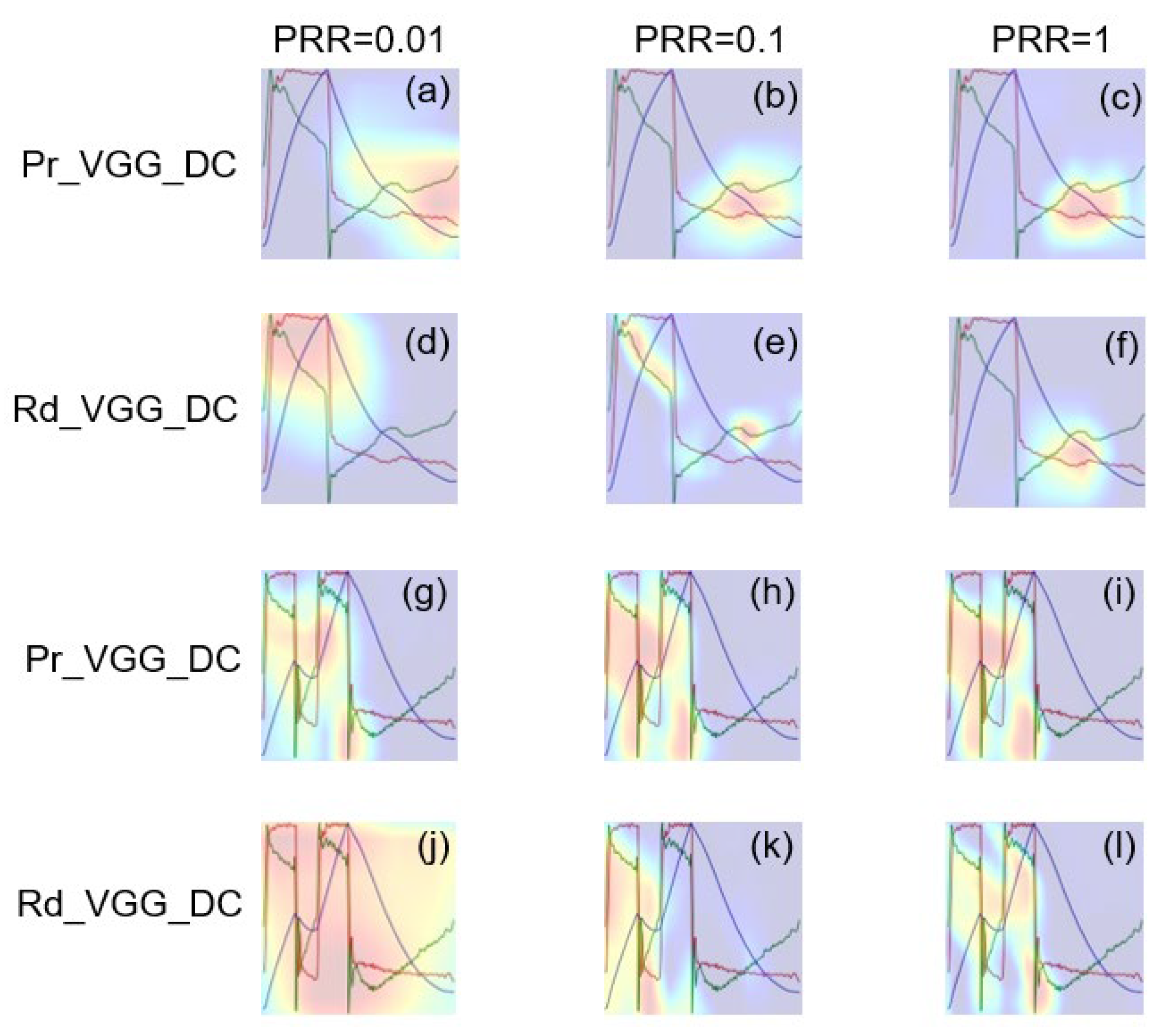
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanch, L.; Villagra, A.; Sales, B.; Montanya, J.; Lucangelo, U.; Lujan, M.; Garcia-Esquirol, O.; Chacon, E.; Estruga, A.; Oliva, J.C.; et al. Asynchronies during mechanical ventilation are associated with mortality. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haro, C.; Sarlabous, L.; Esperanza, J.A.; Magrans, R.; Blanch, L. Monitoring Patient–Ventilator Interaction; ERS Practical Handbook of Invasive Mechanical Ventilation; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2019; p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon, C.S.H.; Foster, G.T. Patient-Ventilator asynchrony. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2001, 7, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, D.C.; Scheinhorn, D.J.; Stearn-Hassenpflug, M. Patient-Ventilator trigger asynchrony in prolonged mechanical ventilation. Chest 1997, 112, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, M.; Miller, K.B.; Green, D.A.; Ostman, H.E.; Gennings, C.; Epstein, S.K. Ineffective triggering predicts increased duration of mechanical ventilation. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 2740–2745. [Google Scholar]
- Tobin, M.J.; Jubran, A.; Laghi, F. Patient-Ventilator interaction. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassoon, C.S. Triggering of the ventilator in patient-ventilator interactions. Respir. Care 2011, 56, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, I.I.; Arellano, D.H.; Adasme, R.S.; Landeros, J.M.; Salinas, F.A.; Vargas, A.G.; Vasquez, F.J.; Lobos, I.A.; Oyarzun, M.L.; Restrepo, R.D. Ability of ICU health-care professionals to identify patient-ventilator asynchrony using waveform analysis. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulqueeny, Q.; Ceriana, P.; Carlucci, A.; Fanfulla, F.; Delmastro, M.; Nava, S. Automatic detection of ineffective triggering and double triggering during mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 2014–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haro, C.; Ochagavia, A.; López-Aguilar, J.; Fernandez-Gonzalo, S.; Navarra-Ventura, G.; Magrans, R.; Montanyà, J.; Blanch, L.; de Haro, C.; López-Aguilar, J.; et al. Patient-Ventilator asynchronies during mechanical ventilation: Current knowledge and research priorities. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2019, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulos, D. Ineffective efforts during mechanical ventilation: The brain wants, the machine declines. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 738–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; Sato, H.; Shirakawa, T. A machine learning model with human cognitive biases capable of learning from small and biased datasets. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, B.; Phan, T.S.; Haddad, W.M.; Cason, A.; Mullis, J.; Price, L.; Bailey, J.M. Replicating human expertise of mechanical ventilation waveform analysis in detecting patient-ventilator cycling asynchrony using machine learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 97, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fauw, J.; Ledsam, J.R.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Nikolov, S.; Tomasev, N.; Blackwell, S.; Askham, H.; Glorot, X.; O’Donoghue, B.; Visentin, D. Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, A.Y.; Rajpurkar, P.; Haghpanahi, M.; Tison, G.H.; Bourn, C.; Turakhia, M.P.; Ng, A.Y. Cardiologist-Level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Jia, M.; Pan, J.; Gong, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, H.; Fang, L. An interpretable 1D convolutional neural network for detecting patient-ventilator asynchrony in mechanical ventilation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 204, 106057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Mao, K.; Duan, K.; Fang, S.; Lu, Y.; Gong, Q.; Lu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Fang, W. Detection of patient-ventilator asynchrony from mechanical ventilation waveforms using a two-layer long short-term memory neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 120, 103721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Sun, F.; Kong, T.; Zhang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, C. A survey on deep transfer learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Rhodes, Greece, 4–7 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Raghu, S.; Sriraam, N.; Temel, Y.; Rao, S.V.; Kubben, P.L. EEG based multi-class seizure type classification using convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Neural Netw. 2020, 124, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.; Taheri, S.; Yuan, J.S. ECG arrhythmia classification using transfer learning from 2-dimensional deep CNN features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Cleveland, OH, USA, 17–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kacmarek, R.; Stoller, J.; Heuer, A. Fundamentals of Respiratory Care; Elsevier: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2017; p. 1059. [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy, S.; Jubran, A.; Tobin, M.J. Cycling of inspiratory and expiratory muscle groups with the ventilator in airflow limitation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokioka, H.; Tanaka, T.; Ishizu, T.; Fukushima, T.; Iwaki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Kosogabe, Y. The effect of breath termination criterion on breathing patterns and the work of breathing during pressure support ventilation. Anesth. Analg. 2001, 92, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, A.; Quintavalle, F.; Fernandez, R.; Blanch, L.; Ferluga, M.; Lena, E.; Fabris, F.; Lucangelo, U. An effective pressure-flow characterization of respiratory asynchronies in mechanical ventilation. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2021, 35, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasu, P.N.; SivaSai, J.G.; Ijaz, M.F.; Bhoi, A.K.; Kim, W.; Kang, J.J. Classification of skin disease using deep learning neural networks with MobileNet V2 and LSTM. Sensors 2021, 21, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xie, M.; Miao, P.; Qu, W.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Wong, T.-T. Perceptual-aware sketch simplification based on integrated VGG layers. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2019, 27, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.H.; Fan, R.R.; Cao, G.; Zhang, Y.D.; Guo, T. Teeth category classification via seven-layer deep convolutional neural network with max pooling and global average pooling. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2019, 29, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Hong, J.; Yang, M. Sensorineural hearing loss identification via nine-layer convolutional neural network with batch normalization and dropout. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 15135–15150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottile, P.D.; Albers, D.; Higgins, C.; Mckeehan, J.; Moss, M. The Association Between Ventilator Dyssynchrony, Delivered Tidal Volume, and Sedation Using a Novel Automated Ventilator Dyssynchrony Detection Algorithm. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Rosasco, L.; Caponnetto, A. On early stopping in gradient descent learning. Constr. Approx. 2007, 26, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Huh, J.-H.; Kim, Y.J.E. Python TensorFlow Big Data Analysis for the Security of Korean Nuclear Power Plants. Electronics 2020, 9, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 2020, 395, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Dey, N.; Fong, S.; Ashour, A.S. Deep back propagation-long short-term memory network based upper-limb sEMG signal classification for automated rehabilitation. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 40, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohmantri, R.; Surantha, N. Arrhythmia Classification using 2D Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, N.; Chiew, Y.; Tan, C.; Arunachalam, G.; Ralib, A.; Mat-Nor, M.-B. A machine learning model for real-time asynchronous berathing monitoring. IFAC Pap. Online 2018, 51, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Pretrained Model | No. of Respiratory Sequences |
|---|---|
| PVA–DT a | 20,398 |
| PVA–IEE | 26,453 |
| OTHER b | 470,770 |
| Total c | 516,210 |
| Pretrained Model | No. of Weights | No. of Features | Input Image Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNet | 3,230,914 | 1024 | 224 224 |
| VGG-16 network | 14,721,602 | 1024 | 224 224 |
| Inception–ResNetV2 | 54,339,810 | 1536 | 224 224 |
| Type | Model Name | Feature Extractor | Classifiers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pr_CNN_DC | Pr_Mobile_DC | Pretrained MobileNet extractor | Dense |
| Pr_VGG_DC | Pretrained VGGNet extractor | Dense | |
| Pr_InceRes _DC | Pretrained Inception–ResNetV2 extractor | Dense | |
| Pr_CNN_SVM | Pr_Mobile_SVM | Pretrained MobileNet extractor | SVM |
| Pr_VGG_SVM | Pretrained VGGNet extractor | SVM | |
| Pr_InceRes _SVM | Pretrained Inception–ResNetV2 extractor | SVM | |
| Rd_CNN_DC | Rd_Mobile_DC | MobileNet extractor with r.i.w. * | Dense |
| Rd_VGG_DC | VGGNet extractor with r.i.w. | Dense | |
| Rd_InceRes_DC | Inception–ResNetV2 extractor with r.i.w. | Dense | |
| Rd_CNN_SVM | Rd_Mobile_ SVM | MobileNet extractor with r.i.w. | SVM |
| Rd_VGG_ SVM | VGGNet extractor with r.i.w. | SVM | |
| Rd_InceRes_ SVM | Inception–ResNetV2 extractor with r.i.w. | SVM | |
| Manual_SVM | Manual feature design | SVM | |
| LSTM | 2-layer LSTM network | Dense |
| ACC | SPE | SEN | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual_SVM | 0.9210.004 | 0.9460.003 | 0.8950.005 | 0.9180.004 |
| Pr_CNN_SVM | 0.9660.005 | 0.9580.007 | 0.9730.009 | 0.9650.005 |
| Rd_CNN_SVM | 0.9490.012 | 0.9430.009 | 0.9570.018 | 0.9490.013 |
| ACC | SPE | SEN | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual_SVM | ||||
| Pr_CNN_SVM | ||||
| Rd_CNN_SVM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Q.; Jia, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J.; Lu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, L.; Ge, H. Identifying Patient–Ventilator Asynchrony on a Small Dataset Using Image-Based Transfer Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124149
Pan Q, Jia M, Liu Q, Zhang L, Pan J, Lu F, Zhang Z, Fang L, Ge H. Identifying Patient–Ventilator Asynchrony on a Small Dataset Using Image-Based Transfer Learning. Sensors. 2021; 21(12):4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124149
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Qing, Mengzhe Jia, Qijie Liu, Lingwei Zhang, Jie Pan, Fei Lu, Zhongheng Zhang, Luping Fang, and Huiqing Ge. 2021. "Identifying Patient–Ventilator Asynchrony on a Small Dataset Using Image-Based Transfer Learning" Sensors 21, no. 12: 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124149
APA StylePan, Q., Jia, M., Liu, Q., Zhang, L., Pan, J., Lu, F., Zhang, Z., Fang, L., & Ge, H. (2021). Identifying Patient–Ventilator Asynchrony on a Small Dataset Using Image-Based Transfer Learning. Sensors, 21(12), 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21124149







