Seabed Topography Changes in the Sopot Pier Zone in 2010–2018 Influenced by Tombolo Phenomenon
Abstract
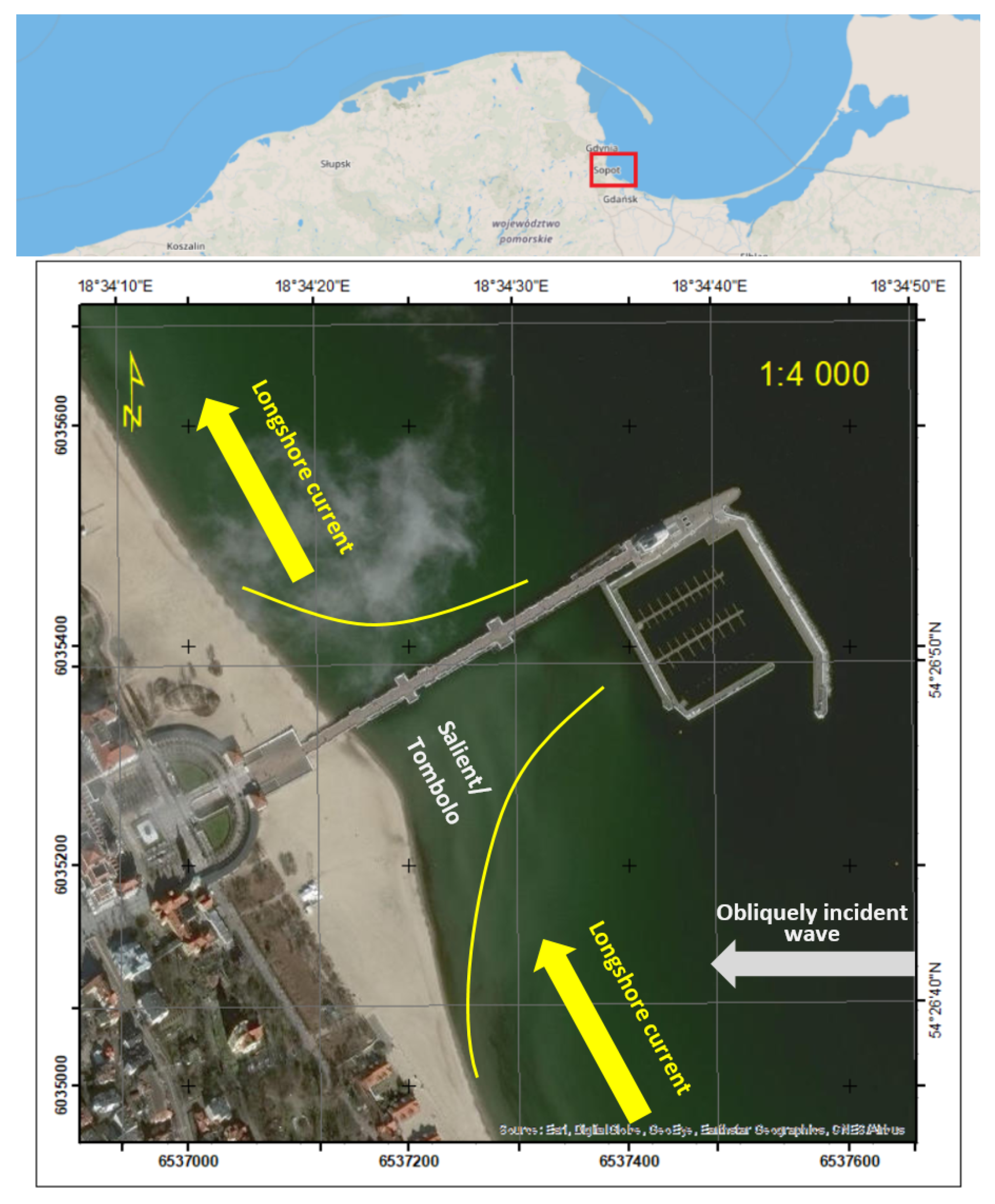
1. Introduction
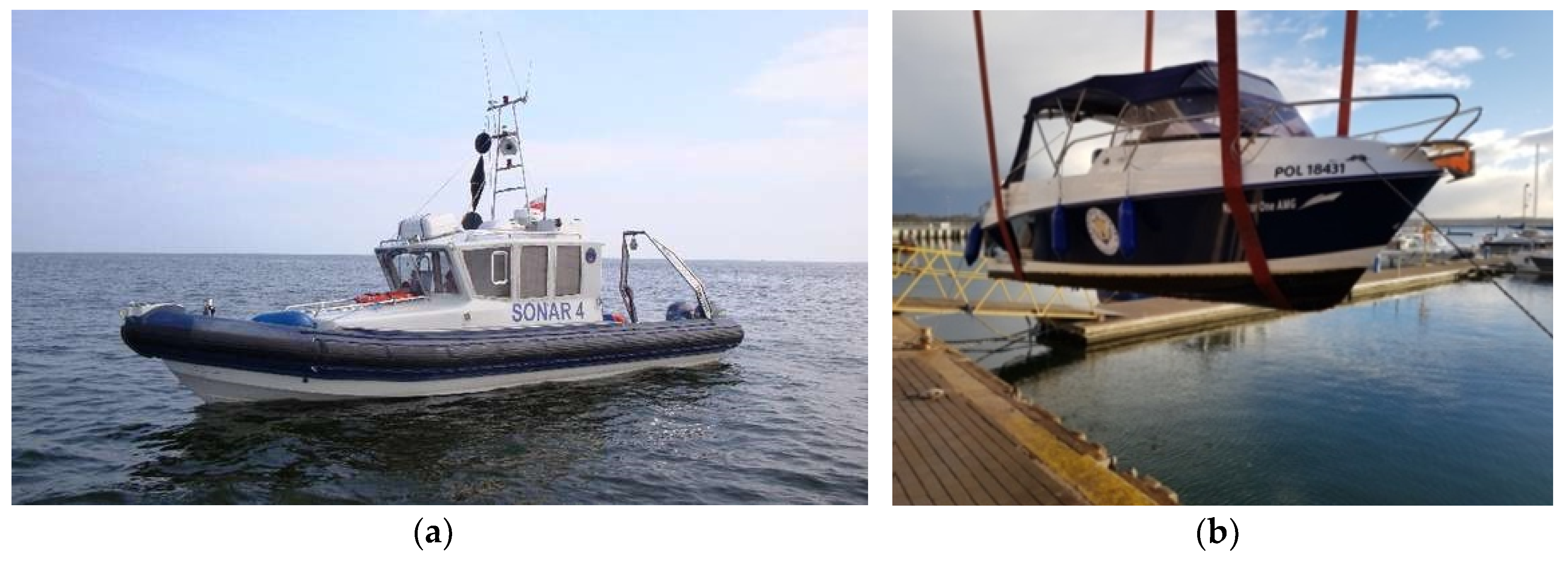
- Using a typical hydrographic vessel with a very low draught of less than 30 cm (used in the research—Figure 1a,b).
- Using an unmanned, directly controlled vessel (from the telemanipulator), which means that they are not able to navigate independently on survey profiles.
- Using an unmanned vessel capable of automatically navigating along a set route.
- Bathymetric surveys from the period before the marina was built. They were performed by the Maritime Office in Gdynia (2010).
- Bathymetric surveys taken after the marina was built. They were performed by the Maritime Office in Gdynia (2012 and 2015).
- Bathymetric surveys carried out by us in 2018.
- Electronic navigational charts made by the Hydrographic Office of the Polish Navy in the years: 2011, 2014 and 2018.
2. Materials and Methods
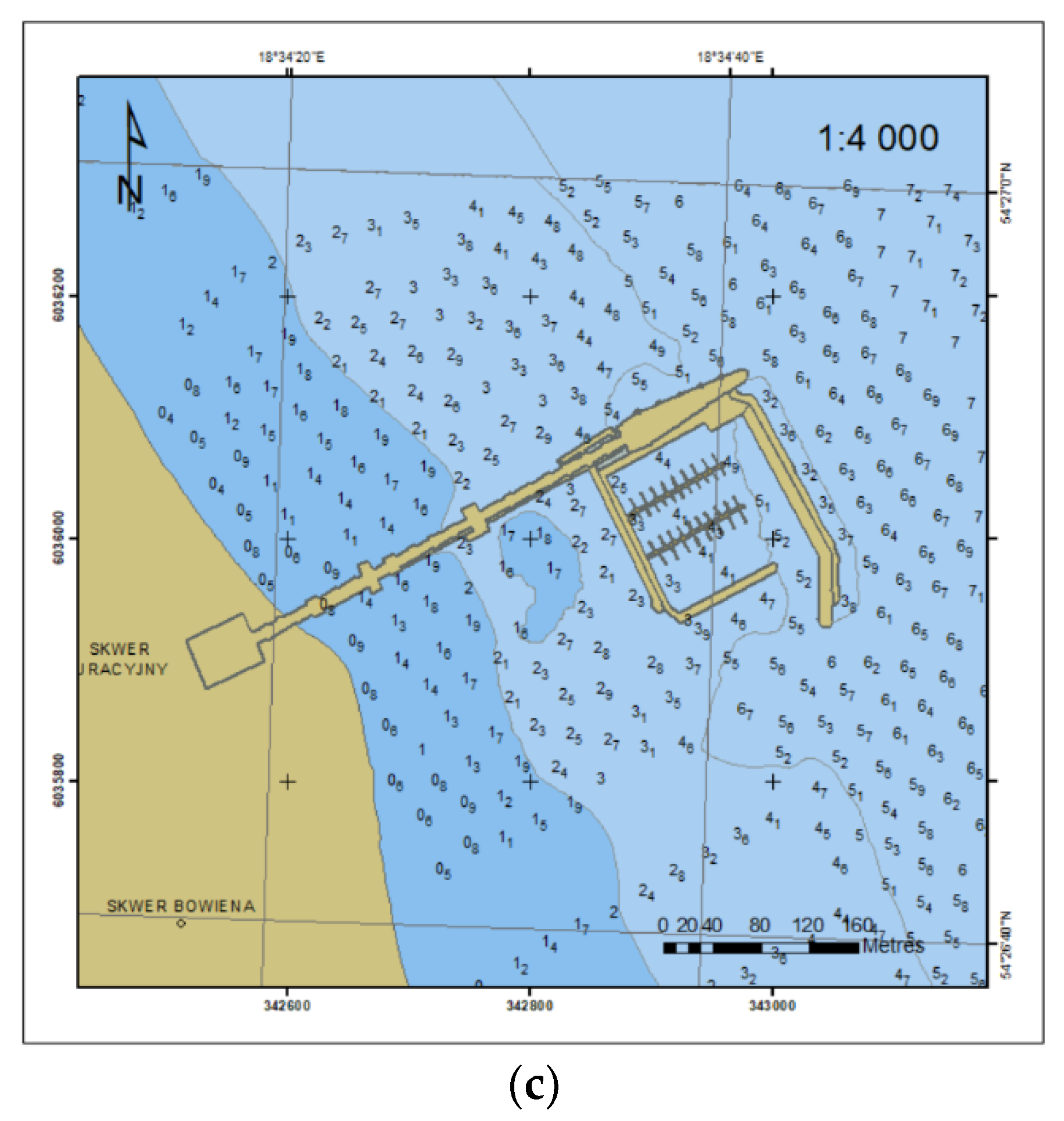
2.1. Archival Hydrographic Data: 2010 and 2012
2.2. Geospatial Data Contained in the Electronic Navigational Charts: 2011, 2014, 2018
2.3. Bathymetric Surveys Using SBES: 2018
2.4. Comparative Analysis of Research Material
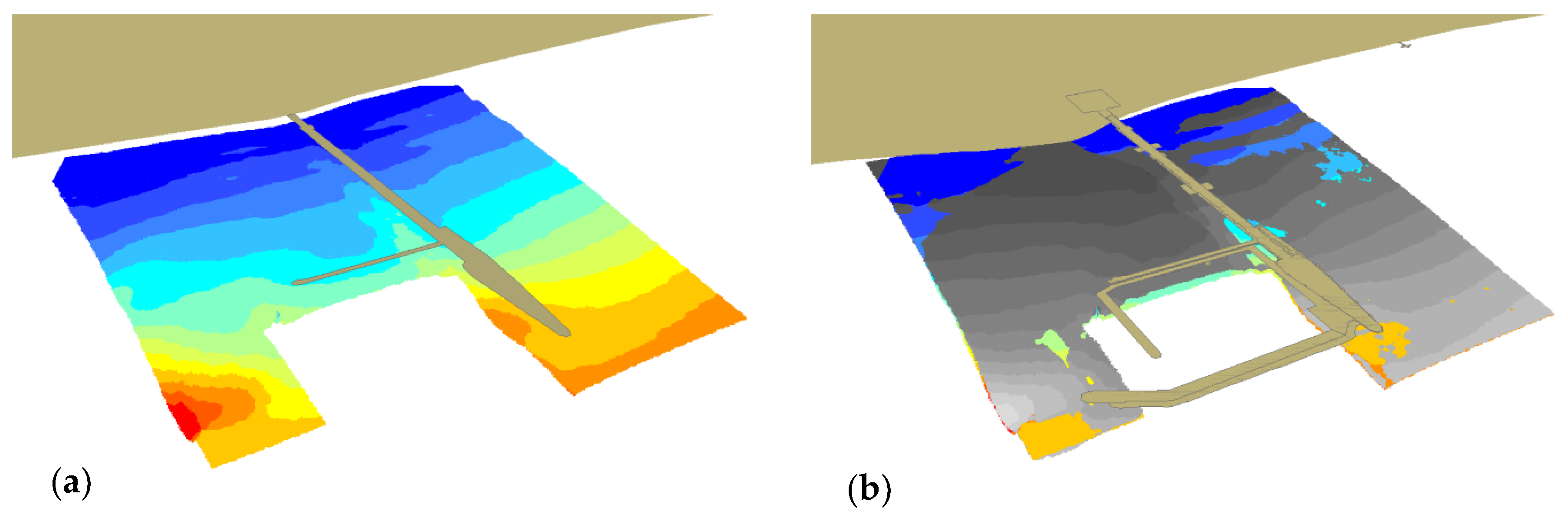
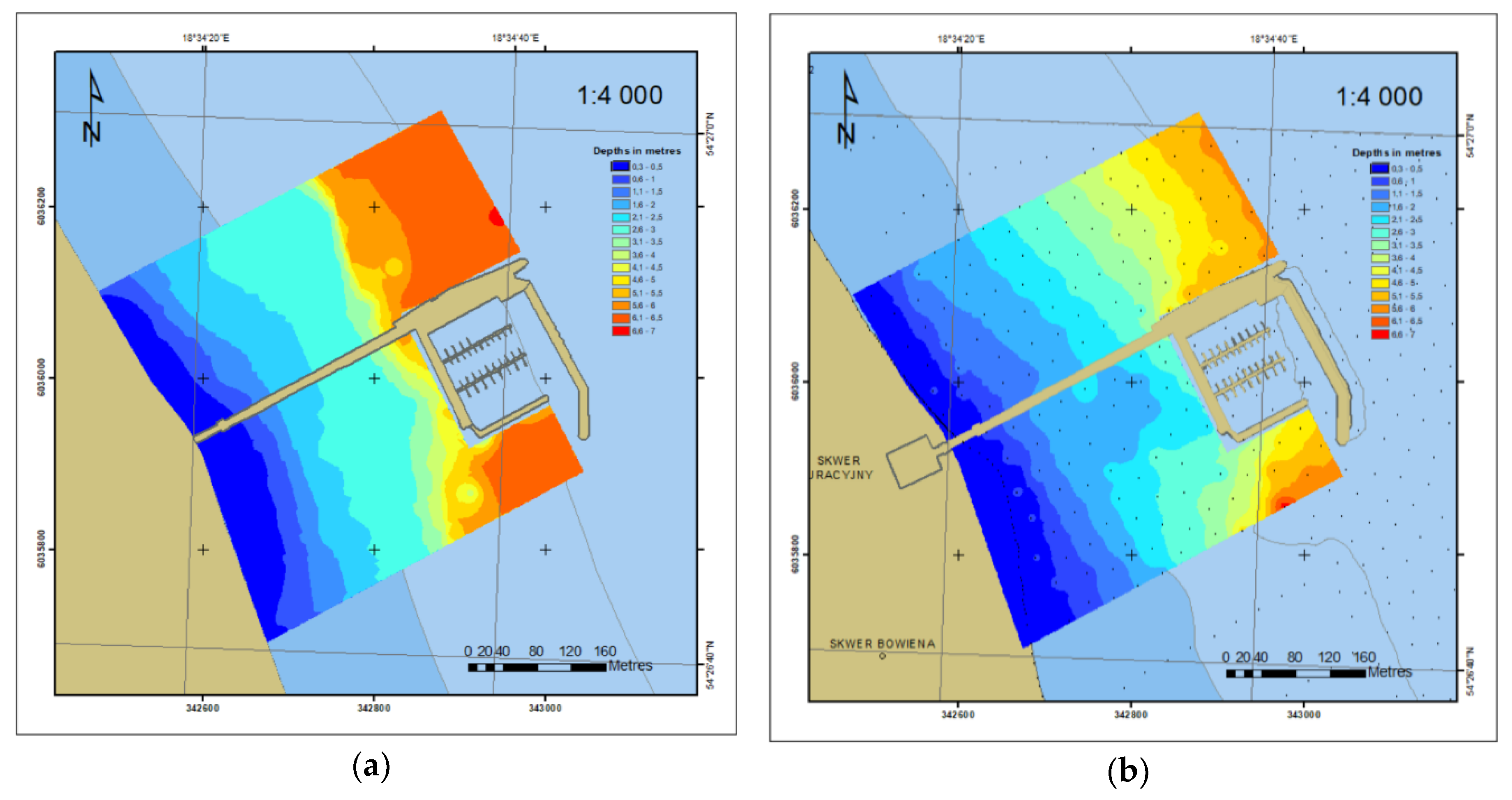
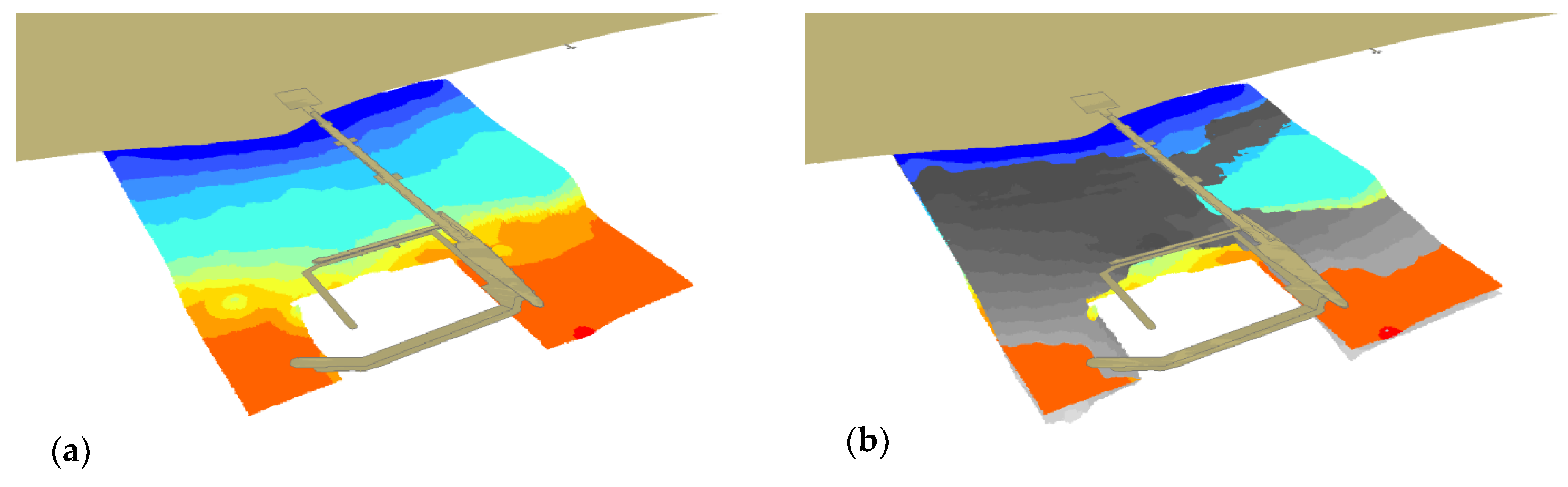
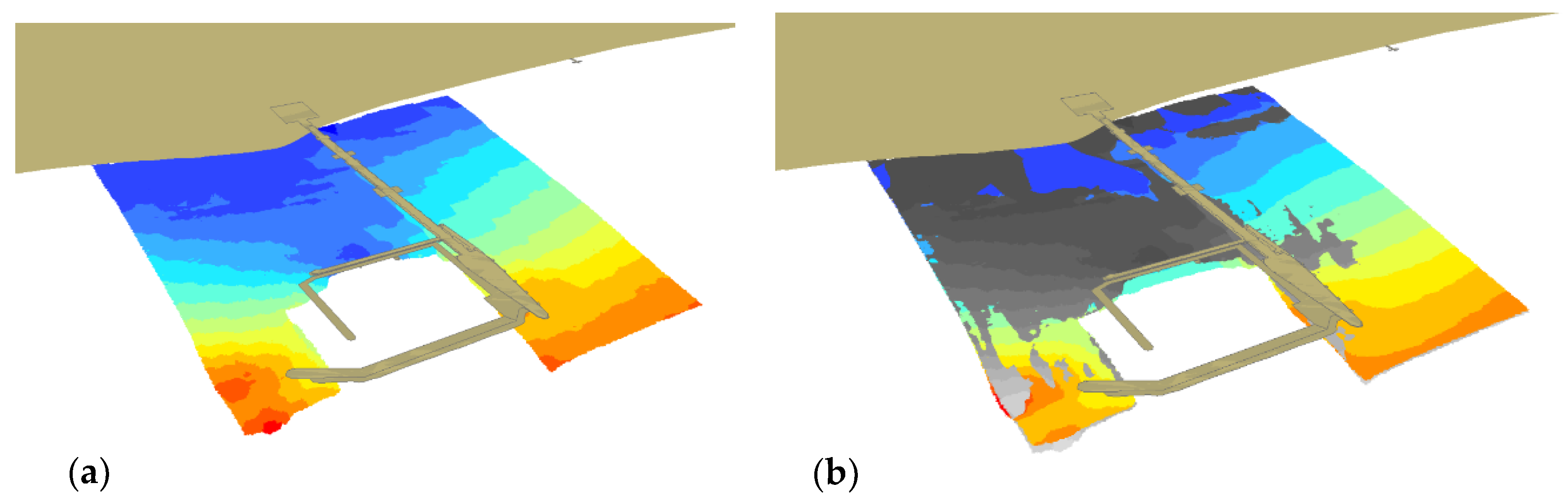
3. Results and Discussion
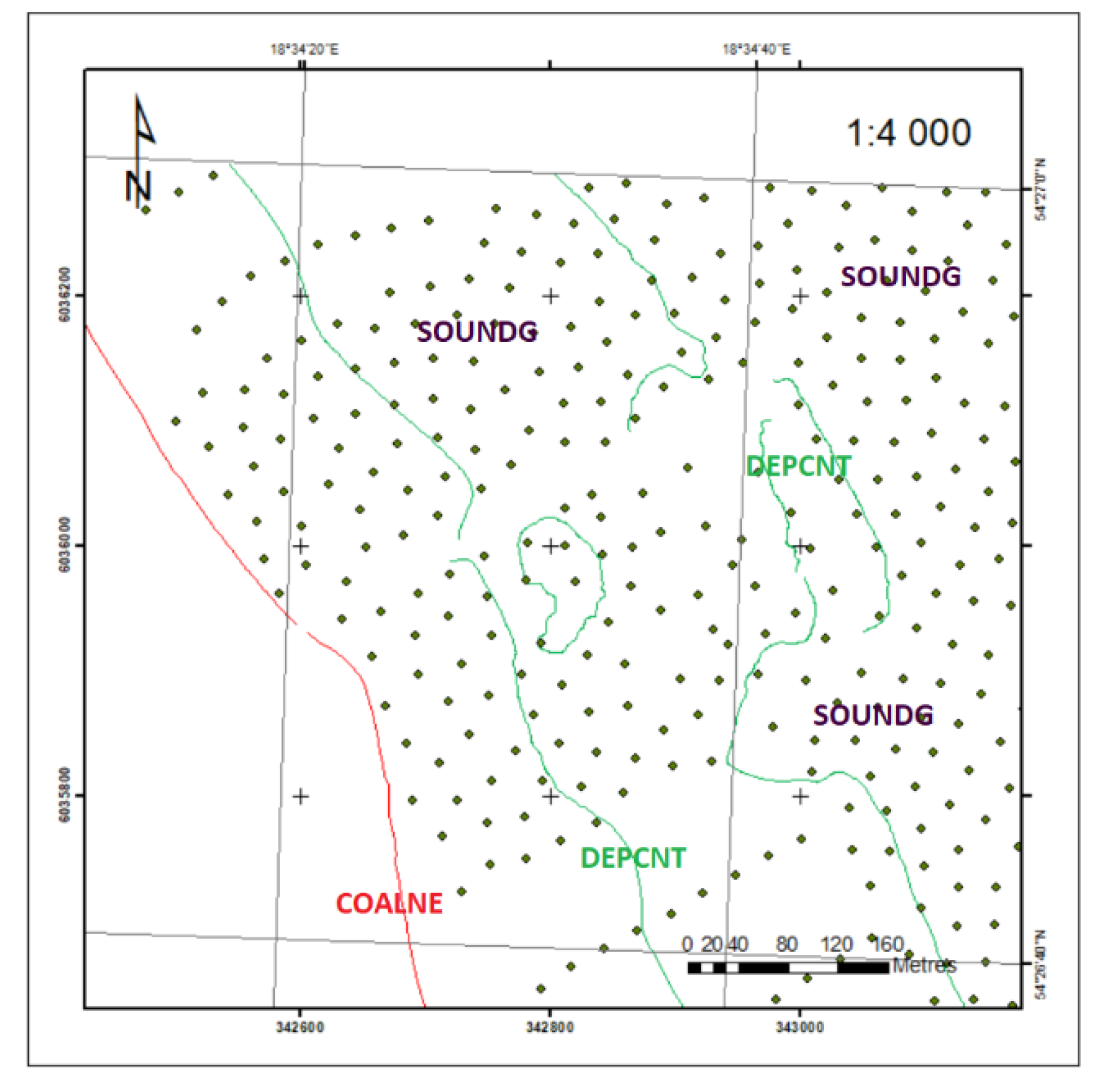
3.1. Extraction of Geospatial Data from ENC
3.2. Digital Sea Bottom Model by Inverse Distance Weighted Method
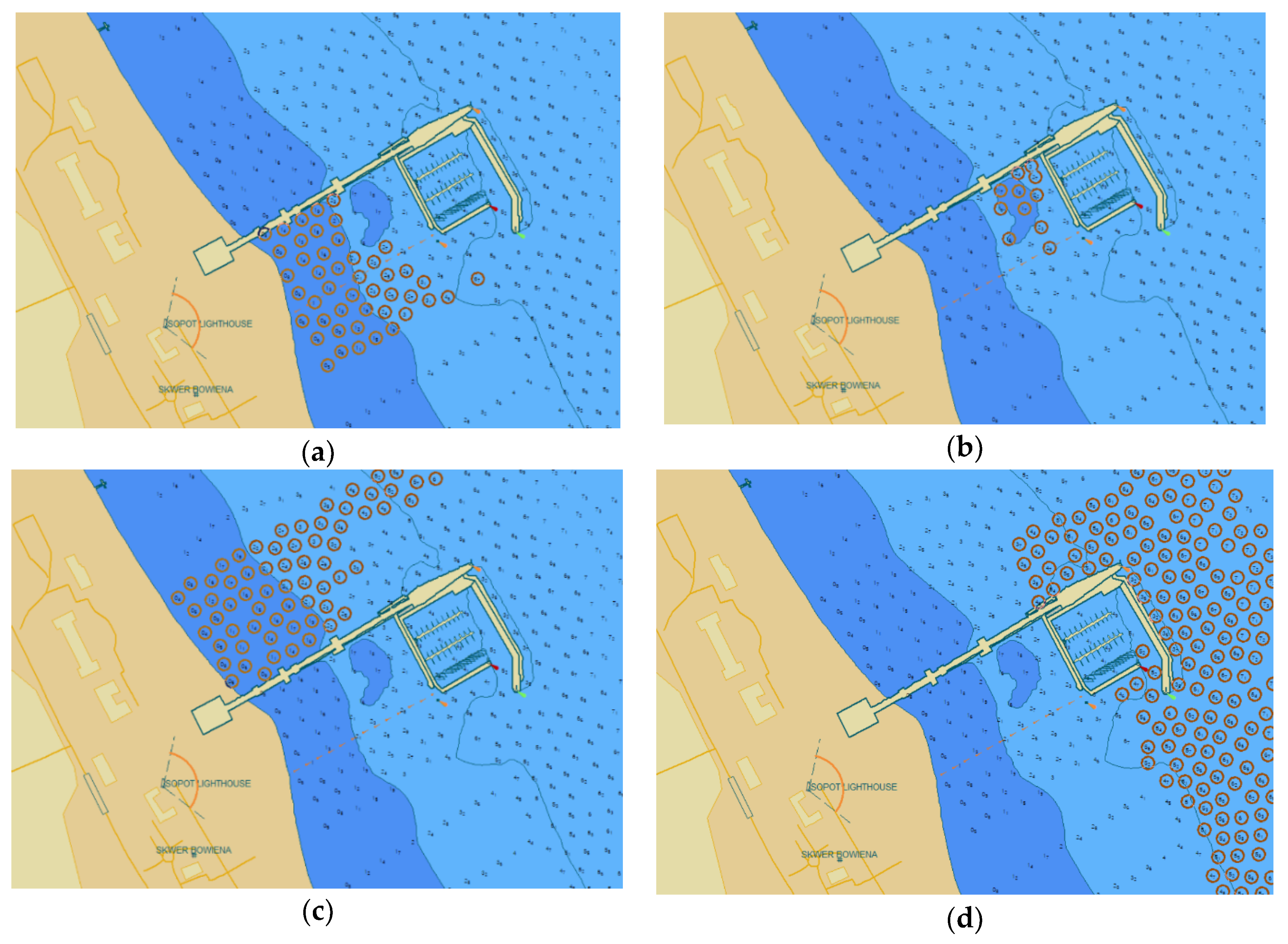
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Charts from 2010 and 2012 (SBES)
3.4. Comparative Analysis of the 2014 and 2018 (ENC)
3.5. Comparative Analysis of 2012 and 2018 SBES Soundings
3.6. Cell Size and DBSM Reliability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Specht, M.; Specht, C.; Wąż, M.; Naus, K.; Grządziel, A.; Iwen, D. Methodology for Performing Territorial Sea Baseline Measurements in Selected Waterbodies of Poland. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grządziel, A.; Wąż, M. The Invention and Developing of Multibeam Echosounder Technology. Pol. Hyperb. Res. 2018, 62, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stateczny, A.; Włodarczyk-Sielicka, M.; Grońska, D.; Motyl, W. Multibeam Echosounder and LiDAR in Process of 360-Degree Numerical Map Production for Restricted Waters with HydroDron. In Proceedings of the 2018 Baltic Geodetic Congress, Gdańsk, Poland, 21–23 June 2018; pp. 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Stateczny, A.; Grońska, D.; Motyl, W. Hydrodron–New Step for Professional Hydrography for Restricted Waters. In Proceedings of the 2018 Baltic Geodetic Congress, Gdańsk, Poland, 21–23 June 2018; pp. 226–230. [Google Scholar]
- Stateczny, A.; Burdziakowski, P. Universal autonomous control and management system for multipurpose unmanned surface vessel. Pol. Marit. Res. 2019, 26, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Sieradzki, R.; Baryla, R. Multi-GNSS high-rate RTK, PPP and novel direct phase observation processing method: Application to precise dynamic displacement detection. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2018, 29, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziewicki, M.; Specht, C. Position Accuracy Evaluation of the Modernized Polish DGPS. Pol. Marit. Res. 2009, 16, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, C.; Pawelski, J.; Smolarek, L.; Specht, M.; Dąbrowski, P. Assessment of the Positioning Accuracy of DGPS and EGNOS Systems in the Bay of Gdansk Using Maritime Dynamic Measurements. J. Navig. 2019, 72, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szot, T.; Specht, C.; Specht, M.; Dabrowski, P.S. Comparative Analysis of Positioning Accuracy of Samsung Galaxy Smartphones in Stationary Measurements. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Cheng, Y.T.; Zhou, T.; Ravi, R.; Hasheminasab, S.M.; Flatt, J.E.; Troy, C.; Habib, A. Evaluation of UAV LiDAR for Mapping Coastal Environments. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, C.; Harley, M.; Turner, I.; Abdul, M.; Matheen, N.; Glamore, W. UAV Applications to Coastal Engineering. In Proceedings of the Australasian Coasts & Ports Conference, Auckland, New Zealand, 15–18 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolakopoulos, K.G.; Kozarski, D.; Kogkasc, S. Coastal areas mapping using UAV photogrammetry. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10428, Earth Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing/GIS Applications VIII, 104280O, Warsaw, Poland, 5 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stateczny, A.; Kazimierski, W.; Burdziakowski, P.; Motyl, W.; Wisniewska, M. Shore Construction Detection by Automotive Radar for the Needs of Autonomous Surface Vehicle Navigation. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuba, Y.; Sato, S. Nearshore bathymetry estimation using UAV. Coast. Eng. J. 2018, 60, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsma, E.; Almar, R.; Almeida, L.P.; Sall, M. On the operational use of UAVs for video-derived bathymetry. Coast. Eng. 2019, 152, 103527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, F.; Shimozono, T.; Matsuba, Y. UAV-based mapping of nearshore bathymetry over broad areas. Coast. Eng. J. 2020, 62, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrafiotis, P.; Skarlatos, D.; Georgopoulos, A.; Karantzalos, K. Shallow Water Bathymetry Mapping from UAV Imagery Based on Machine Learning. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W10, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, I.; Marfai, M.A. Shoreline changes analysis of Kendal Coastal Area. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 451, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, A.; Snyder, A.; Richmond, B. National Assessment of Shoreline Change-Historical Shoreline Change Along the North Coast of Alaska, Icy Cape to Cape Prince of Wales. Open-File Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, D.; Mahapatra, M. Extracting Shoreline from Satellite Imagery for GIS Analysis. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, A. Determination of Inland Areas Coastlines. In Proceedings of the 18th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 2–8 July 2018; Volume 18, pp. 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, A.; Specht, C.; Specht, M.; Dąbrowski, P.; Szafran, M. Integrated Geodetic and Hydrographic Measurements of the Yacht Port for Nautical Charts and Dynamic Spatial Presentation. Geosciences 2020, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdziakowski, P.; Janowski, A.; Kholodkov, A.; Matysik, K.; Matysik, M.; Przyborski, M.; Szulwic, J.; Tysiąc, P.; Wojtowicz, A. Maritime Laser Scanning As The Source For Spatial Data. Pol. Marit. Res. 2015, 22, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, C.; Specht, M.; Cywiński, P.; Skóra, M.; Marchel, Ł.; Szychowski, P. A (2019c) New Method for Determining the Territorial Sea Baseline Using an Unmanned, Hydrographic Surface Vessel. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 35, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, L.; Martell Dubois, R.; Ressl, R.; Silva, R.; Cruz, C.; Muñoz-Pérez, J. Dynamics of coastline changes in Mexico. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of coastline change based on remote sensing measurement. J. Hohai Univ. 2011, 40, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. Three-Dimensional Sediment Transport Model. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, B.A.; Nicholson, J. A three-dimensional model of suspended particulate sediment transport. Coast. Eng. 1998, 12, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, M.; Kamphuis, J.W.; Kuchiishi, T.; Matsubara, Y.; Noda, H. Medium-term Q-3D coastal area model with shoreline change around coastal structures. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, 19–24 September 2004; pp. 2194–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, A.; Maruyama, K.; Shimizu, T.; Sakakiyama, T. A numerical prediction model of threedimensional beach deformation around a structure. Coast. Eng. Jpn. 1986, 29, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Kumagai, T.; Watanabe, A. Improved 3-D beach evolution model coupled with the shoreline model (3D-SHORE). In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Coastal Engineering (ICCE 1996), Orlando, FL, USA, 2–6 September 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jörissen, J.G.L. Strandhoofden Gemodelleerd in Delft3D-RAM: Strandhoofden als Instrument Voor Het Regelen van Het Langstransport. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, P.T. Numerical Model of Beach Topography Evolution Due to Waves and Currents. Special Emphasis on Coastal Structures. 2020. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/c5af/bff0cb81a3dff8f2cc3528016c85bb1b1107.pdf?_ga=2.233758174.1954626850.1580128302-234920152.1580128302 (accessed on 27 January 2020).
- Kuchiishi, T.; Kato, K.; Kuroiwa, M.; Matsubara, Y.; Noda, H. Applicability of 3D morphodynamic model with shoreline change using a quasi-3D nearshore current model. In Proceedings of the 14th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference (ISOPE 2004), Toulon, France, 23–28 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Roelvink, D.; Giles, L.; van der Wegen, M. Morphological modelling of the wet-dry interface at various timescales. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Hydroscience and Engineering (ICHE 2006), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–13 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- van Koningsveld, M.; van Kessel, T.; Walstra, D.-J.R. A hybrid modelling approach to coastal morphology. In Proceedings of the 5th Coastal Dynamics International Conference (CD 2005), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Irham, M.; Suryati, S.; Maulinda, M.; Miswar, E.; Tarmizi, T. The synthetic study of coastline change using one-line numerical model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 348, 012124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Park, D.; Lim, H.S. Simulation of tombolo evolution by using CST3D-WA. Vibroeng. Procedia 2017, 12, 196–201. [Google Scholar]
- International Hydrographic Organization. Standards for Hydrographic Surveys, Special Publication No. 44, 5th ed.; International Hydrographic Organization: Monaco, Monaco, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hydrographic Office of the Polish Navy. Maritime Hydrography—Organization and Research Rules; Hydrographic Office of the Polish Navy: Gdynia, Poland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hydrographic Office of the Polish Navy. Maritime Hydrography—Rules of Data Collecting and Results Presentation; Hydrographic Office of the Polish Navy: Gdynia, Poland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Transport, Construction and Maritime Economy. Ordinance of the Minister of Transport, Construction and Maritime Economy of 23 October 2006 on the Technical Conditions for the Use of Marine Hydraulic Structures and the Detailed Scope of Inspections to Be Carried out on Such Structures, 2006; Ministry of Transport, Construction and Maritime Economy: Warsaw, Poland, 2006. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Chiocci, F.L.; Casalbore, D. Unexpected fast rate of morphological evolution of geologically-active continental margins during Quaternary: Examples from selected areas in the Italian seas. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 82, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalbore, D.; Clare, M.A.; Pope, E.L.; Quartau, R.; Bosman, A.; Chiocci, F.L.; Romagnoli, C.; Santos, R. Bedforms on the submarine flanks of insular volcanoes: New insights gained from high resolution seafloor surveys. Sedimentology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwolinski, Z. Searching research problems of contemporary geomorphology. Landf. Anal. 2012, 20, 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Bosman, A.; Casalbore, D.; Romagnoli, C.; Chiocci, F.L. Formation of an ‘a’ā lava delta: Insights from time-lapse multibeam bathymetry and direct observations during the Stromboli 2007 eruption. Bull. Volcanol. 2014, 76, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalbore, D.; Bosman, A.; Chiocci, F.L. Study of recent small-scale landslides in geologically active marine areas through repeated multibeam surveys: Examples from the southern Italy. In Submarine Mass Movements and Their Consequences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 573–582. [Google Scholar]
- Anzidei, M.; Bosman, A.; Carluccio, R.; Casalbore, D.; Caracciolo, F.D.; Esposito, A.; Nicolosi, I.; Pietrantonio, G.; Vecchio, A.; Carmisciano, C.; et al. Flooding scenarios due to land subsidence and sea-level rise: A case study for Lipari Island (Italy). Terra Nova 2017, 29, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massel, S.R. Hydrodynamic Processes in Marine Ecosystems; Gdańsk University Publishing House: Gdańsk, Poland, 2010. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Benac, Č.; Bočić, N.; Ružić, I. On the origin of both a recent and submerged tombolo on Prvić Island in the Kvarner area (Adriatic Sea, Croatia). Geol. Croat. 2019, 72, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, J.; Smith, M. Geomorphological mapping. In Geomorphological Techniques; Clarke, L.E., Nield, J.M., Eds.; British Society for Geomorphology: London, UK, 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, M.L.; Grano, O.; Pyokari, M. Spits and tombolos in the southwest archipelago of Finland. J. Coast. Res. 1989, 5, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Burdziakowski, P.; Specht, C.; Dabrowski, P.S.; Specht, M.; Lewicka, O.; Makar, A. Using UAV Photogrammetry to Analyse Changes in the Coastal Zone Based on the Sopot Tombolo (Salient) Measurement Project. Sensors 2020, 20, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, M.; Specht, C.; Mindykowski, J.; Dąbrowski, P.S.; Masnicki, R.; Makar, A. Geospatial Modeling of the Tombolo Phenomenon in Sopot using Integrated Geodetic and Hydrographic Measurement Methods. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, A. Verification of the Digital Sea Bottom Model Built by Bathymetric Data–Deep Water Study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Geo Sciences GEOLINKS 2019, Athens, Greece, 26–29 March 2019; Volume 1, pp. 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Makar, A. Reliability of the Digital Sea Bottom Model Sourced by Multibeam Echosounder in Shallow Water. In Proceedings of the 5th World Multidisciplinary Earth Sciences Symposium WMESS, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Makar, A. Modeling of Sea Bottom Using Bézier Pieces. Hydroacoustics 2010, 13, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Makar, A. Modeling of Sea Bottom Using Uniform Rectangular Bézier Pieces. Hydroacoustics 2011, 14, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Piegl, L.; Tiller, W. The NURBS Book; Springer: Berlin/Heideberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Makar, A. The Sea Bottom Surface Described by Coons Pieces. Sci. J. Mar. Uni. Szcz. 2016, 45, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilleos, G. The Inverse Distance Weighted interpolation method and error propagation mechanism–creating a DEM from an analogue topographical map. J. Spat. Sci. 2011, 56, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnero, G.; Godone, D. Comparisons between different interpolation techniques. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences XL-5 W, Padua, Italy, 27–28 February 2013; Volume 3, pp. 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Salekin, S.; Burgess, J.H.; Morgenroth, J.; Mason, E.G.; Meason, D.F. A Comparative Study of Three Non-Geostatistical Methods for Optimising Digital Elevation Model Interpolation. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stateczny, A. (Ed.) Methods of the Comparative Navigation; Gdansk Science Society: Gdansk, Poland, 2004; ISBN 83-87359-88-2. [Google Scholar]






| Year | Echosounder | Model | North 1 | South 2 | East 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | SBES | Reson Navisound 515 | + | + | |
| 2011 | SBES | Reson Navisound 515 | + | ||
| 2012 | SBES | Reson Navisound 640 | + | + | |
| 2013 | MBES | Reson Seabat 8125 | + | ||
| 2015 01 | MBES | Reson Seabat 8125 | + | ||
| 2015 05 | SBES | Reson Navisound 640 | + | + | + |
| 2017 | MBES | Kongsberg EM3002 | + | ||
| 2018 | MBES | R2Sonic 2024 | + | ||
| 2018 | SBES | Ohmex SonarMite | + | + |
| Date | 28 April 2010 | 28 June 2012 |
| Positioning | Trimble NT300D | Trimble SPS 461 |
| Depth measurement | Reson Navisonud 515 | Reson Navisonud 640 |
| Projection | UTM | UTM |
| Reference system | WGS84 | WGS84 |
| Chart datum | 500 NN55 Harbor Master’s Office—Northern Port in Gdańsk | 500 NN55 Harbor Master’s Office—Northern Port in Gdańsk |
| Device | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| SBES Ohmex SonarMite | Frequency | 200 kHz |
| Beam spread | 8°–10° | |
| Depth range | 0.3–75 m | |
| GNSS Receiver Trimble R10 | Systems | GPS + GLONASS |
| Frequency | L1 + L2 | |
| GBAS | VRS.net |
| Area | Year | Data Source | Total Number of Data | Number of Data Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southern | 2010 | SBES | 4066 | 2875 |
| 2011 | ENC | 41 | 13 | |
| 2012 | SBES | 7312 | 2415 | |
| 2015 | SBES | 2305 | 127 | |
| 2015 | ENC | 298 | 87 | |
| 2018 | SBES | 6520 | 3436 | |
| 2018 | ENC | 249 | 101 | |
| Northern | 2010 | SBES | 4999 | 3313 |
| 2011 | ENC | 76 | 30 | |
| 2012 | SBES | 6163 | 3425 | |
| 2015 | SBES | 845 | 178 | |
| 2015 | ENC | 130 | 83 | |
| 2018 | SBES | 3788 | 2042 | |
| 2018 | ENC | 194 | 144 |
| Object | Acronym | Type | Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coastline | COALNE | L | 30 |
| Depth Contour | DEPCNT | L | 43 |
| Sounding | SOUNDG | P | 129 |
| Year | Data Source | Cell Size (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | SBES | 2.778 |
| 2011 | ENC | 3.838 |
| 2012 | SBES | 3.237 |
| 2014 | ENC | 3.838 |
| 2015 05 | SBES | 6.428 |
| 2018 | SBES | 3.639 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makar, A.; Specht, C.; Specht, M.; Dąbrowski, P.; Burdziakowski, P.; Lewicka, O. Seabed Topography Changes in the Sopot Pier Zone in 2010–2018 Influenced by Tombolo Phenomenon. Sensors 2020, 20, 6061. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216061
Makar A, Specht C, Specht M, Dąbrowski P, Burdziakowski P, Lewicka O. Seabed Topography Changes in the Sopot Pier Zone in 2010–2018 Influenced by Tombolo Phenomenon. Sensors. 2020; 20(21):6061. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216061
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakar, Artur, Cezary Specht, Mariusz Specht, Paweł Dąbrowski, Paweł Burdziakowski, and Oktawia Lewicka. 2020. "Seabed Topography Changes in the Sopot Pier Zone in 2010–2018 Influenced by Tombolo Phenomenon" Sensors 20, no. 21: 6061. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216061
APA StyleMakar, A., Specht, C., Specht, M., Dąbrowski, P., Burdziakowski, P., & Lewicka, O. (2020). Seabed Topography Changes in the Sopot Pier Zone in 2010–2018 Influenced by Tombolo Phenomenon. Sensors, 20(21), 6061. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216061








