Piezoceramic-Based Damage Monitoring of Concrete Structure for Underwater Blasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Damage Detection of Rock and Concrete Materials
2. Detection Principle
2.1. Piezoelectric Transducers and Active Sensing Based on Piezoelectric Transducer
2.2. Piezoceramic Transducers
2.3. Piezoceramic-Enabled Active Sensing
2.4. Proposed Blasting-Damage Index
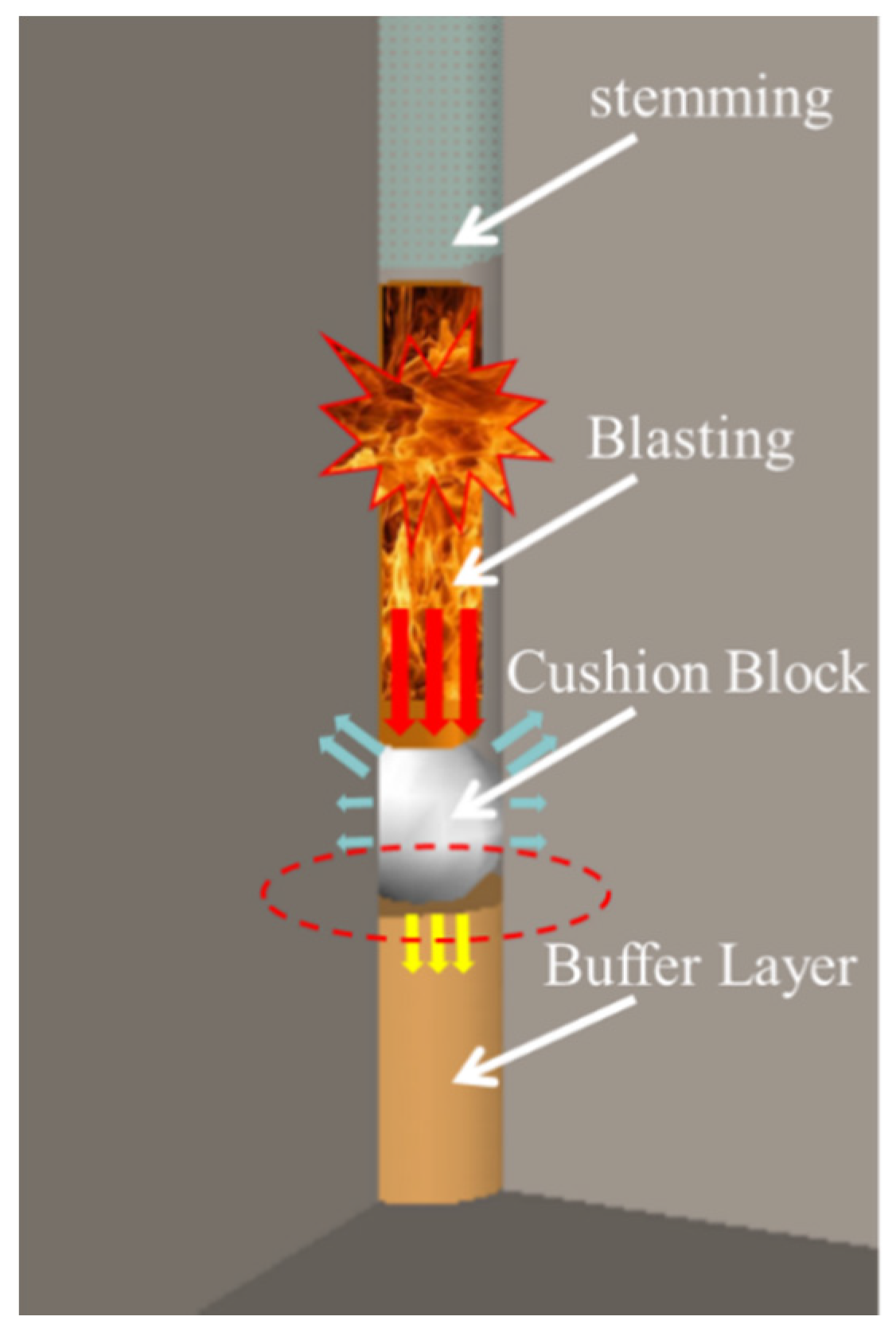
3. Experiment Setup and Procedure
3.1. Specimens
3.2. Experiment Setup
3.3. Experiment Procedure
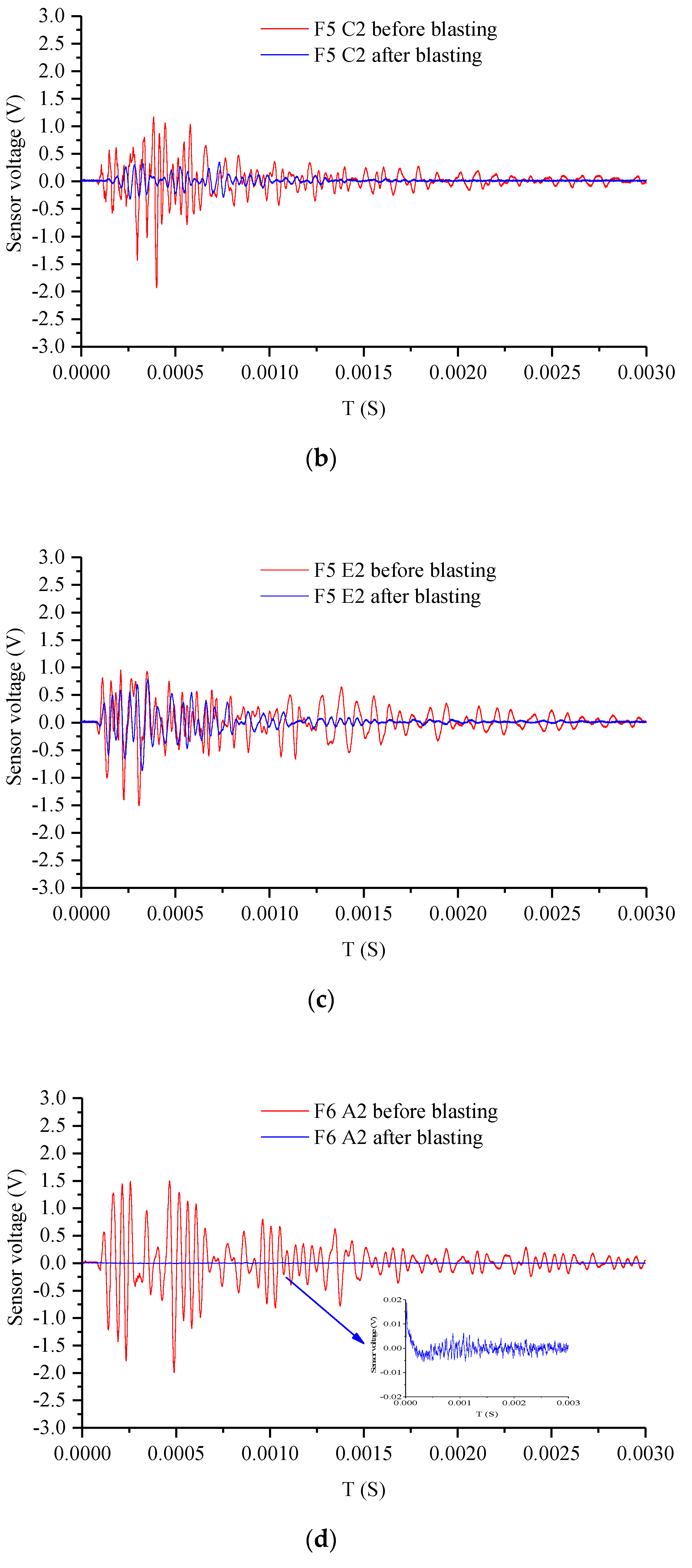
4. Experiment Results and Analysis
5. Conclusion
- piezoelectric-transducer-based active-sensing technology can effectively identify the blasting damage of concrete materials with sensitivity to the degree and depth of damage;
- piezoelectric-signal analysis before and after blasting showed that an energy-relieving structure protects the rock mass below the blast hole in underwater drilling and blasting; and
- protective energy-relieving structures can be used in underwater-foundation excavation engineering to mitigate the effects of blasting damage on the surface of the underwater foundation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Dong, J.; Chen, J. Geomechanical model test on dam stability and application to Jinping High arch dam. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2015, 76, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.X.; Zhang, Q.B.; Gu, J.C. Damage evolution mechanism in production blasting excavation under different stress fields. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory. 2019, 97, 101969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, G.; Lu, W.; Yan, P.; Chen, M. Damage assessment and mitigation measures of underwater tunnel subjected to blast loads. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 94, 103131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, Q.; Li, G. Study on deformation and control measures of columnar jointed basalt for Baihetan super-high arch dam foundation. Rock Mech Rock Eng. 2019, 51, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, H.; Dong, G. A Preliminary Study on the Design Method for Large-Diameter Deep-Hole Presplit Blasting and its Vibration-Isolation Effect. Shock Vib. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Yoon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y. Evaluation of Condition of Concrete Structures Using Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchev, I.; Slavchev, V. About the Possible Limitations in the Usage of the Non-Destructive Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Method for Assessment of Cracks in Reinforced Concrete Structures, Subjected to Direct Environmental Exposure. Buildings 2019, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sossa, V.; Pérez-Gracia, V.; González-Drigo, R.; A Rasol, M. Lab Non Destructive Test to Analyze the Effect of Corrosion on Ground Penetrating Radar Scans. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, I.; Abdel-Jaber, H.; Glisic, B. Quantitative attribute analyses with ground penetrating radar for infrastructure assessments and structural health monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, T.; Svecova, D.; Cha, Y.J. Semi-Automated Air-Coupled Impact-Echo Method for Large-Scale Parkade Structure. Sensors 2018, 18, 1018. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Y. Repeated penetration and different depth explosion of ultra-high performance concrete. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 84, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Yan, P.; Chen, M.; Yang, J. A method to identify blasting-induced damage zones in rock masses based on the P-wave rise time. Geotech. Test. J. 2017, 41, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldas, G.U.; Kadioglu, S.; Ulugergerli, E. The usage of ground penetrating radar (GPR) in designing blast pattern. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2006, 39, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, M.; Keuser, M. Reinforced Concrete after accidental loading-damage assessment using non-destructive echo techniques. BAUINGENIEUR 2008, 83, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Tashakori, S.; Baghalian, A.; Unal, M.; Fekrmandi, H.; McDaniel, D.; Tansel, I.N. Contact and noncontact approaches in load monitoring applications using surface response to excitation method. Measurement 2016, 89, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakori, S.; Baghalian, A.; Senyurek, V.Y.; Unal, M.; McDaniel, D.; Tansel, I.N. Implementation of heterodyning effect for monitoring the health of adhesively bonded and fastened composite joints. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2018, 72, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Peng, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Cai, C.S. Comparative assessment of mechanical properties of HPS between electrochemical corrosion and spray corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, J.; Cai, C.S.; Wang, L. Flexural behavior of corroded HPS beams. Eng. Struct. 2019, 195, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolandi, H.; Lajnef, N.; Jiao, P.; Barri, K.; Hasni, H.; Alavi, A.H. A Novel Data Reduction Approach for Structural Health Monitoring Systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenthal, G.; Eick, J.F.; Rau, S.; Taraben, J. Wireless Sensor Networks Composed of Standard Microcomputers and Smartphones for Applications in Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Robert, R.; Silva, P.; Mo, Y. Cyclic crack monitoring of a reinforced concrete column under simulated pseudo-dynamic loading using piezo-based smart aggregates. App. Sci. 2016, 6, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ho, S.C.M.; Song, G. Modeling and analysis of an impact-acoustic method for bolt looseness identification. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2019, 133, 106249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Ding, Z.; Wang, N.; Pan, M.; Song, G. A Novel Waveform Optimization Scheme for Piezoelectric Sensors Wire-Free Charging in the Tightly Insulated Environment. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1936–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, B.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Song, G. Investigation of bonding behavior of FRP and steel bars in self-compacting concrete structures using acoustic emission method. Sensors 2019, 19, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yin, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, L. Debonding Detection of Reinforced Concrete (RC) Beam with Near-Surface Mounted (NSM) Pre-stressed Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Plates Using Embedded Piezoceramic Smart Aggregates (SAs). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Parvasi, S.M.; Ho, S.C.M.; Franchek, M.; Song, G. Wireless energy harvesting using time reversal technique: An experimental study with numerical verification. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 2705–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ji, Q.; Chen, S.; Song, G. An experimental study of ultra-low power wireless sensor-based autonomous energy harvesting system. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2017, 9, 054702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, V.; Franchek, M.A.; Song, G. Active multimodal vibration suppression of a flexible structure with piezoceramic sensor and actuator by using loop shaping. J. Vib. Control. 2011, 17, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; He, S.; Ren, Y.; Wang, N.; Ho, S.C.M.; Song, G. Design of a new stress wave-based pulse position modulation (PPM) communication system with piezoceramic transducers. Sensors 2019, 19, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Yu, N.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, K.; Zhou, S. Scavenging vibrational energy with a novel bistable electromagnetic energy harvester. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 025022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Olmi, C.; Gu, H. An overeight vehicle-bridge collision monitoring system using piezoelectric transducers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; Ho, S.C.M. A review of rock bolt monitoring using smart sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huo, L.; Liu, C.; Song, G. Wear Degree Quantification of Pin Connections Using Parameter-Based Analyses of Acoustic Emissions. Sensors 2018, 18, 3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.C.; Wang, Q.H.; Liu, X.; Wang, W. Predicting the Loose Zone of Roadway Surrounding Rock Using Wavelet Relevance Vector Machine. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ho, S.C.M.; Patil, D.; Song, G. Acoustic emission monitoring and finite element analysis of debonding in fiber-reinforced polymer rebar reinforced concrete. Struct. Health Monit. 2017, 16, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, Y.; Song, G.; Chen, D.; Ye, Y. Identification of the structural damage mechanism of BFRP bars reinforced concrete beams using smart transducers based on time reversal method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 220, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.C.; Ho, D.D.; Dang, N.L.; Kim, J.T. Sensor Fault Diagnosis for Impedance Monitoring Using a Piezoelectric-Based Smart Interface Technique. Sensors 2020, 20, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Sohn, H.; Farrar, C.R.; Inman, D.J. Overview of Piezoelectric Impedance-Based Health Monitoring and Path Forward. Shock. Vib. Digest 2003, 35, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Gu, H.; Mo, Y.L. Smart aggregates: Multi-functional sensors for concrete structures—a tutorial and a review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Haider, M.F.; Joseph, R.; Migot, A.; Giurgiutiu, V. Recent advances in piezoelectric wafer active sensors for structural health monitoring applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoco, H.A.; Cardona, C.I.; Peña, F.M.; Gomez, J.P.; Roldan-Restrepo, S.I.; Velasco-Mejia, M.A.; Barco, D.R. Evaluation of a piezo-actuated sensor for monitoring elastic variations of its support with impedance-based measurements. Sensors 2019, 19, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ahmad, S.; Yun, C.B.; Roh, Y. Multiple crack detection of concrete structures using impedance-based structural health monitoring techniques. Exp. Mech. 2006, 46, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Li, C.; Jiang, T.; Li, H.N. Feasibility study of steel bar corrosion monitoring using a piezoceramic transducer enabled time reversal method. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ho, S.C.M.; Song, G. Monitoring of early looseness of multi-bolt connection: A new entropy-based active sensing method without saturation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 10LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Song, G. Monitoring of multi-bolt connection looseness using entropy-based active sensing and genetic algorithm-based least square support vector machine. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2020, 136, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y. A feasibility study on timber damage detection using piezoceramic-transducer-enabled active sensing. Sensors 2018, 18, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Song, G.; Dhonde, H. Concrete early-age strength monitoring using embedded piezoelectric transducers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Gu, H.; Mo, Y.L. Concrete Structural Health Monitoring Using Embedded Piezoceramic Transducers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.K.; Tareen, N.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Park, I. Real-time strength monitoring for concrete structures using EMI technique incorporating with fuzzy logic. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, J.W.; Koh, H.M. Evaluation of early-age concrete compressive strength with ultrasonic sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Park, S. Artificial neural network-based early-age concrete strength monitoring using dynamic response signals. Sensors 2017, 17, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, D.; Zhu, H.; Luo, H.; Wang, C. Mechanical impedance based embedded piezoelectric transducer for reinforced concrete structural impact damage detection: A comparative study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ho, S.C.M.; Kong, Q.; Patil, D.; Mo, Y.L.; Song, G. Estimation of impact location on concrete column. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 055037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhao, S.; Qi, B.; Kong, Q. Damage evaluation of concrete column under impact load using a piezoelectric-based EMI technique. Sensors 2018, 18, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Moslehy, Y.; Sanders, D. Multi-functional smart aggregate-based structural health monitoring of circular reinforced concrete columns subjected to seismic excitations. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Deng, Q.; Cai, L.; Ho, S.; Song, G. Damage detection of a concrete column subject to blast loads using embedded piezoceramic transducers. Sensors 2018, 18, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, M.; Hei, C.; Song, G. Quantitative Evaluation of Debond in Concrete-filled Steel Tubular Member (CFSTM) Using Piezoceramic Transducers and Ultrasonic Head Wave Amplitude. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 075033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Cheng, H.; Kong, Q.; Chen, X. Bond-slip monitoring of concrete structures using smart sensors—a review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Ren, C.; Deng, Q.; Jin, Q.; Chen, X. Real-time monitoring of bond slip between GFRP bar and concrete structure using piezoceramic transducer-enabled active sensing. Sensors 2018, 18, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Luo, M.; Li, W.; Song, G. Grout compactness monitoring of concrete-filled fiber-reinforced polymer tube using electromechanical impedance. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 055008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Kong, Q.; Wang, W.; Huo, L.; Song, G. Monitoring of grouting compactness in a post-tensioning tendon duct using piezoceramic transducers. Sensors 2016, 16, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kong, Q.; Ho, S.C.M.; Mo, Y.L.; Song, G. Feasibility study of using smart aggregates as embedded acoustic emission sensors for health monitoring of concrete structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.C.; Wang, Q.H.; Liu, X.Y. Stability Prediction Model of Roadway Surrounding Rock Based on Concept Lattice Reduction and a Symmetric Alpha Stable Distribution Probability Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huo, L.; Liu, C.; Peng, Y.; Song, G. Feasibility Study of Real-Time Monitoring of Pin Connection Wear Using Acoustic Emission. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, N.; Zou, G.P.; Taheri, F. Piezoelectric-based degradation assessment of a pipe using Fourier and wavelet analyses. Comput-Aided Civ. Inf. Eng. 2005, 20, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.L.; Hao, H.; Li, Z.X. Application of wavelet packet transform in subsea pipeline bedding condition assessment. Eng. Struct. 2003, 25, 50–65. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.L.; Hao, H.; Li, Z.X.; Fan, K.Q. Experimental study on subsea pipeline bedding condition assessment using wavelet packet transform. Eng. Struct. 2013, 48, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
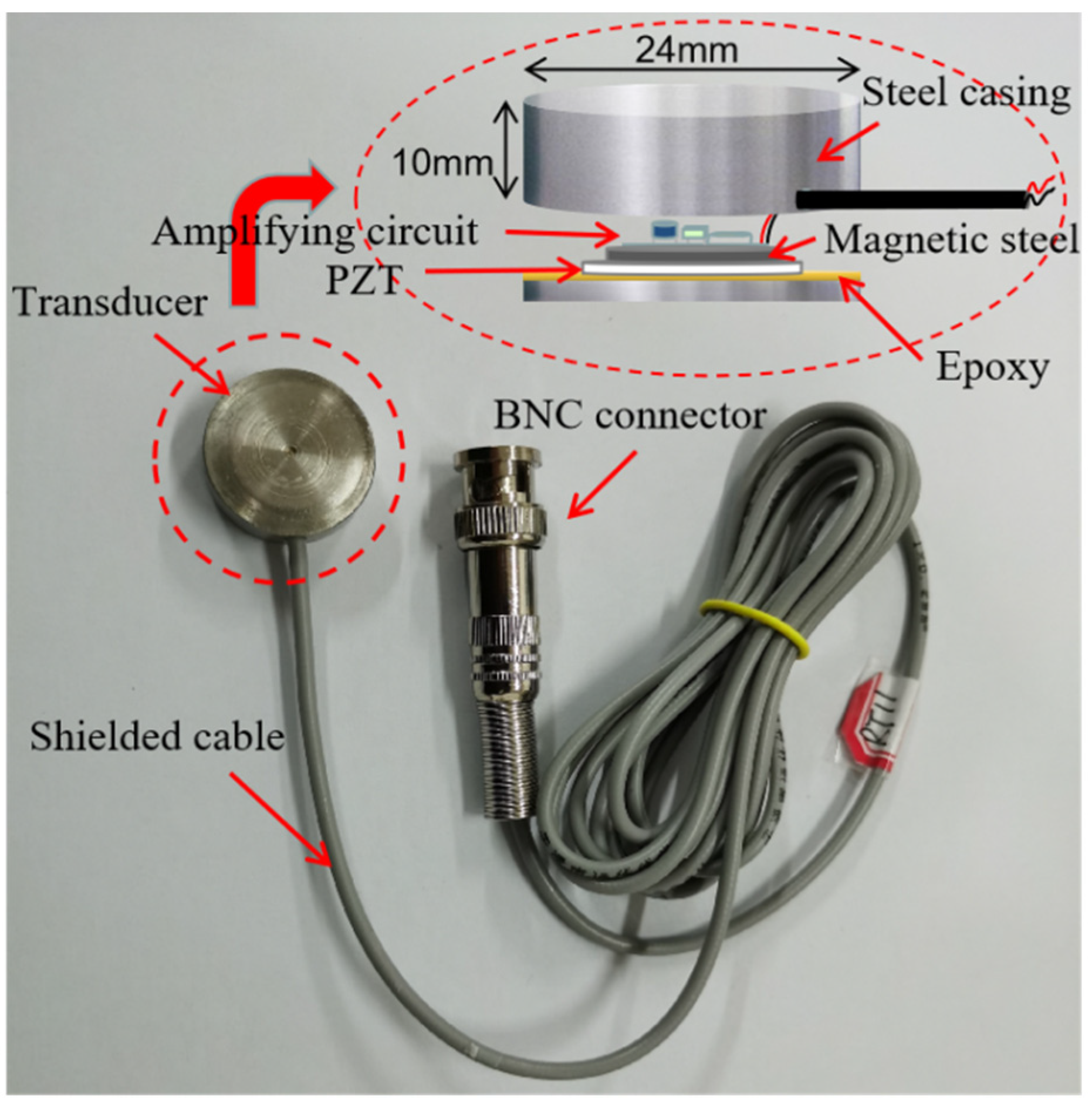














| Density (g/cm3) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete C30 | 2.36 | 1.87 | 21.63 | 27 |
| Group | Sample No. | Charge-Structure Diagram | Charge | Water Depth(m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment specimen | F5 |  | 1 detonator + 2 g PETN | 40 |
| Control specimen | F6 |  | 1 detonator + 2 g PETN | 40 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Si, J.; Zhong, D.; Xiong, W. Piezoceramic-Based Damage Monitoring of Concrete Structure for Underwater Blasting. Sensors 2020, 20, 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061672
Si J, Zhong D, Xiong W. Piezoceramic-Based Damage Monitoring of Concrete Structure for Underwater Blasting. Sensors. 2020; 20(6):1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061672
Chicago/Turabian StyleSi, Jianfeng, Dongwang Zhong, and Wei Xiong. 2020. "Piezoceramic-Based Damage Monitoring of Concrete Structure for Underwater Blasting" Sensors 20, no. 6: 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061672
APA StyleSi, J., Zhong, D., & Xiong, W. (2020). Piezoceramic-Based Damage Monitoring of Concrete Structure for Underwater Blasting. Sensors, 20(6), 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061672




