Label-Free Quantification of Anti-TNF-α in Patients Treated with Adalimumab Using an Optical Biosensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Rreagents
2.2. Plasma Ccollection
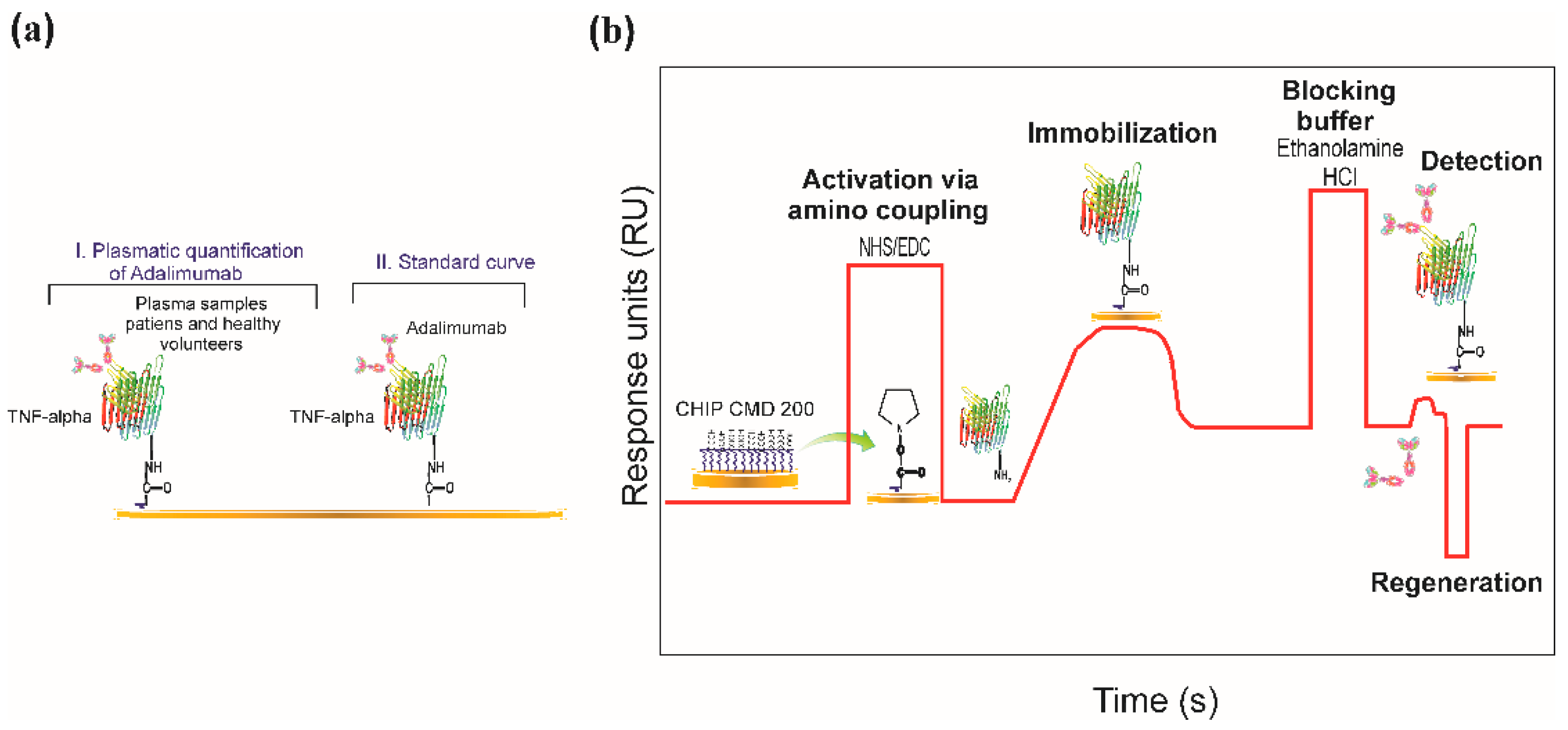
2.3. Biosensor System
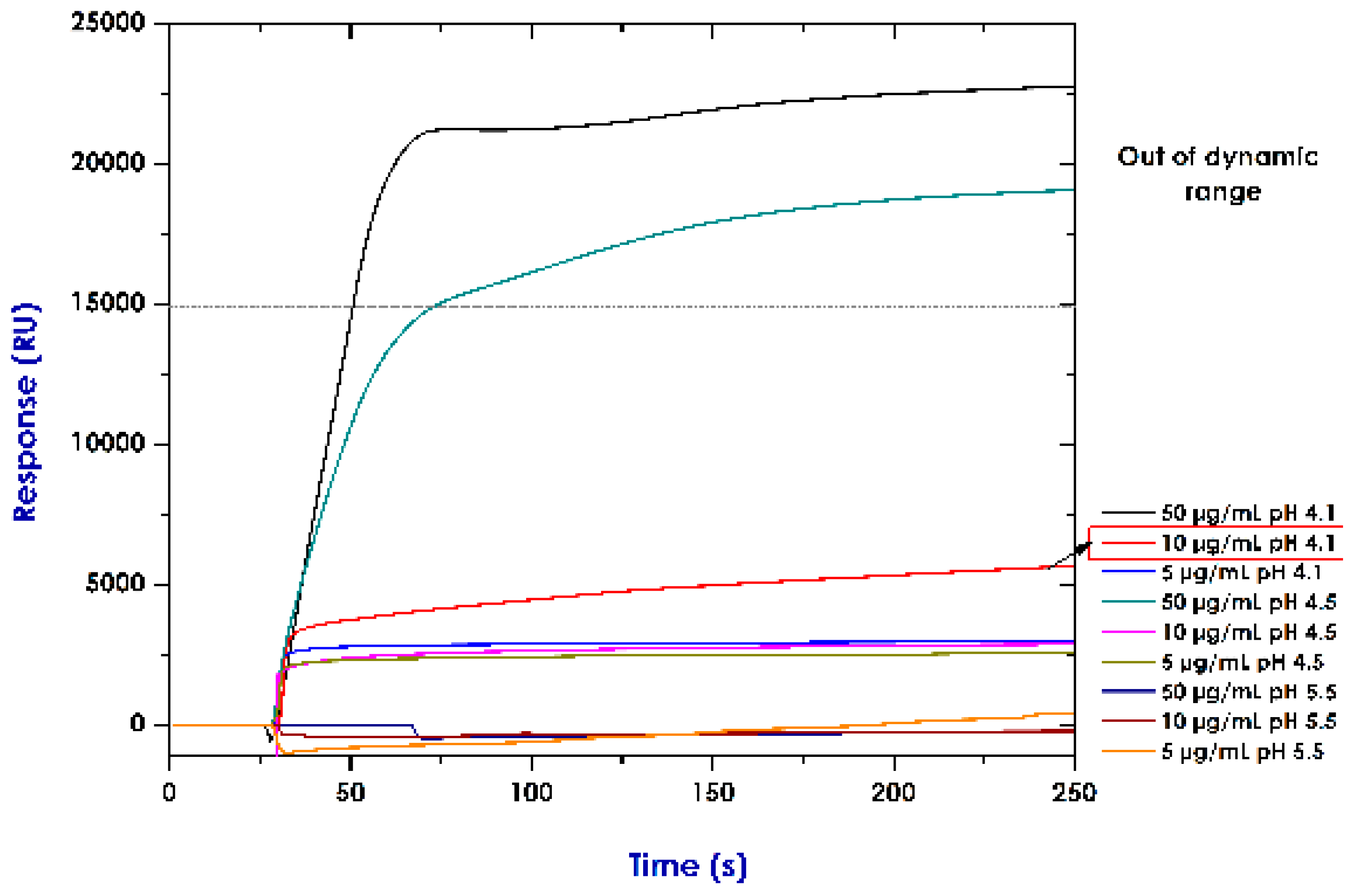
2.4. Establishing Conditions for Immobilising Recombinant Proteins (Pre-Concentration Assays)
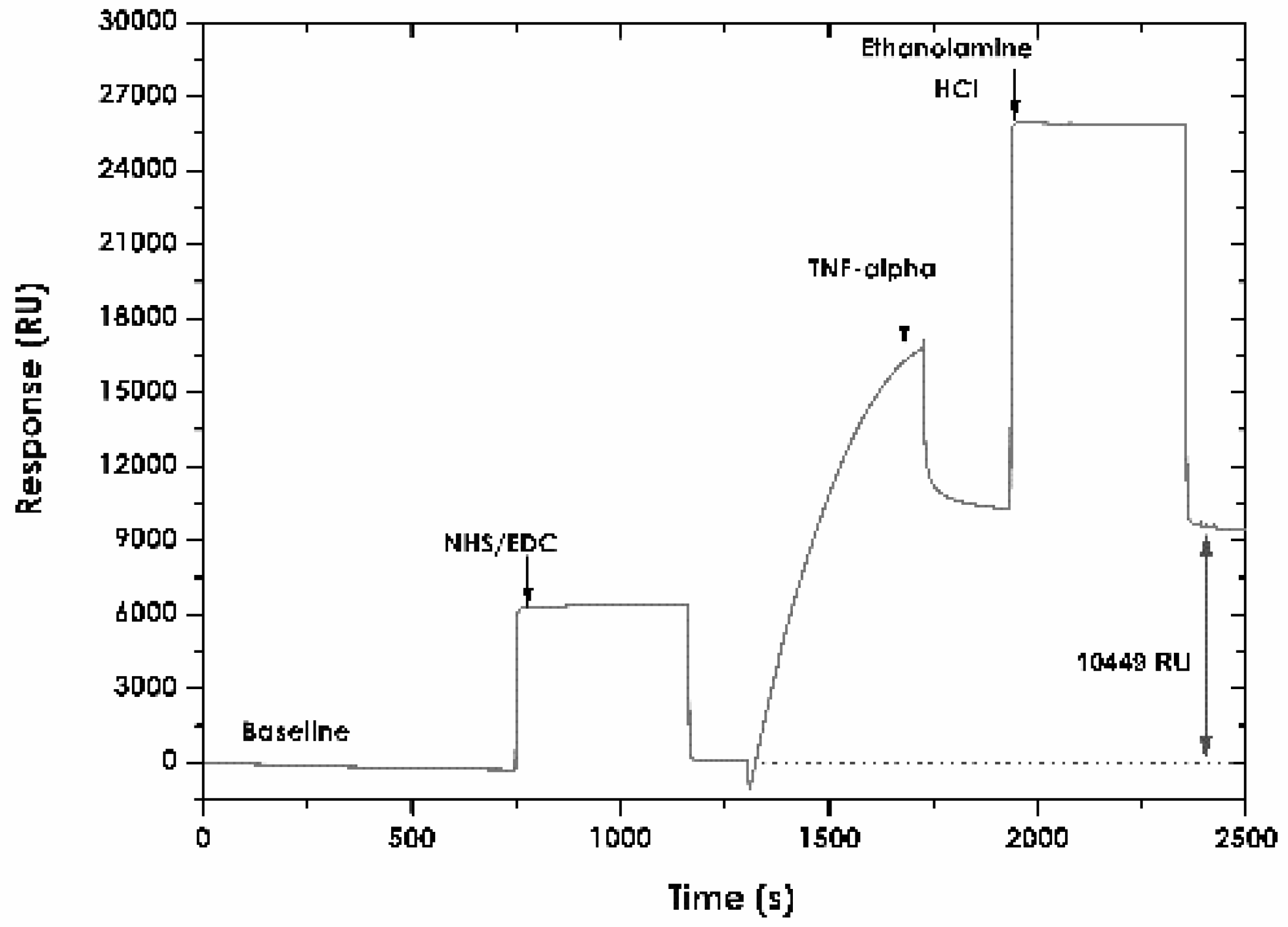
2.5. Immobilising TNF-α Recombinant Protein
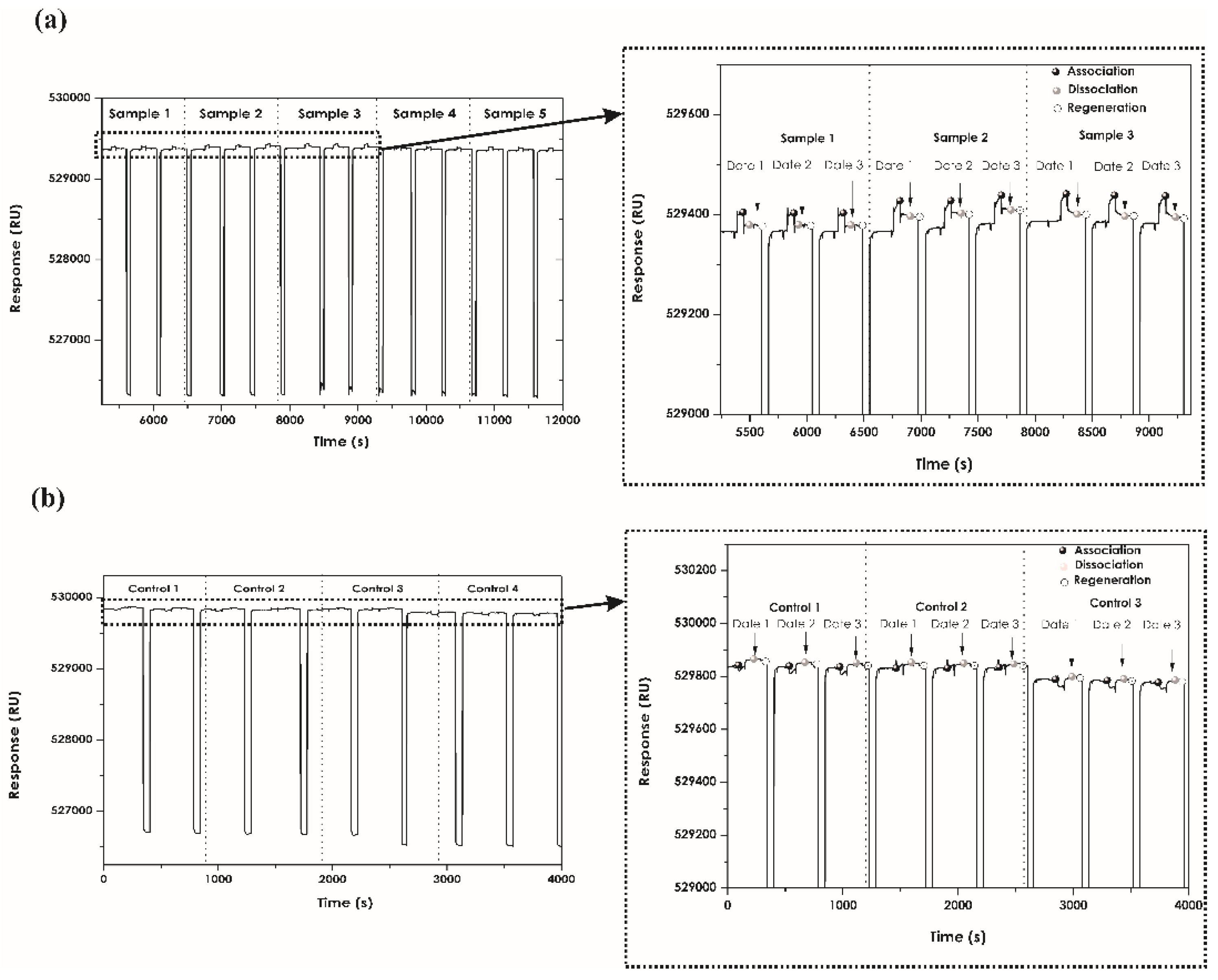
2.6. Regeneration Assays
2.7. SPR-Based Real-Time Quantification
2.8. ELISA Assays
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. A Description of the Patients
3.2. Establishing Conditions for Immobilising Rrecombinant Pproteins (Pre-Concentration Assays)
3.3. Immobilising TNF-α Recombinant Protein
3.4. Regeneration Assays
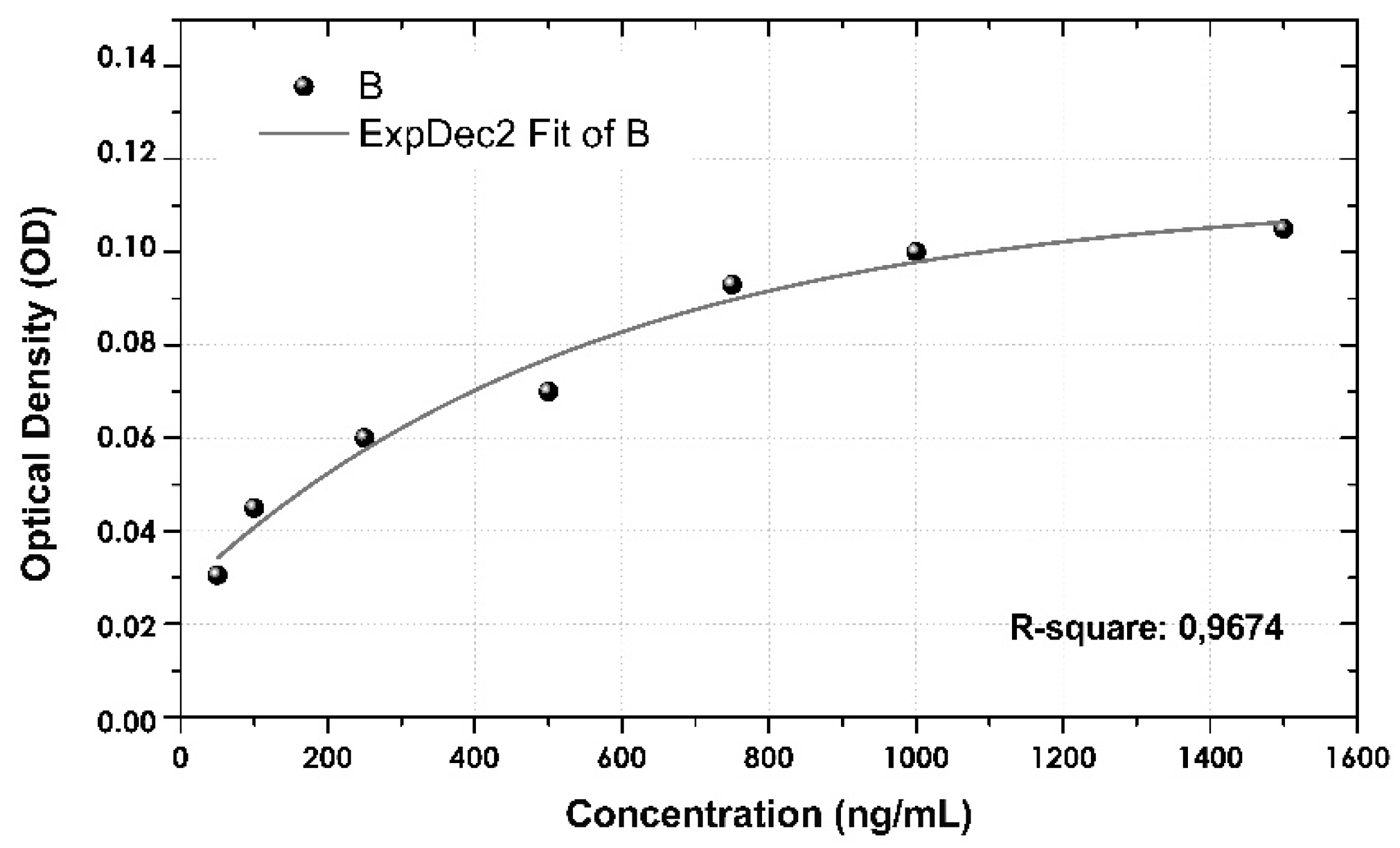
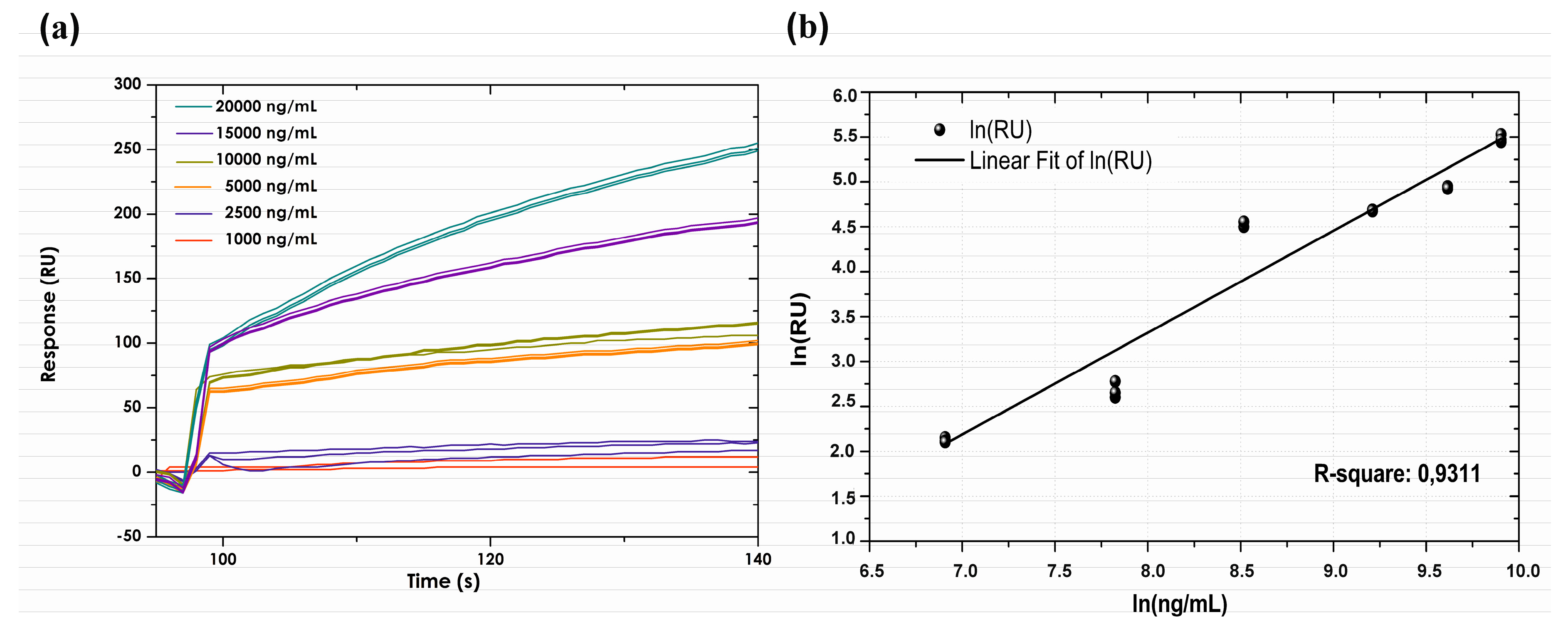
3.5. Calibration Curve
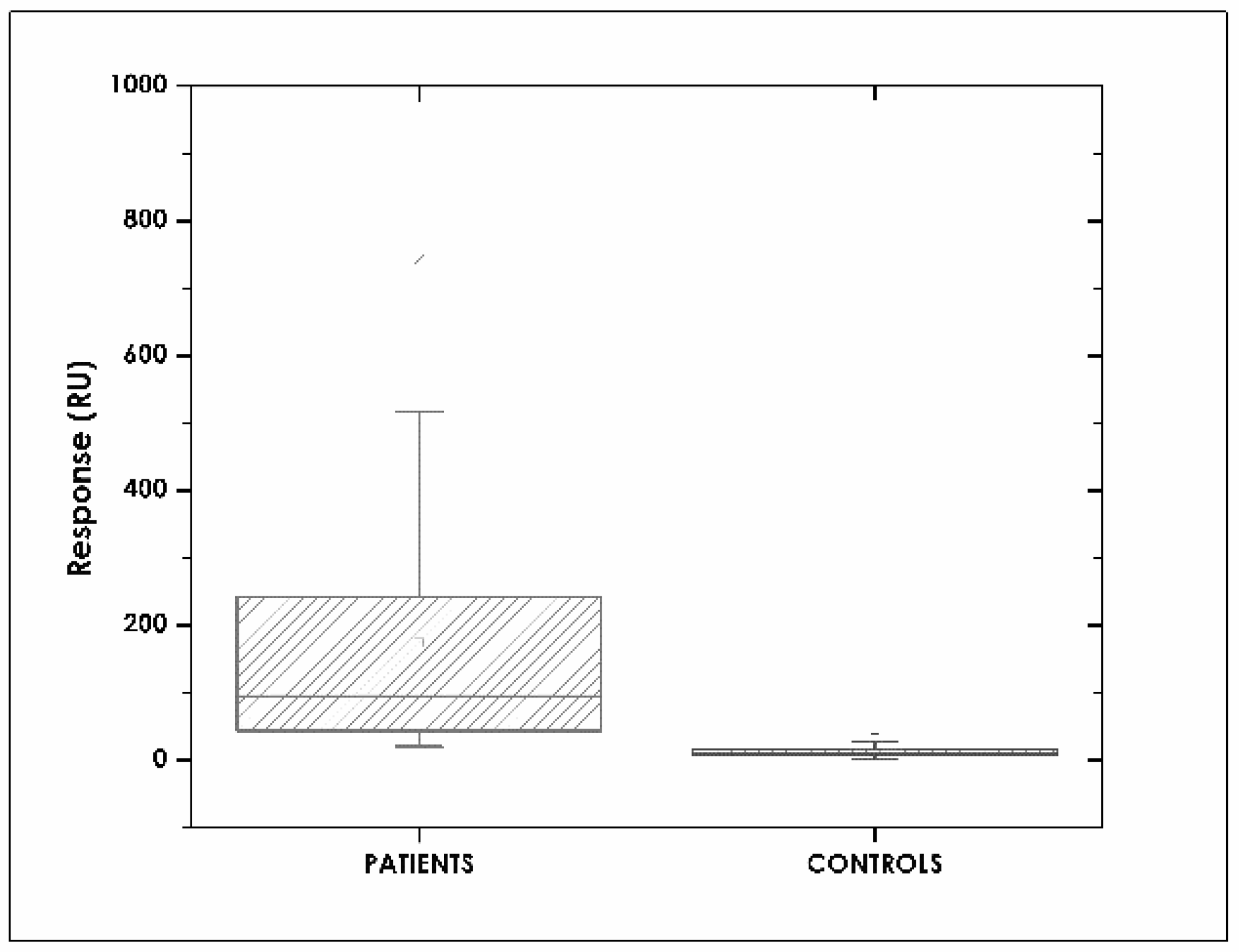
3.6. Assay Specificity
3.7. Correlation between SPR and ELISA Assays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Feagan, B.G.; Choquette, D.; Ghosh, S.; Gladman, D.D.; Ho, V.; Meibohm, B.; Zou, G.; Xu, Z.; Shankar, G.; Sealey, D.C.; et al. The challenge of indication extrapolation for infliximab biosimilars. Biologicals 2014, 42, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtzen, K.; Svenson, M. Enzyme Immunoassays and Radioimmunoassays for Quantification of Anti-TNF Biopharmaceuticals and Anti-Drug Antibodies. In Detection and Quantification of Antibodies to Biopharmaceuticals; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on Immunogenicity Assessment of Biotechnology-Derived Therapeutic Proteins. 2015. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2015/10/WC500194507.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2017).
- US Food and Drug Administration. Biosimilars Guidances; US FDA: New Hampshire, MD, USA, 2017.
- WHO (World Health Organization). Guidelines of Evaluation for Similar Biotherapeutics Products (SBPs). 2009. Available online: http://www.who.int/biologicals/areas/biological_therapeutics/BIOTHERAPEUTICS_FOR_WEB_22APRIL2010.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Ternant, D.; Paintaud, G. Pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationships of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and fusion proteins. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2005, 5, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Targeted antibody therapy and relevant novel biomarkers for precision medicine for rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunol. 2017, 29, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmier, J.; Ogden, K.; Nickman, N.; Halpern, M.T.; Cifaldi, M.; Ganguli, A.; Bao, Y.; Garg, V. Costs of Providing Infusion Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Hospital-based Infusion Center Setting. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 1600–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einodshofer, M.T.; Duren, L.N. Cost Management through Care Management, Part 2: The Importance of Managing Specialty Drug Utilization in the Medical Benefit. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2012, 5, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Batticciotto, A.; Ravasio, R.; Riva, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Efficacy and Treatment Costs of Monotherapy with bDMARDs in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Patients Intolerant to or Inappropriate to Continue Treatment with Methotrexate. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 1360–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, U.; Cross, R.K. Primary and secondary nonresponse to infliximab: Mechanisms and countermeasures. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordas, I.; Mould, D.R.; Feagan, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J. Anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease: Pharmacokinetics-based dosing paradigms. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 91, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, A.V. Translational pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of monoclonal antibodies. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2016, 21–22, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Jin, F.; Prabhu, S.; Iyer, S. Monoclonal antibodies: What are the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations for drug development? Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, E.D.; Hansen, R.J.; Balthasar, J.P. Antibody pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 2645–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, E.Q.; Balthasar, J.P. Monoclonal antibody pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 84, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Lichtenstein, L.; Assa, A.; Mazor, Y.; Weiss, B.; Levine, A.; Ron, Y.; Kopylov, U.; Bujanover, Y.; Rosenbach, Y.; et al. Levels of drug and antidrug antibodies are associated with outcome of interventions after loss of response to infliximab or adalimumab. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schie, K.A.; Wolbink, G.J.; Rispens, T. Cross-reactive and pre-existing antibodies to therapeutic antibodies—Effects on treatment and immunogenicity. MAbs 2015, 7, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, M.; Nadler, S.G. Immunogenicity to Biotherapeutics—The Role of Anti-drug Immune Complexes. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jani, M.; Isaacs, J.D.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Plant, D.; Hyrich, K.L.; Chinoy, H.; Barton, A.; BRAGGSS. High frequency of antidrug antibodies and association of random drug levels with efficacy in certolizumab pegol-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the BRAGGSS cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, F.B.; Morand, E.F.; Murphy, K.; Mackay, F.; Mariette, X.; Marcelli, C. Antidrug antibodies (ADAb) to tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-specific neutralising agents in chronic inflammatory diseases: A real issue, a clinical perspective. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolbink, G.J.; Vis, M.; Lems, W.; Voskuyl, A.E.; de Groot, E.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Stapel, S.; Tak, P.P.; Aarden, L.; Dijkmans, B. Development of antiinfliximab antibodies and relationship to clinical response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, M.S.; Bendtzen, K.; Andrade, L.E.C. Biological anti-TNF drugs: Immunogenicity underlying treatment failure and adverse events. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelds, G.M.; Krieckaert, C.L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Lems, W.F.; Twisk, J.W.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Aarden, L.; Wolbink, G.J. Development of antidrug antibodies against adalimumab and association with disease activity and treatment failure during long-term follow-up. JAMA 2011, 305, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, K.; Zhou, H. Pharmacokinetic drug-drug interaction potentials for therapeutic monoclonal antibodies: Reality check. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, M.; Burke, J.M.; Hellriegel, E.; Robertson, P., Jr.; Phillips, L.; Ludwig, E.; Munteanu, M.C.; Bond, M. An evaluation of the potential for drug-drug interactions between bendamustine and rituximab in indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 73, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Sharma, A. Therapeutic protein-drug interactions: Plausible mechanisms and assessment strategies. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matucci, A.; Nencini, F.; Pratesi, S.; Maggi, E.; Vultaggio, A. An overview on safety of monoclonal antibodies. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 16, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doessegger, L.; Banholzer, M.L. Clinical development methodology for infusion-related reactions with monoclonal antibodies. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2015, 4, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vultaggio, A.; Maggi, E.; Matucci, A. Immediate adverse reactions to biologicals: From pathogenic mechanisms to prophylactic management. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 11, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel, T.T.; Kropshofer, H.; Singer, T.; Mitchell, J.A.; George, A.J. The safety and side effects of monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vultaggio, A.; Matucci, A.; Nencini, F.; Pratesi, S.; Parronchi, P.; Rossi, O.; Romagnani, S.; Maggi, E. Anti-infliximab IgE and non-IgE antibodies and induction of infusion-related severe anaphylactic reactions. Allergy 2010, 65, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntharalingam, G.; Perry, M.R.; Ward, S.; Brett, S.J.; Castello-Cortes, A.; Brunner, M.D.; Panoskaltsis, N. Cytokine storm in a phase 1 trial of the anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody TGN1412. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wing, M. Monoclonal antibody first dose cytokine release syndromes-mechanisms and prediction. J. Immunotoxicol. 2008, 5, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.; Khalid, T.; Hughes, S.; Bonney, D.; Wynn, R. Rituximab-induced Cytokine Storm in the Absence of Overt Lymphoproliferative Disease. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 38, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, H.E.; Worsley, A.; Smith, J.M.; Thomas, S.H. Anti-TNF agents for rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 51, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminati, M.; Senna, G.; Stefanizzi, G.; Bellamoli, R.; Longhi, S.; Chieco-Bianchi, F.; Guarnieri, G.; Tognella, S.; Olivieri, M.; Micheletto, C. Drop-out rate among patients treated with omalizumab for severe asthma: Literature review and real-life experience. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowatzke, W.L.; Rogers, K.; Wells, E.; Bowsher, R.R.; Ray, C.; Unger, S. Unique challenges of providing bioanalytical support for biological therapeutic pharmacokinetic programs. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bezooijen, J.S.; Koch, B.C.; van Doorn, M.B.; Prens, E.P.; van Gelder, T.; Schreurs, M.W. Comparison of Three Assays to Quantify Infliximab, Adalimumab, and Etanercept Serum Concentrations. Ther. Drug Monit. 2016, 38, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, K.; Connock, M.; Auguste, P.; Taylor-Phillips, S.; Mistry, H.; Shyangdan, D.; Court, R.; Arasaradnam, R.; Sutcliffe, P.; Clarke, A. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of use of therapeutic monitoring of tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitors [LISA-TRACKER(R) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits, TNF-alpha-Blocker ELISA kits and Promonitor(R) ELISA kits] versus standard care in patients with Crohn’s disease: Systematic reviews and economic modelling. Health Technol. Assess. 2016, 20, 1–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chellaraj, V.; Cicero, K.; Abuarjah, K.; Lundberg, L.; Desai, H.; Gadkari, S.; Hantash, J.; Scott, G.; Beaver, C. Comparison Between Two UV ELISA Kits and an Electrochemiluminescence ELISA Method for the Quantification of HUMIRA® (Adalimumab) in Human Serum. 2012. Available online: http://www.inventivhealthclinical.com/497801ee-21a9-4235-91b1-2d3c9e279b38/download.htm (accessed on 5 November 2017).
- Bendtzen, K.; Geborek, P.; Svenson, M.; Larsson, L.; Kapetanovic, M.C.; Saxne, T. Individualized monitoring of drug bioavailability and immunogenicity in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with the tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3782–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svenson, M.; Geborek, P.; Saxne, T.; Bendtzen, K. Monitoring patients treated with anti-TNF-alpha biopharmaceuticals: Assessing serum infliximab and anti-infliximab antibodies. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1828–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radstake, T.R.; Svenson, M.; Eijsbouts, A.M.; van den Hoogen, F.H.; Enevold, C.; van Riel, P.L.; Bendtzen, K. Formation of antibodies against infliximab and adalimumab strongly correlates with functional drug levels and clinical responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&ved=0ahUKEwiL9riFmLvZAhXMEbwKHdWOAwMQFgglMAA&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.ipqpubs.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2010%2F06%2FUSP_1032.pdf&usg=AOvVaw2leNseZklkroyS3UtgspjB (accessed on 20 January 2018).
- Moberg, A.; Lager, A.; Hamalainen, M.D.; Jarhede, T. Increased sensitivity of SPR assays in plasma through efficient parallel assay optimization. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 78–79, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, S.; Mytych, D. The use of Surface Plasmon Resonance for the Detection and Characterization of Antibodies. In Detection and Quantification of Antibodies to Biopharmaceuticals; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mire-Sluis, A.R.; Barrett, Y.C.; Devanarayan, V.; Koren, E.; Liu, H.; Maia, M.; Parish, T.; Scott, G.; Shankar, G.; Shores, E. Recommendations for the design and optimization of immunoassays used in the detection of host antibodies against biotechnology products. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 289, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damborsky, P.; Svitel, J.; Katrlik, J. Optical biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Nanda, R.; Sahoo, S.; Mohapatra, E. Biosensors in Health Care: The Milestones Achieved in Their Development towards Lab-on-Chip-Analysis. Biochem. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Kim, M. Surface plasmon resonance: A versatile technique for biosensor applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 10481–10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Gallego, R.; Bosch, J.; Such-Sanmartin, G.; Segura, J. Surface plasmon resonance immunoassays—A perspective. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2009, 19, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmborg, A.C.; Michaelsson, A.; Ohlin, M.; Jansson, B.; Borrebaeck, C.A. Real time analysis of antibody-antigen reaction kinetics. Scand. J. Immunol. 1992, 35, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mytych, D.T.; La, S.; Barger, T.; Ferbas, J.; Swanson, S.J. The development and validation of a sensitive, dual-flow cell, SPR-based biosensor immunoassay for the detection, semi-quantitation, and characterization of antibodies to darbepoetin alfa and epoetin alfa in human serum. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwa, M.; Bird, C.; Dilger, P.; Gaines-Das, R.; Thorpe, R. Strategies for detection, measurement and characterization of unwanted antibodies induced by therapeutic biologicals. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 278, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA). 2017. Available online: https://www.cms.gov/Regulations-and-Guidance/Legislation/CLIA/index.html?redirect=/CLIA (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Van der Merwe, A. Surface Plasmon Resonance. 2011. Available online: http://www.biophysics.bioc.cam.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2011/02/spr1.pdf (accessed on 14 November 2017).
- O’Shannessy, D.J.; Brigham-Burke, M.; Peck, K. Immobilization chemistries suitable for use in the BIAcore surface plasmon resonance detector. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 205, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trilling, A.K.; Beekwilder, J.; Zuilhof, H. Antibody orientation on biosensor surfaces: A minireview. Analyst 2013, 138, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, K.; Areskoug, D.; Hardenborg, E. Exploring buffer space for molecular interactions. J. Mol. Recognit. 1999, 12, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GE Healthcare. BiacoreTM Assay Handbook. 2012. Available online: http://proteins.gelifesciences.com/~/media/protein-purification-ib/documents/handbooks/biacore_assay_handbook.pdf?la=en (accessed on 15 November 2017).
- Bustos, R.H.; Suesca, E.; Millan, D.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Fontanilla, M.R. Real-time quantification of proteins secreted by artificial connective tissue made from uni- or multidirectional collagen I scaffolds and oral mucosa fibroblasts. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquart, J.A. Surface Plasmon Resonance and Biomolecular Interaction Analysis Theory and Practice. 2014. Available online: http://www.lulu.com/shop/ja-marquart/surface-plasmon-resonance-and-biomolecular-interaction-analysis/hardcover/product-21404460.html (accessed on 20 February 2018).
- Homola, J.; Piliarik, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Sensors; Springer Series on Chemical Sensors and Biosensors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, D.; Chae, G.; Shin, S. Analysis of Surface Plasmon Resonance Curves with a Novel Sigmoid-Asymmetric Fitting Algorithm. Sensors 2015, 15, 25385–25398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundström, I. Real-time biospecific interaction analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1994, 9, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanquin. Adalimumab Level Elisa M1885. 2015. Available online: https://www.sanquin.nl/repository/reagentia/ifu/Product_flyer_Adalimumab_ELISA_kit.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2017).
- Bian, S.; Stappen, T.V.; Baert, F.; Compernolle, G.; Brouwers, E.; Tops, S.; Vries, A.; Rispens, T.; Lammertyn, J.; Vermeire, S.; et al. Generation and characterization of a unique panel of anti-adalimumab specific antibodies and their application in therapeutic drug monitoring assays. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 125, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Neut Kolfschoten, M.; Schuurman, J.; Losen, M.; Bleeker, W.K.; Martinez-Martinez, P.; Vermeulen, E.; den Bleker, T.H.; Wiegman, L.; Vink, T.; Aarden, L.A. Anti-inflammatory activity of human IgG4 antibodies by dynamic Fab arm exchange. Science 2007, 317, 1554–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizeli, E.; Lowe, C. Biomolecular Sensors; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Van Stappen, T.; Spasic, D.; Delport, F.; Vermeire, S.; Gils, A.; Lammertyn, J. Fiber optic-SPR platform for fast and sensitive infliximab detection in serum of inflammatory bowel disease patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, S.; Lu, J.; Delport, F.; Vermeire, S.; Spasic, D.; Lammertyn, J.; Gils, A. Development and validation of an optical biosensor for rapid monitoring of adalimumab in serum of patients with Crohn’s disease. Drug Test. Anal. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real Fernandez, F.; Di Pisa, M.; Rossi, G.; Auberger, N.; Lequin, O.; Larregola, M.; Benchohra, A.; Mansuy, C.; Chassaing, G.; Lolli, F. Antibody recognition in multiple sclerosis and Rett syndrome using a collection of linear and cyclic N-glucosylated antigenic probes. Biopolymers 2015, 104, 560–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real-Fernandez, F.; Cimaz, R.; Rossi, G.; Simonini, G.; Giani, T.; Pagnini, I.; Papini, A.M.; Rovero, P. Surface plasmon resonance-based methodology for anti-adalimumab antibody identification and kinetic characterization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7477–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, Y.J.; Zeenathul, N.A.; Rezaei, M.A.; Mustafa, N.H.; Azmi, M.L.M.; Bahaman, A.R.; Lo, S.C.; Tan, J.S.; Hani, H.; Rasedee, A. Wide dynamic range of surface-plasmon-resonance-based assay for hepatitis B surface antigen antibody optimal detection in comparison with ELISA. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, E.M.; van de Kerkhof, D.; Hamann, D.; van Dongen, J.L.; Kuijper, P.H.; Brunsveld, L.; Scharnhorst, V.; Broeren, M.A. Therapeutic drug monitoring of infliximab: Performance evaluation of three commercial ELISA kits. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanquin. Adalimumab Level ELISA. 2009. Available online: http://78.41.76.137/antibodyshop/datasheet/sanquin/M1885.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2018).

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bustos, R.H.; Zapata, C.; Esteban, E.; García, J.-C.; Jáuregui, E.; Jaimes, D. Label-Free Quantification of Anti-TNF-α in Patients Treated with Adalimumab Using an Optical Biosensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030691
Bustos RH, Zapata C, Esteban E, García J-C, Jáuregui E, Jaimes D. Label-Free Quantification of Anti-TNF-α in Patients Treated with Adalimumab Using an Optical Biosensor. Sensors. 2018; 18(3):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030691
Chicago/Turabian StyleBustos, Rosa Helena, Carlos Zapata, Efraín Esteban, Julio-César García, Edwin Jáuregui, and Diego Jaimes. 2018. "Label-Free Quantification of Anti-TNF-α in Patients Treated with Adalimumab Using an Optical Biosensor" Sensors 18, no. 3: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030691
APA StyleBustos, R. H., Zapata, C., Esteban, E., García, J.-C., Jáuregui, E., & Jaimes, D. (2018). Label-Free Quantification of Anti-TNF-α in Patients Treated with Adalimumab Using an Optical Biosensor. Sensors, 18(3), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18030691