Does RAIM with Correct Exclusion Produce Unbiased Positions?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Estimation and Testing
2.1. Estimation
2.2. Testing
3. Estimation Bias Due to Testing
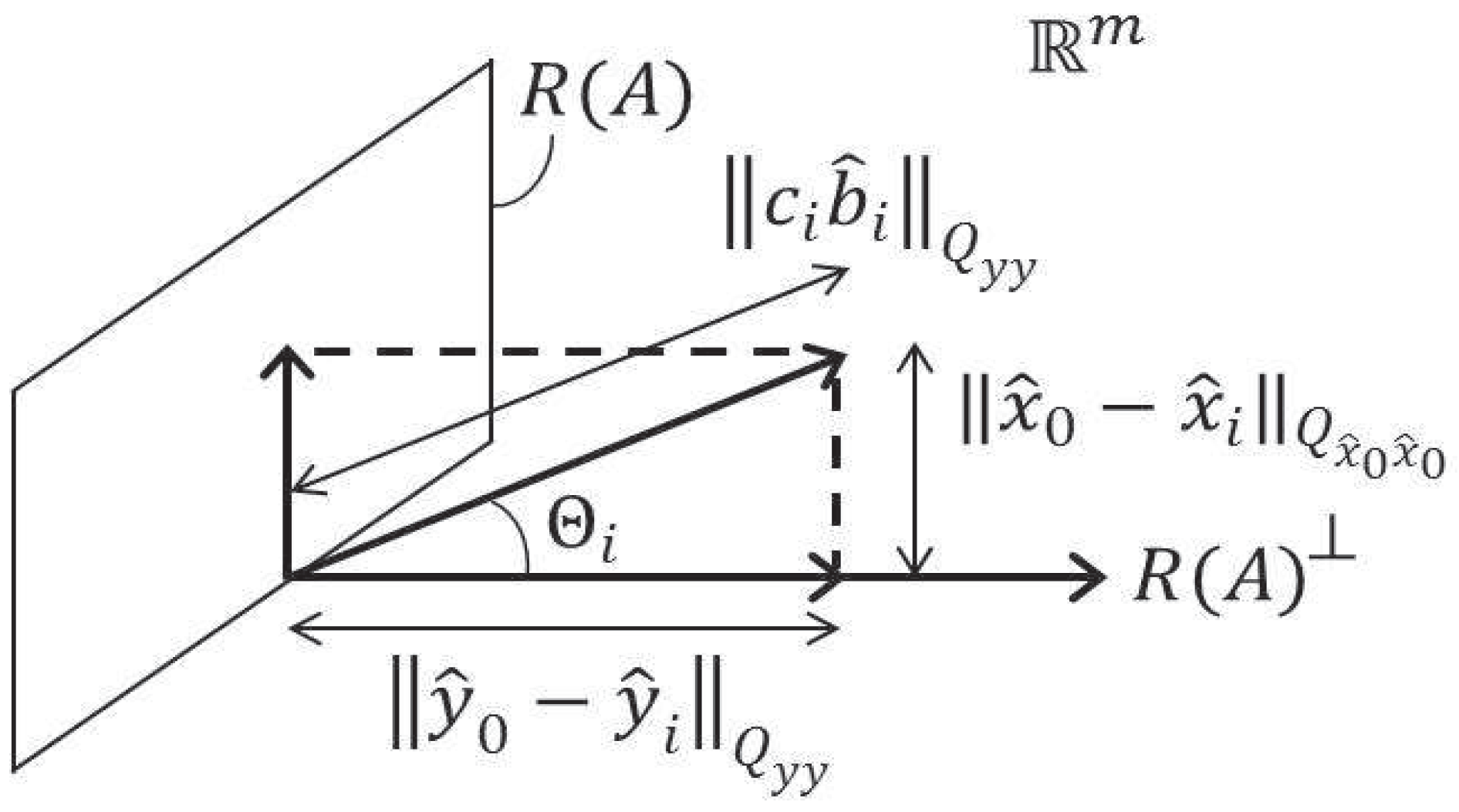
3.1. The Estimator Revisited
3.2. The One-Dimensional Case
3.3. The Conditional Mean
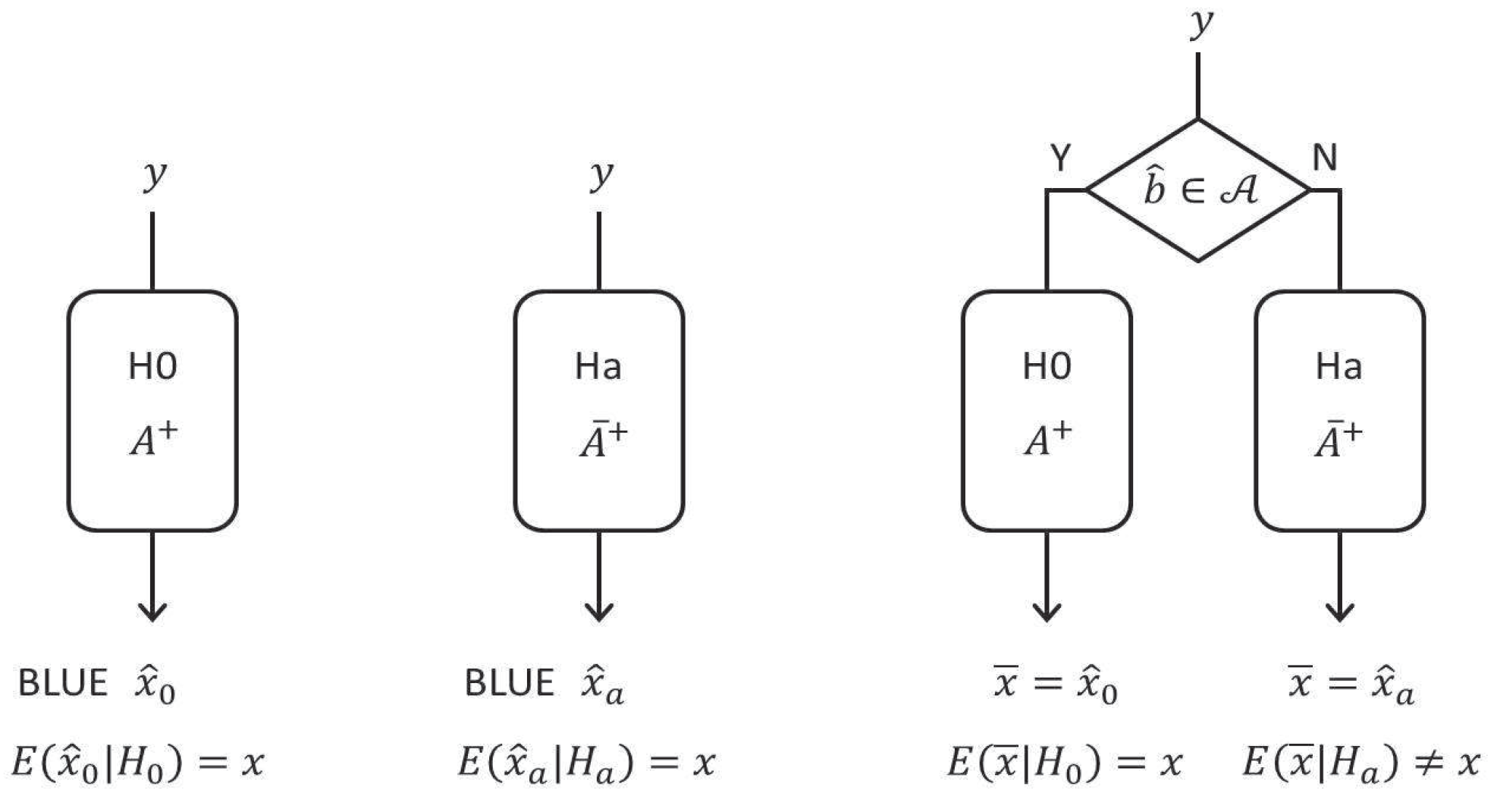
4. Multiple Alternative Hypotheses
4.1. Test Procedure
4.2. Alternative Statistics
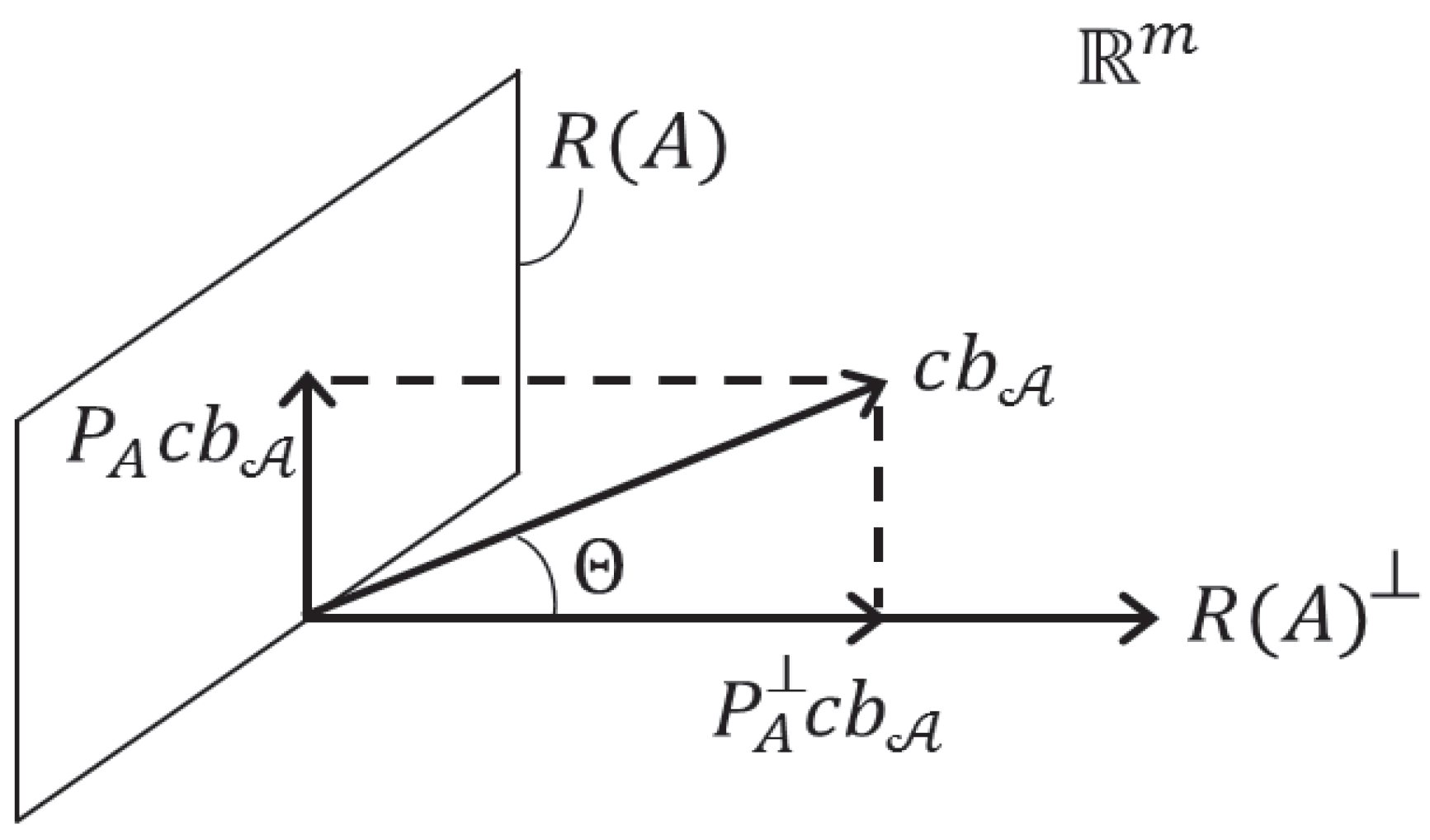
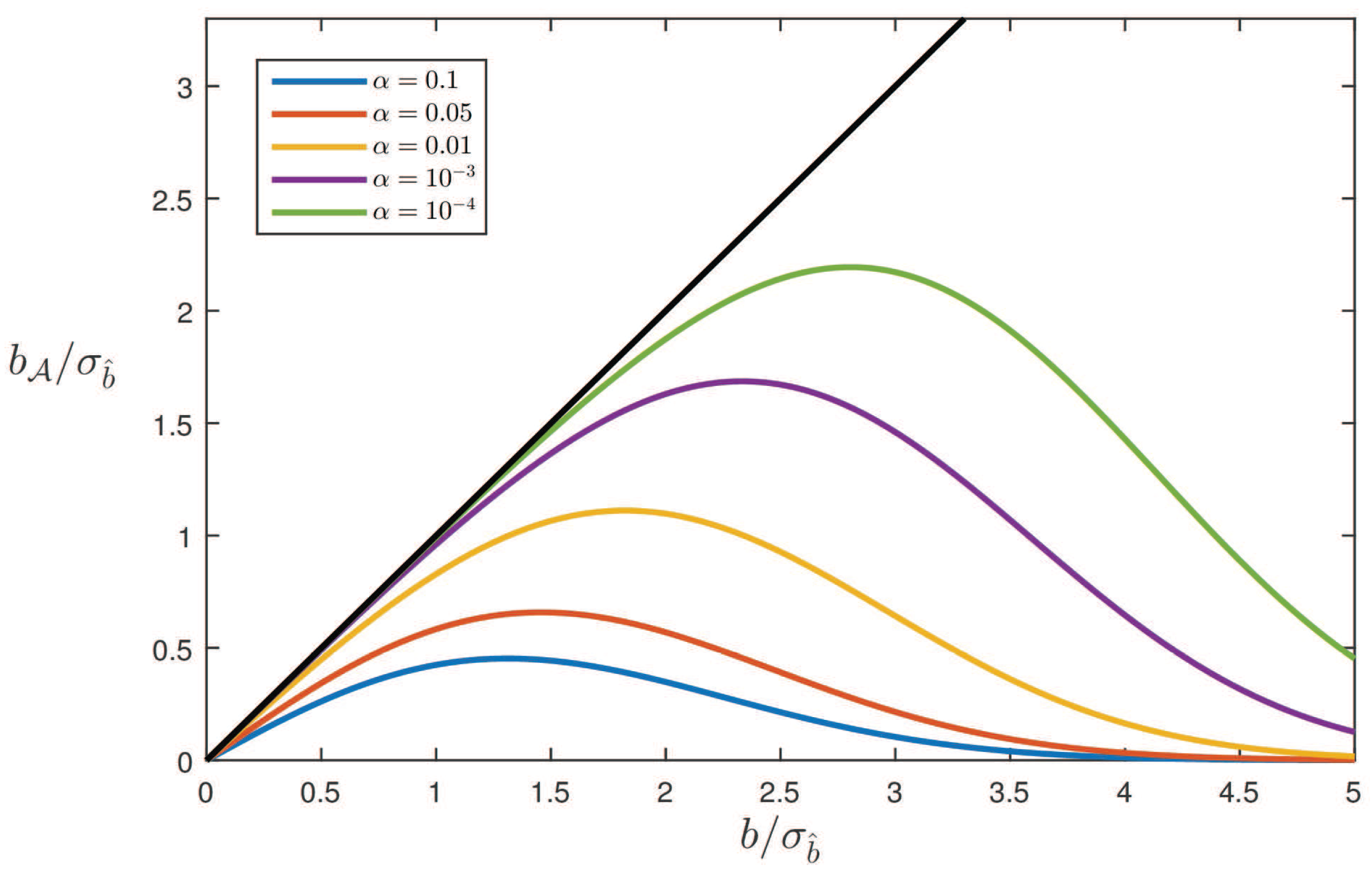
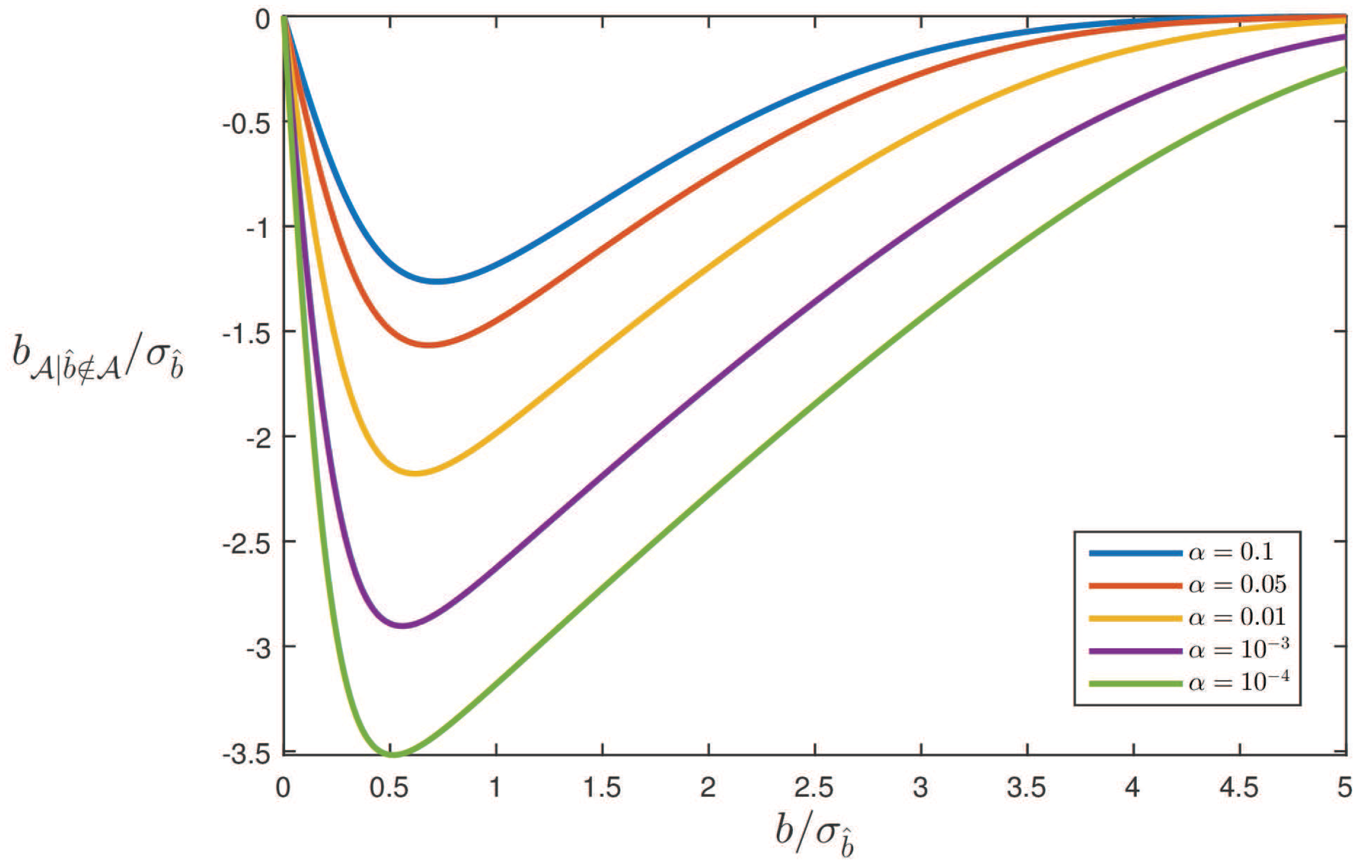
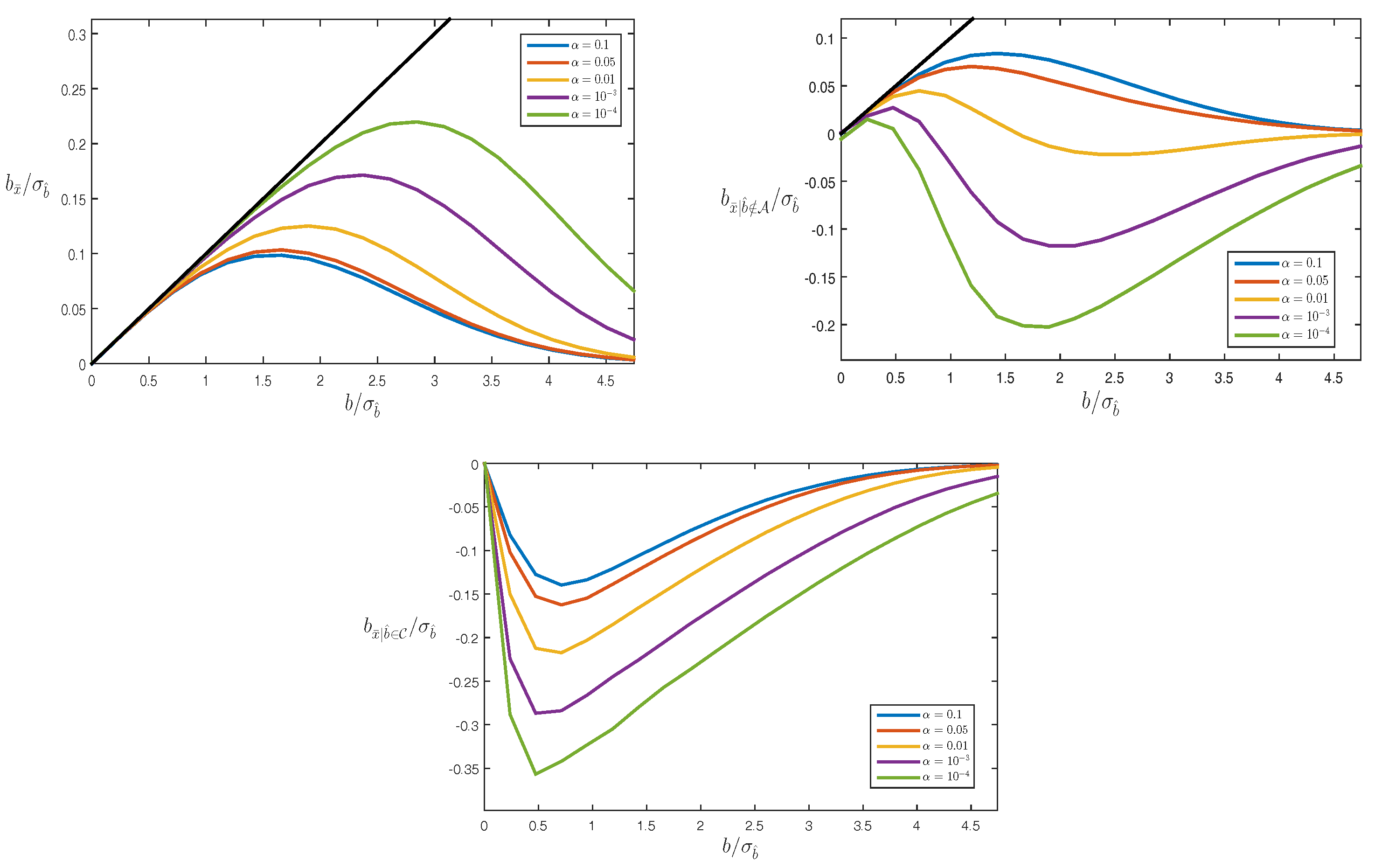
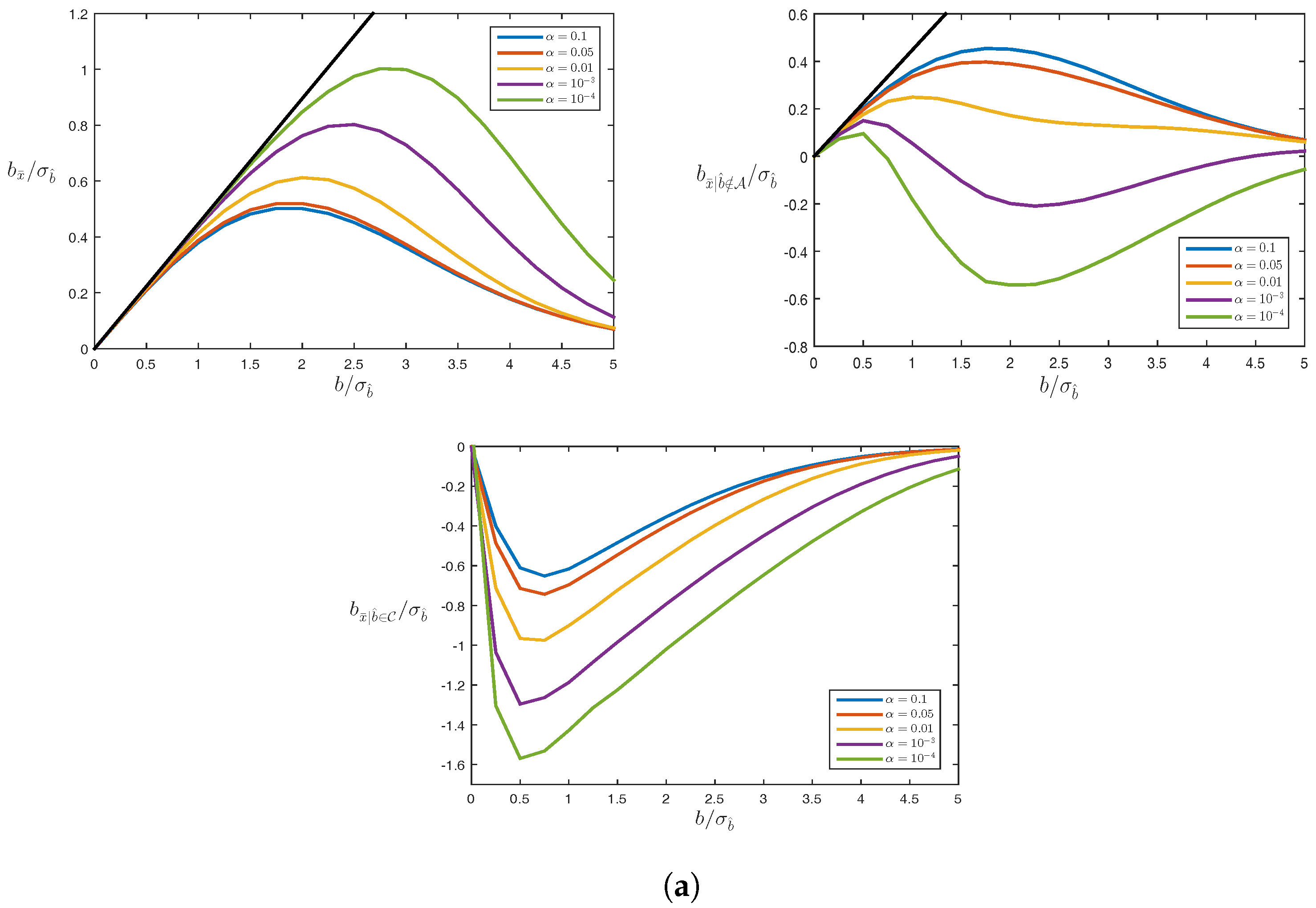
4.3. Biases
Example: Averaging
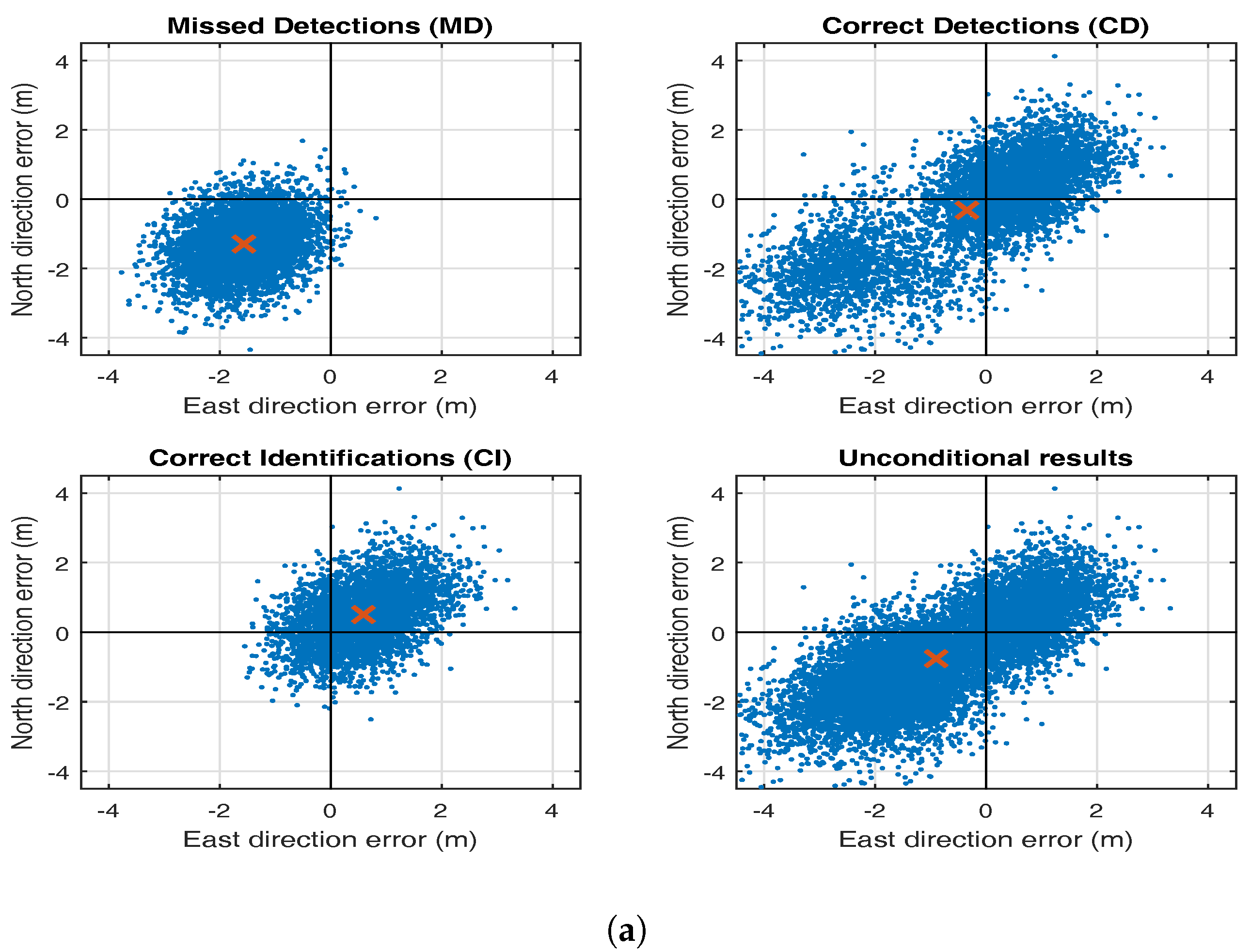
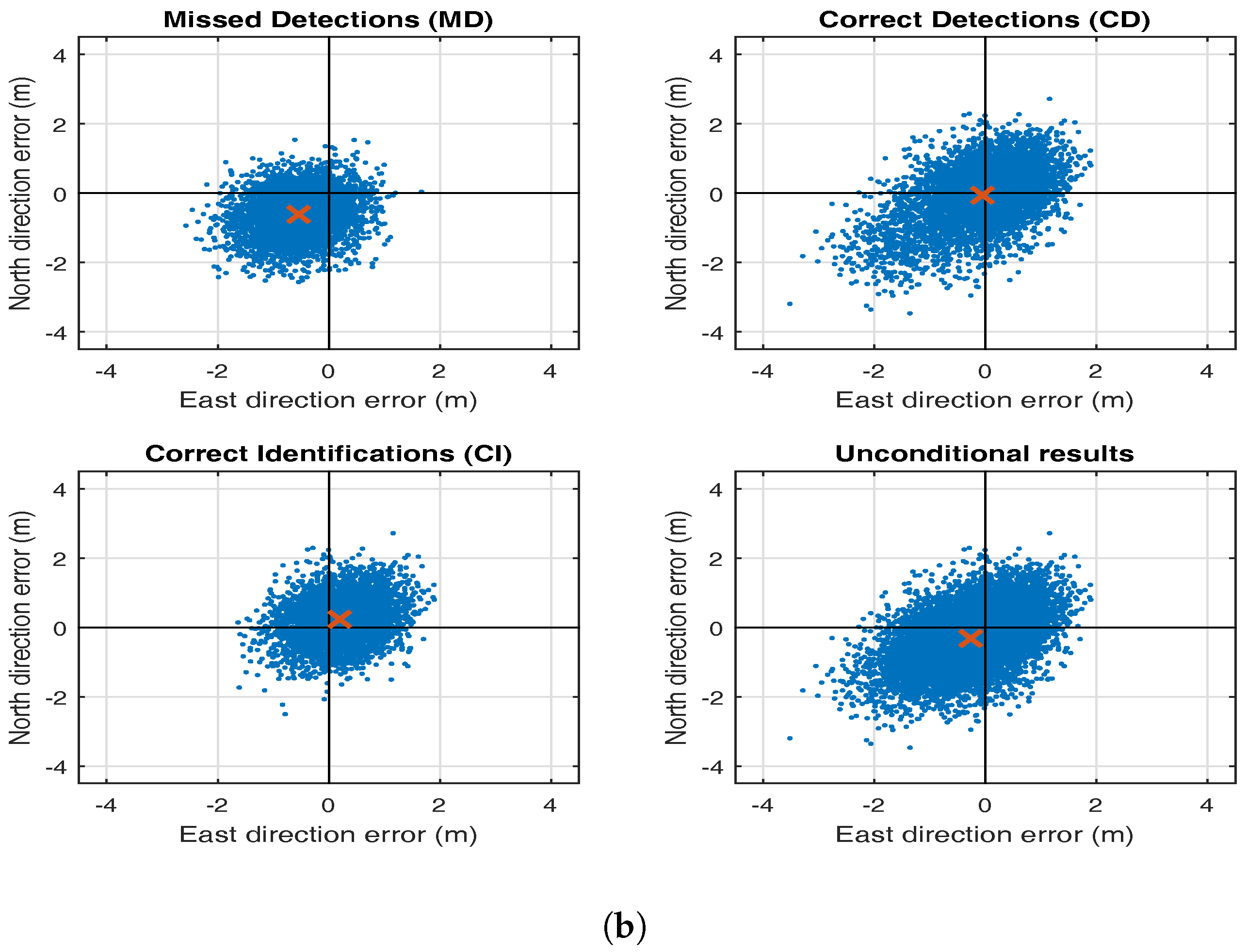
5. Testing Bias in RAIM
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, Y.C. Analysis of range and position comparison methods as a means to provide GPS integrity in the user receiver. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, Seattle, WA, USA, 24–26 June 1986; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, B.W.; Axelrad, P. Autonomous GPS integrity monitoring using the pseudorange residual. NAVIGATION 1988, 35, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturza, M. Navigation system integrity monitoring using redundant measurements. NAVIGATION 1988, 35, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, T.; Enge, P. Weighted RAIM for precision approach. In Proceedings of the ION GPS-95, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 12–15 September 1995; pp. 1995–2004. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. An integrity and quality control procedure for use in multi sensor integration. In Proceedings of the ION GPS-1990, Colorado Spring, CO, USA, 19–21 September 1990; Republished in ION Red Book Series. Volume 7, pp. 513–522. [Google Scholar]
- Powe, M.; Owen, J. A flexible RAIM algorithm. In Proceedings of the ION GPS 1997, Kansas City, MO, USA, 16–19 September 1997; pp. 439–449. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Testing Theory: An Introduction; Series on Mathematical Geodesy and Positioning; Delft University Press: Delft, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Joerger, M.; Chan, F.C.; Pervan, B. Solution Separation Versus Residual-Based RAIM. NAVIGATION 2014, 61, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerger, M.; Pervan, B. Fault detection and exclusion using solution separation and chi-squared ARAIM. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 726–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.S.Y.; McGraw, G.A. Fault Detection and Exclusion Using Normalized Solution Separation and Residual Monitoring Methods. NAVIGATION 2003, 50, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervan, B.; Pullen, S.; Christie, J. A Multiple Hypothesis Approach to Satellite Navigation Integrity. NAVIGATION 1998, 45, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokalp, E.; Gungor, O.; Boz, Y. Evaluation of Different Outlier Detection Methods for GPS Networks. Sensors 2008, 8, 7344–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Cao, X.; Wang, J. Vision-Aided RAIM: A New Method for GPS Integrity Monitoring in Approach and Landing Phase. Sensors 2015, 15, 22854–22873. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Shu, B.; Xu, L.; Zhang, R. A Geometry-Based Cycle Slip Detection and Repair Method with Time-Differenced Carrier Phase (TDCP) for a Single Frequency Global Position System (GPS) + BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) Receiver. Sensors 2016, 16, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borio, D.; Gioia, C. Galileo: The Added Value for Integrity in Harsh Environments. Sensors 2016, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zair, S.; Hégarat-Mascle, S.; Seignez, E. Outlier Detection in GNSS Pseudo-Range/Doppler Measurements for Robust Localization. Sensors 2016, 16, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, B.; Shen, Y.; Rizos, C. Extension of Internal Reliability Analysis Regarding Separability Analysis. J. Surv. Eng. 2017, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh-Nejad, F.; Amiri-Simkooei, A.; Sharifi, M.; Asgari, J. Cycle slip detection and repair of undifferenced single-frequency GPS carrier phase observations. GPS Solut. 2017, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.; Gu, Y.; Kamijo, S. NLOS Correction/Exclusion for GNSS Measurement Using RAIM and City Building Models. Sensors 2015, 15, 17329–17349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S. The Theory of Linear Models and Multivariate Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Imparato, D. GNSS Based Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring for Aircraft Navigation; TU Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teunissen, P.J.G.; Imparato, D.; Tiberius, C.C.J.M. Does RAIM with Correct Exclusion Produce Unbiased Positions? Sensors 2017, 17, 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071508
Teunissen PJG, Imparato D, Tiberius CCJM. Does RAIM with Correct Exclusion Produce Unbiased Positions? Sensors. 2017; 17(7):1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071508
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeunissen, Peter J. G., Davide Imparato, and Christian C. J. M. Tiberius. 2017. "Does RAIM with Correct Exclusion Produce Unbiased Positions?" Sensors 17, no. 7: 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071508
APA StyleTeunissen, P. J. G., Imparato, D., & Tiberius, C. C. J. M. (2017). Does RAIM with Correct Exclusion Produce Unbiased Positions? Sensors, 17(7), 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071508





