Multi-Sensor Fusion: A Simulation Approach to Pansharpening Aerial and Satellite Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Purpose of the Study
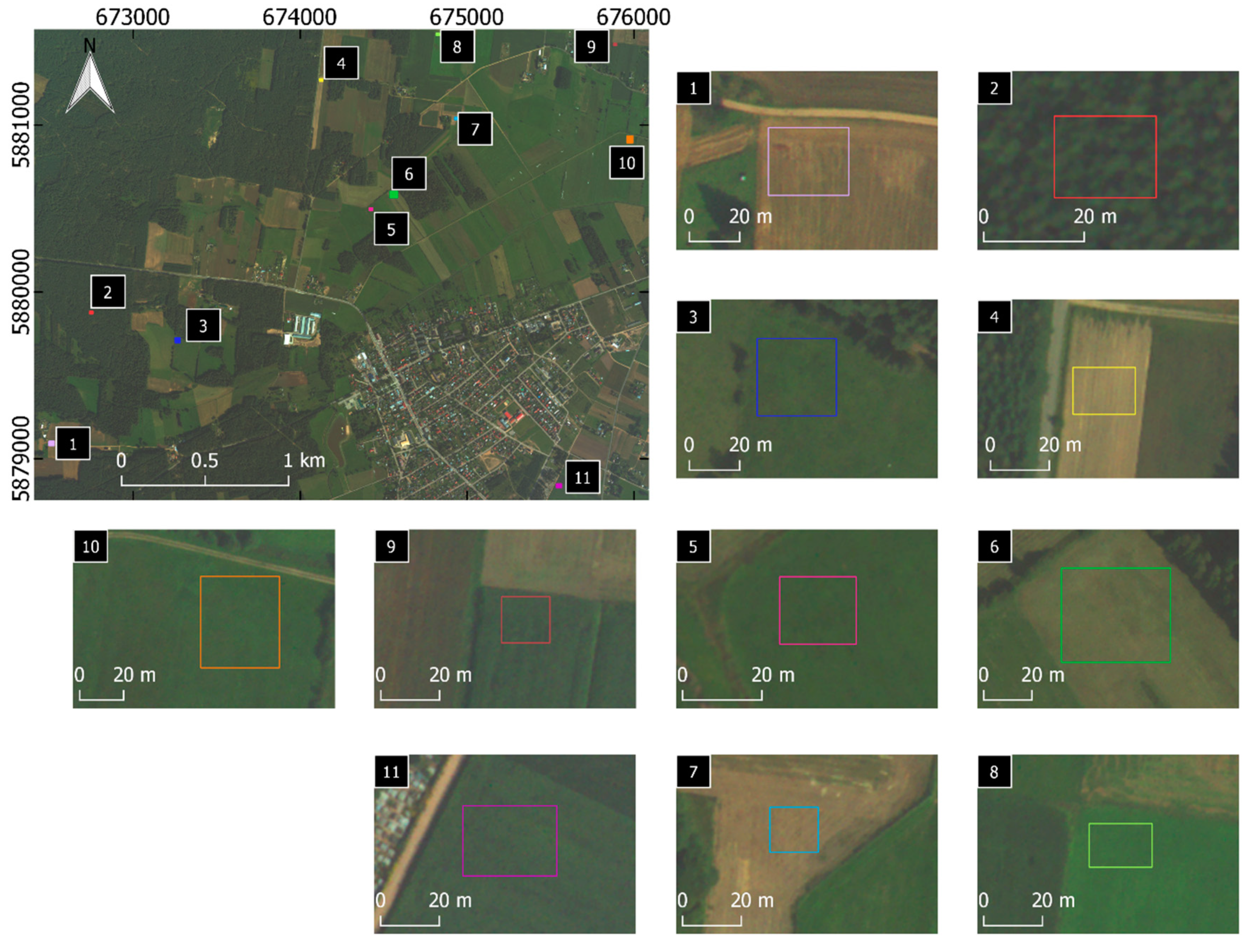
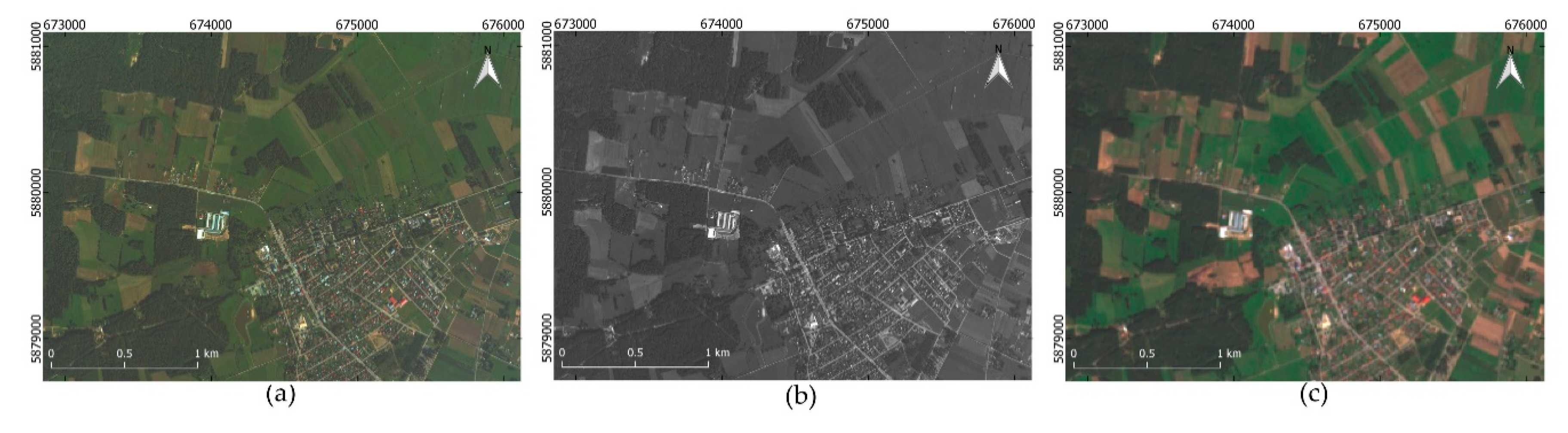
3. Data and Preprocessing
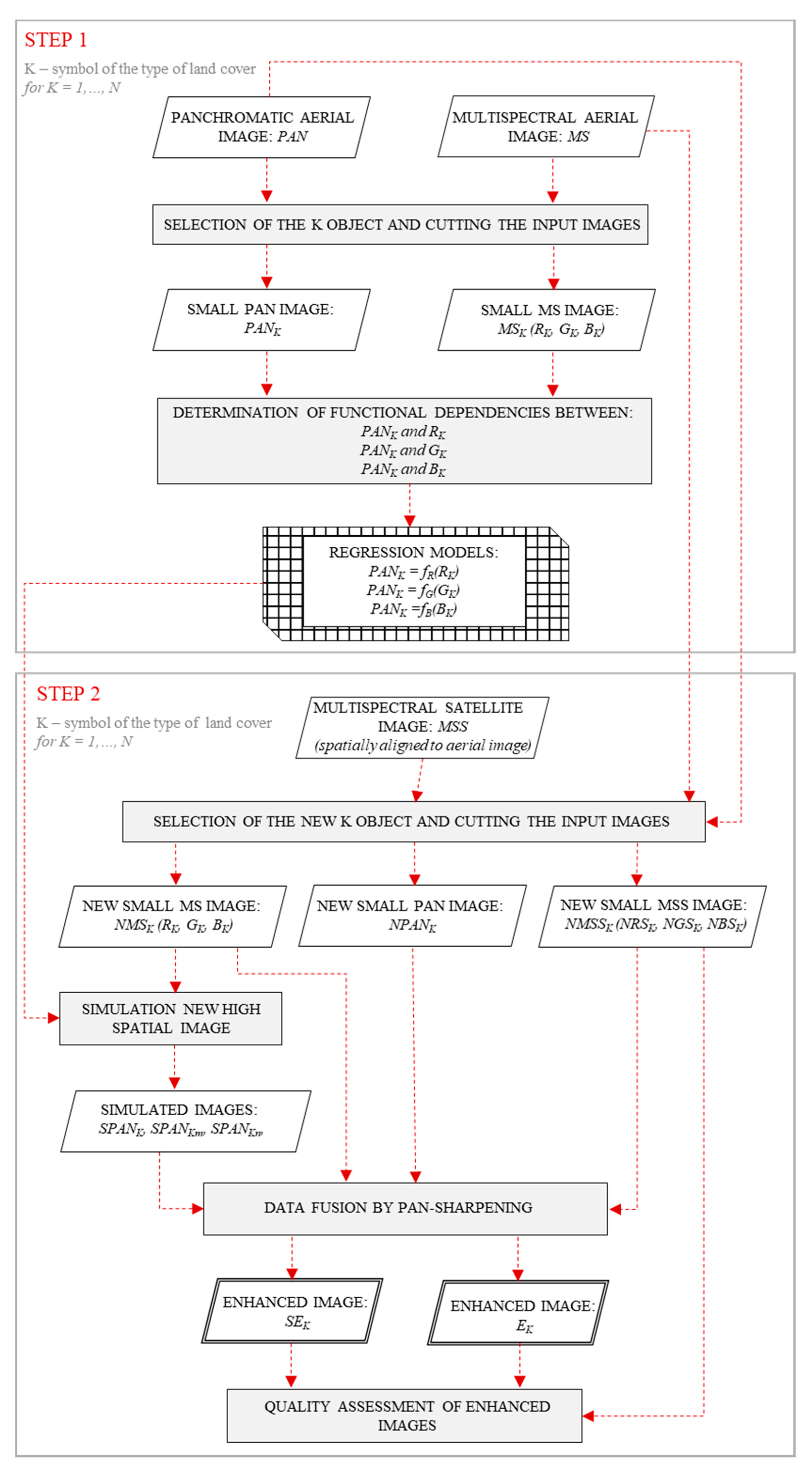
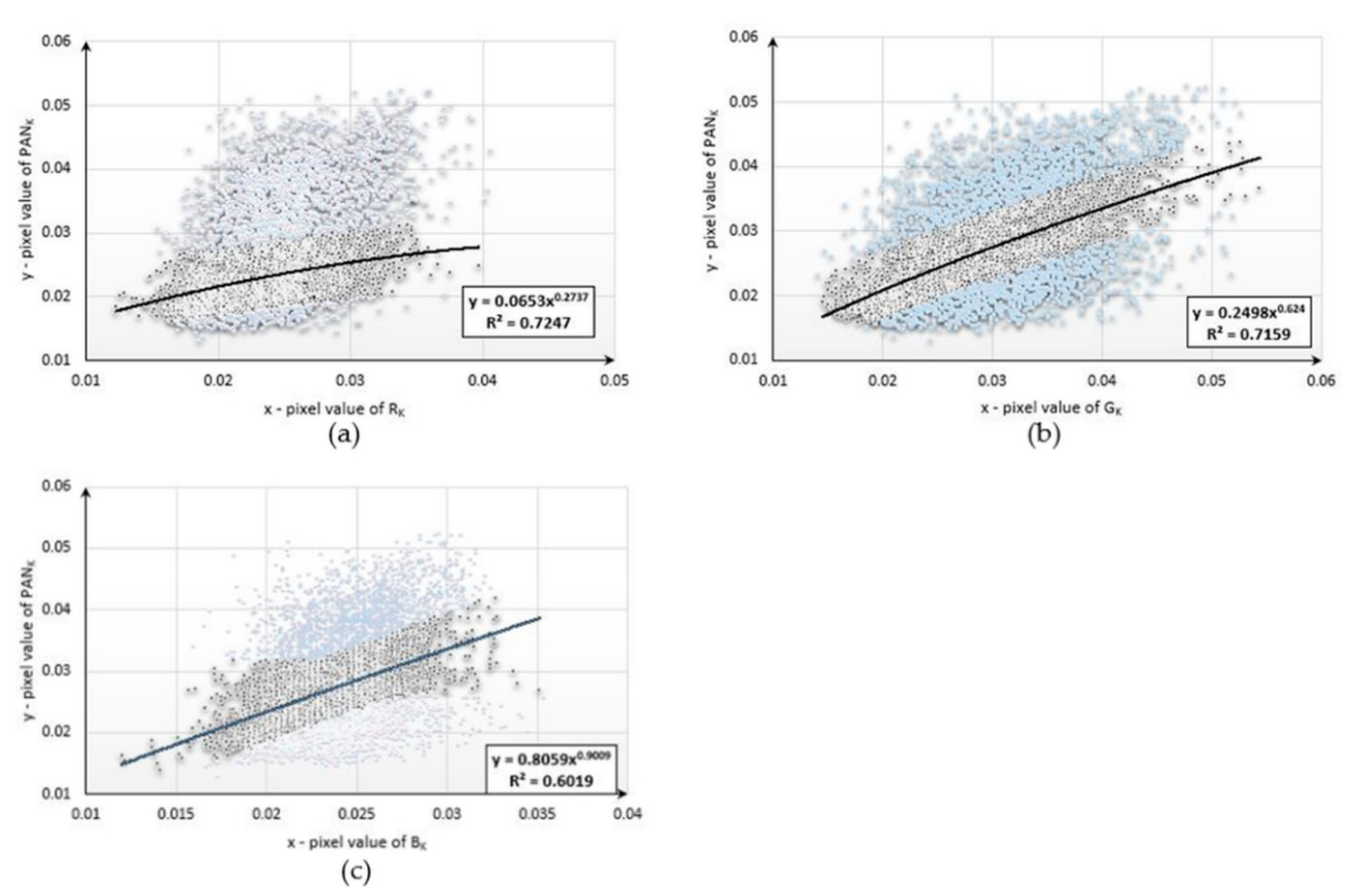
4. Methodology
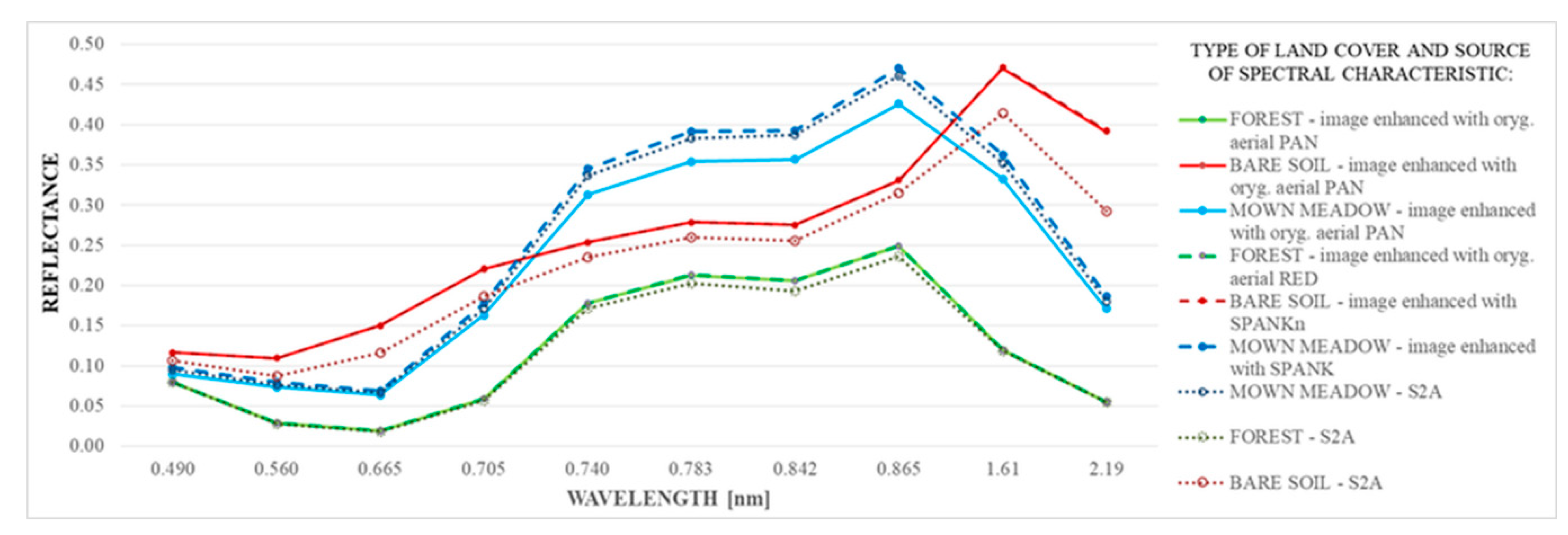
5. Results
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B

References
- Zhang, J. Multi-source remote sensing data fusion: Status and trends. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2010, 1, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Ranchin, T.; Wald, L.; Chanussot, J. Synthesis of Multispectral Images to High Spatial Resolution: A Critical Review of Fusion Methods Based on Remote Sensing Physics. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, L.; Ranchin, T.; Mangolini, M. Fusion of satellite images of different spatial resolutions: Assessing the quality of resulting images. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 691–699. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Zhuang, D.; Huang, Y.; Fu, J. Advances in multi-sensor data fusion: Algorithms and applications. Sensors 2009, 9, 7771–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenerowicz, A.; Siok, K.; Woroszkiewicz, M.; Dabrowski, R. The fusion of satellite and UAV data. The accuracy analysis of data fusion results. In Fifth Recent Advances in Quantitative Remote Sensing; Sobrino, J.A., Ed.; Universitat de València: Valencia, Spain, 2018; pp. 425–429. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, M.; Jacobsen, K.; Schiewe, J. High resolution image data and GIS. In ASPRS Manual GIS; Madden, M., Ed.; American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2009; pp. 721–777. [Google Scholar]
- Siok, K.; Ewiak, I. The simulation approach to the interpretation of archival aerial photographs. Open Geosci. 2020, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenerowicz, A.; Siok, K.; Woroszkiewicz, M.; Orych, A. The fusion of satellite and UAV data: Simulation of high spatial resolution band. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XIX, Warsaw, Poland, 11–14 September 2017; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10421, p. 104211Z. [Google Scholar]
- Siok, K.; Jenerowicz, A.; Ewiak, I. A simulation approach to the spectral quality of multispectral images enhancement. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, P.; Wald, L.; Ranchin, T. Importance and Effect of Co-Registration Quality in an Example of “Pixel to pIxel” Fusion Process. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference “Fusion of Earth Data: Merging Point Measurements, Raster Maps and Remotely Sensed Images”, Sophia Antipolis, France, 28–30 January 1998; SEE/URISCA: Nice, France, 1998; pp. 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Švab, A.; Oštir, K. High-resolution image fusion: Methods to preserve spectral and spatial resolution. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuhendra, J.; Kuze, H. Performance analyzing of high resolution pan-sharpening techniques: Increasing image Quality for Classification using supervised kernel support vector machine. Res. J. Inf. Technol. 2011, 8, 12–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jenerowicz, A.; Woroszkiewicz, M. The pan-sharpening of satellite and UAV imagery for agricultural applications. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XVIII, Edinburgh, UK, 26–29 September 2016; Volume 9998, p. 99981S. [Google Scholar]
- Gevaert, C.M.; Tang, J.; García-Haro, F.J.; Suomalainen, J.; Kooistra, L. Combining hyperspectral UAV and multispectral Formosat-2 imagery for precision agriculture applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Lausanne, Switzerland, 24–27 June 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Siok, K.; Ewiak, I.; Jenerowicz, A. Enhancement of spectral quality of natural land cover in the pan-sharpening process. In Proceedings of the Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXIV, Berlin, Germany, 10–12 September 2018; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10789, p. 107891P. [Google Scholar]
- Siok, K.; Jenerowicz, A.; Ewiak, I. The simulation of new spectral bands for the purpose of data pan-sharpening. In Fifth Recent Advances in Quantitative Remote Sensing; Sobrino, J.A., Ed.; Servicio Publicacions Universitat de Valencia: Valencia, Spain, 2018; pp. 430–435. [Google Scholar]
- Jenerowicz, A.; Siok, K. Fusion of radar and optical data for mapping and monitoring of water bodies. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XIX, Warsaw, Poland, 11–14 September 2017; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10421, p. 1042126. [Google Scholar]
- Jenerowicz, A.; Kaczynski, R.; Siok, K.; Schismak, A. Data fusion for high accuracy classification of urban areas. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing Technologies and Applications in Urban Environments III, Berlin, Germany, 10–11 September 2018; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10793, p. 1079315. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Li, G.; Moran, E.; Dutra, L.; Batistella, M. A comparison of multisensor integration methods for land cover classification in the Brazilian Amazon. GISci. Remote Sens. 2011, 48, 345–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Tateishi, R. Fusion of multisensor multitemporal satellite data for land cover mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siok, K.; Jenerowicz, A.; Woroszkiewicz, M. Enhancement of spectral quality of archival aerial photographs using satellite imagery for detection of land cover. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 36001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimaris, D.; Patias, P.; Mallinis, G.; Georgiadis, C. Data Fusion of Scanned Black and White Aerial Photographs with Multispectral Satellite Images. Sci 2020, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.; Diemer, C.; Stöver, O.; Udelhoven, T. A local correlation approach for the fusion of remote sensing data with different spatial resolutions in forestry applications. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 32, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Pu, H.; Wang, B.; Jiang, G.-M. Fusion of hyperspectral and multispectral images: A novel framework based on generalization of pan-sharpening methods. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.C. Combining panchromatic and multispectral imagery from dual resolution satellite instruments. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 21, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, M. Multi-spectral and hyperspectral image fusion using 3-D wavelet transform. J. Electron. 2007, 24, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Z/I DMC® II230 Camera System. Available online: https://www.aerial-survey-base.com (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Petrie, G. The Intergraph DMC II Camera Range. GeoInformatics 2010, 13, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Aschbacher, J.; Milagro-Pérez, M.P. The European Earth monitoring (GMES) programme: Status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenovský, Z.; Rott, H.; Cihlar, J.; Schaepman, M.E.; García-Santos, G.; Fernandes, R.; Berger, M. Sentinels for science: Potential of Sentinel-1,-2, and-3 missions for scientific observations of ocean, cryosphere, and land. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L.S.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Sundberg, R.L.; Levine, R.Y.; Perkins, T.C.; Berk, A.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Felde, G.; Hoke, M.L. Validation of the QUick atmospheric correction (QUAC) algorithm for VNIR-SWIR multi- and hyperspectral imagery. In Proceedings of the Proc. SPIE 5806, Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XI, Orlando, FL, USA, 28 March–1 April 2005; p. 668. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 111834328X. [Google Scholar]
- Tempfli, K.; Huurneman, G.; Bakker, W.; Janssen, L.L.F.; Feringa, W.F.; Gieske, A.S.M.; Grabmaier, K.A.; Hecker, C.A.; Horn, J.A.; Kerle, N. Principles of Remote Sensing: An Introductory Textbook; ITC: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2009.
- Adamczyk, J.; Będkowski, K. Metody cyfrowe w teledetekcji; Warsaw University of Life Sciences: Warsaw, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, W.K. Image enhancement. In Digital Image Processing: PIKS Inside, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 247–305. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, Y.; Sri Sumantyo, J.T.; Kuze, H. Spectral information analysis of image fusion data for remote sensing applications. Geocarto Int. 2013, 28, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F. A Global Quality Measurement of Pan-Sharpened Multispectral Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagalingam, P.; Hegde, A.V. A review of quality metrics for fused image. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water bodies’ mapping from Sentinel-2 imagery with modified normalized difference water index at 10-m spatial resolution produced by sharpening the SWIR band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoya, N.; Grohnfeldt, C.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral and Multispectral Data Fusion: A comparative review of the recent literature. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shen, H.-W. Information theory in scientific visualization. Entropy 2011, 13, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.-Y.; Lee, Y.; Matsuyama, E. Information entropy measure for evaluation of image quality. J. Digit. Imaging 2008, 21, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, M.B.A.; Aghagolzadeh, A.; Seyedarabi, H. A non-reference image fusion metric based on mutual information of image features. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2011, 37, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Huang, H.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference image quality assessment based on spatial and spectral entropies. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2014, 29, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Zou, B. Fusion of satellite images in urban area: Assessing the quality of resulting images. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. Boltzmann entropy-based unsupervised band selection for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. A hierarchy-based solution to calculate the configurational entropy of landscape gradients. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. An efficient analytical method for computing the Boltzmann entropy of a landscape gradient. Trans. GIS 2018, 22, 1046–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, S.A. Calculating the configurational entropy of a landscape mosaic. Landsc. Ecol. 2016, 31, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P. Boltzmann Entropy for Spatial Information of Images; Hong Kong Polytechnic University-Dissertations: Hong Kong, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. Boltzmann Entropy for the Spatial Information of Raster Data. Abstr. Int. Cartogr. Assoc. 2019, 1, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparavigna, A.C. Entropy in Image Analysis. Entropy 2019, 21, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekrecka, A.; Kedzierski, M. Integration of Satellite Data with High Resolution Ratio: Improvement of Spectral Quality with Preserving Spatial Details. Sensors 2018, 18, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palubinskas, G. Joint quality measure for evaluation of pansharpening accuracy. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9292–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jing, L.; Tang, Y. Assessment of pansharpening methods applied to worldview-2 imagery fusion. Sensors 2017, 17, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, M.; Klonus, S.; Johan Åstrand, P.; Rosso, P. Multi-sensor image fusion for pansharpening in remote sensing. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2010, 1, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wassai, F.A.; Kalyankar, N.V.; Al-Zaky, A.A. Multisensor images fusion based on feature-level. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1108.4098. [Google Scholar]
- Ghimire, P.; Lei, D.; Juan, N. Effect of Image Fusion on Vegetation Index Quality—A Comparative Study from Gaofen-1, Gaofen-2, Gaofen-4, Landsat-8 OLI and MODIS Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| DMC II 230 | S2A | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral Bands | FWHW 1 (nm) | Centre Wavelength (nm) | Spectral Bands | FWHW (nm) | Centre Wavelength (nm) | ||||
| Lower | Upper | Upper—Lower | Lower | Upper | Upper—Lower | ||||
| Blue | 430 | 485 | 55 | 457.5 | Blue | 459.4 | 525.4 | 66 | 492.4 |
| Green | 505 | 560 | 55 | 532.5 | Green | 541.8 | 577.8 | 36 | 559.8 |
| Red | 600 | 665 | 65 | 632.5 | Red | 649.1 | 680.1 | 31 | 664.6 |
| PAN | 450 | 690 | 240 | 570.0 | Vegetation Red Edge | 696.6 | 711.6 | 15 | 704.1 |
| The spectral range of the aerial panchromatic band mostly includes the spectral ranges of the blue, green, and red bands of Sentinel-2. For the other Sentinel-2 bands, there is no coverage. The aerial blue band spectrally covers the satellite blue band to some extent; mutual coverage between the red bands is present to a lesser extent. The aerial green band, on the other hand, partially covers the range of the blue band and the green band of the Sentinel-2 satellite. | Vegetation Red Edge | 733 | 748 | 15 | 740.5 | ||||
| Vegetation Red Edge | 772.8 | 792.8 | 20 | 782.8 | |||||
| NIR | 779.8 | 885.8 | 106 | 832.8 | |||||
| Vegetation Red Edge | 854.2 | 875.2 | 21 | 864.7 | |||||
| SWIR 2 | 1568.2 | 1659.2 | 91 | 1613.7 | |||||
| SWIR | 2114.9 | 2289.9 | 175 | 2202.4 | |||||
| Number of Sentinel-2 Band (Spatial Resolution (m)) | Forest | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIQI | SSIM | PSNR | CC | SAM | ||||||
| Orig. Aerial PAN | Orig. Aerial Red | Orig. Aerial PAN | Orig. Aerial Red | Orig. Aerial PAN | Orig. Aerial Red | Orig. Aerial PAN | Orig. Aerial Red | Orig. Aerial PAN | Orig. Aerial RED | |
| 2 (10) | 0.224 | 0.226 | 0.591 | 0.593 | 33.704 | 33.791 | 0.456 | 0.461 | 0.027 | 0.028 |
| 3 (10) | 0.227 | 0.232 | 0.895 | 0.896 | 42.035 | 42.105 | 0.413 | 0.422 | ||
| 4 (10) | 0.243 | 0.248 | 0.948 | 0.949 | 45.409 | 45.481 | 0.430 | 0.440 | ||
| 5 (20) | 0.129 | 0.136 | 0.598 | 0.608 | 32.049 | 32.121 | 0.146 | 0.155 | ||
| 6 (20) | 0.113 | 0.121 | 0.218 | 0.226 | 22.470 | 22.542 | 0.129 | 0.138 | ||
| 7 (20) | 0.111 | 0.119 | 0.188 | 0.197 | 20.963 | 21.035 | 0.126 | 0.136 | ||
| 8 (10) | 0.227 | 0.231 | 0.316 | 0.319 | 25.172 | 25.259 | 0.427 | 0.434 | ||
| 8a (20) | 0.113 | 0.122 | 0.171 | 0.179 | 19.599 | 19.671 | 0.129 | 0.139 | ||
| 11 (20) | 0.123 | 0.131 | 0.319 | 0.328 | 25.859 | 25.930 | 0.140 | 0.149 | ||
| 12 (20) | 0.142 | 0.150 | 0.628 | 0.639 | 32.623 | 32.623 | 0.161 | 0.170 | ||
| Arithmetic Mean: | 0.165 | 0.172 | 0.487 | 0.493 | 29.988 | 30.056 | 0.256 | 0.264 | ||
| Number of Sentinel-2 Band (Spatial Resolution (m)) | Mown Meadow | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIQI | SSIM | PSNR | CC | SAM | ||||||
| Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANK | Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANK | Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANK | Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANK | Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANK | |
| 2 (10) | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 33.1 | 35.1 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.072 | 0.040 |
| 3 (10) | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 35.4 | 37.4 | 0.89 | 0.93 | ||
| 4 (10) | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 37.5 | 39.1 | 0.91 | 0.94 | ||
| 5 (20) | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 25.7 | 27.3 | 0.79 | 0.85 | ||
| 6 (20) | 0.74 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.84 | 18.8 | 20.9 | 0.75 | 0.84 | ||
| 7 (20) | 0.73 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.84 | 17.4 | 19.6 | 0.74 | 0.84 | ||
| 8 (10) | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 19.3 | 21.6 | 0.83 | 0.90 | ||
| 8a (20) | 0.74 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.84 | 15.9 | 18.1 | 0.74 | 0.84 | ||
| 11 (20) | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.78 | 0.85 | 19.5 | 21.1 | 0.79 | 0.85 | ||
| 12 (20) | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 25.4 | 27.0 | 0.79 | 0.85 | ||
| Arithmetic Mean: | 0.80 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 24.8 | 26.7 | 0.81 | 0.87 | ||
| Number of Sentinel-2 Band (Spatial Resolution (m)) | Bare Soil | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIQI | SSIM | PSNR | CC | SAM | ||||||
| Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANKn | Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANKn | Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANKn | Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANKn | Orig. Aerial PAN | SPANKn | |
| 2 (10) | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 54.0 | 54.4 | 0.79 | 0.84 | 0.023 | 0.022 |
| 3 (10) | 0.60 | 0.65 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 48.0 | 48.7 | 0.68 | 0.78 | ||
| 4 (10) | 0.62 | 0.66 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 41.3 | 42.4 | 0.75 | 0.87 | ||
| 5 (20) | 0.46 | 0.55 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 32.1 | 38.8 | 0.57 | 0.66 | ||
| 6 (20) | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 32.7 | 39.3 | 0.63 | 0.67 | ||
| 7 (20) | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.80 | 0.82 | 30.3 | 36.5 | 0.62 | 0.64 | ||
| 8 (10) | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 44.7 | 46.5 | 0.82 | 0.89 | ||
| 8a (20) | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 29.6 | 36.1 | 0.63 | 0.65 | ||
| 11 (20) | 0.30 | 0.47 | 0.52 | 0.66 | 23.4 | 31.0 | 0.36 | 0.60 | ||
| 12 (20) | 0.44 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 21.8 | 29.0 | 0.53 | 0.68 | ||
| Arithmetic Mean: | 0.53 | 0.59 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 35.8 | 40.3 | 0.64 | 0.73 | ||
| Panchromatic Band | Forest | Mown Meadow | Bare Soil |
|---|---|---|---|
| orig. aerial PAN | 3.1551 | 2.8360 | 2.4999 |
| orig. aerial blue | 2.0270 | 1.7048 | 1.3274 |
| orig. aerial green | 2.1597 | 2.0589 | 1.4207 |
| orig. aerial red | 2.5023 | 2.3871 | 1.6698 |
| SPANK | 2.2088 | 3.1394 | 1.8792 |
| SPANKm | 2.2780 | 2.8125 | 1.8269 |
| SPANKn | 2.3294 | 2.9678 | 1.9965 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siok, K.; Ewiak, I.; Jenerowicz, A. Multi-Sensor Fusion: A Simulation Approach to Pansharpening Aerial and Satellite Images. Sensors 2020, 20, 7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20247100
Siok K, Ewiak I, Jenerowicz A. Multi-Sensor Fusion: A Simulation Approach to Pansharpening Aerial and Satellite Images. Sensors. 2020; 20(24):7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20247100
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiok, Katarzyna, Ireneusz Ewiak, and Agnieszka Jenerowicz. 2020. "Multi-Sensor Fusion: A Simulation Approach to Pansharpening Aerial and Satellite Images" Sensors 20, no. 24: 7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20247100
APA StyleSiok, K., Ewiak, I., & Jenerowicz, A. (2020). Multi-Sensor Fusion: A Simulation Approach to Pansharpening Aerial and Satellite Images. Sensors, 20(24), 7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20247100





