Non-Uniformly Powered and Spaced Corporate Feeding Power Divider for High-Gain Beam with Low SLL in Millimeter-Wave Antenna Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design and Optimization of Antenna Array
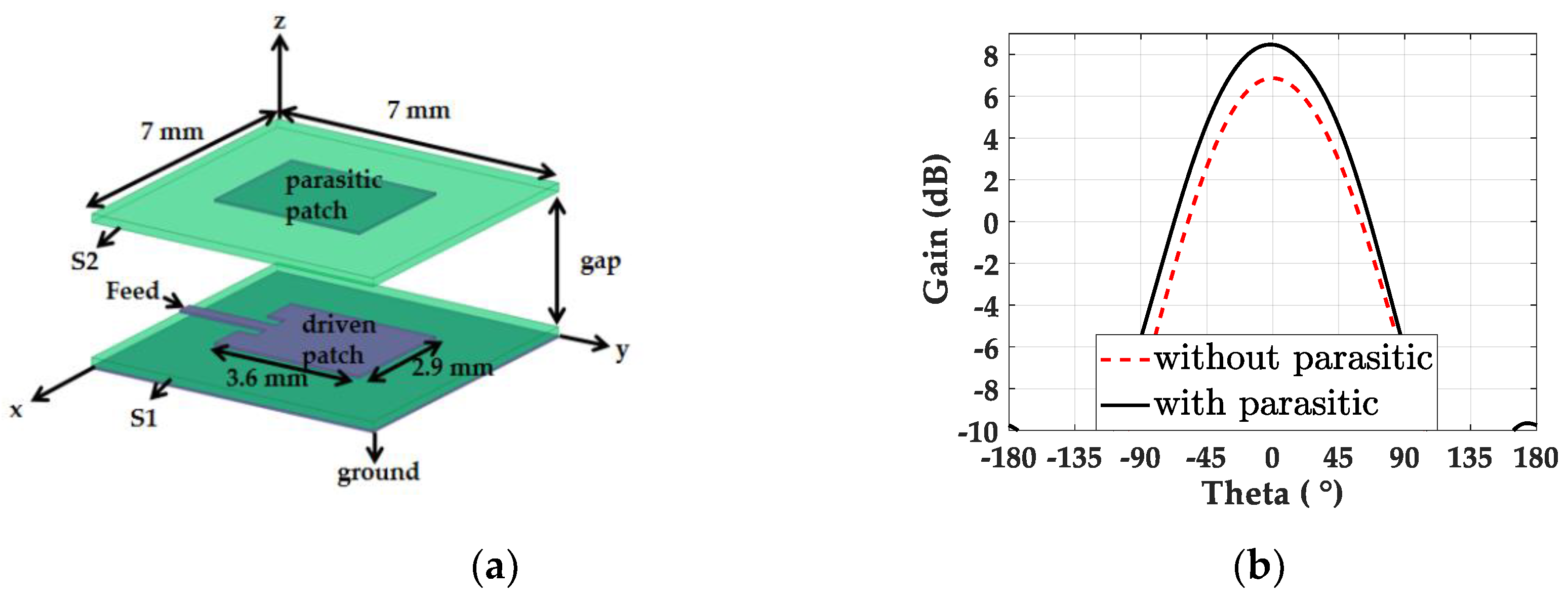
2.1. Design of Single Patch with Parasitic Element
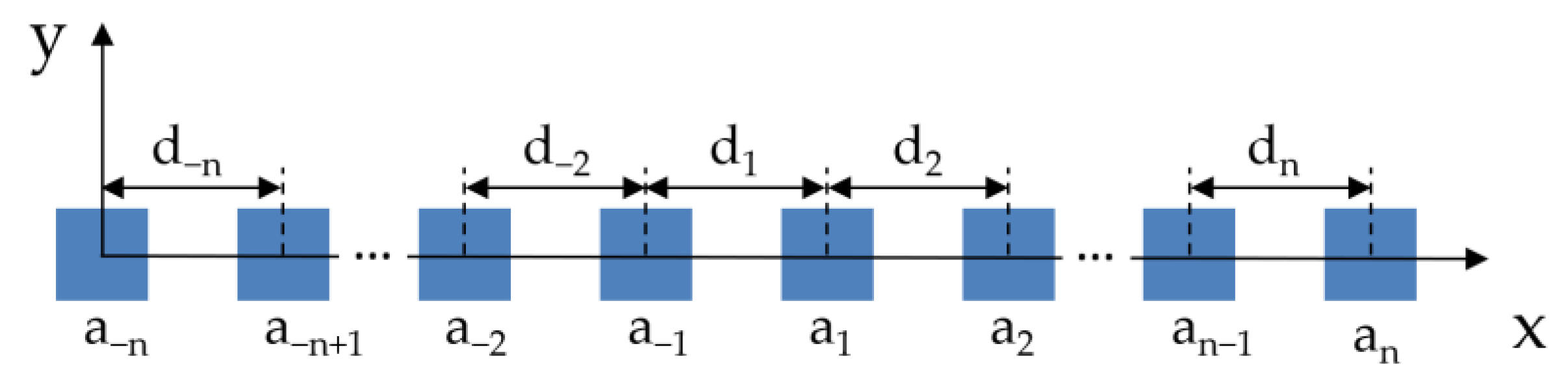
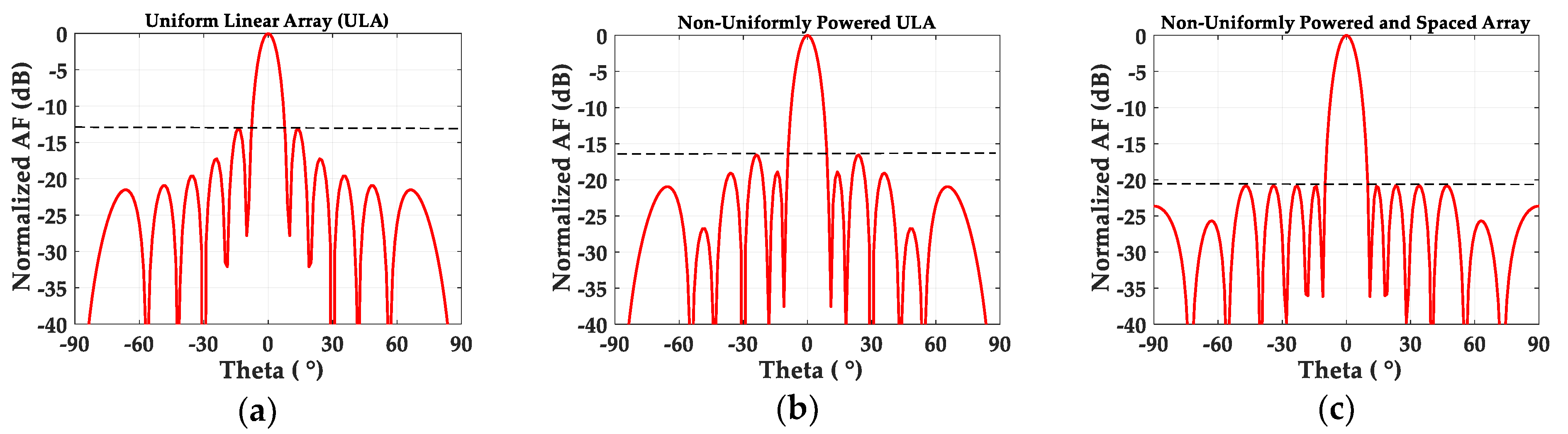
2.2. Effect of Non-Uniform Excitation and Spacing on SLL
2.3. Design of Non-Uniformly Powered and Uniformly Spaced Antenna Array
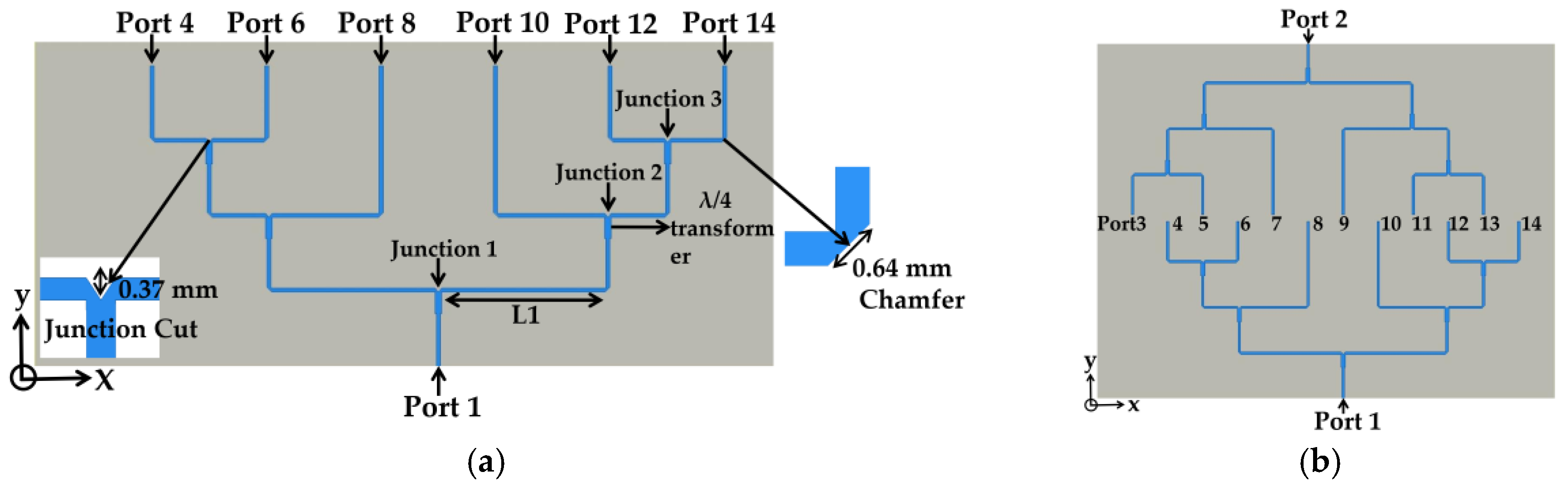
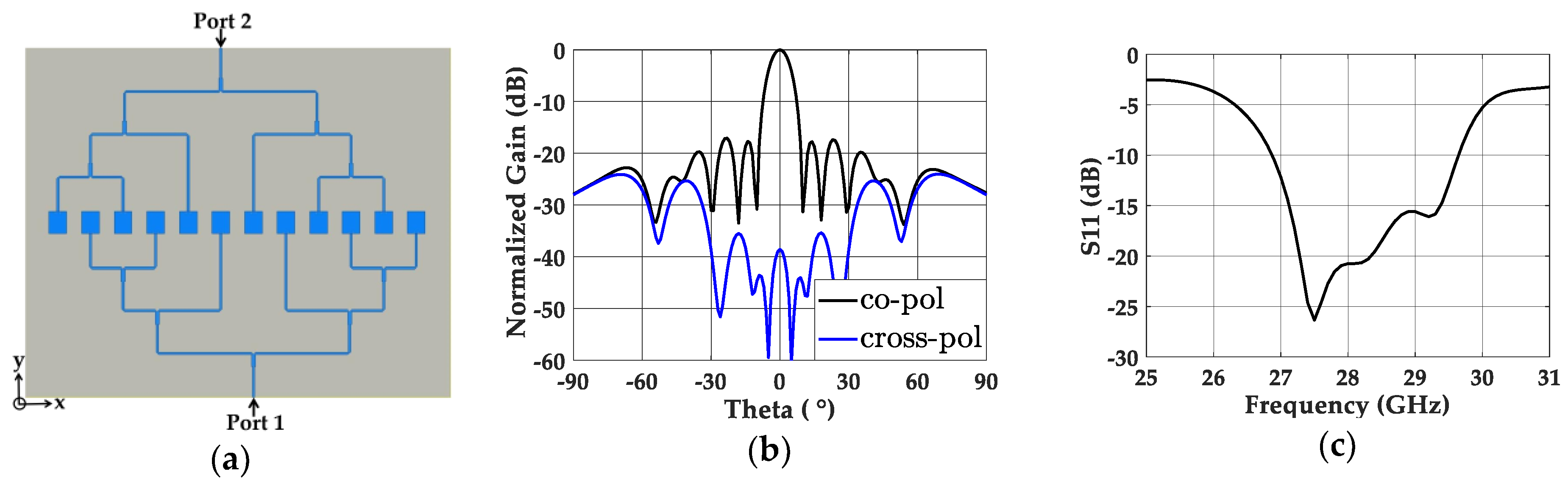
2.3.1. Non-Uniformly Powered and Uniformly Spaced Power Divider Design
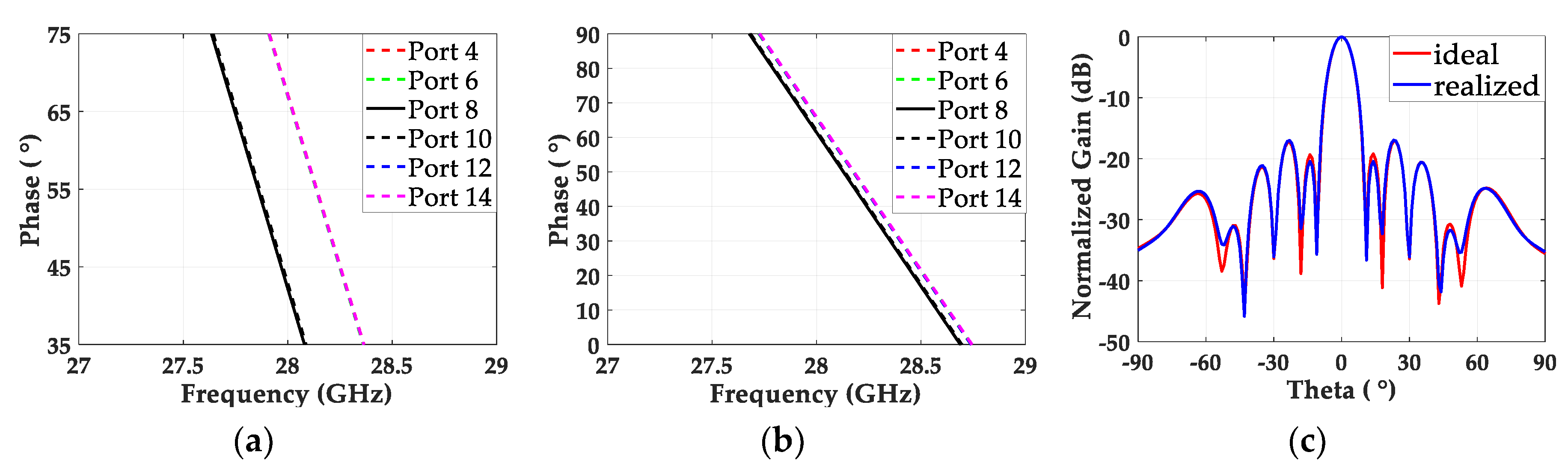
2.3.2. Phase Correction of Power Divider
2.3.3. Non-Uniformly Powered and Uniformly Spaced Antenna Array
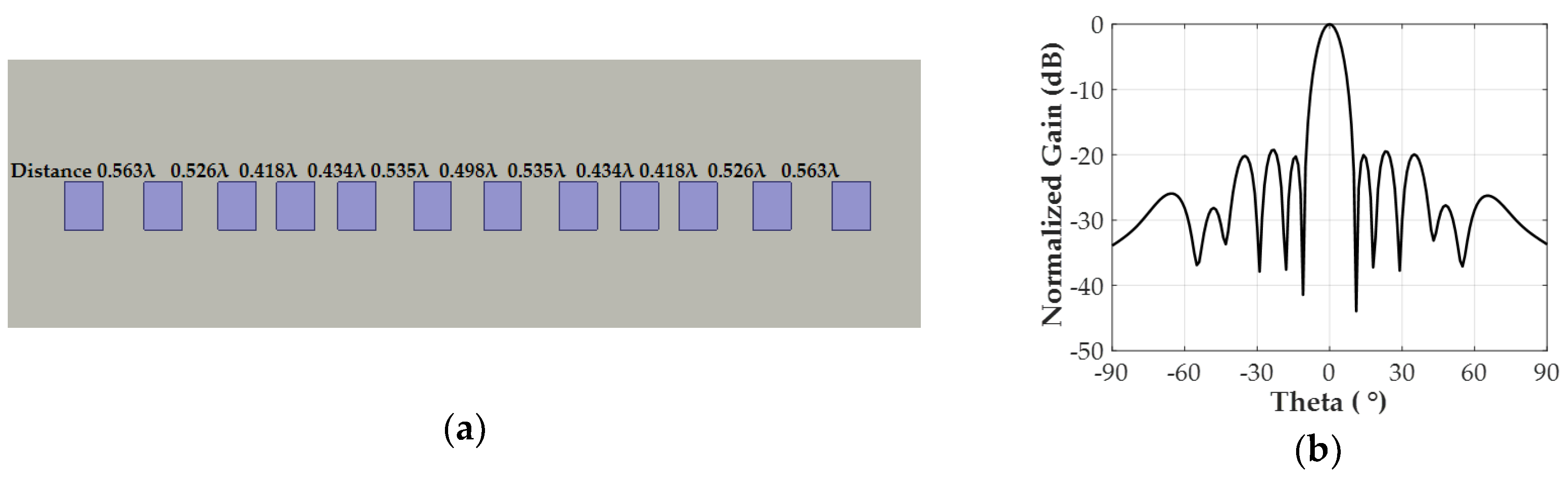
2.4. Design of Non-Uniformly Spaced Antenna Array
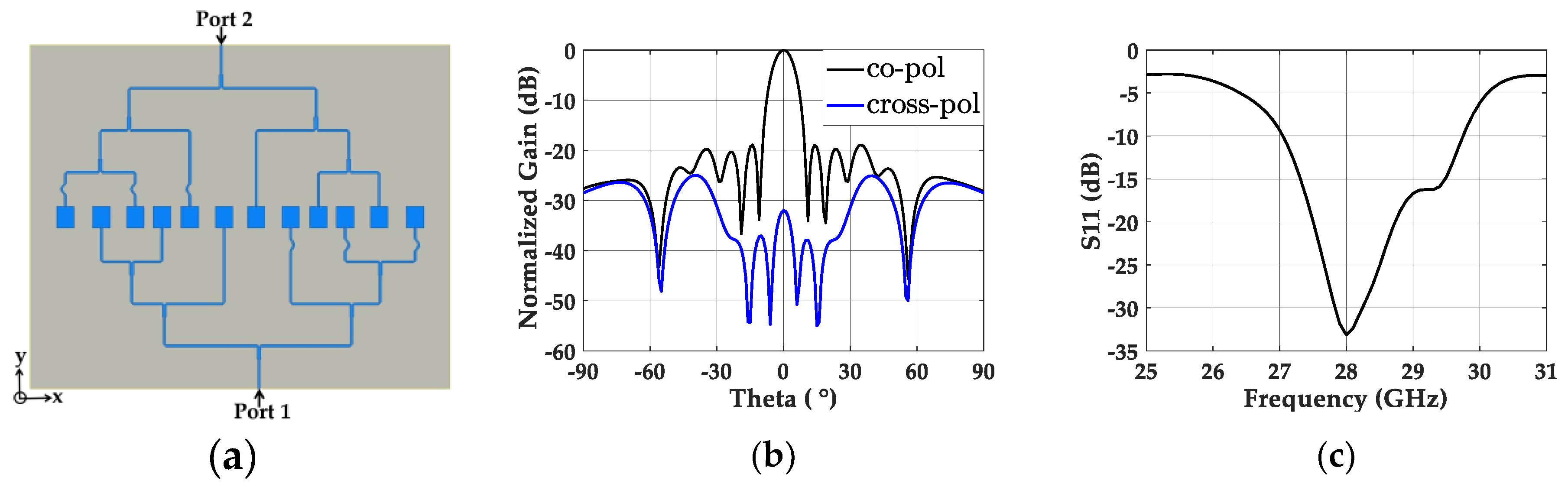
2.4.1. Non-Uniformly Powered and Spaced Power Divider Design
2.4.2. Non-Uniformly Powered and Spaced Antenna Array
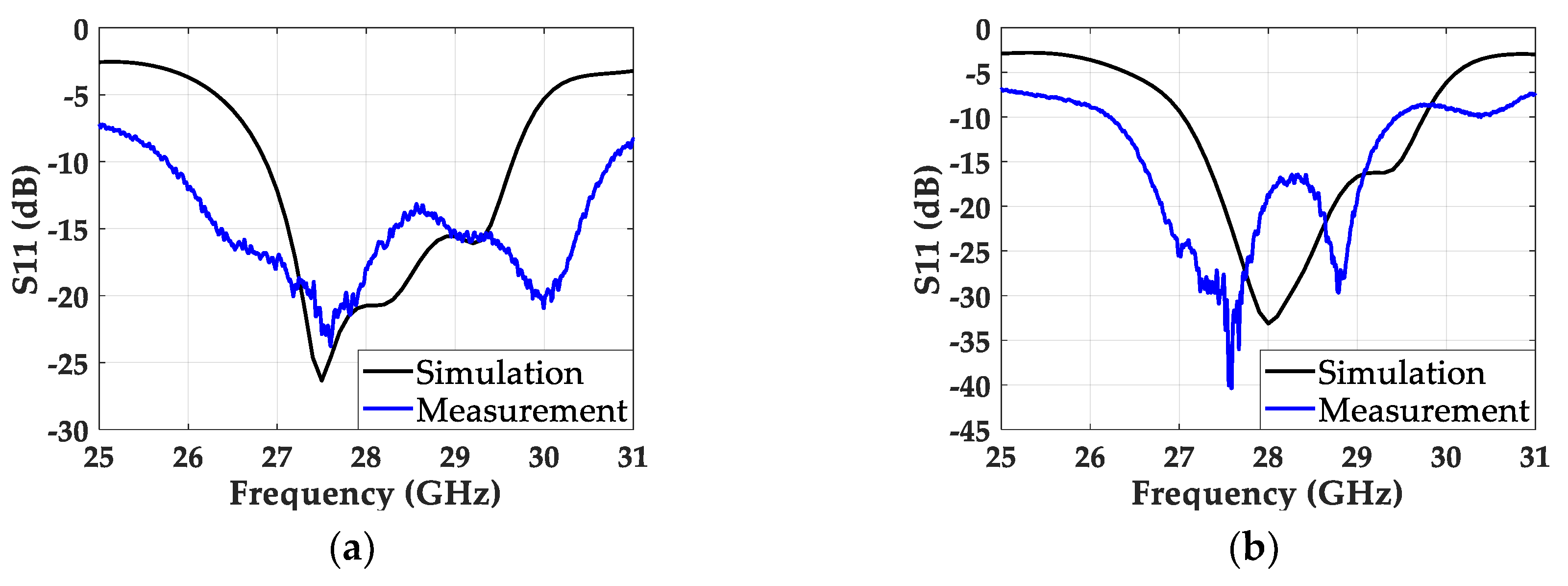
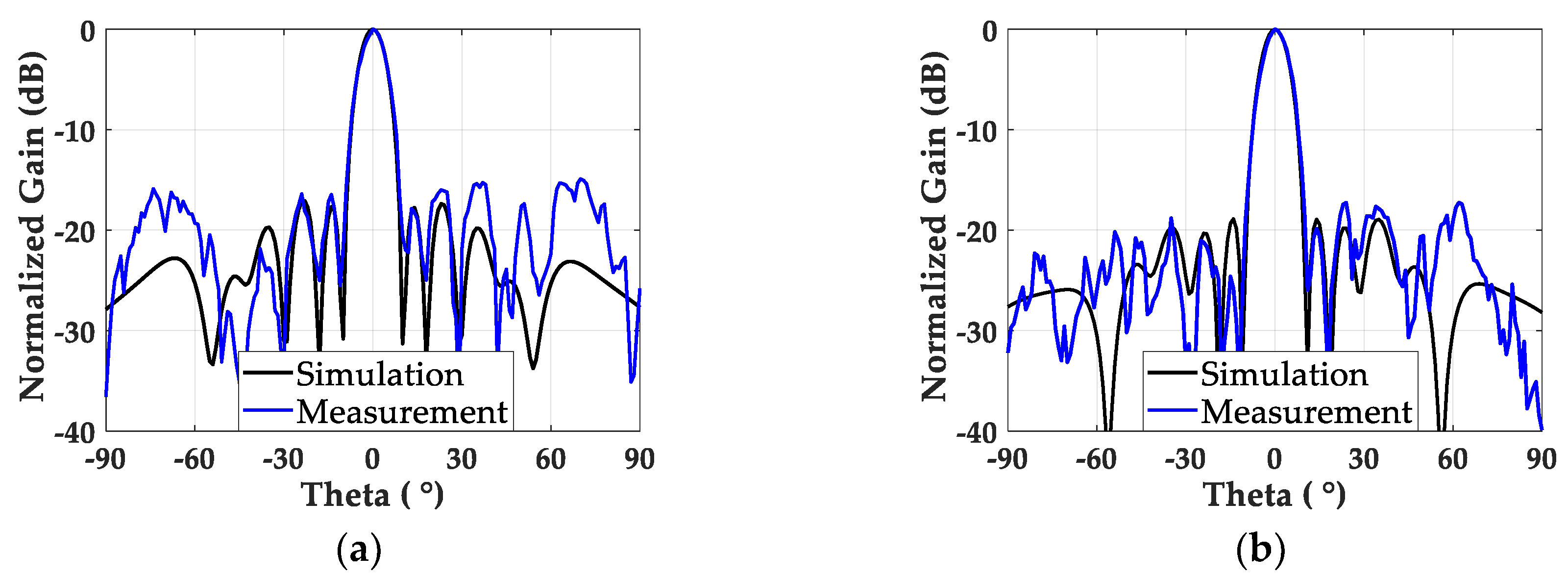
3. Fabrication and Measurement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rappaport, T.S.; Sun, S.; Mayzus, R.; Zhao, H.; Azar, Y.; Wang, K.; Wong, G.N.; Schulz, J.K.; Samimi, M.; Gutierrez, F. Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5G cellular: It will work! IEEE Access 2013, 1, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Z.; Khan, F. An introduction to millimeter-wave mobile broadband systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2011, 49, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Heath, R.W. Coverage and rate analysis for millimeter-wave cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 2014, 14, 1100–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Baek, K.-H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.; Ko, S.-T. Study and prototyping of practically large-scale mmWave antenna systems for 5G cellular devices. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejos, A.V.; Sanchez, M.G.; Cuinas, I. Measurement and analysis of propagation mechanisms at 40 GHz: Viability of site shielding forced by obstacles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 57, 3369–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Syrytsin, I.; Pedersen, G.F. A planar switchable 3-D-coverage phased array antenna and its user effects for 28-GHz mobile terminal applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 6413–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzagbletey, P.A.; Jung, Y.-B. Stacked microstrip linear array for millimeter-wave 5G baseband communication. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Honma, N.; Nishikawa, K.; Tsunekawa, K. Millimeter-wave high-efficiency multilayer parasitic microstrip antenna array on teflon substrate. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 2005, 53, 2101–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Farahani, M.; Sebak, A.R.; Denidni, T.A. A 30GHz high-gain circularly-polarized pattem-steerable antenna based on parasitic patches. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Paris, France, 19–24 March 2017; pp. 3044–3046. [Google Scholar]
- Khalily, M.; Tafazolli, R.; Xiao, P.; Kishk, A.A. Broadband mm-wave microstrip array antenna with improved radiation characteristics for different 5G applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 4641–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, A. Wideband 28 GHz ground reflected dipole antenna and array for 5G mobile handset. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 243–244. [Google Scholar]
- Haraz, O.M.; Elboushi, A.; Alshebeili, S.A.; Sebak, A.-R. Dense dielectric patch array antenna with improved radiation characteristics using EBG ground structure and dielectric superstrate for future 5G cellular networks. IEEE Access 2014, 2, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.-X.; Khalily, M.; Xiao, P.; Brown, T.W.; Gao, S. Planar sub-millimeter-wave array antenna with enhanced gain and reduced sidelobes for 5G broadcast applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 67, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Lu, Y.; You, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Z.-C.; Huang, J. Wideband full-corporate-feed waveguide continuous transverse stub antenna array. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 76673–76681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Marín, E.; Masa-Campos, J.L.; Sánchez-Olivares, P.; Ruiz-Cruz, J.A. Evaluation of Additive Manufacturing Techniques Applied to Ku-Band Multilayer Corporate Waveguide Antennas. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 2114–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 323–325. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, R.; Kumar, G. Series-fed binomial microstrip arrays for extremely low sidelobe level. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 4275–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jackson, D.R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Long, Y. Investigations of SIW leaky-wave antenna for endfire-radiation with narrow beam and sidelobe suppression. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 4489–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayderkhani, R.; Hassani, H.R. Wideband and low sidelobe slot antenna fed by series-fed printed array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 3898–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.-F.; Ding, C.; Qian, Z.-P.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Cao, W.-Q.; Dutkiewicz, E. An SIW-based large-scale corporate-feed array antenna. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 2969–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Shin, D.-H.; Park, S.-O. Low side-lobe substrate-integrated-waveguide antenna array using broadband unequal feeding network for millimeter-wave handset device. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 64, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potelon, T.; Ettorre, M.; Sauleau, R. Long Slot Array Fed by a Nonuniform Corporate Feed Network in PPW Technology. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 5436–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.L. 94 GHz substrate integrated waveguide dual-circular-polarization shared-aperture parallel-plate long-slot array antenna with low sidelobe level. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 5855–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.-W.; Ban, Y.-L.; Zhu, J.-Q.; Guo, J.; Chen, Z. Planar 2-D scanning SIW low multibeam array with sidelobe level for millimeter-wave applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 4570–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Feng, Z. Low-sidelobe air-filled slot array fabricated using silicon micromachining technology for millimeter-wave application. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 4067–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurtsov, S.; Koziel, S. On alternative approaches to design of corporate feeds for low-sidelobe microstrip linear arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 3781–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wu, Q.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Hong, W. Low-sidelobe-level series-fed microstrip antenna array of unequal interelement spacing. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Li, L.; Han, J.; Shi, Y. Traveling-Wave Series-Fed Patch Array Antenna Using Novel Reflection-Canceling Elements for Flexible Beam. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 111466–111476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaqa, A.; Dib, N. Position-only side lobe reduction of a uniformly excited elliptical antenna array using evolutionary algorithms. IET Microwaves Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurtsov, S.; Koziel, S. Systematic approach to sidelobe reduction in linear antenna arrays through corporate-feed-controlled excitation. IET Microwaves Antennas and Propag. 2016, 11, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legay, H.; Shafai, L. New stacked microstrip antenna with large bandwidth and high gain. IEE Proc. Microwaves Antennas Propag. 1994, 141, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS HFSS: High Frequency Structure Simulator. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/products/electronics/ansys-hfss (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Horng, T.-S.; Alexopoulos, N.G. Corporate feed design for microstrip arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1993, 41, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M.; Kaufman, B. Design considerations for low sidelobe microstrip arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1990, 38, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, M.; Huang, Y.; Loh, T.; Xu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H. A high gain steerable millimeter-wave antenna array for 5G smartphone applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Paris, France, 19–24 March 2017; pp. 1320–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wen, P. A compact gain-enhanced Vivaldi antenna array with suppressed mutual coupling for 5G mmWave application. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



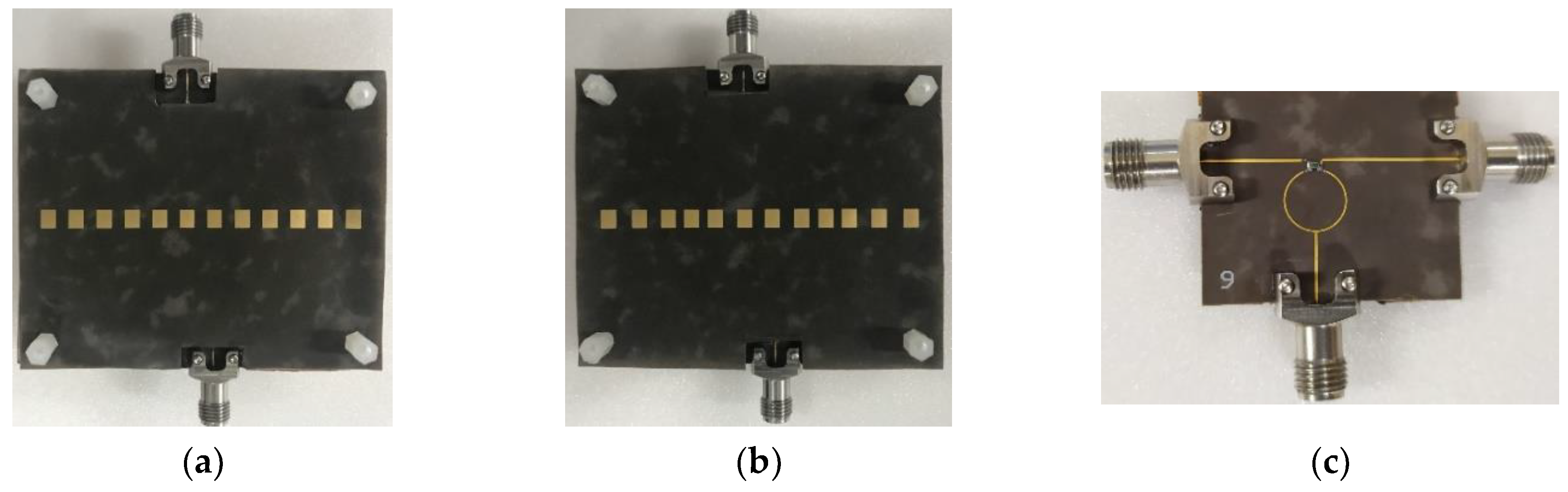
| Port | Transmission Coefficient (dB) | Power (%) | Normalized Power | Normalized Excitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | −9 | 12.5 | 0.5 | 0.707 |
| 6 | −9 | 12.5 | 0.5 | 0.707 |
| 8 | −6 | 25 | 1 | 1 |
| 10 | −6 | 25 | 1 | 1 |
| 12 | −9 | 12.5 | 0.5 | 0.707 |
| 14 | −9 | 12.5 | 0.5 | 0.707 |
| Port | Transmission Coefficient (dB) | Power (%) | Normalized Power | Normalized Excitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | −10.22 | 9.5 | 0.454 | 0.673 |
| 6 | −10.25 | 9.44 | 0.45 | 0.670 |
| 8 | −6.79 | 20.94 | 1 | 1 |
| 10 | −6.80 | 20.89 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| 12 | −10.23 | 9.48 | 0.452 | 0.672 |
| 14 | −10.19 | 9.57 | 0.457 | 0.676 |
| Port | Phase (Degree) Tuning L1 and L2 | Phase (Degree) Tuning L1, L2 and Meander Line |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 87.7 | 86.18 |
| 6 | 87.58 | 86 |
| 8 | 86.52 | 85.03 |
| 10 | 98.71 | 90.12 |
| 12 | 102.11 | 88.68 |
| 14 | 102.21 | 89.26 |
| Ref# | Power Dist. | Element Spacing | Element No# | fo (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | SLL 1 (dB) | Impedance Bandwidth | Radiation Efficiency | Half Power Beam Width |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [12] | uniform | uniform | 4 | 28 | 16.3 | −11.6 | 17.85% | 71.8% | 11° |
| [35] | uniform | uniform | 8 | 28 | 13 | ~ | 21.4% | 75% | ~ |
| [36] | uniform | uniform | 8 | 28 | 11.32 | ~ | 14.1% | ~ | ~ |
| [11] | uniform | uniform | 8 | 28 | 12 | −12.5 | 17.87% | >65% | 12.5° |
| [13] | non-uniform | uniform | 8 | 26 | 12 | −15 | 21.15% | >90% | 13.3° |
| [10] | uniform | uniform | 16 | 28 | 19.66 | −13.4 | 24.4% | 86% | 5° |
| This work | non-uniform | uniform | 12 | 28 | 16.3 | −15.36 | 15.35% | ~80% | 8.84° |
| non-uniform | non-uniform | 12 | 28 | 16.56 | −17.27 | 11.5% | ~80% | 8.9° |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uddin, M.N.; Choi, S. Non-Uniformly Powered and Spaced Corporate Feeding Power Divider for High-Gain Beam with Low SLL in Millimeter-Wave Antenna Array. Sensors 2020, 20, 4753. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174753
Uddin MN, Choi S. Non-Uniformly Powered and Spaced Corporate Feeding Power Divider for High-Gain Beam with Low SLL in Millimeter-Wave Antenna Array. Sensors. 2020; 20(17):4753. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174753
Chicago/Turabian StyleUddin, Md Nazim, and Sangjo Choi. 2020. "Non-Uniformly Powered and Spaced Corporate Feeding Power Divider for High-Gain Beam with Low SLL in Millimeter-Wave Antenna Array" Sensors 20, no. 17: 4753. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174753
APA StyleUddin, M. N., & Choi, S. (2020). Non-Uniformly Powered and Spaced Corporate Feeding Power Divider for High-Gain Beam with Low SLL in Millimeter-Wave Antenna Array. Sensors, 20(17), 4753. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174753






