Deep Learning-Based Violin Bowing Action Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
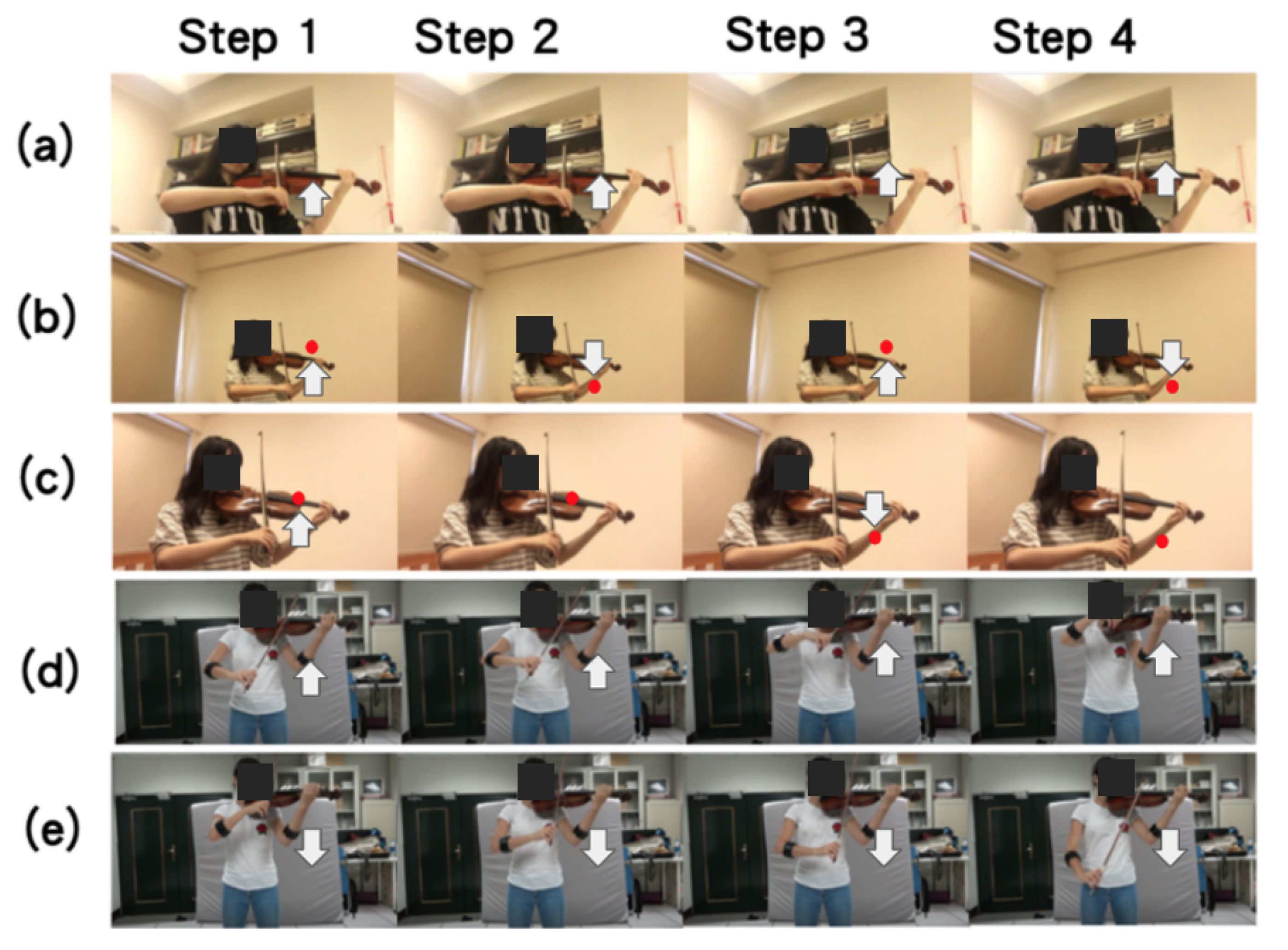
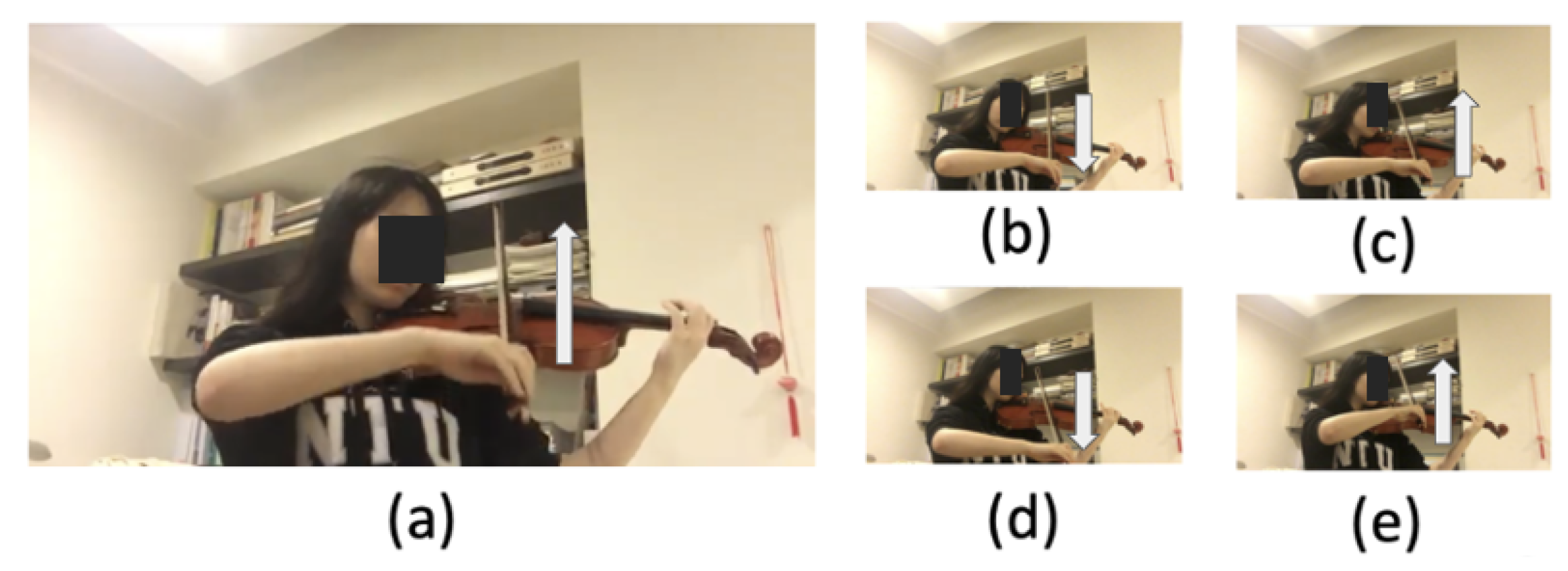
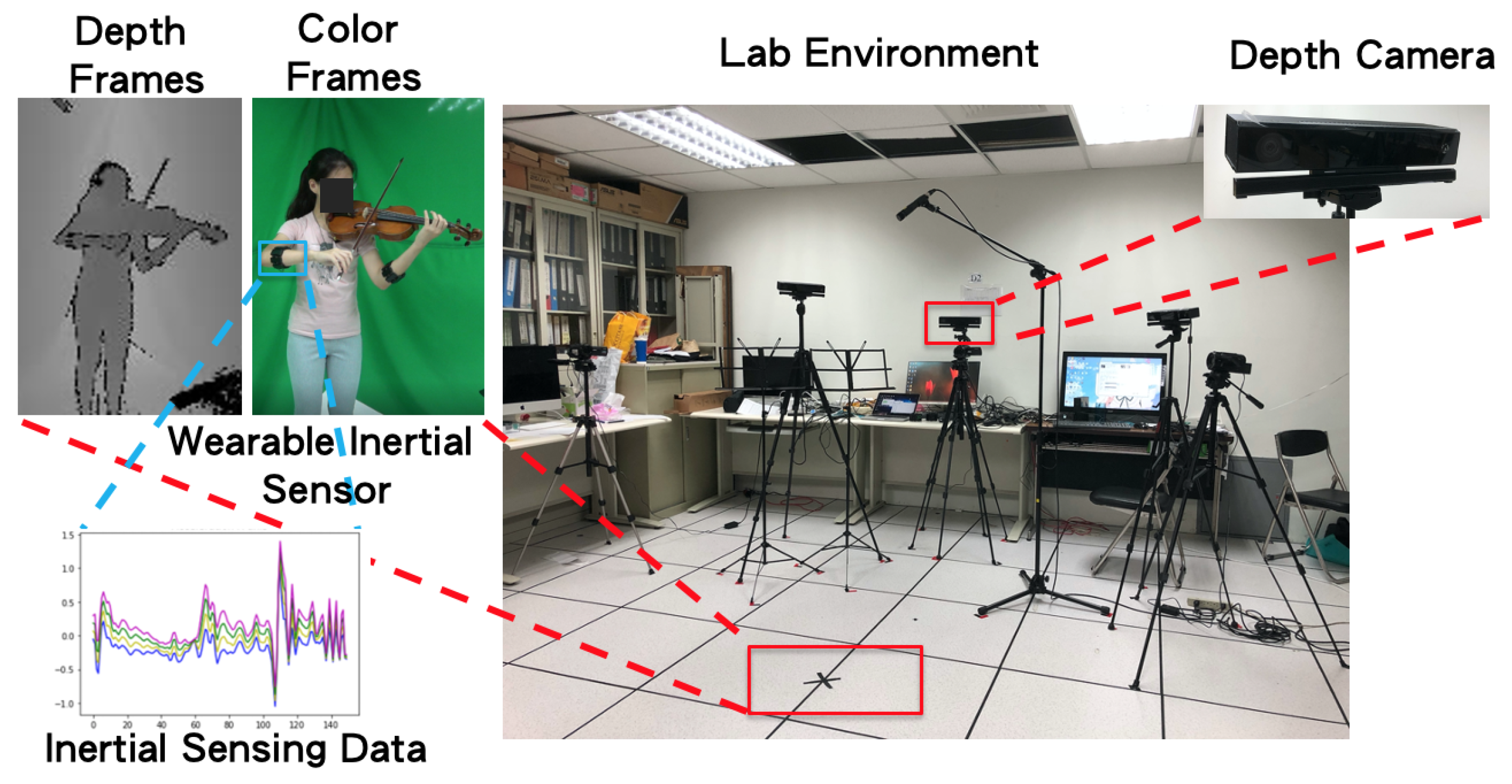
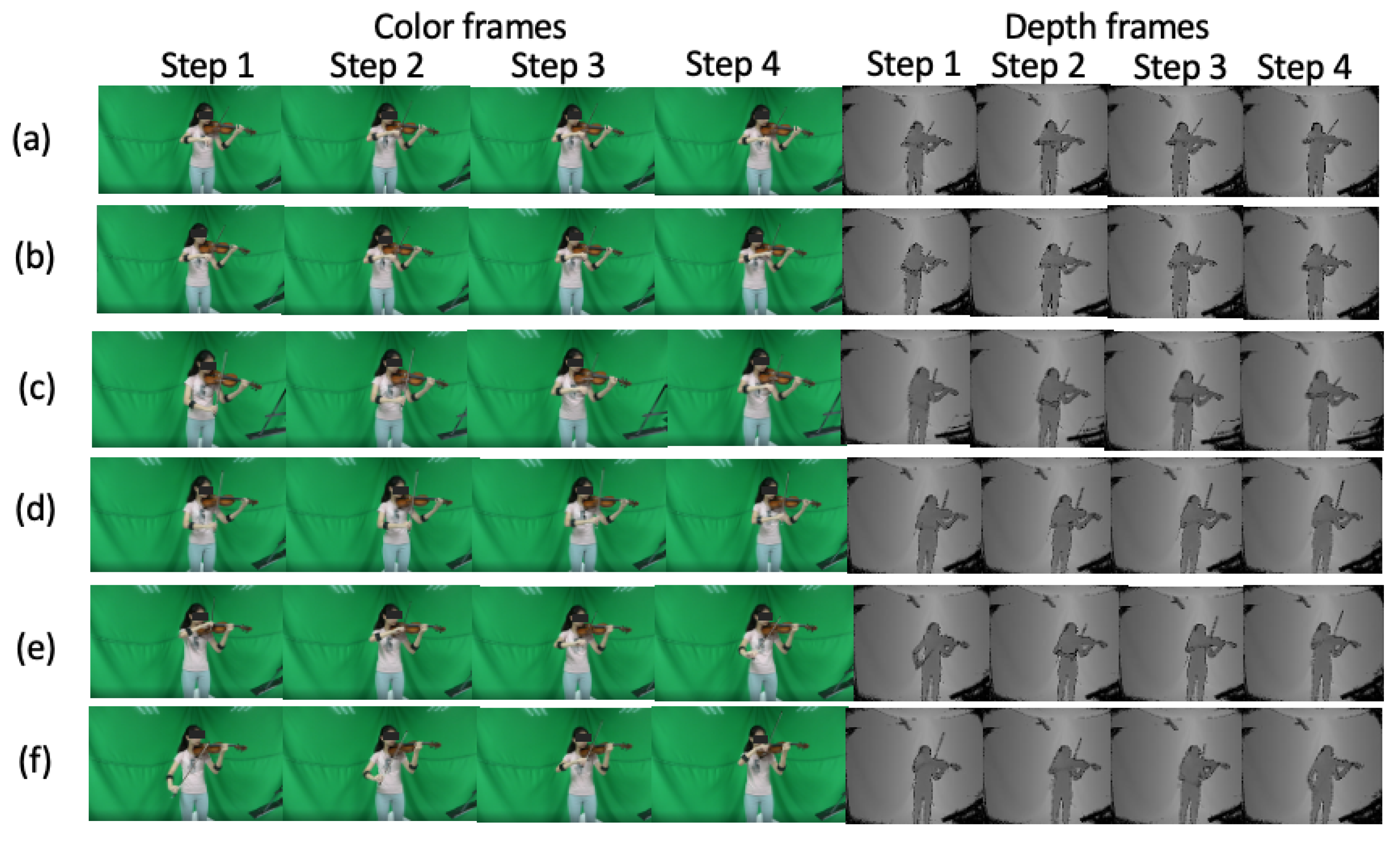
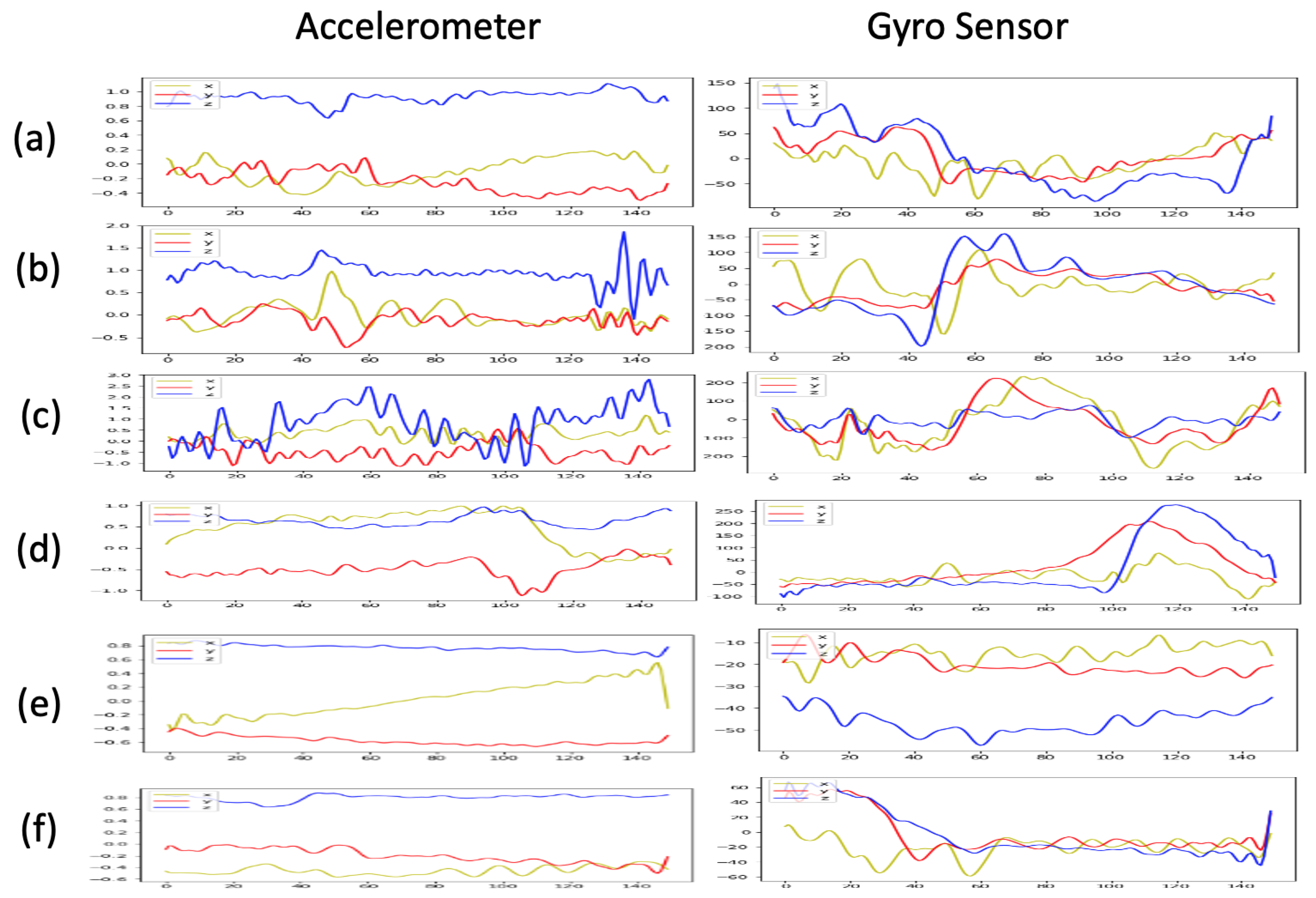
3. Bowing Action Dataset Collected from a Violinist Performing Complete Pieces
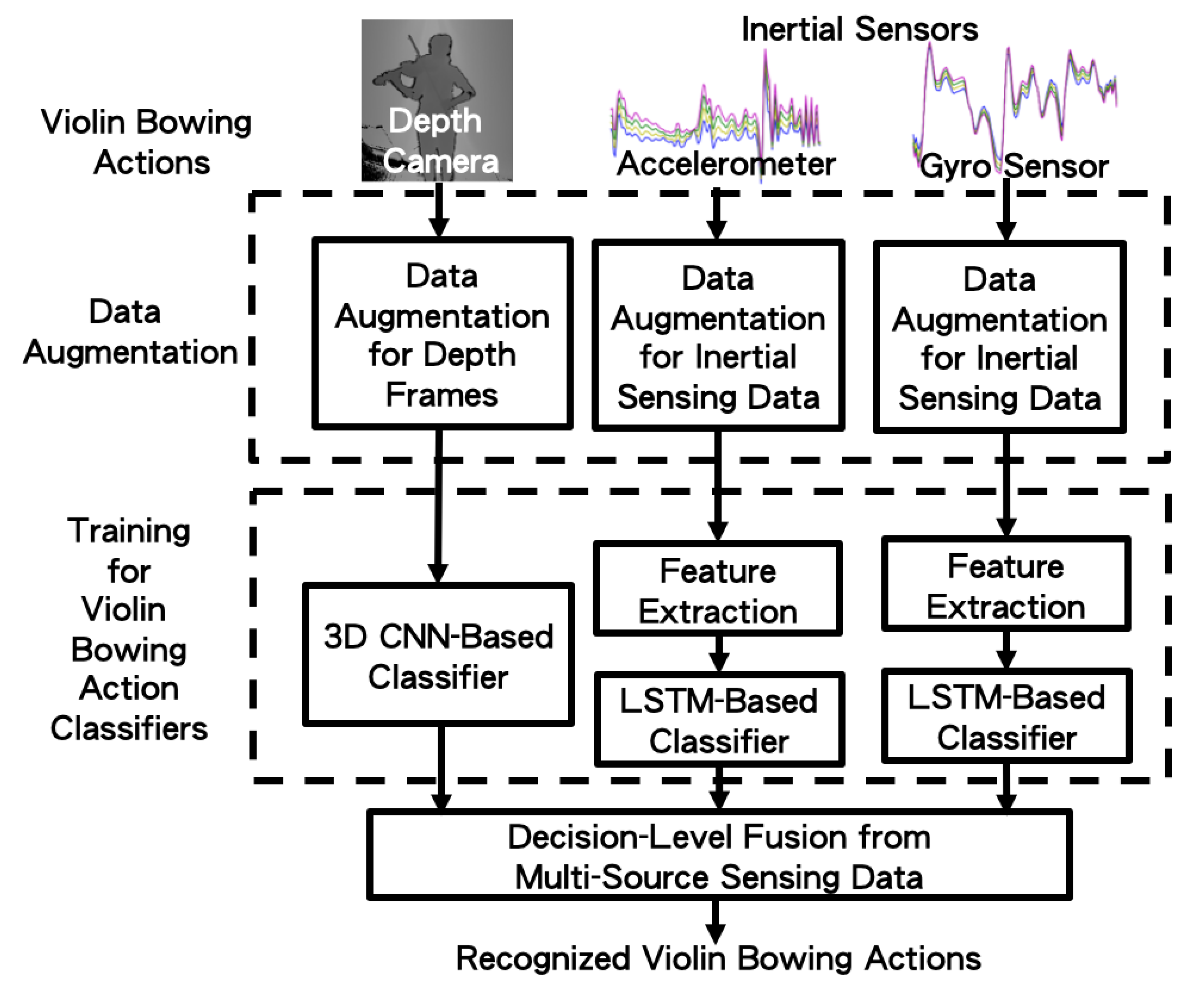
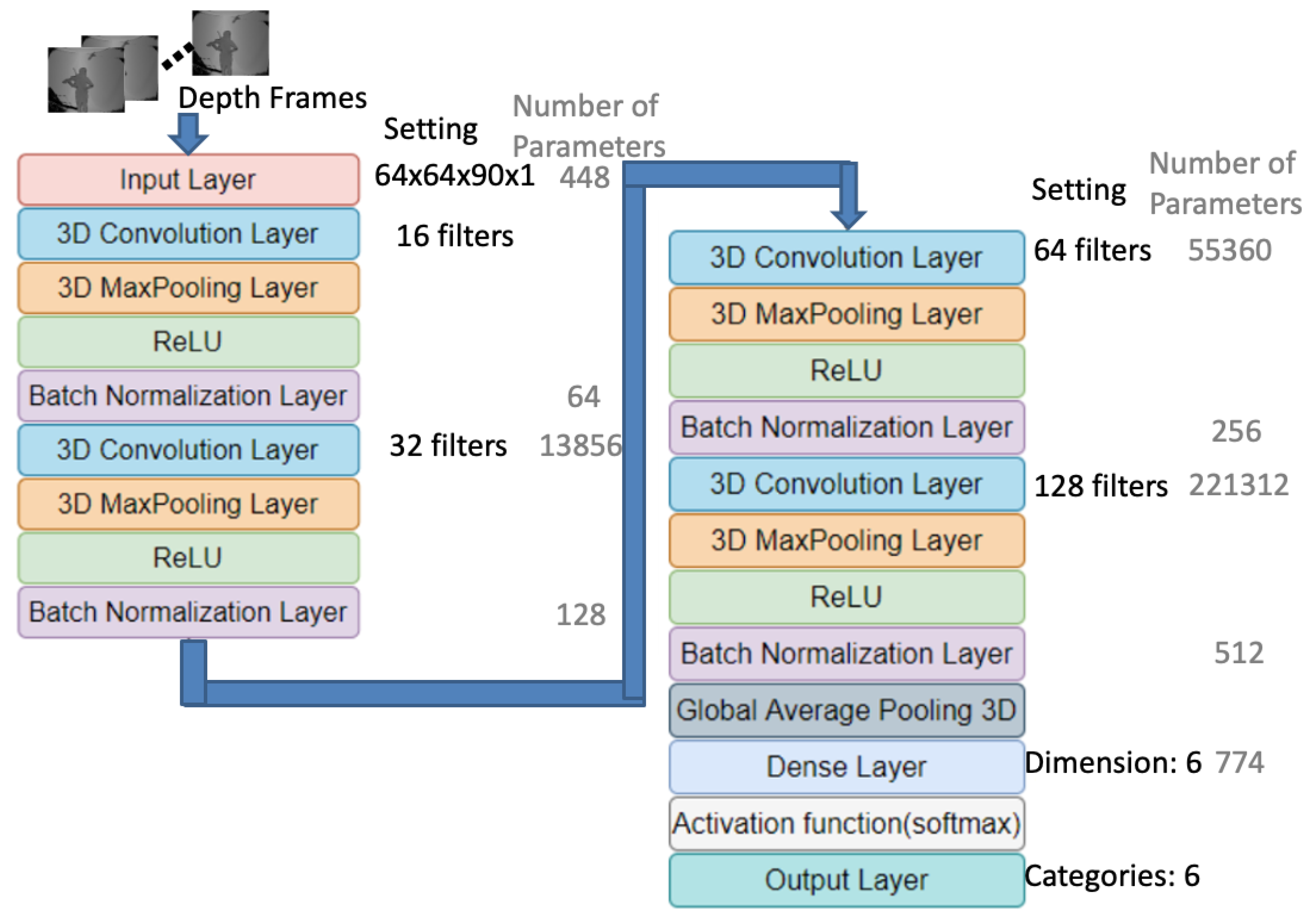
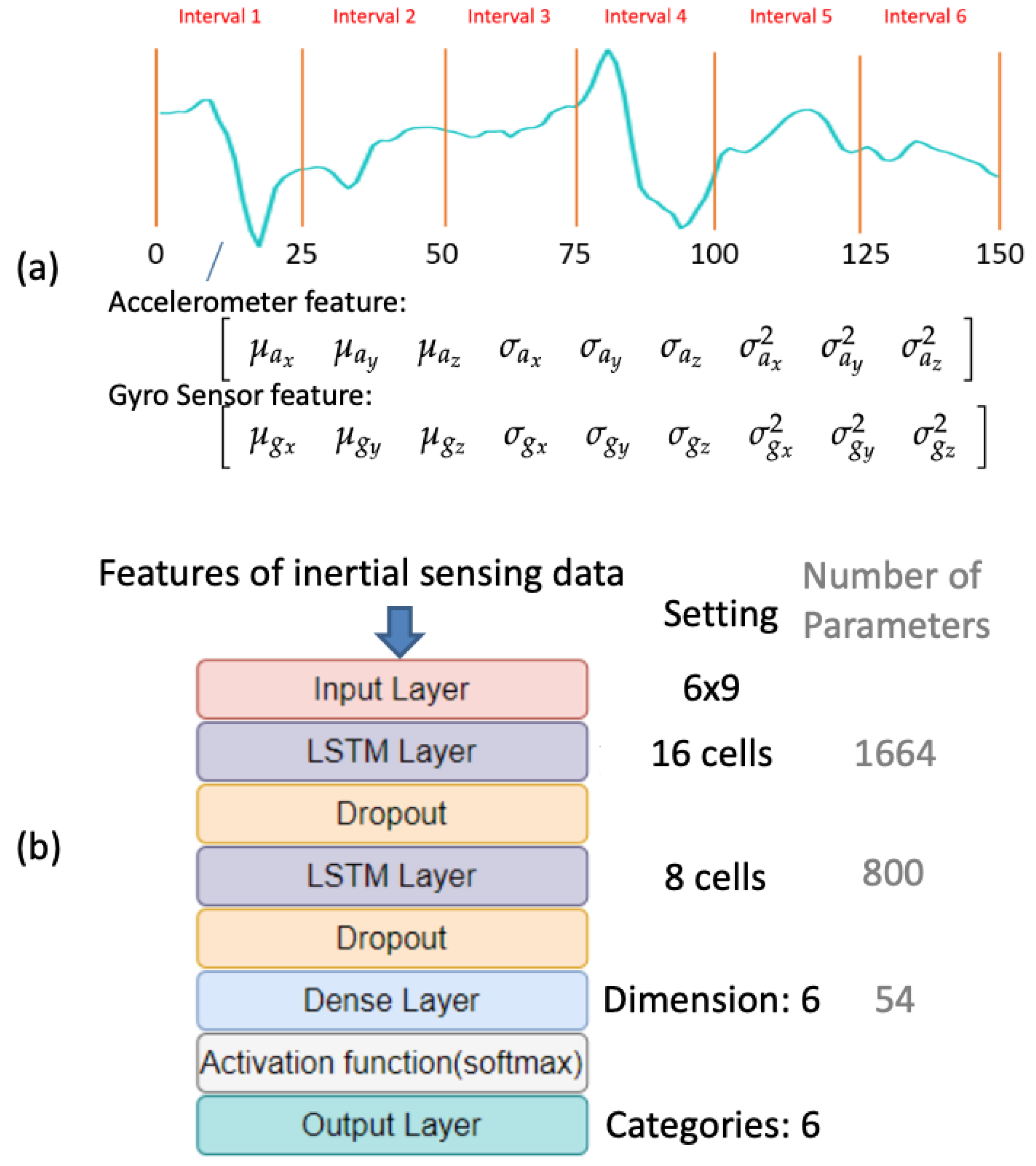
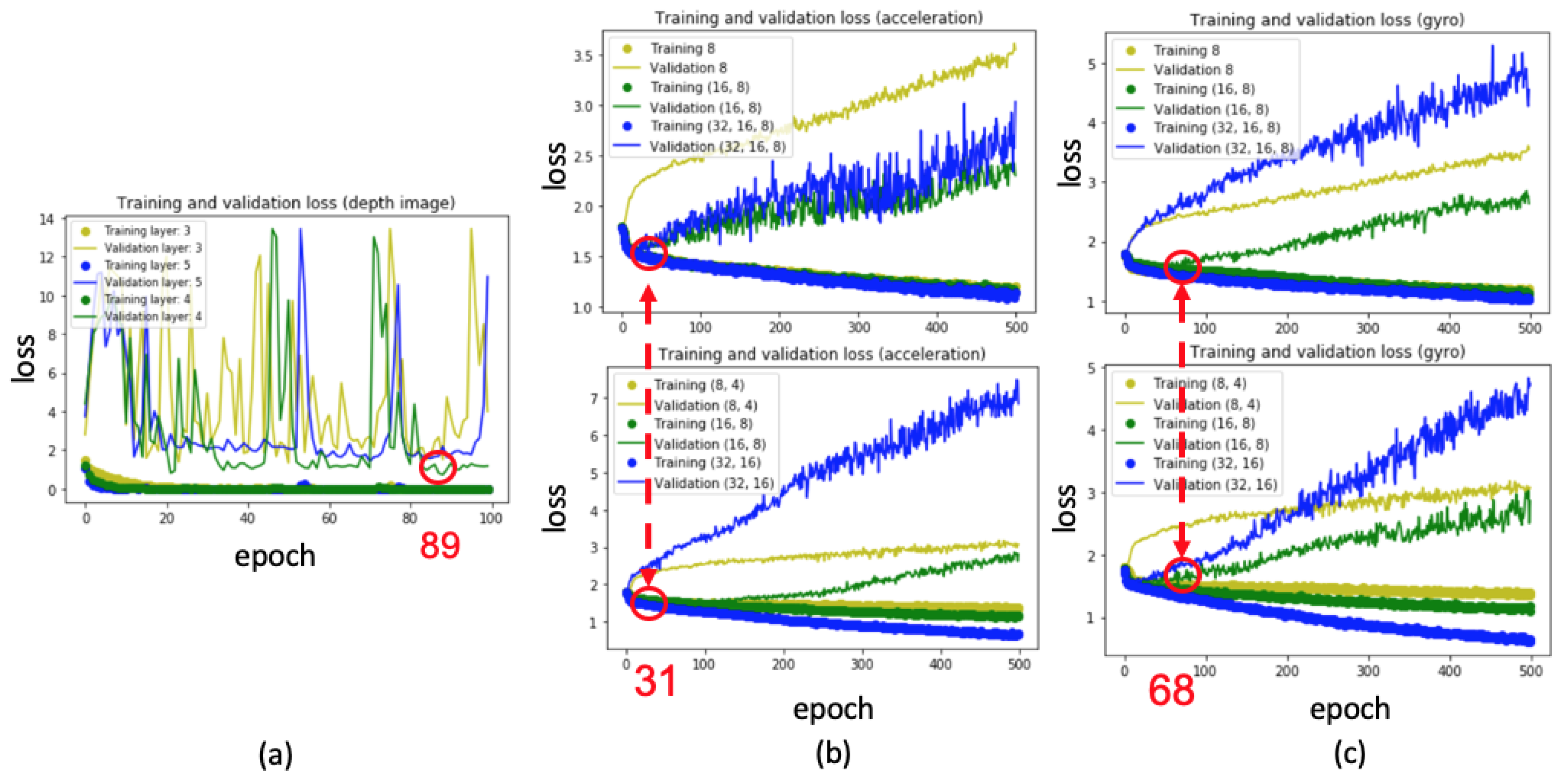
4. Proposed Deep Learning–Based Violin Bowing Action Recognition System
4.1. Data Augmentation
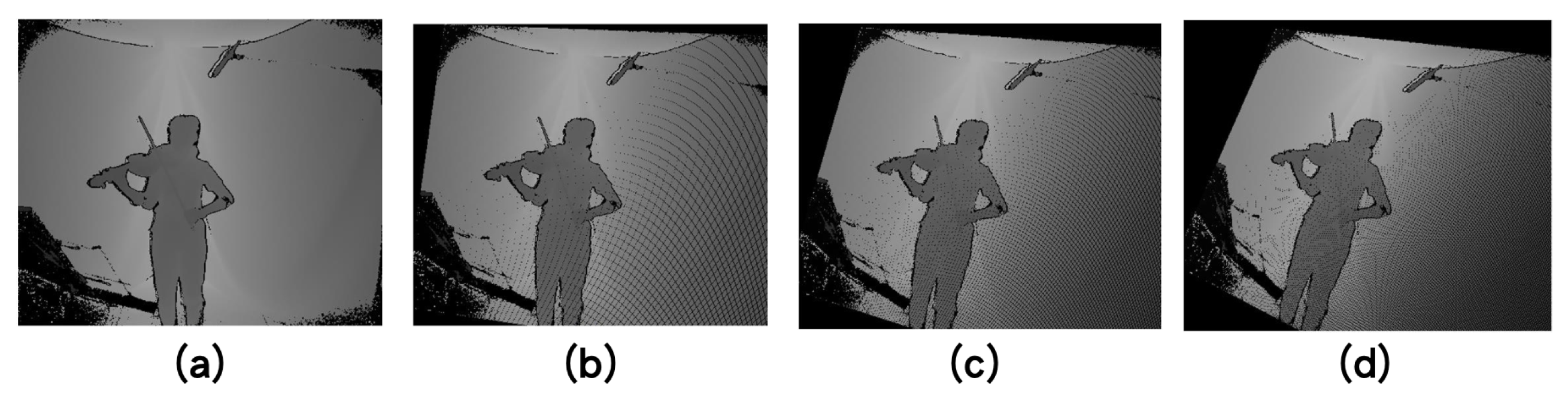
4.1.1. Data Augmentation for Depth Frames
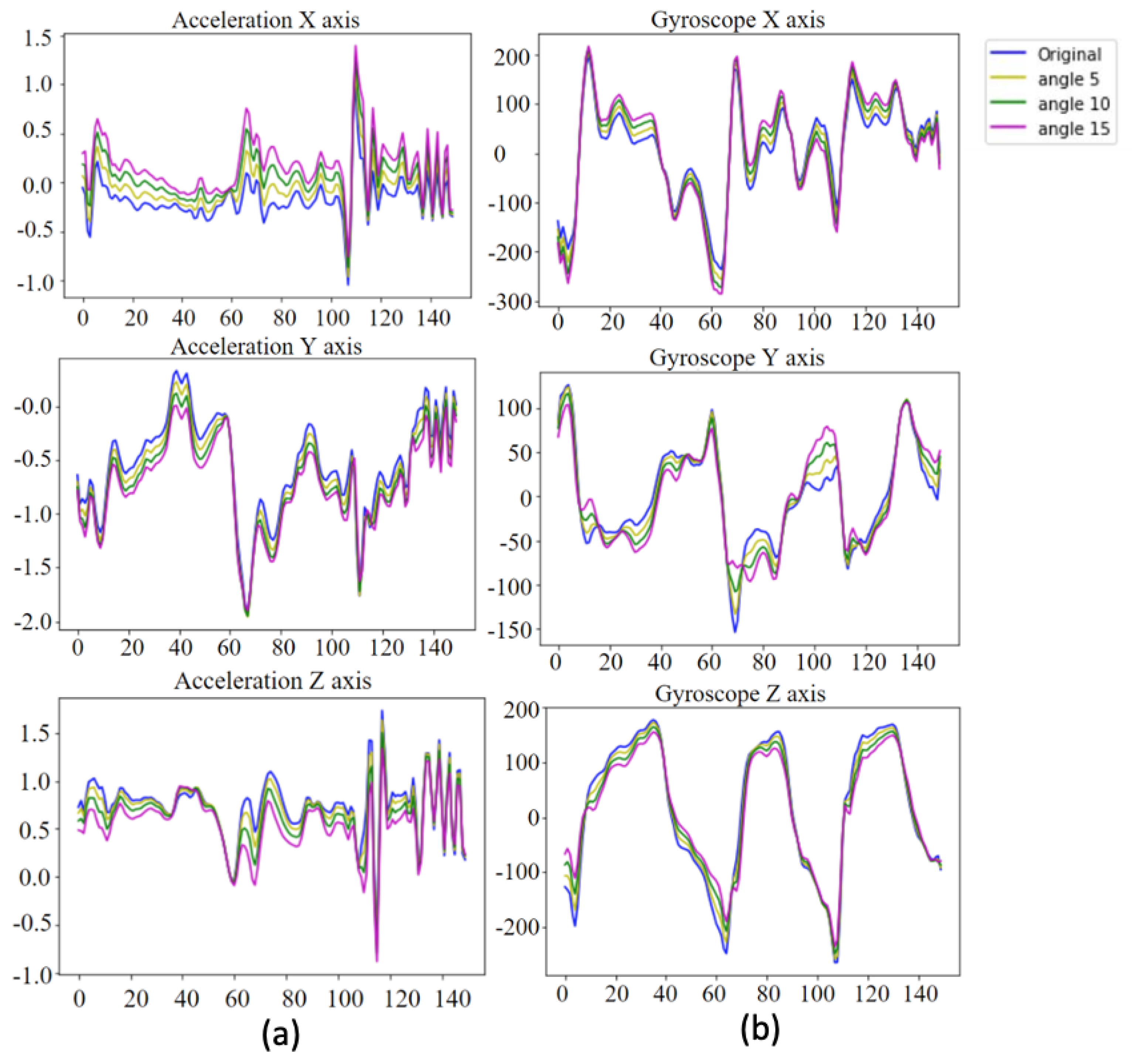
4.1.2. Data Augmentation for Inertial Sensing Data
4.2. Training of Violin Bowing Action Classifier
4.2.1. 3D-CNN-Based Classifiers for Depth Frames
4.2.2. LSTM-Based Classifiers for Inertial Sensing Data
4.3. Decision-Level Fusion from Multi-Source Sensing Data
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Quantitative Evaluation
5.2. Complexity Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zelnik-Manor, L.; Irani, M. Statistical analysis of dynamic actions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, Z.; Sohn, W. Abnormal human activity recognition system based on R-transform and kernel discriminant technique for elderly home care. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2011, 57, 1843–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Sridhar, S.; Sotnychenko, O.; Rhodin, H.; Shafiei, M.; Seidel, H.P.; Xu, W.; Casas, D.; Theobalt, C. VNect: Real-time 3D human pose estimation with a single RGB camera. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 44:1–44:14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shotton, J.; Fitzgibbon, A.; Cook, M.; Sharp, T.; Finocchio, M.; Moore, R.; Kipman, A.; Blake, A. Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Barcelona, Spain, 6 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, M.; Khamis, S.; Degtyarev, Y.; Davidson, P.; Fanello, S.R.; Kowdle, A.; Escolano, S.O.; Rhemann, C.; Kim, D.; Taylor, J.; et al. Fusion4d: Real-time performance capture of challenging scenes. ACM Trans. Graph. 2016, 35, 114:1–114:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, R.; Cao, J. Accelerometer-based hand gesture recognition by neural network and similarity matching. IEEE Sens.J. 2016, 16, 4537–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.P.; Chudgar, H.S.; Mukherjee, S.; Dutta, T.; Sharma, K. A continuous hand gestures recognition technique for human-machine interaction using accelerometer and gyroscope sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6425–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jafari, R.; Kehtarnavaz, N. A real-time human action recognition system using depth and inertial sensor fusion. IEEE Sens J. 2016, 16, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, N.; Ostadabbas, S.; Kehtarnavaz, N. Data augmentation in deep learning-based fusion of depth and inertial sensing for action recognition. IEEE Sens Lett. 2019, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmazzo, D.; Ramirez, R. Air violin: A machine learning approach to fingering gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the ACM International Workshop on Multimodal Interaction for Education, Glasgow, UK, 13 November 2017; pp. 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Dalmazzo, D.; Ramirez, R. Bowing gestures classification in violin performance: A machine learning approach. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Microsoft. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=44561 (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Getmyo. Available online: https://support.getmyo.com/hc/en-us (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Wang, P.; Li, W.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Ogunbona, P. Action recognition from depth maps using deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Human-Mach. Syst. 2016, 46, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtman, A.; Barshan, B. Activity recognition invariant to sensor orientation with wearable motion sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, S.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Yu, K. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 13, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S. Network in network. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.4400. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Shao, W.; Peng, Z. Towards understanding regularization in batch normalization. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.00846. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.W.; Mou, T.C.; Fang, C.C.; Chang, P.C.; Hua, K.L.; Shih, H.C. Baseball player behavior classification system using long short-term memory with multimodal features. Sensors 2019, 19, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Prasad, S.; Fowler, J.E. Decision fusion in kernel-induced spaces for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3399–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Chen, C.; Su, H.; Du, Q. Local binary patterns and extreme learning machine for hyperspectral imagery classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3681–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Tensorflow. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Keras. Available online: https://keras.io/ (accessed on 1 August 2020).




| Depth Frames (D) | Accelerometer (A) | Gyro Sensor (G) | D + A | D + G | A + G | D + A + G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| violin performer 1 | |||||||
| violin performer 2 | |||||||
| violin performer 3 | |||||||
| violin performer 4 | |||||||
| violin performer 5 | |||||||
| violin performer 6 | |||||||
| violin performer 7 | |||||||
| violin performer 8 | |||||||
| average |
| Time (seconds) | Training for D | Training for A | Training for G | Testing for D+A+G | Inference Time per Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| violin performer 1 | |||||
| violin performer 2 | |||||
| violin performer 3 | |||||
| violin performer 4 | |||||
| violin performer 5 | |||||
| violin performer 6 | |||||
| violin performer 7 | |||||
| violin performer 8 | |||||
| average |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.-W.; Liu, B.-Y.; Chang, P.-C. Deep Learning-Based Violin Bowing Action Recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20205732
Sun S-W, Liu B-Y, Chang P-C. Deep Learning-Based Violin Bowing Action Recognition. Sensors. 2020; 20(20):5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20205732
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Shih-Wei, Bao-Yun Liu, and Pao-Chi Chang. 2020. "Deep Learning-Based Violin Bowing Action Recognition" Sensors 20, no. 20: 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20205732
APA StyleSun, S.-W., Liu, B.-Y., & Chang, P.-C. (2020). Deep Learning-Based Violin Bowing Action Recognition. Sensors, 20(20), 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20205732






