Strategy for Fault Diagnosis on Train Plug Doors Using Audio Sensors †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. Data Acquisition
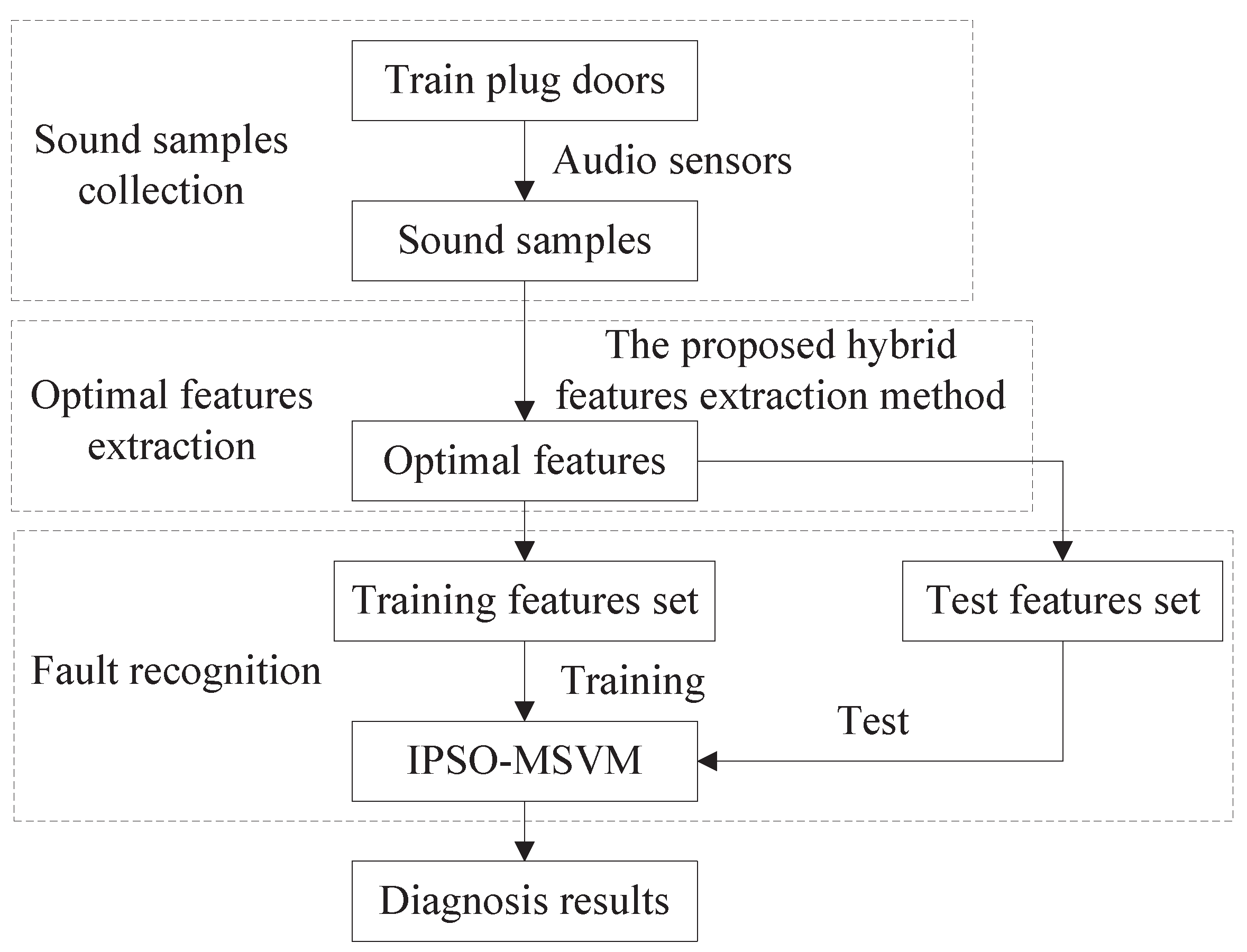
2.2. Intelligent Diagnosis Strategy for Train Plug Doors
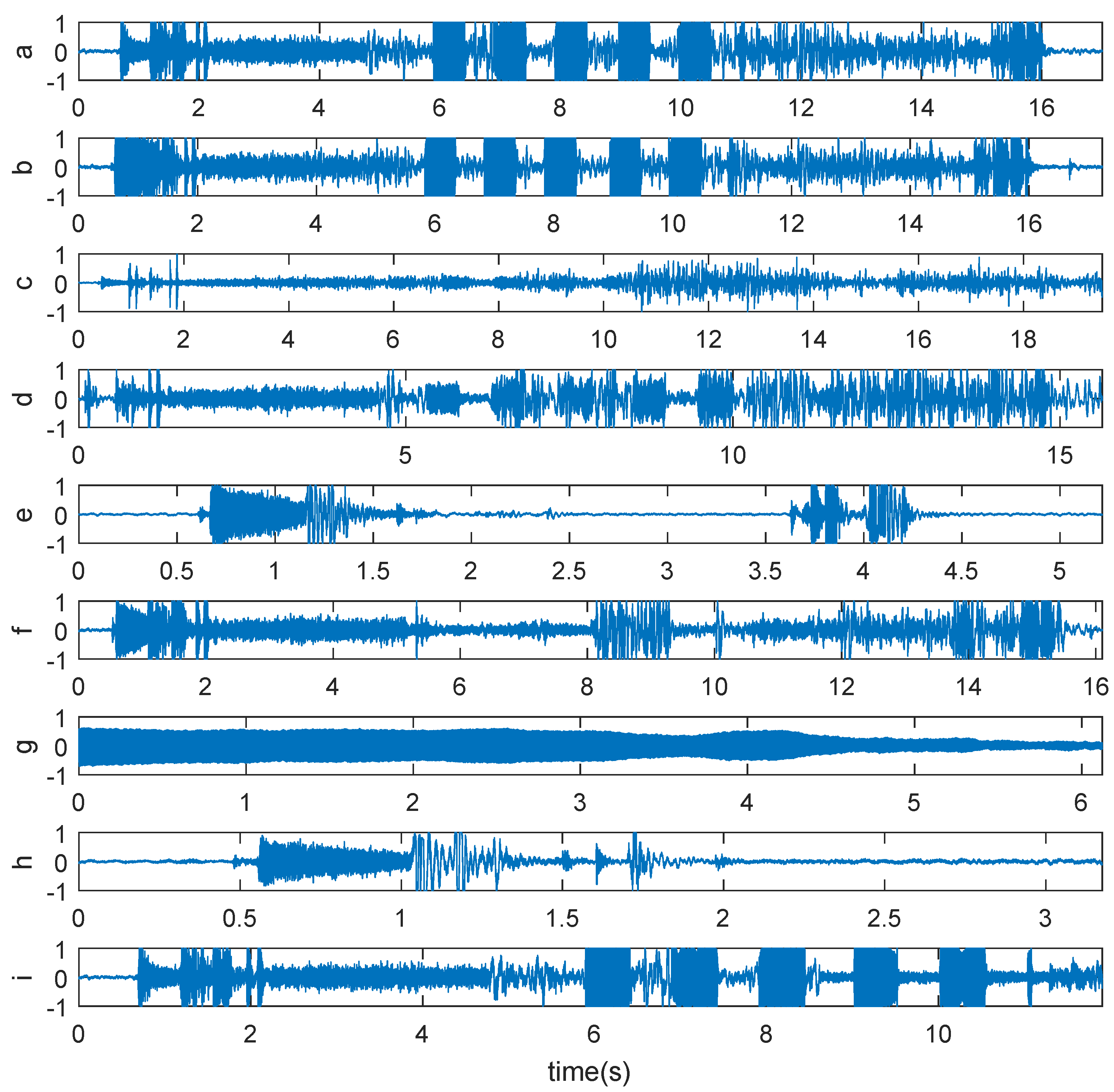
- Step1: Sound samples collectionTo ensure the data reliability and fault identification accuracy, collect sound samples under different working conditions using high-precision audio sensor.
- Step2: Optimal features extractionSelect proper parameters for the proposed hybrid features extraction method. Then, obtain the optimal features using the hybrid method.
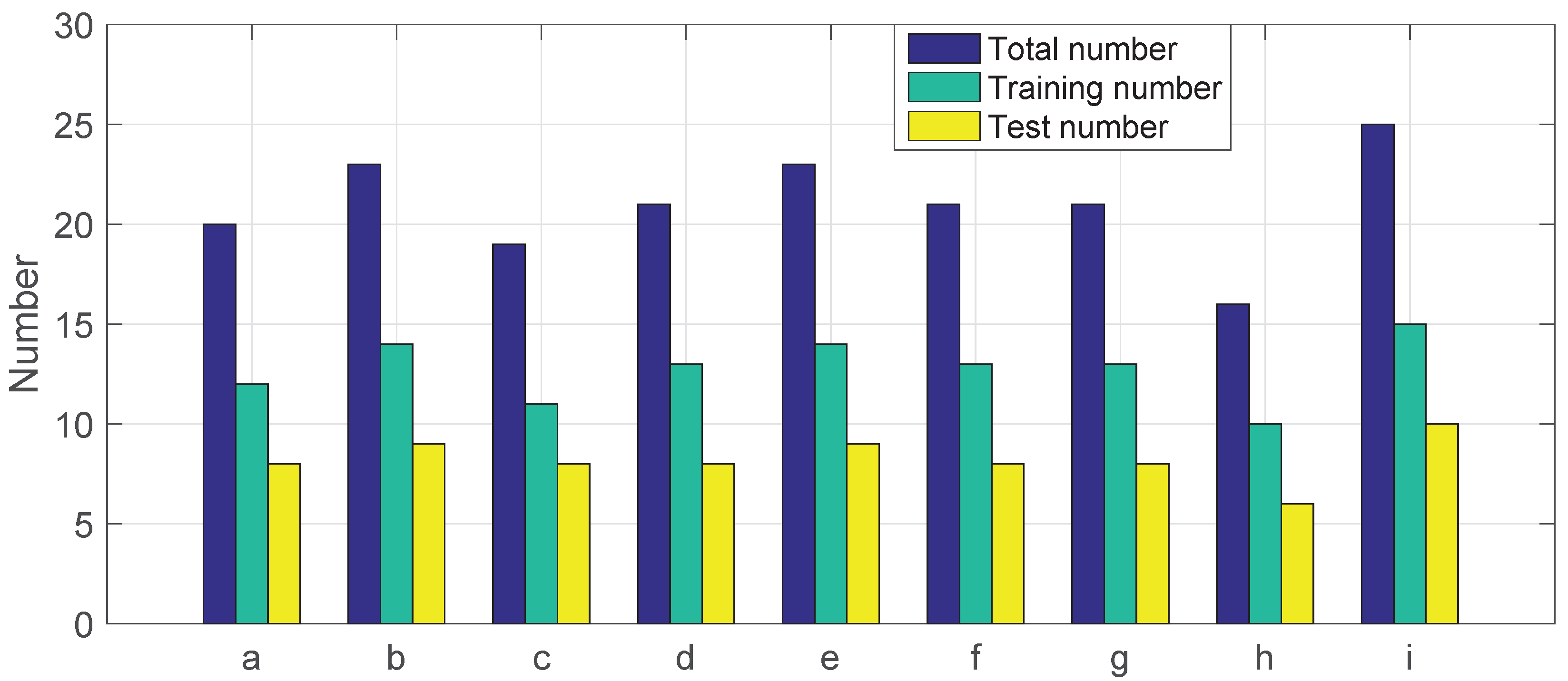
- Step3: Fault recognition using IPSO-MSVMDivide the extracted features into training set and test set by split ratio of 6:4. The training set is used to train the classifier, whereas the test set is used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed diagnosis method.
3. Features Extraction Methods for Sound Signals
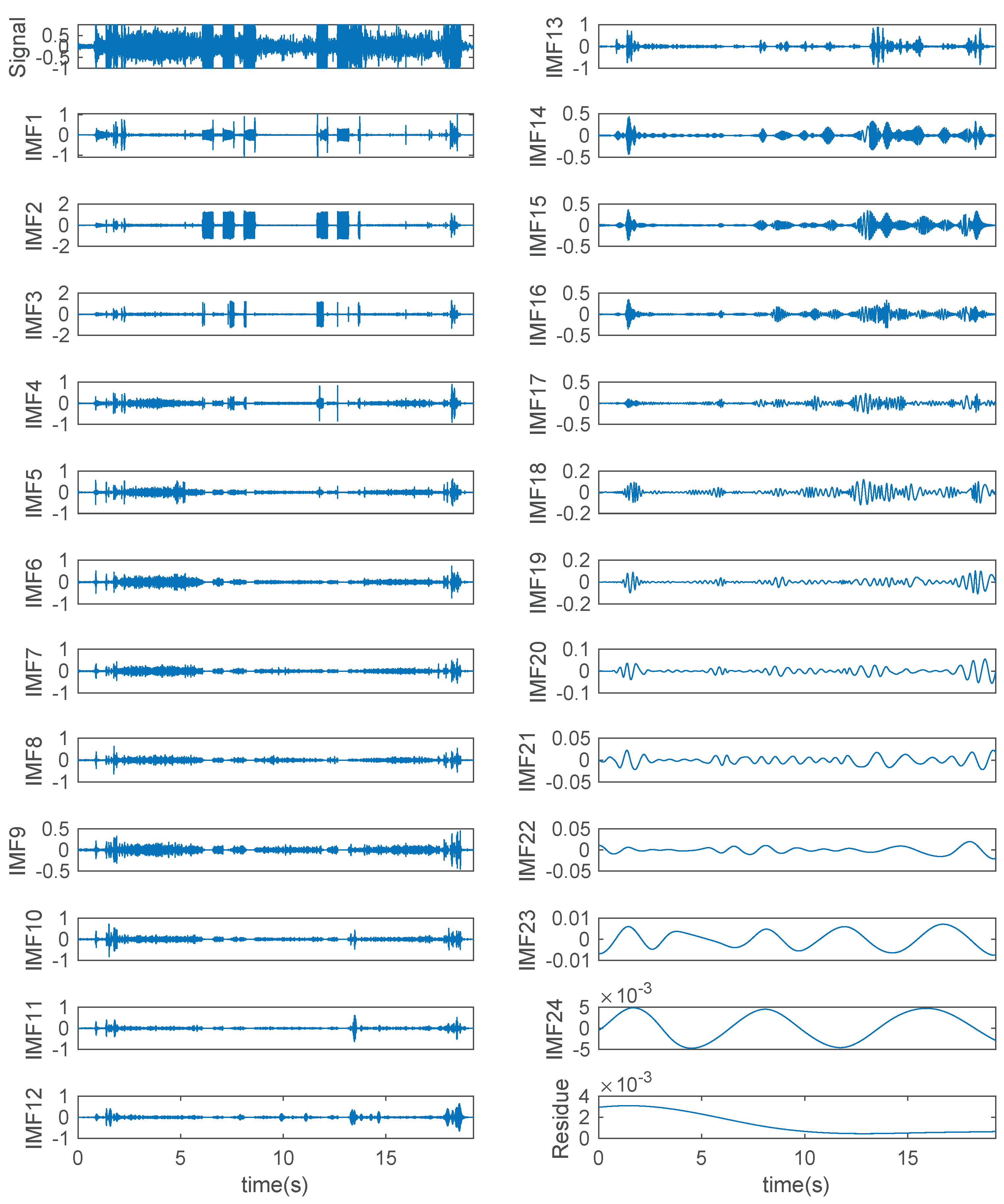
3.1. Empirical Mode Decomposition
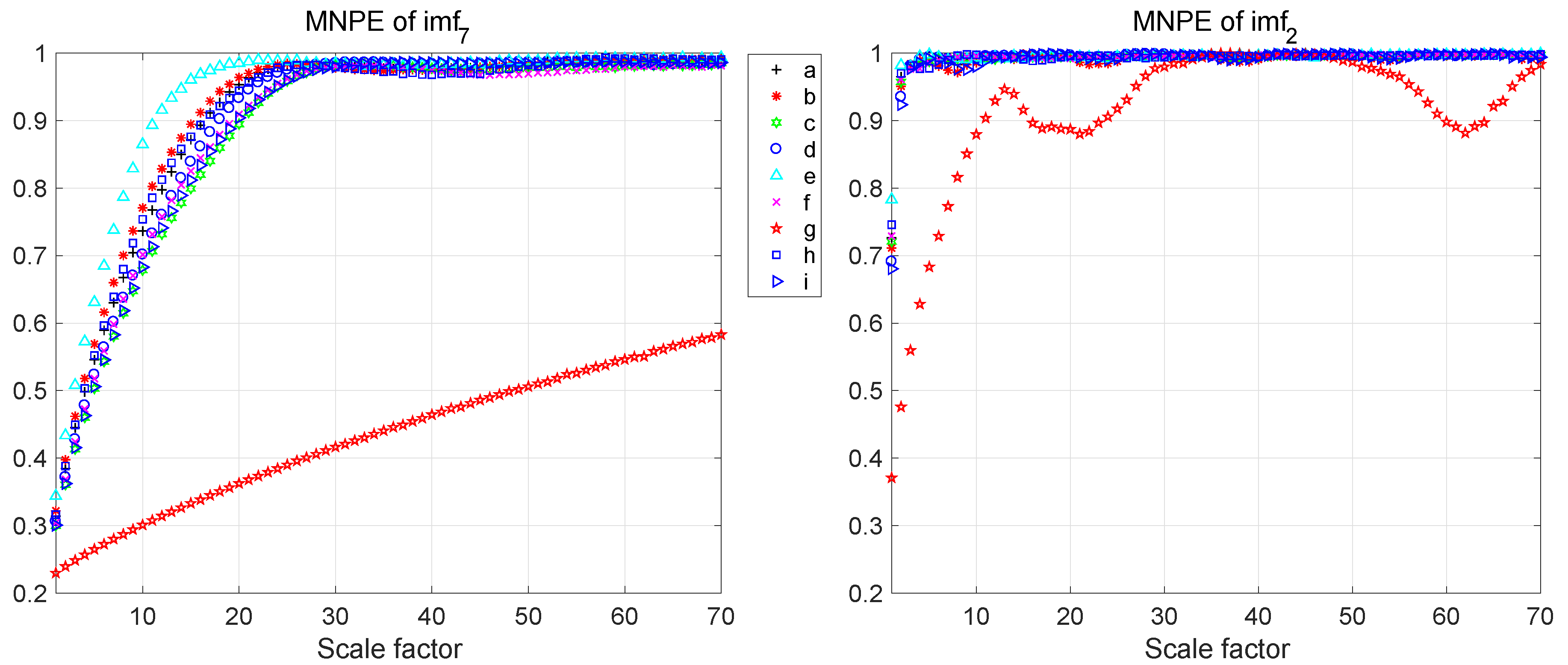
3.2. Multi-Scale Normalized Permutation Entropy
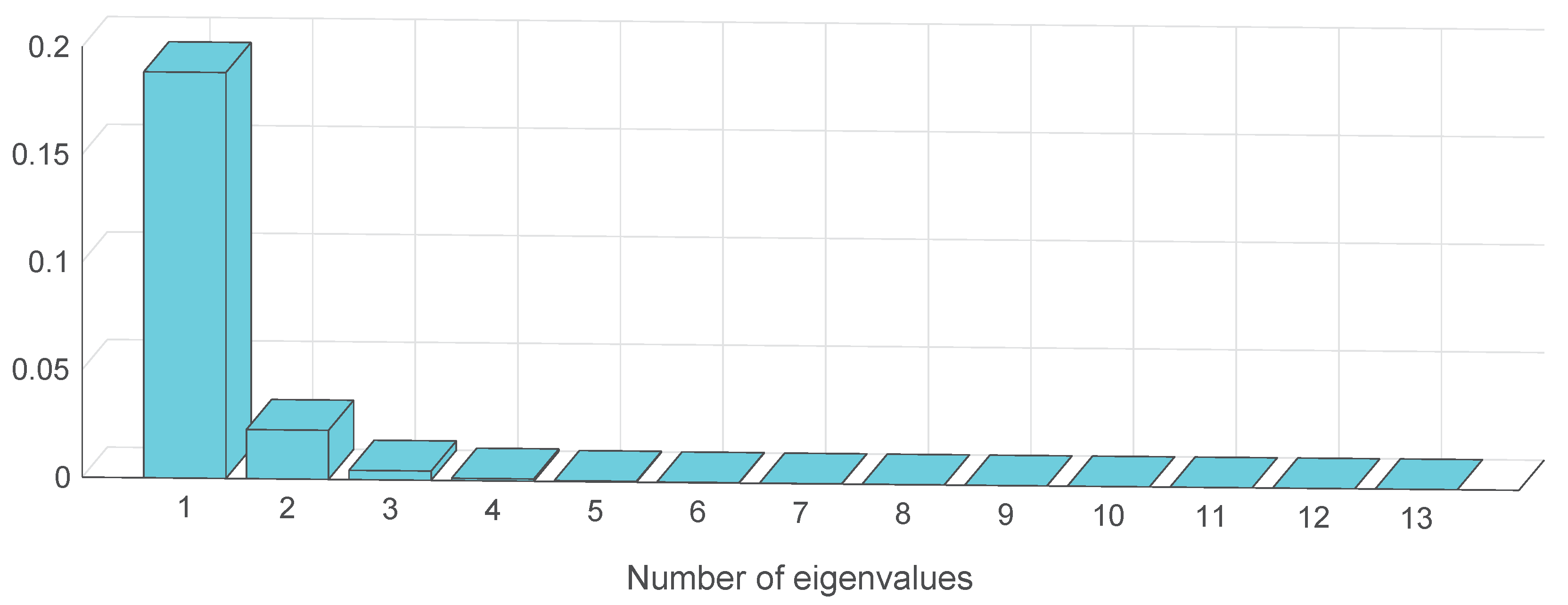
3.3. The Hybrid Feature Extraction Method
4. Multi-Class SVM Based on Improved PSO
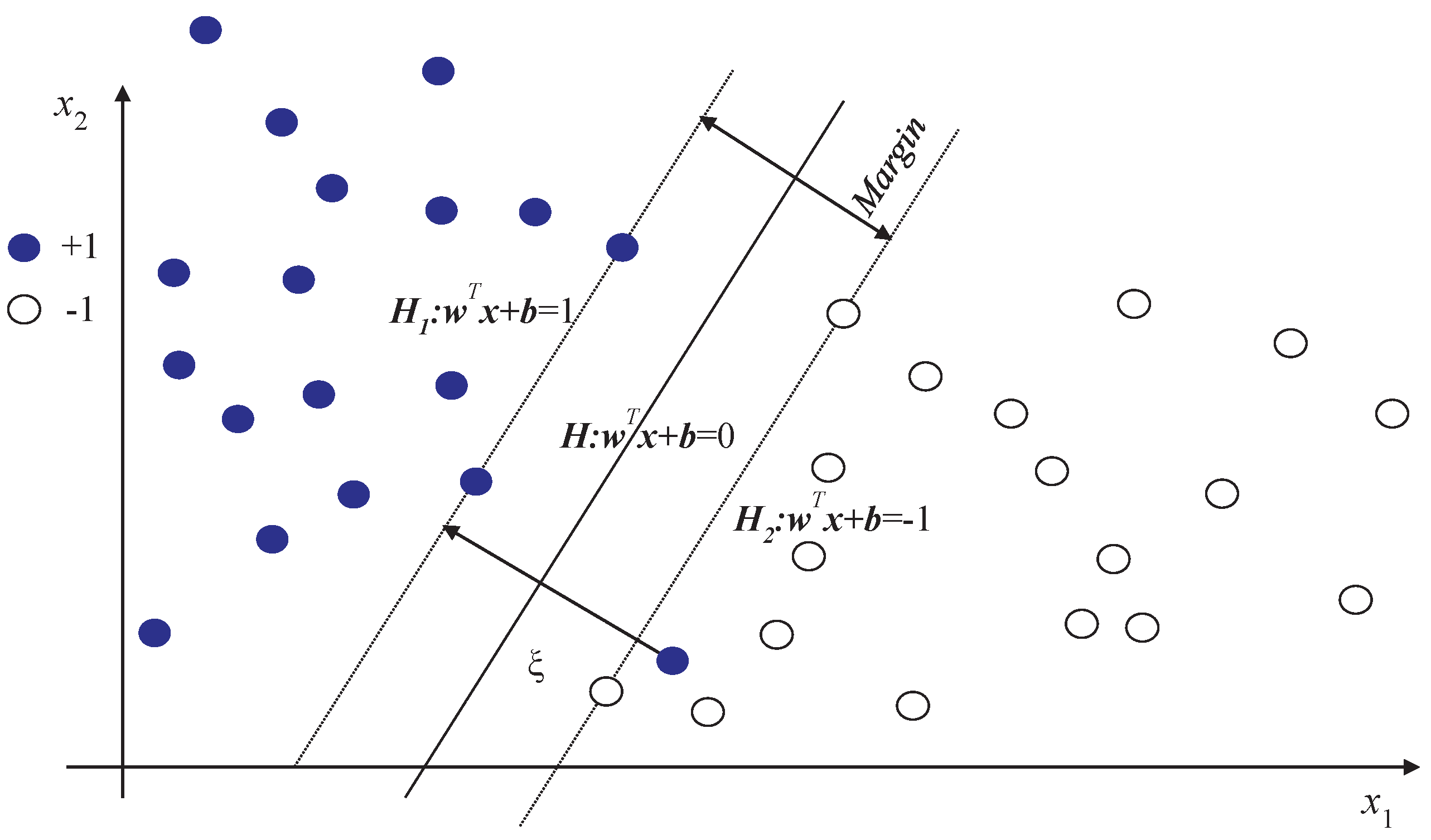
4.1. Multi-Class SVM
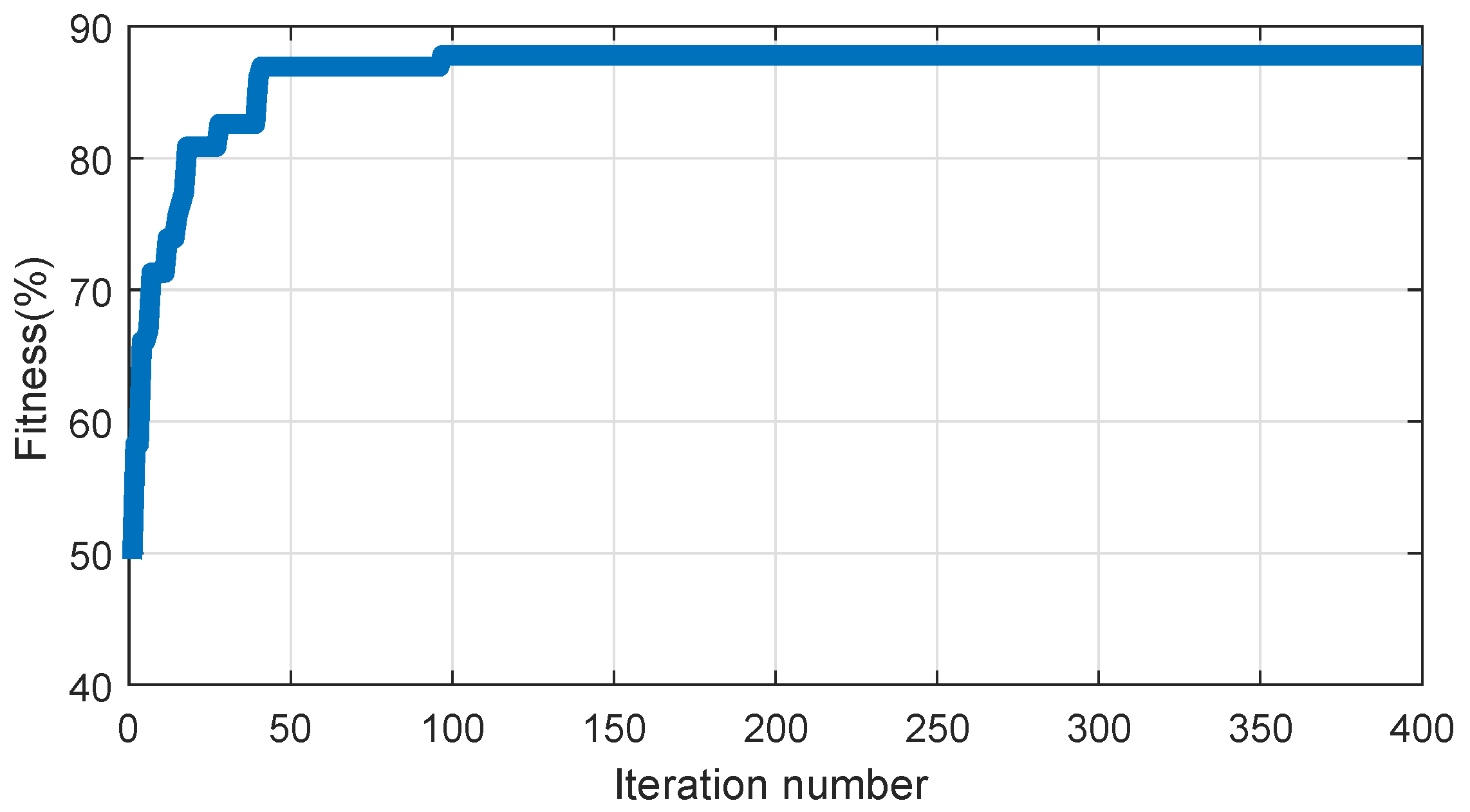
4.2. Improved PSO
4.3. Multi-Class SVM Optimized via IPSO
5. Results and Discussions
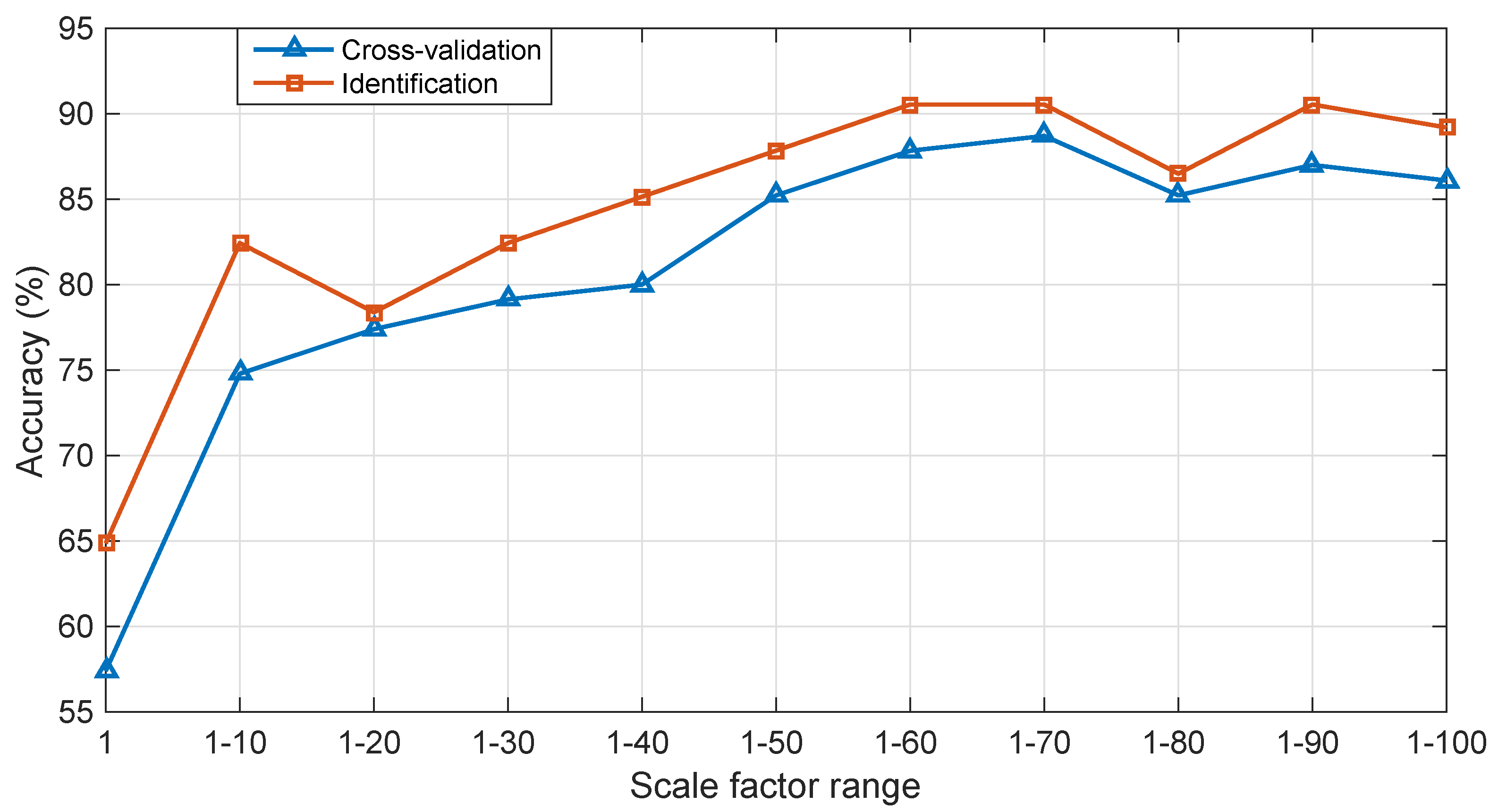
5.1. The Selection of Optimal Scale Factor Range
5.2. Diagnosis Results Comparison among BP Neural Network, 1NN, PSO-MSVM, and IPSO-MSVM Classifiers
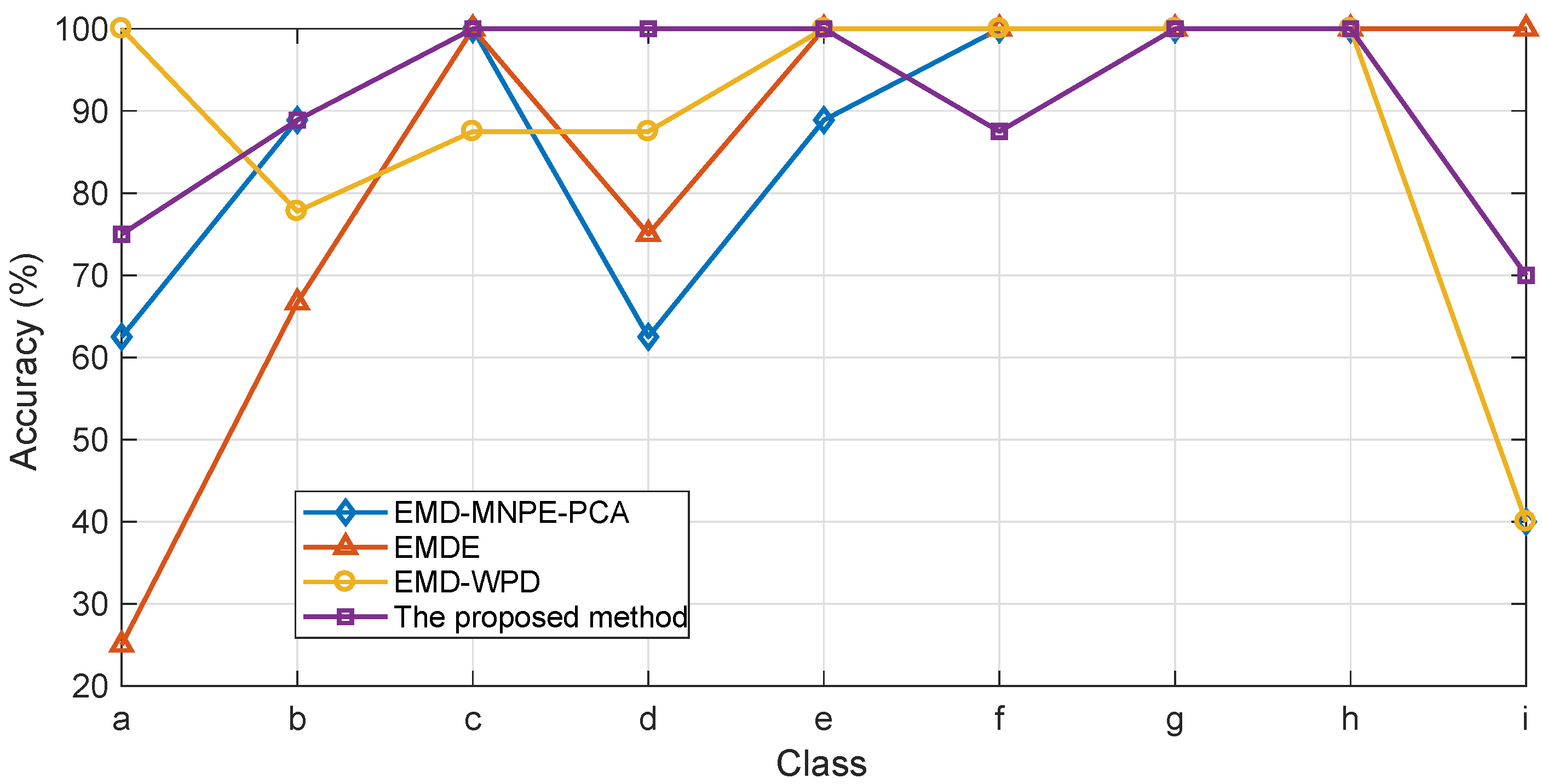
5.3. Diagnosis Results Comparison among Different Feature Extraction Methods
5.4. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MNPE | Multi-scale normalized permutation entropy |
| IPSO | Improved particle swarm optimization |
| MSVM | Multi-class support vector machine |
| EMD | Empirical mode decomposition |
| IMF | Intrinsic mode functions |
| TBM | Time based maintenance |
| FTA | Fault tree analysis |
| FEMA | Failure mode and effects analysis |
| WPD | Wavelet package decomposition |
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| BP | Backpropagation |
| CRH5A | China railway CRH5 size A |
| PCA | Principle component analysis |
| EMDE | Empirical mode decomposition entropy |
References
- Huang, N.T.; Chen, H.J.; Cai, G.W.; Fang, L.H.; Wang, Y.Q. Mechanical fault diagnosis of high voltage circuit breakers based on variational mode decomposition and multi-layer classifier. Sensors 2016, 16, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Song, Y.D.; Liu, W.; Qin, M. Monitoring of wind turbines: A bio-inspired fault tolerant approach. Meas. Control 2011, 44, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrall, S.; Agamennoni, G.; Ward, J.; Nebot, E. Fault detection for vehicular Ad-Hoc wireless networks. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2014, 6, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.Z. Parallel processing algorithm for railway signal fault diagnosis data based on cloud computing. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 88, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, L.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Application of fuzzy predictive control technology in automatic train operation. Cluster Comput. 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, W.G.; Ma, L.C. Local fractional functional method for solving diffusion equations on cantor sets. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Xing, Z.Y.; Wang, X.H. Fault diagnosis research for metro door based on FTA. Modul. Mach. Tool Autom. Manuf. Tech. 2014, 4, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.H.; Hua, P.; Fu, Z.L.; Gao, F. Case study on FMECA and risk assessment for the door system in high speed train. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 655, 2335–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.C.; Tian, L.; Wang, L. Bayesian diagnostic network model for sliding plug door. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 219, 1496–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Q.; Xu, Q.J.; Xu, Y.X. Study of remote monitoring system of working states of metro door system. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Harbin, China, 7–10 August 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Jia, L.M.; Qin, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, Y.H. Research on urban rail train passenger door system fault diagnosis using PCA and rough set. Open. Mech. Eng. J. 2014, 8, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.X.; Jia, L.M.; Qin, Y.; Cheng, X.Q. Rail train door system hidden danger identification based on extended time and probability Petri net. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies for Rail Transportation, Zhuzhou, China, 28–30 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cauffriez, L.; Grondel, S.; Loslever, P.; Aubrun, C. Bond Graph modeling for fault detection and isolation of a train door mechatronic system. Control Eng. Pract. 2016, 49, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, Y.K.; Ma, L.C. A fault diagnosis method for train plug doors via sound signals. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018. Under review. [Google Scholar]
- Mollasalehi, E.; Wood, D.; Sun, Q. Indicative fault diagnosis of wind turbine generator bearings using tower sound and vibration. Energies 2017, 10, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, V.H.; Yoon, J.; He, D. Low speed bearing fault diagnosis using acoustic emission sensors. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 105, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, H.; Park, D.; Chung, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Yoon, S. Fault detection and diagnosis of railway point machines by sound analysis. Sensors 2016, 16, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Francq, P.; Huang, J.F. Incipient fault diagnosis of roller bearing using optimized wavelet transform based multi-speed vibration signatures. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 19442–19456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Y.; He, D. Rotational machine health monitoring and fault detection using EMD-based acoustic emission feature quantification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation entropy: A natural complexity measure for time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlazzo, E.; Mammone, N.; Cianci, V.; Gasparini, S.; Gambardella, A.; Labate, A.; Latella, M.A.; Sofia, V.; Elia, M.; Morabito, F.C.; et al. Permutation entropy of scalp EEG: A tool to investigate epilepsies Suggestions from absence epilepsies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, M.; Kochs, E.F.; Schneider, G.; Jordan, D. Non-stationarity of EEG during wakefulness and anaesthesia: Advantages of EEG permutation entropy monitoring. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2014, 28, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.L.; Song, W.Q.; Taheri, S. Improved LMD, Permutation entropy and optimized K-means to fault diagnosis for roller bearings. Entropy 2016, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Gupta, V.K.; Kankar, P.K. Bearing fault diagnosis based on multi-scale permutation entropy and adaptive neuro fuzzy classifier. J. Vib. Control 2015, 21, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.D.; Wu, L.; Zhao, H.Y. A Reciprocating compressor fault feature extraction method based on LMD and MPE. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Material Engineering and Mechanical Engineering (MEME), Hangzhou, China, 23–25 Octobor 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.X.; Yang, C.L.; Wang, H.C.; Wang, Y.Y. Investigation of ANN and SVM based on limited samples for performance and emissions prediction of a CRDI-assisted marine diesel engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 111, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmahamed, Y.; Teguar, M.; Boubakeur, A. Application of SVM and KNN to duval pentagon 1 for transformer oil diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 3443–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Dargaville, R.; Cao, Y.; Li, D.Y.; Xia, J. Storage aided system property enhancing and hybrid robust smoothing for large-scale PV systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2871–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.W.; Hsieh, C.J.; Chang, K.W.; Ringgaard, M.; Lin, C.J. Training and testing low-degree polynomial data mappings via linear SVM. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 1471–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Borhani, T.N.G.; Bagheri, M.; Manan, Z.A. Molecular modeling of the ideal gas enthalpy of formation of hydrocarbons. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2013, 360, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks (ICNN), Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.L.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, N.H.; Crutchfield, J.P.; Farmer, J.D.; Shaw, R.S. Geometry from a Time Series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Y.; Wang, L.; Yan, R.Q. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on wavelet packet decomposition and multi-scale permutation entropy. Entropy 2015, 17, 6447–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.K.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xu, C. A novel life prediction method for railway safety relays using degradation parameters. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 10, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daengduang, S.; Vateekul, P. Applying One-Versus-One SVMs to classify multi-label data with large labels using spark. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology, Pattaya, Thailand, 1–4 February 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, R.X.; Cao, Y.; Li, D.Y.; Xie, G. Multiobjective sizing optimization for island microgrids using a triangular aggregation model and levy-harmony algorithm. IEEE. Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 3495–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.B.; Huo, H.Y. Improved PSO-based task scheduling algorithm in cloud computing. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2012, 9, 3821–3829. [Google Scholar]
- Rauber, T.W.; Boldt, F.D.A.; Varejao, F.M. Heterogeneous feature models and feature selection applied to bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Wang, K.Y.; Jin, W.D.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.K. Fault feature analysis of high-speed train bogie based on empirical mode decomposition entropy. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2014, 49, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

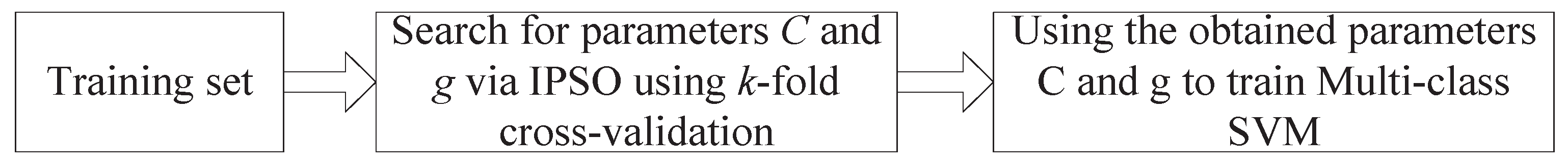

| J | 4.22 | 3.9 | 6.44 | 5.99 | 6.22 | 9.97 | 15.84 | 9.48 | 4.1 | 3.61 | 4.52 | 3.63 | 2.06 |
| Class of | Number of | Number of Correctly Identified Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sound Signals | Test Samples | BP Neural Network | 1NN | PSO-MSVM | IPSO-SVM |
| a | 8 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 6 |
| b | 9 | 5 | 9 | 8 | 8 |
| c | 8 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 8 |
| d | 8 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 |
| e | 9 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 9 |
| f | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 |
| g | 8 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| h | 6 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| i | 10 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 7 |
| Total | 74 | 40 | 58 | 65 | 67 |
| Accuracy (%) | 60.81 | 78.38 | 87.84 | 90.54 | |
| Class of | Number of | Number of Correctly Identified Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sound Signals | Test Samples | EMD-MNPE-PCA | EMDE | EMD-WPD | The Proposed Method |
| a | 8 | 5 | 2 | 8 | 6 |
| b | 9 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| c | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 |
| d | 8 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| e | 9 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| f | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 7 |
| g | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| h | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| i | 10 | 4 | 10 | 4 | 7 |
| Total | 74 | 60 | 63 | 64 | 67 |
| Accuracy (%) | 81.08 | 85.14 | 86.49 | 90.54 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Xie, G.; Cao, Y.; Wen, T. Strategy for Fault Diagnosis on Train Plug Doors Using Audio Sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010003
Sun Y, Xie G, Cao Y, Wen T. Strategy for Fault Diagnosis on Train Plug Doors Using Audio Sensors. Sensors. 2019; 19(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yongkui, Guo Xie, Yuan Cao, and Tao Wen. 2019. "Strategy for Fault Diagnosis on Train Plug Doors Using Audio Sensors" Sensors 19, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010003
APA StyleSun, Y., Xie, G., Cao, Y., & Wen, T. (2019). Strategy for Fault Diagnosis on Train Plug Doors Using Audio Sensors. Sensors, 19(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010003





