Genetic Diversity in A Core Subset of Wild Barley Germplasm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wild Barley Collection and Core Subset
2.2. DNA Extraction and SSR Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SSR Polymorpshim
3.2. Genetic Diversity
| Marker † | Type † | Linkage group † | Position (cM) † | Na ‡ | Nr ‡ | Size range (base pair) | Maf ‡ | PIC ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bmag0211 | G | 1H | 60.42 | 17 | 8 | 186–223 | 0.059 | 0.920 |
| GBM1204 | E | 1H | 139.81 | 6 | 3 | 89–205 | 0.168 | 0.488 |
| GBM1216 | E | 1H | 64.1 | 9 | 5 | 236–265 | 0.113 | 0.750 |
| WMC1E8 | G | 1H | 131.93 | 4 | 2 | 200–250 | 0.253 | 0.572 |
| Bmac0134 | G | 2H | 10.87 | 26 | 18 | 133–190 | 0.038 | 0.941 |
| Bmag0711 | G | 2H | 79.52 | 18 | 10 | 161–202 | 0.056 | 0.905 |
| Ebmac0415 | G | 2H | 117.86 | 17 | 12 | 243–279 | 0.059 | 0.859 |
| GBM1459 | E | 2H | 64.35 | 5 | 1 | 177–185 | 0.201 | 0.687 |
| HVM36 | G | 2H | 30.97 | 12 | 9 | 104–175 | 0.084 | 0.772 |
| GBM1233 | E | 3H | 89.66 | 15 | 8 | 242–385 | 0.069 | 0.834 |
| GBM1405 | E | 3H | 86.33 | 11 | 5 | 283–314 | 0.093 | 0.842 |
| GBM1413 | E | 3H | 49.69 | 4 | 0 | 169–184 | 0.249 | 0.737 |
| HvLTPBB | G | 3H | 20.49 | 17 | 8 | 132–256 | 0.104 | 0.581 |
| HVM62 | G | 3H | 139.43 | 17 | 10 | 212–287 | 0.060 | 0.900 |
| Bmag0808 | G | 4H | 53.04 | 14 | 7 | 172–211 | 0.072 | 0.800 |
| EBmac0701 | G | 4H | 96.17 | 18 | 12 | 131–161 | 0.057 | 0.908 |
| Bmac0096 | G | 5H | 53.12 | 19 | 11 | 173–217 | 0.053 | 0.902 |
| GBM1176 | E | 5H | 18.59 | 8 | 5 | 297–314 | 0.125 | 0.620 |
| scssr02306 | E | 5H | 6.13 | 7 | 2 | 171–183 | 0.143 | 0.769 |
| scssr03907 | E | 5H | 183.45 | 19 | 13 | 129–177 | 0.053 | 0.865 |
| Bmac0018 | G | 6H | 61.79 | 6 | 0 | 147–157 | 0.167 | 0.786 |
| Bmac0316 | G | 6H | 7.16 | 32 | 25 | 140–232 | 0.033 | 0.941 |
| Bmag0496 | G | 6H | 63.75 | 35 | 25 | 131–250 | 0.029 | 0.947 |
| GBM1419 | E | 7H | 95.75 | 7 | 3 | 103–148 | 0.143 | 0.685 |
| GBM1464 | E | 7H | 53.43 | 16 | 10 | 142–235 | 0.063 | 0.840 |
| Total or mean | 359 | 212 | 0.102 | 0.794 | ||||
| Country/Region † | N ‡ | Na ‡ | Nu ‡ | Nr ‡ | Maf ‡ | Fst ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | ||||||
| Japan (E) | 7 | 80 | 1 | 24 | 0.325 | 0.247/0.246 |
| China (E | 2 | 28 | 1 | 6 | 0.929 | 0.286/ |
| Afghanistan (E) | 8 | 90 | 0 | 18 | 0.285 | 0.241/0.241 |
| Tajikistan (E) | 1 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Turkmenistan (E) | 12 | 93 | 3 | 26 | 0.283 | 0.248/0.246 |
| Iran (E) | 23 | 168 | 4 | 62 | 0.155 | 0.236/0.237 |
| Syria (W) | 35 | 181 | 13 | 72 | 0.144 | 0.233/0.236 |
| Iraq (W) | 3 | 62 | 1 | 16 | 0.430 | 0.247/ |
| Israel (W) | 36 | 228 | 15 | 102 | 0.118 | 0.227/0.231 |
| Jordan (W) | 28 | 224 | 15 | 104 | 0.117 | 0.227/0.231 |
| Lebanon (W) | 16 | 39 | 1 | 5 | 0.648 | 0.284/0.274 |
| Turkey (W) | 31 | 183 | 4 | 66 | 0.142 | 0.235/0.237 |
| Greece (W) | 26 | 99 | 7 | 31 | 0.265 | 0.254/0.251 |
| Cyprus (W) | 29 | 104 | 3 | 30 | 0.245 | 0.249/0.247 |
| Ethiopia (W) | 2 | 31 | 0 | 5 | 0.774 | 0.277/ |
| Morocco (W) | 10 | 55 | 1 | 13 | 0.473 | 0.263/0.257 |
| Region | ||||||
| Western | 216 | 349 | 147 | 202 | 0.075 | 0.074 |
| Eastern | 53 | 212 | 10 | 89 | 0.123 | 0.075 |
| Country | Israel | Jordan | Lebanon | Turkey | Greece | Cyprus | Morocco |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | 144 * | −41 *** | −25 *** | ||||
| Afghanistan | −51 * | 93 *** | −35 *** | ||||
| Turkmenistan | 135 *** | 131 *** | −54 *** | −38 * | |||
| Iran | 60 ** | 56 *** | −129 *** | −69 *** | −64 *** | −113 *** | |
| Syria | 47 *** | 43 *** | −142 *** | −82 *** | −77 *** | −126 * | |
| Iraq | −23 *** | −7 *** | |||||
| Israel | −189 *** | −45 *** | −129 *** | −124 *** | −173 *** | ||
| Jordan | −185 *** | −41 *** | −125 *** | −120 *** | −169 *** | ||
| Lebanon | 144 *** | 60 * | 16 *** | ||||
| Turkey | −84 *** | −79 *** | −128 ** |
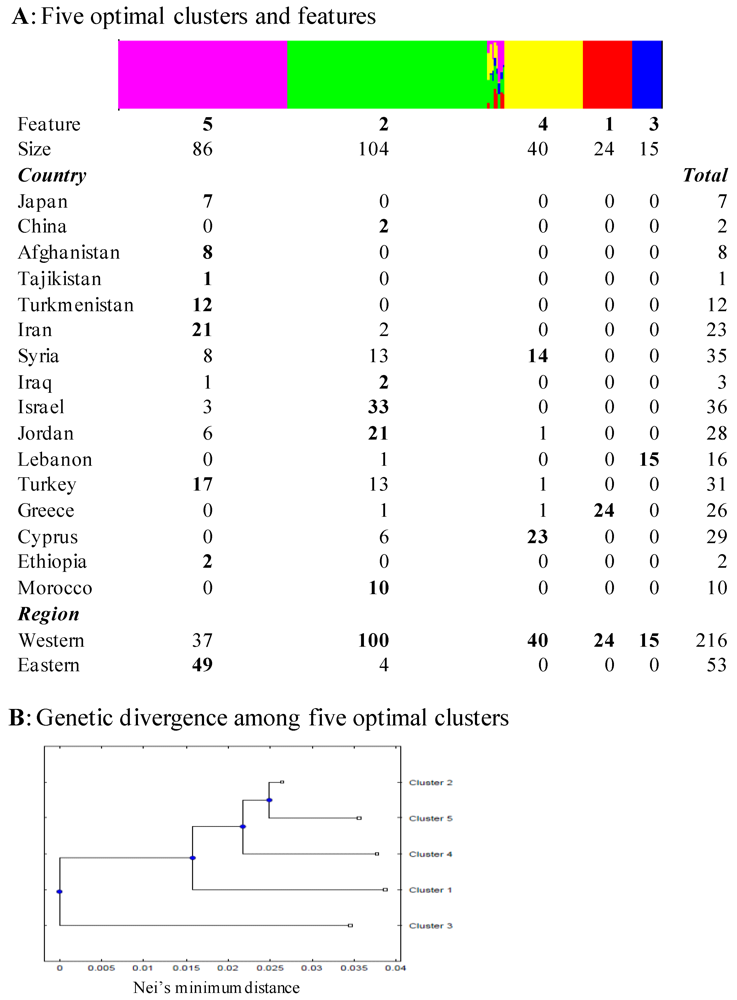
3.3. Prior Defined Genetic Structure
| Model/source | df | Sum of squares | Variance component | Percent of variation | p-value † |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country-16 | |||||
| Among countries | 15 | 1376.05 | 4.74 | 24.23 | <0.00001 |
| Within countries | 253 | 3752.30 | 14.83 | 75.77 | |
| Country-12 | |||||
| Among countries | 11 | 1275.48 | 4.74 | 24.16 | <0.00001 |
| Within countries | 249 | 3705.30 | 14.88 | 75.84 | |
| Region | |||||
| Between regions | 1 | 146.10 | 1.50 | 7.43 | <0.00001 |
| Within regions | 267 | 4982.25 | 18.66 | 92.57 | |
| Optimal clusters by BAPS | |||||
| Among clusters | 4 | 858.76 | 4.13 | 20.33 | <0.00001 |
| Within clusters | 264 | 4269.60 | 16.17 | 79.67 | |
| Optimal clusters by STRUCTURE | |||||
| Among clusters | 3 | 655.01 | 3.29 | 16.31 | <0.00001 |
| Within clusters | 265 | 4473.33 | 16.88 | 83.69 | |
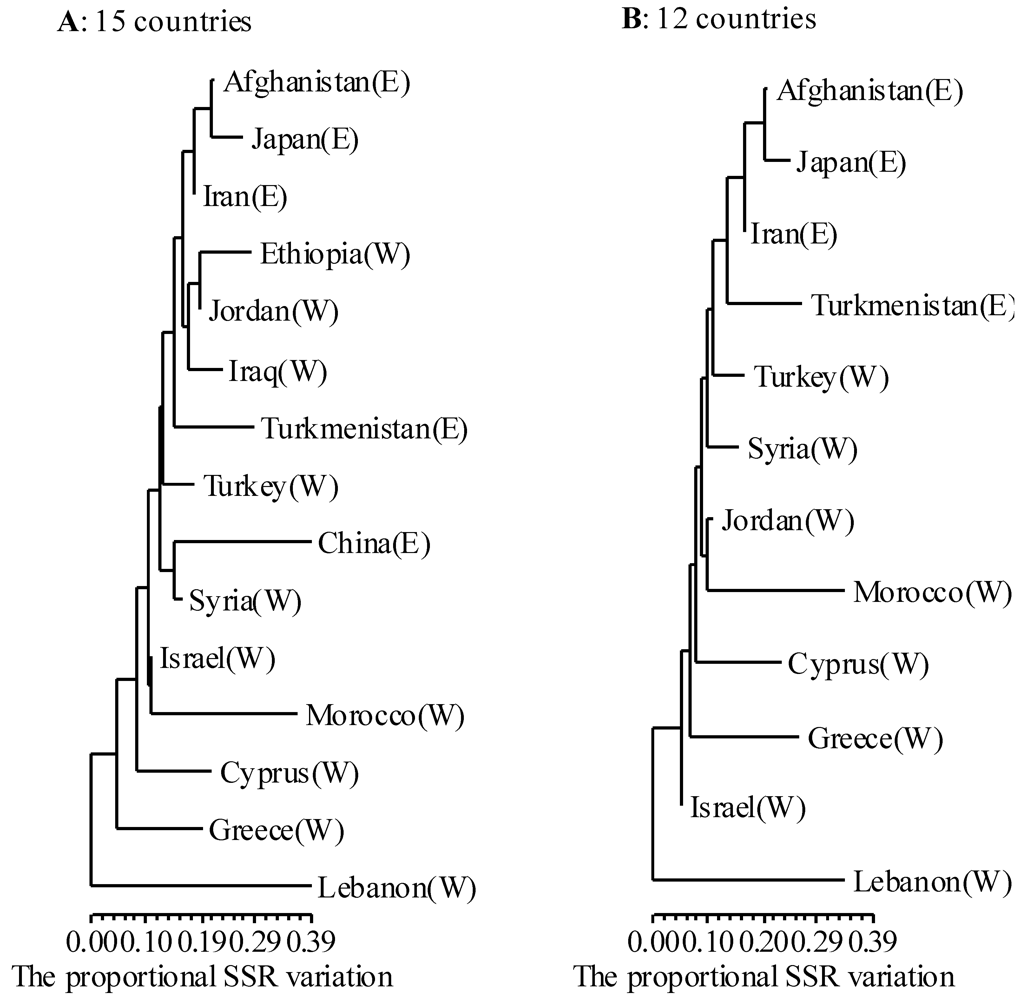
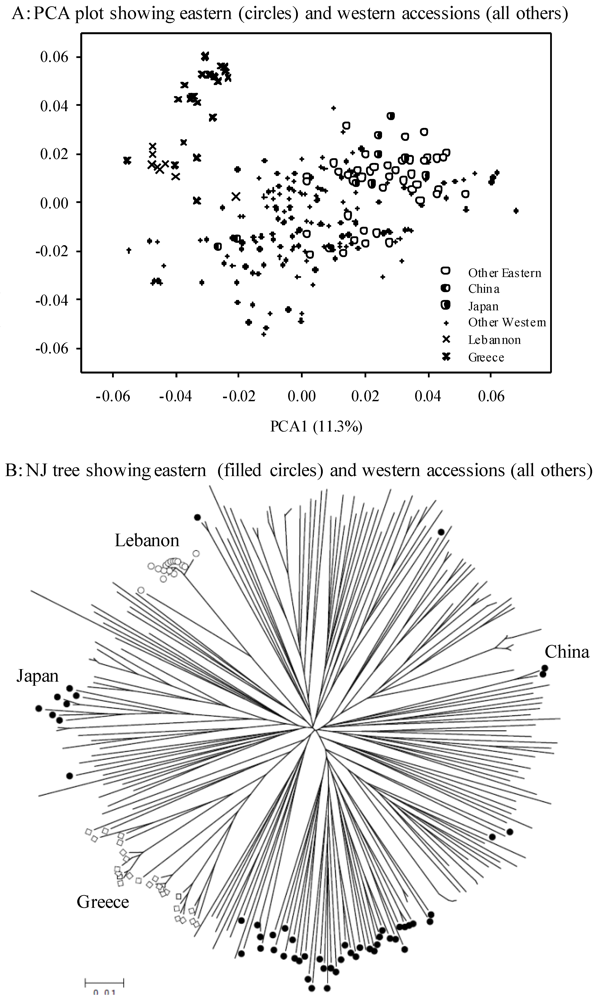
3.4. Model-based Genetic Structure
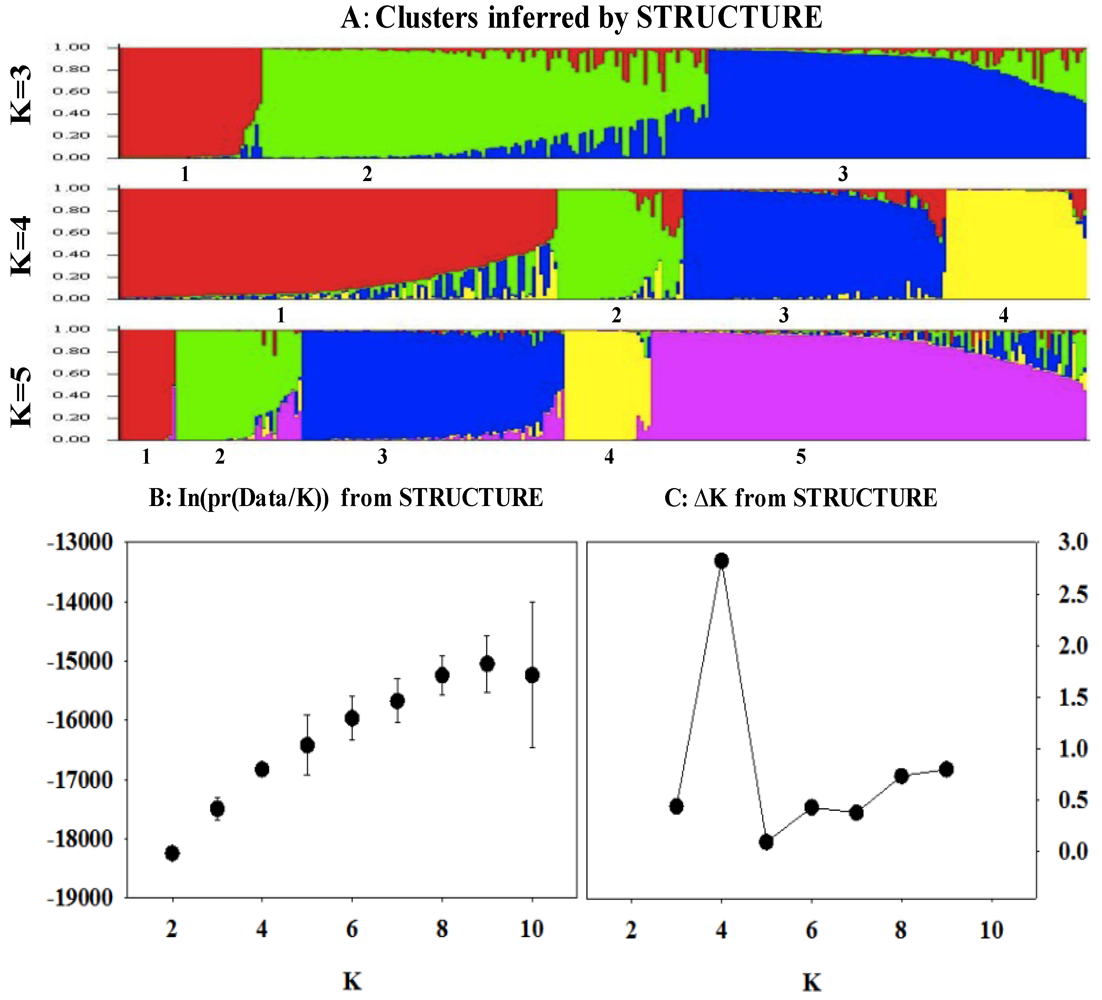
4. Discussions
Acknowledgements
References
- Maxted, N.; Ford-Lloyd, B.V.; Kell, S.P.; Iriondo, J.M.; Dulloo, M.E.; Turok, J. Crop Wild Relative Conservation and Use; CABI Publishing Series: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kole, C. Wild Crop Relatives: Genomic and Breeding Resources: Cereals; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, S.L.; Hari, D.; Upadhyaya, H.; Stalker, T.; Blair, M.W.; Bertioli, D.J.; Nielen, S.; Ortiz, R. Enhancing crop gene pools with beneficial traits using wild relatives. Plant Breed. Rev. 2008, 30, 179–230. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.B.; Somers, D.J. Genome-wide reduction of genetic diversity in wheat breeding. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, E.; Fu, Y.B.; Pavlicek, T.; Khalifa, S.; Tavasi, M.; Beiles, A. Evolution of wild cereals during 28 years of global warming in Israel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3412–3415. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott-Allen, R.; Prescott-Allen, C. Genes From the Wild: Using Wild Genetic Resources for Food and Raw Materials; Earthscan Publications: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, B.S.; Huang, L.; Kuraparthy, V.; Raupp, W.J.; Wilson, D.L.; Friebe, B. Alien genetic resources for wheat leaf rust resistance, cytogenetic transfer, and molecular analysis. Aus. J. Agric. Res. 2008, 59, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanksley, S.D.; McCouch, S.R. Seed banks and molecular maps: Unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 1997, 277, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, E.; Carrari, F.; Liu, Y.-S.; Fernie, A.R.; Zamir, D. Zooming in on a quantitative trait for tomato yield using interspecific introgressions. Science 2004, 305, 1786–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Von Bothmer, R.; Komatsuda, T. Barley origin and related species. In Barley: Production, Improvement, and Uses; Ullrich, S.E., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 14–62. [Google Scholar]
- Harlan, J.R.; Zohary, D. Distribution of wild wheats and barley. Science 1966, 153, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Nevo, E. Origin, evolution, population genetics and resources for breeding of wild barley Hordeum spontaneum in the fertile crescent. In Barley: Genetics, Biochemistry, Molecular Biologyand Biotechnology; Shewry, P.R., Ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1992; pp. 19–43. [Google Scholar]
- Von Bothmer, R.; van Hintum, T.J.L.; Knüpffer, H.; Sato, K. Diversity in Barley (Hordeum vulgare); Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nevo, E. Genome evolution of wild cereal diversity and prospects for crop improvement. Plant Genet. Res. 2006, 4, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetch, T.G.; Steffenson, B.J., Jr.; Nevo, E. Diversity and sources of multiple disease resistance in Hordeum spontaneum. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.P.; Forster, B.P.; Robinson, D.; Handley, L.L.; Gordon, D.C.; Russell, J.R.; Powell, W. Wild barley: A source of genes for crop improvement in the 21st century? J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.C.; Gutterman, Y. The trade—Off between breaking of dormancy of caryopses and revival ability of young seedlings of wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum). Can. J. Bot. 2003, 81, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Korff, M.; Wang, H.; Leon, J.; Pillen, K. Detection of QTL for agronomic traits in an advanced backcross population with introgressions from wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum). In Proceedings of the 17th EUCARPIA General Congress, Tulln, Austria, 8–11 September 2004; pp. 207–211.
- Vanhala, T.K.; Stam, P. Quantitative trait loci for seed dormancy in wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum C. Koch). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2006, 53, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lebold, K.; Lansky, E.P.; Traber, M.G.; Nevo, E. Tocol-omic” diversity in wild barley. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockelman, H.E.; Valkoun, J. Barley germplasm conservation and resources. In Barley: Production, Improvement, and Uses; Ullrich, S.E., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 144–159. [Google Scholar]
- FAO, The Second Report on the State of the World’s Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010.
- Van Hintum, T.J.L.; Menting, F.B.J. Diversity in ex Situ genebank collections of barley. In Diversity in Barley (Hordeum vulgare); von Bothmer, R., van Hintum, T.J.L., Knüpffer, H., Sato, K., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 247–257. [Google Scholar]
- Knüpffer, H.; van Hintum, T.J.L. Summarised Diversity—The Barley Core Collection. In Diversity in Barley (Hordeum vulgare); von Bothmer, R., van Hintum, T.J.L., Knüpffer, H., Sato, K., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 259–267. [Google Scholar]
- Steffenson, B.J.; Olivera, P.; Roy, J.K.; Jin, Y.; Smith, K.P.; Muehlbauer, G.J. A walk on the wild side: Mining wild wheat and barley collections for rust resistance genes. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 58, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, G.-L.; Salomon, B.; von Bothmer, R. Characterization of genetic diversity in core collection accessions of wild barley, Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum. Hereditas 2002, 136, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, J.K.; Smith, K.P.; Muehlbauer, G.J.; Chao, S.; Close, T.J.; Steffenson, B.J. Association mapping of spot blotch resistance in wild barley. Mol. Breed. 2010, 26, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, E.; Brown, A.H.D.; Zohary, D. Genetic diversity in the wild progenitor of barley in Israel. Experientia 1979, 35, 1027–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, B.R.; Nevo, E.; Johnson, D.A.; Beiles, A. Genetic diversity in wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum Koch) in the Near East: A molecular analysis using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 1997, 44, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakniyat, H.; Powell, W.; Baird, E.; Handley, L.L.; Robinson, D.; Scrimgeour, C.M.; Nevo, E.; Hackett, C.A.; Caligari, P.D.S.; Forster, B.P. AFLP variation in wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum C. Koch) with reference to salt tolerance and associated ecogeography. Genome 1997, 40, 332–341. [Google Scholar]
- Turpeinen, T.; Tenhola, T.; Manninen, O.; Nevo, E.; Nissilä, E. Microsatellite diversity associated with ecological factors in Hordeum spontaneum populations in Israel. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 1577–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.K.; Bundock, P.C.; Henry, R.J.; Nevo, E. Adaptive climatic molecular evolution in wild barley at the Isa defense locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, S.; Pietrzak, L.N. Comparative assessment of genetic diversity in wild and primitive cultivated barley in a center of diversity. Genetics 1988, 119, 981–990. [Google Scholar]
- Turpeinen, T.; Vanhala, T.; Nevo, E.; Nissilä, E. AFLP genetic polymorphism in wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum) populations in Israel. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Nevo, E.; Beiles, A.; Zohary, D. Genetic resources of wild barley in the Near East: Structure, evolution and application in breeding. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1986, 27, 355–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Z.; Brown, A.H.D.; Clegg, M.T. Heterogeneous geographic patterns of nucleotide sequence diversity between two alcohol dehydrogenase genes in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare subspecies spontaneum ). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 531–536. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-Z.; Morrell, P.L.; Clegg, M.T. The influence of linkage and inbreeding on patterns of nucleotide sequence diversity at duplicate alcohol dehydrogenase loci in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Genetics 2002, 162, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Morrell, P.L.; Lundy, K.E.; Clegg, M.T. Distinct geographic patterns of genetic diversity are maintained in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum) despite migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10812–10817. [Google Scholar]
- Dávila, J.A.; Loarce, Y.; Ramsay, L.; Waugh, R.; Ferrer, E. Comparison of RAMP and SSR markers for the study of wild barley genetic diversity. Hereditas 1999, 131, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.B. Genetic structure in a core subset of cultivated barley germplasm. Crop Sci. 2012, 52, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, O.H.; Brown, A.H.D. Plant genetic resources today: A critical appraisal. In Crop Genetic Resources: Conservation and Evaluation; Holden, J.H.W., Williams, J.T., Eds.; George Allen and Unwin: Winchester, UK, 1984; pp. 249–268. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.H.D. Core collection: A practical approach to genetic resources management. Genome 1989, 31, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohary, D.; Hopf, M. Domestication of Plants in the Old World; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Morrell, P.L.; Clegg, M.T. Genetic evidence for a second domestication of barley (Hordeum vulgare) east of the Fertile Crescent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3289–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.K.; Marcel, T.C.; Ramsay, L.; Russell, J.; Röder, M.S.; Stein, N.; Waugh, R.; Langridge, P.; Niks, R.E.; Graner, A. A high density barley microsatellite consensus map with 775 SSR loci. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 114, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuelke, M. An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat. Biotech. 2000, 18, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R.W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar]
- The SAS System for Windows V8.02, SAS Institute Incorporated: Cary, NC, USA, 2008.
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.B. FPTEST: A SAS routine for testing differences in allelic count. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2010, 10, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver. 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J. NTSYS-pc 2.1. Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System; Exeter Software: Setauket, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Corander, J.; Waldmann, P.; Marttinen, P.; Sillanpää, M.J. BAPS 2: Enhanced possibilities for the analysis of genetic population structure. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2363–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar]
- Hubisz, M.; Falush, D.; Stephens, M.; Pritchard, J.K. Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2009, 9, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*. In Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Tamura, K.; Nei, M. MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 2004, 5, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.B. Genetics redundancy and distinctness of flax germplasm as revealed by RAPD dissimilarity. Plant Genet. Resour. 2006, 4, 177–124. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, H.J.; Beharav, A.; Nevo, E. Ecological-genomic diversity of microsatellites in wild barley, Hordeum spontaneum, populations in Jordan. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 397–410. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, A.; Müller, K.; Schäfer-Pregl, R.; El Rabez, H.; Effgen, S.; Ibrahim, H.H.; Pozzi, C.; Rohde, W.; Salamini, F. On the origin and domestication history of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 14, 499–510. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.H.D.; Spillane, C. Implementing core collections—Principles, procedures, progress, problems and promise. In Collections for Today and Tomorrow; Johnson, R.C., Hodgkin, T., Eds.; International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy, 1999; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Nevo, E. Personal Communication. Institute of Evolution, University of Haifa: Haifa, Israel, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Waugh, R.; Jannink, J.-L.; Muehlbauer, G.J.; Ramsay, L. The emergence of whole genome association scans in barley. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.-B.; Horbach, C. Genetic Diversity in A Core Subset of Wild Barley Germplasm. Diversity 2012, 4, 239-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/d4020239
Fu Y-B, Horbach C. Genetic Diversity in A Core Subset of Wild Barley Germplasm. Diversity. 2012; 4(2):239-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/d4020239
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yong-Bi, and Carolee Horbach. 2012. "Genetic Diversity in A Core Subset of Wild Barley Germplasm" Diversity 4, no. 2: 239-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/d4020239
APA StyleFu, Y.-B., & Horbach, C. (2012). Genetic Diversity in A Core Subset of Wild Barley Germplasm. Diversity, 4(2), 239-257. https://doi.org/10.3390/d4020239






