On-Orbit Signal-to-Noise Ratio Test Method for Night-Light Camera in Luojia 1-01 Satellite Based on Time-Sequence Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. On-Orbit SNR Test Method
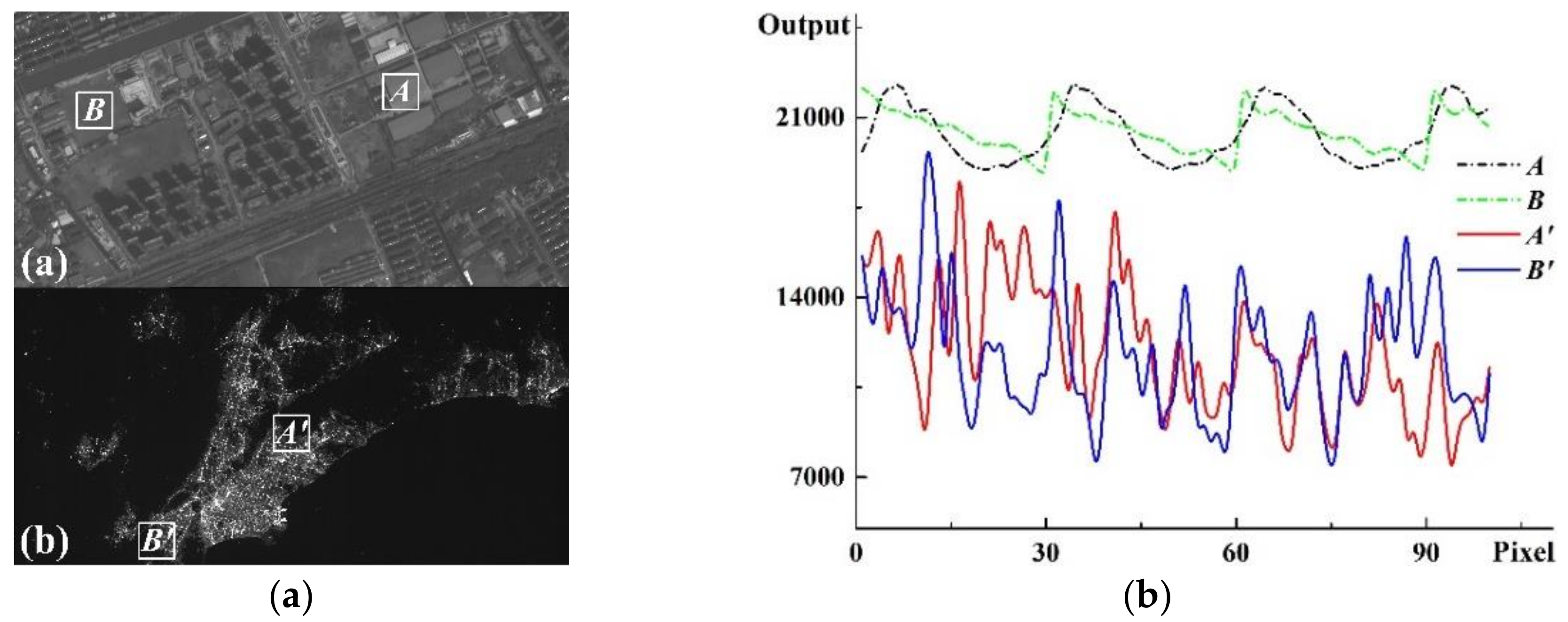
2.1. Spatial-Sequence-Based SNR Test Method
2.2. Limitation of Night-Light Remote Sensing
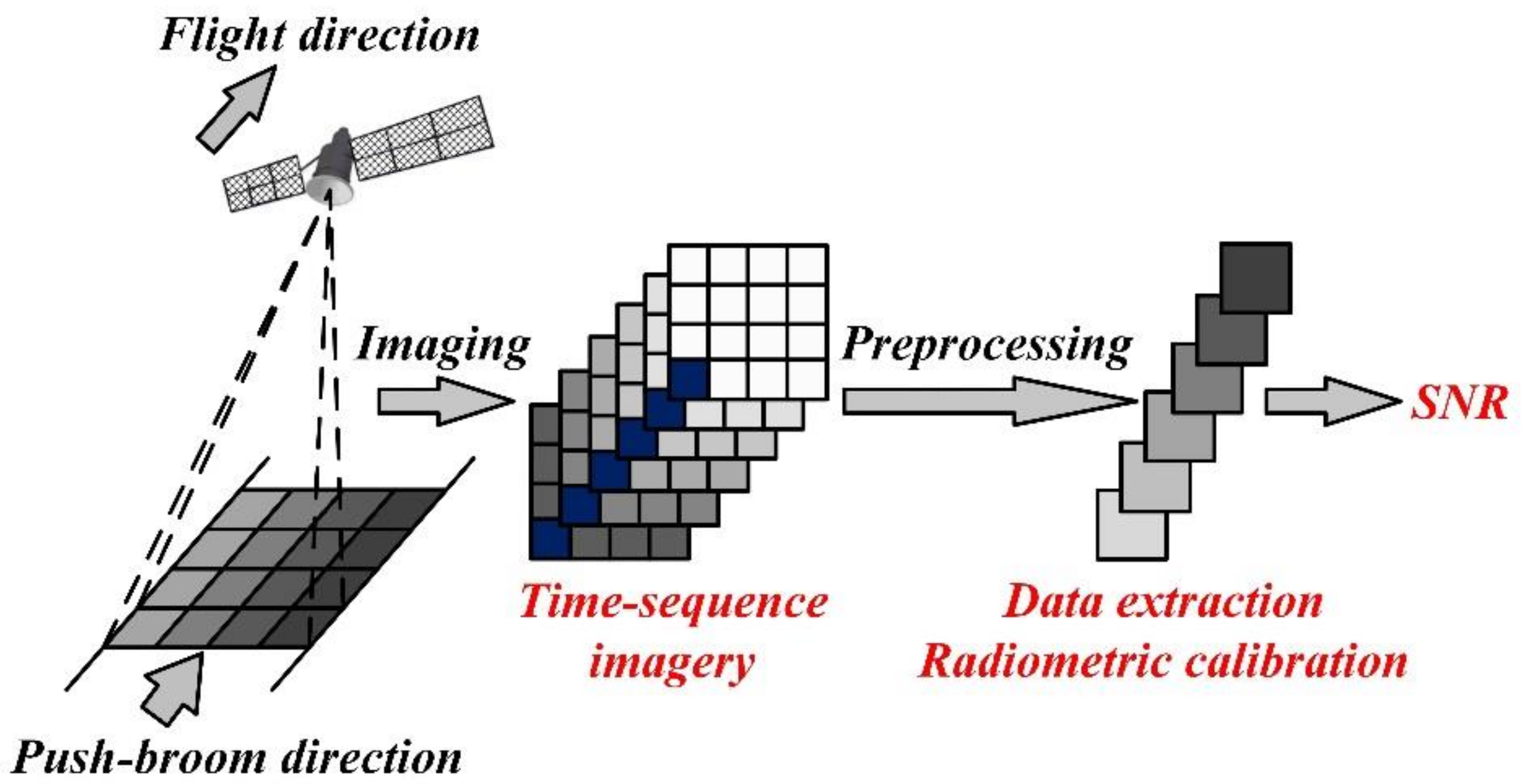
2.3. Time-Sequence-Based SNR Test Method
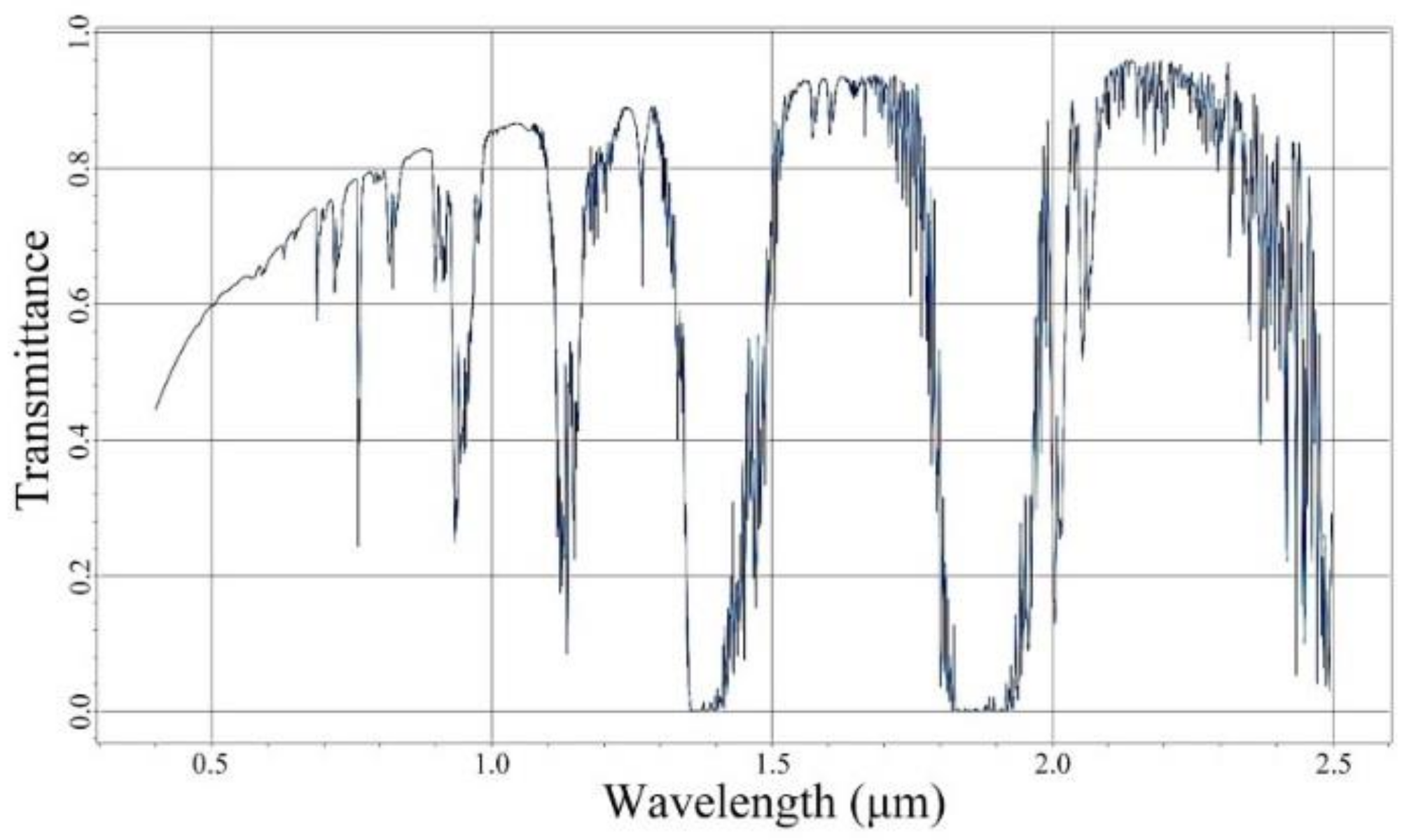
3. Radiative Transfer Model
4. Theoretical SNR Model
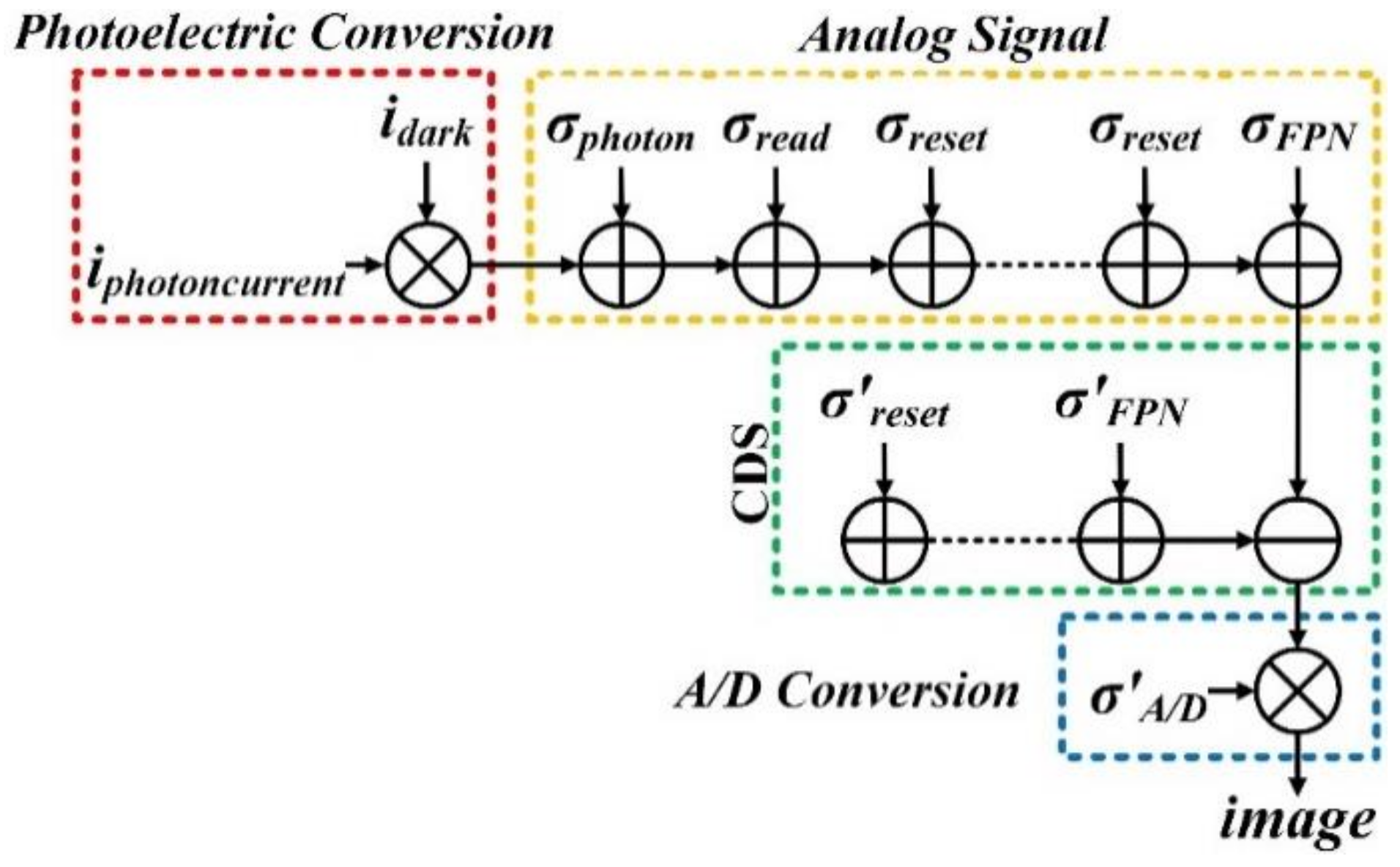
4.1. Signal Electrons Model
4.2. Noise Electrons Model
4.3. Conversion of Radiometry and Photometry
5. Results and Discussion
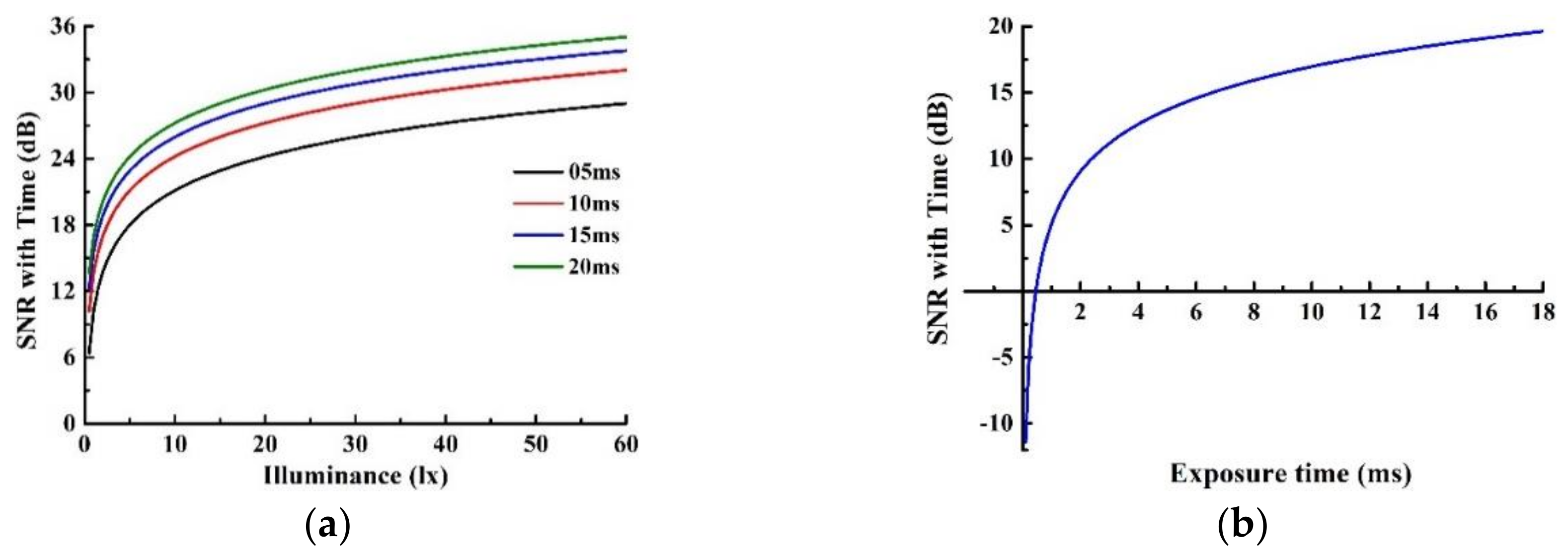
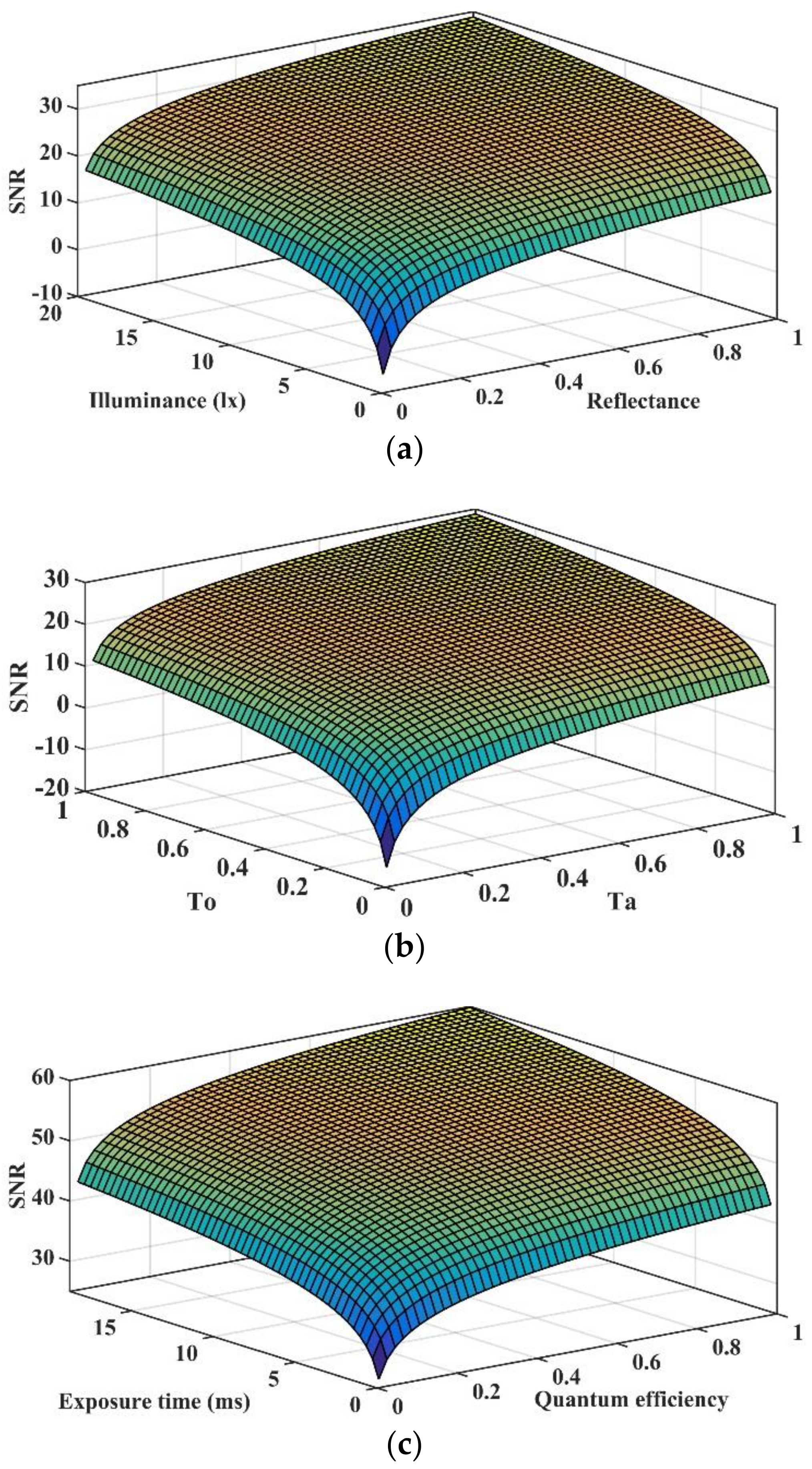
5.1. Theoretical Prediction of SNR
5.2. On-Orbit Test of SNR
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, K.; Qi, K.; Guan, Q.; Wu, C.; Yu, J.; Qing, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wu, H.; Li, X. A Scientometric Visualization Analysis for Night-Time Light Remote Sensing Research from 1991 to 2016. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Pettit, D.R.; Cinzano, P.; Sutton, P.C.; Small, C. Overview of the Nightsat mission concept. In Proceedings of the 2007 Urban Remote Sensing Joint Event, Paris, France, 11–13 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baugh, K.; Elvidge, C.D.; Ghosh, T.; Ziskin, D. Development of a 2009 Stable Lights Product using DMSP-OLS data. Proc. Asia Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 30, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Application of DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Images: A Meta-Analysis and a Systematic Literature Review. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6844–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, C.J.; Wu, B.F. Nighttime Vehicle Detection for Driver Assistance and Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Safran, J.; Tuttle, B.; Sutton, P.; Cinzano, P.; Pettit, D.; Arvesen, J.; Small, C. Potential for global mapping of development via a nightsat mission. Geojournal 2007, 69, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yang, D.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Xia, F. Regional Inequality in China Based on NPP-VIIRS Night-Time Light Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K. Can Night-Time Light Data Identify Typologies of Urbanization? A Global Assessment of Successes and Failures. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3476–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Ma, Q. Dynamics of Urbanization Levels in China from 1992 to 2012: Perspective from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1721–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K.C. Mapping urbanization dynamics at regional and global scales using multi-temporal DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the Ability of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data to Estimate the Gross Domestic Product and the Electric Power Consumption of China at Multiple Scales: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamir, R.; Lerner, A.; Haspel, C.; Dubinsky, Z.; Iluz, D. The spectral and spatial distribution of light pollution in the waters of the northern Gulf of Aqaba (Eilat). Sci. Rep. UK 2017, 7, 42329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spitschan, M.; Aguirre, G.K.; Brainard, D.H.; Sweeney, A.M. Variation of outdoor illumination as a function of solar elevation and light pollution. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 26756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Guo, H.; Yin, R.; Leng, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. Potentiality of Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery to Investigate Artificial Light Pollution. Sensors 2018, 18, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölker, F.; Moss, T.; Griefahn, B.; Kloas, W.; Voigt, C.C.; Henckel, D.; Hänel, A.; Kappeler, P.M.; Völker, S.; Schwope, A.; et al. The Dark Side of Light: A Transdisciplinary Research Agenda for Light Pollution Policy. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Deng, Y.; He, B.; Jia, K. The Impact of Precipitation Deficit and Urbanization on Variations in Water Storage in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Luan, Y.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Miao, L.; Cui, X. A new global anthropogenic heat estimation based on high-resolution nighttime light data. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, C.; Dou, Y. Quantifying the Anthropogenic Footprint in Eastern China. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 24337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, M.; Wang, L.; Zou, S.; Shi, C. Modeling the Census Tract Level Housing Vacancy Rate with the Jilin1-03 Satellite and Other Geospatial Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sutton, P.C.; Elvidge, C.D. Relationships between Nighttime Imagery and Population Density for Hong Kong. Proc. Asia-Pac. Adv. Netw. 2011, 31, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharti, N.; Tatem, A.J. Fluctuations in anthropogenic nighttime lights from satellite imagery for five cities in Niger and Nigeria. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.; Jendryke, M.; Li, D.; Wu, C. Night-Time Light Dynamics during the Iraqi Civil War. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Dietz, J.B.; Bland, T.; Sutton, P.C.; Kroehl, H.W. Radiance Calibration of DMSP-OLS Low-Light Imaging Data of Human Settlements. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, D. On-Orbit Relative Radiometric Calibration of the Night-Time Sensor of the LuoJia1-01 Satellite. Sensors 2018, 18, 4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, X.H.; Tang, L.L.; Li, C.R. Review on Methods for SNR Estimation of Optical Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2010, 25, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Wang, Q.; Wei, Z.; He, C.; Li, D. High Sensitive Night-time Light Imaging Camera Design and In-orbit Test of Luojia1-01 Satellite. Sensors 2019, 19, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.M.; Zhang, W.; Cong, M.Y. Analysis of Signal-to-Noise Ratio Calculation for Satellite-Based Infrared Staring Sensor. J. Astronaut. 2007, 4, 955–959. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, O.; Raya, J.G.; Reeder, S.B.; Reiser, M.F.; Schoenberg, S.O. Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: Influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 26, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.L. Assessing low-light cameras with photon transfer curve method. J. Innov. Opt. Heal. Sci. 2016, 9, 1630008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeder, S.B.; Wintersperger, B.J.; Dietrich, O.; Lanz, T.; Greiser, A.; Reiser, M.F.; Glazer, G.M.; Schoenberg, S.O. Practical approaches to the evaluation of signal-to-noise ratio performance with parallel imaging: Application with cardiac imaging and a 32-channel cardiac coil. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 54, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Zhang, L.F.; Tong, Q.X. Estimation of Signal to Noise Ratio of Remote Sensing Images. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 1999, 4, 360–365. [Google Scholar]
- Roger, R.E.; Arnold, J.F. Reliably estimating the noise in AVIRIS hyperspectral images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Tian, Y.; Han, C.Y.; Wu, G.D.; Ma, D.M. Assessment of signal-to-noise ratio of space optical remote sensor using artificial neural network. Opto-Electron. Eng. 2006, 33, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.F.; Lin, Z.J.; Fan, L.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.F.; Liu, Y.G. Research on Methods for Computing the Volume of Information of Remote Sensing Image. J. Shandong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2008, 27, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Hillger, D.W.; Haar, T.H.V. Estimating noise levels of remotely sensed measurements from satellites using spatial structure analysis. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 5, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.C. An operational method for estimating signal to noise ratios from data acquired with imaging spectrometers ☆. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 43, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.R.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Q. Study on the Method for Estimating the Noise in Remote Sensing Images on Local Standard Deviation. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 11, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; He, T.; Zhao, L. Anisotropic characteristic of artificial light at night-Systematic investigation with VIIRS DNB multi-temporal observations. Remote Sens Environ. 2019, 233, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.J. Modern Optical Engineering, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.E.; Stamnes, K. Radiative Transfer in the Atmosphere and Ocean. Phys. Today 2000, 53, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Z.; Ren, J.W.; Li, X.S.; Zhao, G.J.; Ren, J.Y. Analysis of signal-to-noise ratio for remote sensing TDI CCD camera based on radiative transfer model. Infrared Laser Eng. 2008, 37, 497–500. [Google Scholar]
- Bazell, R.J. Star Bright, Street Light, Which Will They See Tonight? Science 1971, 171, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coesfeld, J.; Anderson, S.; Baugh, K.; Elvidge, C.; Schernthanner, H.; Kyba, C. Variation of Individual Location Radiance in VIIRS DNB Monthly Composite Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Keith, D.M.; Tuttle, B.T.; Baugh, K.E. Spectral identification of lighting type and character. Sensors 2010, 10, 3961–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.Y.; Tan, H.Y. Engineering Optics, 4th ed.; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, K.; Hu, Y.N.; Cheng, C.; Chen, B. Transferability of Economy Estimation Based on DMSP/OLS Night-Time Light. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.B.; Qin, Z.H. The Transmission Model of Atmospheric Radiation and the Computation of Transmittance of MODTRAN. Geomat. Spat. Inform. Technol. 2004, 27, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Hide, R. Optics of the Atmosphere: Scattering by Molecules and Particles; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Zheng, W.; Singh, D.J. Light scattering and surface plasmons on small spherical particles. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, S. Accurate Atmospheric Scattering. In GPU Gems; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bruneton, E.; Neyret, F. Precomputed Atmospheric Scattering. Comput. Graph. Forum 2008, 27, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janesick, J.R. Photon Transfer; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; p. 5249. ISBN 978-0-8194-6722-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquot, B.C.; Bolla, B.M.; Maguire, S. Hybrid approach to mean-variance and photon transfer measurement. In Proceedings of the Image Sensing Technologies: Materials, Devices, Systems, & Applications II, Baltimore, MA, USA, 22–23 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.X.; Wan, Z.; Li, S.X.; Li, B.Y.; Shao, Y.R. Influence factors on SNR of TDICCD space camera. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2015, 23, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, S.L.; Shi, W.X.; Wang, F.; Deng, D.X. Linear CCD camera System for industry measurement and its noise evaluation. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2016, 24, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardis, J.E. 100 years of photometry and radiometry. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, San Diego, CA, USA, 1–2 August 2001; Volume 4450, pp. 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Simonot, L.; Boulenguez, P. Generalization of the geometric description of a light beam in radiometry and photometry. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2013, 30, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulli, T.; Dönsberg, T.; Poikonen, T.; Manoocheri, F.; Kärhä, P.; Ikonen, E. Advantages of white LED lamps and new detector technology in photometry. Light Sci. Appl. 2015, 4, e332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Satellite | Satellite Payload | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| DMSP | OLS | 2700 m @ 850 km 1 |
| Suomi NPP | VIIRS | 740 m @ 830 km |
| SAC-C | HSTC | 200~300 m @ 705 km |
| SAC-D | HSC | 200 m @ 661 km |
| Luojia 1-01 | - | 129 m @ 645 km |
| International Space station | - | 30~50 m @ 300~450 km |
| Jilin-1 Smart Verification Satellite | - | 5 m @ 638 km |
| EROS-B | PIC-2 | 0.7 m @ 520 km |
| Parameters | Symbol | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Operation waveband | λ | 0.5~0.9 μm @ 0.625 μm |
| Optical transmittance | to | 70% |
| GSD | GSD | 129 m @ 645 km |
| Relative aperture | 1/F | 1:2.8 |
| Central obscuration | ε | 0 |
| Parameters | Symbol | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Dark current | De | 31.28e−/s/pixel @ 25 °C |
| Readout noise | σread | 1.47e− |
| Full well capacity | NFW | 120ke− |
| Pixel size | Ad | 11 × 11 μm2 |
| Integral series | M | 1 |
| Quantization bits | b | 15 bits |
| Region | Exposure Time | Logging Mode | Gain | Bit Depth | Image Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mexico City | 13.7 ms | HDR | 1.85x | 16 bits | 13 |
| New Delhi | 13.7 ms | HDR | 3.68x | 16 bits | 10 |
| Columbia | 13.7 ms | HDR | 1.85x | 16 bits | 19 |
| Gain | Exposure Time | HDR Low-Gain Mode | HDR High-Gain Mode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | Intercept | Slope | Intercept | ||
| 1.85x | 2 ms | 2263.10 | 177.71 | 17,025.89 | 219.97 |
| 5 ms | 4566.74 | 191.77 | 40,291.63 | 186.73 | |
| 10 ms | 8903.24 | 196.49 | 84,850.39 | 167.80 | |
| 18.8 ms | 16,253.92 | 227.31 | 157,173.66 | 166.79 | |
| 3.68x | 2 ms | 3932.83 | 201.42 | 36,073.88 | 197.02 |
| 5 ms | 8797.50 | 189.43 | 85,919.26 | 179.34 | |
| 10 ms | 17,092.27 | 225.21 | 171,150.67 | 172.92 | |
| 18.8 ms | 32,913.00 | 204.48 | 337,970.41 | 113.84 | |
| Region | Sampling | Output | SNR | Radiance | Illuminance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mexico City | 13 × 9 | 208~2557 | 20.03~42.94 | 3.10 × 10−4~2.06 × 10−2 | 1.62~107.55 |
| New Delhi | 10 × 11 | 193~1326 | 15.84~39.93 | 4.94 × 10−4~5.41 × 10−3 | 2.58~28.27 |
| Columbia | 19 × 6 | 266~1560 | 22.10~33.01 | 1.17 × 10−3~1.16 × 10−2 | 6.12~60.70 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Zhong, X.; Su, Z. On-Orbit Signal-to-Noise Ratio Test Method for Night-Light Camera in Luojia 1-01 Satellite Based on Time-Sequence Imagery. Sensors 2019, 19, 4077. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194077
Wang W, Zhong X, Su Z. On-Orbit Signal-to-Noise Ratio Test Method for Night-Light Camera in Luojia 1-01 Satellite Based on Time-Sequence Imagery. Sensors. 2019; 19(19):4077. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194077
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei, Xing Zhong, and Zhiqiang Su. 2019. "On-Orbit Signal-to-Noise Ratio Test Method for Night-Light Camera in Luojia 1-01 Satellite Based on Time-Sequence Imagery" Sensors 19, no. 19: 4077. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194077
APA StyleWang, W., Zhong, X., & Su, Z. (2019). On-Orbit Signal-to-Noise Ratio Test Method for Night-Light Camera in Luojia 1-01 Satellite Based on Time-Sequence Imagery. Sensors, 19(19), 4077. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194077






