Three-Dimensional Imaging Method for Array ISAR Based on Sparse Bayesian Inference
Abstract
1. Introduction
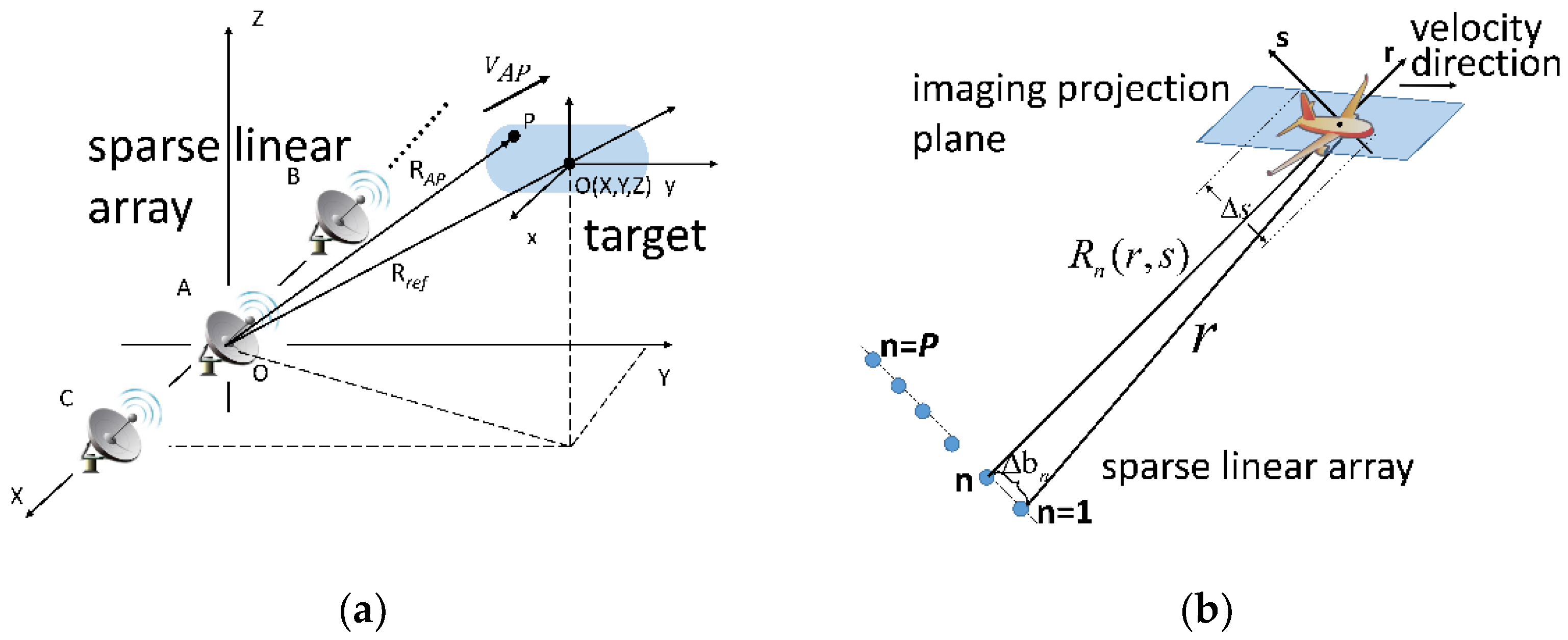
2. 3D Imaging Model of the Array ISAR System
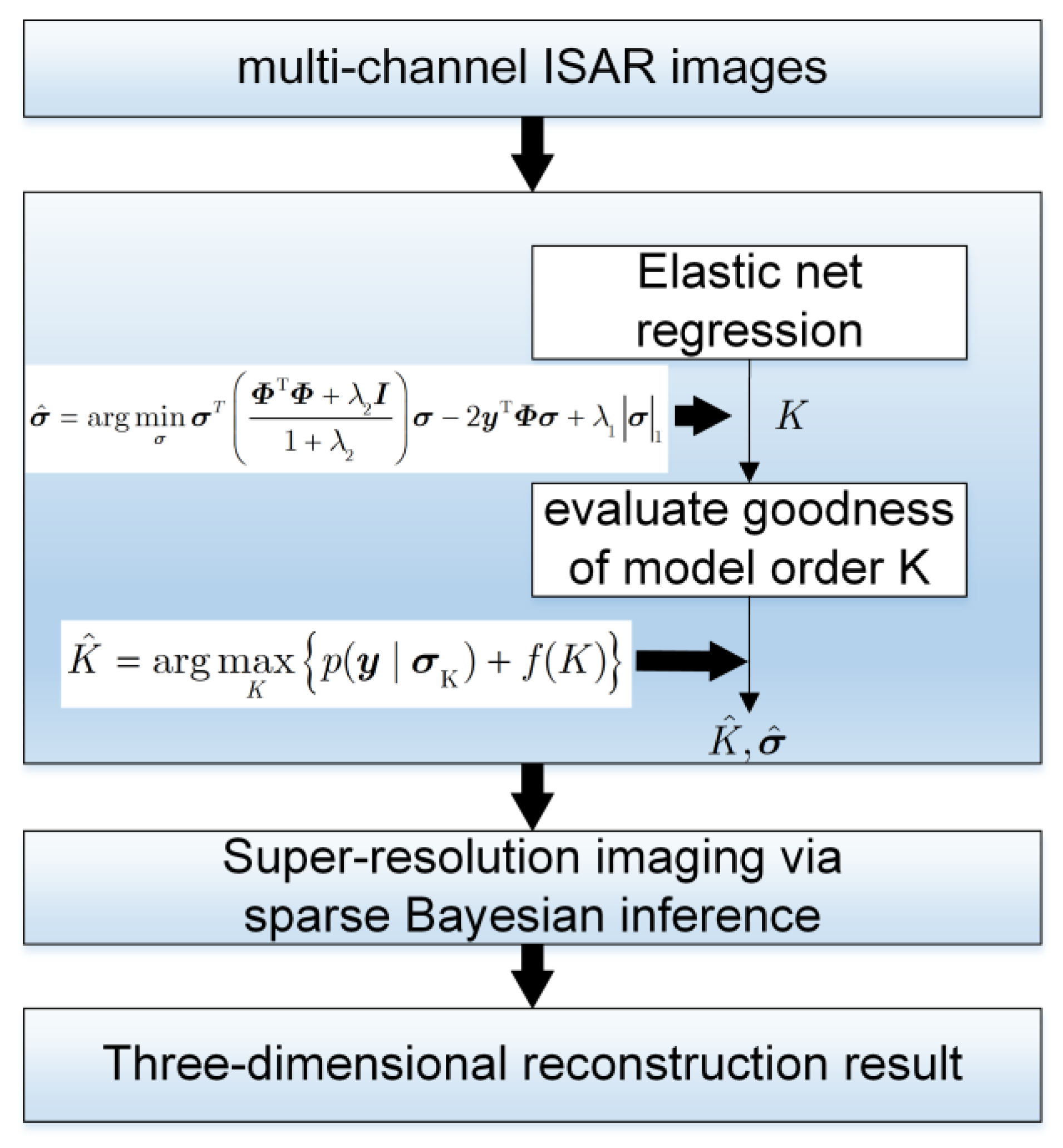
3. Array ISAR Three-Dimensional Imaging Method Based on SBI
3.1. Model Order Selection Based on Elastic Net Regression
3.2. 3D Reconstruction Based on Sparse Bayesian Inference
3.2.1. Elevation Reconstruction Model with Off-Grid Mismatch
3.2.2. 3D Reconstruction Algorithm Based on SBI
3.2.3. Bayesian Cramér-Rao Lower Bound for Proposed Method
4. Experimental Results
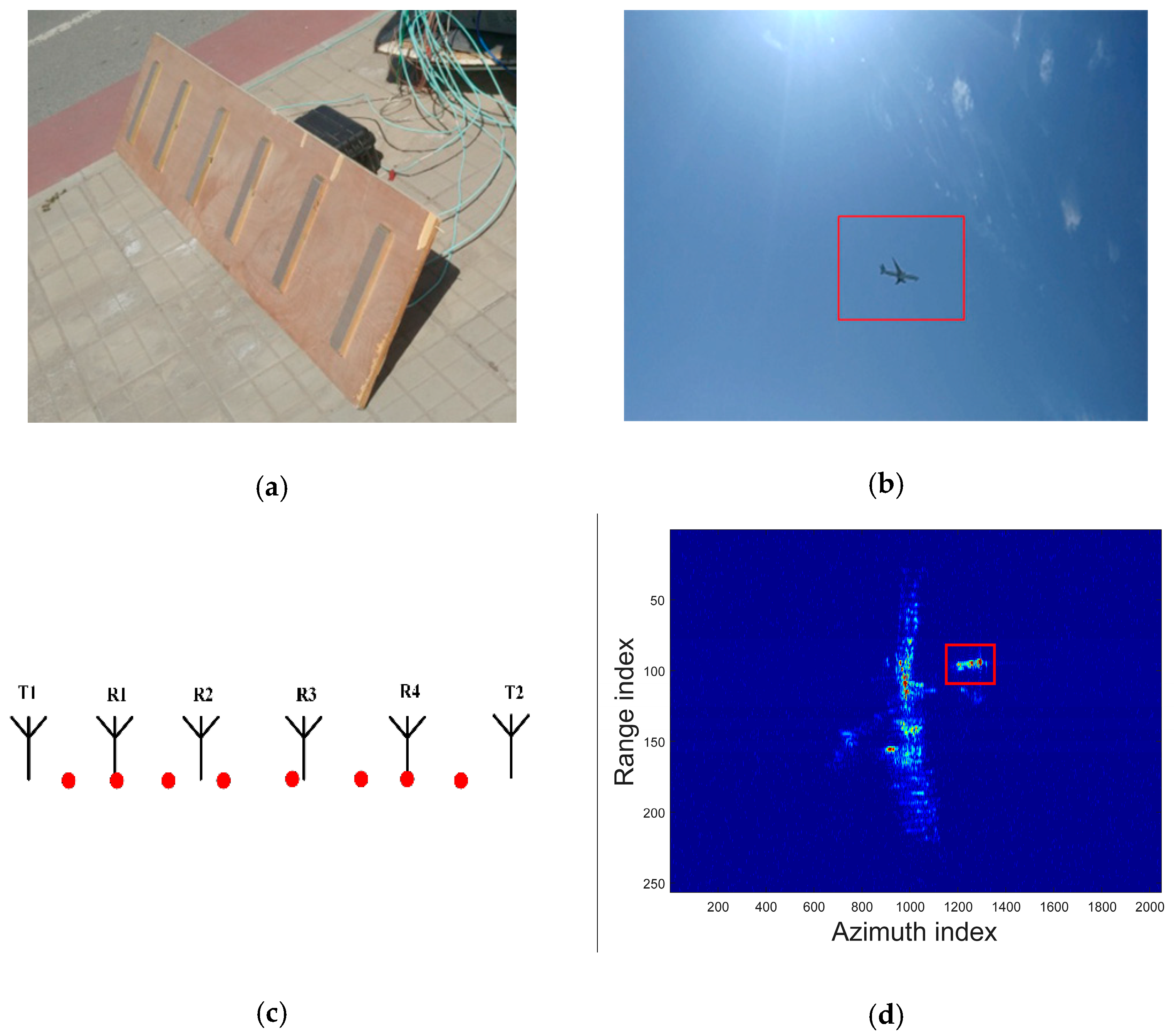
4.1. Array ISAR System Configuration and Model Selection
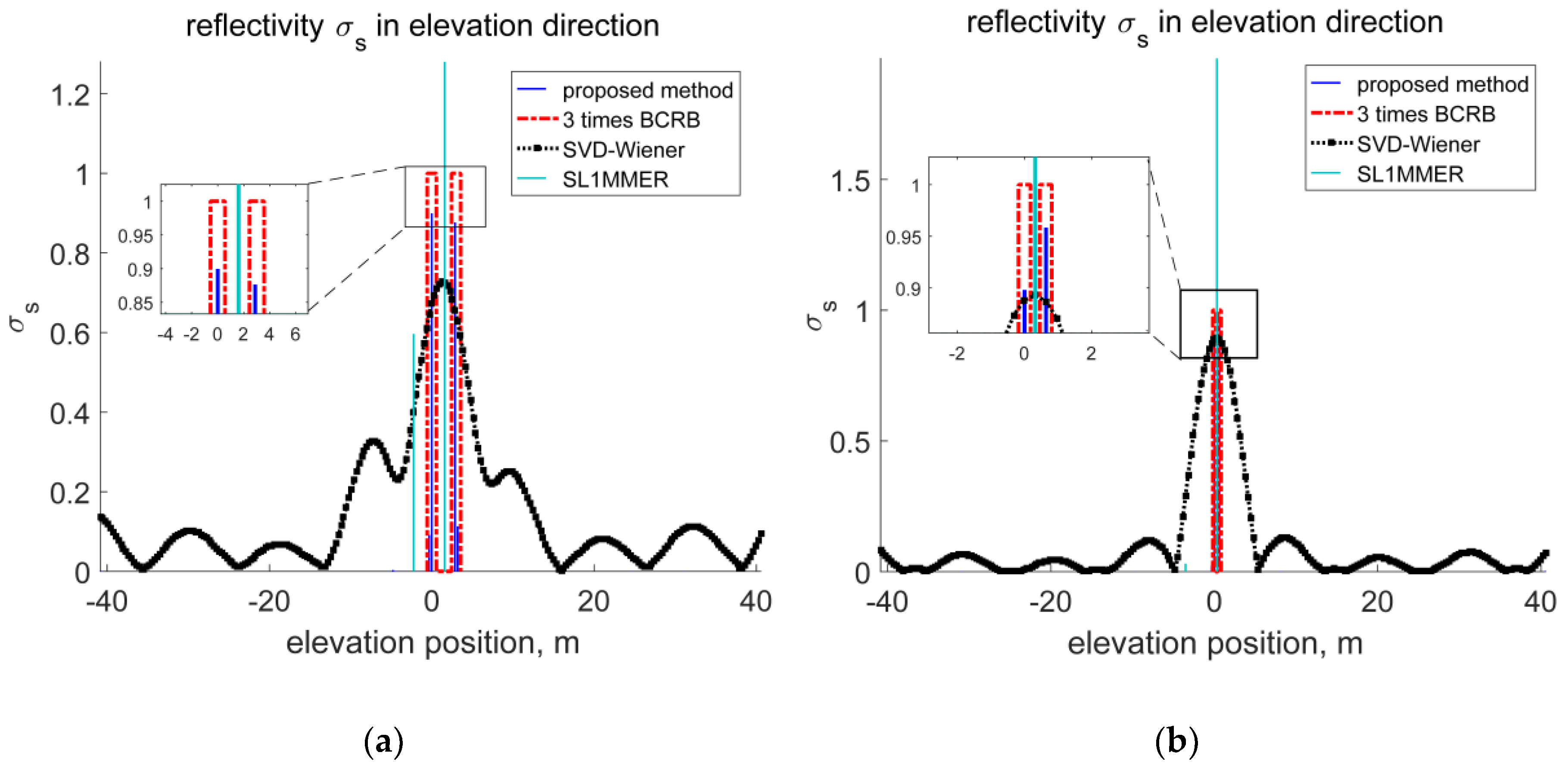
4.2. Performance Analysis with Simulations
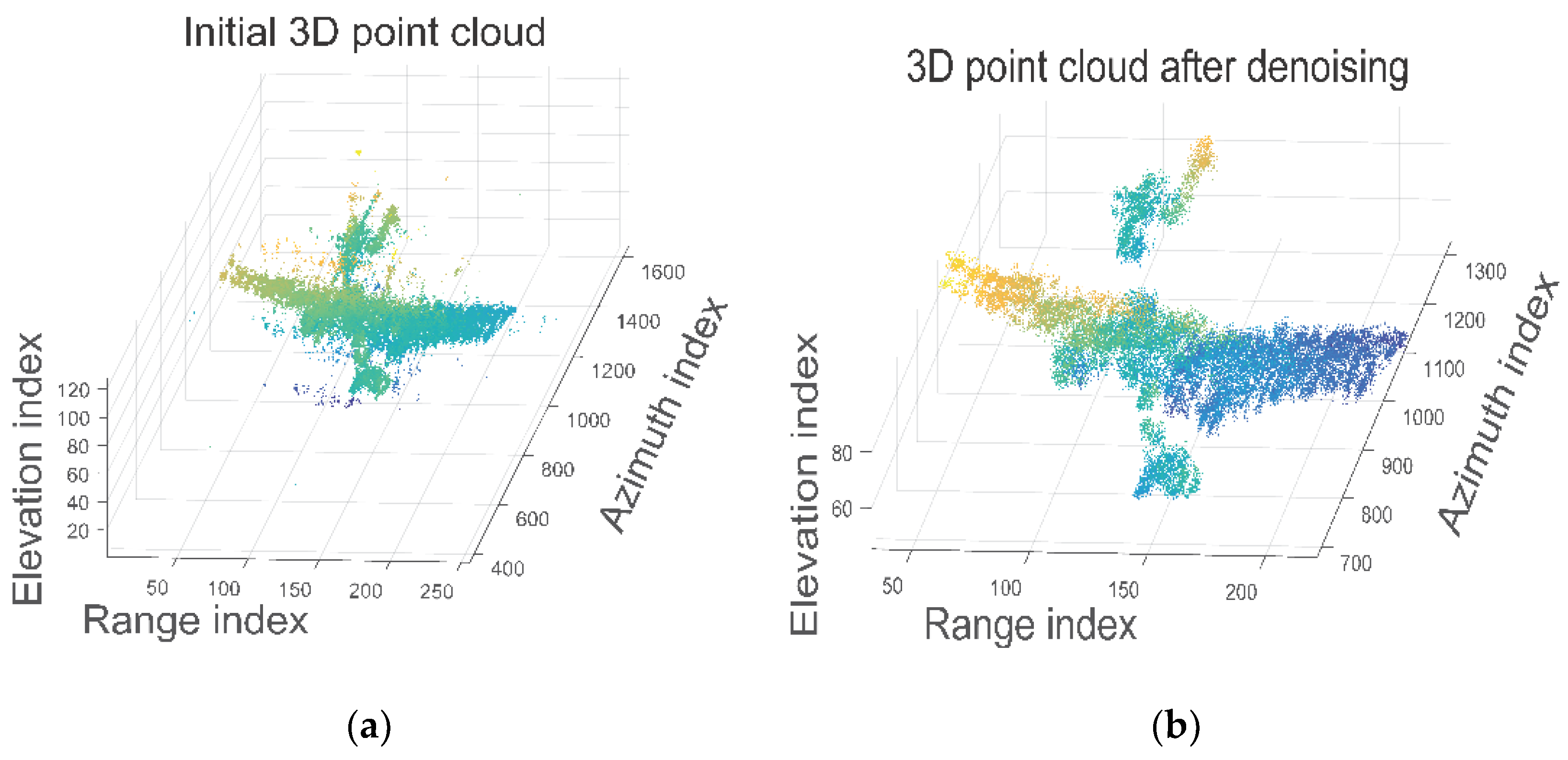
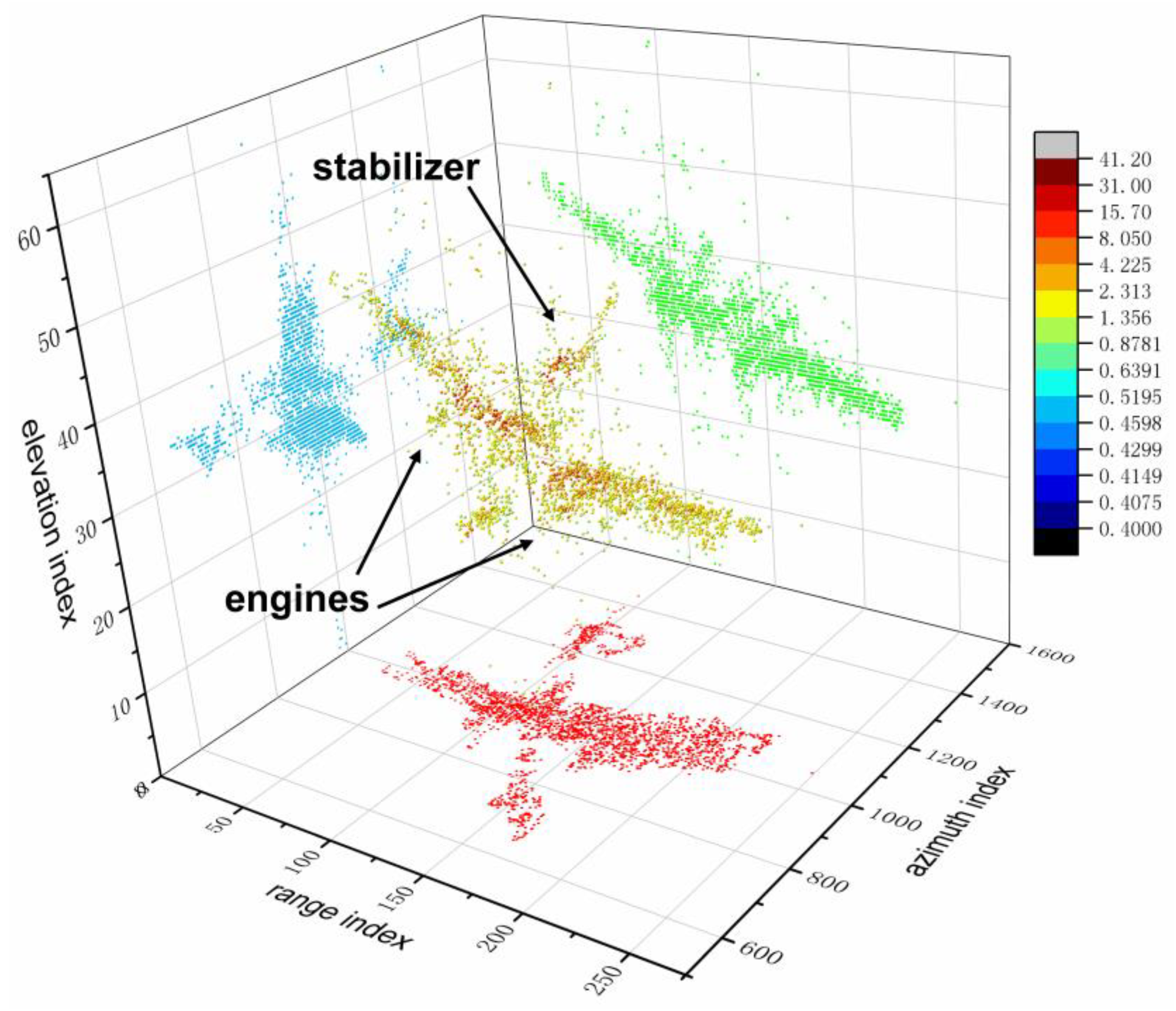
4.3. 3D Reconstruction Results Based on Measured Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, G.Q.; Wang, D.W.; Ma, X.Y.; Su, Y. Three-dimensional imaging via wideband MIMO radar system. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 7, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yeo, T.S.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, H.S.; Wang, J. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging based on antenna array. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wei, G.; Wu, S.; Wang, D. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging method for high-speed targets in short-range using impulse radar based on SIMO array. Sensors 2016, 16, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Yeo, T.S.; Tan, C.S.; Liu, Z. Three-dimensional imaging of targets using colocated MIMO radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3009–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Review on Interferometric ISAR 3D Imaging: Concept, Technology and Experiment. Signal Proc. 2018, 153, 164–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xia, X.G.; Chen, V.C. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets using three receivers. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Yeo, T.S.; Tan, C.S.; Tan, H.S. Sparse array 3-D ISAR imaging based on maximum likelihood estimation and CLEAN technique. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 2127–2142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Yeo, T.S.; Tan, H.S.; Wang, J.; Chen, B. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging using a two-dimensional sparse antenna array. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 378–382. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Yeo, T.S.; Tan, C.S.; Li, J.Y.; Shang, Y. Three-dimensional imaging using colocated MIMO radar and ISAR technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3189–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xing, M.; Xia, X.G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Bao, Z. 3D geometry and motion estimations of maneuvering targets for interferometric ISAR with sparse aperture. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 2005–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y. Achieving High-Quality Three-Dimensional InISAR Imageries of Maneuvering Target via Super-Resolution ISAR Imaging by Exploiting Sparseness. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 828–832. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z. Efficient Sampling Schemes for 3-D ISAR Imaging of Rotating Objects in Compact Antenna Test Range. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, F.A. New experiments in inverse synthetic aperture radar image exploitation for maritime surveillance. In Proceedings of the SPIE DEFENSE + SECURITY, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5–9 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Goyette, T.M.; Dickinson, J.C.; Waldman, J.; Nixon, W.E.; Carter, S. Fully polarimetric W-band ISAR imagery of scale-model tactical targets using a 1.56-THz compact range. In Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VIII; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; pp. 229–241. [Google Scholar]
- Goyette, T.M.; Dickinson, J.C.; Wetherbee, R.H.; Cook, J.D.; Gatesman, A.J.; Nixon, W.E. 3D radar imaging using interferometric ISAR. In Radar Sensor Technology XXII; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10633, p. 1063303. [Google Scholar]
- Martorella, M.; Stagliano, D.; Salvetti, F.; Battisti, N. 3D interferometric ISAR imaging of noncooperative targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 3102–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, T. Ship 3D model estimation from an ISAR image sequence. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, Australia, 3–5 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, T.; Martorella, M.; Haywood, B.; Gibbins, D. Use of 3D ship scatterer models from ISAR image sequences for target recognition. Digit. Signal Prog. 2006, 16, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Three-dimensional reconstruction from a multiview sequence of sparse ISAR imaging of a space target. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwa, K.; Wakayama, T.; Iwamoto, M. Three-dimensional target geometry and target motion estimation method using multistatic ISAR movies and its performance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2361–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. 3-D information of a space target retrieved from a sequence of high-resolution 2-D ISAR images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Qiao, Z.; Hu, M. Attitude estimation of space targets by extracting line features from ISAR image sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Xiamen, China, 22–25 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, B.D.; Kanade, T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 August 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi, C.; Kanade, T. Shape and motion from image streams under orthography: A factorization method. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1992, 9, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, F.; Bai, X.R.; Tao, M.L.; Zhang, Z.J. Joint cross-range scaling and 3D geometry reconstruction of ISAR targets based on factorization method. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1-norm regularization—The compressive sensing approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3839–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2005, 67, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieze, S.I. Model selection and psychological theory: A discussion of the differences between the Akaike information criterion (AIC) and the Bayesian information criterion (BIC). Psychol. Methods 2012, 17, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L.; Zhang, C. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liang, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, X. 3D surface reconstruction of layover areas in continuous terrain for multi-baseline SAR interferometry using a curve model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 2093–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Kucukelbir, A.; McAuliffe, J.D. Variational inference: A review for statisticians. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2017, 112, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Murthy, C.R. Cramér-Rao-type bounds for sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 4296–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Z.; Gray, D.A.; Bogner, R.E.; Homer, J.; Longstaff, I.D. Three-dimensional space-borne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging with multiple pass processing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 4357–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaochun, X.; Yunhua, Z. 3D ISAR imaging based on MIMO radar array. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xi’an, China, 26–30 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. An efficient tomographic inversion approach for urban mapping using meter resolution SAR image stacks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Ge, N.; Shahzad, M. Joint sparsity in SAR tomography for urban mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Jiang, C.; Lin, Y.; Tan, W.; Wang, Z.; Hong, W. Measurement matrix optimization and mismatch problem compensation for DLSLA 3-D SAR cross-track reconstruction. Sensors 2016, 16, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | fc | 15 GHz |
| Bandwidth | Bw | 500 MHz |
| Pulse repetition frequency | PRF | 1 KHz |
| Velocity of plane | v | 63.5 m/s |
| Reference range | Rref | 836.4 m |
| Number of APCs | P | 8 |
| Maximum baseline | 1.31 m |
| Zero-Order | 1st Order | 2nd Order | 3rd Order | 4th Order | 5th Order | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P*SNR | −10.091 | 1.0498 | 0.099758 | −0.011345 | 2.8687 × 10−4 | 0 |
| Phase error | 25.083 | −14.242 | 3.797 | −0.17337 | −0.097998 | 0.012569 |
| Amplitude error | 31.017 | −35.754 | 13.942 | −0.55709 | −0.71587 | 0.10677 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, Z.; Ding, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F. Three-Dimensional Imaging Method for Array ISAR Based on Sparse Bayesian Inference. Sensors 2018, 18, 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103563
Jiao Z, Ding C, Chen L, Zhang F. Three-Dimensional Imaging Method for Array ISAR Based on Sparse Bayesian Inference. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103563
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Zekun, Chibiao Ding, Longyong Chen, and Fubo Zhang. 2018. "Three-Dimensional Imaging Method for Array ISAR Based on Sparse Bayesian Inference" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103563
APA StyleJiao, Z., Ding, C., Chen, L., & Zhang, F. (2018). Three-Dimensional Imaging Method for Array ISAR Based on Sparse Bayesian Inference. Sensors, 18(10), 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103563





