An Enhanced Dynamic Simulation Model of a Hybrid Magnetic Bearing Taking Account of the Sensor Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
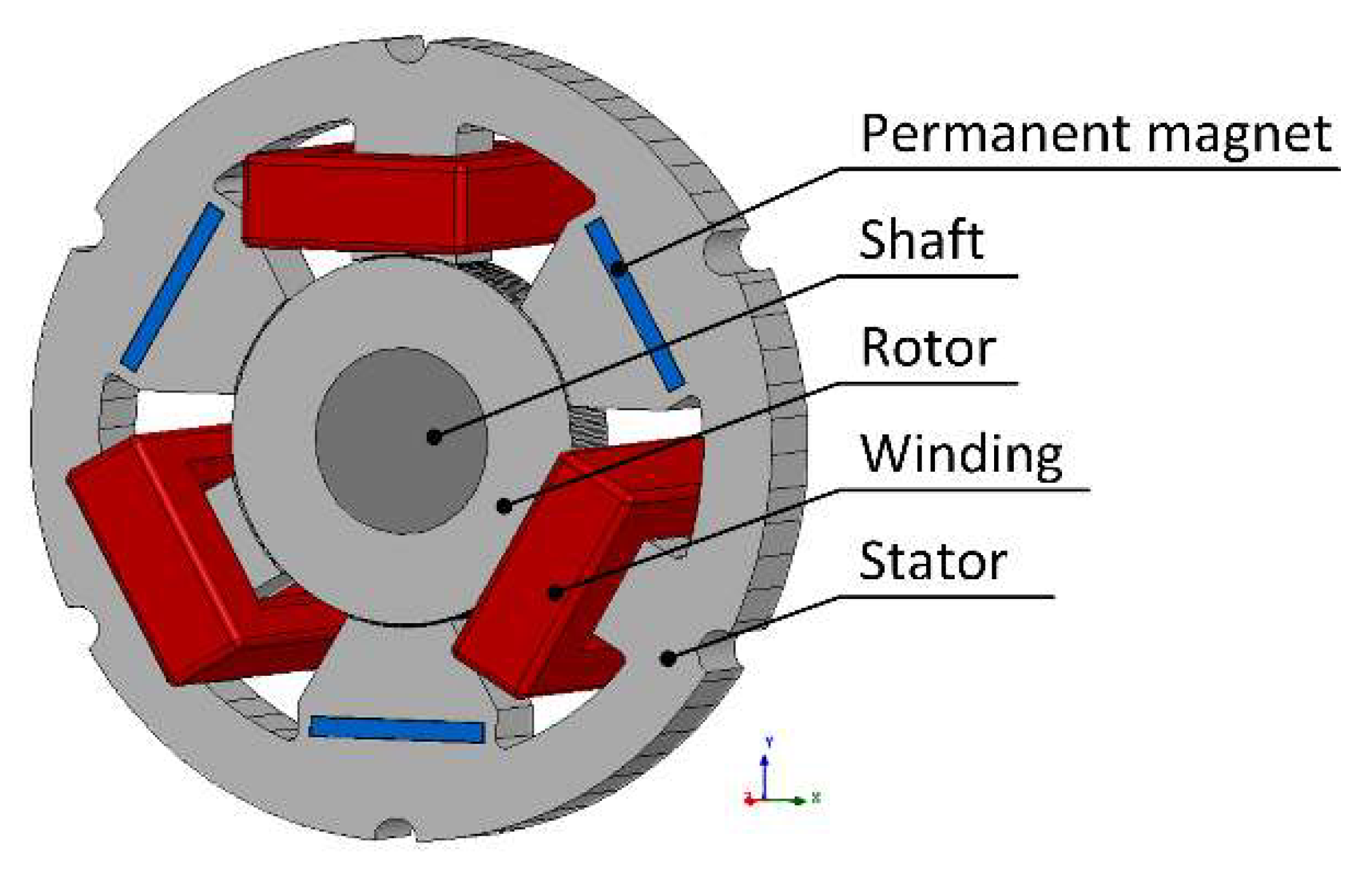
2. Description of the Hybrid Magnetic Bearing
3. The dynamic simulation model of the HMB
3.1. Equations for the Dynamic Simulation Model
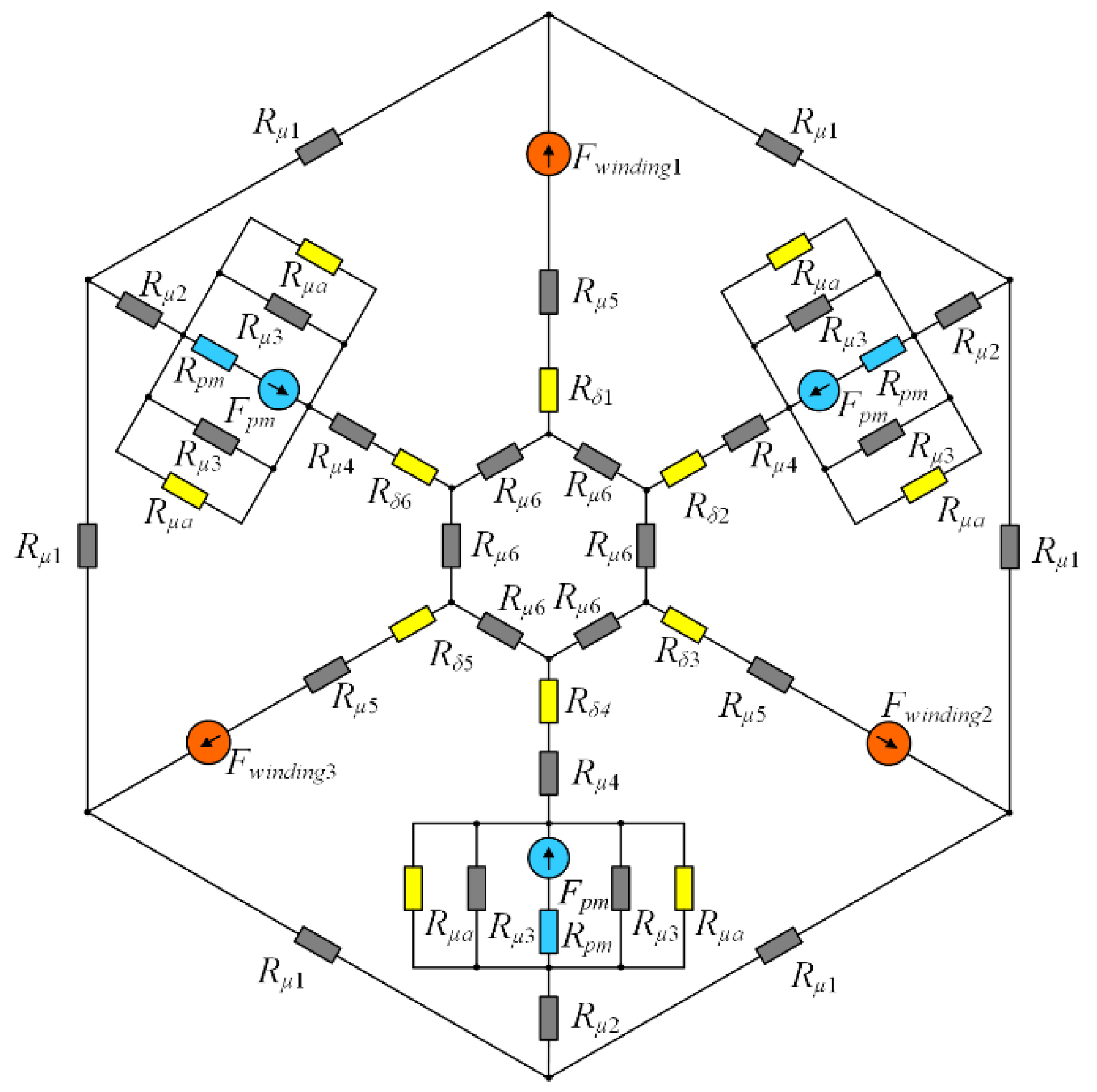
3.2. The Nonlinear Magnetic Equivalent Circuit of the HMB
3.3. Description of the Control System
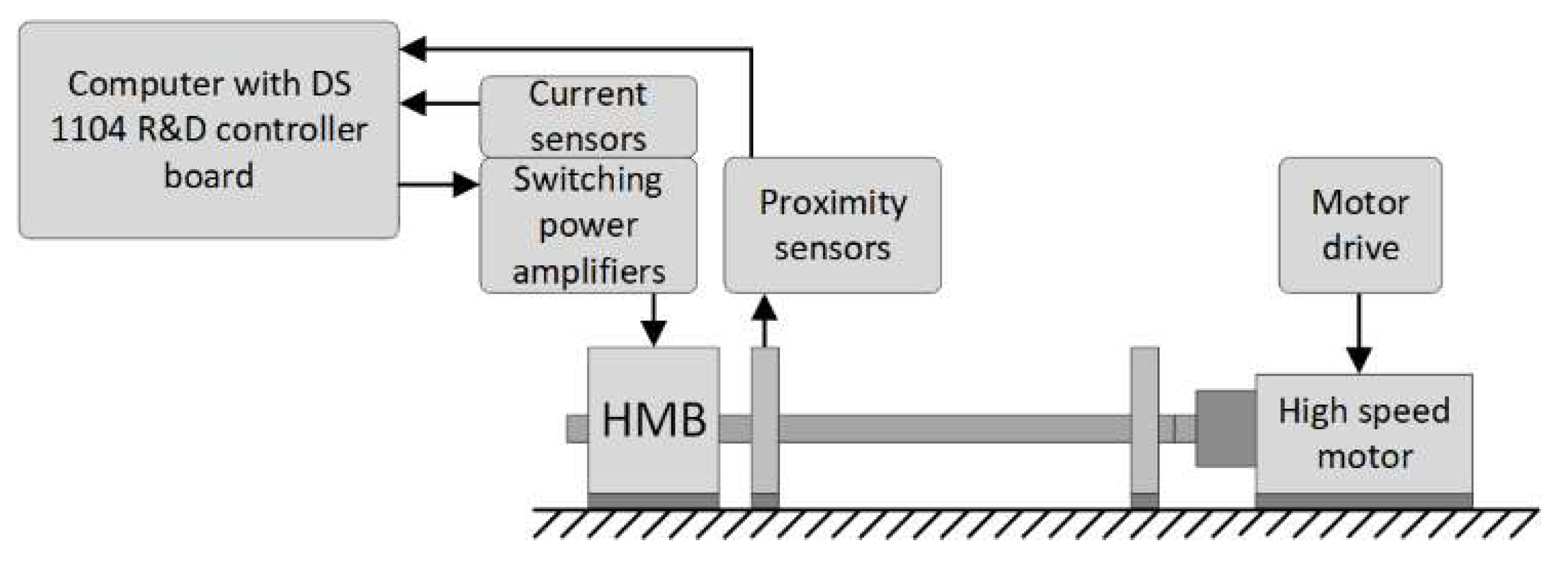
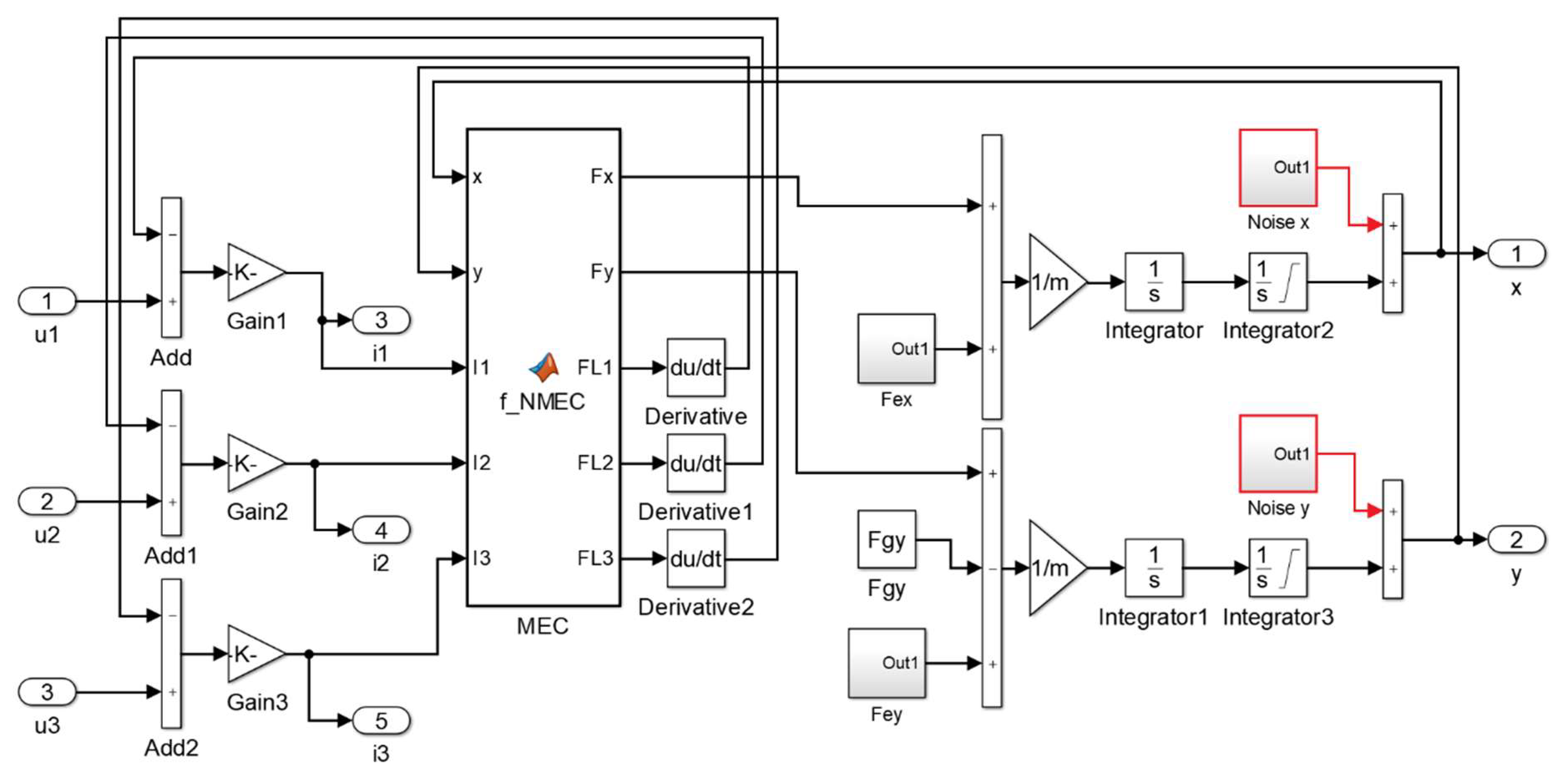
3.4. Implementation of the Dynamic Simulation Model
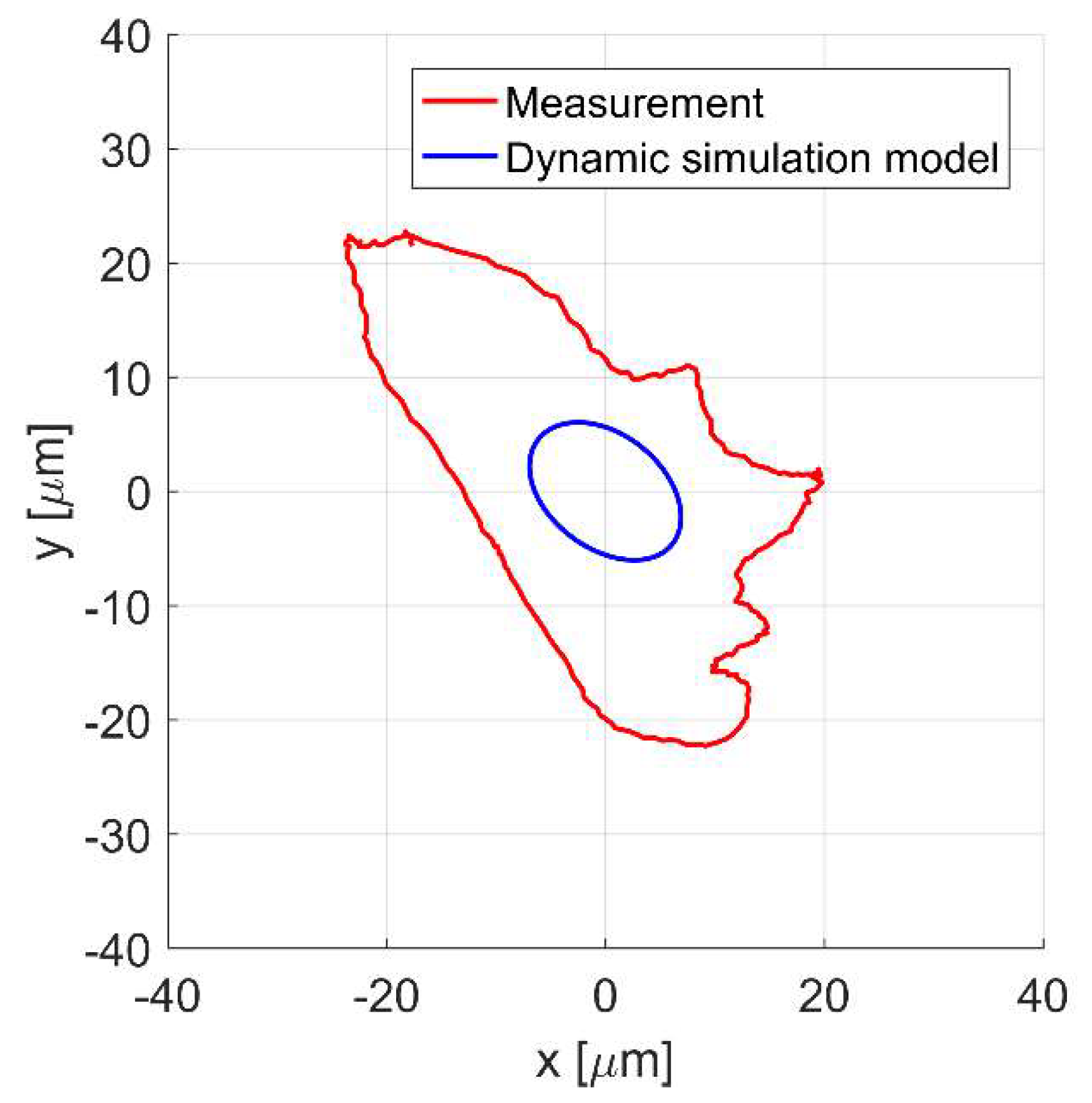
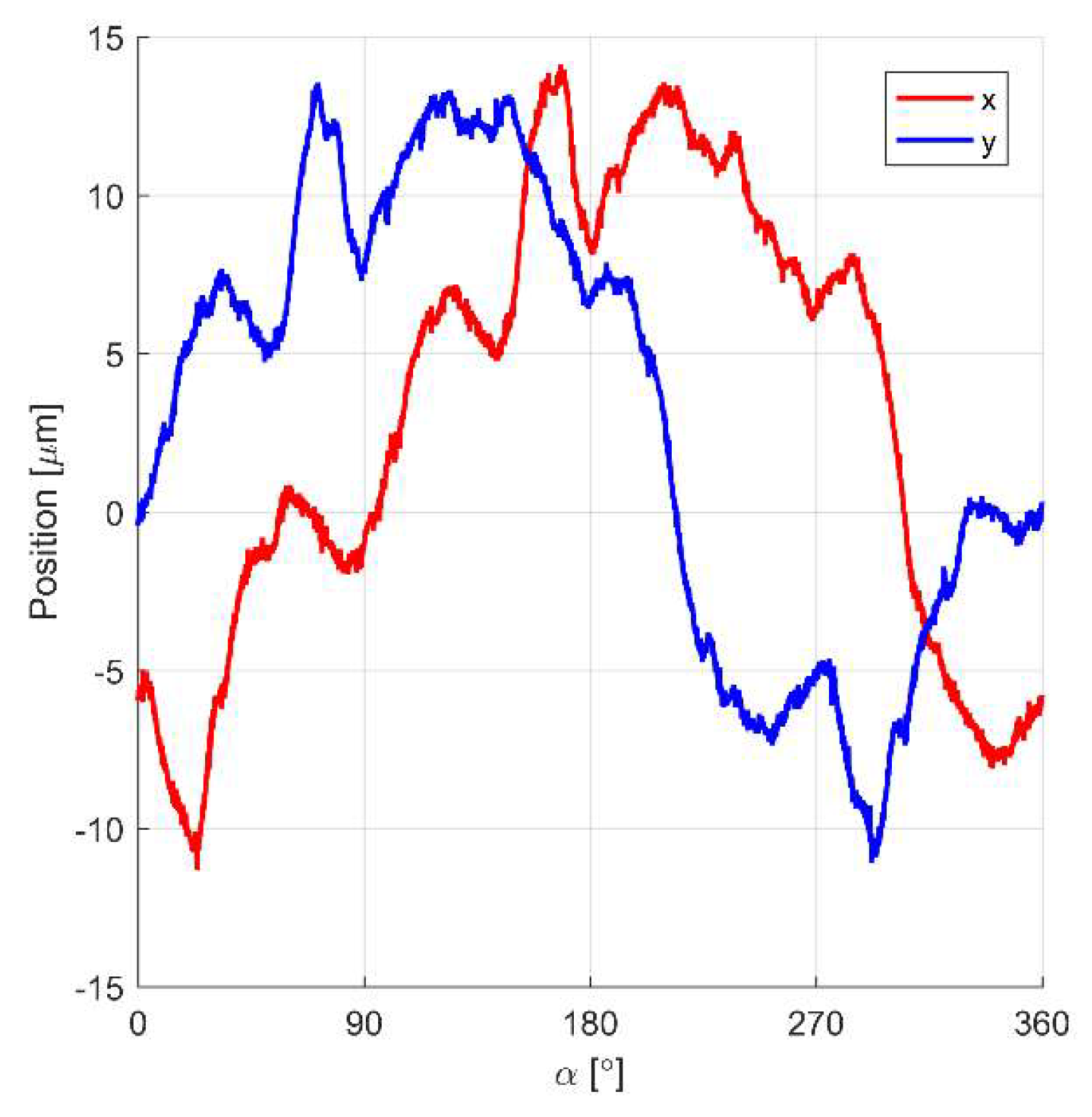
4. Simulation Results and Measurements
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piriou, F.; Razek, A. Finite Element Analysis in Electromagnetic Systems Accounting for Electric Circuits. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, Y.; Wang, S.; Oui, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhu, J. Transient Performance Analysis of Induction Motor Using Field-Circuit Coupled Finite-Element Method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 7021604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, L.; Mikołajewicz, J. Field-circuit model of the dynamics of electromechanical device supplied by electronic power converters. Compel 2004, 23, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrowski, W. 3D analysis of influence of stator winding asymmetry on axial flux. Compel 2013, 32, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demenko, A.; Mendrela, E.; Szeląg, W. Finite element analysis of saturation effects in a tubular linear permanent magnet machine. Compel 2006, 25, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Barba, P.; Gotszalk, T.; Majstrzyk, W.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Orłowska, K.; Wiak, S.; Sierakowski, A. Optimal design of electromagnetically actuated MEMS cantilevers. Sensors 2018, 18, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilat, A. Modelling. Investigation, Simulation, and PID Current Control of Active Magnetic Levitation FEM Model. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Methods & Models in Automation & Robotics (MMAR 2013), Międzyzdroje, Poland, 26–29 August 2013; pp. 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Barański, M. Field-circuit analysis of lspms motor supplied with distorted voltage. Electr. Eng. 2017, 91, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idziak, P.; Kowalski, K.; Nowak, L.; Knypiński, K. FE transient analysis of the magnetostrictive actuator. Int. J. Appl. Electrom. 2016, 51, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barański, M.; Demenko, A.; Łyskawiński, W.; Szeląg, W. Finite element analysis of transient electromagnetic-thermal phenomena in a squirrel cage motor. Compel 2011, 30, 832–840. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczuk, B.; Wajnert, D. Field–circuit model of the radial active magnetic bearing system. Electr. Eng. 2018, 100, 2319–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczuk, B.; Sobol, M. A field-network model of a linear oscillating motor and its dynamics characteristics. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczuk, B.; Waindok, A.; Wajnert, D. Transients in the Electromagnetic Actuator with the Controlled Supplier. J. Vibroeng 2012, 14, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Waindok, A.; Piekielny, P. Analysis of an iron-core and ironless railguns powered sequentially. Compel 2018, 37, 1707–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieras, J.; Piech, Z.; Tomczuk, B. Linear synchronous motors. CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pollanen, R.; Nerg, J.; Pyrhonen, O. Reluctance network method based dynamic model of radial active magnetic bearings. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Magnetics Conference, Nagoya, Japan, 4–8 April 2005; pp. 715–716. [Google Scholar]
- Ostović, V. Dynamics of Saturated Electric Machines; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hecquet, M.; Brochet, P. Time variation of forces in a synchronous machine using electric coupled network model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1998, 34, 3214–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykulski, J.; Stoll, J.; Sikora, R.; Pawluk, K.; Turowski, J.; Zakrzewski, K. Computational Magnetics; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Demenko, A.; Wojciechowski, R. Loop analysis of multi-branch, multi-node non-linear circuits using singular formulation. Compel 2009, 28, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, D.; Demenko, A. Reluctance network model of Halbach magnetized permanent magnet machines. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny 2009, 85, 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Wojciechowski, R.; Jędryczka, C.; Łukaszewicz, P. Analysis of high speed permanent magnet motor with powder core material. Compel 2012, 31, 1528–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Zeng, L.; Li, X. Magnetic Field Analysis of Lorentz Motors Using a Novel Segmented Magnetic Equivalent Circuit Method. Sensors 2013, 13, 1664–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Le, D.; Nguyen, V. Inductive Displacement Sensors with a Notch Filter for an Active Magnetic Bearing System. Sensors 2014, 14, 12640–12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajnert, D.; Tomczuk, B. Nonlinear magnetic equivalent circuit of the hybrid magnetic bearing. Compel 2019, 38, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.M. Practical quasi-newton methods for solving nonlinear systems. J Comput. Appl. Math. 2000, 124, 97–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, G.; Maslen, H. Magnetic Bearings, Theory, Design, and Application to Rotating Machinery; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Piłat, A. PD control strategy for 3 coils AMB. In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings, Martigny, Switzerland, 21–23 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gosiewski, Z.; Mystkowski, A. Robust control of active magnetic suspension: Analytical and experimental results. Mech. Syst. Signal Pp. 2008, 22, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grega, W.; Piłat, A. Comparison of linear control methods for an AMB system. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2005, 15, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Wajnert, D. A field-circuit model of the hybrid magnetic bearing. Arch. Mech. Eng. 2019, 66, 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, G.; Powell, J.; Emami-Naeini, A. Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems; Prentice Hall: Newark, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]








| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Position stiffness ksx | 140.99 N/mm |
| Current stiffness kix | 23.22 N/A |
| Position stiffness ksy | 141.21 N/mm |
| Current stiffness kiy | 23.16 N/A |
| Dynamic inductance Ld | 4.95 mH |
| Velocity induced voltage ev | 18.29 Vs/m |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Winding resistances R1, R2, R3 | 0.35 Ω |
| Mass of the rotor reduced to the bearing plane m | 1.40 kg |
| Eccentricity es | 4 μm |
| Parameter | Position Controller in the Axis x | Position Controller in the Axis x |
|---|---|---|
| KP [A/m] | 8424 | 8852 |
| KI [As/m] | 120 342 | 126 500 |
| KD [A/ms] | 13.03 | 15.26 |
| Sampling time Ts [μs] | 100 | 100 |
| Filter coefficient for derivative N | 1000 | 1000 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| KP [1/A] | 0.35 |
| KI [1/As] | 400 |
| Sampling time Ts [μs] | 100 |
| Parameter | The Rotor Movement ±20 μm in the x-axis | The Rotor Movement ±20 μm in the y-axis |
|---|---|---|
| RMSEx | 8.25 μm | 1.63 μm |
| RMSEix | 124.9 mA | 27.0 mA |
| RMSEy | 1.84 μm | 4.27 μm |
| RMSEiy | 45.3 mA | 94.5 mA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wajnert, D.; Sykulski, J.K.; Tomczuk, B. An Enhanced Dynamic Simulation Model of a Hybrid Magnetic Bearing Taking Account of the Sensor Noise. Sensors 2020, 20, 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041116
Wajnert D, Sykulski JK, Tomczuk B. An Enhanced Dynamic Simulation Model of a Hybrid Magnetic Bearing Taking Account of the Sensor Noise. Sensors. 2020; 20(4):1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041116
Chicago/Turabian StyleWajnert, Dawid, Jan K. Sykulski, and Bronislaw Tomczuk. 2020. "An Enhanced Dynamic Simulation Model of a Hybrid Magnetic Bearing Taking Account of the Sensor Noise" Sensors 20, no. 4: 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041116
APA StyleWajnert, D., Sykulski, J. K., & Tomczuk, B. (2020). An Enhanced Dynamic Simulation Model of a Hybrid Magnetic Bearing Taking Account of the Sensor Noise. Sensors, 20(4), 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041116






