Seismic Data Augmentation Based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
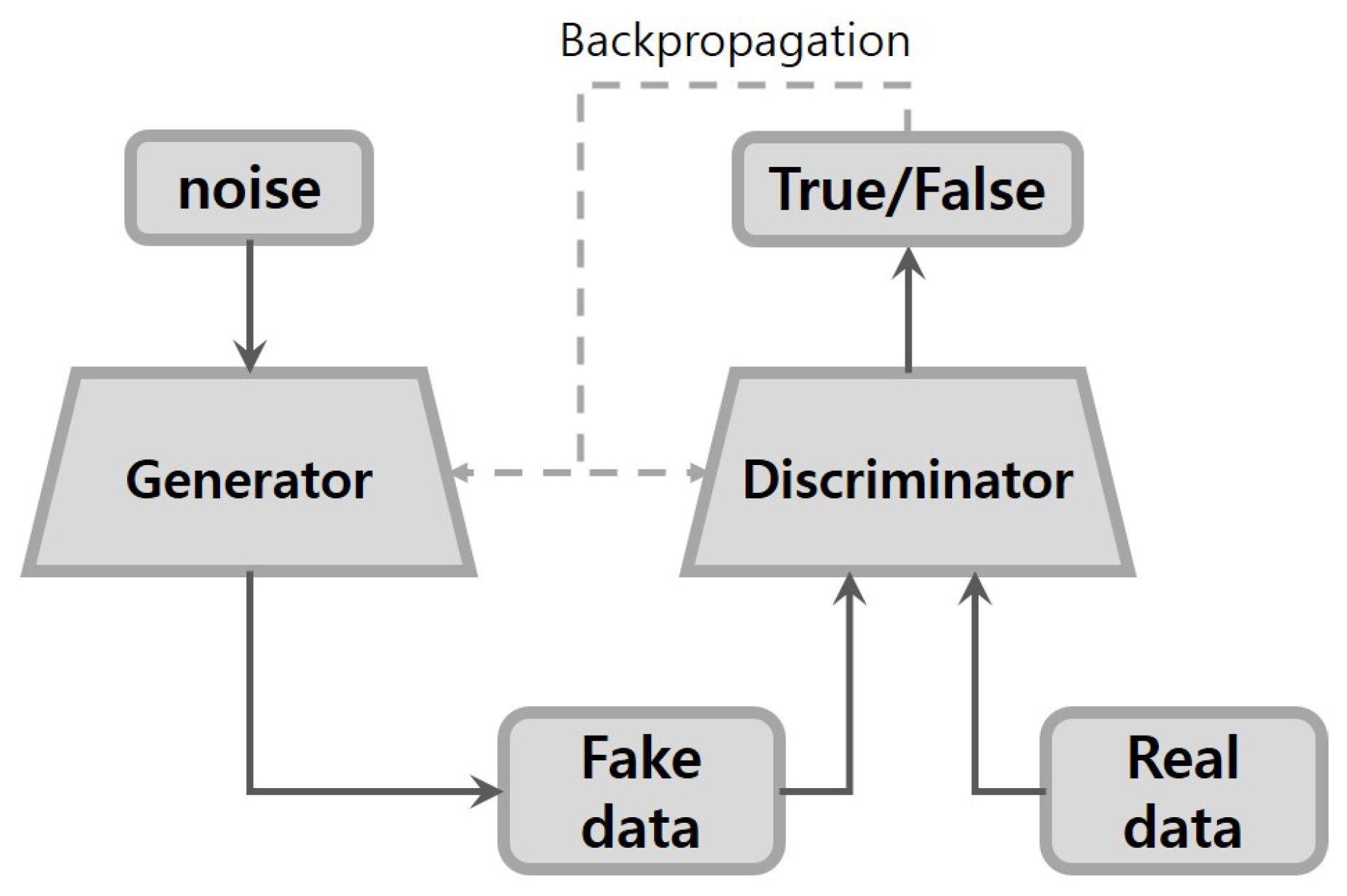
2.1. GANs
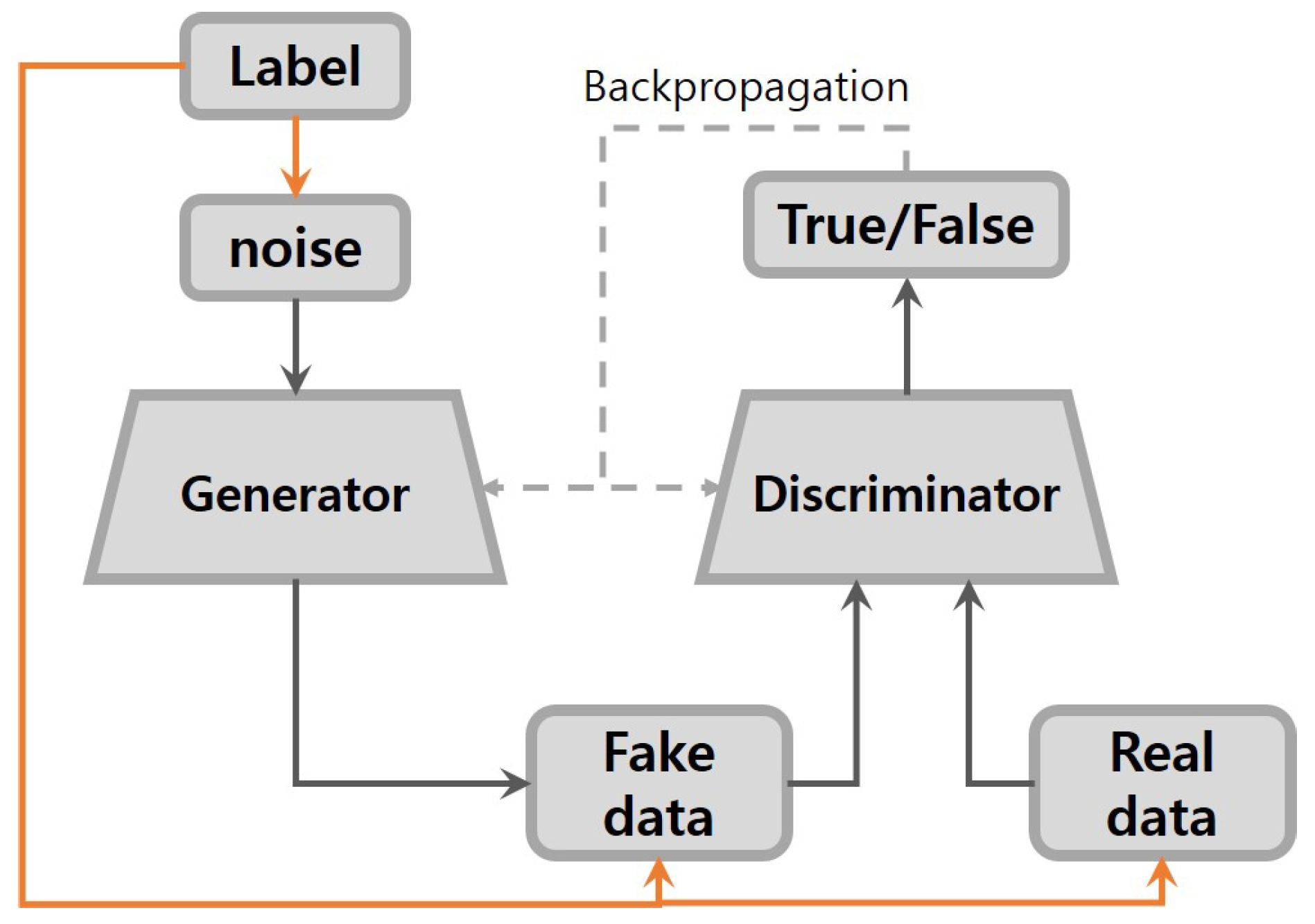
2.2. Conditional GANs
3. Seismic Signal Synthesis with Conditional GANs
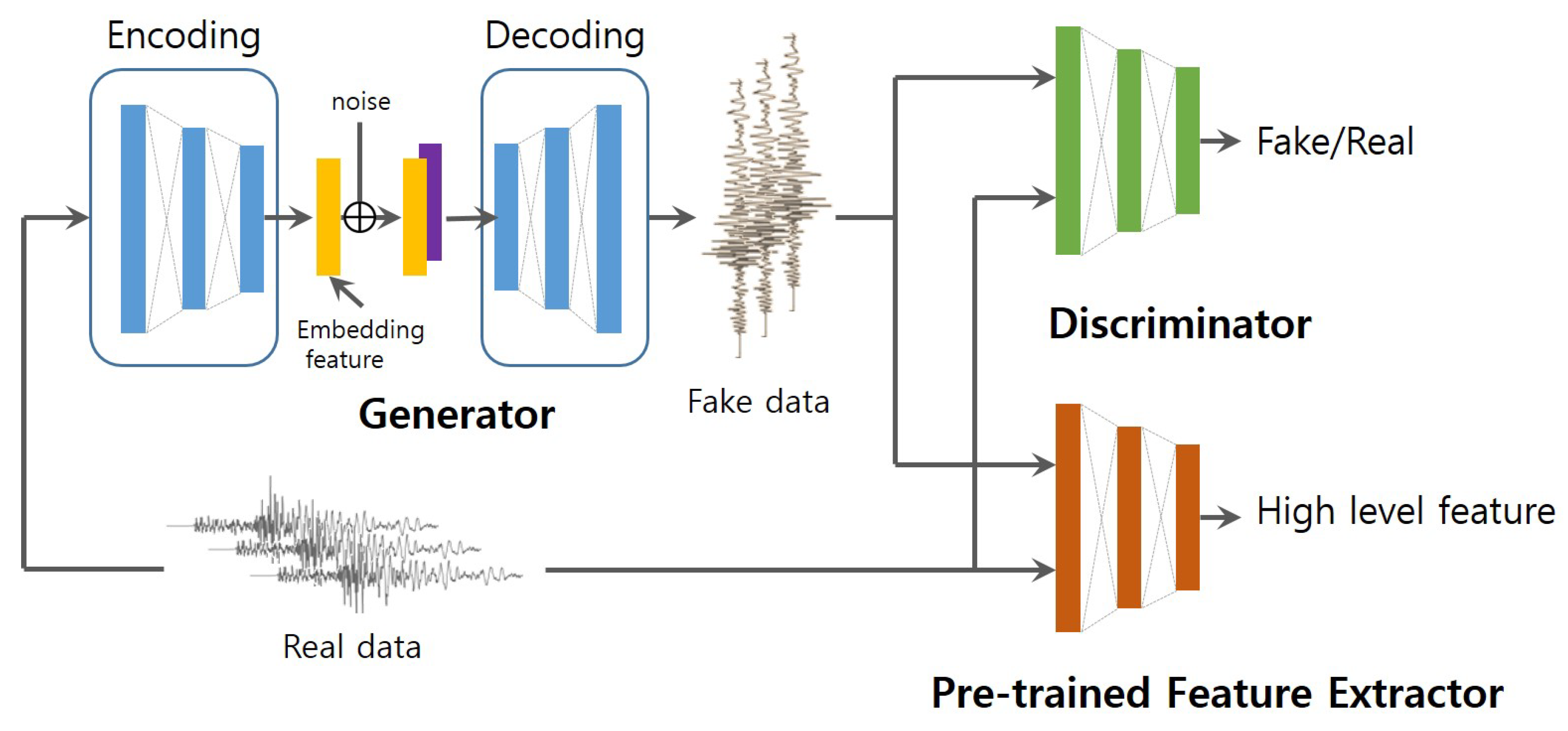
3.1. Network Architecture
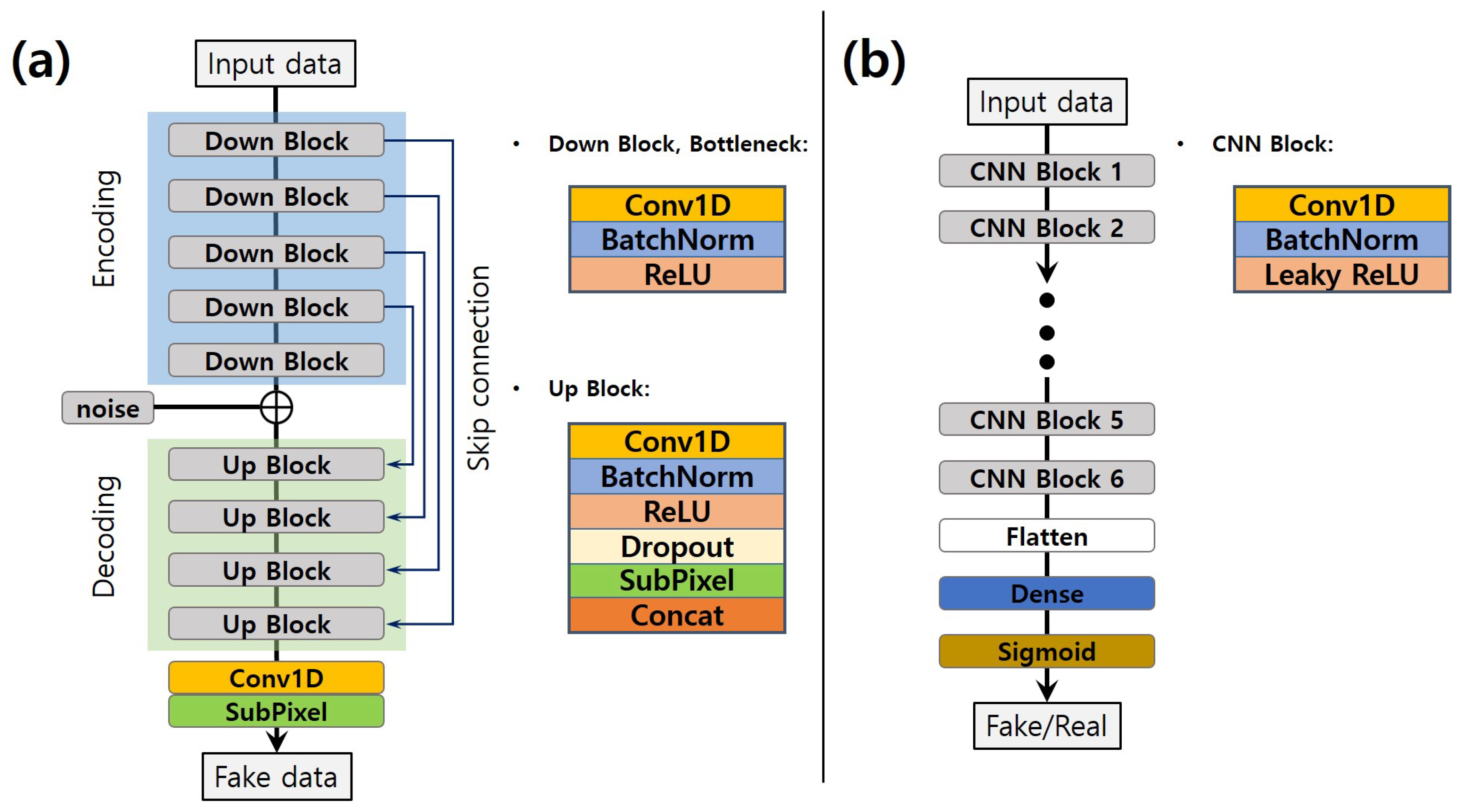
3.1.1. Generator
3.1.2. Discriminator
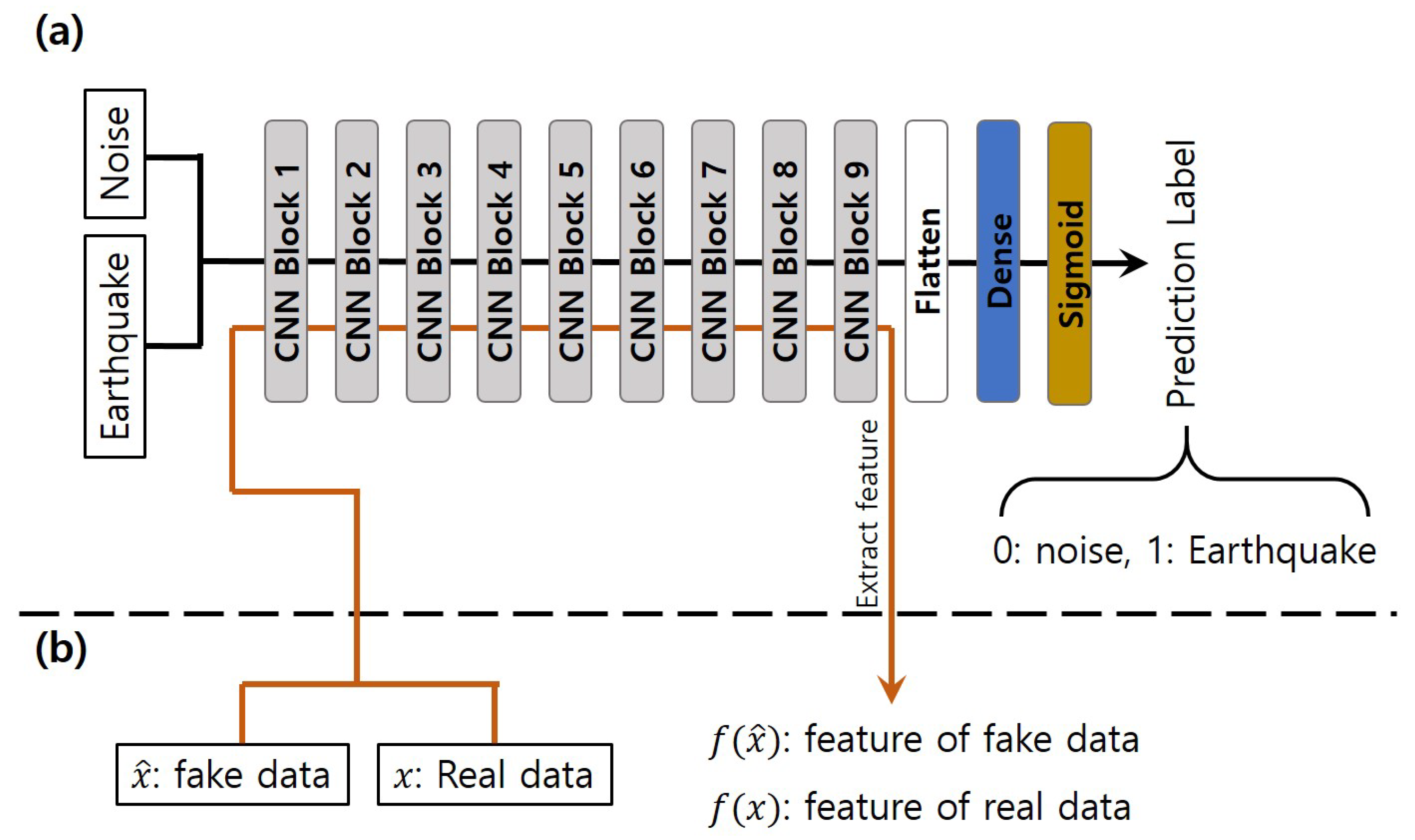
3.1.3. Pre-Trained Feature Extractor
3.2. Loss Function
4. Experiment and Analysis of Results
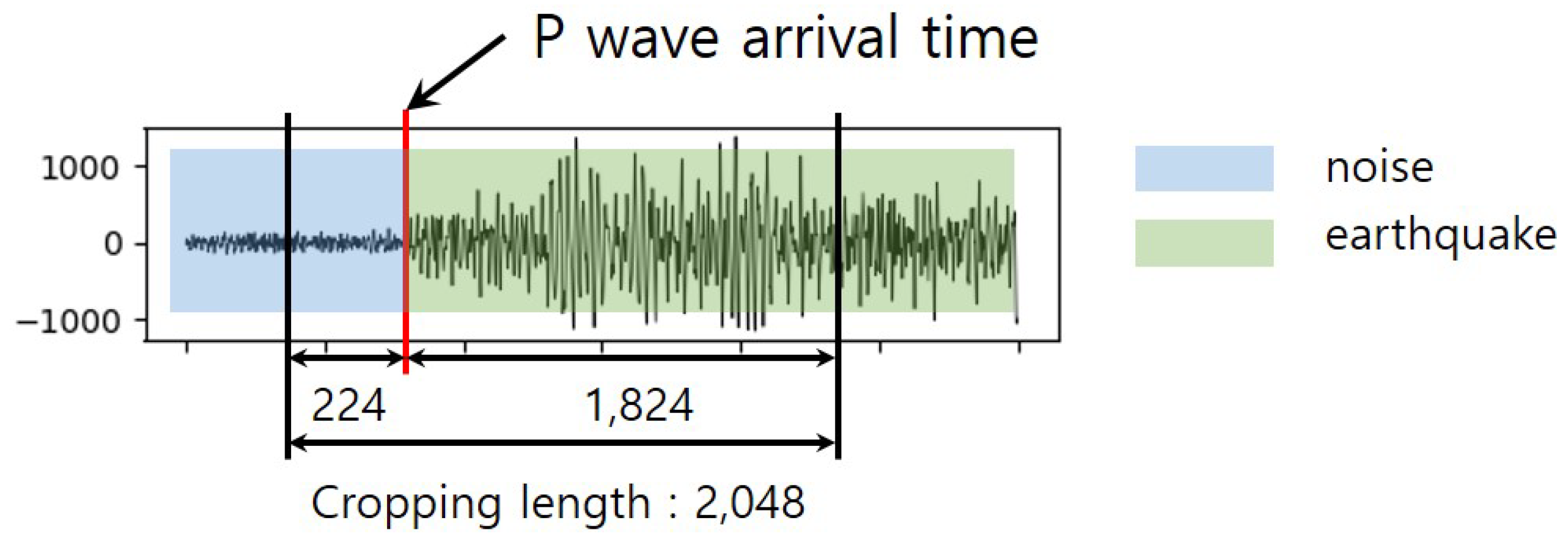
4.1. Training Details and Data Preprocessing
4.2. Results and Discussion
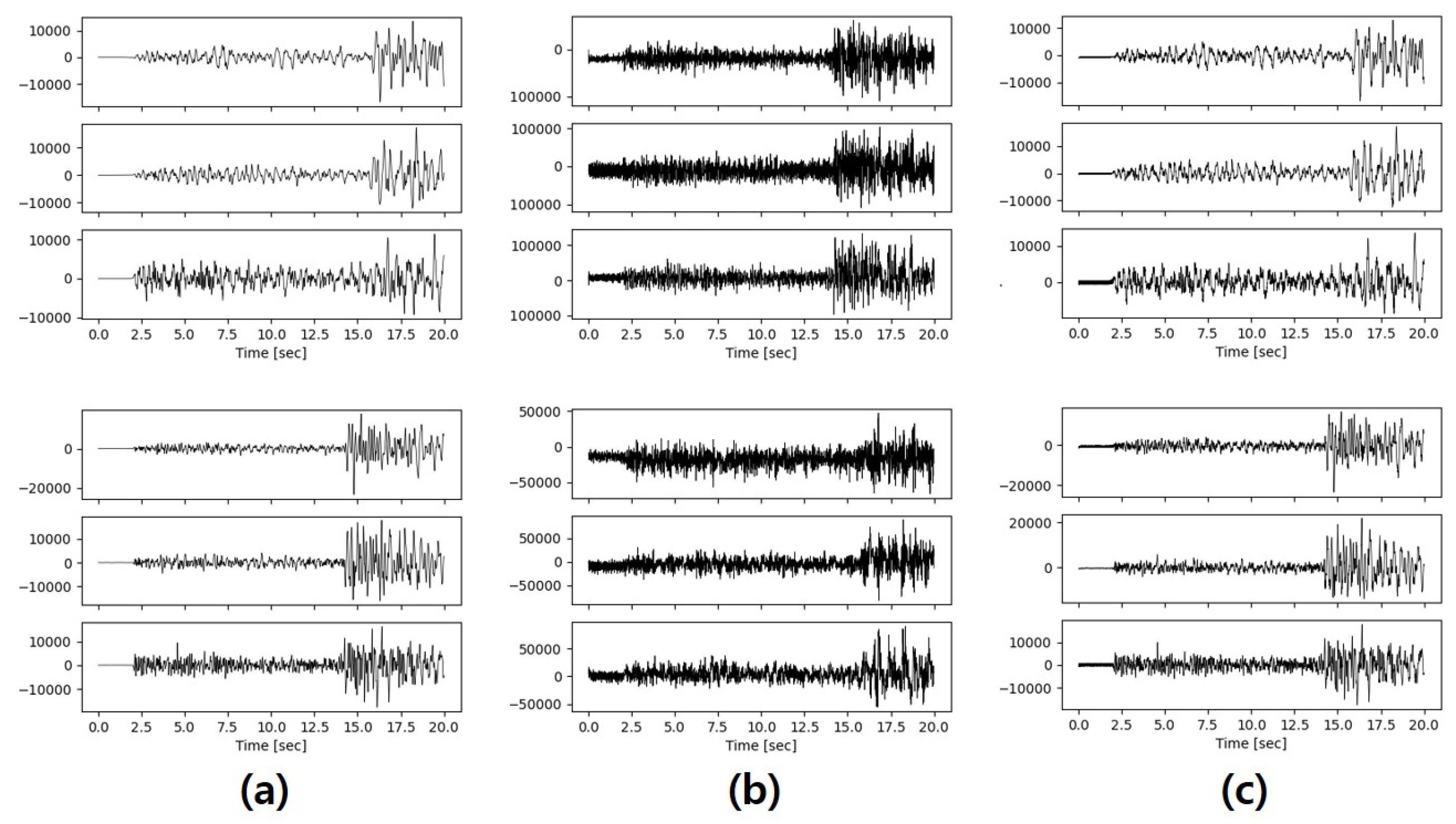
4.2.1. Analysis Results by Visual Comparison
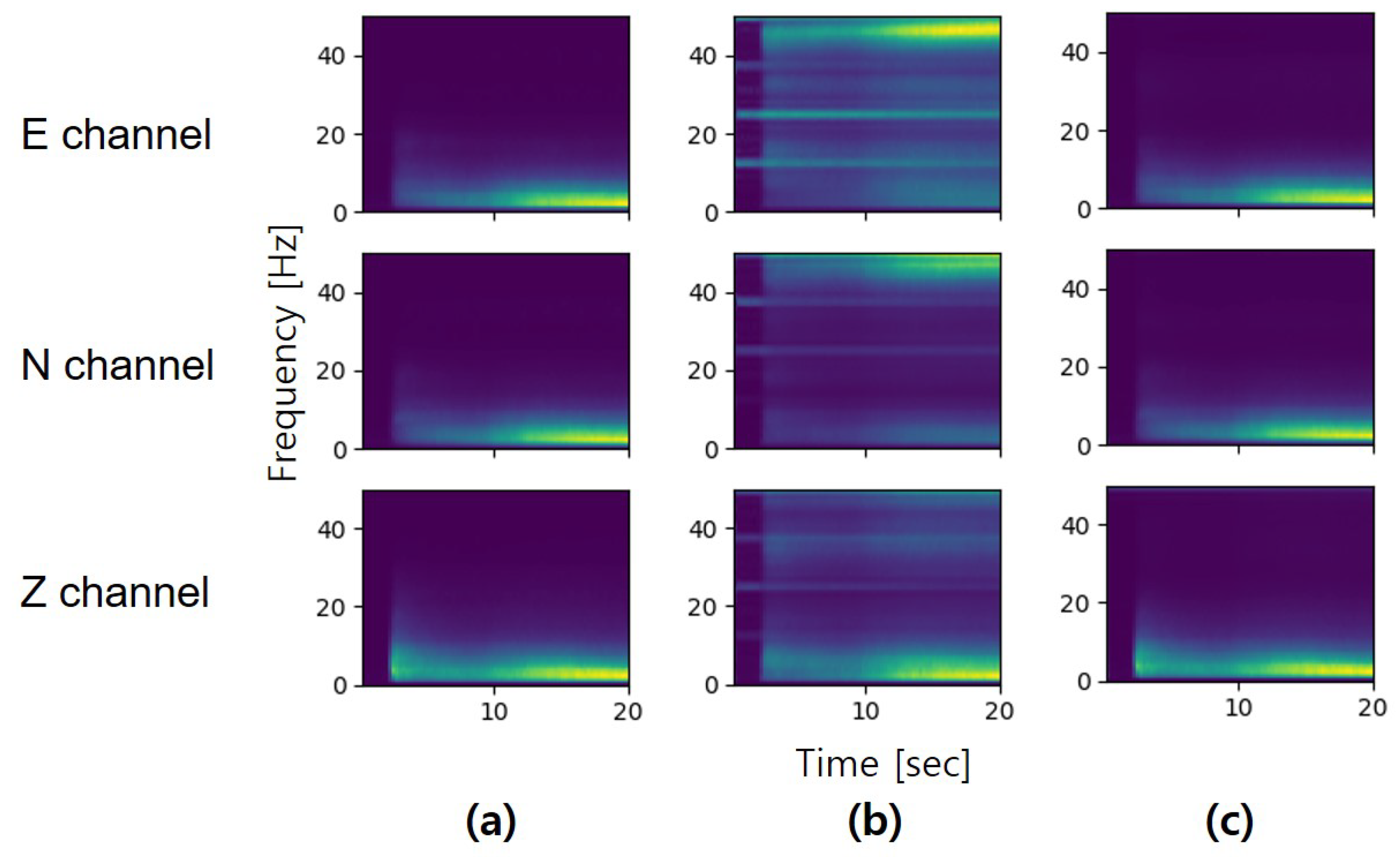
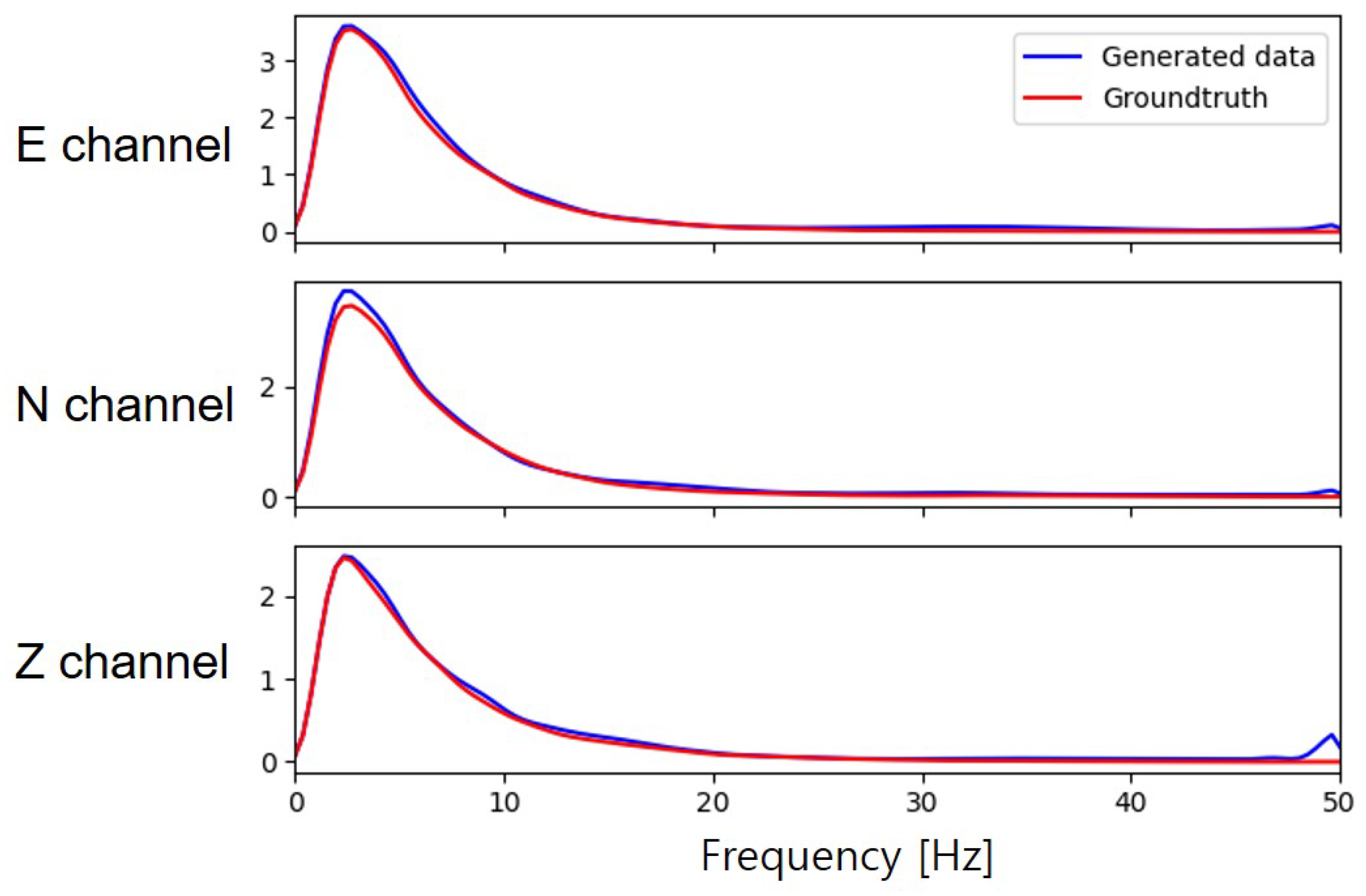
4.2.2. Time-Frequency Domain Analysis
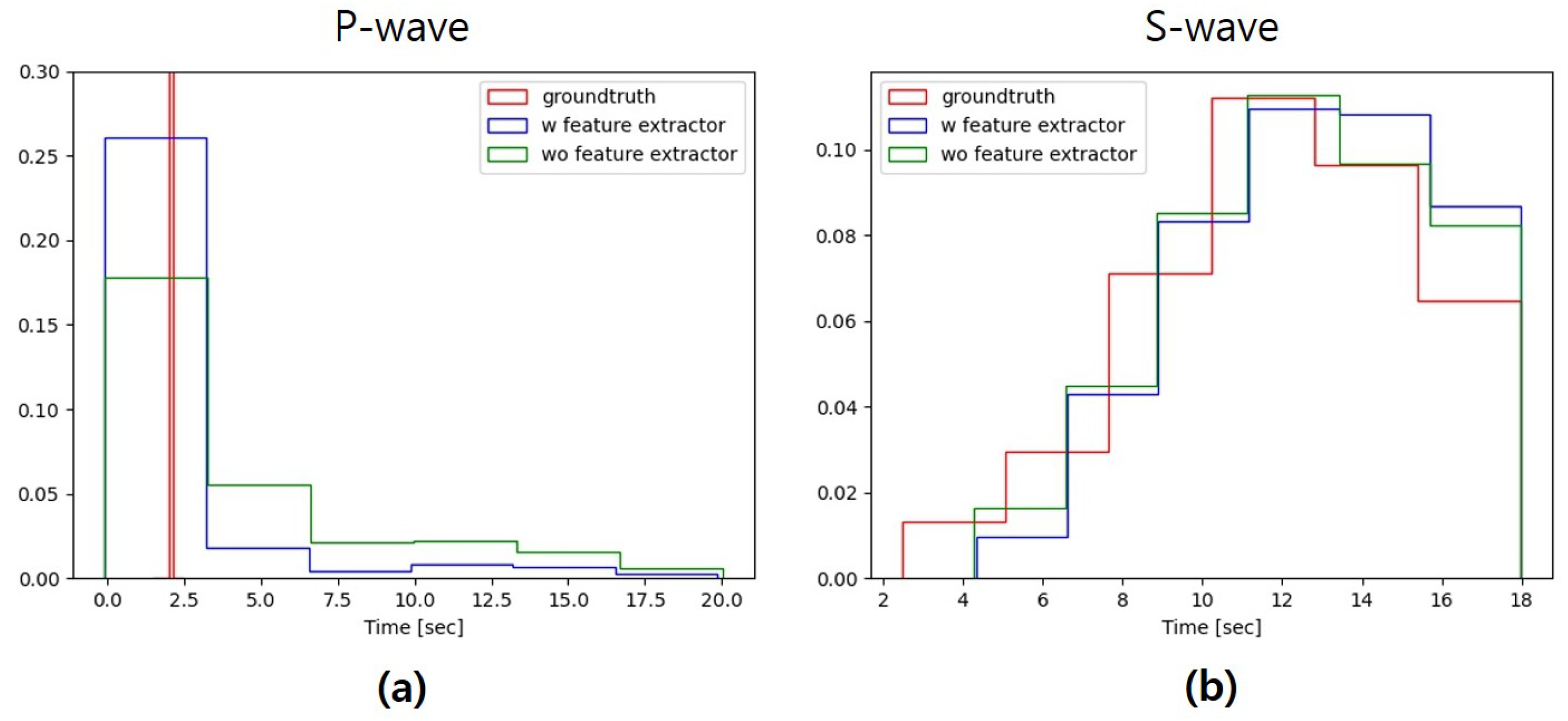
4.2.3. Analysis Results by Classification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shearer, P. Earthquakes and source theory. In Introduction to seismology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 241–300. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D.; Dodge, D. An autonomous system for grouping events in a developing aftershock sequence. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2011, 101, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.A.; Beroza, G.C. An empirical approach to subspace detection. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2014, 85, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.E.; O’Reilly, O.; Bergen, K.J.; Beroza, G.C. Earthquake detection through computationally efficient similarity search. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1501057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM. 2017, 60, pp. 84–90. [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perol, T.; Gharbi, M.; Denolle, M. Convolutional neural network for earthquake detection and location. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, e1700578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, D.; Yao, Z. Deep learning for picking seismic arrival times. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 6612–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Yuan, X. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Moving Ground Target Classification Using Raw Seismic Waveforms as Input. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5751–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, C.; McAuley, J.; Puckette, M. Adversarial audio synthesis. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.04208. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06434. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, T.; Kameoka, H.; Tanaka, K.; Hojo, N. Cyclegan-vc2: Improved cyclegan-based non-parallel voice conversion. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 6820–6824. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 694–711. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Meier, M.A.; Hauksson, E.; Zhan, Z.; Andrews, J. Machine learning seismic wave discrimination: Application to earthquake early warning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4773–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. EarthquakeGen: Earthquake generator using generative adversarial networks. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2019; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2019; pp. 2674–2678. [Google Scholar]
- Uehara, M.; Sato, I.; Suzuki, M.; Nakayama, K.; Matsuo, Y. Generative adversarial nets from a density ratio estimation perspective. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.02920. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Odena, A.; Olah, C.; Shlens, J. Conditional image synthesis with auxiliary classifier GANs. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 2642–2651. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Sheng, Y.; Zhu, W.; Beroza, G.C. STanford EArthquake Dataset (STEAD): A Global Data Set of Seismic Signals for AI. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 179464–179476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Zhu, W.; Sheng, Y.; Beroza, G.C. CRED: A deep residual network of convolutional and recurrent units for earthquake signal detection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Dataset | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real | 96.84 | 99.96 | 91.54 | 0.956 |
| Synthetic | 90.45 | 97.86 | 75.94 | 0.855 |
| Real + 20% | 94.60 | 99.93 | 91.04 | 0.953 |
| Real + 40% | 95.65 | 99.95 | 88.32 | 0.938 |
| Real + 60% | 97.92 | 98.74 | 95.62 | 0.972 |
| Real + 80% | 95.55 | 96.03 | 91.82 | 0.939 |
| Real + 100% | 94.80 | 88.28 | 99.14 | 0.934 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Ku, B.; Zhang, S.; Ahn, J.-K.; Ko, H. Seismic Data Augmentation Based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 6850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236850
Li Y, Ku B, Zhang S, Ahn J-K, Ko H. Seismic Data Augmentation Based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks. Sensors. 2020; 20(23):6850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236850
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuanming, Bonhwa Ku, Shou Zhang, Jae-Kwang Ahn, and Hanseok Ko. 2020. "Seismic Data Augmentation Based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks" Sensors 20, no. 23: 6850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236850
APA StyleLi, Y., Ku, B., Zhang, S., Ahn, J.-K., & Ko, H. (2020). Seismic Data Augmentation Based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks. Sensors, 20(23), 6850. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236850






