A Kalman Filter for Multilinear Forms and Its Connection with Tensorial Adaptive Filters †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Multilinear Framework for MISO System Identification
3. Kalman Filter for the Identification of Multilinear Forms
4. Connection with Tensor-Based Adaptive Filters
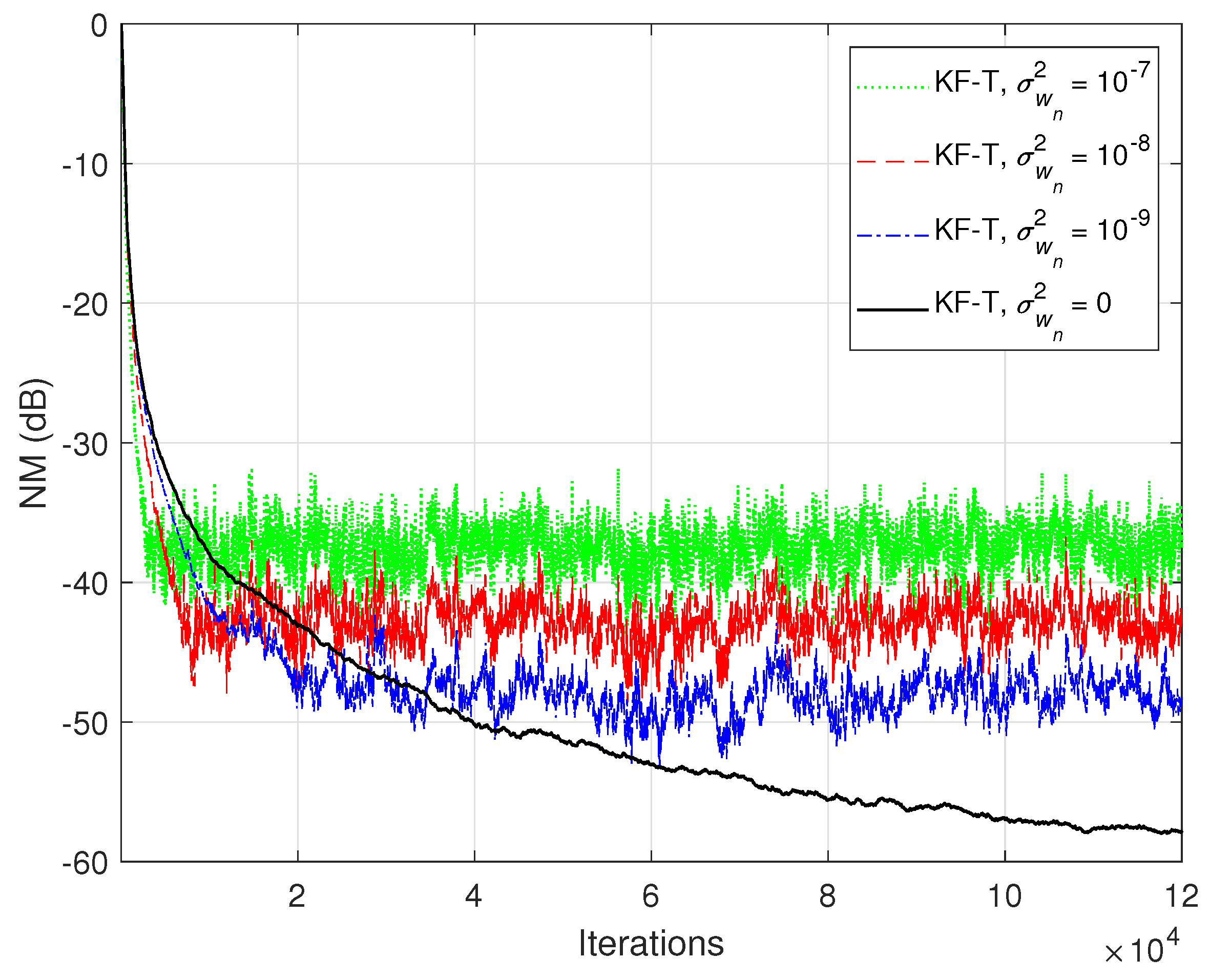
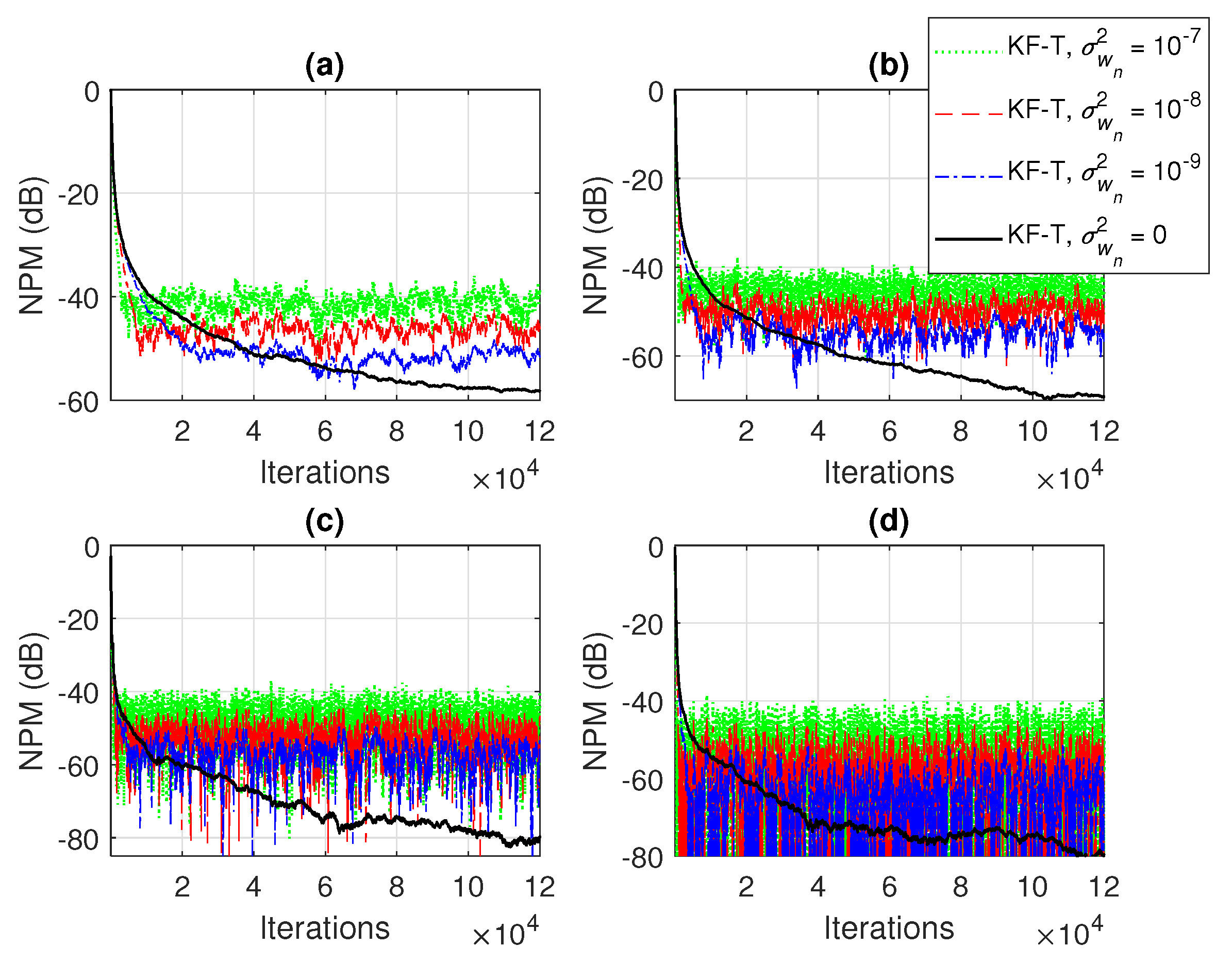
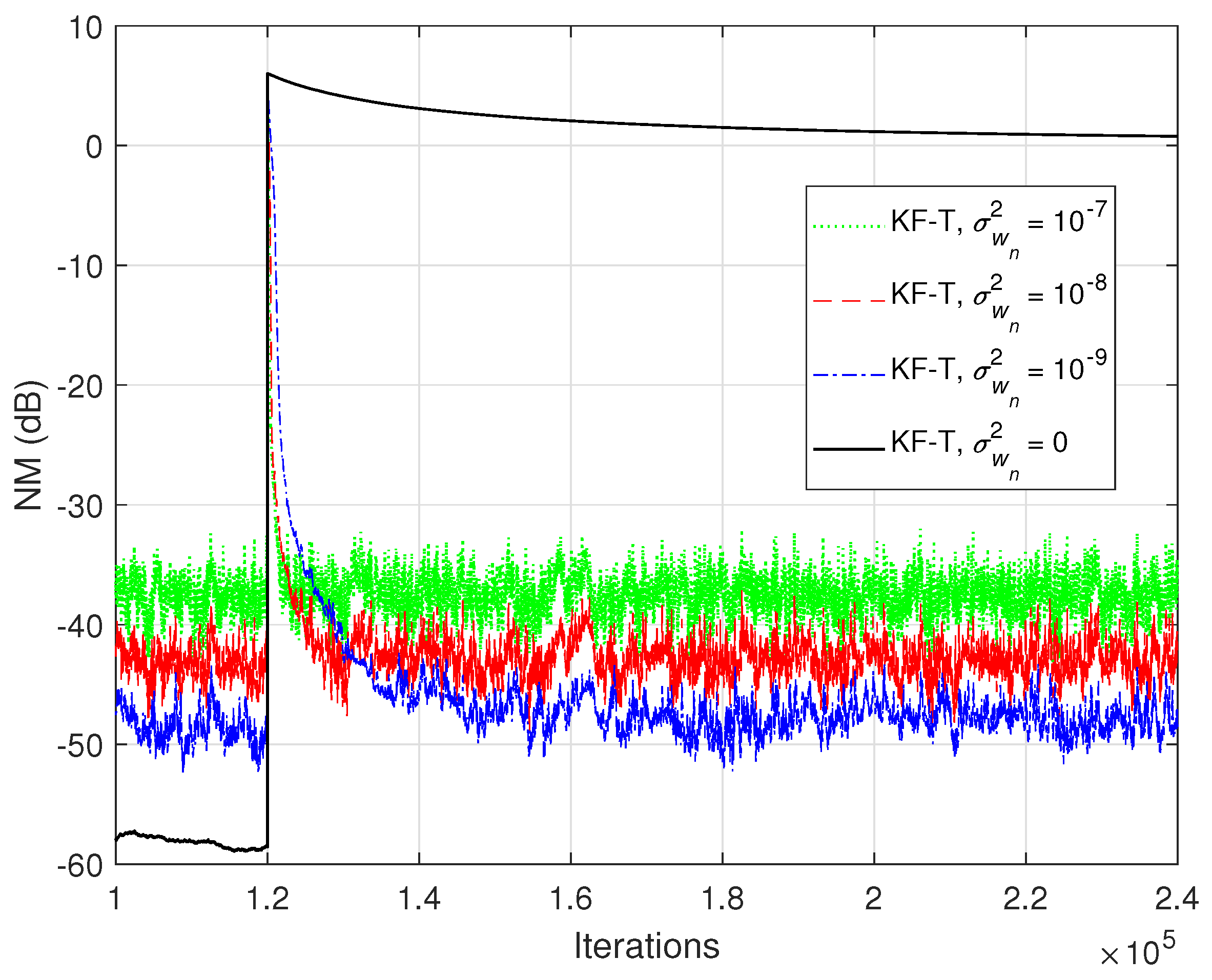
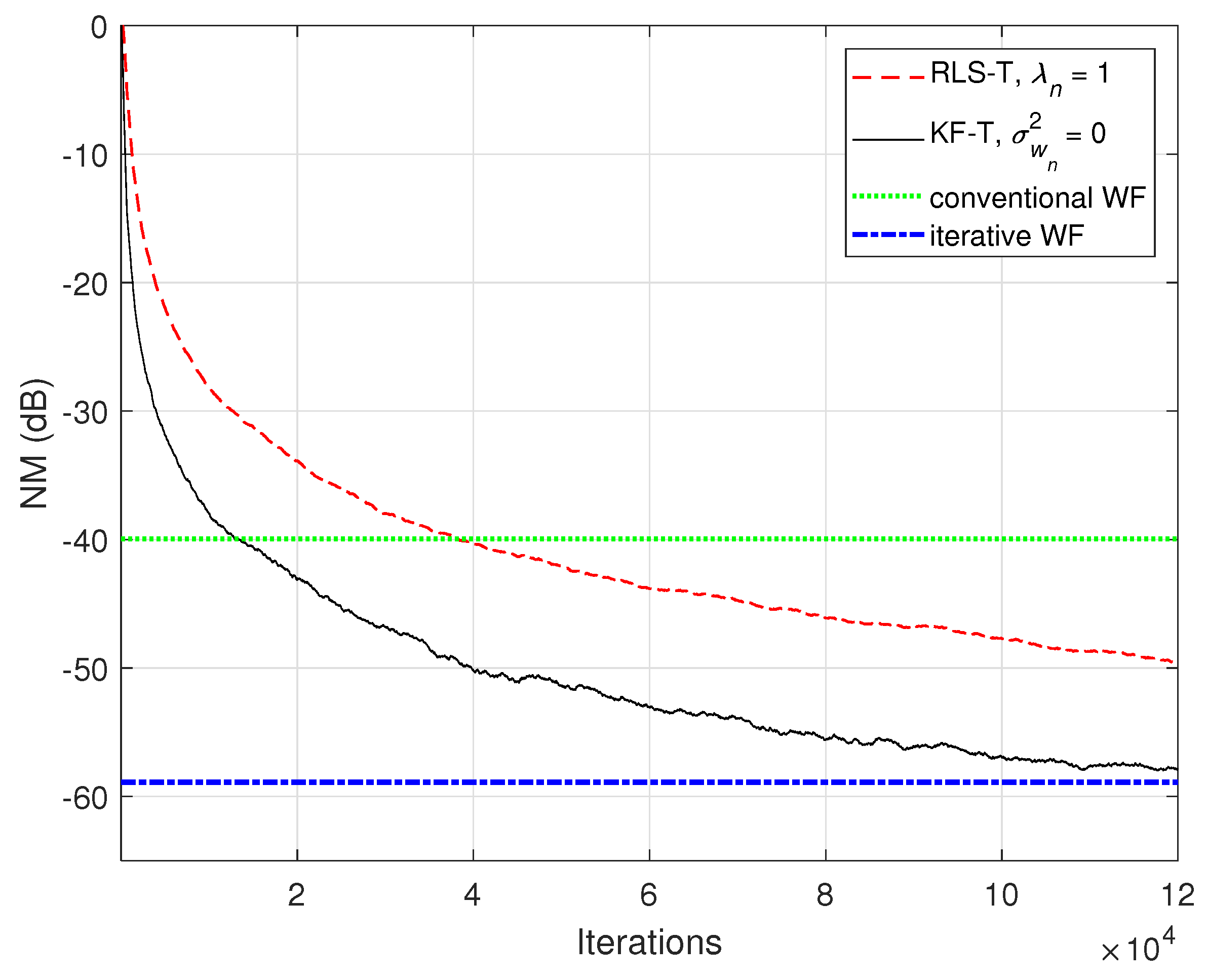
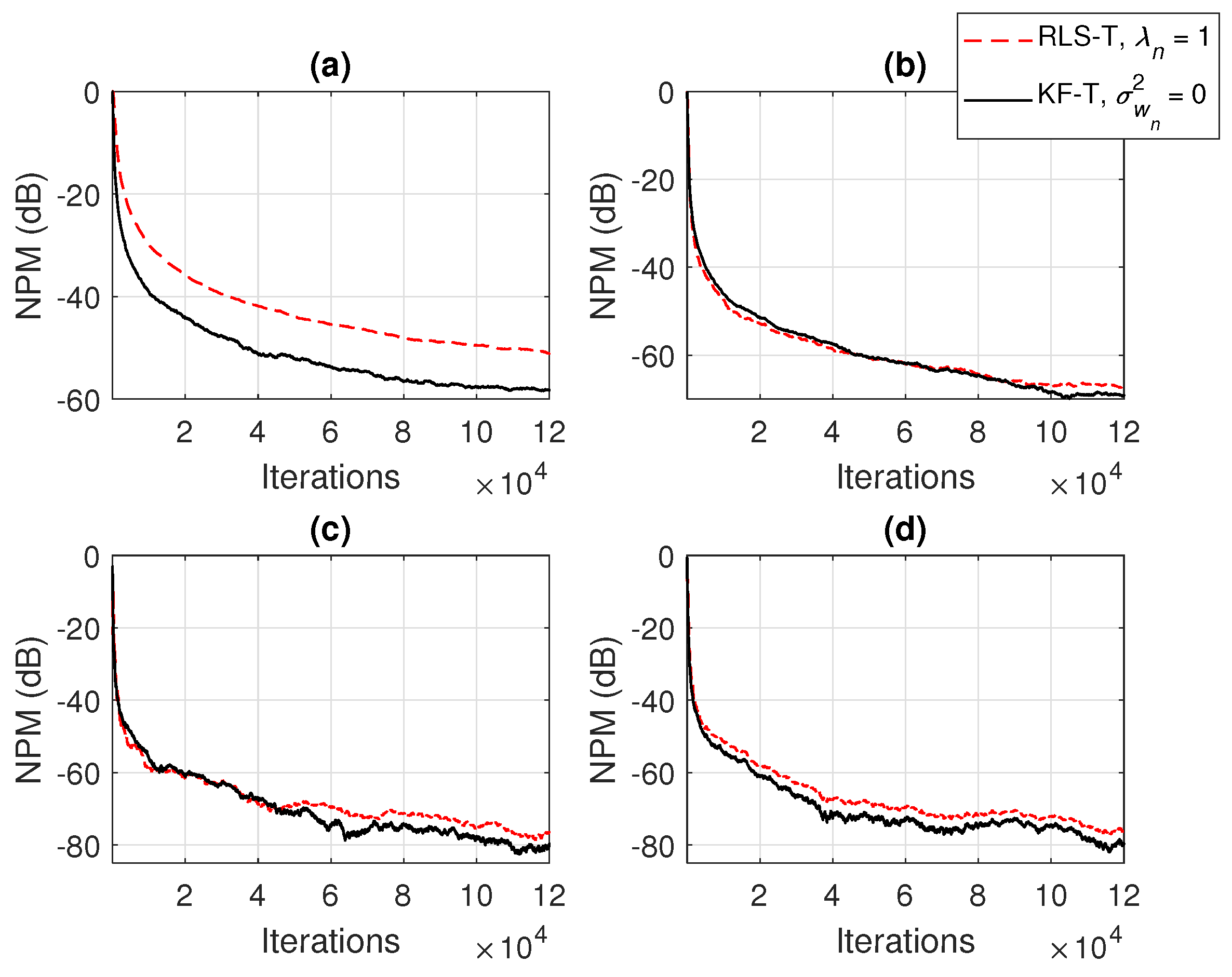
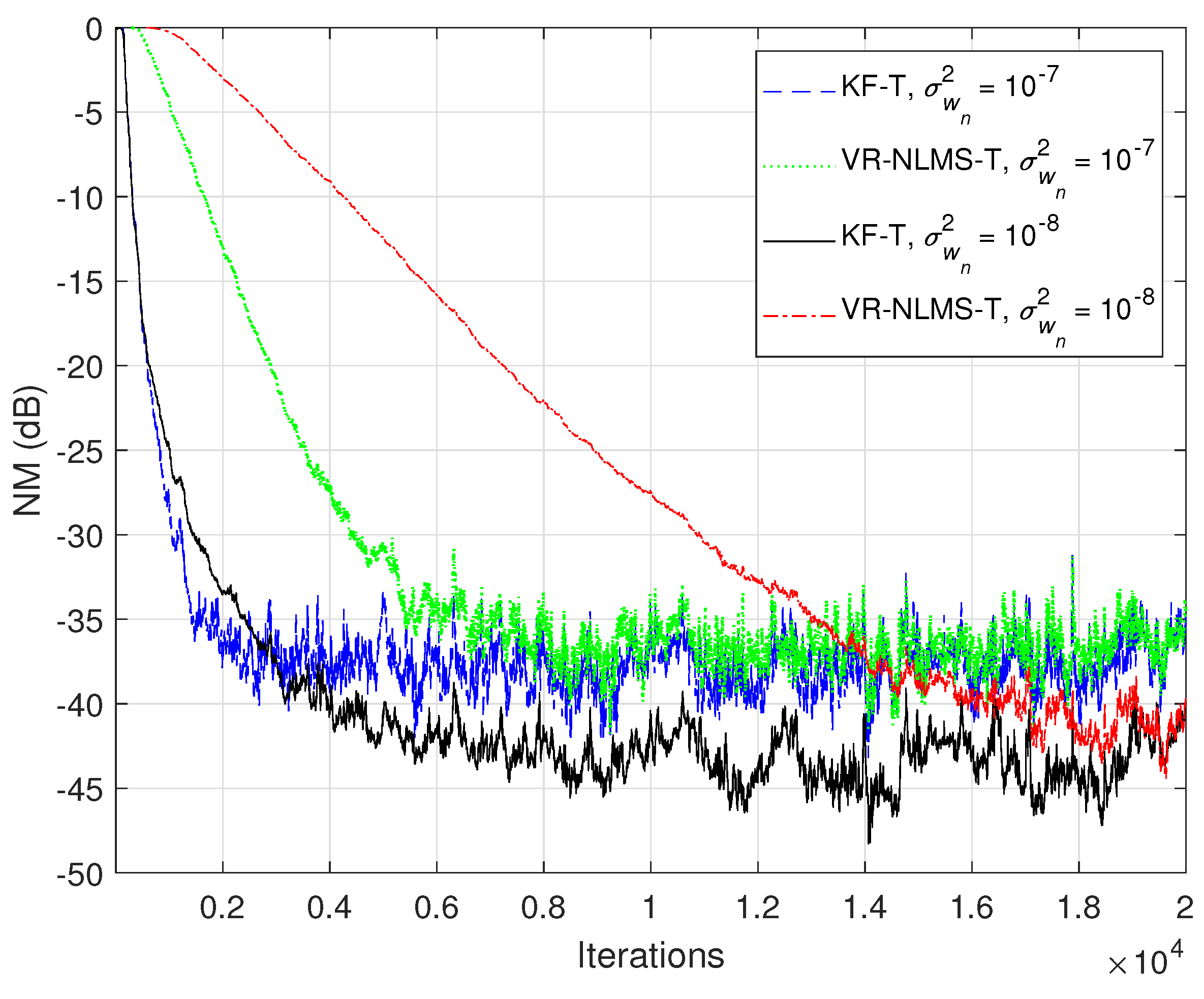
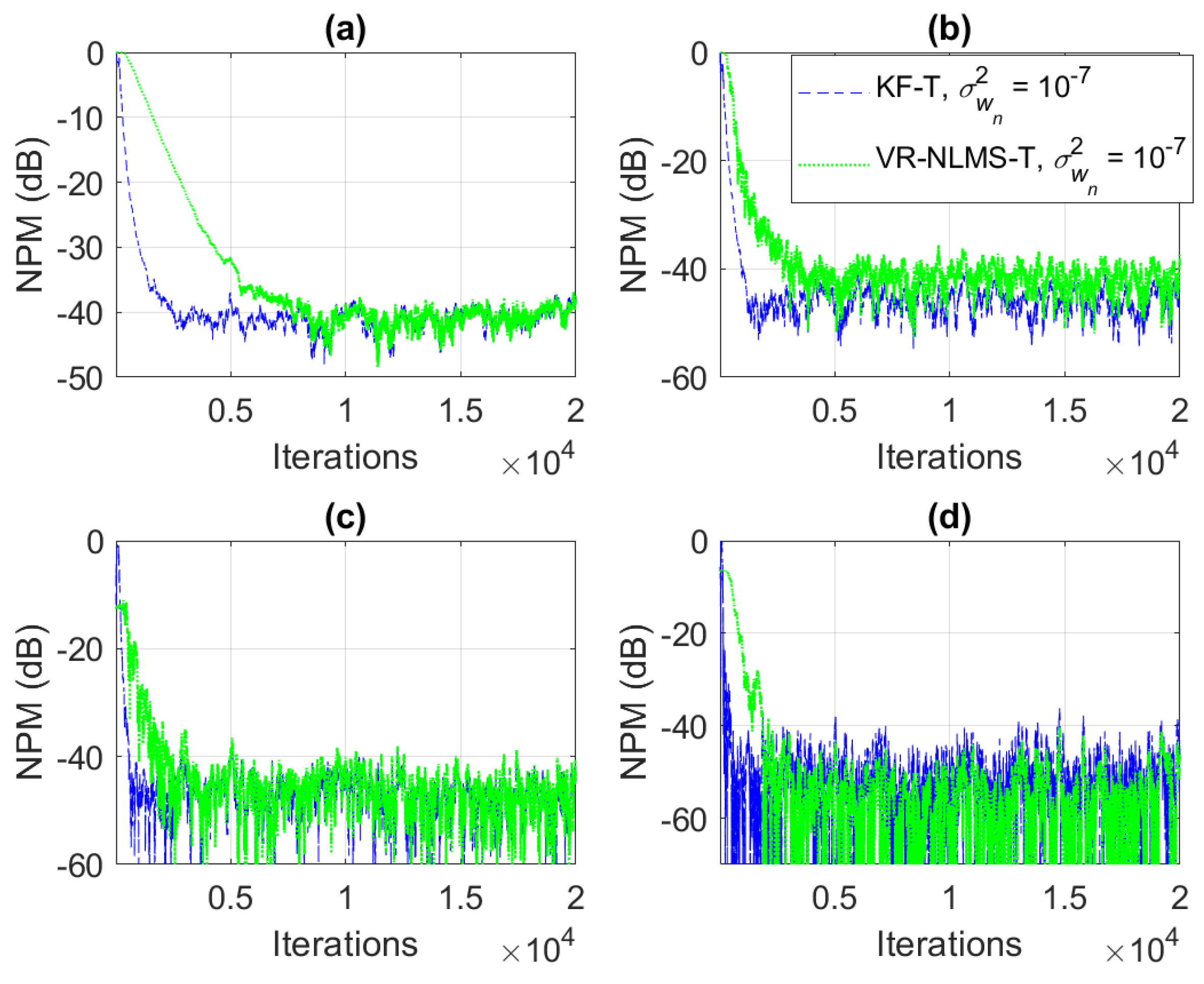
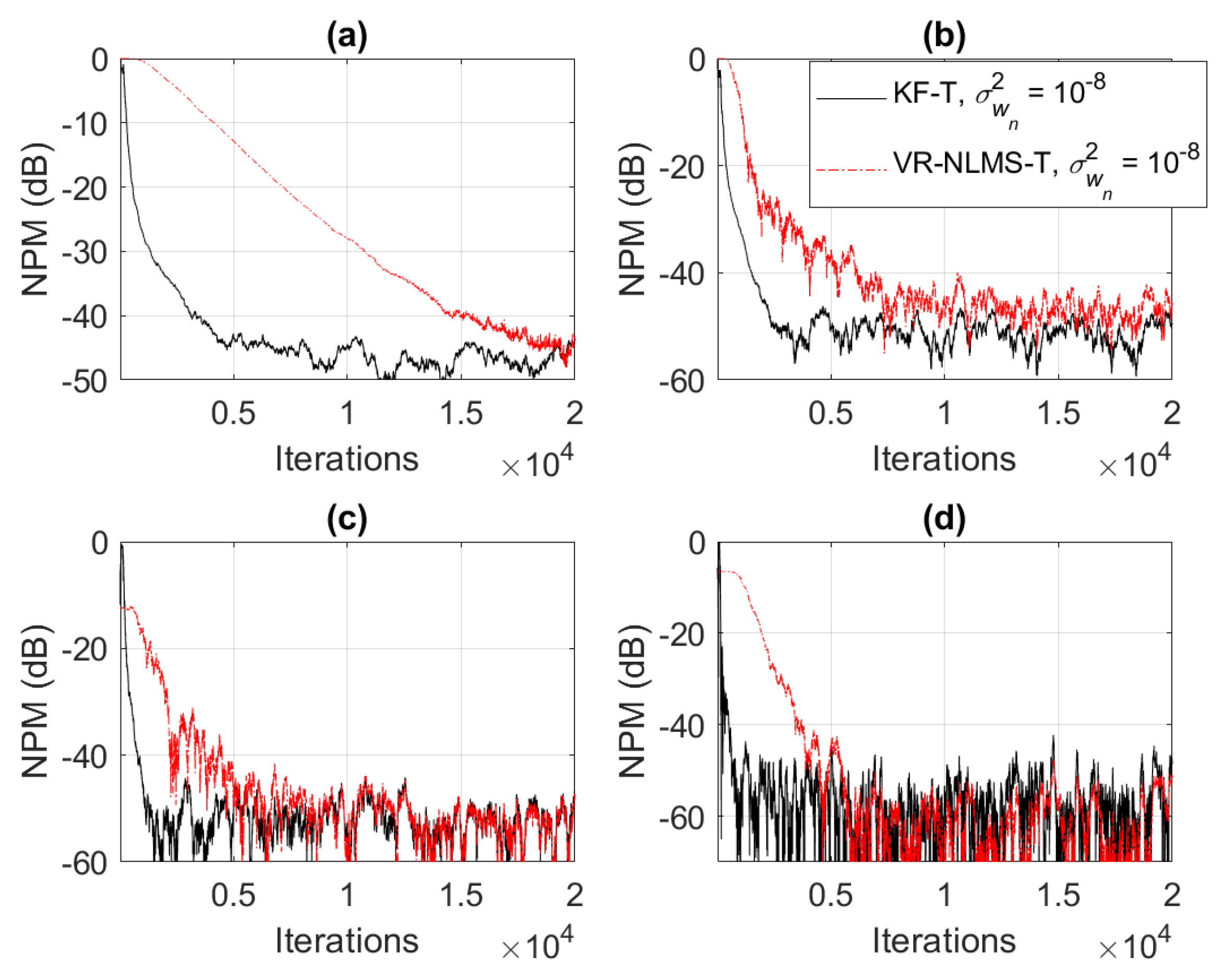
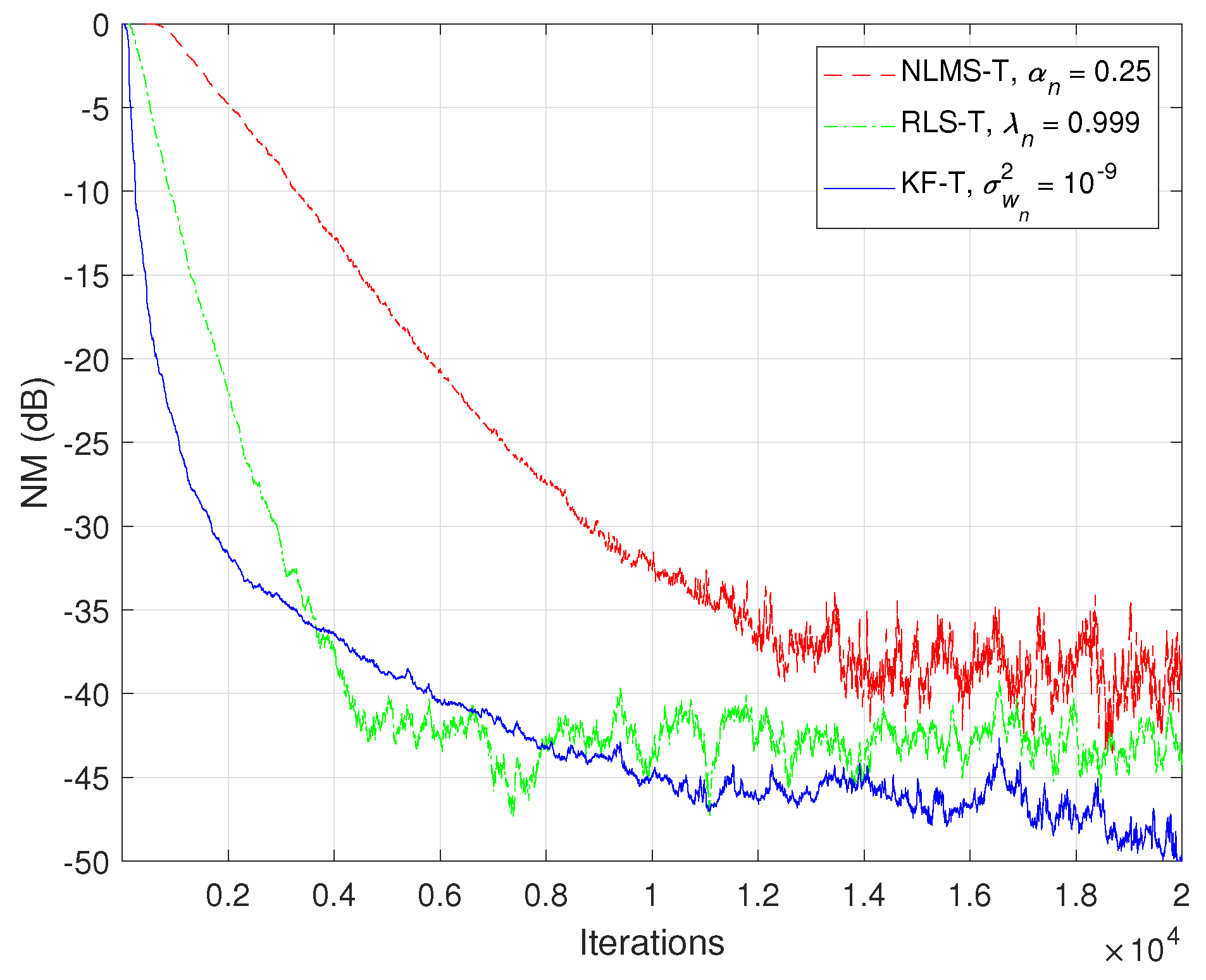
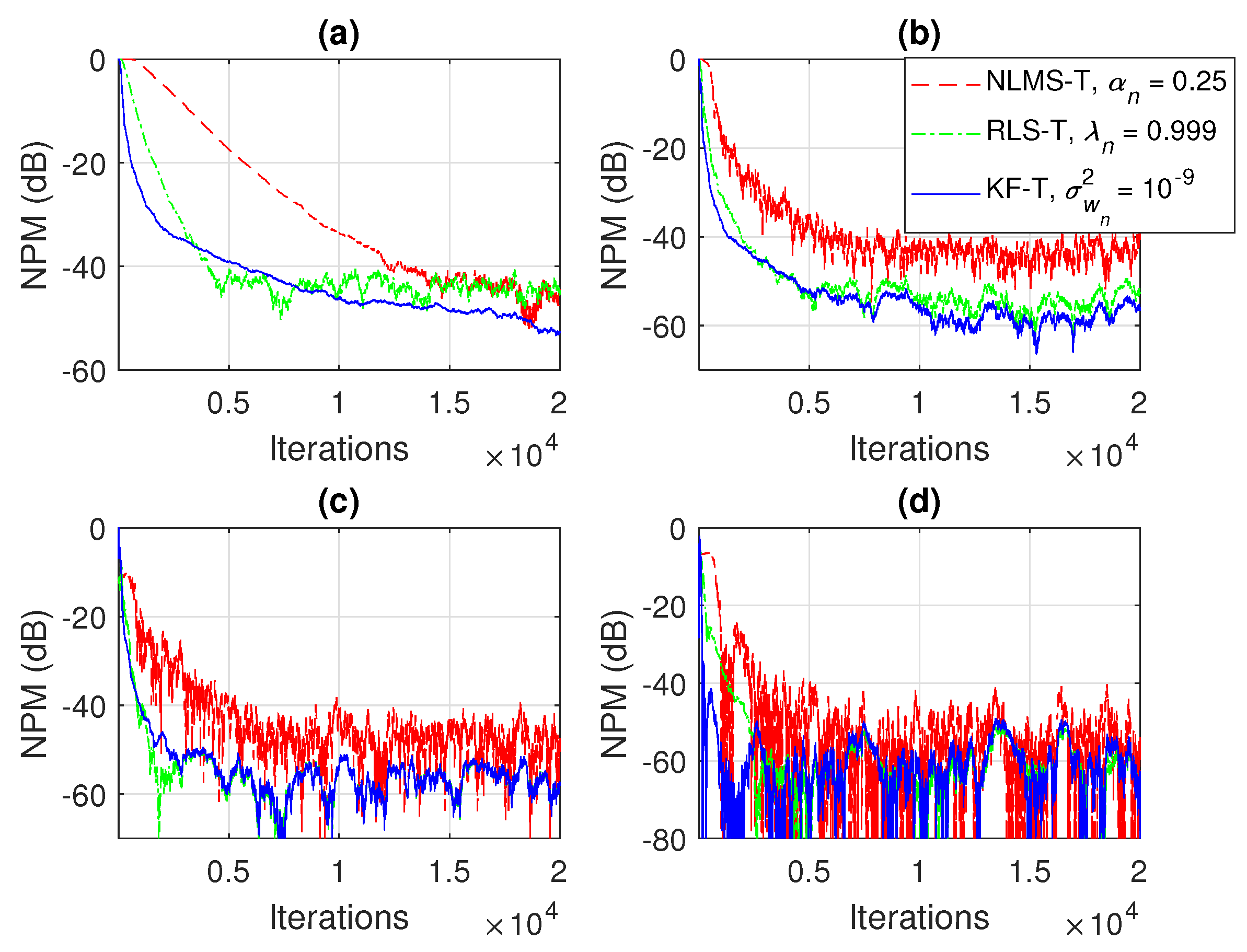
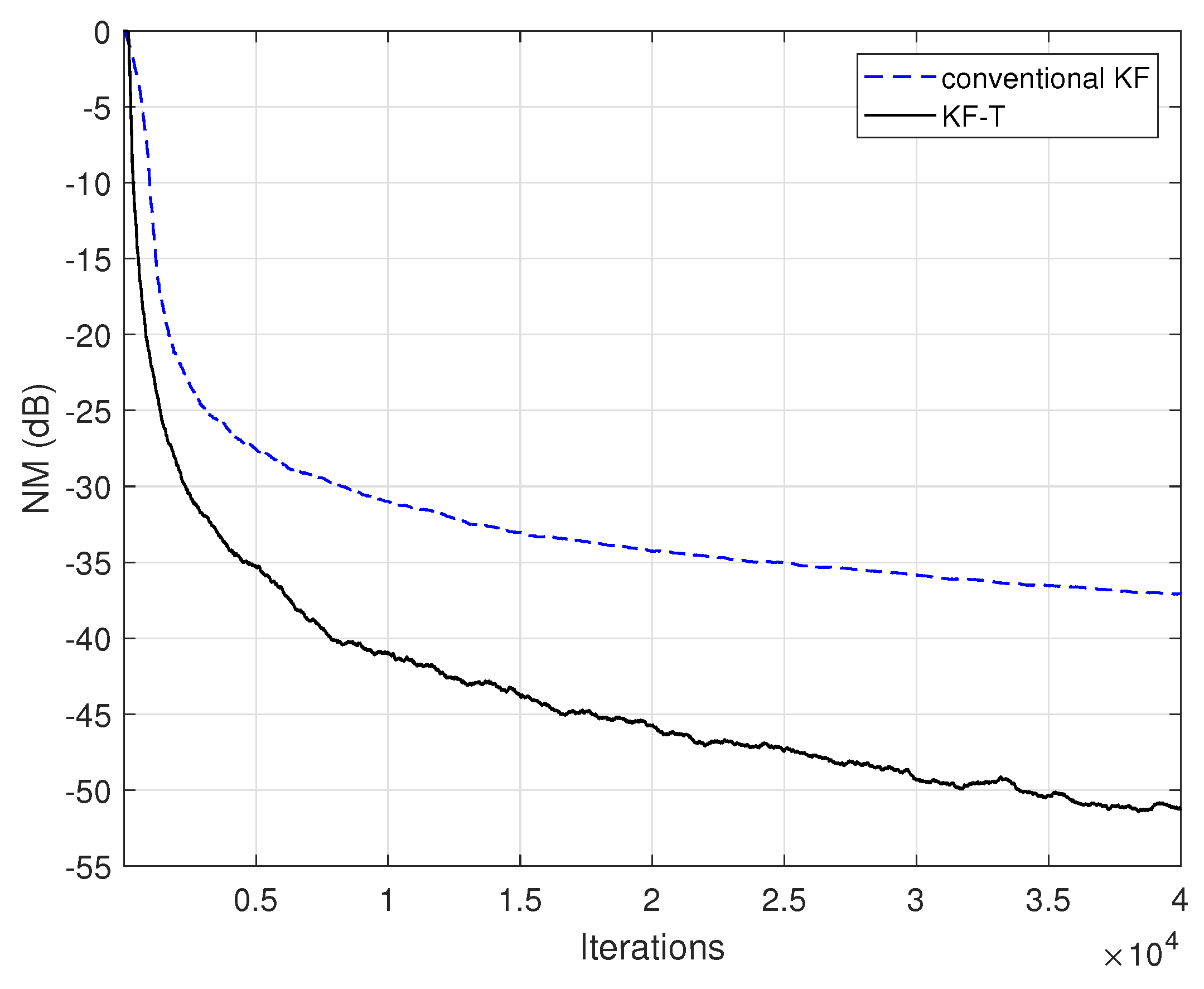
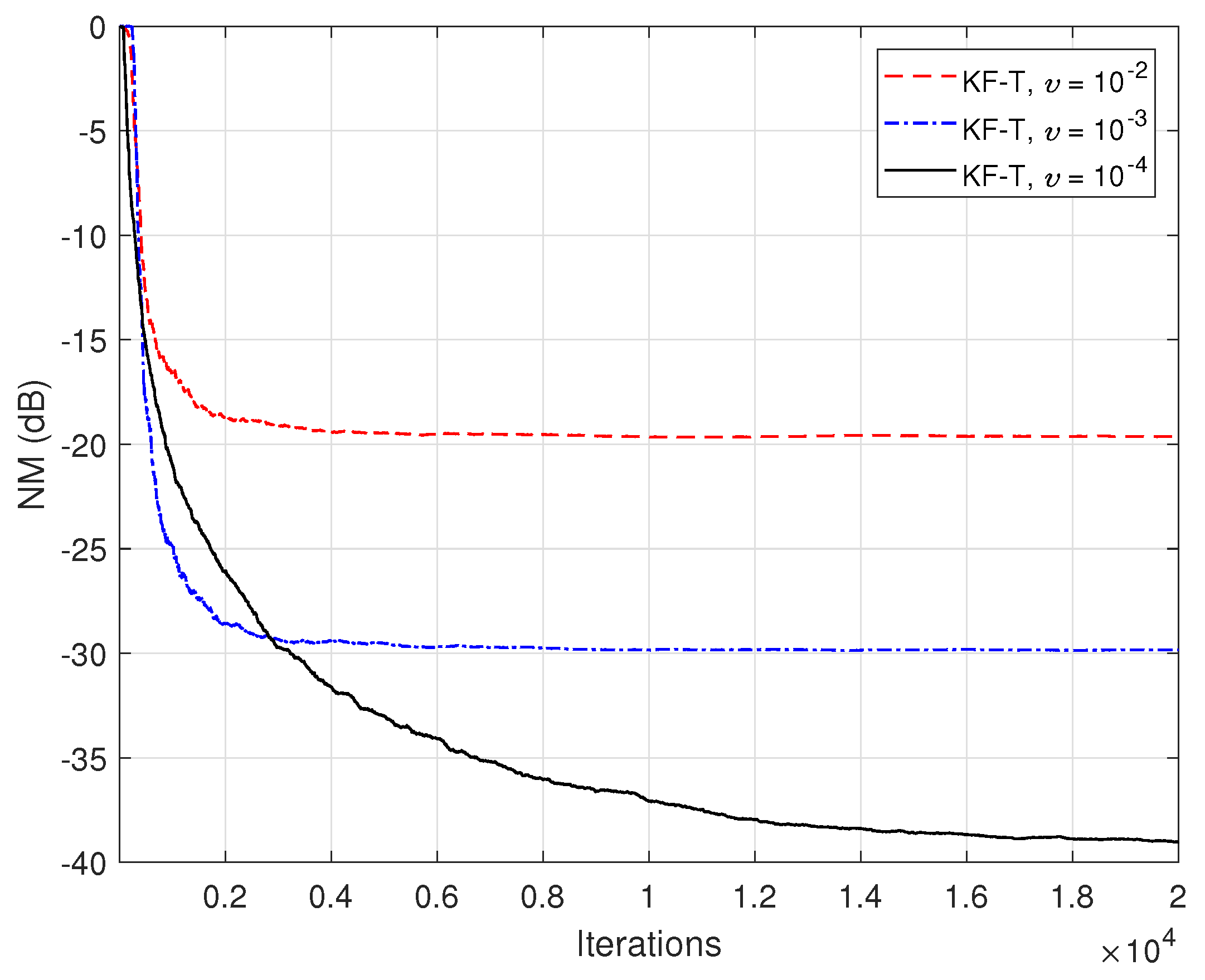
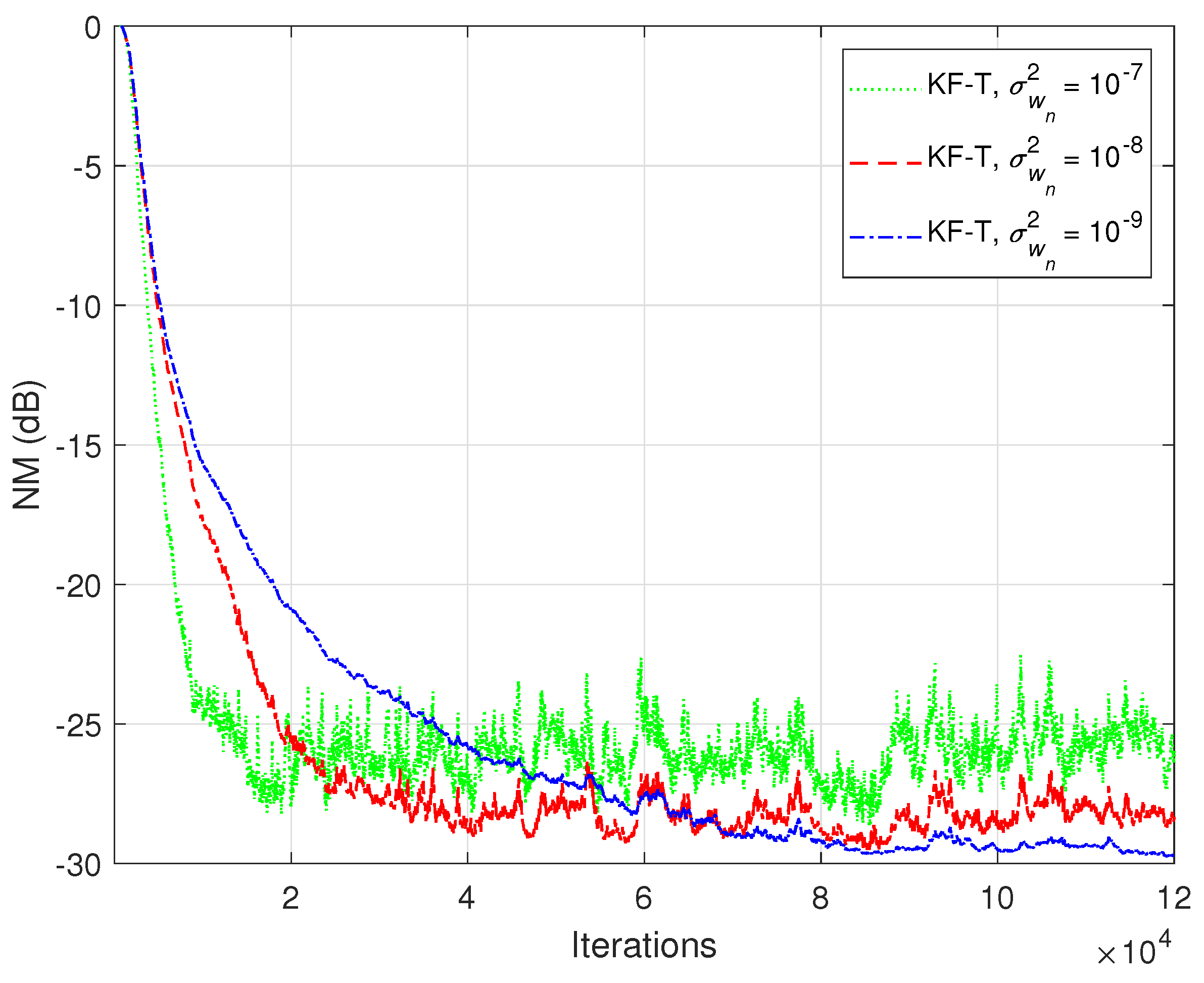
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gesbert, D.; Duhamel, P. Robust blind joint data/channel estimation based on bilinear optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Statistical Signal and Array Processing (WSSAP), Corfu, Greece, 24–26 June 1996; pp. 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, L.N.; Schwarz, S.; Rupp, M.; de Almeida, A.L.F.; Mota, J.C.M. A low-complexity equalizer for massive MIMO systems based on array separability. In Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Kos, Greece, 28 August–2 September 2017; pp. 2522–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Stenger, A.; Kellermann, W. Adaptation of a memoryless preprocessor for nonlinear acoustic echo cancelling. Signal Process. 2000, 80, 1747–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Skoglund, J.; Luebs, A. Practically efficient nonlinear acoustic echo cancellers using cascaded block RLS and FLMS adaptive filters. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 596–600. [Google Scholar]
- Cichocki, A.; Zdunek, R.; Pan, A.H.; Amari, S. Nonnegative Matrix and Tensor Factorizations: Applications to Exploratory Multiway Data Analysis and Blind Source Separation; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Boussé, M.; Debals, O.; Lathauwer, L.D. A tensor-based method for large-scale blind source separation using segmentation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesty, J.; Cohen, I.; Chen, J. Array Processing–Kronecker Product Beamforming; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, L.N.; de Almeida, A.L.F.; Mota, J.C.M. Separable linearly constrained minimum variance beamformers. Signal Process. 2019, 158, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, M.A.O.; Kim, E. Compositional hierarchical tensor factorization: Representing hierarchical intrinsic and extrinsic causal factors. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; 9p. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilescu, M.A.O.; Kim, E.; Zeng, X.S. CausalX: Causal eXplanations and block multilinear factor analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2020; 8p. [Google Scholar]
- Vervliet, N.; Debals, O.; Sorber, L.; Lathauwer, L.D. Breaking the curse of dimensionality using decompositions of incomplete tensors: Tensor-based scientific computing in big data analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, A.; Mandic, D.; Lathauwer, L.D.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, Q.; Caiafa, C.; Phan, A.H. Tensor decompositions for signal processing applications: From two-way to multiway component analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2015, 32, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiropoulos, N.; Lathauwer, L.D.; Fu, X.; Huang, K.; Papalexakis, E.; Faloutsos, C. Tensor decomposition for signal processing and machine learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 3551–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, M.N.; Favier, G.; Romano, J.M.T. Tensor modelling of MIMO communication systems with performance analysis and Kronecker receivers. Signal Process. 2018, 145, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.M.; Morgan, D.R. Active Noise Control Systems: Algorithms and DSP Implementations; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Stoica, P. Robust Adaptive Beamforming; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y. Microphone Array Signal Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Benesty, J.; Paleologu, C.; Ciochină, S. On the identification of bilinear forms with the Wiener filter. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogariu, L.-M.; Ciochină, S.; Benesty, J.; Paleologu, C. System identification based on tensor decompositions: A trilinear approach. Symmetry 2019, 11, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Adaptive Filter Theory, 4th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Benesty, J.; Huang, Y. (Eds.) Adaptive Signal Processing–Applications to Real-World Problems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, P.S.R. Adaptive Filtering: Algorithms and Practical Implementation, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rupp, M.; Schwarz, S. A tensor LMS algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 3347–3351. [Google Scholar]
- Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Ciochină, S. Adaptive filtering for the identification of bilinear forms. Digit. Signal Process. 2018, 75, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisei-Iliescu, C.; Stanciu, C.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Anghel, C.; Ciochină, S. Efficient recursive least-squares algorithms for the identification of bilinear forms. Digit. Signal Process. 2018, 83, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisei-Iliescu, C.; Dogariu, L.-M.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Enescu, A.A.; Ciochină, S. A recursive least-squares algorithm for the identification of trilinear forms. Algorithms 2020, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogariu, L.; Paleologu, C.; Ciochină, S.; Benesty, J.; Piantanida, P. Identification of bilinear forms with the Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4134–4138. [Google Scholar]
- Dogariu, L.-M.; Ciochină, S.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J. A connection between the Kalman filter and an optimized LMS algorithm for bilinear forms. Algorithms 2018, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.H.; Kailath, T. A state-space approach to adaptive RLS filtering. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1994, 11, 18–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faragher, R. Understanding the basis of the Kalman filter via a simple and intuitive derivation. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Ciochină, S. Study of the general Kalman filter for echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2013, 21, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, H.; Enzner, G.; Sezgin, A. State-space adaptive nonlinear self-interference cancellation for full-duplex communication. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 2810–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogariu, L.-M.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Ciochină, S. An efficient Kalman filter for the identification of low-rank systems. Signal Process. 2020, 166, 107239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, H.; Han, S. Multiple linear regression with Kalman filter for predicting end prices of online auctions. In Proceedings of the IEEE DASC/PiCom/CBDCom/CyberSciTech, Calgary, AB, Canada, 17–22 August 2020; pp. 182–191. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, C.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Z. Multi-fading factor and updated monitoring strategy adaptive Kalman filter-based variational Bayesian. Sensors 2021, 21, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Robust SCKF filtering method for MINS/GPS in-motion alignment. Sensors 2021, 21, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogariu, L.-M.; Ciochină, S.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Oprea, C. An iterative Wiener filter for the identification of multilinear forms. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Milan, Italy, 7–9 July 2020; pp. 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Dogariu, L.-M.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Oprea, C.; Ciochină, S. LMS algorithms for multilinear forms. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Electronics and Telecommunications (ISETC), Timişoara, Romania, 5–6 November 2020; 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Dogariu, L.-M.; Stanciu, C.L.; Elisei-Iliescu, C.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Ciochină, S. Tensor-based adaptive filtering algorithms. Symmetry 2021, 13, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsekas, D.P. Nonlinear Programming, 2nd ed.; Athena Scientific: Belmont, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Loan, C.F.V. The ubiquitous Kronecker product. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2000, 123, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.M. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing, Volume I: Estimation Theory; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ciochină, S.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Enescu, A.A. On the influence of the forgetting factor of the RLS adaptive filter in system identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Signals, Circuits and Systems (ISSCS), Iaşi, Romania, 9–10 July 2009; pp. 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Digital Network Echo Cancellers; ITU-T Recommendations G.168; ITU: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- Iqbal, M.A.; Grant, S.L. Novel variable step size NLMS algorithm for echo cancellation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March–4 April 2008; pp. 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Paleologu, C.; Ciochină, S.; Benesty, J. Double-talk robust VSSNLMS algorithm for under-modeling acoustic echo cancellation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March–4 April 2008; pp. 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, D.R.; Benesty, J.; Sondhi, M.M. On the evaluation of estimated impulse responses. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1998, 5, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dogariu, L.-M.; Paleologu, C.; Benesty, J.; Stanciu, C.-L.; Oprea, C.-C.; Ciochină, S. A Kalman Filter for Multilinear Forms and Its Connection with Tensorial Adaptive Filters. Sensors 2021, 21, 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103555
Dogariu L-M, Paleologu C, Benesty J, Stanciu C-L, Oprea C-C, Ciochină S. A Kalman Filter for Multilinear Forms and Its Connection with Tensorial Adaptive Filters. Sensors. 2021; 21(10):3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103555
Chicago/Turabian StyleDogariu, Laura-Maria, Constantin Paleologu, Jacob Benesty, Cristian-Lucian Stanciu, Claudia-Cristina Oprea, and Silviu Ciochină. 2021. "A Kalman Filter for Multilinear Forms and Its Connection with Tensorial Adaptive Filters" Sensors 21, no. 10: 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103555
APA StyleDogariu, L.-M., Paleologu, C., Benesty, J., Stanciu, C.-L., Oprea, C.-C., & Ciochină, S. (2021). A Kalman Filter for Multilinear Forms and Its Connection with Tensorial Adaptive Filters. Sensors, 21(10), 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103555









