Abstract
Spaceborne multistatic synthetic aperture radar (SAR) tomography (SMS-TomoSAR) systems take full advantage of the flexible configuration of multistatic SAR in the space, time, phase, and frequency dimensions, and simultaneously achieve high-precision height resolution and low-deformation measurement of three-dimensional ground scenes. SMS-TomoSAR currently poses a series of key issues to solve, such as baseline optimization, spatial transmission error estimation and compensation, and the choice of imaging algorithm, which directly affects the performance of height-dimensional imaging and surface deformation measurement. This paper explores the impact of baseline distribution on height-dimensional imaging performance for the baseline optimization issue, and proposes a feasible baseline optimization method. Firstly, the multi-base multi-pass baselines of an SMS-TomoSAR system are considered equivalent to a group of multi-pass baselines from monostatic SAR. Secondly, we establish the equivalent baselines as a symmetric-geometric model to characterize the non-uniform characteristic of baseline distribution. Through experimental simulation and model analysis, an approximately uniform baseline distribution is shown to have better SMS-TomoSAR imaging performance in the height direction. Further, a baseline design method under uniform-perturbation sampling with Gaussian distribution error is proposed. Finally, the imaging performance of different levels of perturbation is compared, and the maximum baseline perturbation allowed by the system is given.
1. Introduction
Knaell proposed two azimuth-range two-dimensional synthetic aperture acquisition techniques—curve SAR (CurviLinear SAR, CLSAR) [1] and SAR tomography (TomoSAR) [2]—in 1994 and 1995, respectively. Compared with interferometric SAR (InSAR) [3], CLSAR and TomoSAR truly qualify as 3D imaging. In TomoSAR, the use of a stack of complex-valued images, by synthesizing apertures along the height direction, makes it possible to separate different scatterers in one range-azimuth resolution cell and achieves height resolution, so as to provide the full 3D scene reflectivity profile in azimuth, range, height, and average velocity deformation [4].
Since the first practical demonstration of TomoSAR [5], it has been successfully applied in many application contexts, such as forestry [6,7], 3D urban reconstruction [8,9], and glaciers [10]. TomoSAR consists of resolving an inversion problem. To date, various spectral analysis methods have been developed for TomoSAR [11] to perform tomography inversion. These methods can be divided into three groups: (1) nonparametric spectral estimation [12,13,14], (2) parametric spectral estimation [15,16,17], and (3) compressive sensing (CS) [18,19,20,21]. Each of the three groups of TomoSAR methods has its respective advantages and drawbacks. For instance, the nonparametric spectral estimators (e.g., beamforming [12,13] and Capon [13,14]) are robust to focusing artifacts but obtain a low height resolution. The parametric spectral estimators, such as the multiple signal classification (MUSIC) estimator [15], the maximum likelihood (ML) estimators [16], and the weighted subspace fitting (WSF) estimators [16,17], can obtain a better height resolution than the nonparametric spectral estimators.
On the other hand, in [22], the single-pass multi-baseline TomoSAR system has 3D resolution, including height-resolving ability in a single-pass platform because there are multiple channels in the cross-track direction. However, the Rayleigh resolution in the height direction is very limited due to the limited baseline length in a single-pass platform. To obtain larger baseline length for better height resolution, the concept of Multistatic SAR [23] was introduced to the TomoSAR research. Moreover, multistatic SAR systems have great application potential in high-resolution wide-swath imaging, moving target detection, interferometric altimetry, 3D/4D imaging, anti-interference, multi-level imaging, etc. Therefore, the concept of a spaceborne multistatic TomoSAR (SMS-TomoSAR) system was proposed. SMS-TomoSAR has multi-baseline, multi-temporal detection capabilities in spatial and temporal dimensions, which can further realize spatial resolution in the height direction, and small surface deformation measurement of the 3D ground scene (i.e., 3D/4D imaging). To date, very limited research has been reported on this aspect of SMS-TomoSAR. Further, a series of key technical issues, such as baseline optimization design, phase error compensation, and imaging processing, directly affect the performance of high-precision resolution imaging in the height direction of SMS-TomoSAR systems.
In this paper, the multi-base multi-pass baselines of SMS-TomoSAR systems are considered equivalent to a group of multi-pass baselines of monostatic SAR. Secondly, the equivalent baselines are established as a symmetric-geometric model to characterize the non-uniform characteristics of baseline distribution. The model is centered on the main image, and baselines on both sides satisfy symmetric-geometric distribution. It is concluded that an approximately uniform baseline distribution has better SMS-TomoSAR imaging performance in the height direction. Further, a baseline design method under uniform-perturbation sampling with normal distribution error is proposed. The imaging performance of different levels of perturbation is compared, and the maximum baseline perturbation allowed by the system is given. Finally, our experimental simulation results verify the effectiveness of the proposed baseline optimization method.
2. Baseline Equivalence Analysis of SMS-TomoSAR
SMS-TomoSAR systems employ several small satellites in a formation to observe and measure the target area. In particular, SMS-TomoSAR could be considered to be monostatic SAR when an SMS-TomoSAR system employs only one satellite. Compared with monostatic SAR, SMS-TomoSAR obtains more spatial sampling in a single flight, which can reduce the number of revisits and increase the number of samples. Figure 1 shows the spatial geometry model of an SMS-TomoSAR system. The multi-base multi-pass tracks of an SMS-TomoSAR system is expressed as:
where is the satellite in the satellite formation, is the flight of the satellite formation, and is the track group of the flight of the satellite formation.
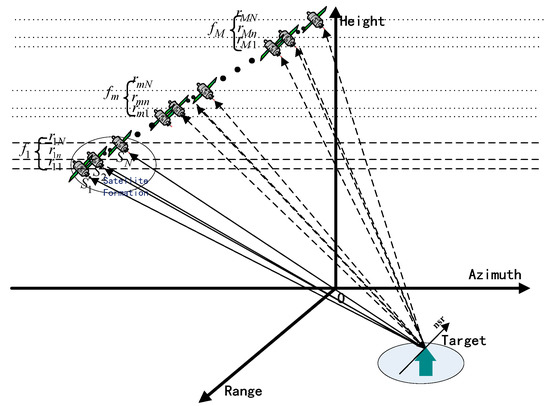
Figure 1.
Spatial geometry model of a spaceborne multistatic synthetic aperture radar tomography (SMS-TomoSAR) system (normal-slant-range (nsr) direction).
TomoSAR uses beam-forming technology to obtain high-precision height resolution capability, but tomographic processing requires a large number of spatial samples in different perspectives. Currently, data acquisition systems mainly include single-antenna multi-pass SAR systems, multi-antenna multi-pass In-SAR systems, and single-pass antenna array SAR systems. Essentially, an SMS-TomoSAR system does not differ from other systems in data acquisition, so the multi-base multi-pass baselines of an SMS-TomoSAR system can be considered equivalent to a group of multi-pass baselines of monostatic SAR. Selecting the image obtained by the track as the main image returns baselines from tracks.
The baseline in a single flight of a satellite formation is referred to as a same-track baseline, and these same-track baselines of flights constitute a repeat-track baseline. Considering that there is no essential difference between the baselines of different institutional systems in terms of data acquisition, the repeat-track baseline of SMS-TomoSAR systems is equivalent to:
In addition, the proposed baseline equivalence analysis of an SMS-TomoSAR system is helpful to further explore and obtain the optimal baseline design method. Figure 2a shows the baseline equivalent diagram of an SMS-TomoSAR system.
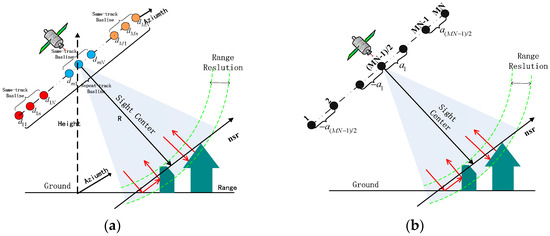
Figure 2.
(a) Baseline equivalent schematic diagram of an SMS-TomoSAR system; (b) Schematic diagram of the symmetric-geometric baseline model.
3. Three-dimensional Imaging Analysis of an SMS-TomoSAR System
As shown in Figure 2, an SMS-TomoSAR system observes the same target from different spatial positions, and obtains SAR Single Light Complex (SLC) images after azimuth-range two-dimensional compression. The appropriate main image is selected based on factors such as image correlation. After pairing and de-ramping, the complex value of the image at the same position [24] is expressed as:
where is the radar wavelength; is the electromagnetic scattering characteristic function of the target in height domain; is the distance from the phase center of the radar antenna to the reference point where the height is 0 at the time of capturing the main image; is the height span of the target; is the spatial frequency corresponding to the height , and its relationship between the spatial angular frequency is , b⊥p for the vertical baseline. The specific derivation process is given in [24,25].
Overall, it can be seen from the above derivation process that the complex value of the same-name resolution unit is the discrete sampling in of the spectrum of the electromagnetic scattering characteristic function of the target in the height direction after de-ramping. Therefore, imaging along the height direction is essentially a problem of reconstructing the original signal using spectral discrete sampling, while the vertical baseline directly affects system measurement results. Thus, this paper explores the baseline design issues by directly analyzing the vertical baseline, and all baselines discussed below refer to the vertical baseline.
4. Spatial Baseline Optimization Method for SMS-TomoSAR systems
4.1. Baseline Model Construction
Under the given experimental scenario parameters, especially the number of baseline and baseline spans, the effect of the relative intensity of the vertical baseline on the imaging performance of SMS-TomoSAR systems is explored. The vertical baseline was planned according to Figure 3. The image centered by the relative position (considered for image correlation and other factors) was selected as the main image, and the baselines on both sides of the main image were assumed to be symmetrically distributed. Taking the images as an example (herein referred to as the Positive Baseline Image Group), the baseline interval of the image group satisfied the equivalent relationship:
where is the baseline interval geometric coefficient, and is the baseline span. Since only the positive baseline image group was analyzed here, the positive baseline span was . It can be easily obtained from the above baseline analysis that when , , that is, the farther from the main image, the more dispersed the baseline distribution. When , , that is, the farther from the main image, the denser the baseline distribution. Especially, when , , that is, the baseline of the image satisfies the uniform distribution. Similarly, the above analysis was satisfied for the image (i.e., the Negative Baseline Image Group), and will not be discussed again. Figure 3 shows the baseline distribution with varying .
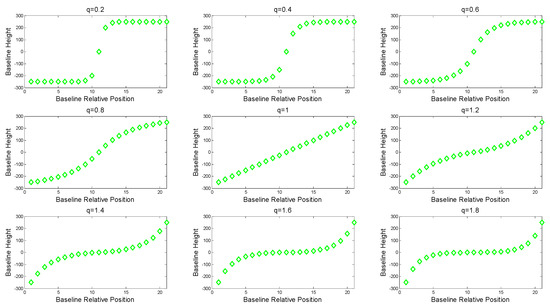
Figure 3.
The baseline distribution with changing (take MN = 21 as an example).
By adjusting to change the baseline distribution within the fixed baseline span, image data with different non-uniform characteristics was simulated, and then the imaging and result analysis were performed to explore the influence of different non-uniform characteristics of the baseline on the imaging performance of an SMS-TomoSAR system. Finally, the experimental simulation results showed that an approximate uniform baseline distribution had better SMS-TomoSAR height-dimensional imaging performance.
4.2. Maximum Perturbation Estimation Method
To further explore the effect of baseline perturbation on the imaging performance, the experiment defined the ratio of the vertical baseline deviation of the actual track and the predetermined track to double baseline interval under uniform sampling as the baseline perturbation , and assumed that was subject to Gaussian distribution, and satisfied
where is the vertical baseline deviation and is the maximum baseline perturbation, in which the probability of the vertical baseline perturbation falling in is 99.45%. The actual simulated baseline can be expressed as:
where is a random sample of the baseline perturbation .
The experiment simulated T groups of actual simulated baselines for every maximum vertical baseline perturbation, performed height-dimensional imaging performance analysis, and then used the root mean square error (RMSE) to reflect the impact of the maximum vertical baseline deviation on Peak side lobe ratio (PSLR) and integrated side lobe ratio (ISLR). The RMSE expression on PSLR and ISLR for maximum baseline perturbation is given as follows:
where and are the RMSE values of PSLR and ISLR for ; and are the PSLR and ISLR values of the group of experiments; and and are the mean values of T groups of experiments.
The experimental simulation analysis and summary showed that as the baseline perturbation increased, the RMSE value of PSLR and ISLR exhibited a growing trend, that is, the system became more unstable to image in the height direction.
We then define as the performance control factor (PCF),
where and are the PSLR and ISLR performance control factors; and respectively represent the optimal value and the performance control threshold of PSLR; and similarly, and respectively represent the optimal value and performance control threshold of ISLR.
We then use
to obtain the maximum allowable baseline perturbation. The experimental simulation showed that the SMS-TomoSAR system had better height-dimensional imaging performance when the baseline met the maximum baseline perturbation.
5. Experimental Verification
In this experiment, the proposed baseline analysis model was used to simulate different baseline-intensity images using Matlab software. The experiment was based on the simulation parameters for SMS-TomoSAR systems given in Table 1. The length of the synthetic antenna was 500 m. From Table 1, we know that the experiment simulated 21 baselines. In Figure 1, we define the same-track vertical baseline length as the length of vertical baseline interval of an adjacent track in the satellite formation, and the repeat-track vertical baseline length as the vertical baseline interval of an adjacent track of the same satellite. Compared with an SMS-TomoSAR system, monostatic SAR does not demonstrate same-track vertical baseline length, which directly limits the baseline span of monostatic SAR. In addition, as previously stated, we can consider SMS-TomoSAR as monostatic SAR when an SMS-TomoSAR system employs only one satellite. However, when we specify the number of flights as , the monostatic SAR has only six baselines, which is insufficient to obtain high-precision height resolution images. In practice, we need to obtain enough data to complete an urgent mission within a fixed time, so monostatic SAR is not adequate. Overall, we sought to identify a baseline optimization method for SMS-TomoSAR instead of monostatic SAR, for optimal height-dimensional resolution from one flight of a multi-satellite formation.

Table 1.
Simulation parameters.
In this paper, we consider the applicability of the optimal baseline design, discrete Fourier transform (DFT), non-uniform discrete Fourier transform (NDFT) and compressive sensing (CS, here in the BP algorithm) imaging algorithms. Further, we compared and analyzed the imaging results in the height direction of those three imaging algorithms for SMS-TomoSAR.
5.1. Analysis of Imaging Intensity Results
The experiment set the step size , and then simulated the satellite image data in , thereby focusing the image through three imaging algorithms: DFT, NDFT, and CS. Given the main image height and baseline span, the Rayleigh resolution of the three imaging algorithms satisfies
Table 2 shows the actual imaging height and phase of three imaging algorithms under nine different values. The experiment set the target height and the target phase . It can be seen from Table 2 that all three imaging algorithms could accurately obtain the target height and phase information.

Table 2.
Actual imaging height error and phase. CS: compressive sensing; DFT: discrete Fourier transform; NDFT: non-uniform discrete Fourier transform.
Figure 4 shows the PSLR, ISLR, and broadening coefficient (actual imaging resolution/Rayleigh resolution) of DFT, NDFT, and CS imaging algorithms under different intensity data. It can be seen from the above results that both the NDFT imaging algorithm and the CS imaging algorithm could achieve and exceed the imaging performance along the height direction of the DFT imaging algorithm when . For the NDFT imaging algorithm, the values of PSLR and ISLR at were close to the imaging results of the DFT imaging algorithm, where the actual imaging resolution became gradually worse as increased. The PSLR and ISLR of the CS imaging algorithm at also achieved and exceeded the imaging results of the DFT imaging algorithm, but with increasing , the actual imaging resolution gradually became worse.
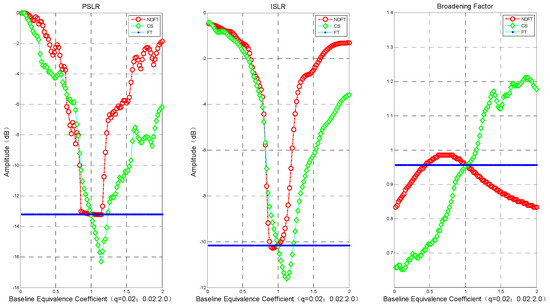
Figure 4.
Imaging performance in the height direction: PSLR, ISLR, broadening coefficient. The blue dotted line in the figure only represents the imaging result when the baseline is uniformly distributed.
And as increased (i.e., the baseline position gradually moved away from or close to the track of the main image), PSLR and ISLR generally increased gradually. In order to ensure a weak target is not obscured by an adjacent strong target, the system requires that the PSLR must be less than 13 dB. It can be seen from Figure 4 and Figure 5 that the imaging algorithm had better imaging performance when the baseline distribution had close to 0 (i.e., the baseline tended to be uniformly distributed).
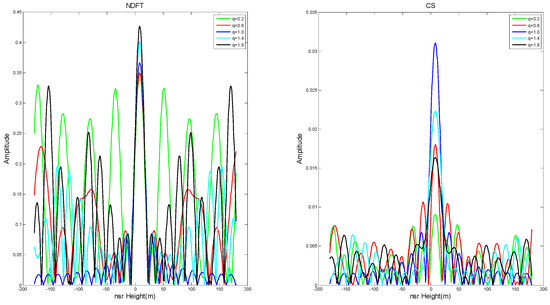
Figure 5.
The imaging results of NDFT and CS at q = 0.2, 0.6, 1.0, 1.4, and 1.8.
In order to further verify the above conclusion, the experiment evaluated the imaging results where PSLR < −10 dB, i.e., , and took the step size . The experimental results are shown in Figure 6.
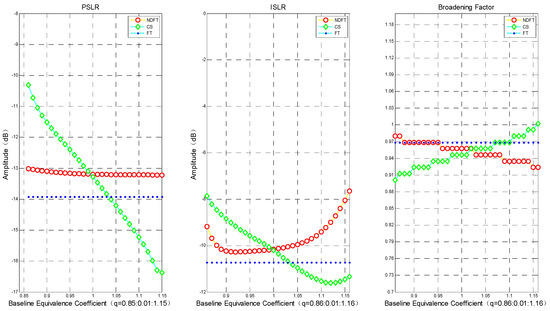
Figure 6.
The imaging performance along the deviation direction with : PSLR, ISLR, broadening coefficient.
The imaging performance in the height direction of the NDFT and CS imaging algorithms changed gradually. The PSLR of the NDFT imaging algorithm increased at , and the imaging performance along the height direction declined sharply when the PSLR of the CS imaging algorithm was greater than −11 dB at . Notably, the actual imaging accuracy decreased significantly at . At , the baseline distribution tended to be uniformly distributed, and the broadening coefficient of those three imaging algorithms only varied within , as shown in Figure 6. Therefore, summarizing the above analysis results leads to the following conclusion: the system has stable and good imaging performance along the height direction when the baseline satisfies the weak-deviation uniform distribution. We could then use the above conclusion to design the baseline.
5.2. Baseline Perturbation Analysis
According to the experimental analysis above, when the baseline satisfied uniform sampling within a certain baseline perturbation, the system could achieve optimal imaging performance along the height direction with the aforementioned baseline model. Considering the actual situation of the baseline deviation, was selected and is the iteration step size, then and were set. The actual baseline was simulated to explore the effect of the maximum baseline deviation on the RMSE value of PSLR and ISLR. The results are shown in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9.
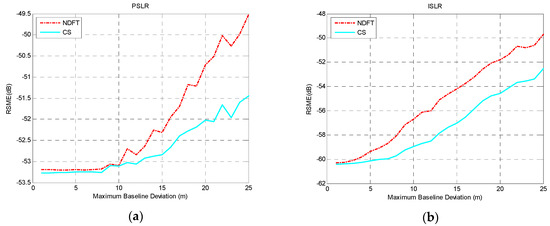
Figure 7.
The imaging performance with : (a) PSLR; (b) ISLR.
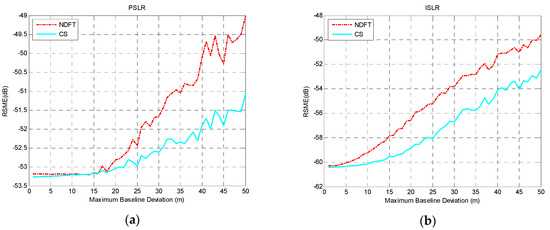
Figure 8.
The imaging performance with : (a) PSLR; (b) ISLR.
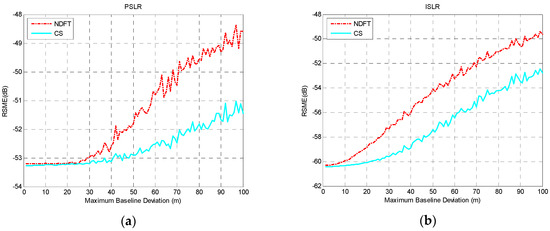
Figure 9.
The imaging performance with : (a) PSLR; (b) ISLR.
It can be seen from the experimental results that the height-dimensional imaging performance of the system was basically stable within a certain baseline perturbation, and as baseline deviation increased, the height-dimensional imaging performance was reduced, which can be seen from the mean and variance of PSLR and ISLR.
In order to ensure adequate imaging performance within the baseline deviation, the experiment selected and to obtain the result of the maximum baseline deviation with , as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
The relationship of baseline span and critical deviation about the performance stability.
It can be seen from the above results that as the baseline span increased, the maximum baseline perturbation of the imaging performance increased linearly.
The results of generating 100 sets of baseline with and , and subsequent height-dimensional imaging performances are shown in Figure 10.
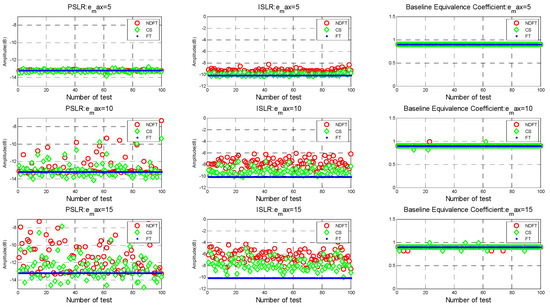
Figure 10.
Imaging performance results when .
It can be seen from the above experimental results that the imaging performance was more unstable as the maximum baseline perturbation increased (i.e., the farther the baseline deviated from the predetermined uniform baseline).
5.3. Baseline Optimization Method Verification
As mentioned above, we can consider SMS-TomoSAR to be monostatic SAR, when . However, monostatic SAR does not exhibit the same-track vertical baseline length, which directly limits the baseline span of monostatic SAR. However, when given the number of flights , monostatic SAR has only six baselines, which is insufficient to image for high-precision height resolution. In Figure 11 and Table 4, based on the parameters in Table 1 and , the performance results of SMS-TomoSAR and monostatic SAR are given. The experiment showed only the results of monostatic SAR under due to the limited baseline span for the same-track vertical baseline length.
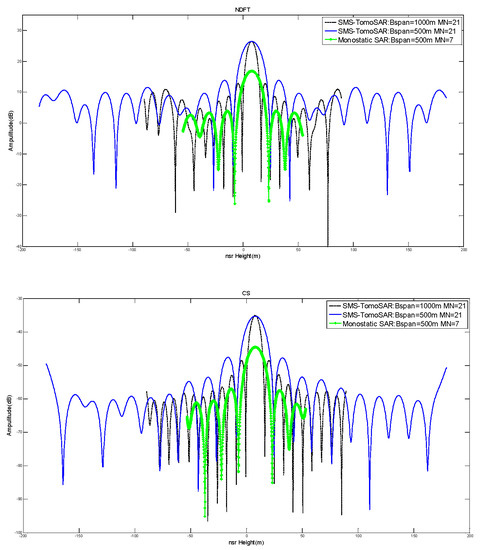
Figure 11.
The imaging results of SMS-TomoSAR and monostatic SAR.

Table 4.
The imaging performance results of SMS-TomoSAR and monostatic SAR for the NDFT and CS algorithms.
From the results above, compared with SMS-TomoSAR, it is obvious that monostatic SAR had smaller height span and fewer baselines. This directly resulted in lower unambiguity height and worse PSLR and ISLR. For an urgent mission within a fixed time, monostatic SAR is not suitable. The proposed method could be used if monostatic SAR obtains the same number of baselines as SMS-TomoSAR by more flights. However, SMS-TomoSAR and monostatic SAR have different influences on some issues, such as spatial transmission error estimation and compensation, as well as deformation measurement. Consequently, in this paper, we focus mainly on the effect of the proposed method for SMS-TomoSAR.
To further verify the validity, we used simulated data to provide tomographic images of scatterers located in the same cross-slant-range line, and obtained the image by inverting the model using the described techniques. Firstly, three isolated and coherent targets A, B, and C were simulated, and then an A and C simulated coherent targets located on the bottom and on the top, respectively, gave a distributed target B with a certain extension, but separated from the coherent target located on the bottom. The simulated target information is seen in Table 5 and Figure 12.

Table 5.
Target information.
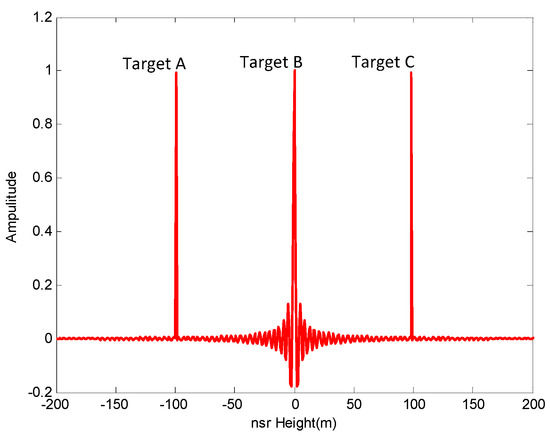
Figure 12.
Simulated target.
According to the conclusion above, we selected and based on Table 1. The simulation results are seen in Figure 13 and Figure 14.
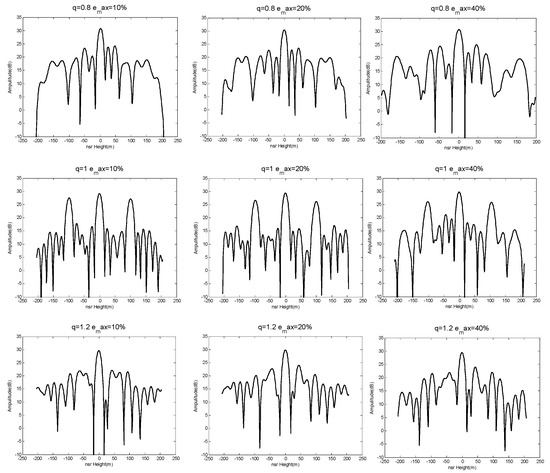
Figure 13.
Results of the NDFT algorithm.
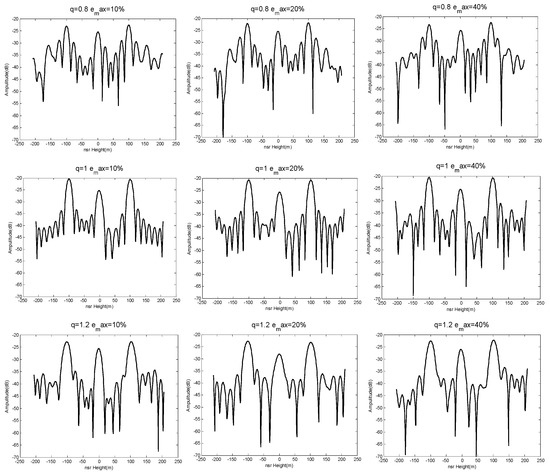
Figure 14.
Results of the CS algorithm.
We can conclude from the results shown in Figure 13 and Figure 14 that the NDFT and CS algorithms were better able to distinguish those three simulated targets when . This verifies the system had stable and good imaging performance in the height direction when the baseline satisfied a weak-deviation uniform distribution. Furthermore, the system had superior height-orientation performance when the baseline of an SMS-TomoSAR system met the allowable maximum baseline perturbation. In other words, the allowable maximum baseline perturbation can provide a reference satellite baseline control deviation for the design or spatial position control of SMS-TomoSAR systems. For example, when the experiment set , with the NDFT imaging algorithm, a maximum baseline perturbation provided optimal height-orientation performance for SMS-TomoSAR systems.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we established a symmetric-geometric baseline analysis model to explore the effect of baseline intensity on the height-dimensional imaging performance within a fixed baseline span, and proposed a maximum baseline deviation estimation method to explore the maximum vertical baseline deviation that ensures adequate height-dimensional imaging performance. From the experimental results above, it can be concluded that the system had superior height-orientation performance when the baseline of an SMS-TomoSAR system met the allowable maximum baseline perturbation, which has practical significance for the actual system baseline design. In other words, the allowable maximum baseline perturbation can provide a reference satellite baseline control deviation for the design or spatial position control of an SMS-TomoSAR system. Finally, we will continue to investigate other issues of SMS-TomoSAR systems, in order to contribute further to the existing body of research in the future.
Author Contributions
J.Z. and A.Y. conceived and designed the experiments; J.Z. performed the experiments; J.Z. and X.Z. analyzed the data; Y.Z. and Z.D. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; J.Z. wrote the paper.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant Nos. 61501477 and 61171123.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the College of Electronic Science and Engineering of National University of Defense Technology for providing the experiment condition.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Knaell, K. Three-dimensional SAR from curvilinear apertures. In Proceedings of the SPIE’s International Symposium on Optical Engineering and Photonics in Aerospace Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 4–8 April 1994; pp. 120–134. [Google Scholar]
- Knaell, K.; Cardillo, G.P. Radar tomography for the generation of three-dimensional images. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 1995, 142, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.C. Synthetic Interferometer Radar for Topographic Mapping. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardini, F. Differential tomography: A new framework for SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigber, A.; Moreira, A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, O.; Morsdorf, F.; Meier, E. Tomographic imaging of a forested area by airborne multi-baseline P-band SAR. Sensors 2008, 8, 5884–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, M.; Shahzad, M.; Zhu, X.X. Reconstruction of individual trees from multi-aspect TomoSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Demonstration of Super-Resolution for Tomographic SAR Imaging in Urban Environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3150–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldini, S.; Rocca, F.; D’Alessandro, M.M.; Ferro-Famil, L. Phase Calibration of Airborne Tomographic SAR Data via Phase Center Double Localization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1775–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Dong, Z.; Yu, A.; Wu, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y. New Approaches for Robust and Efficient Detection of Persistent Scatters in SAR Tomography. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Z.; Gray, D.; Bogner, R.; Homer, J. Three-dimensional SAR imaging via multiple pass processing. In Proceedings of the 1995 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS’95), Florance, Italy, 28 June–2 July 1995; Volume 5, pp. 2389–2391. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardini, F.; Reigber, A. Adaptive Spectral Estimation for Multi-baseline SAR Tomography with Airborne L-band Data. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 3, pp. 2014–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Joshi, S.K.; Govil, H. Spaceborne PolSAR Tomography for Forest Height Retrieval. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 5175–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, S.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A.; Pottier, E. Three-dimensional imaging and scattering mechanism estimation over urban scenes using dual-baseline polarimetric InSAR observations at L-band. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4616–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ferro-Famil, L. 3D characterization of buildings in a dense urban environment using L-band PolInSAR data with irregular baselines. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 3, pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A. Under-foliage Object Imaging Using SAR Tomography and Polarimetric Spectral Estimators. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Romberg, J.; Tao, T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budillon, A.; Evangelista, A.; Schirinzi, G. Three-Dimensional SAR Focusing from Multipass Signals Using Compressive Sampling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Tomographic SAR Inversion by L1-Norm Regularization—The Compressive Sensing Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3839–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budillon, A.; Ferraioli, G.; Schirinzi, G. Localization Performance of Multiple Scatterers in Compressive Sampling SAR Tomography: Results on COSMO-SkyMed Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.C.; Liang, X.D.; Wang, Y. A Unified Algorithm for Channel Imbalance and Antenna Phase Center Position Calibration of a Single-Pass Multi-Baseline TomoSAR System. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auterman, J.L. Phase stability requirements for bistatic SAR. In Proceedings of the IEEE National Radar Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 1984; pp. 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.L. Research on Differential Intereference Based on Bistatic SAR. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Sun, X.L.; Yu, A.X. Research on differential intereference based on bistatic SAR. J. Natl. Def. Sci. Technol. 2008, 30, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).