Time-Resolved Spectroscopy of Fluorescence Quenching in Optical Fibre-Based pH Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fluorescent Silica Microspheres as Fibre-Based pH Sensors
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
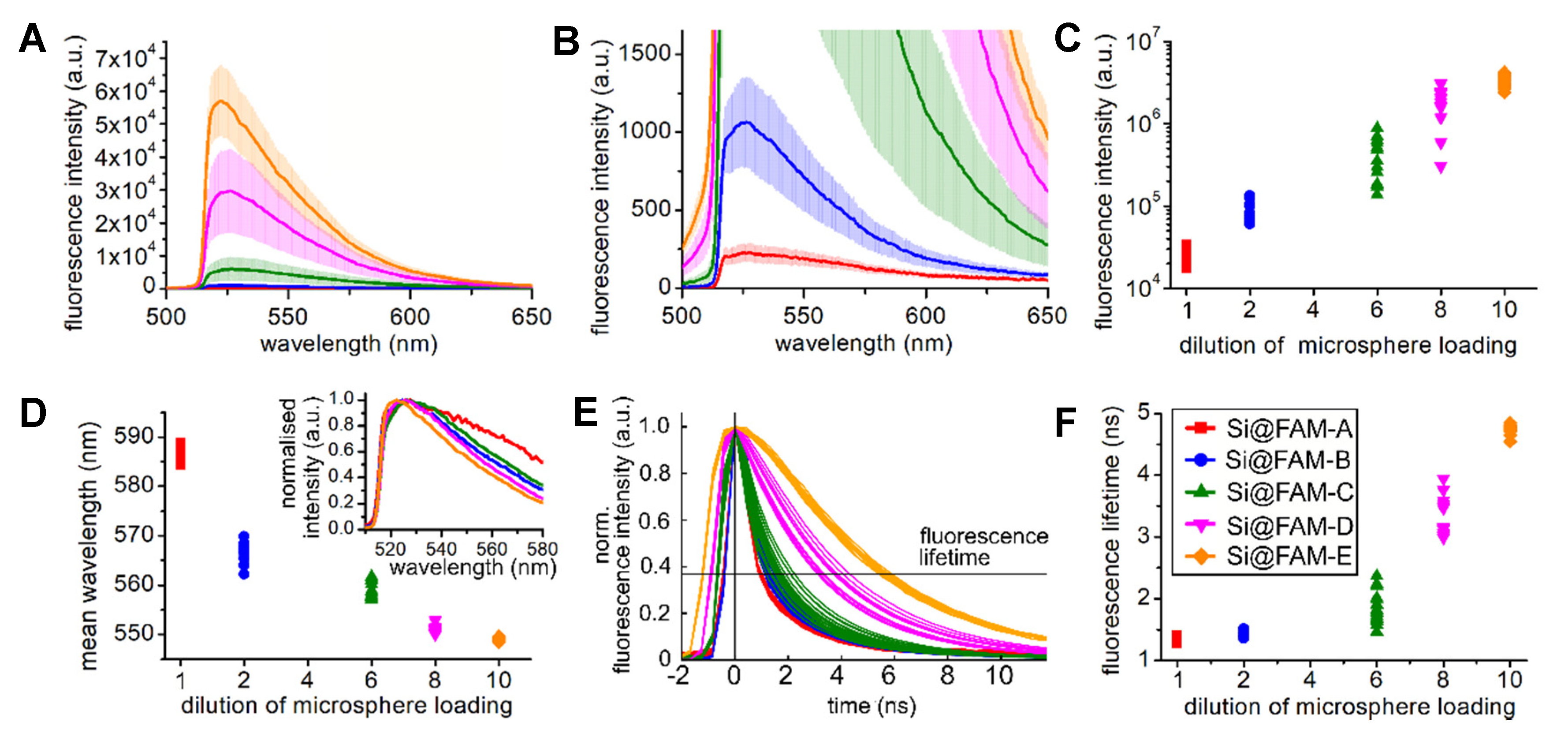
3.1. Changes in the Fluorescence Emission with Bead Loading Density
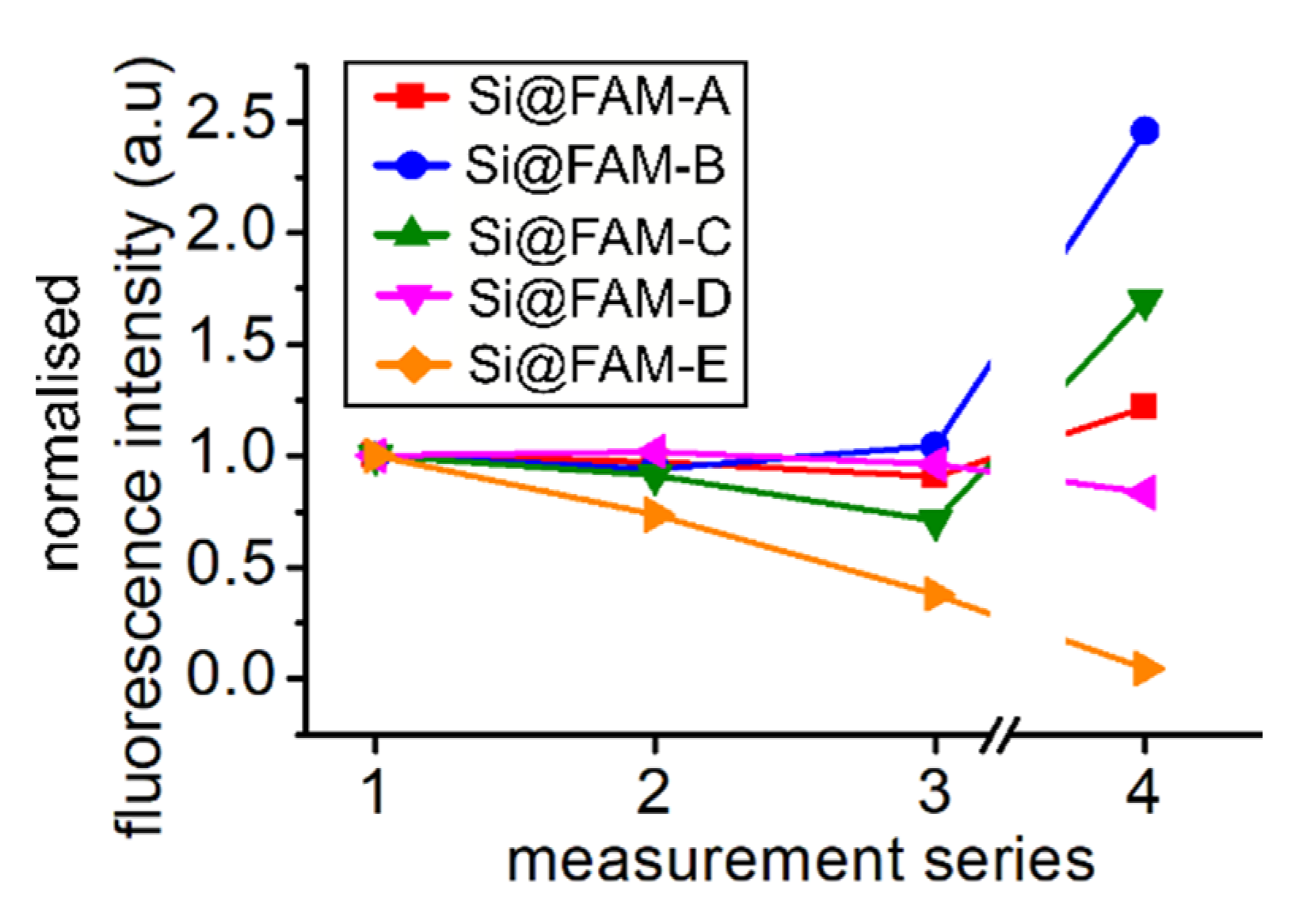
3.2. Photostability
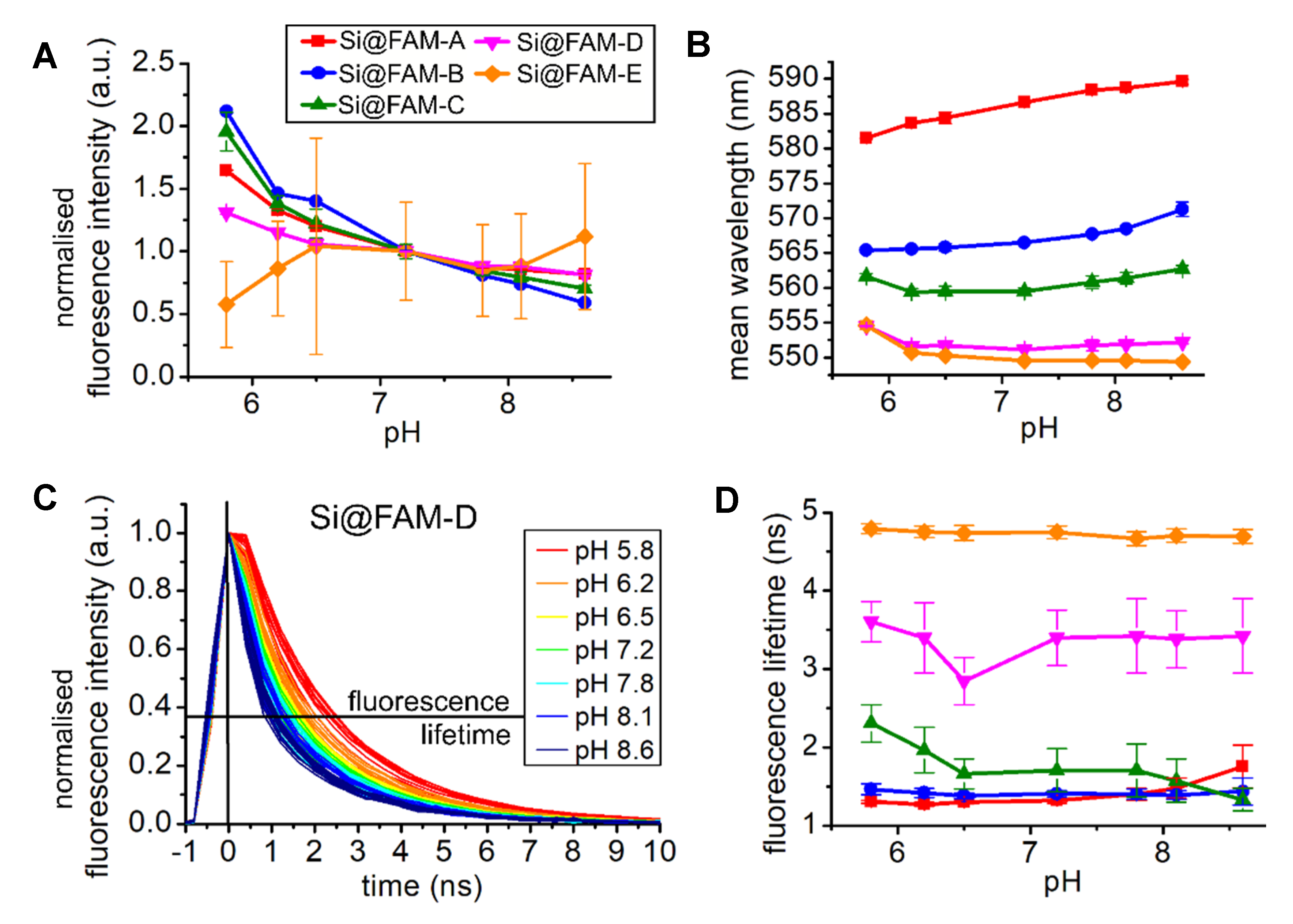
3.3. Response to pH
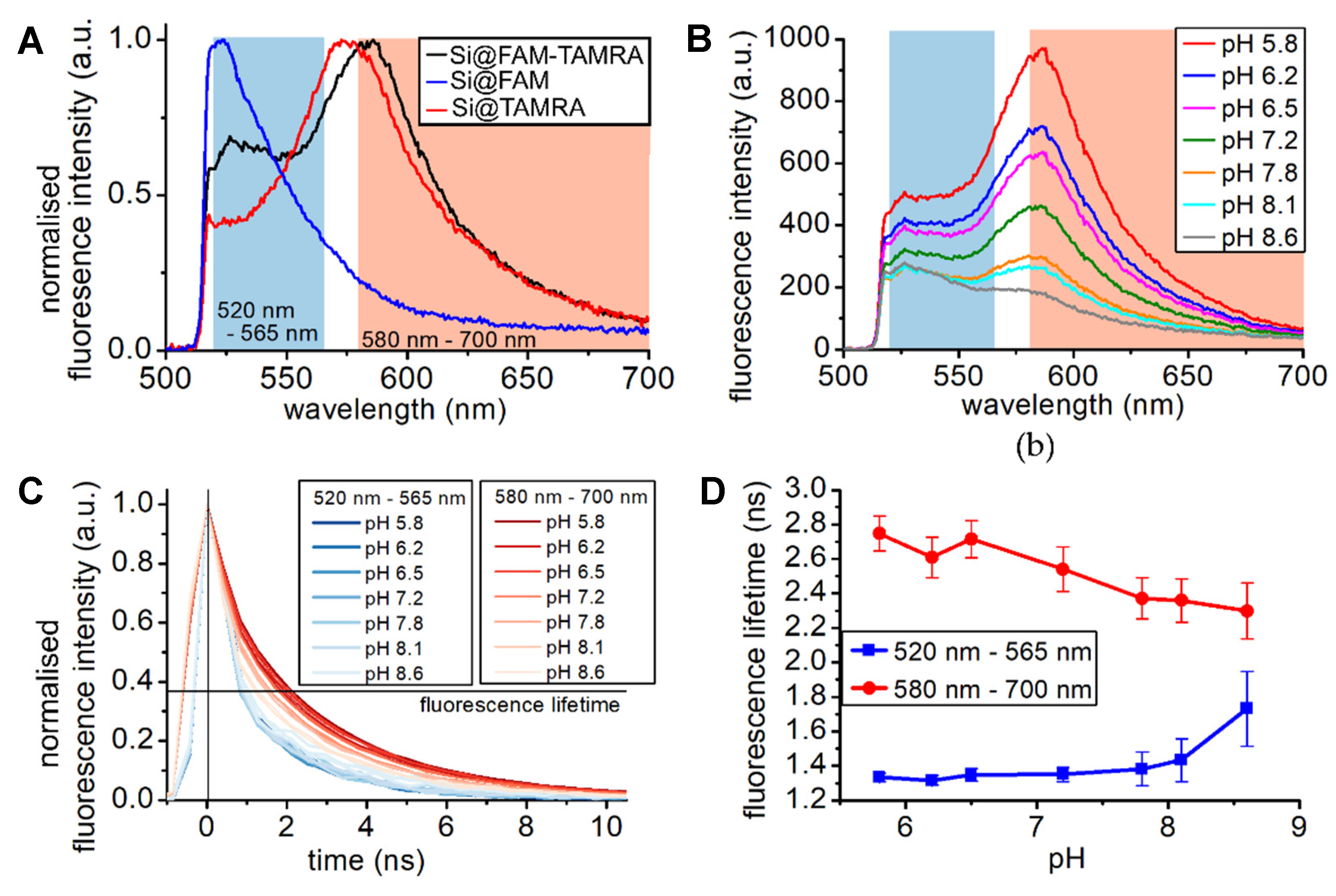
3.4. Ratiometric Dual Fluorophore Optode
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.T.; Gin, J.; Nampoori, V.P.N.; Vallabhan, C.P.G.; Unnikrishnan, N.V.; Radhakrishnan, P. A sensitive fibre optic pH sensor using multiple sol-gel coatings. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2001, 3, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasylevska, G.S.; Borisov, S.M.; Krause, C.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Indicator-Loaded Permeation-Selective Microbeads for Use in Fiber Optic Simultaneous Sensing of pH and Dissolved Oxygen. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4609–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocincova, A.S.; Borisov, S.M.; Krause, C.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Fiber-Optic Microsensors for Simultaneous Sensing of Oxygen and pH, and of Oxygen and Temperature. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8486–8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bradley, M.; Alexander, L.; Duncan, K.; Chennaoui, M.; Jones, A.C.; Sánchez-Martín, R.M. pH sensing in living cells using fluorescent microspheres. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.; Yin, M.-J.; Zhang, A.P.; Qian, J.-W.; He, S. Low-cost high-performance fiber-optic pH sensor based on thin-core fiber modal interferometer. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 22296–22302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.-Y.; Yin, M.-J.; Tam, H.-Y.; Albert, J. Fiber Optic pH Sensor with Self-Assembled Polymer Multilayer Nanocoatings. Sensors 2013, 13, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, F.; Tanner, M.G.; Choudhury, D.; Choudhary, T.R.; Wood, H.A.C.; Harrington, K.; Bradley, M. Controlled core-to-core photo-polymerisation—Fabrication of an optical fibre-based pH sensor. Analyst 2017, 142, 3569–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, T.R.; Tanner, M.G.; Megia-Fernandez, A.; Harrington, K.; Wood, H.A.; Marshall, A.; Zhu, P.; Chankeshwara, S.V.; Choudhury, D.; Monro, G.; et al. High fidelity fibre-based physiological sensing deep in tissue. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, M.; Borisov, S.M.; Klimant, I. Indicators for optical oxygen sensors. Bioanal. Rev. 2012, 4, 115–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, K.; Borisov, S.M.; Klimant, I. Stable optical oxygen sensing materials based on click-coupling of fluorinated platinum(II) and palladium(II) porphyrins—A convenient way to eliminate dye migration and leaching. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 169, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, J.J.; Hickey, M.; Phillips, J.P.; Kyriacou, P.A. Fiber-optic fluorescence-quenching oxygen partial pressure sensor using platinum octaethylporphyrin. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 5603–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Leiner, M.J.P.; Schaffar, B.P.H. Oxygen optrode for use in a fiber-optic glucose biosensor. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2377–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, J.C.; Hussain, F.; Evans, N.D.; Sachedina, N. In vivo glucose monitoring: The clinical reality and the promise. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1897–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxl, T.; Khan, F.; Ferla, M.; Birch, D.; Pickup, J. A fluorescence lifetime-based fibre-optic glucose sensor using glucose/galactose-binding protein. Analyst 2011, 136, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaei, L.; Olthuis, W.; Tsujimura, S.; Sudhölter, E.J.R.; van den Berg, A. Lactate biosensors: Current status and outlook. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiner, M.J.P. Luminescence chemical sensors for biomedical applications: Scope and limitations. Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 255, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Ogawa, M.; Alford, R.; Choyke, P.L.; Urano, Y. New Strategies for Fluorescent Probe Design in Medical Diagnostic Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2620–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.; James, S.; Lee, S.-W.; Morgan, S.P.; Korposh, S. Biomedical application of optical fibre sensors. J. Opt. 2018, 20, 073003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.J.; Eyley, S.; Thielemans, W.; Aylott, J.W. Dual fluorescent labelling of cellulose nanocrystals for pH sensing. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 8929–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, K.; Kufcsák, A.; McAughtrie, S.; Fleming, H.; Krstajic, N.; Campbell, C.J.; Henderson, R.K.; Dhaliwal, K.; Thomson, R.R.; Tanner, M.G. pH sensing through a single optical fibre using SERS and CMOS SPAD line arrays. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 30976–30986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftink, M.R. Chapter: 2. Fluorescence Quenching: Theory and Applications. In Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy: Principles; Lakowicz, J.R., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 53–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jares-Erijman, E.A.; Jovin, T.M. FRET imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M.M.; Lindqvist, L. The pH dependence of fluorescein fluorescence. J. Lumin. 1975, 10, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcu, L. Fluorescence Lifetime Techniques in Medical Applications. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 304–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, K.; Kufcsák, A.; Krstajić, N.; Henderson, R.K.; Thomson, R.R.; Tanner, M.G. Fibre optic time-resolved spectroscopy using CMOS-SPAD arrays. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Optical Fibers and Sensors for Medical Diagnostics and Treatment Applications XVII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 February 2017; Volume 10058. [Google Scholar]
- Kufcsák, A.; Erdogan, A.; Walker, R.; Ehrlich, K.; Tanner, M.; Megia-Fernandez, A.; Scholefield, E.; Emanuel, P.; Dhaliwal, K.; Bradley, M.; et al. Time-resolved spectroscopy at 19,000 lines per second using a CMOS SPAD line array enables advanced biophotonics applications. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 11103–11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fišerová, E.; Kubala, M. Mean fluorescence lifetime and its error. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 2059–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Hohng, S.; Ha, T. A practical guide to single-molecule FRET. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, C.I.; Hsiang, J.-C.; Khalil, A.M.; Hull, N.P.; Dickson, R.M. FRET-Enabled Optical Modulation for High Sensitivity Fluorescence Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6318–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Erdogan, A.T.; Williams, G.O.S.; Usai, A.; Krstajic, N.; Finlayson, N.; Beavil, A.; Beavil, R.; Henderson, R.K. Time-zoomable FRET spectroscopy with a 512 x16 SPAD line sensor. In Proceedings of the Biophysics, Biology and Biophotonics III: The Crossroads, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20 February 2018; Volume 10504, p. 105040M. [Google Scholar]
- Kamaljith, V.; Tanner, M.G.; Wood, H.A.C.; Harrington, K.; Choudhury, A.; Bradley, M.; Thomson, R.R. Ultrafast-laser-ablation-assisted spatially selective attachment of fluorescent sensors onto optical fibers. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2716–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Tanner, M.G.; Venkateswaran, S.; Stone, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Bradley, M. A hydrogel-based optical fibre fluorescent pH sensor for observing lung tumor tissue acidity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1134, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ehrlich, K.; Choudhary, T.R.; Ucuncu, M.; Megia-Fernandez, A.; Harrington, K.; Wood, H.A.C.; Yu, F.; Choudhury, D.; Dhaliwal, K.; Bradley, M.; et al. Time-Resolved Spectroscopy of Fluorescence Quenching in Optical Fibre-Based pH Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216115
Ehrlich K, Choudhary TR, Ucuncu M, Megia-Fernandez A, Harrington K, Wood HAC, Yu F, Choudhury D, Dhaliwal K, Bradley M, et al. Time-Resolved Spectroscopy of Fluorescence Quenching in Optical Fibre-Based pH Sensors. Sensors. 2020; 20(21):6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216115
Chicago/Turabian StyleEhrlich, Katjana, Tushar R. Choudhary, Muhammed Ucuncu, Alicia Megia-Fernandez, Kerrianne Harrington, Harry A. C. Wood, Fei Yu, Debaditya Choudhury, Kev Dhaliwal, Mark Bradley, and et al. 2020. "Time-Resolved Spectroscopy of Fluorescence Quenching in Optical Fibre-Based pH Sensors" Sensors 20, no. 21: 6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216115
APA StyleEhrlich, K., Choudhary, T. R., Ucuncu, M., Megia-Fernandez, A., Harrington, K., Wood, H. A. C., Yu, F., Choudhury, D., Dhaliwal, K., Bradley, M., & Tanner, M. G. (2020). Time-Resolved Spectroscopy of Fluorescence Quenching in Optical Fibre-Based pH Sensors. Sensors, 20(21), 6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216115






