The Unified Form of Code Biases and Positioning Performance Analysis in Global Positioning System (GPS)/BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) Precise Point Positioning Using Real Triple-Frequency Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Unified Forms of Code Biases
2.1. Basic Observation Equations
2.2. Inter Frequency Clock Bias
2.3. Inter System Clock Bias
3. Observation Models in Single or Multi-GNSS
3.1. Uncombined Observation Model with Triple-Frequency Multi-GNSS
3.2. Other Typical Observation Models
4. Analysis And Assessment
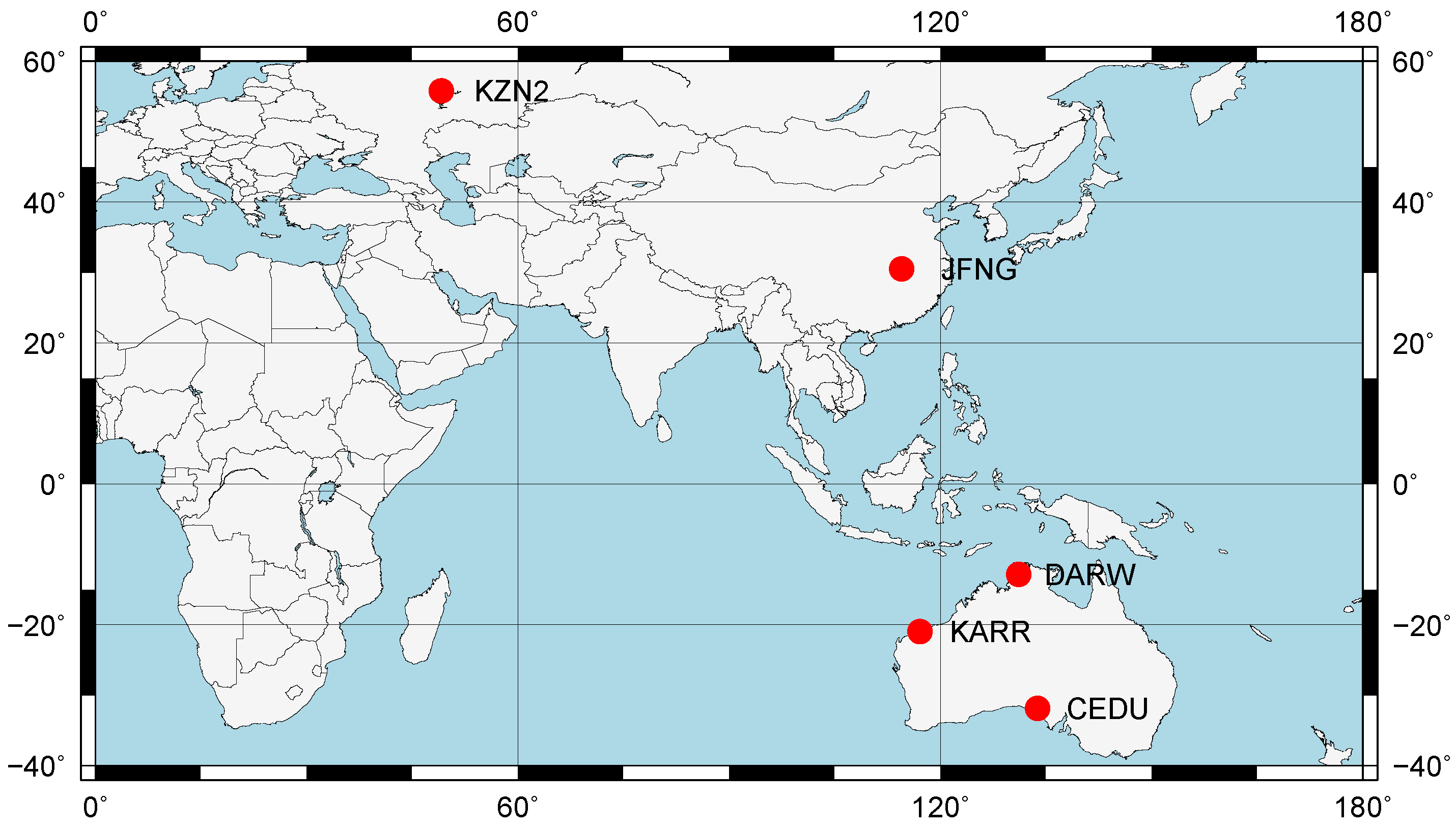
4.1. Experimental Strategy
4.1.1. Configuration Strategy
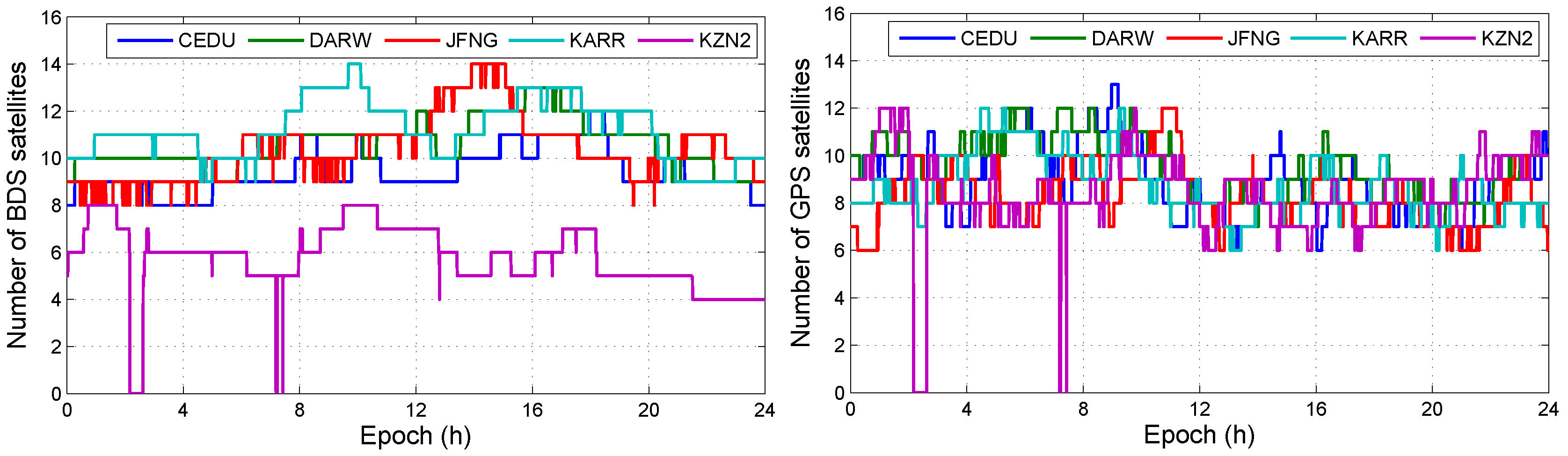
4.1.2. Availability of Multi-Frequency Models
4.2. Influence of Code Biases
4.2.1. Influence of IFB Bias
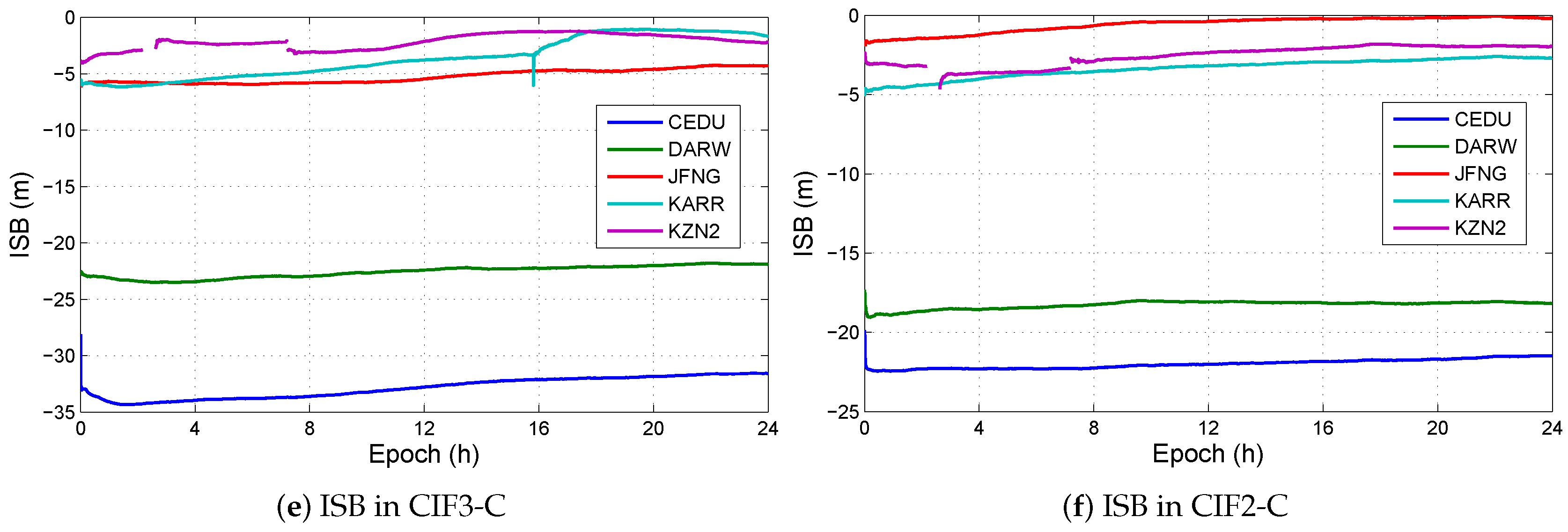
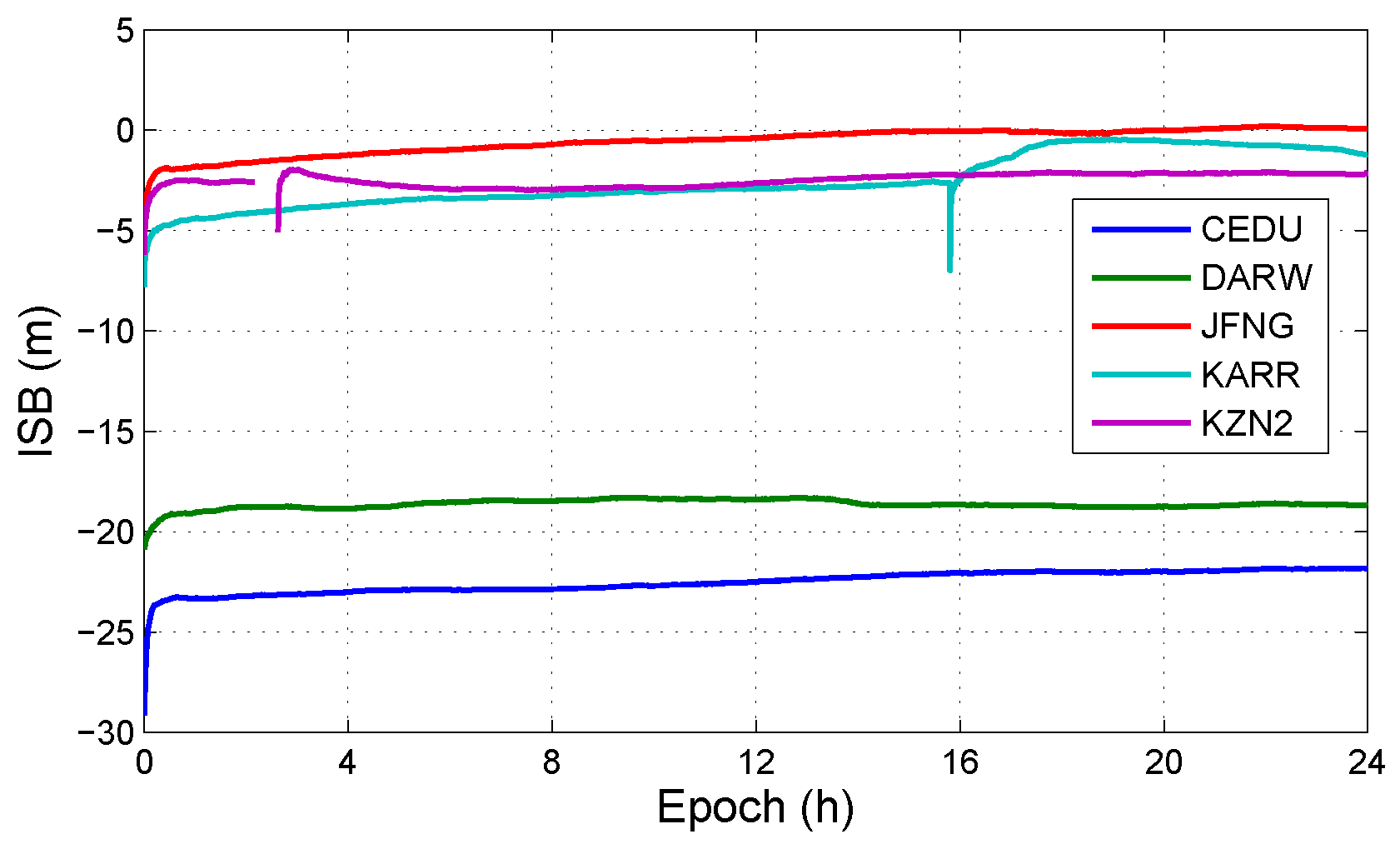
4.2.2. Influence of ISB Bias
4.2.3. Influence of Both IFB and ISB Biases
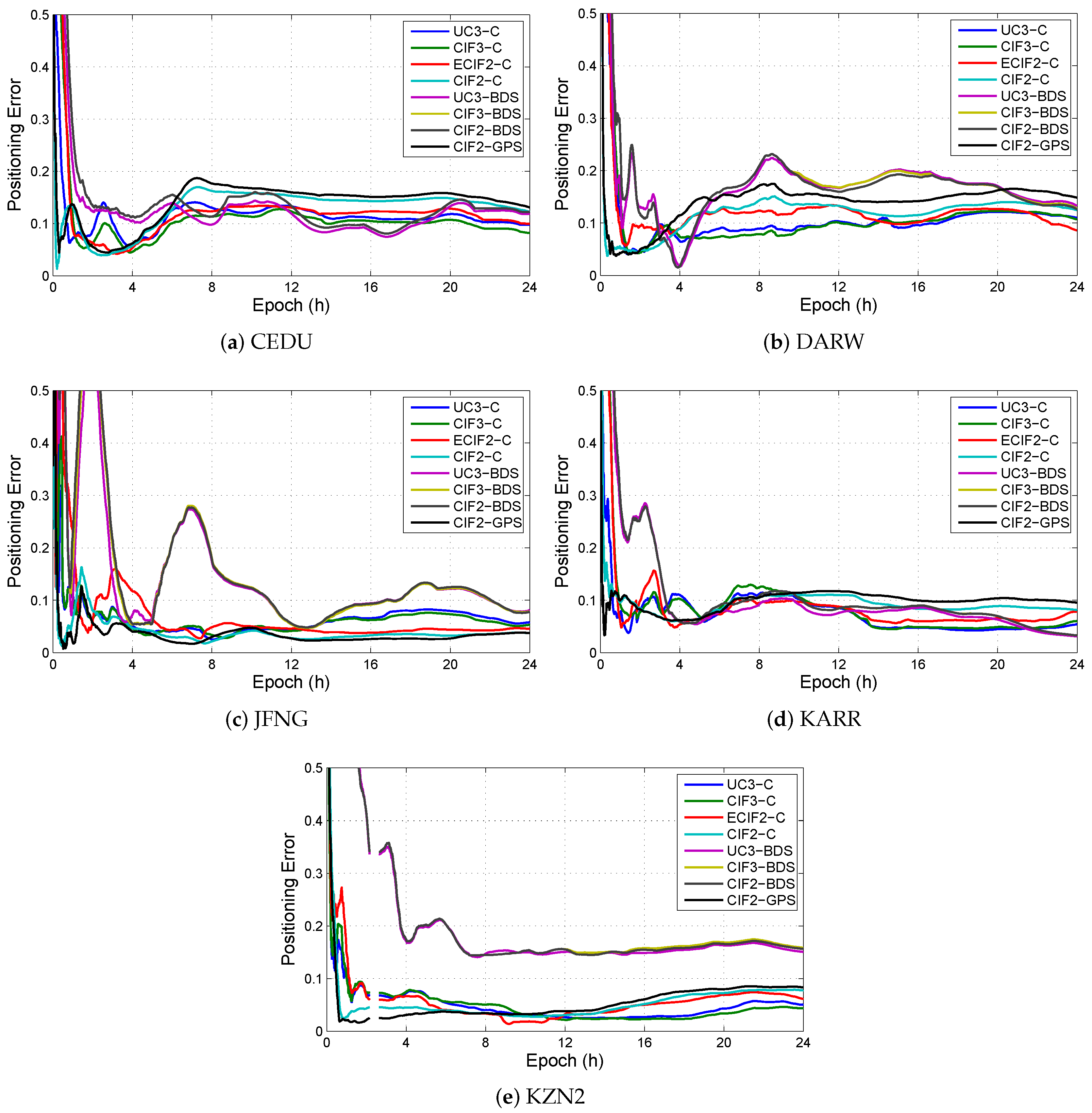
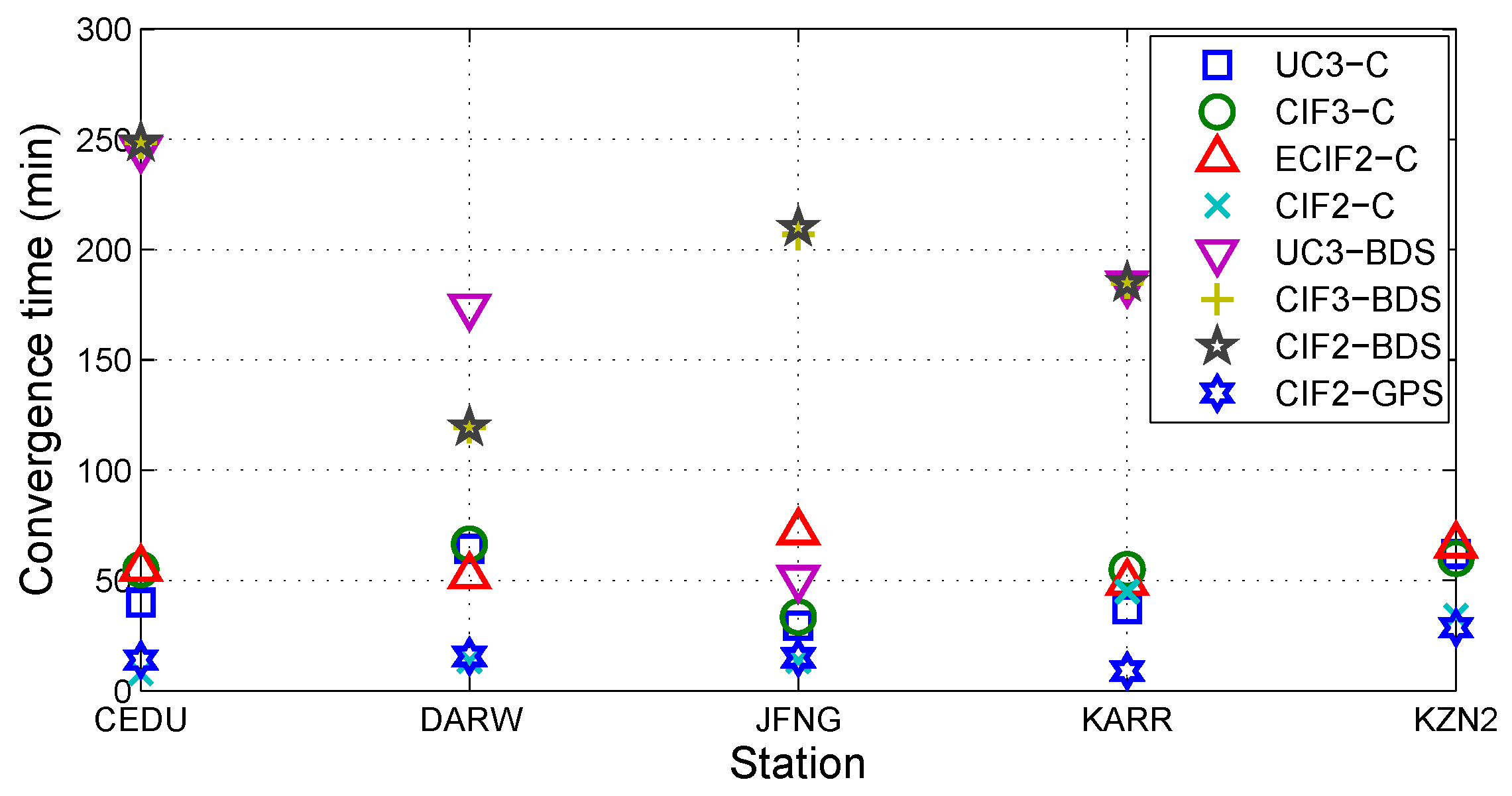
4.3. Results and Discussion of Single and Multi-GNSS PPP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDS | BeiDou Navigation Satellite System |
| CIF | conventional ionosphere-free model |
| CIF2 | conventional ionosphere-free model with dual-frequency |
| CIF2-BDS | conventional ionosphere-free model with dual-frequency BDS-only |
| CIF2-C | conventional ionosphere-free model with dual-frequency BDS+GPS combination |
| CIF2-GPS | conventional ionosphere-free model with dual-frequency GPS-only |
| CIF3 | conventional ionosphere-free model with triple-frequency |
| CIF3-BDS | conventional ionosphere-free model with triple-frequency BDS-only |
| CIF3-C | conventional ionosphere-free model with triple-frequency BDS+GPS combination |
| CORS | Continuously Operating Reference Stations |
| CT | convergence time |
| DCB | differential code bias |
| DOY | day of year |
| ECIF2-C | extended CIF2-C model |
| FCB | fractional cycle bias |
| GMF | Global Mapping Function |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| ICD | Interface Control Document |
| IFB | inter-frequency clock bias |
| ISB | inter-system clock bias |
| ISC | inter-signal correction |
| MGEX | Multi-GNSS Experiment |
| M-W | Melbourne-Wubbena detecting |
| PCO | Antenna Phase Center Offsets |
| PCV | Antenna Phase Center Variations |
| PPP | precise point positioning |
| TGD | timing group delay |
| UC | uncombined model |
| UC2 | uncombined model with dual-frequency |
| UC3 | uncombined model with triple-frequency |
| UC3-BDS | uncombined model based with triple-frequency BDS-only |
| UC3-C | uncombined model with triple-frequency BDS+GPS combination |
| UPD | uncalibrated phase delay |
References
- Zumberge, J.; Heflin, M.; Jefferson, D.; Watkins, M.; Webb, F.H. Precise Point Positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise Point Positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Timing group delay and differential code bias corrections for BeiDou positioning. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, R.; Jung, J.; Enge, P.; Pervan, B. Civilian GPS: The benefits of three frequencies. GPS Solut. 2000, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, H.; Langley, R. The WAAS L5 Signal: An Assessment of Its Behavior and Potential End Use. GPS World 2009, 20, 42–50. Available online: http://www.gpsworld.com/gnss-system/innovation-the-waas-l5-signal-7047 (accessed on 1 May 2009).
- Montenbruck, O.; Hugentobler, U.; Dach, R.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Apparent clock variations of the Block IIF-1 (SVN62) GPS satellite. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Teunissen, P.; Nakamura, S. Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Lu, C.; Wickert, J. Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-3: New-generation navigation signals. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsobeiey, M. Precise point positioning using triple-frequency GPS measurements. J. Navig. 2015, 68, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ren, X. Modeling and assessment of triple-frequency BDS precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Xiao, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, T. Improved method for estimating the inter-frequency satellite clock bias of triple-frequency GPS. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Li, X. Characteristics of inter-frequency clock bias for Block IIF satellites and its effect on triple-frequency GPS precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ye, S.; Song, J. Handling the satellite inter-frequency biases in triple-frequency observations. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Lou, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, J. Impact of GPS differential code bias in dual-and triple-frequency positioning and satellite clock estimation. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Lu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Considering inter-frequency clock bias for BDS triple-frequency precise point positioning. Remote. Sens. 2017, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Guo, F.; Yuan, Y. GPS inter-frequency clock bias modeling and prediction for real-time precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zhao, L.; Song, J.; Chen, D.; Jiang, W. Analysis of estimated satellite clock biases and their effects on precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Geng, J. GPS satellite clock determination in case of inter-frequency clock biases for triple-frequency precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mowafy, A.; Deo, M.; Rizos, C. On biases in precise point positioning with multi-constellation and multi-frequency GNSS data. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 035102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggrey, J.; Bisnath, S. Analysis of multi-GNSS PPP initialization using dual-and triple-frequency data. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, Monterey, CA, USA, 30 January–2 February 2017; pp. 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.; Kleusberg, A. GPS for Geodesy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 187–229. [Google Scholar]
- Leick, A.; Rapoport, L.; Tatarnikov, D. GPS Satellite Surveying; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 11–80. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Xu, Y. GPS: Theory, Algorithms and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 76–145. [Google Scholar]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P. The BeiDou navigation message. J. Glob. Position Syst. 2013, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, M.; Qu, L.; Hu, Z.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Initial results of precise orbit and clock determination for COMPASS navigation satellite system. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C.; Yao, X.; Zheng, F. Precise orbit determination of BeiDou constellation based on BETS and MGEX network. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.S. GPS satellite and receiver instrumental biases estimation using least squares method for accurate ionosphere modelling. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 116, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Su, X.; Li, X. Precise point positioning with the BeiDou navigation satellite system. Sensors 2014, 14, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P. Differential Code Bias Estimation using Multi-GNSS Observations and Global Ionosphere Maps. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2014, 61, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, S.; Steigenberger, P. Determination and use of GPS differential code bias values. In Proceedings of the IGS Workshop, Darmstadt, Germany, 8–12 May 2006; pp. 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Schaer, S. Overview of GNSS Biases; Workshop on GNSS Biases: Bern, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Liu, J. Analysis of BeiDou satellite measurements with code multipath and geometry-free ionosphere-free combinations. Sensors 2016, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F. Theory and Methodology of Quality Control and Quality Analysis for GPS Precise Point Positioning; Wuhan University Press: Wuhan, China, 2016; pp. 69–87. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Witchayangkoon, B. Elements of GPS Precise Point Positioning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X. Improving Ambiguity Convergence in Carrier Phase-based Precise Point Positioning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada, 2002. Available online: https://www.ucalgary.ca/engo_webdocs/YG/02.20170.XiaobingShen.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2002).
- Liu, P.; Qin, H.; Cong, L. The Feasible Combining Observation Models and Equivalence in Dual-Frequency Precise Point Positioning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38618–38629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizos, C.; Montenbruck, O.; Weber, R.; Weber, G.; Hugentobler, U. The IGS MGEX experiment as a milestone for a comprehensive multi-GNSS service. In Proceedings of the ION 2013 Pacific PNT Meeting, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–25 April 2013; pp. 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, S.; Bisnath, S.; Rizos, C. Uncovering common misconceptions in GNSS Precise Point Positioning and its future prospect. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Model | System | Observations | Parameters | Parameter Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UC3 | Single | 6n | 4n+5+1 | X, Y, Z, , , IFB, n*(I,,,) |
| Multi | 6n | 4n+5+m+1 | X, Y, Z, , , ISB, m*IFB, n*(I,,,) | |
| CIF3 | Single | 2n | n+5 | X, Y, Z, , , n*N |
| Multi | 2n | n+5+1 | X, Y, Z, , , ISB, n*N | |
| UC2 | Single | 4n | 3n+5 | X, Y, Z, , , n*(I,,) |
| Multi | 4n | 3n+5+1 | X, Y, Z, , , ISB, n*(I,,) | |
| CIF2 | Single | 2n | n+5 | X, Y, Z, , , n*N |
| Multi | 2n | n+5+1 | X, Y, Z, , , ISB, n*N |
| Model | System | Signal Combination | (Cycle) | Noise (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIF2 | GPS | , | 2.5457 | −1.5457 | 0 | 297.8 | 0.8934 |
| , | 2.5457 | −1.5457 | 0 | 2.978 | 0.0089 | ||
| BDS | , | 2.4872 | −1.4872 | 0 | 289.8 | 0.8694 | |
| , | 2.4872 | −1.4872 | 0 | 2.898 | 0.0087 | ||
| CIF3 | GPS | , , | 2.3269 | −0.3596 | −0.9673 | 254.5 | 0.7635 |
| , , | 2.3269 | −0.3596 | −0.9673 | 2.545 | 0.0076 | ||
| BDS | , , | 2.5664 | −1.2289 | −0.3375 | 286.5 | 0.8596 | |
| , , | 2.5664 | −1.2289 | −0.3375 | 2.865 | 0.0086 |
| Error Corrections | Setting |
|---|---|
| DCB | Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) |
| Cycle slip | Melbourne-Wubbena detecting (M-W) and Ionosphere Residuals |
| Clock slip | Guo [33] |
| Observation weighting | Witchayangkoon [34] and Helmert |
| Earth rotation | Sagnac effect |
| Relativistic effects | Xu and Xu [23] |
| Troposphere | Random walk + Hopfield + Global Mapping Function (GMF) |
| Antenna phase center | Antenna Phase Center Offsets (PCO)+Antenna Phase Center Variations (PCV) |
| Phase windup | Corrected |
| Earth tides correction | Solid/Pole tide |
| Parameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Rinex file | xxxx1000.18o |
| Precise orbit product | gbm19962.sp3 |
| Precise clock product | gbm19962.clk |
| Pole shift/ut1-utc | gbm19962.erp |
| Antenna phase center | igs14.atx |
| Positioning mode | static |
| Estimation algorithm | Standard Kalman Filter |
| Reference coordinate | gbm19962.clk |
| Sample rate | 30 s |
| Elevation cutoff angle |
| Model | CEDU | DARW | JFNG | KARR | KZN2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | E | U | N | E | U | N | E | U | N | E | U | N | E | U | |
| UC3-C | 16 | 23 | 108 | 14 | 47 | 84 | 27 | 34 | 45 | 15 | 64 | 35 | 24 | 19 | 35 |
| CIF3-C | 15 | 19 | 97 | 17 | 50 | 81 | 26 | 34 | 42 | 16 | 70 | 33 | 13 | 24 | 37 |
| ECIF2-C | 17 | 20 | 110 | 5 | 38 | 107 | 30 | 29 | 43 | 6 | 58 | 52 | 14 | 19 | 48 |
| CIF2-C | 18 | 29 | 131 | 8 | 36 | 115 | 21 | 22 | 31 | 4 | 55 | 73 | 11 | 25 | 45 |
| UC3-BDS | 33 | 18 | 108 | 18 | 29 | 164 | 13 | 55 | 165 | 23 | 29 | 64 | 29 | 53 | 147 |
| CIF3-BDS | 33 | 17 | 119 | 21 | 33 | 162 | 11 | 48 | 115 | 23 | 28 | 74 | 26 | 56 | 151 |
| CIF2-BDS | 33 | 17 | 119 | 19 | 34 | 159 | 11 | 48 | 115 | 23 | 28 | 74 | 25 | 56 | 149 |
| CIF2-GPS | 18 | 33 | 139 | 8 | 41 | 136 | 20 | 18 | 24 | 4 | 54 | 84 | 11 | 24 | 49 |
| Model | CEDU | DARW | JFNG | KARR | KZN2 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | E | U | N | E | U | N | E | U | N | E | U | N | E | U | |
| UC3-C | 9 | 10 | 18 | 4 | 12 | 27 | 6 | 9 | 22 | 8 | 22 | 20 | 64 | 13 | 31 |
| CIF3-C | 8 | 10 | 20 | 6 | 13 | 33 | 6 | 10 | 18 | 10 | 27 | 18 | 5 | 9 | 29 |
| ECIF2-C | 6 | 8 | 24 | 4 | 16 | 26 | 12 | 15 | 31 | 5 | 17 | 27 | 7 | 16 | 37 |
| CIF2-C | 5 | 9 | 36 | 3 | 9 | 23 | 8 | 7 | 20 | 4 | 10 | 33 | 7 | 8 | 34 |
| UC3-BDS | 13 | 17 | 22 | 10 | 17 | 34 | 6 | 12 | 60 | 15 | 11 | 21 | 9 | 20 | 9 |
| CIF3-BDS | 13 | 17 | 23 | 11 | 18 | 38 | 6 | 7 | 47 | 15 | 10 | 24 | 9 | 19 | 11 |
| CIF2-BDS | 13 | 17 | 23 | 10 | 18 | 37 | 6 | 7 | 46 | 15 | 10 | 24 | 9 | 20 | 11 |
| CIF2-GPS | 5 | 10 | 37 | 3 | 9 | 26 | 7 | 6 | 19 | 3 | 9 | 37 | 8 | 7 | 30 |
| Model | Accuracy (N,E,U) (mm) | Precision (N,E,U) (mm) | Mean CT (s) | Median CT (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UC3-C | (19, 38, 61) | (7, 13, 24) | 46.6 | 40 |
| CIF3-C | (18, 39, 58) | (7, 14, 23) | 54 | 55 |
| ECIF2-C | (15, 33, 72) | (7, 14, 29) | 58.9 | 55.5 |
| CIF2-C | (12, 33, 79) | (5, 8, 29) | 22.8 | 13.5 |
| UC3-BDS | (23, 37, 130) | (11, 15, 29) | 163.8 | 179.25 |
| CIF3-BDS | (23, 37, 124) | (10, 14, 28) | 190 | 196 |
| CIF2-BDS | (22, 37, 123) | (22, 37, 123) | 191 | 197.5 |
| CIF2-GPS | (12, 34, 86) | (5, 8, 30) | 16.4 | 15 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Qin, H.; Cong, L. The Unified Form of Code Biases and Positioning Performance Analysis in Global Positioning System (GPS)/BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) Precise Point Positioning Using Real Triple-Frequency Data. Sensors 2019, 19, 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112469
Liu P, Qin H, Cong L. The Unified Form of Code Biases and Positioning Performance Analysis in Global Positioning System (GPS)/BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) Precise Point Positioning Using Real Triple-Frequency Data. Sensors. 2019; 19(11):2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112469
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Peng, Honglei Qin, and Li Cong. 2019. "The Unified Form of Code Biases and Positioning Performance Analysis in Global Positioning System (GPS)/BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) Precise Point Positioning Using Real Triple-Frequency Data" Sensors 19, no. 11: 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112469
APA StyleLiu, P., Qin, H., & Cong, L. (2019). The Unified Form of Code Biases and Positioning Performance Analysis in Global Positioning System (GPS)/BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) Precise Point Positioning Using Real Triple-Frequency Data. Sensors, 19(11), 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112469





