Electronic Nose Breathprints Are Independent of Acute Changes in Airway Caliber in Asthma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Methacholine and sham challenges
2.4. Exhaled breath collection and electronic nose sampling
2.5. Data analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Study population
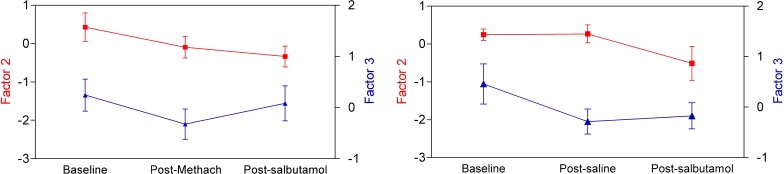
3.2. Methacholine and sham challenges modify breathprints
3.4. Breathprints do not show between-day variability in asthma patients
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- National Heart and Lung Institute, National Institutes of Health USA, and the World Health Organization. Global Initiative for Asthma. December 2008. Update. Available at: http://www.ginasthma.org/ (accessed on 20 September 2010).
- Green, RH; Brightling, CE; McKenna, S; Hargadon, B; Parker, D; Bradding, P; Wardlaw, AJ; Pavord, ID. Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 360, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, AD; Cowan, JO; Brassett, KP; Herbison, GP; Taylor, DR. Use of exhaled nitric oxide measurements to guide treatment in chronic asthma. New Engl. J. Med 2005, 352, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, B; Bodrogi, F; Eibl, G; Lechner, M; Rieder, J; Lirk, P. Mass spectrometric profile of exhaled breath--field study by PTR-MS. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol 2005, 145, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Van Berkel, JJ; Dallinga, JW; Moller, GM; Godschalk, RW; Moonen, E; Wouters, EF; Van Schooten, FJ. Development of accurate classification method based on the analysis of volatile organic compounds from human exhaled air. J. Chromat 2008, 861, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, M; Cataneo, RN; Cummin, AR; Gagliardi, AJ; Gleeson, K; Greenberg, J; Maxfield, RA; Rom, WN. Detection of lung cancer with volatile markers in the breath. Chest 2003, 123, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar]
- Westhoff, M; Litterst, P; Freitag, L; Urfer, W; Bader, S; Baumbach, JI. Ion mobility spectrometry for the detection of volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath of patients with lung cancer: Results of a pilot study. Thorax 2009, 64, 744–748. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, NS. Comparisons between mammalian and artificial olfaction based on arrays of carbon black-polymer composite vapor detectors. Acc. Chem. Res 2004, 37, 663–672. [Google Scholar]
- Röck, F; Barsan, N; Weimar, U. Electronic nose: current status and future trends. Chem. Rev 2008, 108, 705–725. [Google Scholar]
- Hockstein, NG; Thaler, ER; Lin, Y; Lee, DD; Hanson, CW. Correlation of pneumonia score with electronic nose signature: A prospective study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol 2005, 114, 504–508. [Google Scholar]
- Dragonieri, S; Annema, JT; Schot, R; van der Schee, MP; Spanevello, A; Carratu, P; Resta, O; Rabe, KF; Sterk, PJ. An electronic nose in the discrimination of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and COPD. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 2009, 64, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Dragonieri, S; Schot, R; Mertens, BJ; Le Cessie, S; Gauw, SA; Spanevello, A; Resta, O; Willard, NP; Vink, TJ; Rabe, KF; Bel, EH; Sterk, PJ. An electronic nose in the discrimination of patients with asthma and controls. J. Allergy Clinical Immunol 2007, 120, 856–862. [Google Scholar]
- Fens, N; Zwinderman, AH; van der Schee, MP; de Nijs, SB; Dijkers, E; Roldaan, AC; Cheung, D; Bel, EH; Sterk, PJ. Exhaled breath profiling enables discrimination of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Amer. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 2009, 180, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G; Tisch, U; Adams, O; Hakim, M; Shehada, N; Broza, YY; Billan, S; Abdah-Bortnyak, R; Kuten, A; Haick, H. Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nature Nanotechnol 2009, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar]
- Montuschi, P; Santonico, M; Mondino, C; Pennazza, G; Mantini, G; Martinelli, E; Capuano, R; Ciabattoni, G; Paolesse, R; Di Natale, C; Barnes, PJ; D'Amico, A. Diagnostic performance of an electronic nose, fractional exhaled nitric oxide, and lung function testing in asthma. Chest 2010, 137, 790–796. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, MJ. Scientists seek to sniff out diseases: electronic “noses” may someday be diagnostic tools. JAMA 2009, 301, 585–586. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, I; Lazar, Z; Gyulai, N; Kollai, M; Losonczy, G. Exhaled biomarkers in lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J 2009, 34, 261–275. [Google Scholar]
- de Gouw, HW; Hendriks, J; Woltman, AM; Twiss, IM; Sterk, PJ. Exhaled nitric oxide (NO) is reduced shortly after bronchoconstriction to direct and indirect stimuli in asthma. Amer. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 1998, 158, 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, LP; Wood, FT; Robson, A; Innes, JA; Greening, AP. The current single exhalation method of measuring exhales nitric oxide is affected by airway calibre. Eur. Respir. J 2000, 15, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Kharitonov, SA; Sapienza, MA; Barnes, PJ; Chung, KF. Prostaglandins E2 and F2alpha reduce exhaled nitric oxide in normal and asthmatic subjects irrespective of airway caliber changes. Amer. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 1998, 158, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Boot, JD; Tarasevych, S; Sterk, PJ; Schoemaker, RC; Wang, L; Amin, D; Cohen, AF; Diamant, Z. Reversal of the late asthmatic response increases exhaled nitric oxide. Respir. Med 2005, 99, 1591–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Garnier, P; Fajac, I; Dessanges, JF; Dall'Ava-Santucci, J; Lockhart, A; Dinh-Xuan, AT. Exhaled nitric oxide during acute changes of airways calibre in asthma. Eur. Respir. J 1996, 9, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Sterk, PJ; Fabbri, LM; Quanjer, PH; Cockcroft, DW; O'Byrne, PM; Anderson, SD; Juniper, EF; Malo, JL. Airway responsiveness: Standardized challenge testing with pharmacological, physical and sensitizing stimuli in adults. Eur. Repir. J 1993, 16, 53–83. [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch, H; Turner, C; Spooner, A; Chambers, M. Methodological variation in headspace analysis of liquid samples using electronic nose. Sens. Actuat. B: Chem 2009, 139, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Tabary, O; Escotte, S; Couetil, JP; Hubert, D; Dusser, D; Puchelle, E; Jacquot, J. High susceptibility for cystic fibrosis human airway gland cells to produce IL-8 through the I kappa B kinase alpha pathway in response to extracellular NaCl content. J. Immunol 2000, 164, 3377–3384. [Google Scholar]




| Patient Number | Sex | Age, years | Daily ICS (bud eq, μg) | Baseline FVC, % predicted | Baseline FEV1, % predicted | Baseline FEV1/FVC | PC20 MCh, mg/mL | FEV1 change at Visit1& | FEV1 change at Visit2& | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC20 MCh | Post-salb | Post-saline | Post-salb | ||||||||
| 1 | F | 33 | 400 | 102 | 89 | 0.76 | 12.93 | −26 | 0 | −4 | +6 |
| 2 | F | 27 | 800 | 119 | 104 | 0.77 | 5.18 | −54 | −7 | −1 | +13 |
| 3 | M | 29 | 400 | 99 | 82 | 0.71 | 0.22 | −24 | 0 | −6 | 0 |
| 4 | M | 35 | 200 | 129 | 106 | 0.67 | 6.93 | −24 | +7 | −11 | +2 |
| 5 | M | 47 | 200 | 128 | 84 | 0.53 | 0.76 | −28 | +7 | −8 | +11 |
| 6 | F | 33 | 0 | 108 | 98 | 0.80 | 1.33 | −39 | 0 | −1 | +10 |
| 7 | F | 23 | 200 | 103 | 101 | 0.85 | 3.13 | −36 | −1 | 0 | −3 |
| 8 | F | 30 | 0 | 106 | 92 | 0.85 | 0.31 | −20 | +7 | −1 | +11 |
| 9 | M | 30 | 800 | 88 | 72 | 0.67 | 0.58 | −21 | −1 | −4 | +11 |
| 10 | F | 45 | 200 | 87 | 79 | 0.78 | 1.39 | −26 | −4 | −3 | +11 |
| 33 ± 8 | 400 ± 262# | 107 ± 15 | 91 ± 12 | 0.74 ± 0.01 | 1.55 (0.59–4.10) | −31 ± 11 | 1 ± 5 | −4 ± 4 | 7 ± 6 | ||
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazar, Z.; Fens, N.; Maten, J.v.d.; Schee, M.P.v.d.; Wagener, A.H.; Nijs, S.B.d.; Dijkers, E.; Sterk, P.J. Electronic Nose Breathprints Are Independent of Acute Changes in Airway Caliber in Asthma. Sensors 2010, 10, 9127-9138. https://doi.org/10.3390/s101009127
Lazar Z, Fens N, Maten Jvd, Schee MPvd, Wagener AH, Nijs SBd, Dijkers E, Sterk PJ. Electronic Nose Breathprints Are Independent of Acute Changes in Airway Caliber in Asthma. Sensors. 2010; 10(10):9127-9138. https://doi.org/10.3390/s101009127
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazar, Zsofia, Niki Fens, Jan van der Maten, Marc P. van der Schee, Ariane H. Wagener, Selma B. de Nijs, Erica Dijkers, and Peter J. Sterk. 2010. "Electronic Nose Breathprints Are Independent of Acute Changes in Airway Caliber in Asthma" Sensors 10, no. 10: 9127-9138. https://doi.org/10.3390/s101009127
APA StyleLazar, Z., Fens, N., Maten, J. v. d., Schee, M. P. v. d., Wagener, A. H., Nijs, S. B. d., Dijkers, E., & Sterk, P. J. (2010). Electronic Nose Breathprints Are Independent of Acute Changes in Airway Caliber in Asthma. Sensors, 10(10), 9127-9138. https://doi.org/10.3390/s101009127