Comparative Study of the Dual Layer Magnet Array in a Moving-Coil Tubular Linear PM Motor
Abstract
1. Introduction
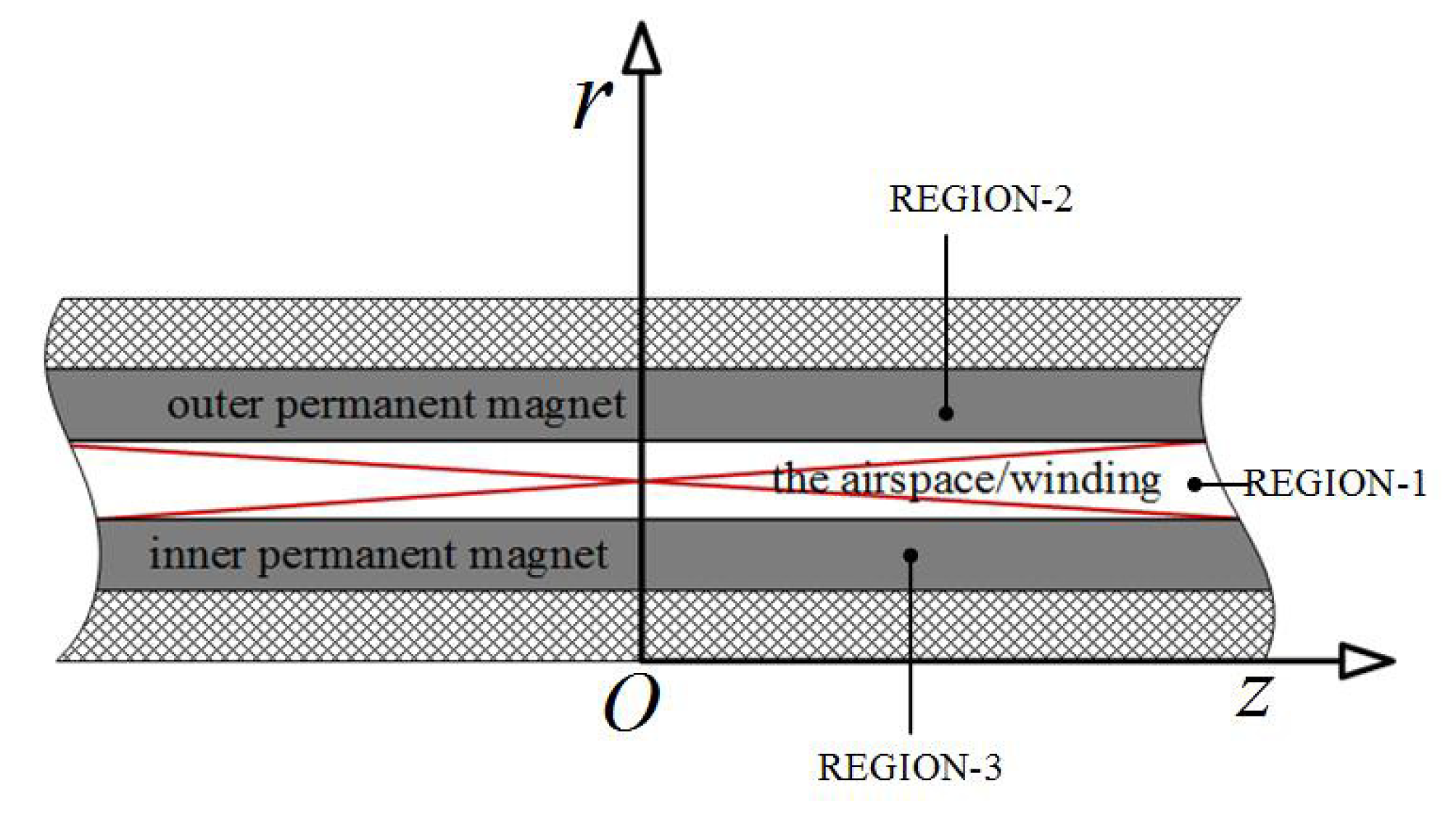
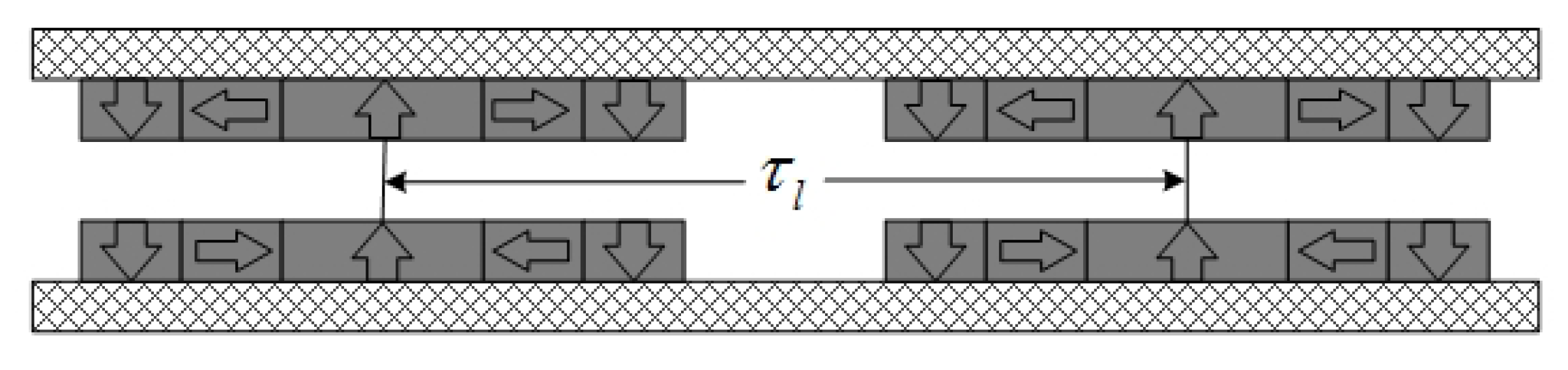
2. Topologies of Magnetic Field Distribution
- (1)
- The axial length of the motor is infinite along the z axis and the motor’s structure is axially symmetric and periodic in the z direction. The edge effects associated with the finite length of the motor will be considered by studying a whole model which includes multiple such length-limited motors with enough long distance between any adjacent two motors for convenient Fourier expansion [29].
- (2)
- The permeability of the iron is infinite, which means saturation is ignored.
- (3)
- The armature is slotless. However, slotting effects, if present, can be taken into account by introducing a Carter coefficient [30].
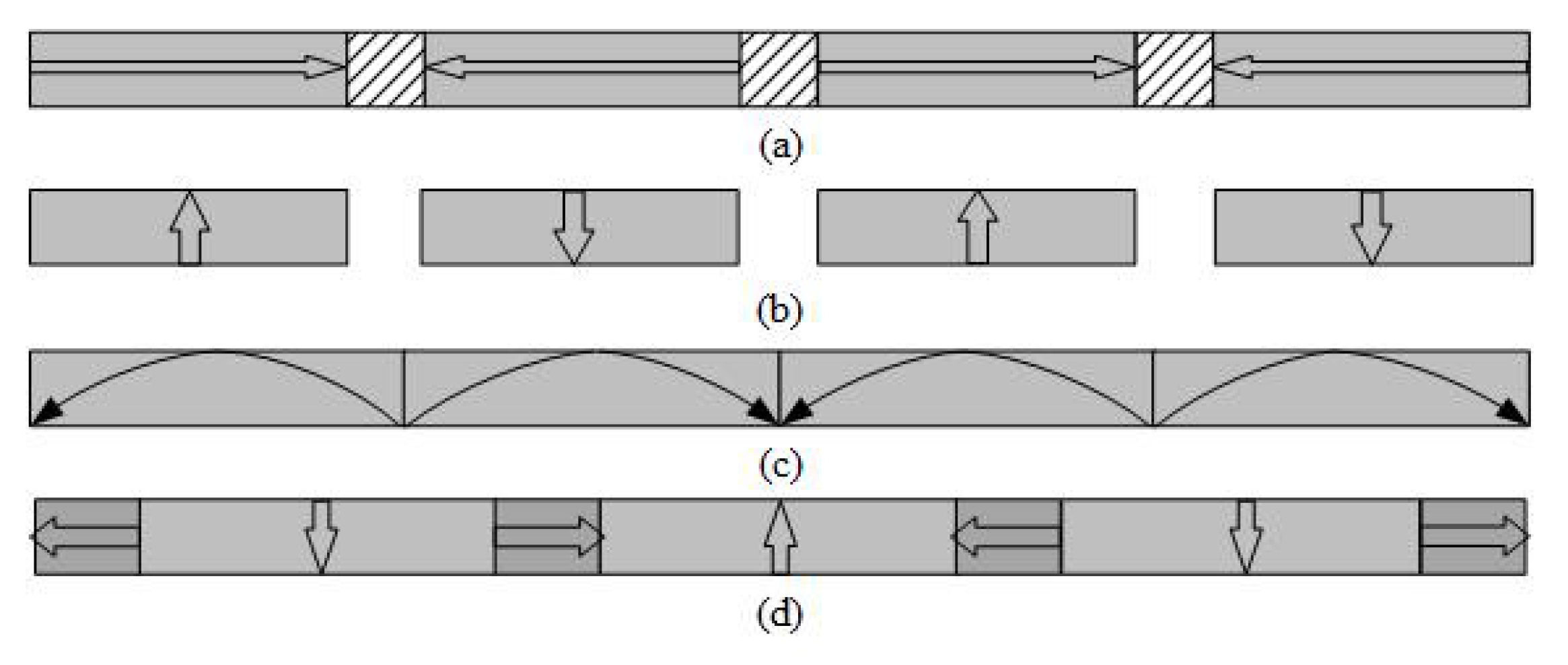
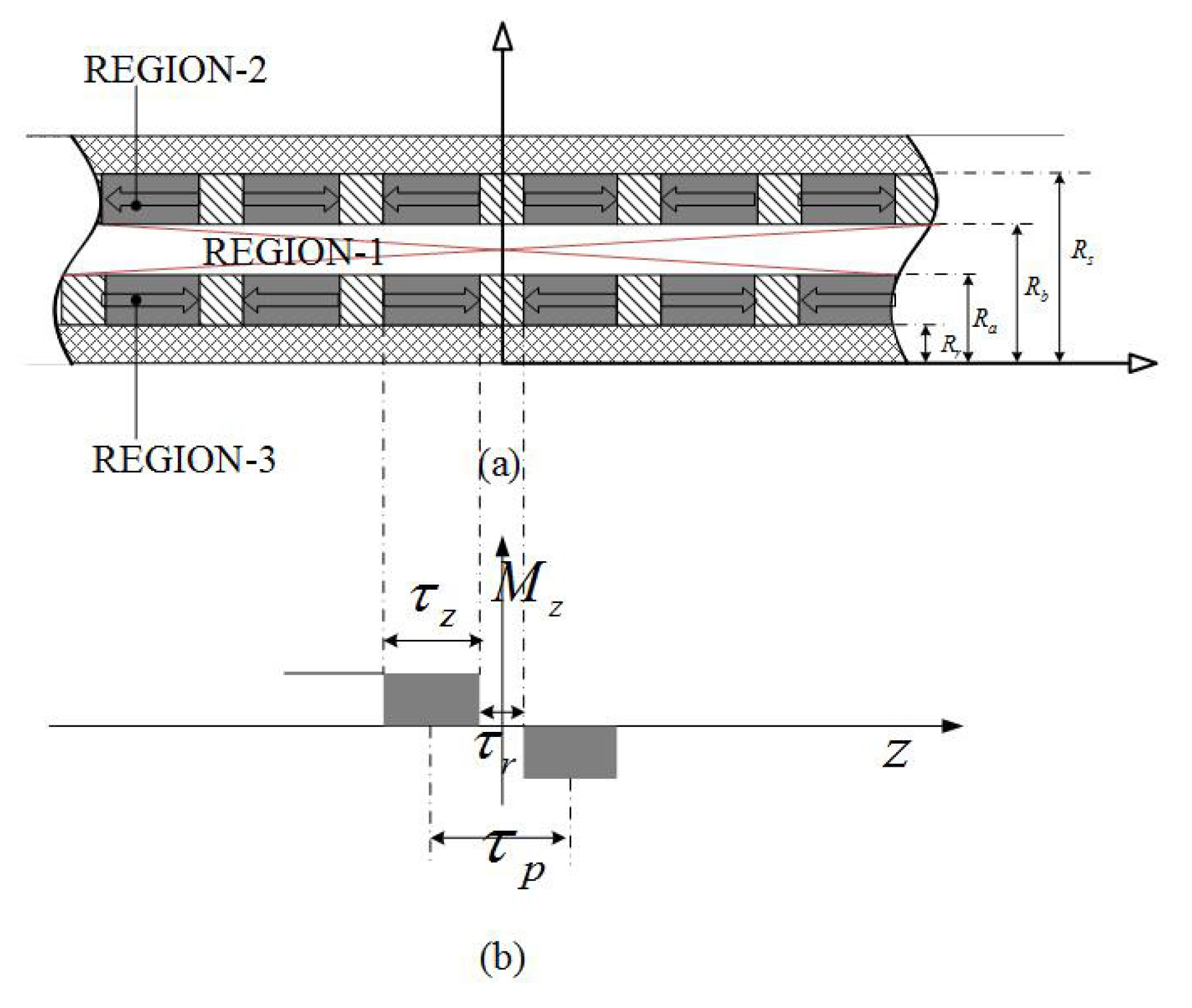
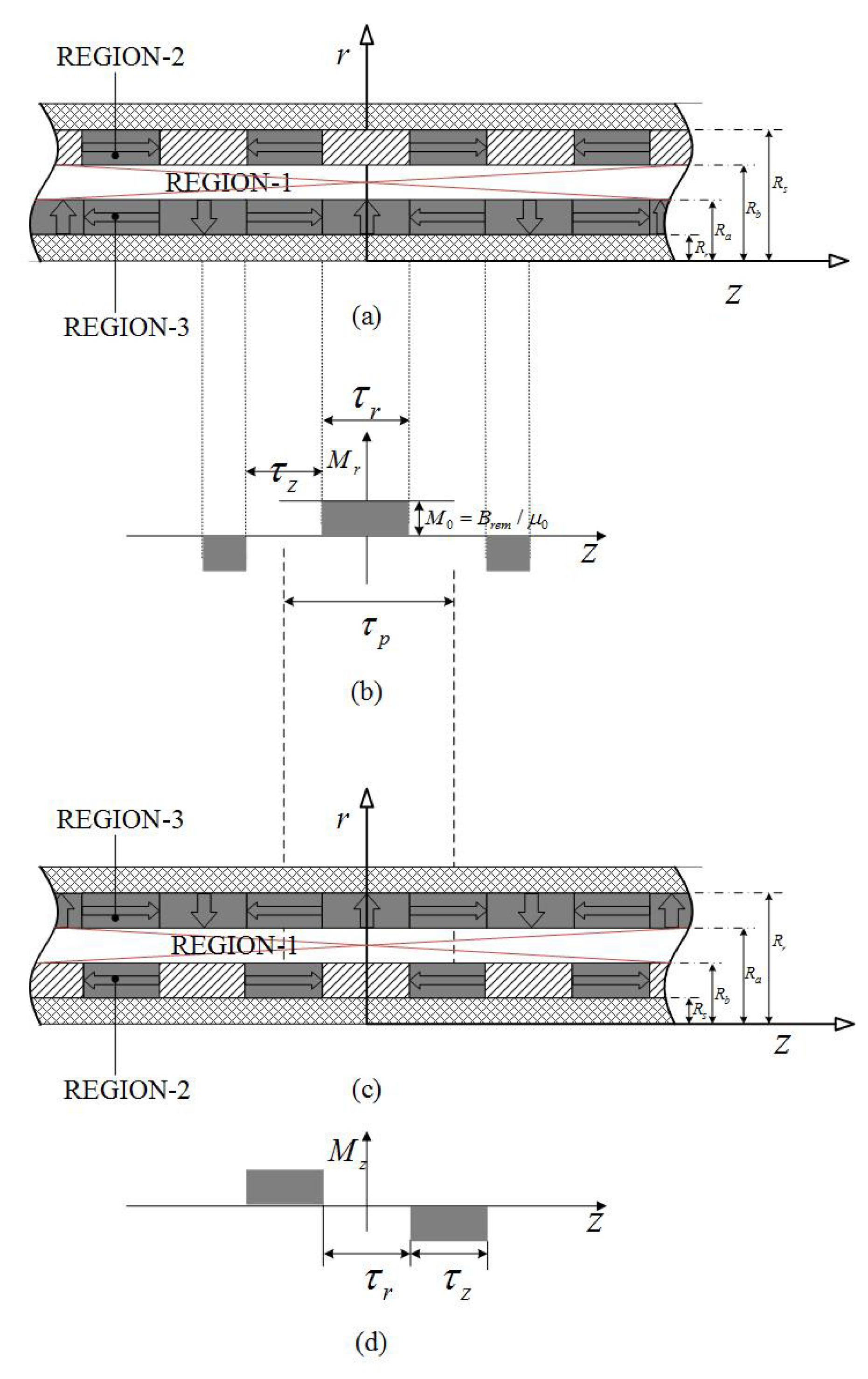
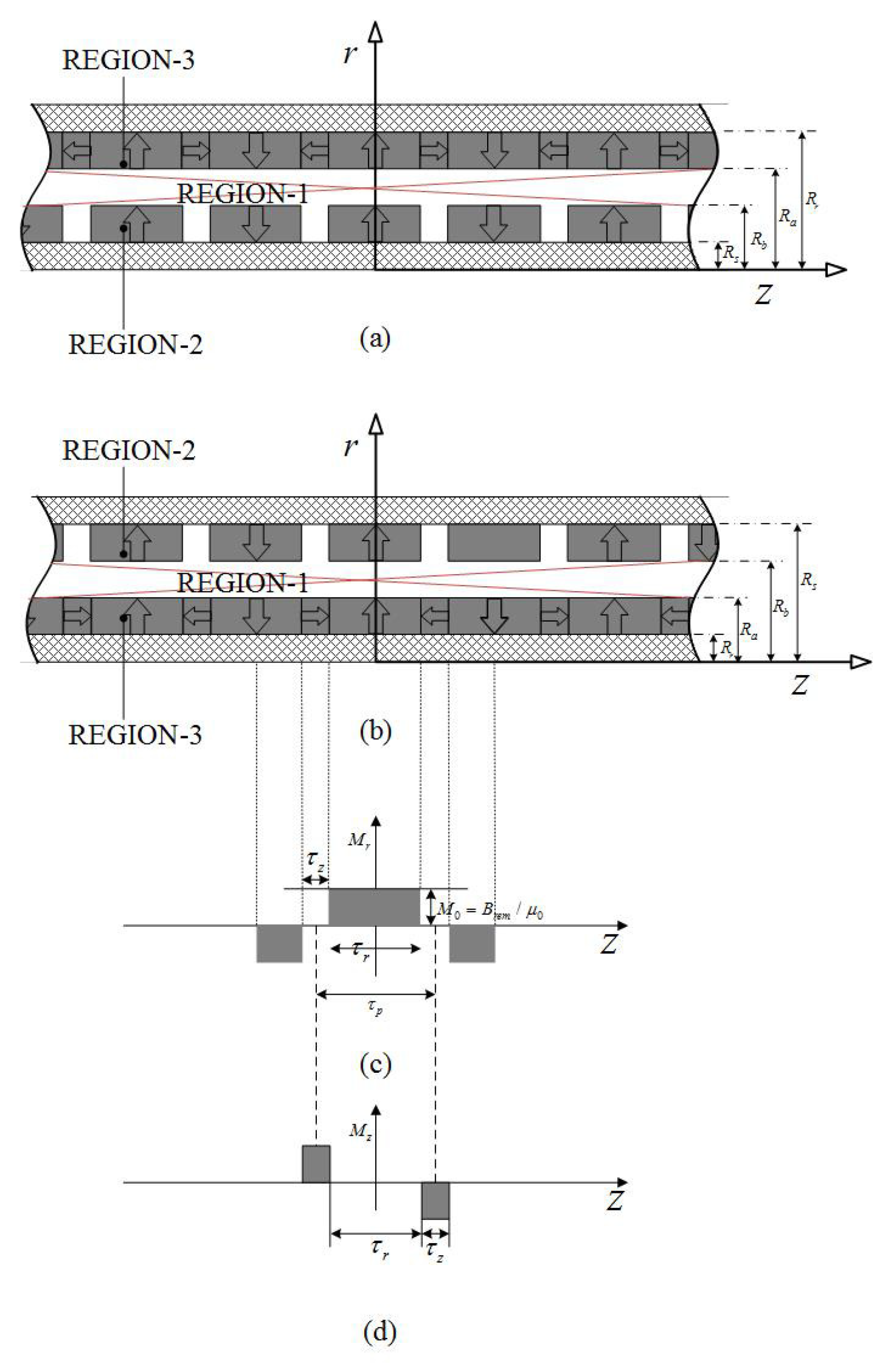
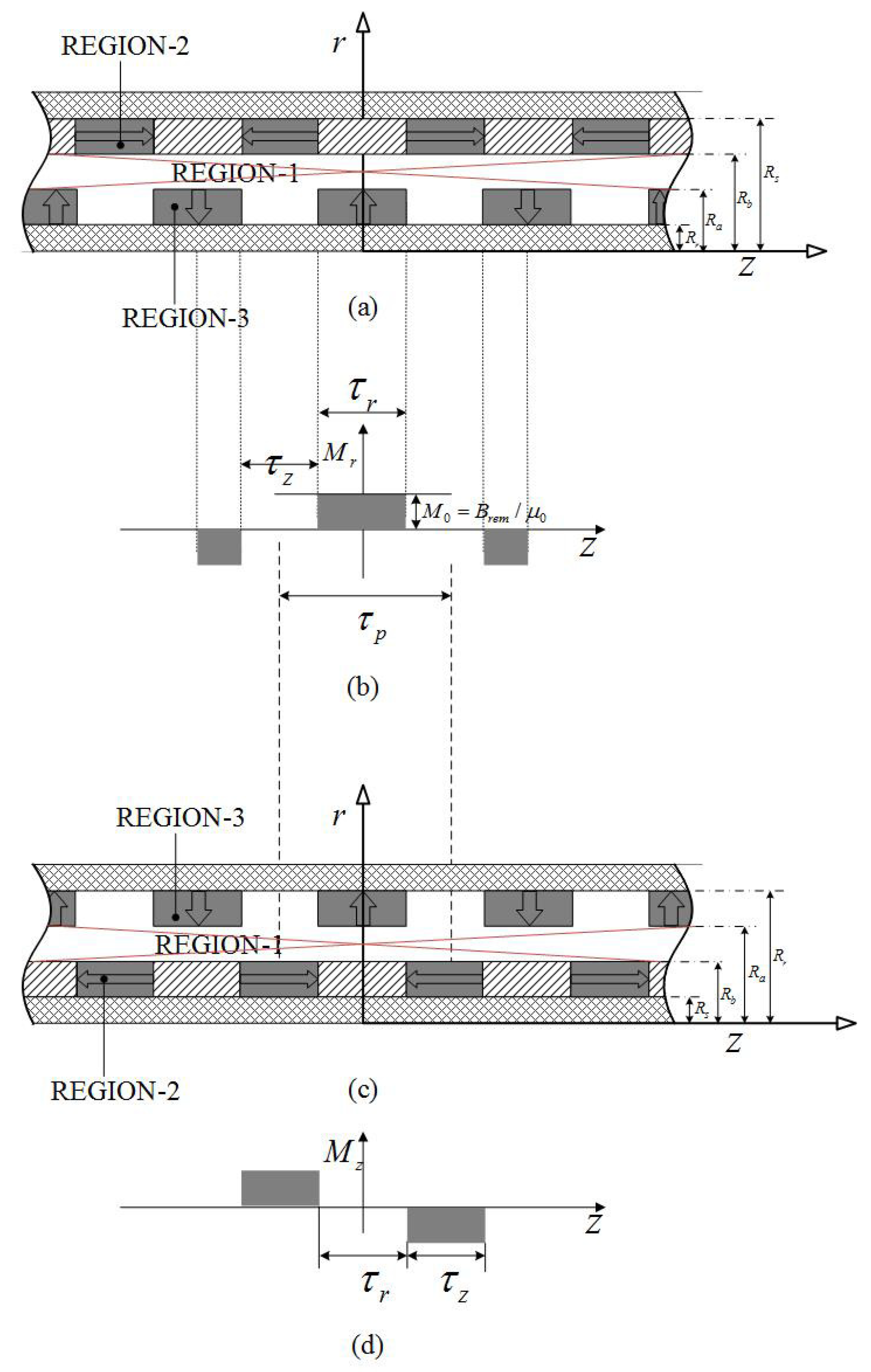
2.1. Dual Layer Halbach Magnetization Topology
2.2. Dual Layer Radial Magnetization Topology
2.3. Dual Layer Axial Magnetization Topology
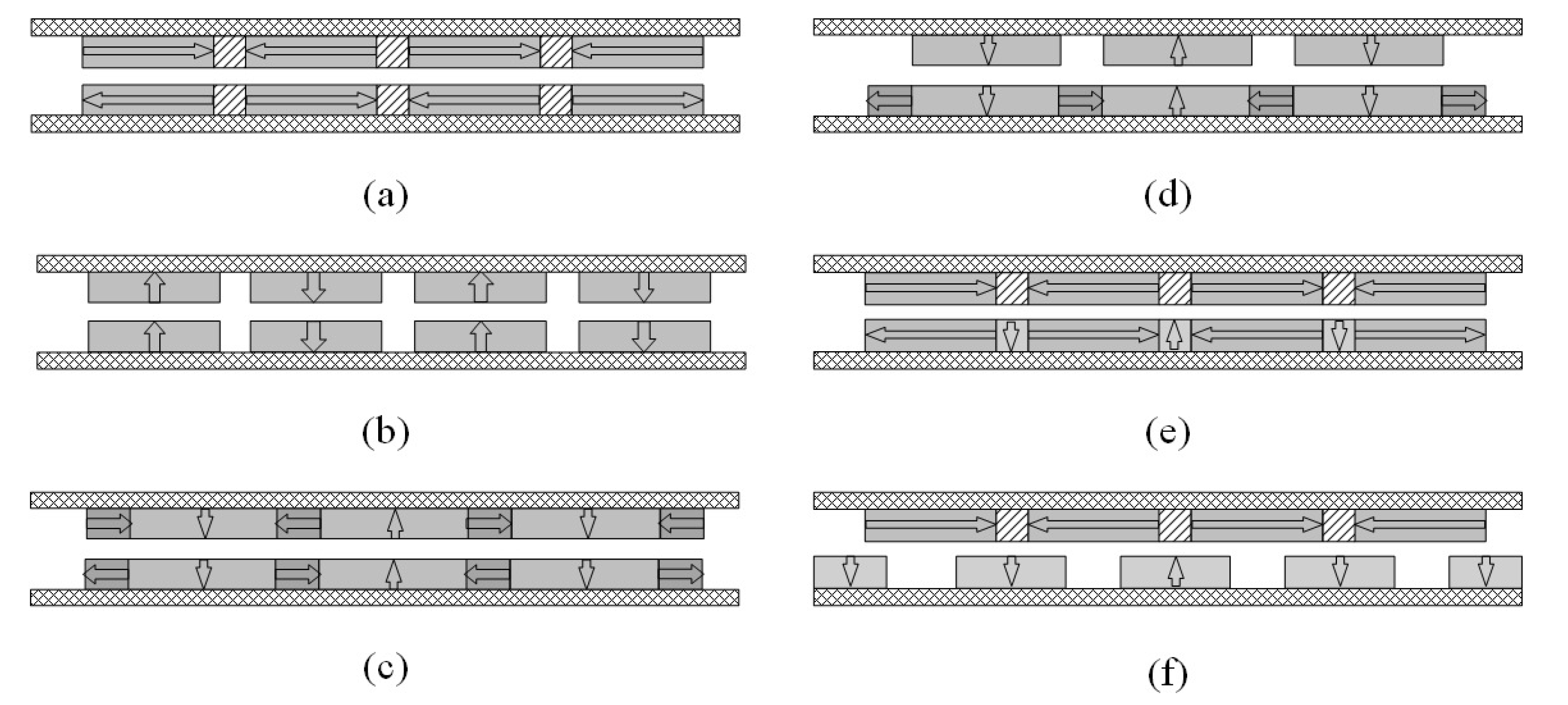
2.4. Axial-Halbach Magnetization Topology
2.5. Radial-Halbach Magnetization
2.6. Axial-Radial Magnetization Topology
3. Numerical Simulation and Experiments
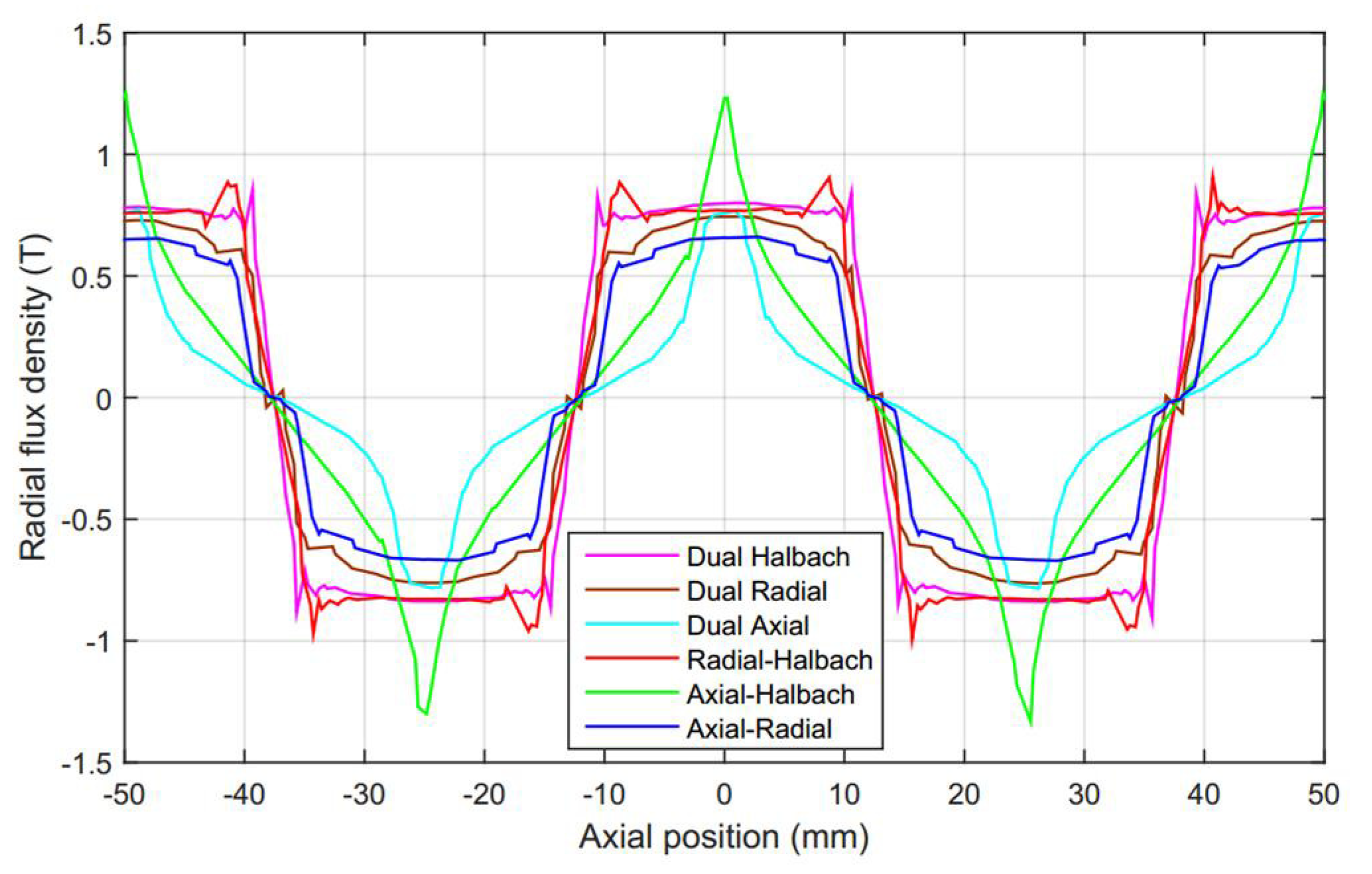
3.1. Magnetic Field Variation of the Topologies
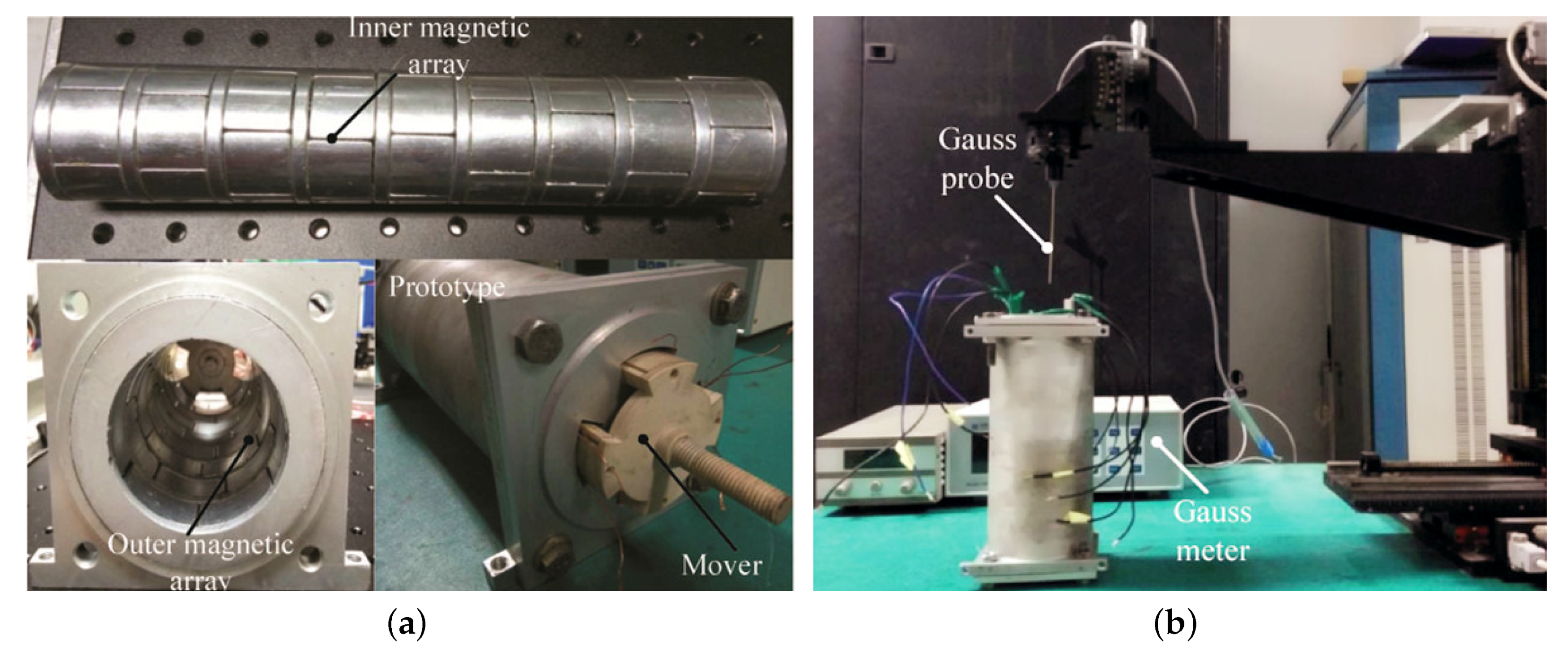
3.2. Prototype and Experimental Apparatus
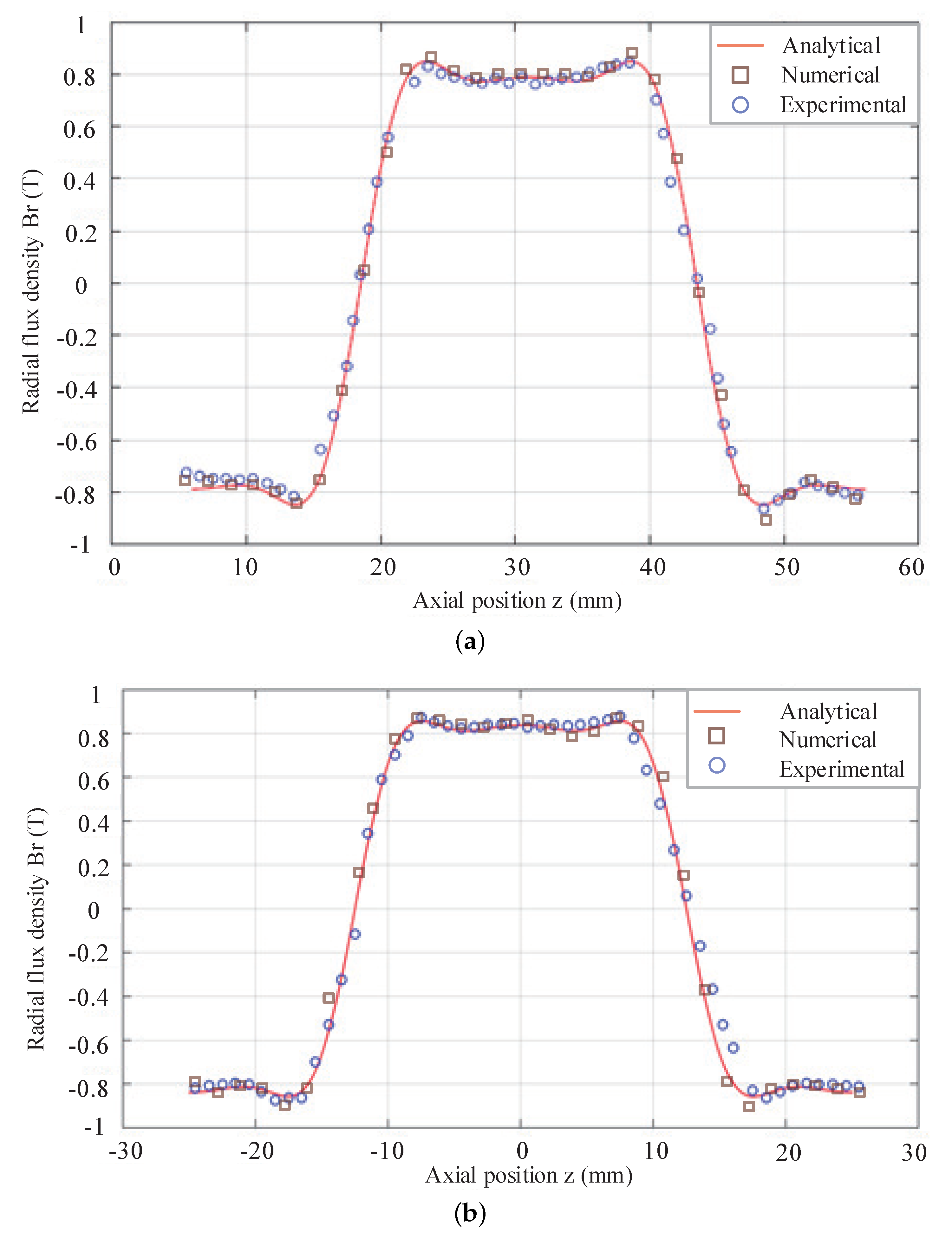
3.3. Validation of Analytical Magnetic Field Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FEM | Finite element methom |
| PM | Permanent magnet |
| PC | Personal computer |
References
- Boldea, I.; Nasar, S.A. Linear Motion Electromagnetic Devices; Taylor Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Boldea, I.; Nasar, S.A. Linear Electric Actuators and Generators; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pompermaier, C.; Kalluf, F.J.H.; Ferreira Da Luz, M.V.; Sadowski, N. Analytical and 3D FEM modeling of a tubular linear motor taking into account radial forces due to eccentricity. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, Vienna, Austria, 3–6 May 2009; pp. 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Eastham, J.F. Novel synchronous machines: Linear and disc. IEE Proc. B Electr. Power Appl. 1990, 137, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieras, J.F.; Eastham, A.R.; Dawson, G.E. Performance calculation for single-sided linear induction motors with a solid steel reaction plate under constant current excitation. IEE Proc. B Electr. Power Appl. 1985, 132, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieras, J.F.; Dawson, G.E.; Eastham, A.R. Performance calculation for single-sided linear induction motors with a double-layer reaction rail under constant current excitation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1986, 22, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, G.E.; Eastham, A.R.; Gieras, J.F.; Ong, R.; Ananthasivam, K. Design of linear induction drives by field analysis and finite-element techniques. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1986, IA-22, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Nam, K. Field-oriented control scheme for linear induction motor with the end effect. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2005, 152, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J. Linear induction motor-equivalent-circuit model. IEE Proc. B Electr. Power Appl. 1983, 130, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Yan, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, S. Magnetic Flux Distribution of Linear Machines with Novel Three-Dimensional Hybrid Magnet Arrays. Sensors 2017, 17, 2662. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, J.G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y. Equivalent circuits for single-sided linear induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 2410–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radun, A.V. Design considerations for the switched reluctance motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Bae, H.K.; Vijayraghavan, P.; Krishnan, R. Design of a linear switched reluctance machine. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Thirty-Fourth IAS Annual Meeting, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 3–7 October 1999; Volume 4, pp. 2267–2274. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, W.D.; Lang, J.H. A simple motion estimator for variable-reluctance motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1990, 26, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filicori, F.; Bianco, C.G.L.; Tonielli, A. Modeling and control strategies for a variable reluctance direct-drive motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1993, 40, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrey, D.A.; Lang, J.H. Modelling a nonlinear variable-reluctance motor drive. IEE Proc. B Electr. Power Appl. 1990, 137, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hor, P.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D.; Rees-Jones, J. Minimization of cogging force in a linear permanent magnet motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1998, 34, 3544–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Otaibi, Z.S.; Jack, A.G. On the design of oscillating linear single phase permanent magnet motors. In Proceedings of the 41st International Universities Power Engineering Conference, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, UK, 6–8 September 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 2, pp. 705–708. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Howe, D. Analysis of axially magnetised, iron-cored, tubular permanent magnet machines. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2004, 151, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.J.; Mueller, M.A.; Spooner, E. Permanent magnet air-cored tubular linear generator for marine energy converters. In Proceedings of the 2004 Second International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives, Edinburgh, UK, 31 March–2 April 2004; IET: Stevenage, UK, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 862–867. [Google Scholar]
- Halbach, K. Design of permanent multipole magnets with oriented rare earth cobalt material. In Nuclear Instruments and Methods; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1980; Volume 169, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.P.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Analytical magnetic field analysis of Halbach magnetized permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Howe, D. Tubular modular permanent-magnet machines equipped with quasi-Halbach magnetized magnets-part I: Magnetic field distribution, EMF, and thrust force. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Z.; Howe, D. Analysis of a short-stroke, single-phase, quasi-Halbach magnetised tubular permanent magnet motor for linear compressor applications. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2008, 2, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jewell, G.W.; Howe, D. Design optimisation and comparison of tubular permanent magnet machine topologies. IEE Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2001, 148, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Jiao, Z.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, I.-M. Magnetic field of tubular linear machines with dual Halbach array. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 136, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, Z. Electromagnetic Linear Machines with Dual Halbach Array-Design and Analysis; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Shang, Y.; Jiao, Z. Back-iron effect of tubular linear motors with dual Halbach permanent magnet arrays. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 10th International Conference on Industrial Informatics, Beijing, China, 25–27 July 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 574–579. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Zhou, L.; Li, L. Influence of design parameters on end effect in long primary double-sided linear induction motor. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2011, 39, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laldin, O.; Sudhoff, S.D.; Pekarek, S. Modified Carter’s Coefficient. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1133–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jewell, G.W.; Howe, D. A general framework for the analysis and design of tubular linear permanent magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 1986–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

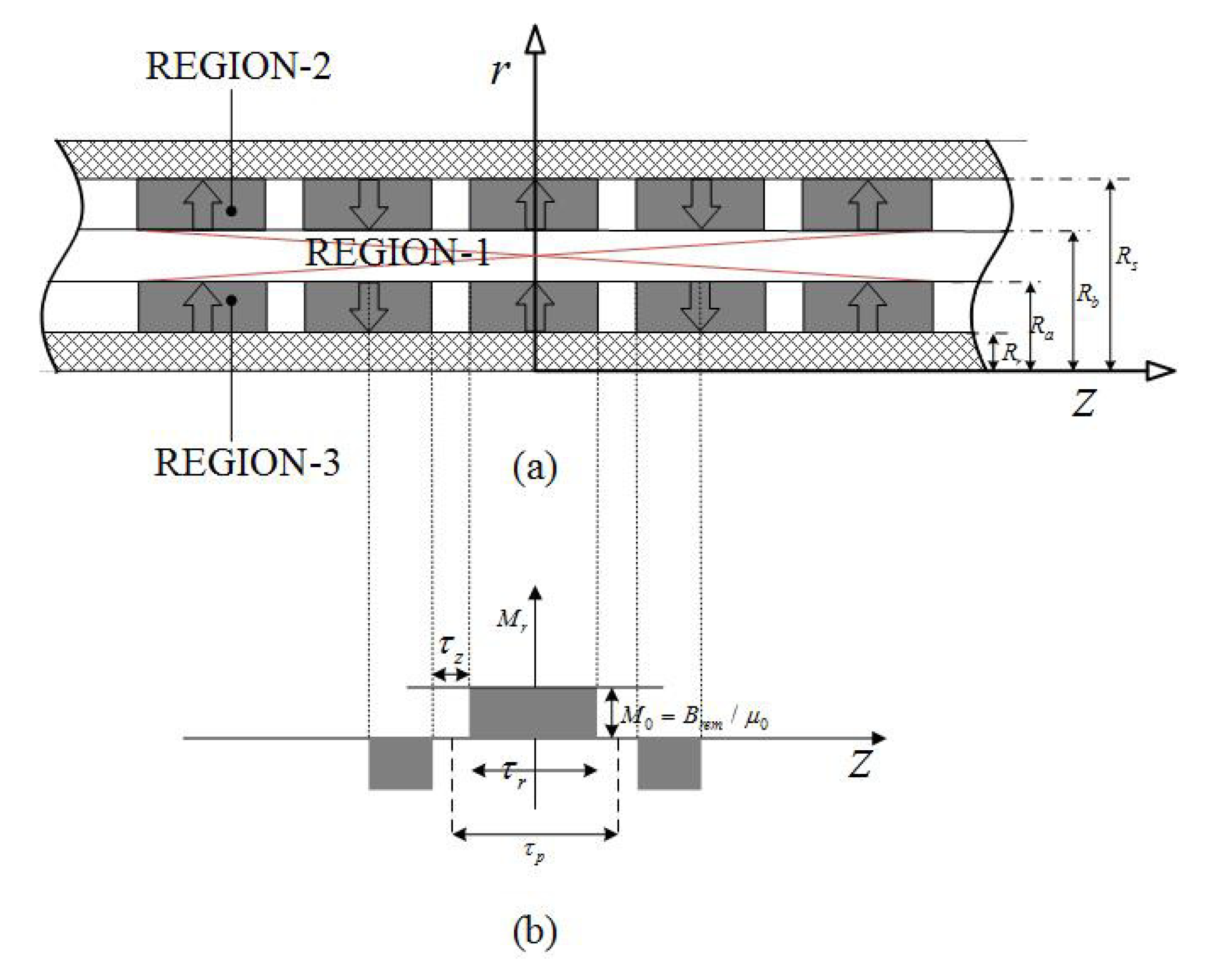
| Motor length L | 250 mm |
| Maximum radius | 50 mm |
| Width of radial PM | 5 mm |
| Pole-pitch | 25 mm |
| Number of poles n | 9 |
| Air gap length g | 1 mm |
| Outer rad of external PM | 45 mm |
| Inner rad of external PM | 32 mm |
| Outer rad of internal PM | 23 mm |
| Inner rad of internal PM | 13 mm |
| Number of winding turns | 60 |
| No. | FEM (T) | Analytical Method (T) | Experimental Method (T) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −0.7324 | −0.7982 | −0.7183 |
| 2 | −0.7882 | −0.7830 | −0.7725 |
| 3 | −0.7910 | −0.8014 | −0.7882 |
| 4 | −0.6902 | −0.7025 | −0.6216 |
| 5 | −0.1413 | −0.1408 | −0.1425 |
| 6 | 0.3922 | 0.3919 | 0.3936 |
| 7 | 0.8381 | 0.8205 | 0.8194 |
| 8 | 0.7914 | 0.7944 | 0.7923 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, L.; Jiao, Z. Comparative Study of the Dual Layer Magnet Array in a Moving-Coil Tubular Linear PM Motor. Sensors 2018, 18, 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061854
Yan L, Zhang L, Peng L, Jiao Z. Comparative Study of the Dual Layer Magnet Array in a Moving-Coil Tubular Linear PM Motor. Sensors. 2018; 18(6):1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061854
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Liang, Lu Zhang, Lei Peng, and Zongxia Jiao. 2018. "Comparative Study of the Dual Layer Magnet Array in a Moving-Coil Tubular Linear PM Motor" Sensors 18, no. 6: 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061854
APA StyleYan, L., Zhang, L., Peng, L., & Jiao, Z. (2018). Comparative Study of the Dual Layer Magnet Array in a Moving-Coil Tubular Linear PM Motor. Sensors, 18(6), 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061854




