Sensor Selection for Decentralized Large-Scale Multi-Target Tracking Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Background
2.1. Labeled RFS and Mδ-GLMB
2.2. Information Inequality to RFS Measurement
2.3. A New Metric for Labeled RFS
3. Problem Formulation
| Algorithm 1. Sensor selection and MTT for the LFC . |
| 1. Prediction: Calculate the current predicted density by , where is the fused density at the last time; |
| 2. SN selection: Select the SN subset and receive a collection of their measurement sets ; |
| 3. Update: Calculate the current posterior density by and then transmit the density to the LFCs connected to the LFC ; |
| 4. Fusion: Receive the posterior densities from the LFC set and then calculate the fused density by the weighted KLA rule , where () is the preset normalized weight; |
| 5. State extraction: Extract the current state estimate from as the output. Go to Step 1. |
4. Lower Bound For LA Metric Based MSE and Sub-Optimization For Sensor Selection
4.1. Derivation of LA Bound
| Algorithm 2. Steps for calculating and . |
| 1. Prediction sampling: Generate samples of multi-target state sets from the predicted density ; |
| 2. PIMS generating: For , generate PIMS of the SN set based on [31]; |
| 3. PIMS partitioning: Divide PIMS into the measurement subspace () according to (30); |
| 4. MC integration: Given the PIMS assigned to , and are obtained by applying MC integral formula [45] to (39) and (42). |
4.2. SMC and GM Implementations for the Bound
4.3. Sub-Optimization Based on Coordinate Descent
| Algorithm 3. Coordinate descent method. |
| Step 1: Set initial iteration number , initial SN switch vector , initial barrier factor and its reduction coefficient ; |
| Step 2: From to , calculate , where are treated as constants; |
| Step 3: If , then go to Step 4; Otherwise, set , go to Step 2; |
| Step 4: If , then output as the solution of (17); Otherwise, set , , and then go to Step 2. |
4.4. Weighted KLA Fusion
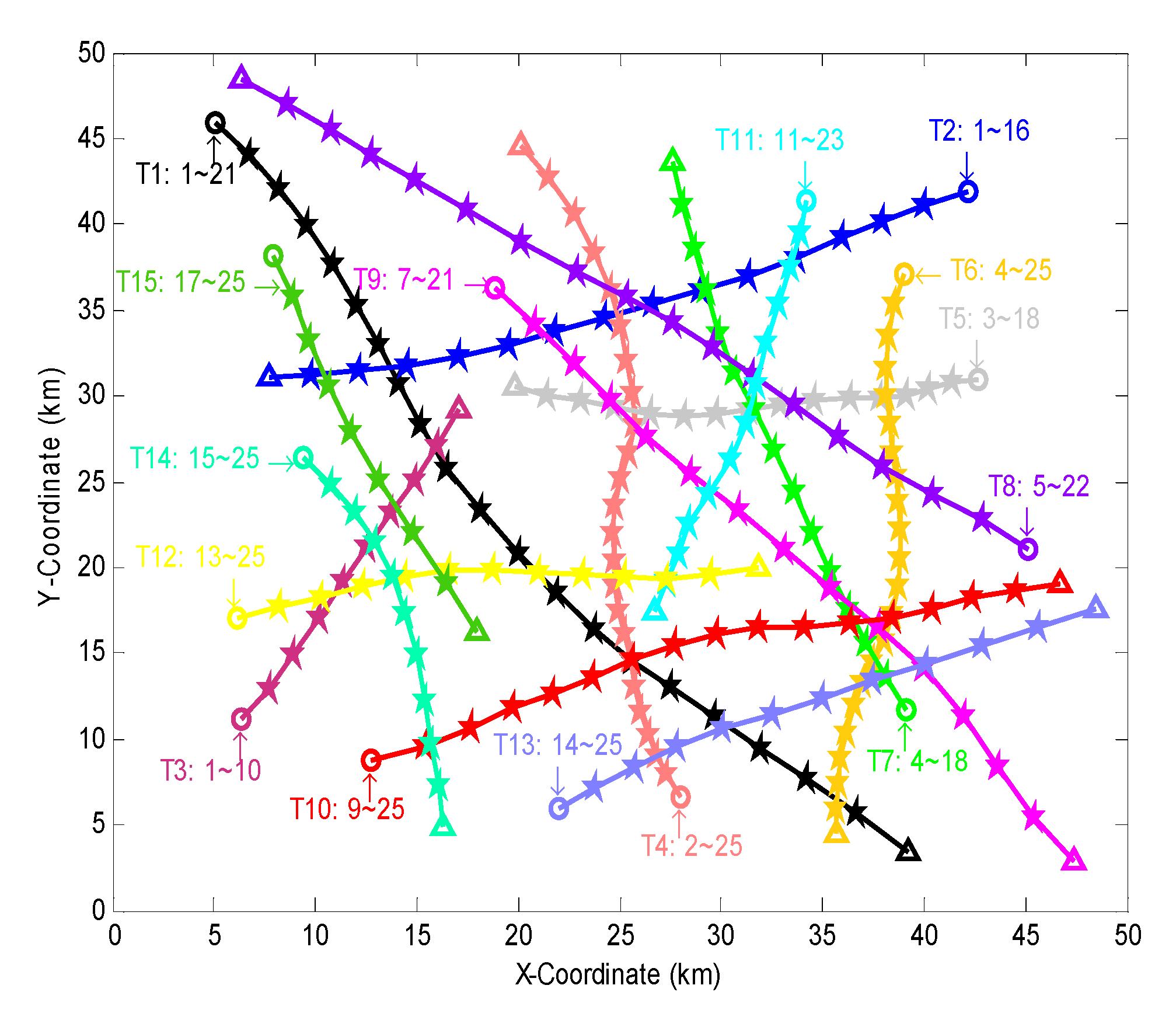
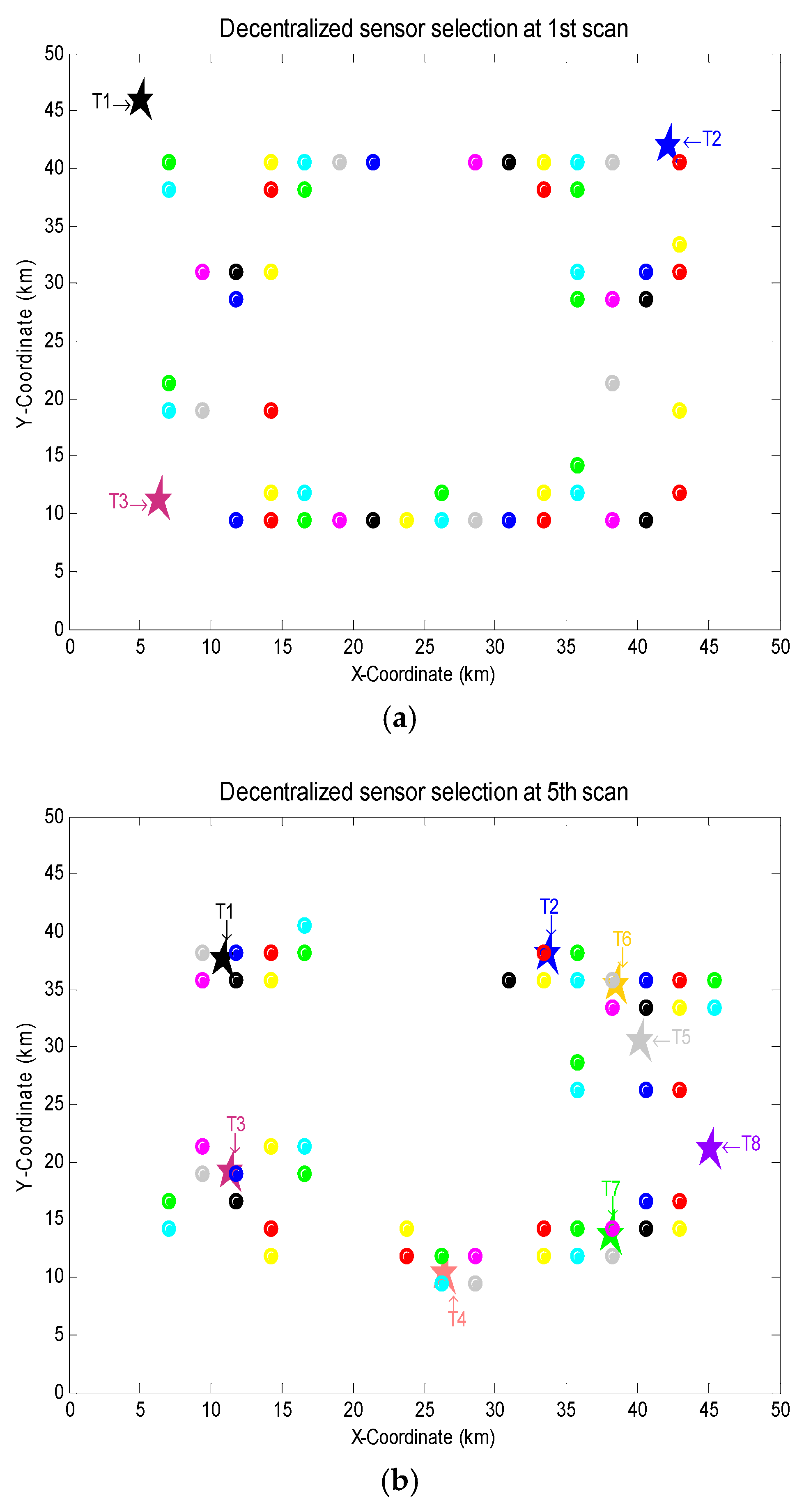
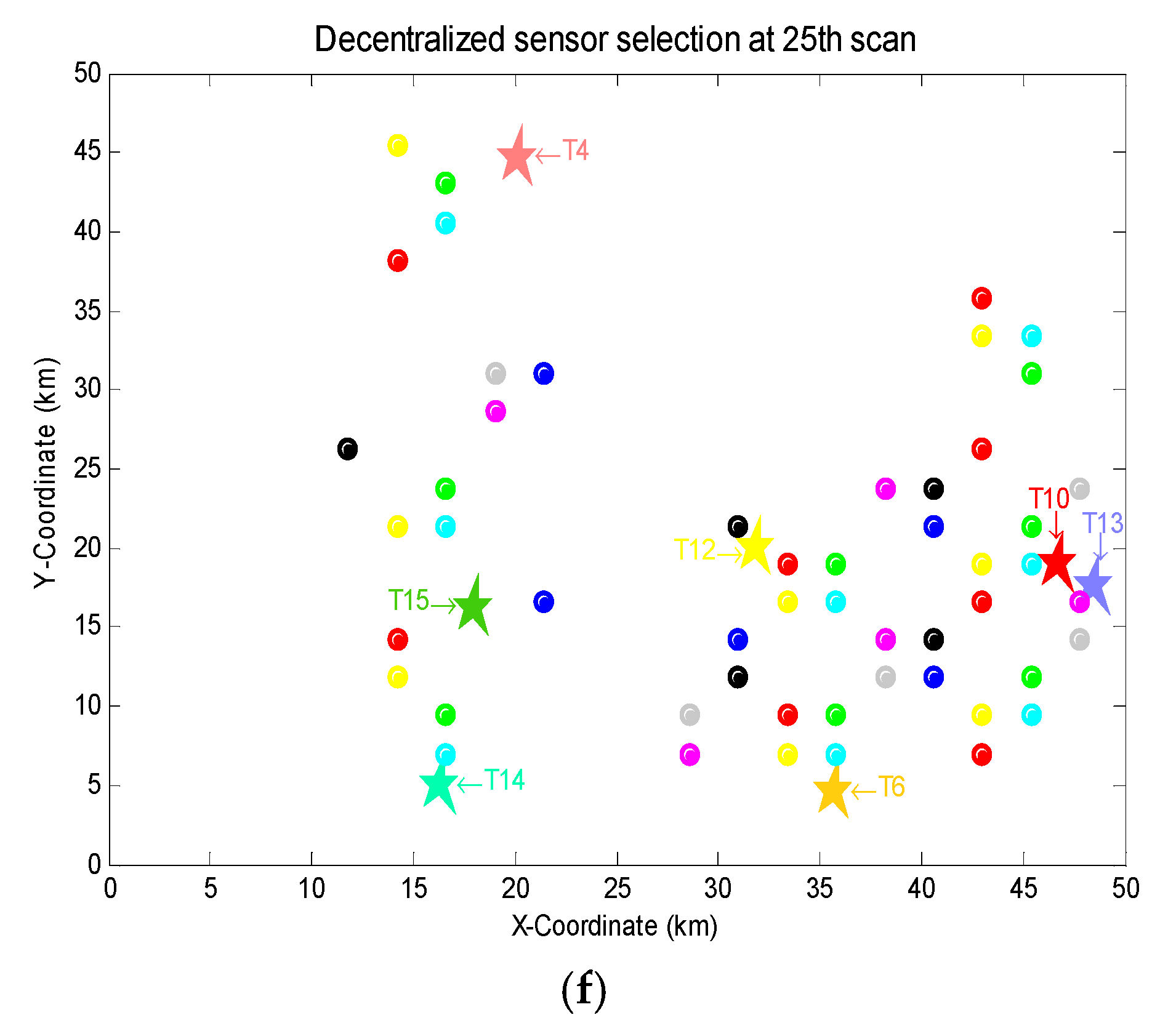
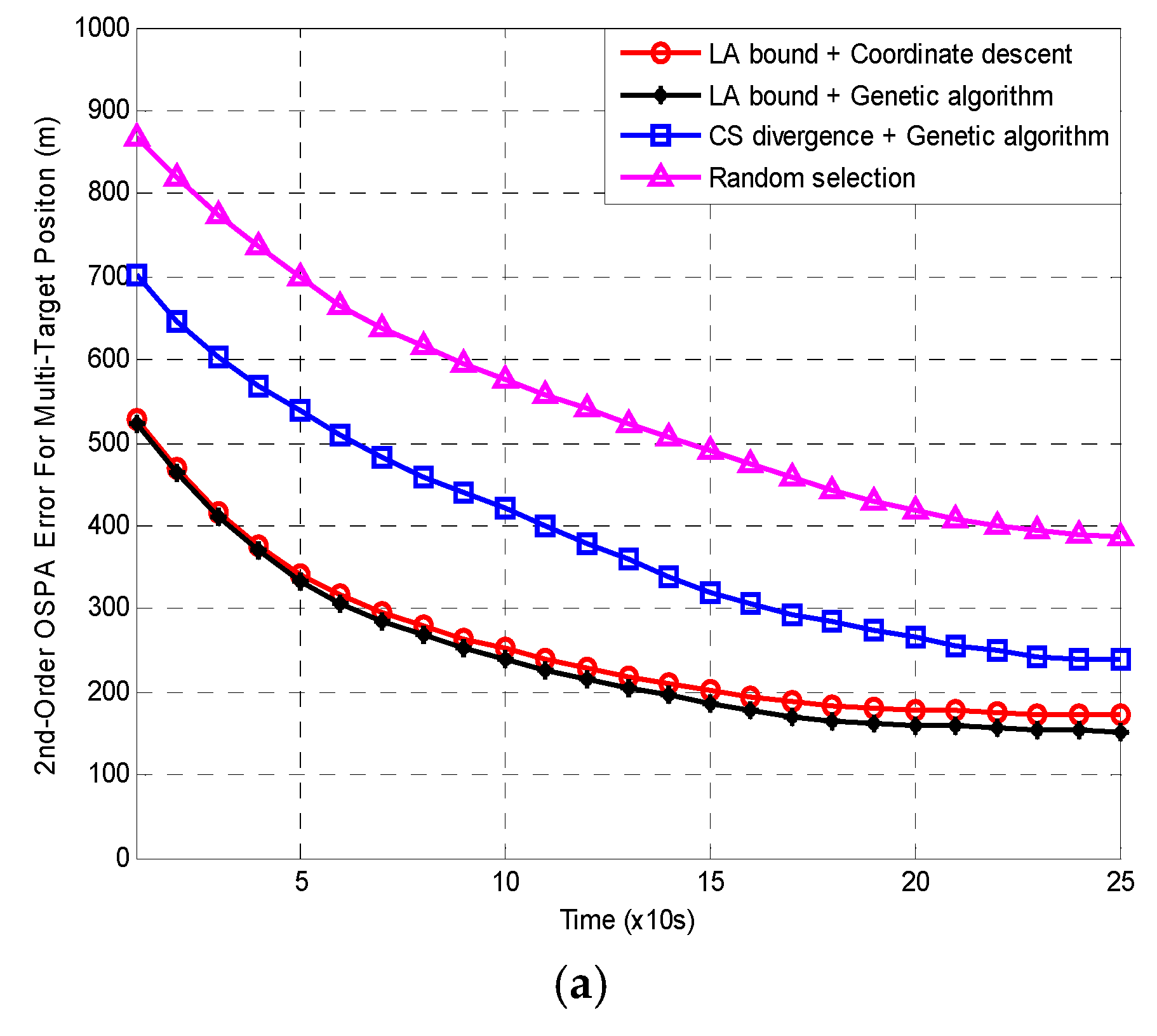
5. Simulations
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A.
Appendix B.
References
- Blackman, S.; Popoli, R. Design and Analysis of Modern Tracking Systems; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hero, A.O.; Castanón, D.A.; Cochran, D.; Kastella, K. Foundations and Applications of Sensor Management; Springler: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tharmarasa, R.; Kirubarajan, T.; Hernandez, M.L.; Sinha, A. PCRLB-based multisensor array management for multitarget tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharmarasa, R.; Kirubarajan, T.; Sinha, A.; Lang, T. Decentralized sensor selection for large-scale multisensor-multitarget tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 1307–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Ling, Q.; Tian, Z. Distributed sensor allocation for multi-target tracking in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 3538–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Asif, A. Decentralized computation of the conditional posterior Cramér-Rao lower bound: Application to adaptive sensor selection. In Proceedings of the 38th IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Herath, S.C.K.; Pathirana, P.N. Optimal sensor arrangements in angle of arrival (AoA) and range based localization with linear sensor arrays. Sensors 2013, 13, 12277–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, X.; Wang, P.; Zhu, Y. The Cramér-Rao bounds and sensor selection for nonlinear systems with uncertain observations. Sensors 2018, 18, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahler, R. Advances in Statistical Multisource-Multitarget Information Fusion; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, B.N.; Singh, S.; Doucet, A. Sequential Monte Carlo methods for multi-target filtering with random finite sets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2005, 41, 1224–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, B.N.; Ma, W.K. The Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4091–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Song, T.L. Improved bearings-only multi-target tracking with GM-PHD filtering. Sensors 2016, 16, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N.; Cantoni, A. Analytic implementations of the cardinalized probability hypothesis density filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 3553–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Wang, L.; Qu, Z. Multi-target tracking using an improved Gaussian mixture CPHD filter. Sensors 2016, 16, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N.; Cantoni, A. The cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter and its implementations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 409–423. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Liu, G. Cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter with error compensation. Sensors 2016, 16, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N. Labeled random finite sets and multi-object conjugate priors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 3460–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.N.; Vo, B.T.; Phung, D. Labeled random finite sets and the Bayes multi-target tracking filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 6554–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Lei, P.; Qi, Y. δ-generalized labeled multi-Bernoulli filter using amplitude information of neighboring cells. Sensors 2018, 18, 1153. [Google Scholar]
- Reuter, S.; Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N.; Dietmayer, K. The labeled multi-Bernoulli filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 3246–3260. [Google Scholar]
- Papi, F.; Vo, B.N.; Vo, B.T.; Fantacci, C.; Beard, M. Generalized labeled multi-Bernoulli approximation of multi-object densities. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 5487–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantacci, C.; Papi, F. Scalable multisensor multitarget tracking using the marginalized δ-GLMB density. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 2016, 23, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantacci, C.; Vo, B.N.; Vo, B.T.; Battistelli, G.; Chisci, L. Robust fusion for multisensor multiobject tracking. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 2018, 25, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.L. Marginal multi-Bernoulli filters: RFS derivation of MHT, JIPDA and association-based MeMBer. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 1664–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fernández Á, F.; Williams, J.L.; Granström, K.; Svensson, L. Poisson multi-Bernoulli mixture filter: Direct derivation and implementation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 1883–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granström, K.; Svensson, L.; Xia, Y.; Williams, J.; García-Femández Á, F. Poisson multi-Bernoulli mixture trackers: Continuity through random finite sets of trajectories. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Information Fusion, Cambridge, UK, 10–13 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ristic, B.; Vo, B.N. Sensor control for multi-object state-space estimation using random finite sets. Automatica 2010, 46, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.; Vo, B.N.; Clark, D. A note on the reward function for PHD filters with sensor control. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, H.G.; Vo, B.T. Sensor management for multi-target tracking via multi-Bernoulli filtering. Automatica 2014, 50, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostar, A.K.; Hoseinnezhad, R.; Bab-Hadiashar, A. Multi-Bernoulli sensor control via minimization of expected estimation errors. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, M.; Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N.; Arulampalam, S. Sensor control for multi-target tracking using Cauchy-Schwarz divergence. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Information Fusion, Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Yi, W.; Kong, L. Multi-sensor control for multi-target tracking using Cauchy-Schwarz divergence. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Information Fusion, Heidelberg, Germany, 5–8 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gostar, A.K.; Hoseinnezhad, R.; Rathnayake, T.; Wang, X.; Bab-Hadiashar, A. Constrained sensor control for labeled multi-Bernoulli filter using Cauchy-Schwarz divergence. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 2017, 24, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hoseinnezhad, R.; Gostar, A.K.; Rathnayake, T.; Xu, B.; Bab-Hadiashar, A. Multi-sensor control for multi-object Bayes filters. Signal Process. 2018, 14, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeian, M.; Vo, B.N. Error bounds for joint detection and estimation of a single object with random finite set observation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulampalam, S.; Maskell, S.; Gordon, N.J.; Clapp, T. A tutorial on particle filters for on-line non-linear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.J. Coordinate descent algorithms. Math. Program. 2015, 151, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristakeva, M.; Shrestha, D. Solving the 0-1 knapsack problem with genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 37th Midwest Instruction and Computing Symposium, Morris, MN, USA, 16–17 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schuhmacher, D.; Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N. A consistent metric for performance evaluation of multi-object filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 3447–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.; Vo, B.N.; Clark, D.; Vo, B.T. A metric for performance evaluation of multi-target tracking algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 3452–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmathullah, A.S.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.F.; Svensson, L. Generalized optimal sub-pattern assignment metric. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Information Fusion, Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Bose, N.K. Multitarget tracking in clutter: Fast algorithms for data association. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1993, 29, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistelli, G.; Chisci, L.; Fantacci, C.; Farina, A.; Graziano, A. Consensus CPHD filter for distributed multitarget tracking. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Sign. Proces. 2013, 7, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistelli, G.; Chisci, L. Kullback-Leibler average, consensus on probability densities and distributed state estimation with guaranteed stability. Automatica 2014, 50, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.J.; Rabinowitz, P.; Rheinbolt, W. Methods of Numerical Integration, 2nd Ed. ed; Mineola; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, B.D.; Moore, J.B. Optimal Filtering; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Julier, S.J.; Uhlmann, J.K. Unscented filtering and nonlinear estimation. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luenberger, D.G.; Ye, Y. Linear and Nonlinear Programming, 4th Ed. ed; Springer: New Yeak, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.R.; Jilkov, V.P. Survey of maneuvering target tracking, part V: Multiple-model methods. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2005, 41, 1255–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, B.N.; Vo, B.T.; Hoang, H.G. An efficient implementation of the generalized labeled multi-Bernoulli filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, M.; Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N. A solution for large-scale multi-object tracking. arXiv. 2018. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.06622 (accessed on 22 November 2018).




| Clutter rate and Detection Probability | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Selection Method | ||||||
| LA bound with coordinate descent | 171.3 | 193.0 | 218.9 | 249.1 | 283.7 | |
| LA bound with genetic algorithm | 151.9 | 170.8 | 193.6 | 220.5 | 251.6 | |
| CS divergence with genetic algorithm | 238.6 | 278.5 | 333.7 | 405.3 | 494.4 | |
| Random selection | 386.7 | 436.0 | 490.5 | 550.1 | 615.2 | |
| Clutter rate and Detection Probability | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Selection Method | ||||||
| LA bound with coordinate descent | 188.8 | 223.9 | 255.0 | 288.6 | 323.9 | |
| LA bound with genetic algorithm | 165.7 | 199.6 | 229.5 | 262.9 | 292.3 | |
| CS divergence with genetic algorithm | 260.1 | 321.2 | 383.9 | 463.9 | 562.8 | |
| Random selection | 426.7 | 500.5 | 564.3 | 634.2 | 710.9 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lian, F.; Hou, L.; Wei, B.; Han, C. Sensor Selection for Decentralized Large-Scale Multi-Target Tracking Network. Sensors 2018, 18, 4115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124115
Lian F, Hou L, Wei B, Han C. Sensor Selection for Decentralized Large-Scale Multi-Target Tracking Network. Sensors. 2018; 18(12):4115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124115
Chicago/Turabian StyleLian, Feng, Liming Hou, Bo Wei, and Chongzhao Han. 2018. "Sensor Selection for Decentralized Large-Scale Multi-Target Tracking Network" Sensors 18, no. 12: 4115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124115
APA StyleLian, F., Hou, L., Wei, B., & Han, C. (2018). Sensor Selection for Decentralized Large-Scale Multi-Target Tracking Network. Sensors, 18(12), 4115. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124115




